Modeling the Joint Influence of Milk Fat Particle Size Micro-Distribution and Absorption on Optical Scattering and Composition Determination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Modified Model for the STRD
2.2. Experimental Methods and Demonstration Calculation of Modified Model Parameters
2.3. Deduction of Mie Key Coefficients Including Particle Size Micro-Distribution
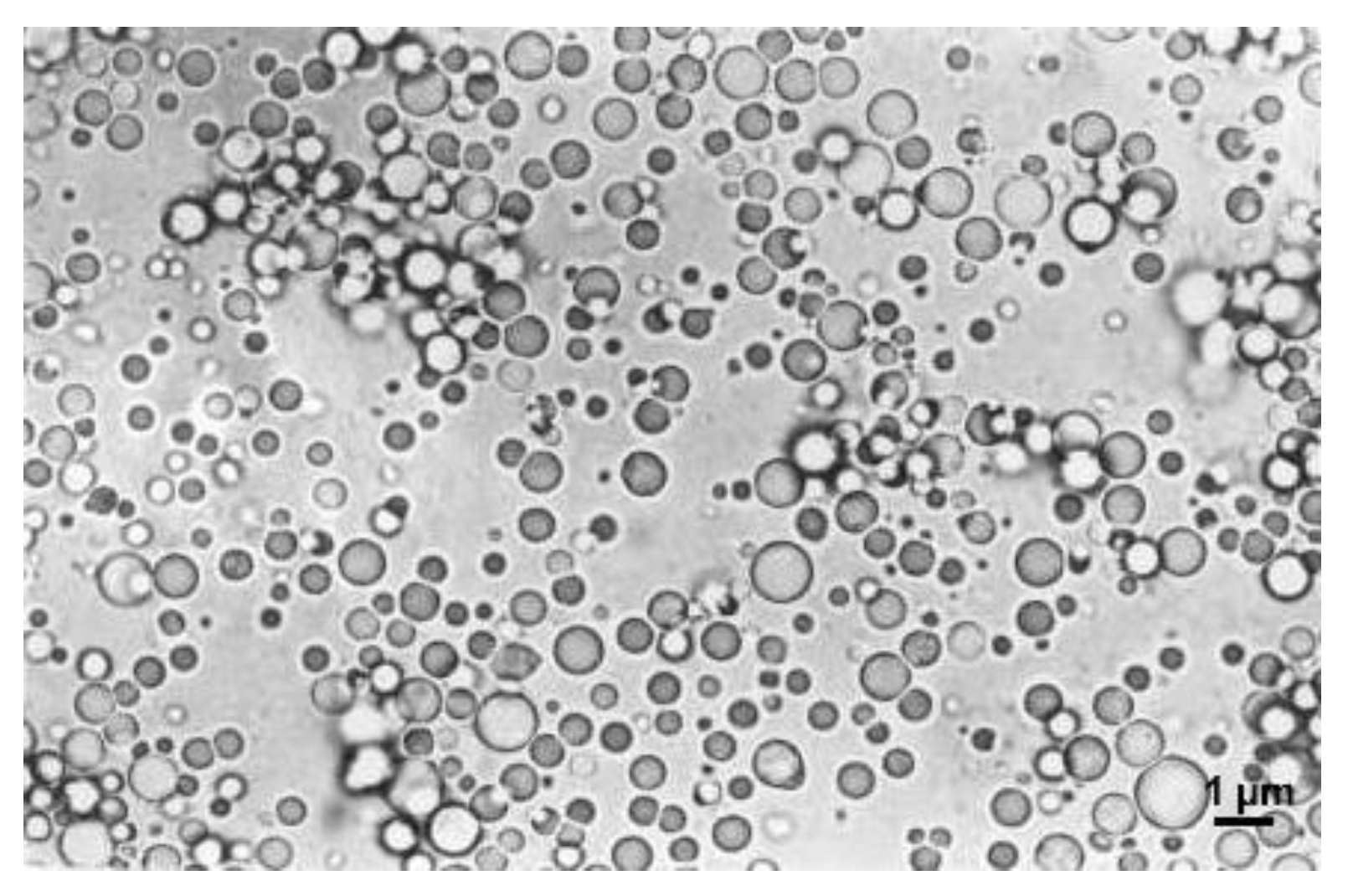
2.4. Particle Size Data Source and Image Processing Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
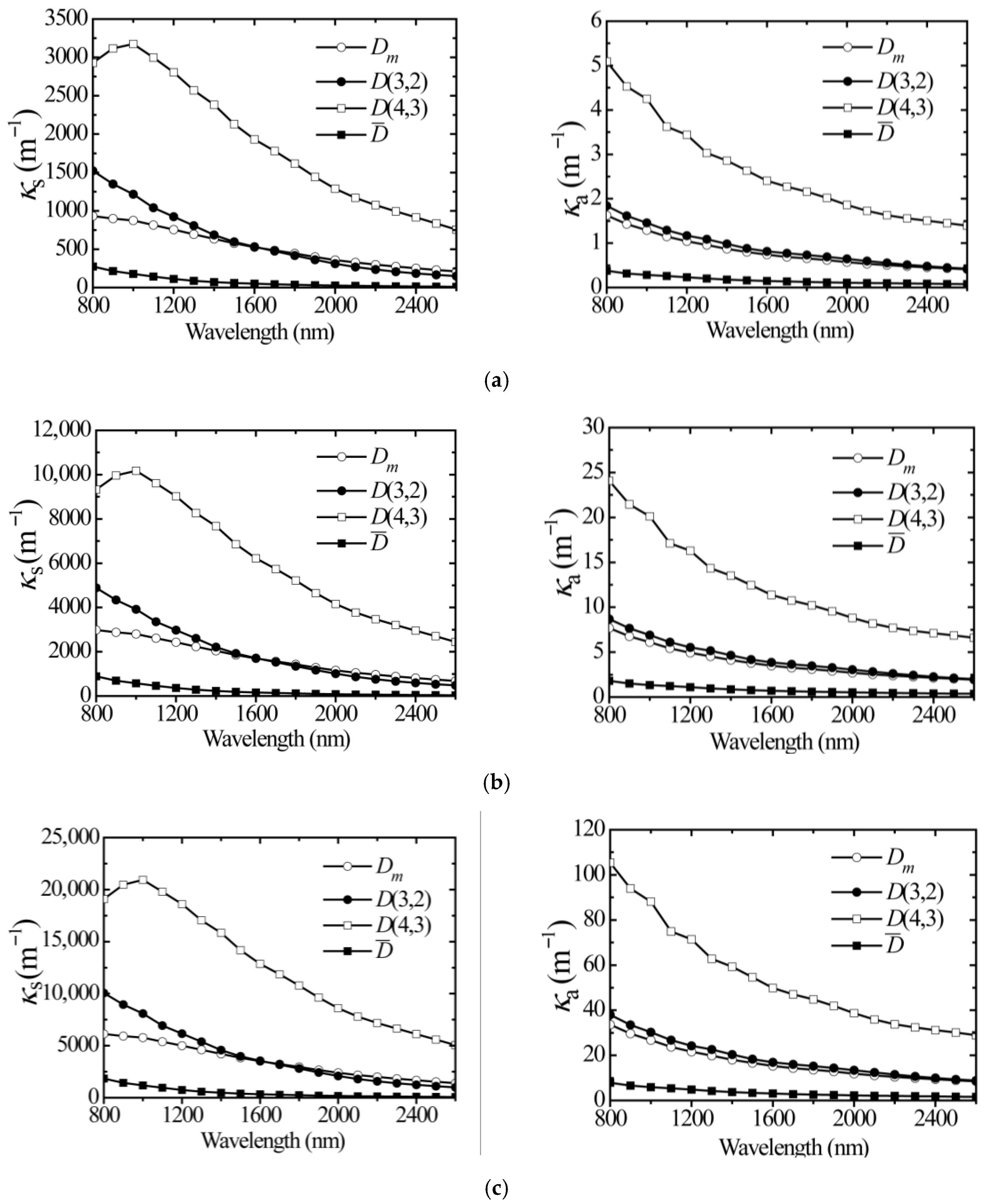
3.1. Influence of Particle Size Micro-Distribution on Mie Key Parameters
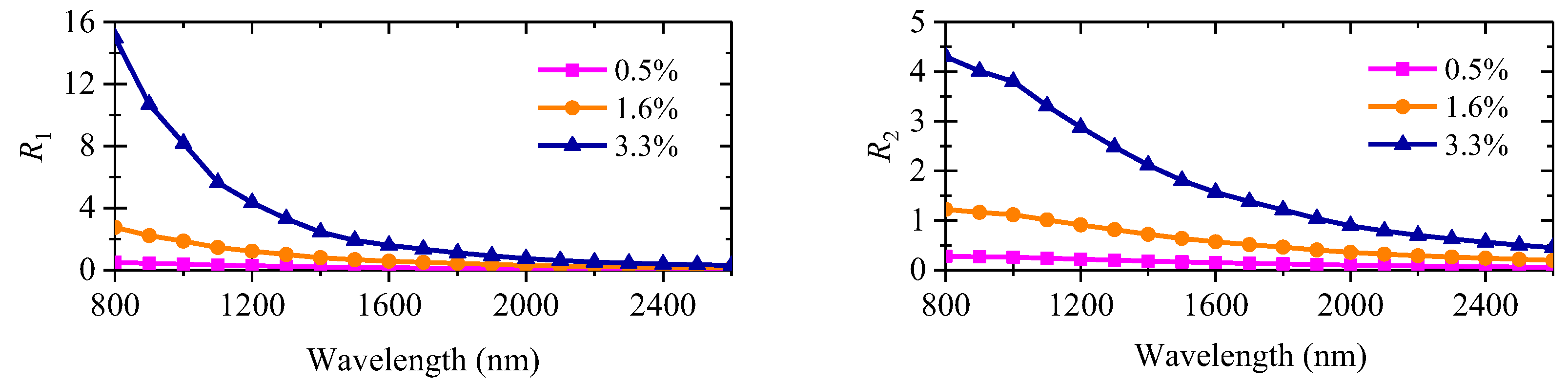
3.2. Influence of Particle Size Micro-Distribution on the Composition Determination Model
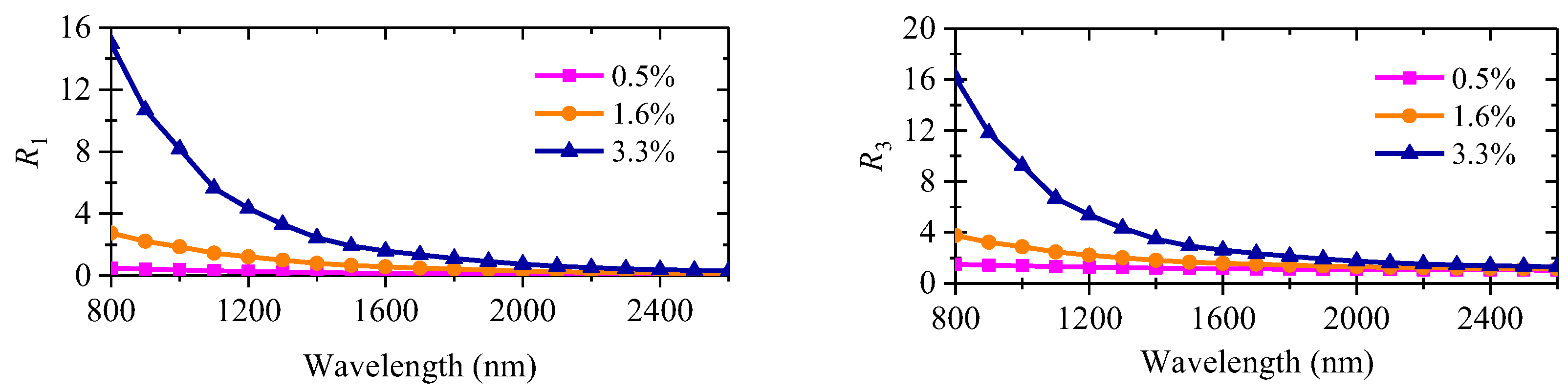
3.3. Influence of Absorption Effect on the Composition Determination Model
3.4. Joint Influence of Particle Size Micro-Distribution and Absorption Effect on Composition Determination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| STRD | Scattering–Transmission Ratio Composition Determination Method |
References
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Su, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H. Development of a New Instrument for the Measurement of the Milk Constituents Based on the Embedded System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 48, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z. Research of Milk Constituents Measurement Based on Scattered Light to Transmitted Light Ratio. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 27, 1185–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Kerker, M. The Scattering of Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Mie, G. Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann. Phys. 1908, 330, 377–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Hulst, H.C. Light Scattering by Small Particles. Phys. Today 1957, 10, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, C.; Every, D.; Petersen, W.; Van Goudoever, J.B.; Steenbergen, W.; Bosschaart, N. Dependency of the Optical Scattering Properties of Human Milk on Fat Content and Homogenization. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkirin, A.V.; Astashev, M.E.; Ignatenko, D.N.; Suyazov, N.V.; Chirikov, S.N.; Kirsanov, V.V.; Pavkin, D.Y.; Lobachevsky, Y.P.; Gudkov, S.V. A Monoblock Light-Scattering Milk Fat Percentage and Somatic Cell Count Sensor for Use in Milking Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surkova, A.; Shmakova, Y.; Salukova, M.; Samokhina, N.; Kostyuchenko, J.; Parshina, A.; Ibatullin, I.; Artyushenko, V.; Bogomolov, A. LED-Based Desktop Analyzer for Fat Content Determination in Milk. Sensors 2023, 23, 6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Na, H.; Yi, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Watanabe, M. Particle Size Distribution Effects on the Light Scattering Properties in Non-Diluted Colloidal Suspensions: A Numerical Study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 678, 134567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koestner, D.; Stramski, D.; Reynolds, R.A. Assessing the Effects of Particle Size and Composition on Light Scattering Through Measurements of Size-Fractionated Samples. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 2565–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postelmans, A.; Aernouts, B.; Saeys, W. Estimation of Particle Size Distributions from Bulk Scattering Spectra: Sensitivity to Distribution Type and Spectral Noise. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wen, J.; Qin, Y.; Huang, H.; Ding, G. Study of Influence Factors of Milk Protein Detection by Light Scattering. Infrared 2010, 31, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Ji, G.; Tian, X.; Huang, J.; Yu, Z. Study on the Measurment of Milk Fat Based on the Ratio of Scattered Intensity to Transmitted Intensity. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2008, 31, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Riemer, N.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Adachi, K.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Laskin, A. Microphysical Properties of Atmospheric Soot and Organic Particles: Measurements, Modeling, and Impacts. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Kong, W.; Ma, Q.; Qi, B.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; et al. Measurement Report: The Influence of Particle Number Size Distribution and Hygroscopicity on the Microphysical Properties of Cloud Droplets at a Mountain Site. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2025, 25, 5711–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Particle Size Amplification of Black Carbon by Scattering Measurement due to Morphology Diversity. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Yin, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, L.; Ma, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Tian, Z.; et al. A Novel Particle Size Distribution Correction Method Based on Image Processing and Deep Learning for Coal Quality Analysis Using NIRS-XRF. Talanta 2025, 285, 127427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepp, T.N.; Kovilakam, M.; Thomason, L.; Miller, S.J. Characterization of Stratospheric Particle Size Distribution Uncertainties Using SAGE II and SAGE III/ISS Extinction Spectra. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 2025–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, S.; Foschum, F.; Krauter, P.; Bergmann, F.; Hohmann, A.; Scalfi Happ, C.; Kienle, A. Broadband optical properties of milk: Scattering and absorption characteristics measured by integrating sphere and collimated transmission. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tran, I.; Tan, S. Characterization of Particle-Size-Based Homogeneity and Mycotoxin Distribution Using Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analysis. Toxins 2023, 15, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Dai, L.; Jiang, X.; Fu, X. Measurement of absorption and scattering properties of milk using a hyperspectral spatial frequency domain imaging system. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramsch, E.; Oyola, P.; Reyes, F.; Vásquez, Y.; Rubio, M.A.; Soto, C.; Pérez, P.; Moreno, F.; Gutiérrez, N. Influence of Particle Composition and Size on the Accuracy of Low Cost PM Sensors: Findings From Field Campaigns. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 751267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Sarma, S.E. Light scattering and transmission measurement using digital imaging for online analysis of constituents in milk. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optical Metrology, Munich, Germany, 23–26 June 2015; Volume 9525, p. 95254A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühle, B.; Krumrey, J.F.; Hodoroaba, V.-D. Workflow towards automated segmentation of agglomerated, non-spherical particles from electron microscopy images using artificial neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Rahaman, M.; Yao, Y.; Ma, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, T.; Grzegorzek, M. A Comprehensive Review of Image Analysis Methods for Microorganism Counting: From Classical Image Processing to Deep Learning Approaches. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 2875–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Ling, H.Z.; Long, T.J.; Zhu, Y. The rapid determination of fat and protein content in fresh raw milk using the laser light scattering technology. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2006, 44, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C. Study on Mechanism and Influence Factors of Optical Measurement of Milk Quality. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2007; pp. 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z. Influence of Fat Particle Size on Light Scattering Properties in Milk Quality Testing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Instrumentation & Measurement, Harbin, China, 18–20 September 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Z. Theoretical Study of the Effect of Multi-Diameter Distribution on the Mie Scattering Characteristics of Milk Fat. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. (New Ser.) 2015, 6, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. The Influence of Milk Fat Particle Size Distribution on Component Testing. Master’s Thesis, Harbin University of Technology, Harbin, China, 2016; pp. 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.-C.; Camier, B.; Briard, V.; Leconte, N.; Gassi, J.-Y.; Goudédranche, H.; Michel, F.; Fauquant, J. The Size of Native Milk Fat Globules Affects Physico-Chemical and Functional Properties of Emmental Cheese. Le Lait. 2004, 84, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaksch, S.; Pipich, V.; Frielinghaus, H. Multiple scattering and resolution effects in small-angle neutron scattering experiments calculated and corrected by the software package MuScatt. J. Appl. Crystallograph. 2021, 54, 1580–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
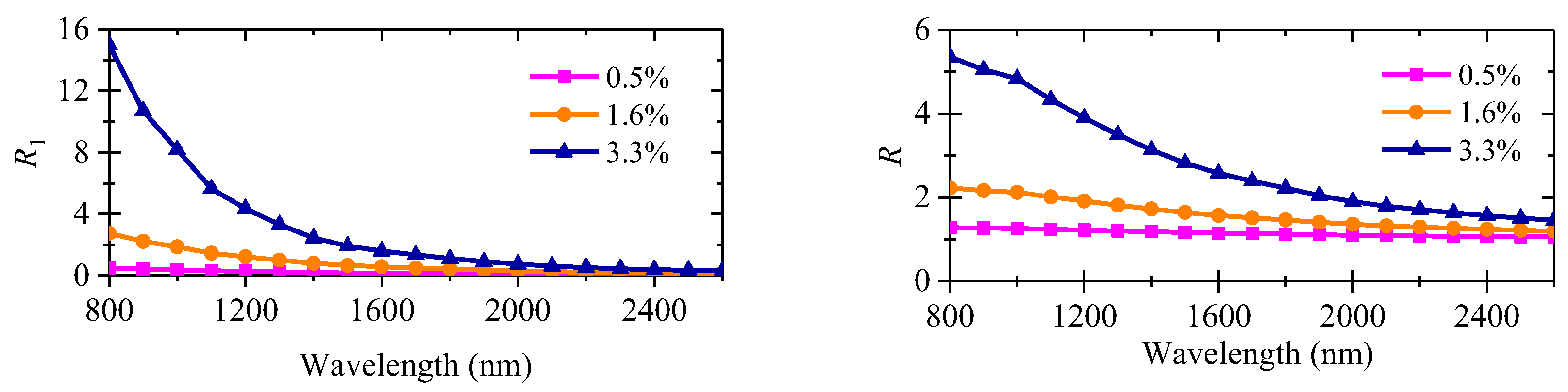
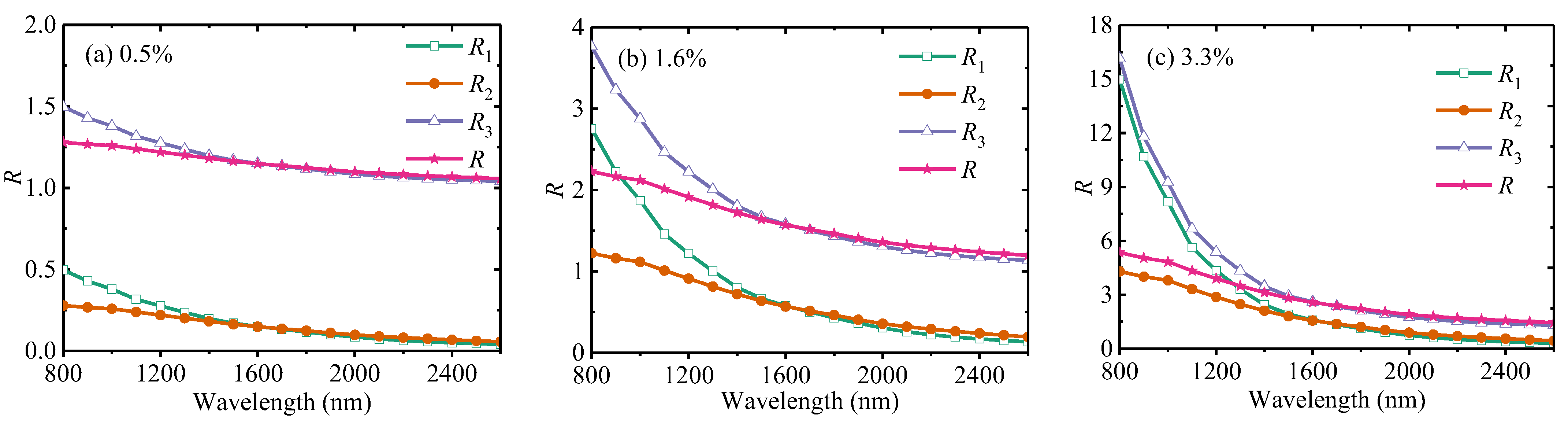
| R | c0 | c1 | c2 | c3 | c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat volume concentration(%) | R = 1.2710 ± 0.008 | 0.50 | 0.867 | 1.417 | 0.252 | 0.412 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Li, A.; Wang, J.; Yang, X. Modeling the Joint Influence of Milk Fat Particle Size Micro-Distribution and Absorption on Optical Scattering and Composition Determination. Processes 2025, 13, 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092846
Zhang S, Wu L, Li A, Wang J, Yang X. Modeling the Joint Influence of Milk Fat Particle Size Micro-Distribution and Absorption on Optical Scattering and Composition Determination. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092846
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Siqi, Linghao Wu, Ang Li, Jiaan Wang, and Xu Yang. 2025. "Modeling the Joint Influence of Milk Fat Particle Size Micro-Distribution and Absorption on Optical Scattering and Composition Determination" Processes 13, no. 9: 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092846
APA StyleZhang, S., Wu, L., Li, A., Wang, J., & Yang, X. (2025). Modeling the Joint Influence of Milk Fat Particle Size Micro-Distribution and Absorption on Optical Scattering and Composition Determination. Processes, 13(9), 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092846





