Abstract
Background: Polyphenols from Sorbus aucuparia L. (rowanberry) fruits are valuable bioactive compounds, yet their efficient extraction remains a challenge. Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) offers a promising technique to enhance yield, but optimization of parameters is necessary. Methods: UAE was performed using a VC750 processor (20 kHz) at ultrasound intensities of 1.3, 7.65, and 14 W/cm2 in pulsed mode (2 s on, 4 s off). Sonication times of 5, 10, and 15 min (total extraction times: 15, 30, 45 min) and ethanol concentrations of 30%, 60%, and 90% were tested. Selected polyphenols (gallic acid, neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, vanillic acid, epicatechin, trans-ferulic acid, rutin, quercetin, cinnamic acid) were quantified using HPLC. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was applied for process optimization. Results: High-quality predictive models were obtained, particularly for neochlorogenic acid. Ethanol concentration exerted the strongest influence on extraction efficiency for most of the studied polyphenols, whereas extraction time showed no significant effect. Conclusions: Ethanol concentration is a key factor in maximizing polyphenol yield from S. aucuparia fruits using UAE. These findings may guide selective extraction strategies for phenolic compounds at early stages of food and nutraceutical processing.
1. Introduction
The Sorbus genus, part of the Rosaceae family, includes around 200 species of trees and shrubs [1]. These plants are commonly found throughout the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, such as Europe, Asia, and North America. They exhibit a wide range of leaf forms—from pinnate to simple leaves—making them relatively easy to distinguish [2,3]. Rowan berries are particularly noted for their rich nutritional profile, containing significant levels of potassium, calcium, phosphorus, vitamin C, unsaturated fatty acids, and especially polyphenols, which are considered their main bioactive compounds [4,5,6,7,8,9].
Arvinte et al. [4] indicate that the chemical composition of rowan is influenced by the following factors: location, origin, species, climatic conditions, and ripening stage. Qualitative analyses of rowan fruits have identified between 13 and 36 polyphenolic compounds, including 2 to 13 flavonols, up to 44 oligomeric procyanidins, and 4 to 9 hydroxycinnamate derivatives, depending on the type of extract, study methodology, and fruit origin [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. A comprehensive study by Rutkowska et al. [12] identified 26 new compounds alongside previously known phenolic constituents.
With the increasing interest in natural ingredients, rowan has emerged as a valuable source of extracts for applications in food processing technologies [13]. Phenolic extracts derived from Sorbus aucuparia L. have demonstrated the ability to protect vegetable oils against thermal and oxidative degradation during frying. Studies by Aladedunye et al. [5] demonstrated that natural rowan extracts are more effective than the synthetic antioxidant BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) and can serve as a natural alternative for preserving vegetable oils during frying and storage. Moreover, the polyphenols found in rowan possess antioxidant activity, which may contribute to cardiovascular protection by scavenging free radicals and lowering oxidative stress, ultimately helping to preserve the integrity of vascular endothelial cells. As an example, proanthocyanidins possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and show potential as agents for improving insulin responsiveness and regulating glucose homeostasis [4].
Bioactive compounds are generally obtained through solid–liquid extraction processes involving different solvents. Conventional methods for isolating plant-derived metabolites encompass techniques such as maceration, percolation, Soxhlet extraction, pressurized extraction, reflux extraction, steam distillation, and acid–base extraction. In recent years, more advanced techniques have been developed, including microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical and subcritical fluid extraction, as well as ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) [14,15,16].
Alongside modern extraction technologies, growing attention is being directed toward alternative “green” solvents that align with the principles of sustainable chemistry. Deep eutectic solvents (DES) and ionic liquids (ILs) have emerged as promising options that can enhance the performance of UAE. DES are biodegradable, biocompatible, usually readily available, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly. Lai et al. [17] demonstrated that a DES composed of choline chloride, acetic acid, and 1,2-propanediol (in a 1:2:3 ratio) exhibited 27% greater extraction efficiency for flavonol glycosides from Ginkgo leaves compared to ethanol. In a subsequent study, the same authors combined UAE with DES and showed that under optimized conditions (ultrasonic power of 320 W, extraction time of 63.6 min, and temperature of 32.5 °C), the yield was 18.4% higher than with ethanol extraction and 8.5% higher than with DES alone. Moreover, the extraction time was significantly reduced from 11.8 h to 63.6 min [18]. Similarly, Mend et al. [19] reported that using DES (choline chloride and levulinic acid) during the ultrasonic extraction of flavonoids from Cercis glabra leaves led to a 1.31-fold increase in yield compared to the conventional 80% ethanol method.
Another innovative approach is ionic liquid-based ultrasonic extraction (IL-UAE). Ionic liquids are salts that remain in a liquid state below 100 °C and consist of organic cations and organic or inorganic anions. They are known for their high thermal stability, very low vapor pressure, non-flammability, and broad solubilizing capabilities for both polar and non-polar compounds [20]. Ferreira et al. [21] used [BMIM][BF4] and [BMIM][Cl] to obtain phenolic-rich extracts from guava by-products, while Zhao et al. [22] applied 0.5 mol/L [BMIM]Br for resveratrol extraction from Polygonum cuspidatum.
UAE is a widely recognized technique for obtaining bioactive compounds such as polyphenols, terpenoids, alkaloids, and organic acids from plant sources and biomass. Its growing popularity stems from a range of benefits that position it as an effective and eco-friendly alternative to traditional extraction methods. UAE improves extraction efficiency by increasing cell membrane permeability and enhancing mass transfer, enabling the efficient isolation of valuable substances. The process is also notably faster and requires less solvent, which helps lower costs and minimizes environmental harm. Operating at low temperatures, UAE protects heat-sensitive compounds from degradation, ensuring extracts of superior quality. Its adaptability makes it suitable for use with a variety of materials, including herbs, fruits, seeds, and industrial residues. Furthermore, UAE supports green chemistry principles by reducing both energy usage and chemical input [23].
Numerous studies have aimed to optimize UAE parameters to enhance process efficiency and extract quality. These investigations have primarily concentrated on evaluating critical variables that affect extraction performance, including ultrasound frequency, duration of exposure, intensity, as well as the type and concentration of the solvent used [24,25,26,27,28]. The findings have provided valuable insights into the effects of these parameters on bioactive compound release, facilitating the development of optimal extraction conditions tailored to specific plant matrices and target compounds.
Attempts to refine UAE parameters, including those for rowan fruits, have typically focused on extracting phenolic derivatives, such as polyphenols, in this case flavonoids, and anthocyanins. Although these studies have identified general conditions that enhance the extraction of these groups, it is still unclear whether the same conditions are optimal for individual compounds within them. Due to the structural variability and distinct physicochemical characteristics of specific bioactive molecules, a more customized strategy may be necessary to ensure maximum extraction efficiency.
The objective of this study was to determine the optimal conditions for UAE of individual polyphenols from the fruits of S. aucuparia L. In this study, we focused on 15 specific phenolic derivatives, including chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, epicatechin, and rutin, as they exhibit well-documented biological activities and are present in this plant at concentrations that enable reliable extraction and analysis. This research focused on analyzing key process parameters, such as extraction time, ultrasound intensity, and ethanol concentration in water, to optimize the recovery of these bioactive compounds. In the works published so far, no attempt has been made to optimize the extraction parameters for individual compounds, which is an important novelty.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
Dried fruits from the S. aucuparia L. plant were obtained from the Runo company (Hajnówka, Poland), certified as organic by the PL-EKO-04 EU Agriculture certificate. The collection of plant material and the experiments were conducted in compliance with applicable guidelines and regulations [29,30].
The raw material was processed using a Zelmer MM 1200 (Rzeszów, Poland) device to crush it. A horizontal sieve shaker (AS400 Control, Retsch, Haan, Germany) was employed to separate the material into various fractions. For further analysis, the fraction that passed through sieves with mesh sizes of 1.0–2.0 mm was selected [29,30].
2.2. UAE
A total of 1.5 g of raw material was added to an extraction vessel with a diameter of 35 mm and submerged in 50 milliliters of a water-based solution containing 30%, 60%, or 90% ethyl alcohol. The extraction vessel was placed in a cooling jacket connected to an ultra-thermostat to maintain consistent temperature control. An ultrasonic probe, 19 mm in diameter, was used to carry out the extraction. The experimental samples were treated using a VC750 Sonics processor (Sonics & Materials, Inc., Newtown, CT, USA) operating at a frequency of 20 kHz, with ultrasound intensities of 1.3, 7.65, and 14 W/cm2. The sonication process was performed in cycles of 2 s on and 4 s off. Sonication durations of 5, 10, or 15 min were applied, resulting in total extraction times of 15, 30, or 45 min [29,30]. The extracts were pre-filtered through soft quantitative filters with a weight of 80.0 ± 4.0 g/m2 and a thickness of 180 ± 2.0 µm and then placed in a centrifuge for 10 min at 650 rpm.
2.3. Determination of Bioactive Compounds by HPLC
Selected polyphenol compounds were determined using an high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) Agilent 1260 system (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany) based on the method described by Cristea et al. [13], with slight modifications. A C18 HPLC column (Hypersil, 2.6 µm; length 250 mm, diameter 4.6 mm; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used. The mobile phases consisted of 1% methanol (A) and 50% methanol (B) (HPLC grade, Sigma Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Steinheim, Germany) in double-deionized water (H2O, 18.2 MΩ·cm, simplicity 185, Millipore SAS, Molsheim, France). The extracts were filtered through polyvinylidene fluoride membrane filter discs (PVDF) syringe filters (0.45 µm, 13 mm diameter) (Frisenette ApS, Knebel, Denmark) into HPLC vials and stored in a refrigerator (4 °C) until HPLC analysis.
Detection was conducted at wavelengths of 256, 265, 280, 324, and 365 nm. The column temperature was maintained at 35 °C.
Gallic acid (certified reference material TraceCert®), neochlorogenic acid (phyproof® Reference Substance, ≥95.0% (HPLC)), chlorogenic acid (primary reference standard, 96.67%), vanillic acid (certified reference material, TraceCERT®), epicatechin (≥98% HPLC, from green tea), trans-ferulic acid (≥99.4%, certified reference material TraceCERT®), rutin (≥97.84%, reference standard), quercetin (≥98%, HPLC), and trans-cinnamic acid (≥98%, analytical standard) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). The retention times of the analyzed compounds are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Retention times (RT) of the analyzed compounds.
2.4. Box–Behnken Experimental Design and Statistical Analyses
This study employed the Box–Behnken experimental design using Design-Expert v13 software (Stat-Ease, Minneapolis, MN, USA) to optimize the extraction conditions for S. aucuparia L. fruit. The design included three independent variables, extraction time, ultrasound intensity, and solvent concentration, and four dependent variables: neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, epicatechin, and rutin.
A total of 15 experimental combinations, including three center points, were tested in a randomized order to estimate pure error and ensure robust statistical analysis. The levels of the three factors assessed in the experimental design are presented in Table 2 [29,30].

Table 2.
The Box–Behnken response surface design.
A generalized, second-order polynomial model was used to explain the effect of the independent variables on each response of interest according to the following equation:
where Y is the response variables (neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, epicatechin, rutin); X1, X2, and X3 are the independent variables; β0 represents the constant; and β1,2,3, β11,23,33, and β12,13,23 are the linear, quadratic, and interactive coefficients, respectively.
Y = β0 + β1×1 + β2X2 + β3X3 + β11X2 + β22X2 + β33X2 + β12X1X2 + β13X1X3 + β23X2X3
The experimental data were analyzed through analysis of variance (ANOVA) to assess statistical significance. The significance of the regression coefficient was examined using an F-test, where p-values less than 0.05 were considered significant. Optimal extraction conditions were forecasted using Derringer’s desirability function to enhance the response for each variable. The model’s accuracy was validated by comparing the experimental results with the predicted values [29,30].
3. Results
The values for gallic acid, neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, vanillic acid, epicatechin, trans-ferulic acid, quercetin, rutin, and cinnamic acid obtained for each of the extraction parameters are presented in Table 3. Further statistical analysis was performed on neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, epicatechin, and rutin, as the content of the remaining compounds was at the limit of detection.

Table 3.
The content of individual chemical compounds depends on the extraction parameters.
3.1. Neochlorogenic Acid
Figure 1 shows the influence of input variables on the content of neochlorogenic acid.
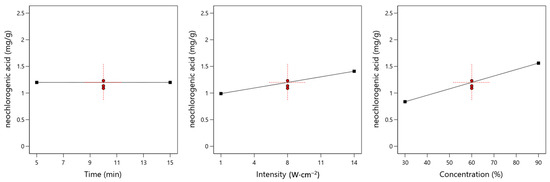
Figure 1.
The effect of time, ultrasound intensity, and solvent concentration on neochlorogenic acid content. The red points correspond to the central data values.
The shape of the curves shown in the figure indicates that the variable time has no effect on the neochlorogenic acid content. Positive linear correlations are observed between ultrasound intensity, solvent concentration, and the neochlorogenic acid content, suggesting that further increases in the values of these input variables should lead to improved extraction efficiency.
To confirm the significance of the influence of the examined input variables on the neochlorogenic acid content, a statistical analysis was performed, and the results are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Influence of the independent variable on the dependent variable and statistical significance for the content of neochlorogenic acid.
The results of the analysis of variance showed that statistically significant effects were found for the linear variables ultrasound intensity and solvent concentration, as well as the interaction effect between time and solvent concentration.
The model is not hierarchical, so it was not possible to derive the equation in actual values, and therefore was expressed in coded (dimensionless) variables:
Yield of neochlorogenic acid = 1.2 + 0.2097X2 + 0.3621X3 + 0.9703X1X3 [mg/g]
The equation in terms of coded factors can be used to make predictions about the response for given levels of each factor.
The model is statistically significant (p < 0.0001), and the lack of fit is statistically insignificant (p = 0.0929), indicating correct model definition. The high value of the R2 coefficient (0.9127) and adjusted R2 (0.8889) indicates a strong correlation between the input variables and the neochlorogenic acid content. The difference between the adjusted and predicted R2 is 0.0862, which means the model has good prediction accuracy. The low CV value (17.68%) indicates that the deviations between experimental and predicted values are small, and the reliability and precision of the experiment are high. Adequate precision was found to be 24.3451, which indicates an adequate signal and confirms that this model is significant for this extraction process.
3.2. Chlorogenic Acid
To determine the significance of the influence of the examined input variables on the chlorogenic acid content, a statistical analysis was performed, and the results are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
The effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable and statistical significance for the content of chlorogenic acid.
The results of the analysis of variance showed that the lack of fit is statistically significant (p = 0.0022), indicating an incorrect model definition.
In the case of chlorogenic acid, the mathematical model was not correctly defined. This means that the plots prepared based on the model do not adequately reflect the experimental data (the differences between predicted and observed values are very large) and may lead to incorrect conclusions. For this reason, we decided not to present the plots showing the relationships between ultrasound treatment parameters and the yield of chlorogenic acid.
3.3. Epicatechin
Figure 2 shows the influence of the input variables on the epicatechin content.
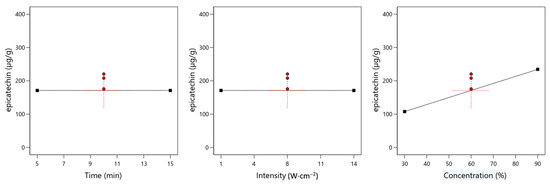
Figure 2.
Relationship between the content of epicatechin and time, ultrasound intensity, and solvent concentration. The red points correspond to the central data values.
The shape of the curves shown in the figure indicates that there is a positive linear correlation between solvent concentration and epicatechin content. To confirm the significance of the influence of the studied input variables on the epicatechin content, a statistical analysis was performed, the results of which are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Influence of the independent variable on the dependent variable and statistical significance for the content of epicatechin.
Results of the analysis of variance showed that the linear effect of the solvent concentration variable and the interaction effect between time and solvent concentration were statistically significant.
The model is not hierarchical, so it was not possible to derive the equation in real values, and it was therefore expressed in coded (dimensionless) variables:
Yield of epicatechin = 171 + 63.41X3 + 141.12X1X3
The model is statistically significant (p = 0.0009), and the lack of fit is not statistically significant (p = 0.1015), indicating proper model validation. The R2 value (0.6903) and the adjusted R2 (0.6387) indicate an average correlation between the input variables and the epicatechin content. The difference between the adjusted and predicted R2 values is 0.197, suggesting that the derived mathematical model predicts results with appropriate accuracy. A high CV value (37.81%) indicates that the deviations between the experimental and predicted values are large. Adequate precision was found to be 14.1465, which indicates an adequate signal-to-noise ratio.
3.4. Rutin
Figure 3 shows the effect of input variables on the rutin content.
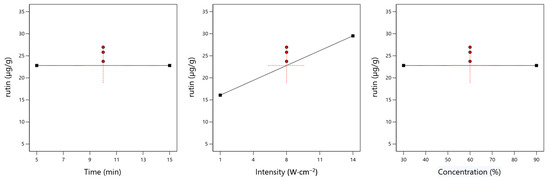
Figure 3.
Dependence of rutin content on time, ultrasound intensity, and solvent concentration. The red points correspond to the central data values.
The shape of the curves shown in the figure indicates that there is a positive linear correlation between ultrasound intensity and rutin content, suggesting that further increases in the value of this input variable should lead to an increase in extraction efficiency.
To confirm the significance of the effect of the studied input variables on rutin content, a statistical analysis was performed, the results of which are presented in the Table 7.

Table 7.
The effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable and statistical significance for rutin content.
Variance analysis results showed that only the linear effect of the ultrasound intensity variable was statistically significant. Based on regression analysis, a model describing the influence of input variables on rutin content was determined:
Yield of rutin = 14.69 + 1.058X2
The model is statistically significant (p = 0.0068), and the lack of fit is statistically insignificant (p = 0.0625), indicating proper model validation. The low R2 (0.4423) and adjusted R2 (0.3994) values indicate a low correlation between the input variables and rutin content. The difference between the adjusted and predicted R2 values is 0.1205. The high CV value (25.97%) indicates significant deviations between experimental and predicted values. Adequate precision was found to be 6.2174, which indicates an adequate signal and confirms that this model is significant for this extraction process.
3.5. Optimization of Process Conditions and Model Validation
The results concerning the evaluation of the quality of the mathematical models developed for the studied phenolic compounds are listed in Table 8.

Table 8.
Quality of the mathematical models for the analyzed polyphenols.
Based on the established criteria, it was found that only one out of the four analyzed models meet the requirements and are suitable for predicting the efficiency of the active compounds in the ultrasonic extraction process. The remaining models do not demonstrate sufficient accuracy, excluding them from being used in properly describing the extraction of bioactive substances. These results highlight the need for further research to better understand the extraction mechanisms and identify additional variables that may influence the process efficiency for these compounds.
Therefore, the optimization process was carried out exclusively for one of the studied compounds: neochlorogenic acid. To calculate the maximum efficiency of the analyzed phenolic acids, Derringer’s desirability predictive tool was used. Additionally, to minimize extraction time, it was assumed that the extraction time should be kept to a minimum of 5 min, as this duration was found to be statistically insignificant in this study.
To validate the developed mathematical models, a re-experiment was conducted under the determined optimal process conditions for neochlorogenic acid (Table 9).

Table 9.
Comparison of experimental and predicted neochlorogenic acid contents under optimized conditions.
The predictive ability of the models was calculated as the ratio of experimental to predicted values. This indicator was 87%, which is considered a good level.
4. Discussion of Results
The content of neochlorogenic acid in the obtained extracts ranged from 0 to 3409.68 µg/g. These results are consistent with those of Orsavová et al. [31], who studied sweet rowanberry cultivars and reported values from 189.7 to 2375.2 µg/g. Comparable results were obtained by Gaivelyte et al. [32], who reported neochlorogenic acid content in the fruits of S. aucuparia cultivar “Alaja Krupnaja” ranging from 930 to 5430 µg/g, and Šavikin et al. [33], who found neochlorogenic acid content in S. aucuparia fruits to range from 670 to 7030 µg/g dry weight. A slightly higher value for neochlorogenic acid was reported by Kylli et al. [9], with 8590 µg/g dry weight. Bobinaite et al. [6] demonstrated that depending on the solvent used, there are differences in neochlorogenic acid content, with ethanol yielding 6044 ± 150 µg/g extract and water yielding 5715 ± 224 µg/g extract.
The content of chlorogenic acid in the obtained extracts ranged from 0 to 2365.44 µg/g. These results are consistent with the findings of Gaivelyte et al. [32], who reported chlorogenic acid content in the fruits of S. aucuparia cultivar “Alaja Krupnaja” to range from 550 to 7500 µg/g. Similar results were obtained by Šavikin et al. [33], who reported chlorogenic acid content in S. aucuparia fruits range from 350 to 1010 µg/g dry weight, and Orsavová et al. [31], who studied sweet rowanberry cultivars and reported values from 1312.2 to 4069.8 µg/g. Kylli et al. [9] reported a value of 5360 ± 0.10 µg/g dry weight. Cristea et al. [13] found chlorogenic acid content to be 28 µg/g. Bobinaite et al. [6] showed differences in chlorogenic acid content based on the solvent used, with ethanol yielding 3970 ± 10 µg/g extract and water yielding 3395 ± 111 µg/g extract. Mrkonjic’ et al. [34] compared different solvents, with water yielding 5.69 ± 0.30 µg/g dry weight and methanol extract yielding 5.80 ± 0.30 µg/g dry weight. Bujor et al. [7] conducted UAE of rowanberry fruits (40 kHz, 3 × 30 min) using a 3 × 600 mL mixture of acetone/water/acetic acid (80:19.5:0.5 v/v/v) and found chlorogenic acid content to be 2030 µg/g.
The content of epicatechin in the obtained extracts ranged from 41.24 to 349.94 µg/g. These results align with those of Cristea et al. [13], who found 74 µg/g of epicatechin in S. aucuparia. The obtained values are higher than those reported by Orsavová et al. [31], who measured epicatechin content in various sweet rowanberry cultivars, reporting values ranging from 3.3 to 31.1 µg/g.
The content of rutin in the obtained extracts ranged from 6.58 to 34.25 µg/g. The obtained results align with the findings of Gaivelyte et al. [32], who reported rutin content in S. aucuparia cultivar “Alaja Krupnaja” to range from 20 to 390 µg/g, and Orsavová et al. [31], who studied sweet rowanberry cultivars and reported values from 9.8 to 71.1 µg/g. Higher values were found by Šavikin et al. [33], who reported rutin content ranging from 40.1 to 598.3 µg/g dry weight. Bobinaite et al. [6] showed differences in rutin content based on the solvent used, with ethanol yielding 123.9 ± 5.9 µg/g extract and water yielding 44.51 ± 1.54 µg/g extract. Mrkonjic’ et al. [34] also compared different solvents, with water yielding 82.3 ± 1.25 µg/g dry weight and methanol extract yielding 80.4 ± 2.76 µg/g dry weight.
4.1. Effect of Time on the Yield of Specific Chemical Compounds
In our study, extraction time did not show a statistically significant effect on extraction efficiency within the tested range, which was a rather unexpected observation. This study analyzed the effect of ultrasound exposure ranging from 5 to 15 min, corresponding to total extraction times from 15 to 45 min, due to the use of a pulsed ultrasonic field with 2 s of ultrasound exposure followed by a 4 s break. A possible explanation for this phenomenon is that during sonication, key processes such as cell wall disruption and the release of bioactive compounds occur rapidly in the initial cycles of ultrasound exposure. Longer extraction times may not provide additional benefits, as most bioactive compounds are released within the first few minutes of the process.
The effect of UAE time on the yield of bioactive compounds from plant raw materials has been extensively studied and described in the literature. In the vast majority of cases, authors reported a significant correlation between ultrasound treatment time and the yield of classes of chemical compounds, most often expressed as total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), or anthocyanins. However, in our study, it was observed that for individual chemical compounds, these relationships became less clear or even insignificant, making it difficult to develop a statistically significant mathematical model to describe these relationships. Similar results to ours were obtained by Madrera and Valles [35] during ultrasound extraction of polyphenols from dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). The models developed for hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives and kaempferol 3-O-acetylglucoside indicated that within the 10 to 30 min range, ultrasound treatment time did not significantly affect the yield of the studied compounds [35].
4.2. Effect of Ultrasound Intensity on the Yield of Specific Chemical Compounds
Ultrasound intensity showed a significant impact on the extraction efficiency for two (rutin and neochlorogenic acid) out of the four studied phenolic compounds. The varying effects of intensity on the yield of individual compounds could be attributed to several factors. For compounds that positively responded to an increase in ultrasound intensity, the enhanced yield might be due to accelerated diffusion of substances from the interior of the cells into the solution, resulting from the stronger acoustic field. In contrast, for other compounds, the lack of significance could be explained by several factors. Within the amplitude range examined, we did not observe a statistically significant effect of ultrasound intensity on the extraction yield of chlorogenic acid and epicatechin (Figure 2 and Table 5 and Table 6). This finding is consistent with reports that mass-transfer enhancement in UAE can reach a plateau as power/amplitude increases, such that further intensification no longer translates into higher recovery of phenolic compounds [36]. At the same time, the literature indicates that overly intense conditions may initiate sonodegradation or isomerization of phenolics (including chlorogenic acid and catechins), which can potentially offset the benefits of stronger cavitation [37,38]. We therefore interpret the absence of an intensity effect under our conditions as a balance between enhanced disruption of the plant matrix and possible losses due to ultrasound-induced chemical transformations. Independent confirmation is provided by the results of Arruda et al. [39], who reported no statistically significant effect of ultrasound power on the yields of epicatechin, rutin, catechin, or ferulic acid during the extraction of polyphenols from araticum peel. Only a few authors have analyzed the impact of ultrasonic intensity on the content of specific chemical compounds. Baite et al. [40] extracted gallic acid from Ficus auriculata leaves using UAE. They demonstrated that the amount of gallic acid increased with sonication level from 83 mg/L at 30% to 224 mg/L at 50% (maximum value) and subsequently decreased. Arruda et al. [39] studied the impact of nominal ultrasonic power (160–640 W) and process time (0.5–5.0 min) on the recovery of phenolic compounds from araticum peel. The linear and quadratic effects of nominal ultrasonic power, as well as the interaction between nominal ultrasonic power and extraction time, were significant (p ≤ 0.1) for the content of rutin and chlorogenic acid. For epicatechin, only the interaction effect between nominal ultrasonic power and extraction time was significant (p ≤ 0.1), while the linear and quadratic coefficients for time were not significant. Ma et al. [41] investigated the impact of ultrasonic power (3.2, 8, 30, and 56 W) at 15 °C for 20 min on the yield of cinnamic acids (caffeic, p-coumaric, ferulic, sinapic) and benzoic acids (protocatechuic, p-hydroxybenzoic, vanillic) from citrus peels (Citrus unshiu Marc). At power levels ranging from 3.2 to 30 W, the yields of caffeic, sinapic, p-cinnamic, and vanillic acids increased from 36.9 to 57.0, 124.0 to 155.6, 79.6 to 106.8, and 28.8 to 32.6 µg/g of dry weight, respectively. The extraction yield of ferulic acid was significantly higher than that of the other acids and showed a clear upward trend as power increased from 3.2 W (951.9 µg/g of dry weight) to 56 W (1420.0 µg/g of dry weight). In contrast, the yields of p-hydroxybenzoic acids notably declined with higher ultrasonic power; for instance, from 3.2 to 30 W, the yields dropped from 37.1 to 31.8 µg/g of dry weight.
4.3. Effect of Ethanol Concentration on the Yield of Specific Chemical Compounds
Ethanol concentration in the solvent has the greatest impact on the extraction efficiency of individual polyphenols. Increasing ethanol concentration positively affected the extraction efficiency of chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, and epicatechin. For rutin no statistically significant relationship was found between their yield and ethanol concentration.
4.3.1. Solubility and Polarity
We attempted to correlate the different extraction yields of the studied compounds to the solubility of individual polyphenols in pure solvents like water and ethanol. However, this attempt was unsuccessful.
The lack of a clear relationship between the solubility of pure polyphenols in water and ethanol and their yield during ultrasonic extraction is attributed to differences in solubility characteristics and the extraction process mechanism itself. The solubility of pure chemical compounds in water or ethanol does not reflect their behavior in the plant matrix, where they are bound to macromolecules such as lignin, cellulose, or proteins. These bindings limit the release of compounds regardless of their theoretical solubility in pure solvents. Additionally, the presence of the acoustic field makes the release of these compounds more dependent on the efficiency of mechanically breaking down the plant matrix rather than on solubility in pure solvents.
Changing the ethanol concentration in the solvent alters its polarity, which plays a significant role in extraction. Polyphenols vary in polarity, meaning that optimal extraction occurs when the solvent’s polarity matches that of the compound. High ethanol concentrations can promote the release of some compounds, even if their solubility in pure alcohol is relatively low. Furthermore, the presence of other polyphenols can influence their mutual solubility in individual solvents.
The ultrasonic extraction process is complex and multifactorial, with efficiency depending on the synergy between the chemical properties of the compound, the characteristics of the plant matrix, and the process parameters. Ultimately, extraction efficiency is often more influenced by the kinetics of compound release and its interactions within the matrix than by solubility in pure solvents. As a result, while the solubility of pure compounds may play a role, it is not a key determinant, as demonstrated in most of the analyzed cases.
Although the mechanisms by which ethanol concentration influences the extraction efficiency of specific polyphenols are not fully understood, the observed relationships can be practically applied for the selective isolation of specific compounds. A key approach is to optimize the extraction parameters to maximize the yield of the target compound while minimizing the extraction of other components. Ethanol concentration in the solvent plays a crucial role here, as different polyphenols show varying yields depending on the water-ethanol ratio.
4.3.2. The Effect of Ethanol Concentration on the Presence of Individual Polyphenolic Compounds
The effect of ethanol concentration on the presence of individual polyphenolic com- pounds has also been observed by other authors. Isaikina et al. [42] demonstrated differences in the flavonoid and phenolic acid composition in rowanberry fruit extracts obtained using 40% and 95% ethanol. In both cases, rutin, apigenin, baicalin, kaempferol, scutellarin, cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, as well as chlorogenic, p-coumaric, vanillic, ferulic, caffeic, and gallic acids were detected. Extracts obtained with 40% ethanol also contained isorhamnetin, while those from 95% ethanol contained quercetin, cinnamic acid, and salicylic acid.
Hu et al. [43] demonstrated that increasing ethanol concentration from 10% to 70% led to higher extraction yields of chlorogenic acid from Lonicera japonica flower buds using ultrahigh pressure extraction. Above 70%, the yield sharply decreased. Bobinaite et al. [6] reported that the chlorogenic acid content in ethanol extracts from rowanberry was 3970 µg/g extract, whereas in our study, chlorogenic acid was absent at 90% ethanol concentration.
In the present study, neochlorogenic acid was absent under the following extraction parameters: time 45 min, ultrasound intensity 7.65 W/cm2, and solvent concentration 30%. Increasing the solvent concentration resulted in higher neochlorogenic acid content. Xia et al. [44] showed that in New Zealand damson plum extract, neochlorogenic acid content did not differ significantly between water and ethanol extracts during 20 and 60 min extractions. Statistically significant differences were observed at 40 min, with higher content in the ethanol extract. The increasing extraction yield of neochlorogenic acid with rising ethanol concentration can be attributed to positional isomerism. Neochlorogenic acid (3-O-CQA) has a slightly different arrangement of hydroxyl groups than chlorogenic acid (5-O-CQA), which alters the polarity distribution and weakens its ability to form hydrogen bonds with water. Adding ethanol lowers the polarity of the water–ethanol mixture and better matches the character of neochlorogenic acid, increasing its solubility and the concentration gradient, and thus the rate of transfer into the liquid phase. Interactions with the plant matrix further differentiate the behavior of the isomers: water causes strong swelling of cell walls and favors the release of more polar compounds such as chlorogenic acid, whereas neochlorogenic acid can bind more strongly to the more hydrophobic wall components (e.g., lignin, pectin) and therefore requires a more “organic” environment for effective desorption. Ultrasound amplifies both effects: in mixtures with higher ethanol content, the lower surface tension and viscosity promote cavitation, which disrupts cell walls and shortens the diffusion path while simultaneously facilitating the dissolution of neochlorogenic acid.
An increase in epicatechin content was observed with increasing ethanol concentration in our study. Koch et al. [45] performed ultrasound-assisted maceration of green tea leaves with water, an ethanol/water mixture (1:1 v/v), and ethanol, obtaining different results. The lowest epicatechin content was found in ethanol extracts (5.88 mg/200 mL), while the highest was in the water/ethanol mixture (14.32 mg/200 mL), and for water alone, the value was 12.25 mg/200 mL. The increasing extraction yield of epicatechin with rising ethanol concentration may result from a better match between the solvent mixture’s properties and the molecule’s character, as well as from the gradual weakening of its interactions with the plant matrix, which together increase solubility, enlarge the concentration gradient, and accelerate transfer into the liquid phase. Epicatechin (a flavan-3-ol) is moderately polar: it has several –OH groups but also an aromatic core; in pure water it readily forms extensive hydrogen bond networks and π–π aggregates, which limits its solubility, whereas the addition of ethanol lowers the dielectric constant of the mixture and leads to preferential solvation of the aromatic fragment, breaking up aggregation and increasing solubility. At the same time, epicatechin forms hydrogen-bonding and hydrophobic complexes with proteins, pectin, and lignin. A higher ethanol fraction weakens these interactions, enabling the epicatechin molecule to desorb more readily from cell-wall surfaces into the liquid phase. As a result, both mechanisms act synergistically, and an increasing ethanol fraction translates into a higher extraction yield.
The studies did not indicate an effect of solvent concentration on rutin content. The lack of a statistically significant effect of ethanol concentration on the extraction yield of rutin may stem from its glycosidic character and from compensating, opposing effects within the matrix. Rutin (quercetin-3-O-rutinoside), owing to its sugar moiety, exhibits strong preferential hydration and a high propensity for hydrogen bonding; thus, within the typical 30–70% v/v ethanol range, it remains distinctly hydrophilic, and its effective solubility changes only slightly because the mixture still provides sufficient water to solvate the glycone part. At the same time, increasing the ethanol fraction reduces tissue swelling (hindering penetration into cell walls) while simultaneously lowering viscosity and surface tension, improving wetting and mass transfer. For rutin, these effects can offset one another, resulting in a similar overall recovery regardless of ethanol concentration. Bobinaite et al. [6] reported the highest rutin content in ethanol extract from rowanberry pomace.
The extraction process can be carried out in multiple stages, adjusting ethanol concentration in subsequent cycles. This allows for the selective isolation of different compound groups in each fraction. Additionally, parameters like temperature, extraction time, and ultrasonic power can be fine-tuned to improve selectivity and extraction efficiency of the target compound.
5. Conclusions
This study aimed to determine the optimal process conditions for the extraction of individual phenolic compounds using ultrasonic extraction. Based on the conducted analysis, statistically significant mathematical models were developed for the following chemical compounds: neochlorogenic acid, epicatechin, and rutin. For chlorogenic acid, the model was found to be statistically insignificant. However, only in one cases—neochlorogenic acid—were acceptable statistical measures obtained, indicating high-quality models. These equations show appropriate values for the determination coefficients and other fitting indicators, which confirm their practical value in predicting the efficiency of the ultrasonic extraction process.
Obtaining statistically significant relationships for individual polyphenols proved to be considerably more challenging than creating models for entire groups of these compounds, such as TPC (total phenolic content) or TFC (total flavonoid content), which are widely discussed in the available literature. A likely reason for this phenomenon is the interactions between the individual polyphenols, which influence their diffusion process from the solid matrix into the solvent.
For all analyzed phenolic compounds, extraction time was found to be an insignificant factor affecting extraction efficiency. This suggests that a 15 min extraction in the presence of a pulsed ultrasonic field is sufficient to achieve optimal yields of these compounds.
The most significant factor affecting the extraction yield of the studied polyphenols was the ethanol concentration. This finding can be utilized for more selective separation of phenolic compounds at the extraction stage. By optimizing this parameter, the extraction conditions can be better adjusted to increase the efficiency of obtaining specific bioactive compounds, while limiting the co-extraction of other, less desirable substances. This approach opens possibilities for designing more selective processes, which is particularly important in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries, where the extraction of specific active ingredients in pure form is crucial.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.K.; methodology, Z.K. and J.L.; software, Z.K.; validation, Z.K.; formal analysis, Z.K. and M.K.; investigation, Z.K., J.L., M.K. and E.I.; resources, Z.K. and M.K.; writing—original draft preparation Z.K. and M.K.; writing—review and editing, Z.K. and M.K.; visualization, E.I.; supervision, Z.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This publication was supported by the Operational Program Integrated Infrastructure within the project: Demand-driven research for the sustainable and innovative food, Drive4SIFood 313011V336, co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bugała, W. Drzewa i Krzewy Iglaste, 1st ed.; Rolnicze i Leśne: Warszawa, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Olczyk, M.; Geszprych, A. Rośliny jadalne i lecznicze z rodzaju Sorbus L. Postępy Fitoterapii 2017, 18, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushforth, K. Trees: Of Britain & Europe; HarperCollins: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Arvinte, O.M.; Senila, L.; Becze, A.; Amariei, S. Rowanberry—A Source of Bioactive Compounds and Their Biopharmaceutical Properties. Plants 2023, 12, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladedunye, F.; Matthäus, B. Phenolic extracts from Sorbus aucuparia (L.) and Malus baccata (L.) berries: Antioxidant activity and performance in rapeseed oil during frying and storage. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobinaite, R.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J.; Šarkinas, A.; Liaudanskas, M.; Žvikas, V.; Viškelis, P.; Rimantas Venskutonis, P. Chemical composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities of the extracts isolated from the pomace of rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujor, A.; Miron, A.; Luca, S.V.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Silion, M.; Ancuceanu, R.; Dinu, M.; Girard, C.; Demougeot, C.; Totoson, P. Metabolite profiling, arginase inhibition and vasorelaxant activity of Cornus mas, Sorbus aucuparia and Viburnum opulus fruit extracts. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 133, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Mellenthin, A. Identification and quantitation of flavonols in rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) juice. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylli, P.; Nohynek, L.; Puupponen-Pimiä, R.; Westerlund-Wikström, B.; McDougall, G.; Stewart, D.; Heinonen, M. Rowanberry Phenolics: Compositional Analysis and Bioactivities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11985–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Krska, B.; Kiprovski, B.; Veberic, R. Bioactive Components and Antioxidant Capacity of Fruits from Nine Sorbus Genotypes. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zymone, K.; Raudone, L.; Raudonis, R.; Marksa, M.; Ivanauskas, L.; Janulis, V. Phytochemical Profiling of Fruit Powders of Twenty Sorbus L. Cultivars. Molecules 2018, 23, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Owczarek, A.; Zakrzewska, A.; Magiera, A.; Olszewska, M.A. Novel insight into biological activity and phytochemical composition of Sorbus aucuparia L. fruits: Fractionated extracts as inhibitors of protein glycation and oxidative/nitrative damage of human plasma components. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, E.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Patras, A.; Socaciu, C.; Pintea, A.; Tudor, C.; Sturza, R. The Influence of Temperature, Storage Conditions, pH, and Ionic Strength on the Antioxidant Activity and Color Parameters of Rowan Berry Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, G.; Blasi, F.; Montesano, D.; Ghisoni, S.; Marcotullio, M.C.; Sabatini, S.; Cossignani, L.; Lucini, L. Impact of conventional/non-conventional extraction methods on the untargeted phenolic profile of Moringa oleifera leaves. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Gilbert-López, B.; Mendiola, J.A.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Ibánez, E. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction and pressurized liquid extraction of phenolic compounds from Moringa oleifera leaves by multiresponse surface methodology. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, D.; Zenker, M.; Heinz, V.; Lee, D.U. Applications and potential of ultrasonics in food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Qu, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Shen, L. A green and recyclable ternary deep eutectic solvent for extracting flavonol glycoside from Ginkgo leaves: Mechanism insights based on molecular level. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 406, 125053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zhou, P.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Y. Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of flavonol glycosides from Ginkgo biloba: Optimization of efficiency and mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 114, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zou, W.; Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Shu, P. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction, characterization, and bioactivities of flavonoids from Cercis glabra leaves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 120, 107434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xie, P.; Hao, W.; Lu, D.; Qi, Y.; Mi, Y. Ionic liquids as electrolytes in aluminum electrolysis. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1014893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.L.; Junior, T.K.; Block, J.M.; Granato, D.; Nunes, I.L. Innovative approach for obtaining phenolic compounds from guava (Psidium guajava L.) coproduct using ionic liquid ultrasound-assisted extraction (IL-UAE). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 38, 102196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Sheng, Z. Optimization of process conditions for ionic liquid-based ultrasound- enzyme-assisted extraction of resveratrol from Polygonum Cuspidatum. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 108, 106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Srivastav, S.; Sharanagat, V.S. Ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) of bioactive compounds from fruit and vegetable processing by-products: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 70, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Centeno, M.R.; Knoerzer, K.; Sabarez, H.; Simal, S.; Rosselló, C.; Femenia, A. Effect of acoustic frequency and power density on the aqueous ultrasonic-assisted extraction of grape pomace (Vitis vinifera L.)—A response surface approach. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramić, M.; Vidović, S.; Zeković, Z.; Vladić, J.; Cvejin, A.; Pavlić, B. Modeling and optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from Aronia melanocarpa by-products from filter-tea factory. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 23, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Castello, E.; Rodriguez-Lopez, A.; Mayor, L.; Ballesteros, R.; Conidi, C.; Cassano, A. Optimization of conventional and ultrasound assisted extraction of flavonoids from grapefruit (Citrus paradisi L.) solid wastes. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus, Z.; Buczaj, A.; Pecyna, A.; Kapica, J.; Findura, P.; Kocira, S. Application of Response Surface Method in Pulsed Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Complex Plant Materials—A Case Study on Cannabis sativa L. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plawgo, M.; Kocira, S.; Bohata, A. Multi-Objective Optimization of the Green Extraction Conditions of Bio-Active Compounds from a Levisticum officinale WDJ Koch: Pareto Optimality and Compromise Solutions for Process Management. Agric. Eng. 2024, 28, 137–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywicka, M.; Kobus, Z. Effect of the Shape of Ultrasonic Vessels on the Chemical Properties of Extracts from the Fruit of Sorbus aucuparia. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus, Z.; Krzywicka, M. Energy Aspects of Flavonoid Extraction from Rowanberry Fruits Using Pulsed Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Energies 2023, 16, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsavová, J.; Juríková, T.; Bednaříková, R.; Mlček, J. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Content, Individual Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Sweet Rowanberry Cultivars. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaivelyte, K.; Jakstas, V.; Razukas, A.; Janulis, V. Variation in the contents of neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid and three quercetin glycosides in leaves and fruits of Rowan (Sorbus) species and varieties from collections in Lithuania. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šavikin, K.P.; Zdunić, G.M.; Krstić-Milošević, D.B.; Šircelj, H.J.; Stešević, D.D.; Pljevljakušić, D.S. Sorbus aucuparia and Sorbus aria as a Source of Antioxidant Phenolics, Tocopherols, and Pigments. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrkonjic, Z.; Nadjpal, J.; Beara, I.; Aleksic-Sabo, V.; Cetojevic-Simin, D.; Mimica-Dukic, N.; Lesjak, M. Phenolic profiling and bioactivities of fresh fruits and jam of Sorbus species. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrera, R.R.; Valles, B.S. Development and validation of ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) and HPLC-DAD method for determination of polyphenols in dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 85, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repajić, M.; Zorić, M.; Magnabosca, I.; Pedisić, S.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Elez Garofulić, I. Bioactive Power of Black Chokeberry Pomace as Affected by Advanced Extraction Techniques and Cryogrinding. Molecules 2025, 30, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Qiu, S.; Chu, B.; Fang, R.; Zheng, F. Degradation kinetics and isomerization of 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid under ultrasound: Influence of epigallocatechin gallate and vitamin C. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, D.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, Y. Investigation of (+)-catechin stability under ultrasonic treatment and its degradation kinetic modeling. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, H.S.; Silva, E.K.; Pereira, G.A.; Angolini, C.F.F.; Eberlin, M.N.; Meireles, M.A.A.; Pastore, G.M. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound process parameters on the phenolic compounds recovery from araticum peel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 50, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baite, T.N.; Mandal, B.; Purkait, M.K. Ultrasound assisted extraction of gallic acid from Ficus auriculata leaves using green solvent. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 128, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, D.H.; Ye, X.Q. Simultaneous extraction of phenolic compounds of citrus peel extracts: Effect of ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaikina, N.V.; Kalinkina, G.I.; Razina, T.G.; Zueva, E.P.; Rybalkina, O.Y.; Ulirich, A.V.; Fedorova, E.P.; Shilova, A.B. Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Is a Source of the Drug for Increasing the Efficiency of Tumor Chemotherapy. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 44, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Guo, T.; Jiang, W.J.; Dong, G.L.; Chen, D.W.; Yang, S.L.; Li, H.R. Effects of ultrahigh pressure extraction on yield and antioxidant activity of chlorogenic acid and cynaroside extracted from flower buds of Lonicera japonica. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Ahmmed, M.K.; Rashidinejad, A. Exploring efficient extraction methods: Bioactive compounds and antioxidant properties from New Zealand damson plums. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W.; Kukuła-Koch, W.; Czop, M.; Helon, P.; Gumbarewicz, E. The Role of Extracting Solvents in the Recovery of Polyphenols from Green Tea and Its Antiradical Activity Supported by Principal Component Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).