Abstract
In order to solve the problem of low thermal efficiency of a 130 t/h industrial circulating fluidized bed boiler, a computational particle fluid dynamic approach was used in this work to study two-phase gas–solid flow, heat transfer, and combustion. The factors influencing coal particle size distributions, air distribution strategies, and operational loads are addressed. The results showed that particle distribution exhibits “core–annulus” flow with a dense-phase bottom region and dilute-phase upper zone. A higher primary air ratio (0.8–1.5) enhances axial gas velocity and bed temperature but reduces secondary air zone (2.5–5.8 m) temperature. A higher primary air ratio also decreases outlet O2 mole fraction and increases fly ash carbon content, with optimal thermal efficiency at a ratio of 1.0. In addition, as the coal PSD decreases and the load increases, the overall temperature of the furnace increases and the outlet O2 mole fraction decreases.
1. Introduction
Circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers are characterized by their wide fuel applicability, high combustion efficiency, and low pollutant emissions, and hence are extensively used in coal-fired power generation, solid waste treatment, and many other fields [1,2,3,4]. In a CFB boiler, the mixing of the gas and particle phases is sufficient, which is beneficial for solid fuel combustion to improve heat and mass transfer. To better understand the operational characteristics of the CFB boiler, many researchers have studied the gas–solid flow and combustion characteristics of the CFB boiler by means of cold and hot test rigs. For example, Kim et al. [5] constructed a cold experimental rig to investigate the cyclical behavior of particles in the return material valve using bed materials of different particle sizes. Shi et al. [6] employed PIV (particle image velocimetry) to visually study particle movement in a circulating fluidized bed, gaining a deeper understanding of the complex two-phase gas–solid flow characteristics within the bed. Ersoy et al. [7] investigated the effect of secondary air injection (SA) on the fluid dynamics of circulating fluidized beds in a riser. They revealed CFB fluidization characteristics but could not directly guide the thermal efficiency optimization of an industrial-scale boiler due to the scale of their experimental apparatus. Furthermore, experimental studies are often costly, and it is often difficult to directly observe what happens within the reactor due to the high temperature and other restrictive conditions.
Numerical simulation has become an effective approach to understanding gas–solid flow and heat and mass transfer in CFB boilers with the development of computer technology [8,9]. A common approach is continuum-based CFD (computational fluid dynamics) [10,11,12,13,14,15]. However, due to the limitations of computational resources, it is still challenging to apply CFD methods to the simulation of a large-scale industrial CFB boiler. In order to overcome this, scholars have developed CPFD (computational particle–fluid dynamics) to study two-phase gas–solid flow at high solid-phase concentrations [16,17,18].
Several researchers have applied the CPFD method to small and medium-sized boilers. Farid et al. [19] investigated particle transport hydrodynamics and coal combustion in a 340 MW CFB combustor via CPFD simulation. The effects of coal feeder positions and coal feeding rates on operating indexes were examined. Huang et al. [20] employed the CPFD method to simulate the co-combustion characteristics of coal, biomass, and oil sludge in a 130 t/h CFB boiler, and conducted a detailed evaluation of the effects of the secondary air jet angle and excess air coefficient on the temperature and gas species distribution. Liu et al. [21] used the CPFD method to investigate the co-firing characteristics of biomass and biogas in a 130 t/h circulating fluidized bed boiler, systematically analyzing the effects of varying biogas blending ratios on combustion behavior and NO emissions. Chang et al. [22] employed the CPFD method to evaluate the effects of primary air volume and coal particle size on combustion and NOx emissions in a 220 t/h CFB boiler. Liu et al. [23] further simulated the impact of varying secondary air ratios and lower secondary air flow rates on combustion dynamics in a 440 t/h CFB boiler, demonstrating that increasing the upper secondary air ratio to 27% significantly enhances the combustion environment. Yan et al. [24] performed CPFD-based simulations on a 600 MW supercritical CFB boiler to investigate the influence of air–coal distribution under different load conditions, revealing and analyzing critical non-uniformity issues in combustion. Based on a literature review, the research findings collectively indicate that the CPFD method can accurately predict gas–solid flow patterns and combustion characteristics, providing a robust foundation for subsequent optimization efforts. However, recent CPFD modeling studies of industrial CFB boilers predominantly concentrated on NO emission mitigation strategies. Investigations focused on enhancing thermal efficiency in small- to large-scale CFB systems warrant continued application and refinement of the CPFD method. The above studies focused on multi-fuel co-firing or NOx emission reduction and did not systematically investigate the impact of the coupling between coal particle size distribution (PSD), air distribution strategy, and load on thermal efficiency. However, few scholars currently combine simulation with industrial tests to optimize boiler thermal efficiency so that the impact of changes in different parameters on the internal thermophysical properties of boilers can be more clearly understood.
CFB boiler thermal efficiency is determined by various heat losses [25]. The significant heat losses affecting thermal efficiency are flue gas heat loss and the heat loss resulting from the incomplete combustion of solids. Flue gas heat loss refers to the heat carried away by the flue gas as it exits through the exhaust system, while the heat loss caused by incomplete combustion of solids refers to the heat lost from solid fuel that is not fully combusted during the combustion process. By adjusting the primary and secondary air ratio, as well as the upper and lower secondary air ratio, the quality of fluidization in the boiler can be improved, leading to better combustion of the fuel. An appropriate coal size and bed material size can help with adjustments to the outlet oxygen concentration and the carbon content in the fly ash [26]. Lower outlet oxygen content and flue gas temperature reduce the heat loss of flue gas, while lower carbon content in the fly ash and bottom ash decreases the heat loss due to the incomplete combustion of solids.
Hence, this simulation study focuses on the key parameters of boiler heat loss, such as outlet oxygen content and fly ash carbon content. The effects of varying air distribution strategies, coal particle size distributions (PSDs), and load conditions on combustion characteristics are investigated. This simulation study is expected to provide useful guidelines for the operation and thermal efficiency optimization of an industrial-scale CFB boiler.
2. Model Description
2.1. Gas-Phase Governing Equations
The CPFD method is a numerical computational technique based on the multiphase particle–cell (MP-PIC) method, which can solve the coupling problem between a fluid and a large number of particles in three-dimensional space. The applicability of the CPFD approach has been well demonstrated in the literature [27,28]. In this approach, the gas phase is calculated by the Eulerian approach, whereas the particle phase is described by the Lagrange method, which is based on the ensemble-averaged Navier–Stokes equation. The large eddy simulation (LES) is employed to simulate the turbulence characteristics in the CFB. The flow of the particle phase is ascertained through the resolution of the transport equation for the particle distribution function (PDF), denoted as ƒ. For convenience, the key gas-phase governing equations are briefly given below.
Mass conservative equation:
Momentum equation of the fluid phase:
Energy equation of the fluid:
where is the volume fraction of the fluid, is the gas-phase density, is the gas-phase velocity, is the mass source term, is the stress tensor of the fluid, is the gravitational acceleration, p is the pressure of the fluid phase, and is the momentum source term of the fluid phase and particle phase within the unit control volume. In the energy governing equation, is the heat transfer from the wall, is the chemical energy transfer between the fluid phase and the solid phase, is the heat transfer from the discrete phase, is the total of molecular and turbulent thermal conductivity, and φ represents the energy dissipation term.
Species conservation equation for the gas phase:
where is the mass fraction of the fluid, and is the diffusion coefficient.
2.2. Particle-Phase Governing Equations
Particle momentum equation:
Motion equation of particles:
Transport equation for particle distribution function:
where designates the velocity of the particle phase, represents the particle density, signifies the volume fraction of the particles, and stands for the normal stress of the particles. is the particle distribution function, and A is the particle acceleration.
Energy equation of particles:
where denotes the temperature of the fluid phase, represents the temperature of the particle phase, symbolizes the heat transfer coefficient between the particles and the fluid, indicates the heat transferred via the chemical reaction occurring between the fluid phase and the particle phase, refers to the heat capacity at a constant volume, stands for the surface area of the particles, and designates the mass of particles.
The drag model of the Wen–Yu/Ergun model is used in this work. This model combines the characteristics of both the Wen–Yu model and the Ergun model and can yield good results in both the dense and dilute phases. The model is given below.
where denotes the volume fraction of particles, and represents the particle volume fraction at close pack. is the drag coefficient in the Wen–Yu drag force model [28], while serves as the drag coefficient in the Ergun model [29].
2.3. Heat Transfer Model
Radiative heat transfer and convective heat transfer are the main heat transfer mechanisms in the furnace of the CFBB. Radiative heat transfer plays a dominant role in the heat transfer within the furnace compared to convective heat transfer. For the CPFD method, radiative heat transfer is calculated by only considering the interactions between the particle phase and the furnace walls, as well as those between the fluid phase and the furnace walls.
2.3.1. Convective Heat Transfer Between Fluid and Wall [30]
2.3.2. Convective Heat Exchange Between Particles and Wall [30]
2.3.3. Radiative Heat Transfer
The radiative heat transfer of particles is not taken into account. Instead, only the radiative heat transfer between particles and the wall surface as well as that between the fluid and particles are considered:
where is the area of the wall, is the temperature of the wall, is the mass-weighted average particle mean temperature within a calculation unit, Fwp is a calculated view factor, σ is the Boltzmann constant, and εwp is the effective emissivity between the wall and the particles.
2.4. Chemical Reaction Model
The chemical reactions in this study are described based on the Arrhenius equation, with the Arrhenius constant represented as
where is the pre-exponential factor, E is the activation energy, E0 is the activation energy constant, R is the universal gas constant, c1 and c2 are constants, and T is the average temperature of the particles and the gas phase. The chemical reaction kinetic models involved in combustion are shown in Table 1 [31,32,33,34,35].

Table 1.
Chemical component reaction model.
3. Simulation Conditions and Model Validation
3.1. Model Boundary Conditions
The CFB boiler model and computational grid used in the simulation are shown in Figure 1. The CFB boiler model mainly consists of the furnace, cyclone separator, and return material valve. At the beginning, the boiler is filled with N2 and heated to a temperature of 850 °C; the temperature at the water-cooled wall is 573 K, and the other walls are set as adiabatic walls. The bed material is packed at the bottom of the furnace, with the dense-phase volume fraction assumed to be 0.47, and the bed height is set at 700 mm. Two coal feeding ports are located at the bottom of the front wall, and 11 secondary air inlets are arranged on both the front and back wall. The 11 secondary air inlets are divided into three rows: five in the upper row, two in the middle, and five in the lower row. The middle and lower rows are collectively referred to as the lower secondary air inlets. In total, 750,000 hexahedral grids, with densification at the secondary air inlet of the furnace. The maximum particle size of the coal does not exceed 13 mm (d50 = 1.8 mm), and the maximum particle size of the bed material does not exceed 3 mm (d50 = 1 mm). The parameters used in the simulation are provided in Table 2. The chemical composition of fuel properties is shown in Table 3, with the data sourced from factory measurements.
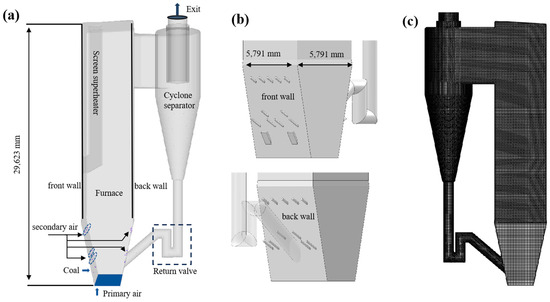
Figure 1.
(a) CFBB geometry, (b) location of the secondary air inlets and coal inlets on the front wall and back wall, and (c) model mesh.

Table 2.
Calculation conditions.

Table 3.
Coal quality analysis.
3.2. Model Validation
The simulation results are compared with industrial experimental data to verify the reliability of the CPFD model. Figure 2a shows the comparison of pressure variation along the furnace height with actual industrial data. For each measurement point, the experimental values agree well with the corresponding simulated values, with the difference ranging from 250 Pa to 542 Pa. Figure 2b shows the comparison of temperature variation along the furnace height with actual industrial data, with the error within a 10% range. These results indicate that although the simulation results deviate somewhat from the industrial data, the relative deviations are generally less than 10%, as shown in Table 4. Thus, the established model is deemed valid and can be applied for further investigation.

Figure 2.
Comparison of simulation results with industrial results: (a) pressure distribution along the furnace height, and (b) temperature distribution along the furnace height.

Table 4.
Comparison of industrial data and simulated data.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Gas–Solid Flow Characteristics
Figure 3 shows the transient distribution of the particle volume fraction from 0 s to 90 s within the CFB boiler, with particles colored by the solid volume fraction. It can be observed that between 0 s and 2.5 s, the coal particles and bed material particles in the furnace flow upward under the influence of the primary and secondary air, with a few particles moving radially outward. At 5 s, a small portion of particles enters the cyclone separator. At 20 s, the particles in the cyclone separator are transported to the return valve, and some particles from the material legs return to the furnace. At 60 s, a full circulation cycle is completed in the CFB boiler, and the flow regime of the entire boiler reaches a quasi-steady state. Therefore, the time-averaged simulation resulting from 60 s to 90 s is used for further analysis.
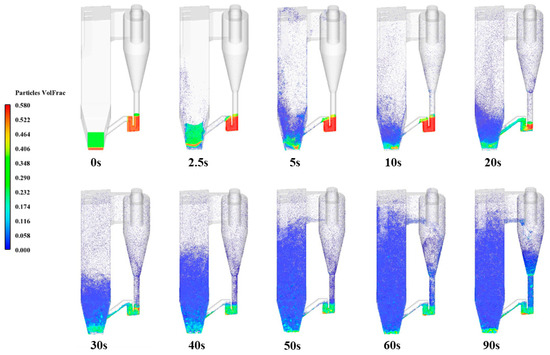
Figure 3.
Transient particle volume fraction distribution in the CFB boiler.
Gas and solid velocities within the CFB boiler provide an intuitive reflection of the gas–solid flow behavior. Figure 4a,b present the time-averaged axial gas and particle velocity distributions, showing that with the height increasing, gas velocity gradually decreases, while particle velocity gradually increases in the middle of the furnace. Figure 4c,d present the time-averaged radial particle velocity distribution in the furnace. In the near-wall regions, particle velocities are mostly of negative value, indicating a downward flow. In the central region, the velocities at different heights are more complex and diverse. At some heights, particles have relatively high velocities, varying between positive and negative values.

Figure 4.
Gas–solid phase flow characteristics in furnace: (a) gas velocity distribution, (b) particle velocity distribution, (c) radial distribution of particle velocities between the front and back walls, and (d) radial distribution of particle velocities between the left and right walls.
As shown in Figure 5a, the bottom of the furnace is primarily composed of bed materials, with a small portion of coal particles. As the height of the furnace increases, only a small amount of fine particles are carried upward by the gas flow. Therefore, the particle volume fraction decreases rapidly and reaches its lowest point at the furnace outlet, forming a dense-phase zone at the bottom and a dilute-phase zone at the upper part of the furnace. Figure 5b,c show the radial variation in the particle volume fraction at different heights. It can be observed that the volume fraction of particles near the wall is significantly larger, indicating that more particles gather near the wall. With the height increasing, particle distribution in the radial direction is more uniform, and the magnitude keeps decreasing.
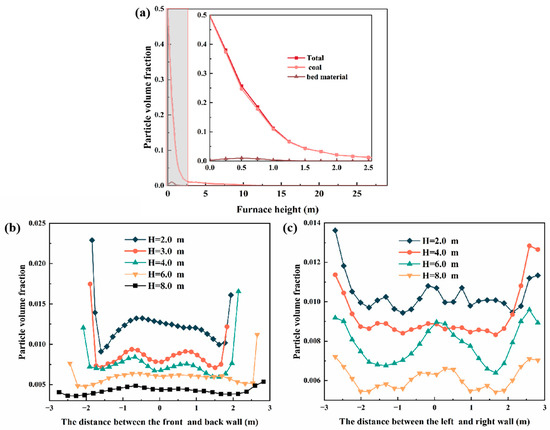
Figure 5.
Particle volume fraction distribution in furnace: (a) distribution of particle volume fraction along the furnace height, (b) distribution of particle volume fraction on the front and rear furnace wall, and (c) distribution of particle volume fraction on the left and right furnace wall.
4.2. Distributions of Temperature and Gas Component
Figure 6a shows the temperature distribution in the CFB boiler. Along the furnace height, the furnace temperature decreases from 910 °C to 870 °C. The temperature in the dense-phase zone at the bottom ranges from 860 °C to 910 °C, while the temperature in the transition zone is approximately 870 °C. After coal enters the furnace at the fuel inlet, it combusts with O2 in the primary and secondary air, releasing a large amount of heat and causing the temperature to rise. After radiative and convective heat transfer with the screen-type superheater and water-cooled wall, the temperature gradually decreases, reaching about 850 °C at the furnace outlet. Figure 6b shows the heat transfer distribution on the furnace wall. Overall, with the height increasing, the heat flux gradually decreases. In the transition zone, intense radiation/convection heat transfer occurs between the high-temperature flue gas, bed material, and water-cooled walls, resulting in the highest heat flux. In the middle of the furnace, the heat from the flue gas is transferred to the wall, raising the wall temperature and lowering the gas temperature, which leads to a fall in heat flux. In the upper region of the furnace, the combined effects of the screen-type superheater and water-cooled wall further reduce the furnace temperature.
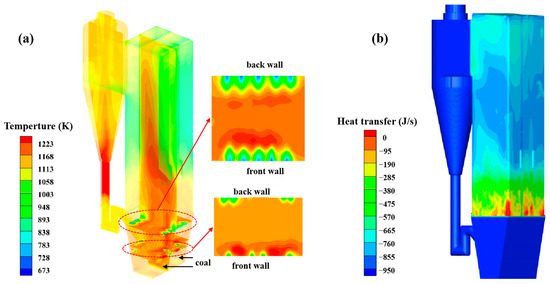
Figure 6.
CFB boiler temperature field: (a) temperature distribution (the inset figures show the local temperatures at the secondary air inlet region); (b) heat flux distribution.
Figure 7 shows the distribution of C content and gas species in the CFB boiler. As shown in Figure 7a, the carbon content in coal particles is highest at the bottom of the furnace. As a portion of these coal particles moves upward with the primary air, the carbon content keeps decreasing. Figure 7b shows the transient O2 concentration distribution in the CFB boiler. O2 is introduced from the bottom of the furnace, where it reacts with the coal and is rapidly consumed. The O2 concentration decreases sharply along the height of the furnace. At the furnace outlet, the O2 concentration drops to around 3.5%. Laterally, due to the additional secondary air introduced at the secondary air inlets, the O2 concentration is higher near the wall but lower in the center of the furnace. Figure 7c,d show the concentration distributions of CO and CO2 within the furnace. At the furnace bottom, oxygen-deficient combustion dominates, resulting in higher CO concentrations. However, after secondary air is introduced at higher positions to supplement additional O2, coal combustion is promoted. Simultaneously, the CO generated can react with O2 to form CO2. Therefore, the CO concentration gradually decreases along with the height of the furnace.
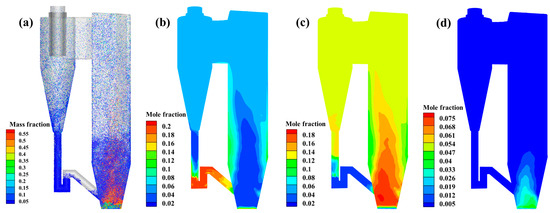
Figure 7.
Mass fraction of different species in the furnace: (a) C content by mass, (b) O2, (c) CO2, and (d) CO.
4.3. Effect of Coal Particle Size Distribution
Particle size distribution (PSD) of coal plays an important role in the combustion of the CFB boiler. It is recognized that the PSD significantly influenced the particle’s flow behavior [36]. The particle size distribution of coal and the volatile matter-to-fixed carbon ratio jointly determine the axial heat release distribution within the furnace, thereby influencing the design of the primary-to-secondary air ratio [37]. In this section, four different PSDs are chosen to evaluate their influence on the furnace performance. The PSDs are categorized into four groups based on their d50 (median particle diameter) of 0.9 mm, 1.8 mm, 3.6 mm, and 7.2 mm, as shown in Figure 8.
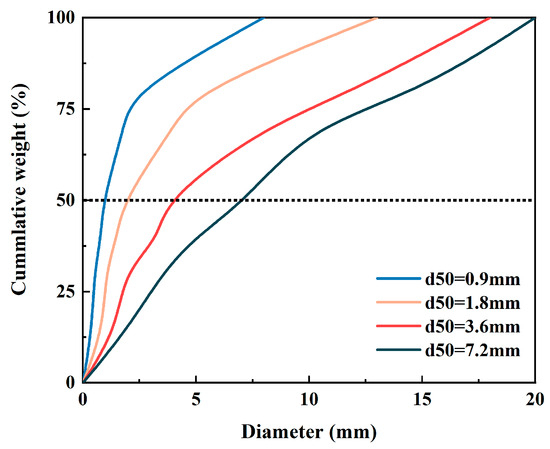
Figure 8.
Coal particle size distributions used in the simulation.
Figure 9 shows the axial mole fraction of O2 and the transient concentration profiles of O2 in the furnace for different PSDs as stable operations are achieved. It can be seen that the mole fraction of O2 reduces by decreasing the PSD. It can be seen that as the PSD decreases, the mole fraction of O2 decreases, and so does the mole fraction of O2 near the front wall. When d50 is dropped to 0.9 mm, a significant oxygen depletion occurs, forming a distinct oxygen-deficient zone in the upper furnace region. Figure 10 shows the fly ash carbon content at the cyclone outlet and the transient profiles of the carbon mass fraction for different PSDs. when the d50 decreases from 7.2 mm to 1.8 mm, the fly ash carbon content exhibits a gradual decreasing trend. However, when the d50 is further reduced to 0.9 mm, the fly ash carbon content increases significantly. Combined with the oxygen concentration profiles shown in Figure 9, the insufficient oxygen supply during the later combustion stage results in incomplete combustion of pulverized coal, leading to excessive carbon content in fly ash.
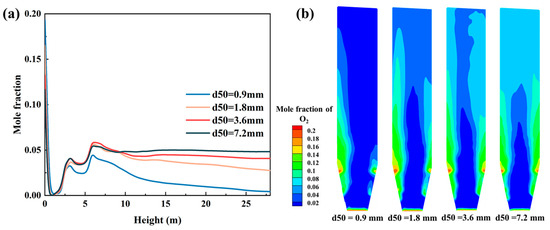
Figure 9.
(a) Furnace outlet carbon content in fly ash for different PSDs of coal and (b) mole fraction distribution of O2 for different PSDs.

Figure 10.
(a) Furnace outlet carbon content in fly ash for different PSDs of coal and (b) transient discrete particle mass fraction C(s) of furnace for different PSDs.
4.4. Effect of the Primary-to-Secondary Air Ratio
The ratio between primary air and secondary air significantly affects the flow characteristics and coal combustion properties in the CFB boiler, thereby influencing the temperature distribution and gas composition within the furnace. A reasonable secondary air ratio benefits combustion in the dense phase. Within a certain range, as the proportion of primary air rises, the carbon content in the fly ash tends to increase, resulting in a higher solid heat loss. In order to evaluate the influence of primary-to-secondary air ratios on combustion while maintaining a constant total air flow, five sets of controlled numerical experiments were conducted with primary-to-secondary air ratios set at 0.8, 1.0, 1.15, 1.3, and 1.5.
Figure 11a,b, respectively, show the axial gas velocity distribution and axial particle volume fraction along the furnace height for different primary-to-secondary air ratios. It can be observed that gas velocity at the furnace bottom (0~6 m) increases with the increase in the primary air ratio. As more particles are carried upward by the primary air, the particle volume fraction at the furnace bottom decreases with the increase in the primary air ratio, but at a height of 5 m, the particle volume fraction increases with the increase in the primary air ratio. This may be attributed to the fact that with a higher primary air ratio, larger particles are lifted higher, resulting in a higher particle concentration at that location. However, since the gas-phase velocity tends to stabilize for different primary-to-secondary air ratios above 5 m, the particle velocity also becomes stable.

Figure 11.
Effect of primary-to-secondary air ratios on the fluid velocity distribution (a) and particle volume fraction distribution (b) at different furnace heights.
Figure 12 shows the effect of the primary-to-secondary air ratio on the axial temperature in the furnace. It can be observed that with the increase in the primary-to-secondary air ratio, the bed temperature increases significantly between 2.5 m and 5 m but decreases gradually over 10 m. This trend is consistent with the variation in the particle volume fraction; with a constant total air flow, an increase in the primary air volume reduces the combustion in the dense-phase zone while increasing the combustion in the secondary air zone, which consequently causes the high-temperature area to move upwards.

Figure 12.
Average temperature distribution along furnace height under different primary-to-secondary air ratios.
Figure 13a illustrates the axial distribution of O2 and CO2 content in the furnace at different primary-to-secondary air ratios. It can be observed that as the primary air volume increases, the O2 content in the upper part of the furnace decreases. CO2 shows the opposite trend, which leads to a lower oxygen content at the furnace outlet, as shown in Figure 13b.
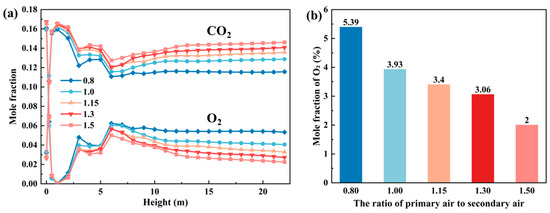
Figure 13.
Effects of different primary-to-secondary air ratios on gas distribution: (a) Changes in O2 and CO2 content along the direction of furnace height. (b) Furnace outlet O2 mole fraction under different primary-to-secondary air ratios.
Figure 14a shows the fly ash carbon content at the outlet under different primary-to-secondary air ratios. The fly ash carbon content increases with the increase in the primary-to-secondary air ratio, indicating that a higher primary air ratio is unfavorable for coal combustion. To improve the boiler’s thermal efficiency, both the flue gas heat loss and the unburned solid heat loss need to be minimized.
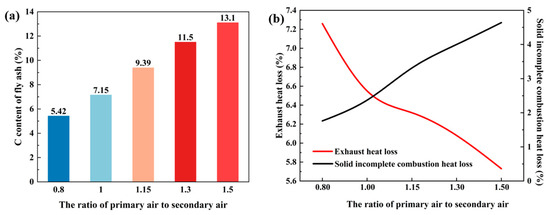
Figure 14.
(a) Furnace outlet carbon content in fly ash under different primary-to-secondary air ratios, and (b) exhaust and solid incomplete combustion heat loss under different primary-to-secondary air ratios.
As shown in Figure 14b, the flue gas heat loss decreases as the primary air ratio increases, while the unburned solid heat loss increases with the increase in the primary air ratio. Under these operating conditions, the flue gas heat loss is approximately 6.62%, the unburned solid heat loss is around 2.58%, and the overall thermal efficiency is about 89.30%. Therefore, when the primary-to-secondary air ratio is around 1.05, the heat loss and the overall thermal efficiency show high performance.
4.5. Effect of Upper-to-Lower Secondary Air Volume Ratio
The distribution of secondary air significantly affects the operational performance of the CFB boiler. It not only influences the combustion air flow within the furnace but also impacts the ignition and subsequent combustion of coal particles. The different methods of secondary air distribution are achieved by adjusting the degree of opening of the upper and lower secondary air valves while the total primary and secondary air flow remains constant. As mentioned in Section 3.1, the secondary air inlet can be divided into upper (five inlets) and lower inlets (six inlets, including two in the middle and four at the bottom). By adjusting the opening of the upper and lower secondary air baffles, the proportion of upper and lower secondary air volume can be controlled. In this study, the primary-to-secondary air ratio is fixed at 1.0, and five sets of comparison experiments are conducted, with the upper and lower secondary air valve openings set as 50%/100%, 75%/100%, 100%/100%, 100%/75%, and 100%/50%, respectively. The corresponding upper-to-lower secondary air flow ratios for these configurations are 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.33, and 2.0.
Figure 15 illustrates the effects of different upper-to-lower secondary air flow ratios on the axial gas velocity and particle volume fraction within the furnace. It can be observed that in the lower secondary air section (0~2.5 m), the gas velocity remains nearly constant (Figure 15a). However, in the region between the upper and lower secondary air (2.5~5.8 m), as the proportion of upper secondary air increases, the velocity gradually decreases. Above the transition zone (greater than 7.5 m), the velocity gradually increases with the increasing upper secondary air ratio. Figure 15b shows the effects of different upper-to-lower secondary air flow ratios on the axial particle volume fraction. In the lower secondary air section, the particle concentration increases with the ratio increasing. This phenomenon can be attributed to the decreased air flow in the lower secondary air section, which results in a lower air volume at the bottom of the furnace.
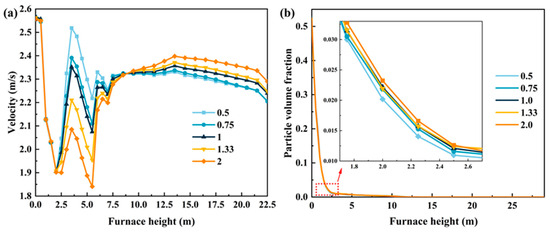
Figure 15.
Effects of upper-to-lower secondary air ratios on the fluid velocity distribution (a) and particle volume fraction distribution (b) at different furnace heights.
Figure 16 shows the effects of different upper-to-lower secondary air flow ratios on the time-averaged axial temperature within the furnace. It can be observed that by increasing the ratio, the temperature in the lower furnace (0~7.5 m) continuously decreases, indicating that the supplemental lower secondary air alleviates the oxygen-deficient combustion in the dense-phase zone. However, the temperature increases above 7.5 m, suggesting that as the volume of upper air increases, more oxygen is available for use, which improves combustion efficiency. At the furnace outlet, the temperature decreases with an increase in the ratio, indicating that when the proportion of upper secondary air is too high, the oxygen in the lower bed is reduced, delaying the coal combustion, which in turn leads to an increase in the temperature at the outlet.
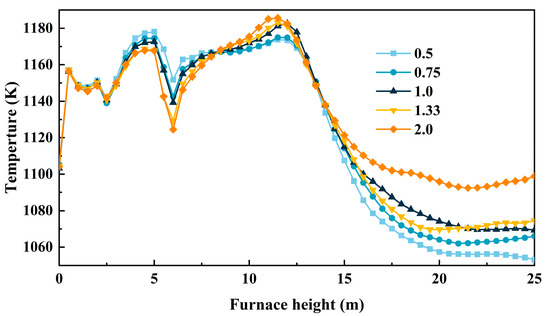
Figure 16.
Average temperature distribution along furnace height under different upper-to-lower secondary air ratios.
Figure 17 shows the effect of the upper-to-lower secondary air ratio on the mole fraction of O2 and CO2 in the furnace as well as the carbon content of the exit fly ash. As observed in Figure 17a, at a ratio of 2.0, oxygen is consumed fastest in the lower furnace, and the carbon dioxide content is also the highest. This may be attributed to the lower air volume and temperature of the secondary air at the lower section, which results in a lower oxygen concentration and higher temperature in this area, thereby accelerating coal combustion and increasing the CO2 content. As the height increases, the oxygen concentration rises with an increase in the upper secondary air volume. Figure 14b compares the simulated fly ash carbon content with industrial data. The simulation results show the same trend as the industrial results, with the highest fly ash carbon content (9%) at an upper-to-lower secondary air ratio of 0.5, and the lowest (6.8%) at a ratio of 1.33.

Figure 17.
Effects of different upper-to-lower secondary air ratios on species distribution: (a) changes in O2 and CO2 content along the furnace height direction, and (b) comparison of carbon content in fly ash between simulation and industrial results.
4.6. Effect of Operation Loads
The impact of operation load variation on the CFB boiler is reflected in multiple aspects, including temperature distribution, gas–solid fluidization, pollutant emissions, and load regulation dynamics [38,39]. In this section, three different boiler loads are investigated to evaluate their impact on furnace performance. These loads correspond to 50%, 60%, and 70% of the boiler maximum continuous rating (BMCR), as defined in Table 5.

Table 5.
Simulation schemes for different operation load conditions.
Figure 18 shows the particle velocity at different heights (2.5 m, 5 m, 10 m) on the left and right walls of the boiler under different load conditions. The velocity of particles in the central area of the furnace tends to zero in the radial direction of the furnace and gradually decreases as it moves closer to the wall. Particles close to the furnace wall are affected by gravity and friction, leading to a mixed reflux phenomenon of particles inside the furnace, which reflects the common core-annular flow features of particles in CFB boilers. As the load increases, the particle velocity near the wall is lower, and the radial change in the particle velocity at 2.5 m inside the furnace is more gentle. However, at 10 m inside the furnace, the radial change in the particle velocity is more intense, and the velocity value is smaller. This indicates that as the load increases, the circulation volume inside the furnace increases, and the interaction between the particles and the wall also strengthens.
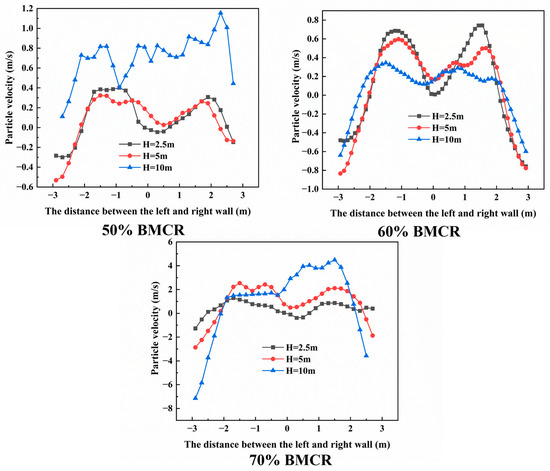
Figure 18.
Radial particle velocities at different heights under different operation loads.
The temperature distribution in the CFB boiler at the cross section of the furnace for different operation load conditions is shown in Figure 19. The temperature distribution in the furnace is mainly concentrated in the center region of the furnace at 50% BMCR, while the temperature in the sidewall region is relatively low. At 50% BMCR, the temperature distribution in the furnace is mainly concentrated in the center region of the furnace while the temperature in the sidewall region is relatively low. At 70% BMCR, the combustion reaction in the furnace is more intense, the heat concentration increases, and the temperature in the sidewall area also increases, but the temperature difference in the radial direction is relatively small. With the operation load increased, the temperature in the center region of the chamber is higher, forming a clear high-temperature core, while the temperature in the sidewall region also increases significantly, especially in the upper and lower sidewall regions of the chamber. Under high operation load conditions, the cyclic flow of particles in the furnace is enhanced, leading to heat transfer and accumulation in the sidewall region.
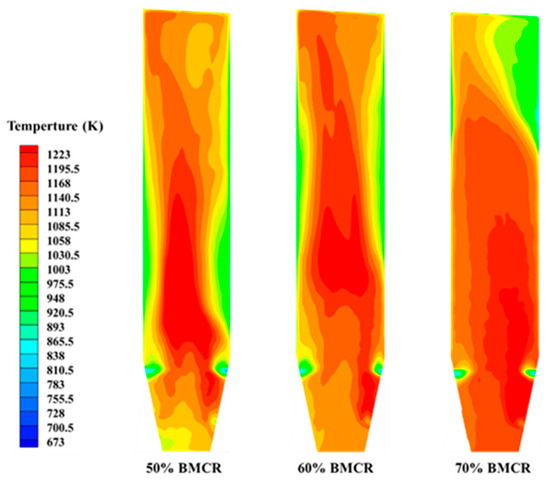
Figure 19.
Cloud diagram of furnace temperature profile under different operation loads.
Figure 20 shows the distribution of the O2 mole fraction under different operation load conditions. The O2 mole fraction is lowest at the furnace bottom, while the distribution of the O2 mole fraction at 50% BMCR conditions is relatively non-uniform, especially in the sidewall region of the chamber, where the O2 mole fraction is higher, and the oxygen-deficient zone in the center of the chamber increases with increasing load.

Figure 20.
Mole fraction distribution of O2 under different operation loads.
5. Conclusions
The CPFD approach is used in this work to study the gas–solid two-phase flow, heat transfer, and combustion in a 130 t/h CFB boiler. The effects of different coal particle size distributions, primary-to-secondary air ratios, upper-to-lower secondary air ratios, and operational loads on the gas–solid flow and combustion characteristics within the furnace are examined and analyzed. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- Particle distribution exhibits “core-annulus” flow with a dense-phase bottom region and dilute-phase upper zone. Maximum temperature (910 °C) occurs in the dense-phase region, decreasing to 850 °C at the outlet.
- (2)
- Rapid carbon depletion and O2-deficient combustion at the bottom of the furnace increases CO, which oxidizes to CO2 when secondary air is injected with O2 supplementation.
- (3)
- A higher primary air ratio (0.8~1.5) enhances axial gas velocity and bed temperature but reduces secondary air zone (2.5~5.8 m) temperature. A higher primary air ratio also decreases the outlet O2 mole fraction and increases the fly ash carbon content. When the primary-to-secondary air ratio is controlled at 1.0, the boiler thermal efficiency is the highest (89.3%). Increasing the upper-to-lower flow ratio lowers velocity in secondary air zones but elevates it above the transition zone. Fly ash carbon minimizes at a ratio of 1.33, correlating with enhanced lower furnace (0~7.5 m) cooling and upper furnace (>7 m) heating. When the upper-to-lower secondary air flow ratio is 1.33, the fly ash carbon content is the lowest (6.8%).
- (4)
- Reducing the median size (d50 = 7.2~1.8 mm) improves combustion (fly ash carbon: 13.5~6.8%; O2 depletion mitigated). Further reduction (d50 = 0.9 mm) shortens particle residence time, increasing fly ash carbon to 18.2%. The most recommended median particle size of pulverized coal is 1.8 mm. High load (70% BMCR) intensifies particle recirculation and wall heat accumulation, while low load (50% BMCR) induces O2 stratification. Under a 70% BMCR load, attention should be paid to the local high temperature caused by enhanced particle circulation. Under a 50% BMCR load, air distribution should be optimized to alleviate oxygen stratification.
The limitations of this study lie in not considering coal composition fluctuations, ash deposition, and sensitivity analysis of key parameters. In the future, research on multi-coal adaptability will be carried out, coupled with dynamic models of ash deposition; supplementary parameter sensitivity tests will be conducted, and industrial trials will be combined to verify the long-term stability of the optimized parameters.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.X. and Z.Z.; methodology, J.X.; software, J.X. and K.Z.; validation, K.Z. and W.H.; formal analysis, F.L. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z.; supervision, Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20232BAB214043) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52276154).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank Guizhou Tianfu Chemical Co., Ltd. for providing experimental and technical support for this project.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Wenbin Huang was employed by the company of Guizhou Tianfu Chemical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Varol, M.; Atimtay, A.T. Effect of biomass-sulfur interaction on ash composition and agglomeration for the co-combustion of high-sulfur lignite coals and olive cake in a circulating fluidized bed combustor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wu, Y.; Lan, X.; Liu, F.; Gao, J. Effects of the riser exit geometries on the hydrodynamics and solids back-mixing in CFB risers: 3D simulation using CPFD approach. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Deng, L.; Che, D. Development and technical progress in large-scale circulating fluidized bed boiler in China. Front. Energy 2020, 14, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Jia, L.; Wu, Y. Some combustion characteristics of biomass and coal cofiring under oxy-fuel conditions in a pilot-scale circulating fluidized combustor. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 7000–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.D. Effects of particle properties on solids recycle in loop-seal of a circulating fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 2002, 124, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.X. Experimental research of flow structure in a gas-solid circulating fluidized bed riser by PIV. J. Hydrodyn. 2007, 19, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, L.E.; Golriz, M.R.; Koksal, M.; Hamdullahpur, F. Circulating fluidized bed hydrodynamics with air staging: An experimental study. Powder Technol. 2004, 145, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Song, J.L.; Ma, J.L.; Chen, X.P.; Wachem, V.B. Gas flow distribution and solid dynamics in a thin rectangular pressurized fluidized bed using CFD-DEM simulation. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lu, B.N.; Wang, W.; Li, J.H. 3D CFD simulation of hydrodynamics of a 150 MWe circulating fluidized bed boiler. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoo, L.M. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of Lafia-Obi bituminous coal in a fluidized-bed chamber for air- and oxy-fuel combustion technologies. Fuel 2015, 140, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Elkamel, A.; Lohi, A. Effect of char combustion product distribution coefficient on the CFD modeling biomass gasification in a circulating fluidized bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywanski, J.; Czakiert, T.; Muskala, W.; Sekret, R.; Nowak, W. Modeling of solid fuels combustion in oxygen-enriched atmosphere in circulating fluidized bed boiler. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, C.; Duan, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, D. A simulation study of coal combustion under O2/CO2 and O2/RFG atmospheres in circulating fluidized bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Zhang, N.; Wang, W. CFD simulations of a full-loop CFB reactor using coarse-grained Eulerian–Lagrangian dense discrete phase model: Effects of modeling parameters. Powder Technol. 2019, 354, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J. Numerical and experimental study on oxy-fuel coal and biomass co-firing in the bubbling fluidized bed. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 5829–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, P.J.; Snider, D.M. Inclusion of collisional return-to-isotropy in the MP-PIC method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 80, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, P.J.; Zhao, P.; Snider, D.M. A model for collisional exchange in gas/liquid/solid fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1784–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, D.M.; Clark, S.M.; O’Rourke, P.J. Eulerian-Lagrangian method for three-dimensional thermal reacting flow with application to coal gasifiers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.M.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Hwang, J. Numerical investigation of particle transport hydrodynamics and coal combustion in an industrial-scale circulating fluidized bed combustor: Effects of coal feeder positions and coal feeding rates. Fuel 2017, 192, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jin, X.; Dong, L.; Li, R.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Che, D. CPFD numerical study on tri-combustion characteristics of coal, biomass and oil sludge in a circulating fluidized bed boiler. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 113, 101550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Xiang, X.; Gong, S.; Jia, C.; Wang, Q.; Sun, B.Z. Simulation of biogas co-combustion in CFB boiler: Combustion analysis using the CPFD method. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 59, 104610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Ma, X.R.; Wang, X.; Li, X.H. CPFD modeling of hydrodynamics, combustion and NOx emissions in an industrial CFB boiler. Particuology 2023, 81, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Sun, H.W.; Bi, Y.; Jia, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.L.; Qin, H.; Wang, Q. Effect of secondary air on NO emission in a 440 t/h circulating fluidized bed boiler based on CPFD method. Particuology 2023, 83, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Lu, X.F.; Wang, Q.H.; Kang, Y.H.; Li, J.B.; Xu, Z.; Lei, X.J.; Zheng, X.; Fan, X.C.; Liu, Z. Study on the influence of secondary air on the distributions of flue gas composition at the lower part of a 600 MW supercritical CFB boiler. Fuel Process Technol. 2019, 196, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.H.; Lu, X.F.; Zhang, R.D.; Li, J.B.; Wu, Z.L.; Liu, Z.C.; Yang, Y.T.; Wang, Q.H.; Kang, Y.H. Methods and applications of full-scale field testing for large-scale circulating fluidized bed boilers. Energier 2024, 17, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Guan, J.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Z. Combustion adjustment test of circulating fluidized bed boiler. Sch. Energ. 2017, 124, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.G.; Wang, H. Eulerian-Lagrangian simulation study of the gas-solid reacting flow in a bubbling fluidized coal gasifier. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Duan, L.; Ma, J.; Xiong, J.; Chen, X. Three-dimensional CFD simulation of oxy-fuel combustion in a circulating fluidized bed with warm flue gas recycle. Fuel 2018, 216, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.Y.; Yu, Y.H. Mechanics of fluidization. Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser. 1966, 62, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ergun, S. Fluid flow through packed columns. Chem. Eng. Prog. 1949, 48, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.C. Books Handbook of Fluidization and Fluid-Particle Systems, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Ma, X.R.; Wang, X.; Li, X.H. Computational particle fluid dynamics modeling and design of in-situ catalytic deNOx in an industrial CFB boiler. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 270, 118502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.R.; Liu, Q.W.; Zhong, W.Q.; Yu, A.B. Study on scale -up characteristics of oxy-fuel combustion in circulating fluidized bed boiler by 3D CFD simulation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 2136–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Song, G.L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, X.T.; Wang, C.; Ji, Z.C.; Lyu, Q.G.; Zhang, X.S. Application of post-combustion ultra-low NOx emissions technology on coal slime solid waste circulating fluidized bed boilers. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.M.; Li, R.B.; Wei, Q.J.; Liu, F.Q.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sohn, H.Y. Numerical simulation on gas-solid flow during circulating fluidized roasting of bauxite by a computational particle fluid dynamics method. Particuology 2024, 90, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Jo, S.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Moon, J.H.; Ra, H.W.; Yoon, S.M.; Lee, J.G.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.K.; et al. Low-NOx emission and amorphous siliceous ash production from rice husk combustion in circulating fluidized bed system. Fuel 2024, 374, 132441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Lan, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J. Effect of particle size distribution on hydrodynamics and solids back-mixing in CFB risers using CPFD simulation. Powder Technol. 2014, 266, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.; Cai, R.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. From a CFB reactor to a CFB boiler—The review of R&D progress of CFB coal combustion technology in China. Powder Technol. 2017, 316, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Zhu, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Lyu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhou, T. Issues in deep peak regulation for circulating fluidized bed combustion: Variation of NOx emissions with boiler load. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).