Study on the Evolution Law of Four-Dimensional Dynamic Stress Fields in Fracturing of Deep Shale Gas Platform Wells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regional Geological Overview and Geological Modeling
2.1. Geological Overview
2.2. 3D Geomechanical Modeling
3. Methodology
3.1. Fluid–Solid Coupling Mathematical Model
3.2. Fracture Propagation Criteria
3.3. Research Methodology
4. Study on the Evolution Laws of 4D Dynamic Stress Fields
4.1. Study on Single-Stage Stress Field Variation Patterns
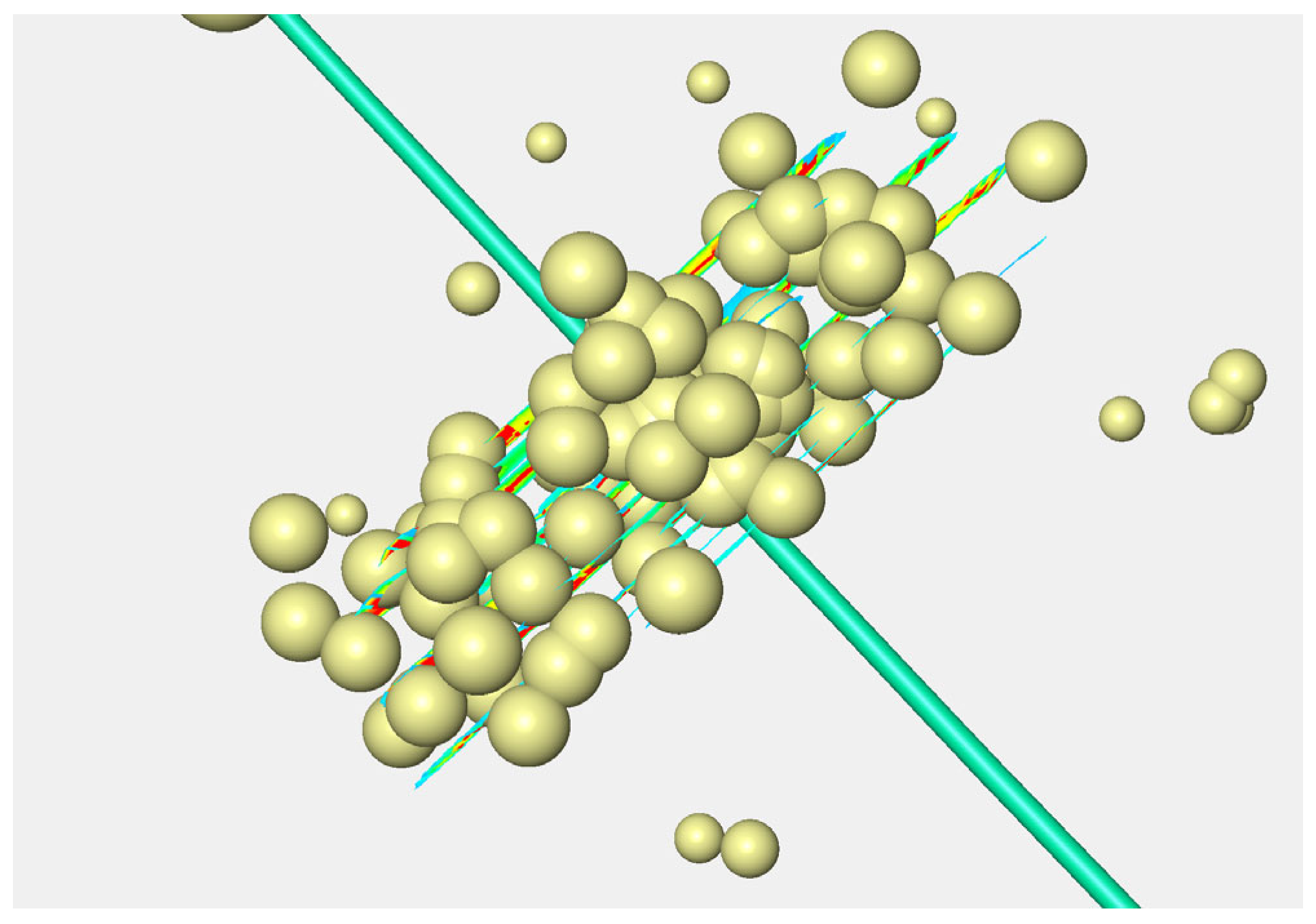
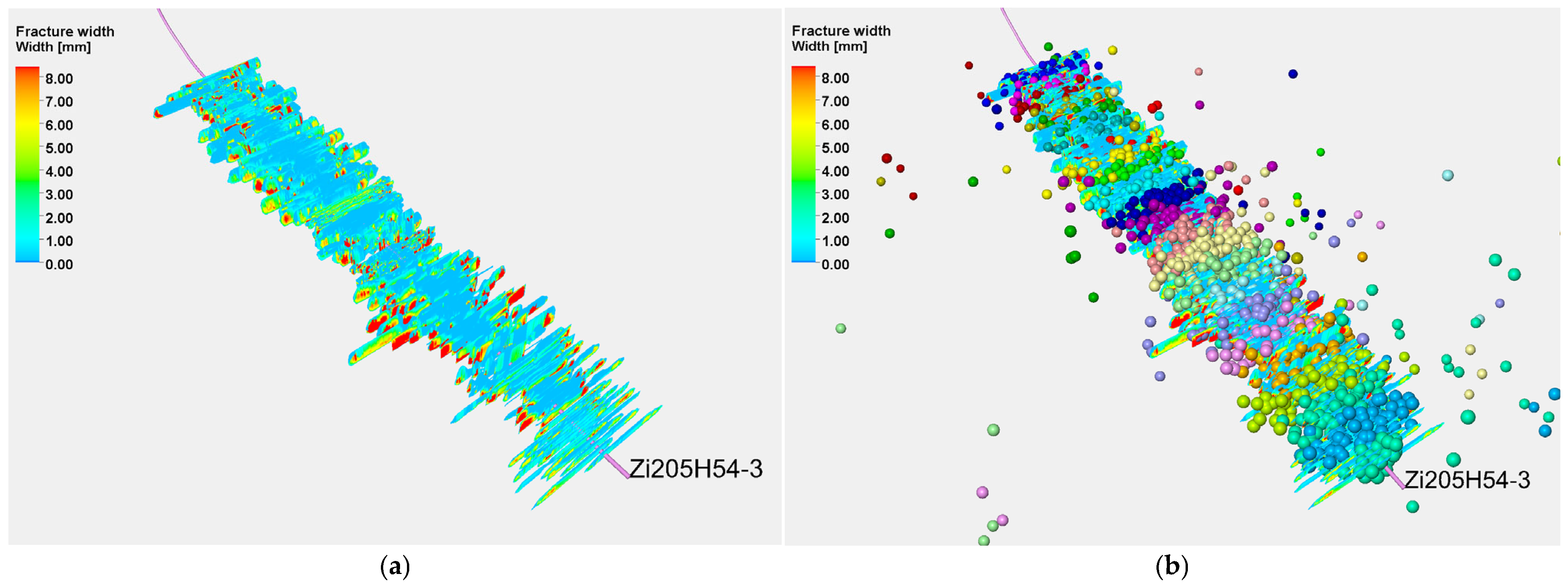
4.1.1. Fracture Propagation
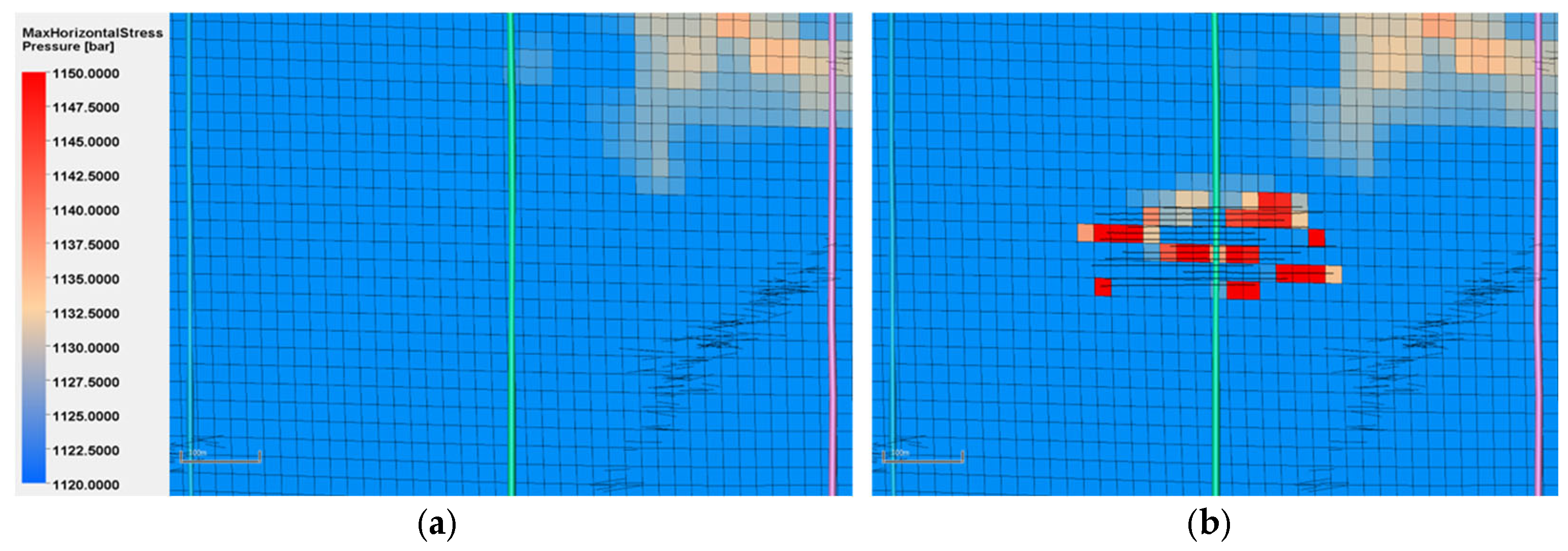
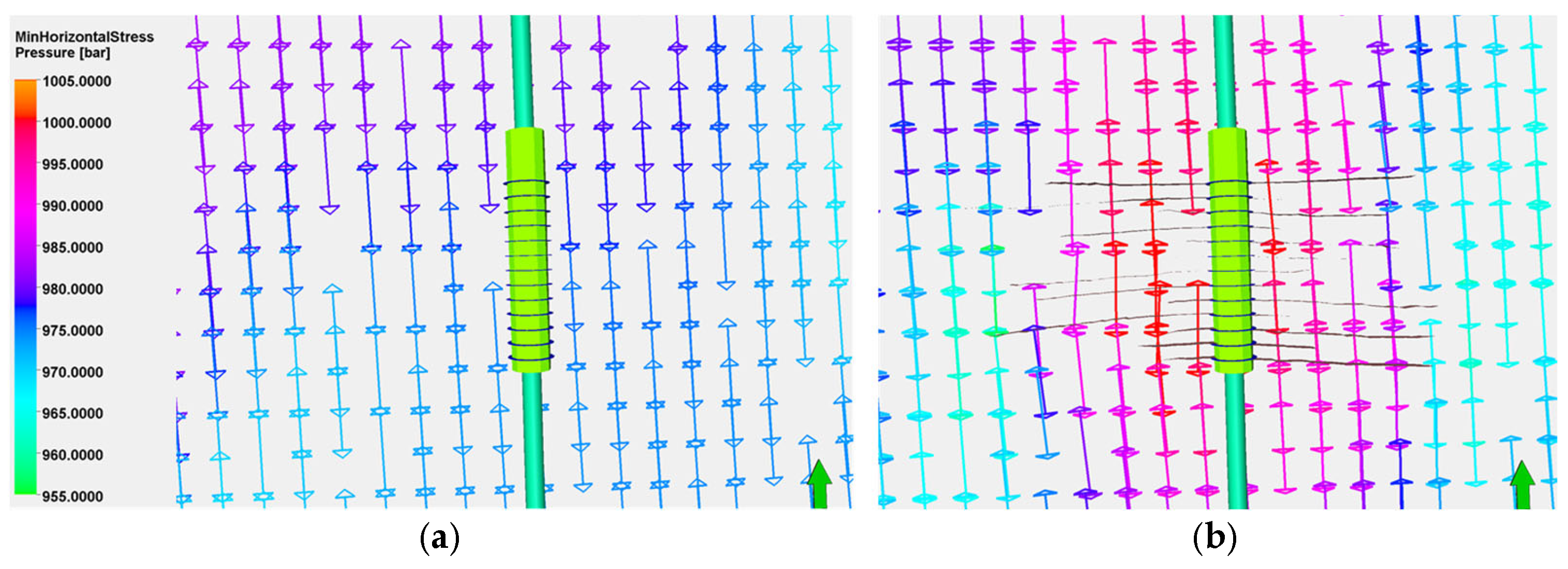
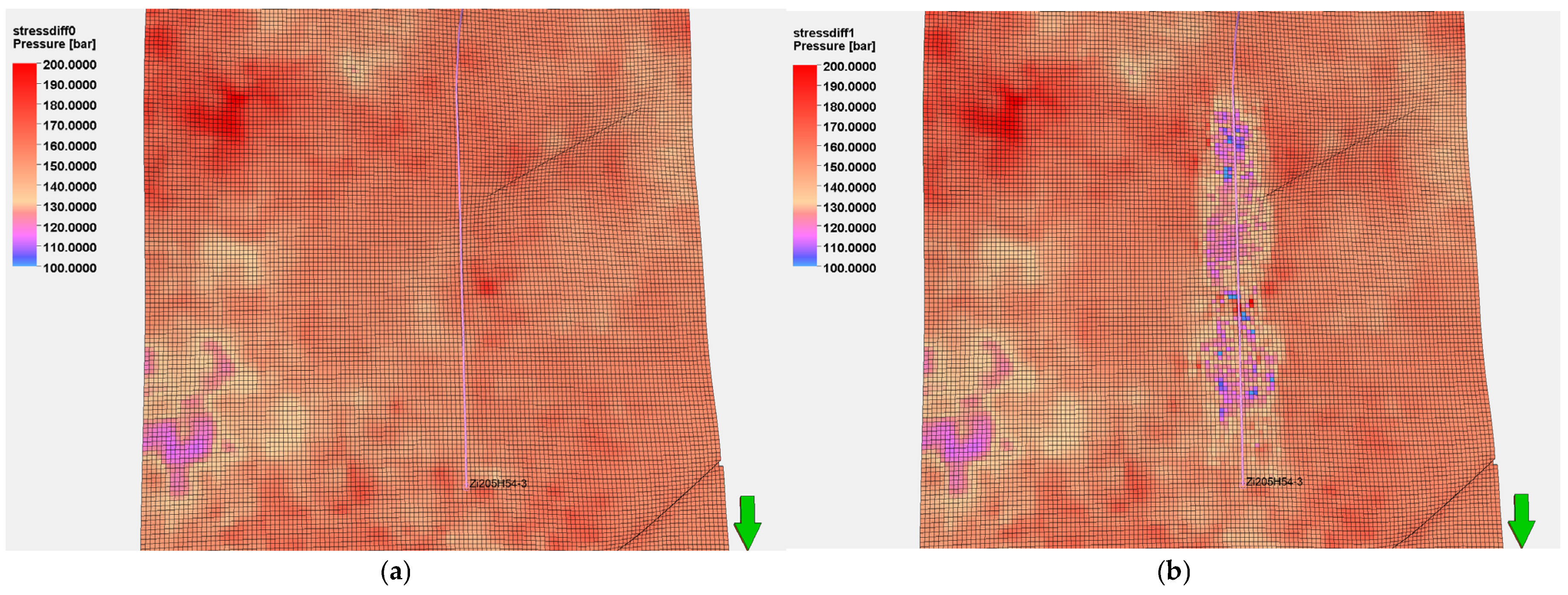
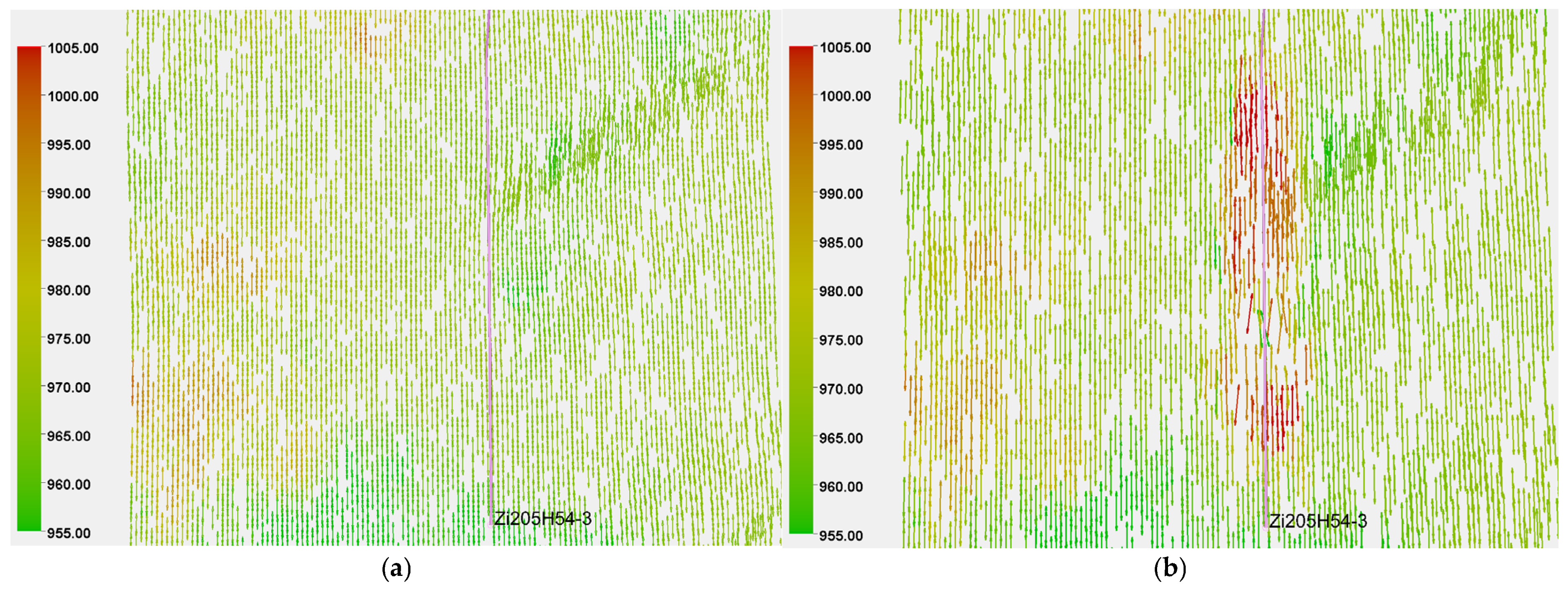
4.1.2. Stress Field Variation
- (1)
- Stress Magnitude Variation
- (2)
- Stress Orientation Variation
4.2. Single-Well Stress Field Evolution Study
4.2.1. Fracture Propagation
4.2.2. Stress Field Changes
- (1)
- Stress Magnitude Changes
- (2)
- Stress Direction Changes
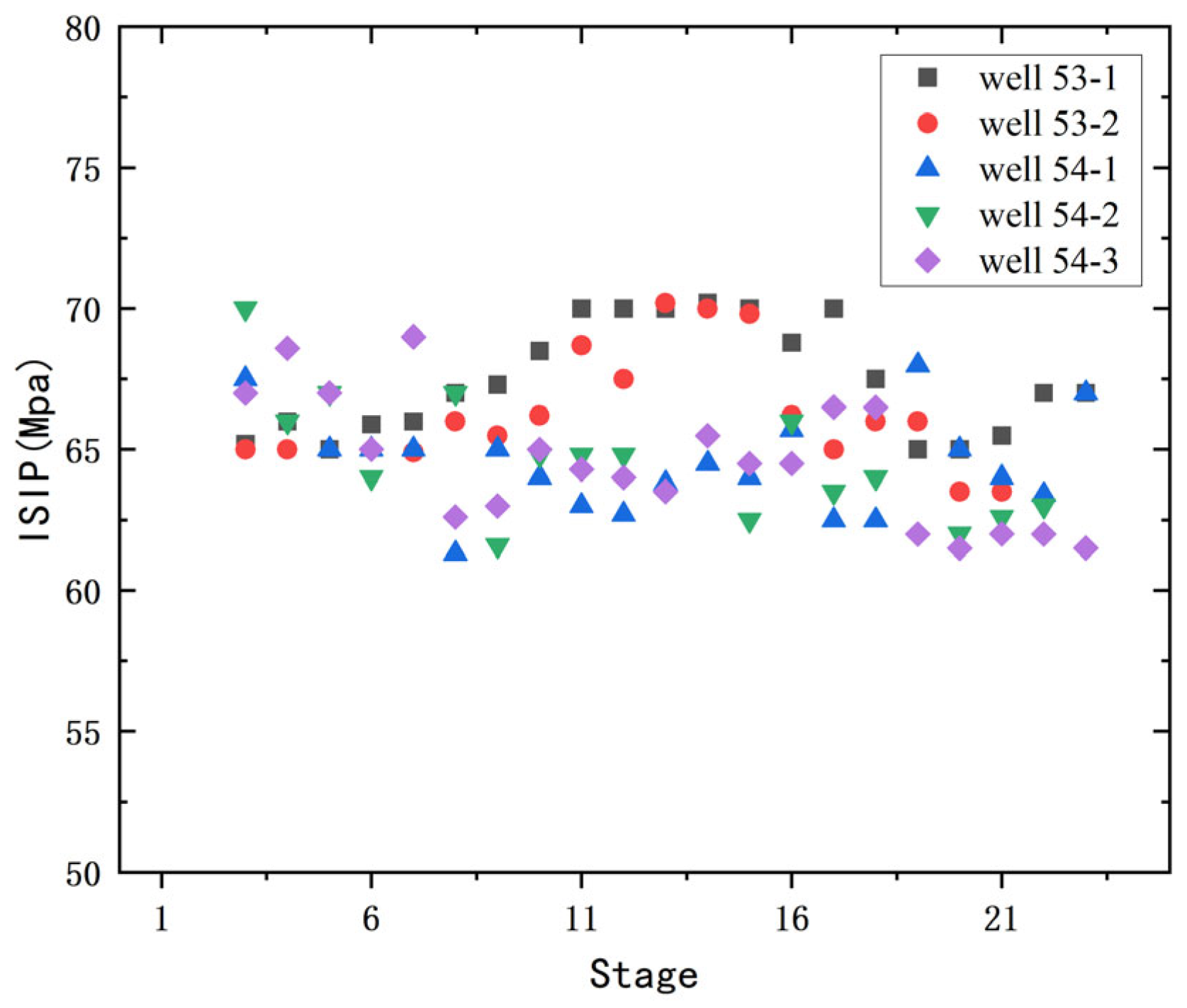
4.3. Platform Stress Field Evolution Study
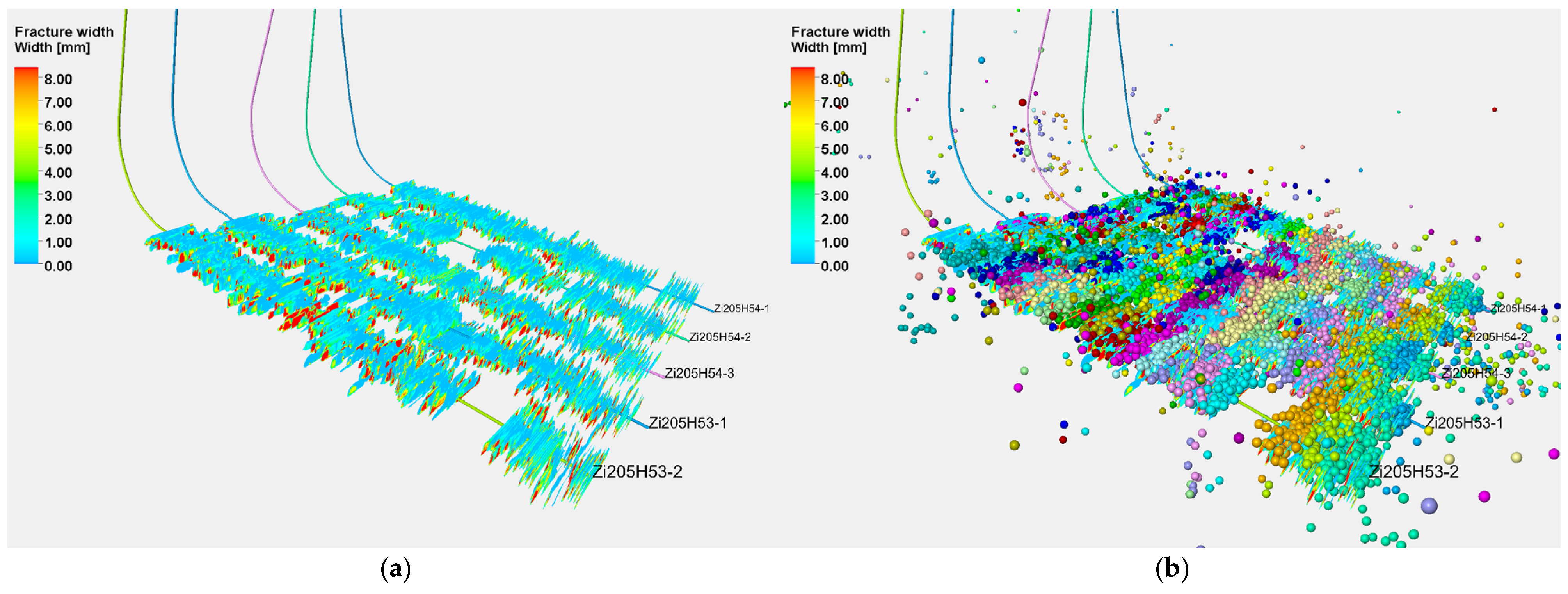
4.3.1. Fracture Propagation
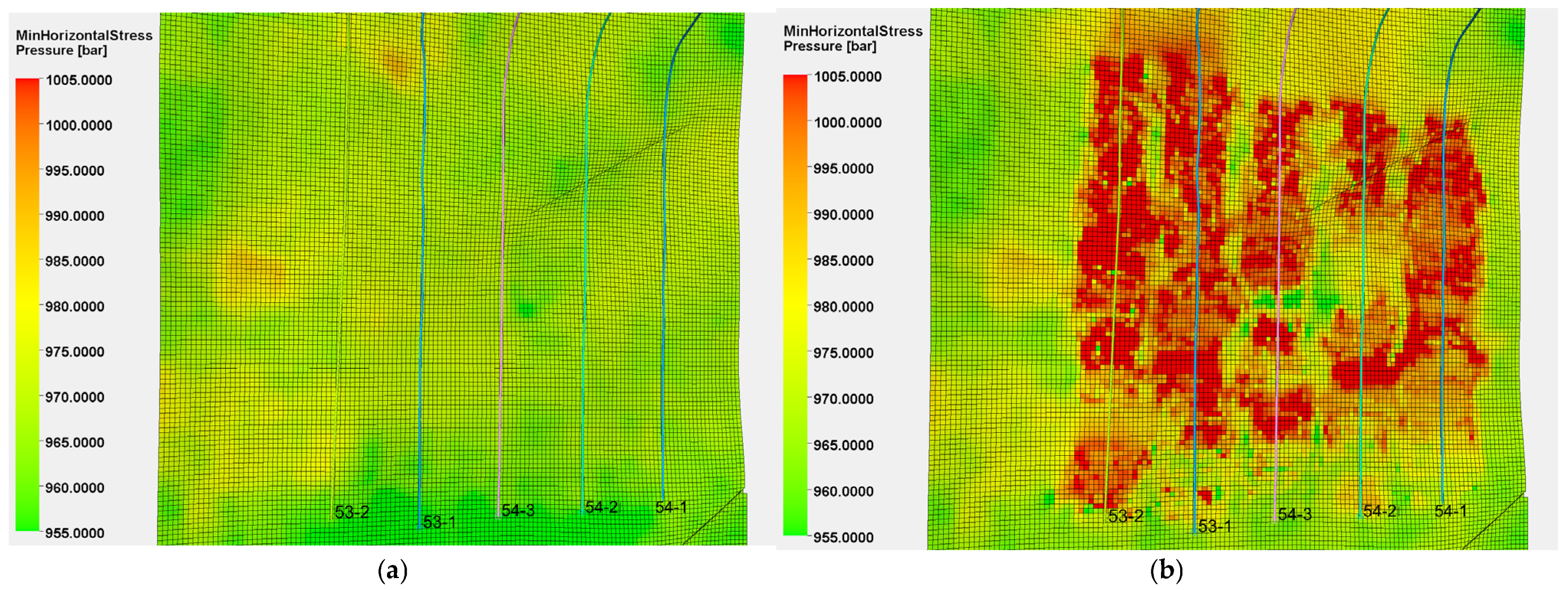
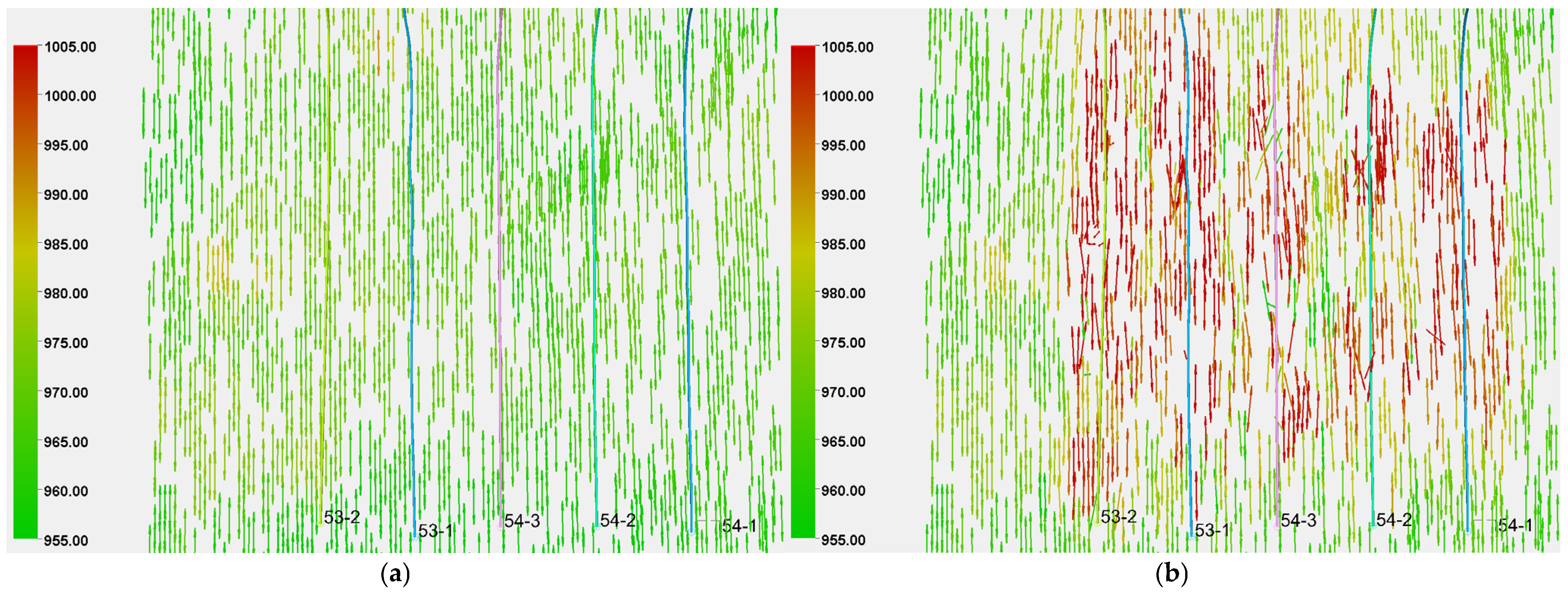
4.3.2. Stress Field Changes
- (1)
- Stress Magnitude Changes
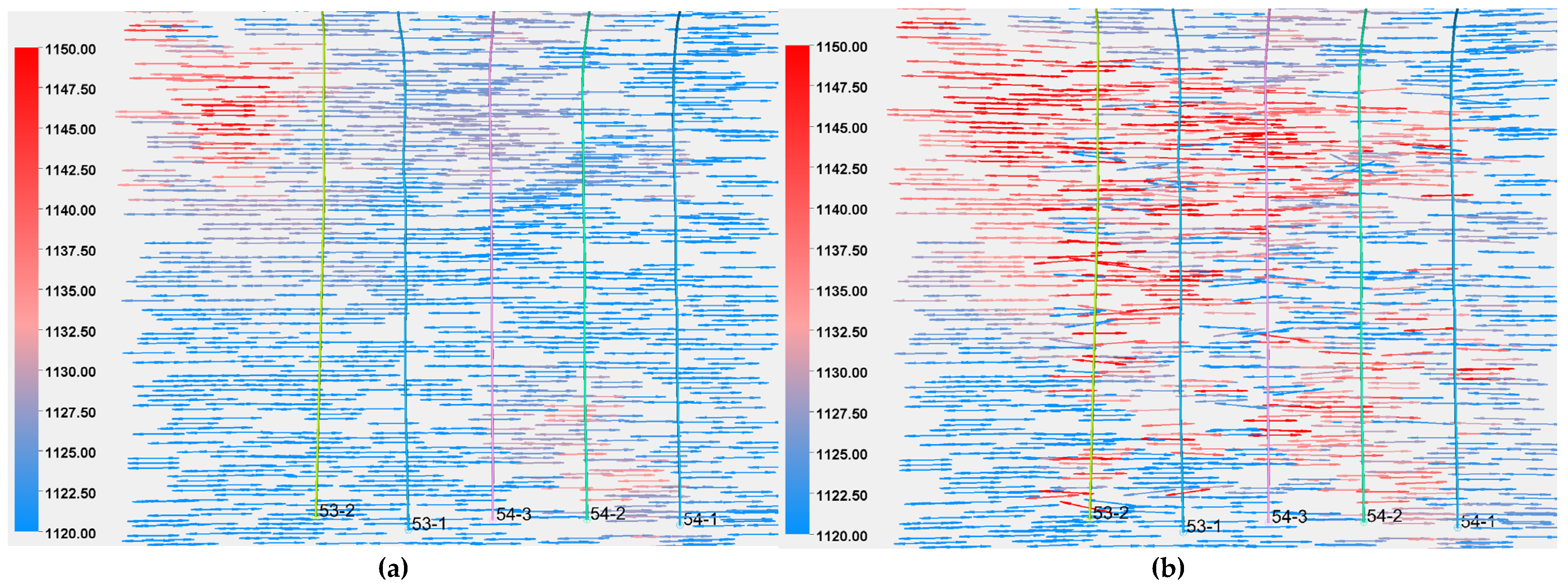
- (2)
- Stress Direction Changes
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The fracturing process has a significant impact on the magnitude and direction of the stress field. With the injection of fracturing fluid, both the minimum and maximum horizontal principal stresses show an increasing trend, with the minimum horizontal principal stress increasing by 1.8–6.4 MPa and the maximum horizontal principal stress increasing by 1.1–3.2 MPa; moreover, near the wellbore, the direction of in-situ stress deflects obviously.
- (2)
- As the number of fracturing stages increases, the minimum horizontal principal stress presents a significant cumulative growth trend, with a more prominent increase in the later stages. There is a phenomenon of stress accumulation along the wellbore, and the stress difference decreases from 15 MPa to 11 MPa.
- (3)
- The on-site adoption of the fracturing operation method featuring overall flush advancement and inter-well staggered fracture placement has achieved good stress balance; comparative analysis shows that the stress communication degree of the 400 m well spacing is weaker than that of the 300 m well spacing.
- (4)
- By studying the evolution laws of the stress field during fracturing and accurately identifying the distribution characteristics of the stress field, it is possible to guide the on-site real-time adjustment of the fracturing sequence, thereby improving the stress field balance and enhancing the fracturing stimulation effect. In future research, real-time in-situ stress measurement technology can be incorporated, and combined with the changes of the stress field during the production process, research on the stress field evolution throughout the whole life cycle of shale gas wells can be carried out.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| P | the fluid pressure, MPa |
| the maximum horizontal principal stress, MPa | |
| the minimum horizontal principal stress, MPa | |
| the total stress tensor, MPa | |
| G | the shear modulus, GPa |
| the Lamé constants | |
| the porosity | |
| the fluid density, kg/m3 | |
| the saturation | |
| the time, s | |
| the flow velocity vector | |
| the gradient operator with respect to three-dimensional coordinates | |
| the permeability, md | |
| the fluid viscosity, cp | |
| the gravitational acceleration constant, m/s2 | |
| the depth with surface as reference zero point, m | |
| the volumetric fluid flow rate per unit time, m3/s | |
| the fluid content in porous media | |
| the effective stress, MPa | |
| the normal stress on the wall of the natural fracture, MPa | |
| the bulk modulus of dry rock matrix, GPa | |
| the bulk modulus of dry solid matrix, GPa | |
| the attenuation coefficient, m−1 | |
| the ratio of the volume strain caused by pore pressure change to the pore pressure change, Pa−1 | |
| the external or body forces, Pa | |
| the equivalent stress intensity factor, Pa·m1/2 | |
| the Mode I stress intensity factor, Pa·m1/2 | |
| the Mode II stress intensity factor, Pa·m1/2 | |
| the shear stress on the fracture wall, MPa | |
| the cohesion of the rock, MPa | |
| the wall friction factor | |
| the net pressure required for the generation of tensile fractures, MPa | |
| the net pressure required for the generation of shear fractures, MPa | |
| the dynamic boundary positions in the x directions, m | |
| the dynamic boundary positions in the y directions, m | |
| the critical start-up pressure gradient, Pa/m |
References
- Guo, X.; Wang, R.; Shen, B.; Wang, G.; Wan, C.; Wang, Q. Geological characteristics, resource potential, and development direction of shale gas in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. Online 2025, 52, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Wu, H.; Yan, J. Key policy needs for the success of China’s shale gas revolution. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 4015–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wu, J.; Zeng, B.; Song, Y.; Yao, Z.; Dong, Y.; Du, Y. Measures and results of prevention and control on casing deformation and frac-hit in deep shale gas wells in southern Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2024, 11, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, X. Overpressure origin and evolution during burial in the shale gas plays of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations of southern Sichuan basin. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 236, 212729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; Li, Z.; Niu, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; et al. Shale gas accumulation patterns in China. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2023, 10, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Nie, H.; Dang, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Lu, Z. Shale Gas Exploration and Development in China: Current Status, Geological Challenges, and Future Directions. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6359–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ren, L.; Jiang, T.; Hu, D.; Wu, L.; Wu, J.; Yin, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lin, R.; et al. Ten years of gas shale fracturing in China: Review and prospect. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2022, 9, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, L.; Tang, X.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y. The distribution patterns of organic-rich shale and exploration prospect of shale gas in China. Adv. Resour. Res. 2022, 2, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, L. Deep shale gas in China: Geological characteristics and development strategies. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Z.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, H.-K.; Zhang, L.-F.; Song, T.; Liu, W.-B.; Li, H.-H.; Xu, Q.-C.; Wei, S.-Y.; Tao, S. Distribution characteristics, exploration and development, geological theories research progress and exploration directions of shale gas in China. China Geol. 2022, 5, 110–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, S.; Chen, X. Characteristics of in-situ stress distribution in Zhengzhuang Region, Southern Qinshui Basin, China and its stress path during depletion. Eng. Geol. 2020, 264, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, J. Prediction of Pore Pressure–Induced Stress Changes during Hydraulic Fracturing of Heterogeneous Reservoirs through Coupled Fluid Flow/Geomechanics. J. Eng. Mech. 2019, 145, 05019001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, J.B.; Müller, B.I.R.; Müller, T.M.; Heidbach, O.; Tingay, M.R.P.; Weißhardt, A. Pore pressure stress coupling in 3D and consequences for reservoir stress states and fault reactivation. Geothermics 2014, 52, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Eichhubl, P. Poroelastic models for fault reactivation in response to concurrent injection and production in stacked reservoirs. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2020, 24, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanzadeh, H.; Hawkes, C.D. Assessing fault reactivation tendency within and surrounding porous reservoirs during fluid production or injection. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 2008, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Eaton, D.W. Fault activation by hydraulic fracturing in western Canada. Science 2016, 354, 1406–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, H.; Ge, H.; He, J. Study on Fracture Propagation Rules of Shale Refracturing Based on CT Technology. Processes 2024, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, I.N. The distribution of stress in the neighbourhood of a crack in an elastic solid. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1946, 187, 229–260. [Google Scholar]
- Crouch, S.L. Solution of plane elasticity problems by the displacement discontinuity method. I. Infinite body solution. Int. J. Numer. Meth Eng. 1976, 10, 301–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.P.; Sharma, M.M. Quantifying Transient Effects in Altered-Stress Refracturing of Vertical Wells. SPE J. 2010, 15, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.P.; Florez, H.A.; Rodriguez, A.A. Hydraulic fracture propagation from infill horizontal wells. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 September–2 October 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Chen, M. Dynamic fracture propagation in hydraulic re-fracturing. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 70, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, H. Comparison of consecutive and alternate hydraulic fracturing in horizontal wells using XFEM-based cohesive zone method. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 143, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. General theory of three-dimensional consolidation. J. Appl. Phys. 1941, 12, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geertsma, J. The effect of fluid pressure decline on volumetric changes of porous rocks. Trans. Aime 1957, 210, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekhnitskii, S.G.; Fern, P.; Brandstatter, J.J.; Dill, E.H. Theory of elasticity of an anisotropic elastic body. Phys. Today 1964, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Sepehrnoori, K. Investigation of parent-well production induced stress interference in multilayer unconventional reservoirs. Rock. Mech. Rock. Eng. 2022, 55, 2965–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Maxwell, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y. Fault reactivation and induced seismicity during multistage hydraulic fracturing: Microseismic analysis and geomechanical modeling. SPE J. 2020, 25, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glubokovskikh, S.; Sherman, C.S.; Morris, J.P.; Alumbaugh, D.L. Transforming microseismic clouds into near real-time visualization of the growing hydraulic fracture. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 234, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.F.; Gowida, A.; Ali, A.; Elkatatny, S. Machine learning application to predict in-situ stresses from logging data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khormali, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Aleksandrov, A.N. Analysis of reservoir rock permeability changes due to solid precipitation during waterflooding using artificial neural network. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2025, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchell, P.; Bourne, S. Rocks under strain: Strain-induced time-lapse time shifts are observed for depleting reservoirs. Lead. Edge 2005, 24, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwanger, J. Seismic geomechanics: How to build and calibrate geomechanical models using 3D and 4D seismic data. In Proceedings of the Fourth EAGE CO2 Geological Storage Workshop, Stavanger, Norway, 23–25 April 2014; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; p. cp-439-00001. [Google Scholar]
- Onaisi, A.; Fiore, J.; Rodriguez-Herrera, A.; Koutsabeloulis, N.; Selva, F. Matching Stress-Induced 4D Seismic Time-Shifts with Coupled Geomechanical Models. In Proceedings of the 49th U.S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2015; p. ARMA-2015-801. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Tang, X.H.; Liu, Q.Y.; Li, K.D.; Xiao, J.L.; Jiang, S.; McLennan, J.D. 4D multi-physical stress modelling during shale gas production: A case study of Sichuan Basin shale gas reservoir, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 167, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, Q.; Jiao, S.; Chen, L.; Guo, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y. Integrated Workflow with Static and Dynamic Geomechanical Modelling for Hydraulic Fracturing Optimization. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 23–25 May 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Singh, H.; Cai, J. Spontaneous imbibition in shale: A review of recent advances. Capillarity 2019, 2, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J. High-performance FEM-FVM solid-fluid coupled dynamic analysis method for soil liquefaction. Jpn. Geotech. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2024, 10, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

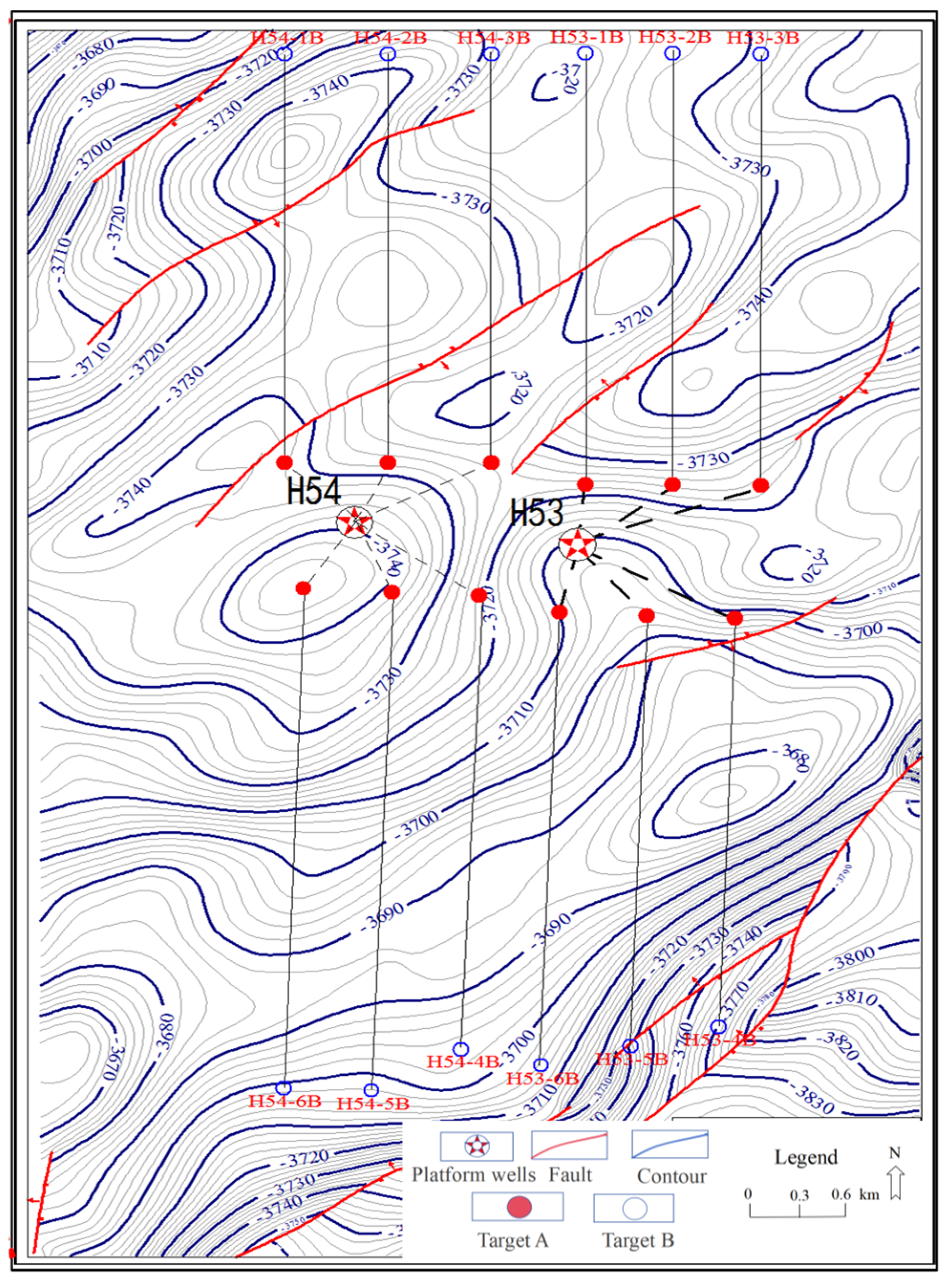
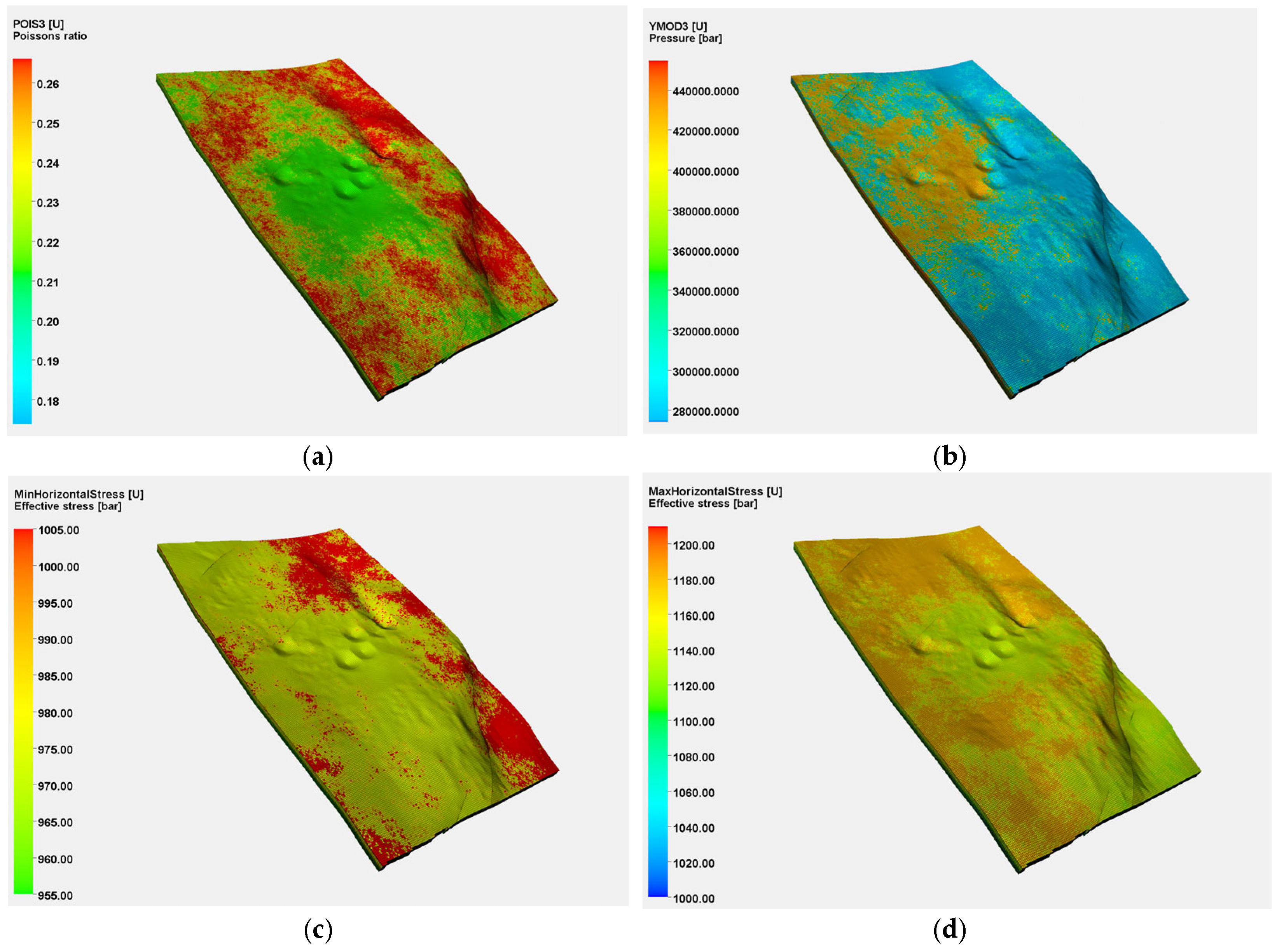









| Formation Pressure/MPa | Permeability/mD | Porosity/% | Young’s Modulus/GPa | Poisson’s Ratio | Minimum Horizontal Stress/MPa | Maximum Horizontal Stress/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 85.6~90.8 | 0.001~0.002 | 2.7~4.5 | 27~45 | 0.17~0.27 | 80~104 | 100~121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, P. Study on the Evolution Law of Four-Dimensional Dynamic Stress Fields in Fracturing of Deep Shale Gas Platform Wells. Processes 2025, 13, 2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092709
Wu Y, Zhu Z, Shen Y, Yu X, Liu G, Liu P. Study on the Evolution Law of Four-Dimensional Dynamic Stress Fields in Fracturing of Deep Shale Gas Platform Wells. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092709
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yongchao, Zhaopeng Zhu, Yinghao Shen, Xuemeng Yu, Guangyu Liu, and Pengyu Liu. 2025. "Study on the Evolution Law of Four-Dimensional Dynamic Stress Fields in Fracturing of Deep Shale Gas Platform Wells" Processes 13, no. 9: 2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092709
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhu, Z., Shen, Y., Yu, X., Liu, G., & Liu, P. (2025). Study on the Evolution Law of Four-Dimensional Dynamic Stress Fields in Fracturing of Deep Shale Gas Platform Wells. Processes, 13(9), 2709. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092709






