Phosphorus Removal from Piggery Wastewater Using Alginate-like Exopolymers from Activated Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biopolymers Recovery and Hydrogel Beads Preparation
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
2.3. Analytical Characterization Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yield of ALE Extraction from AS
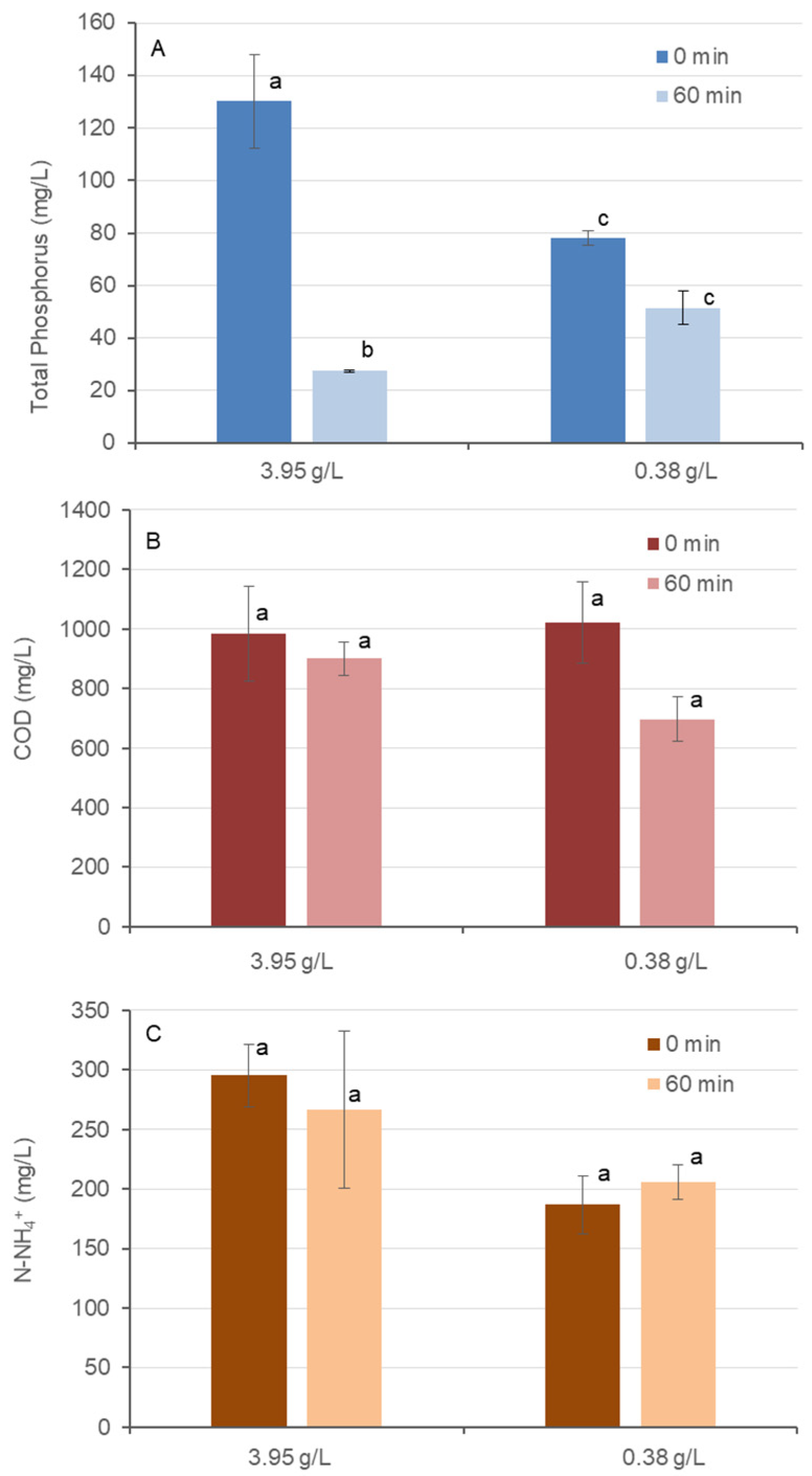
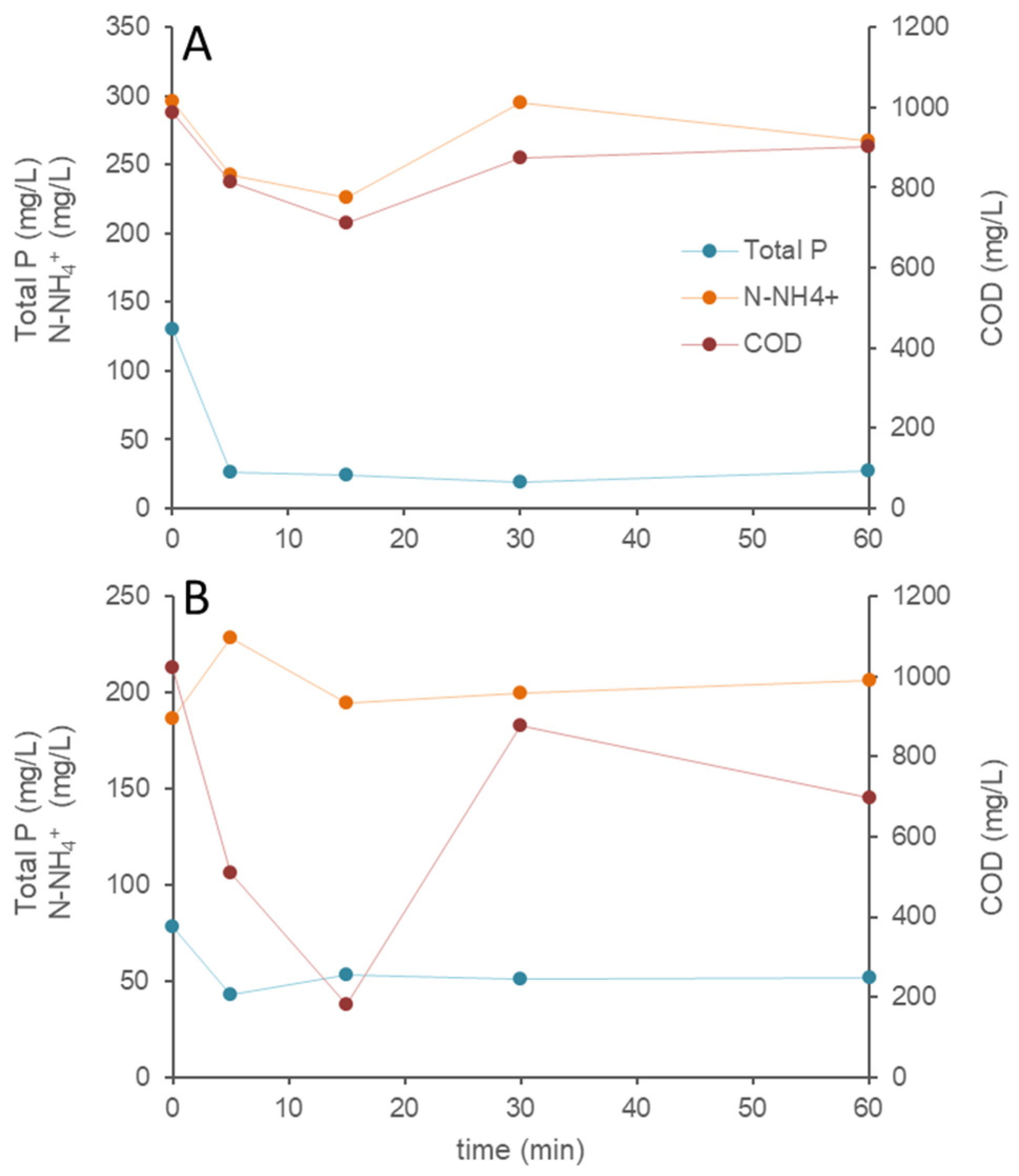
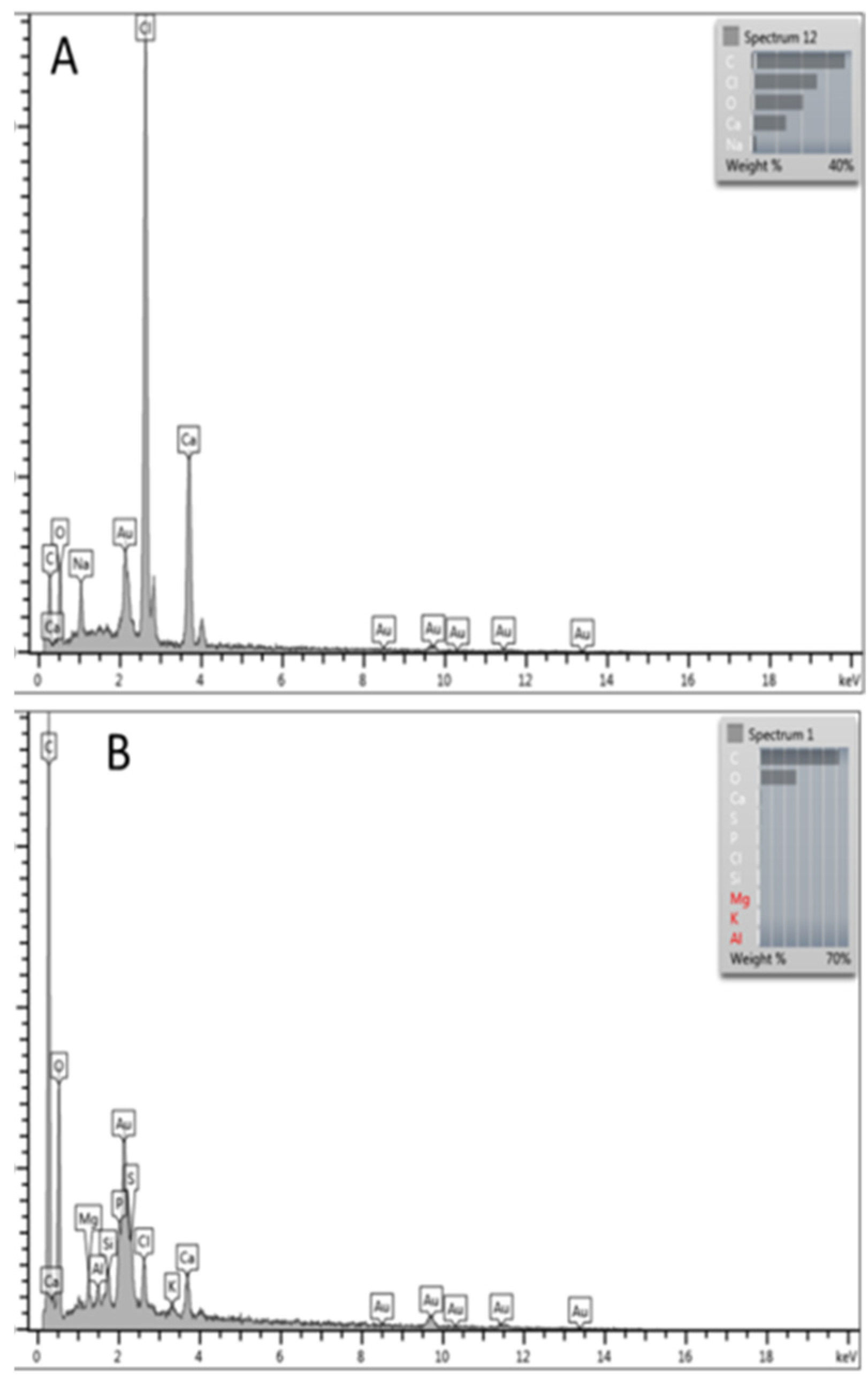
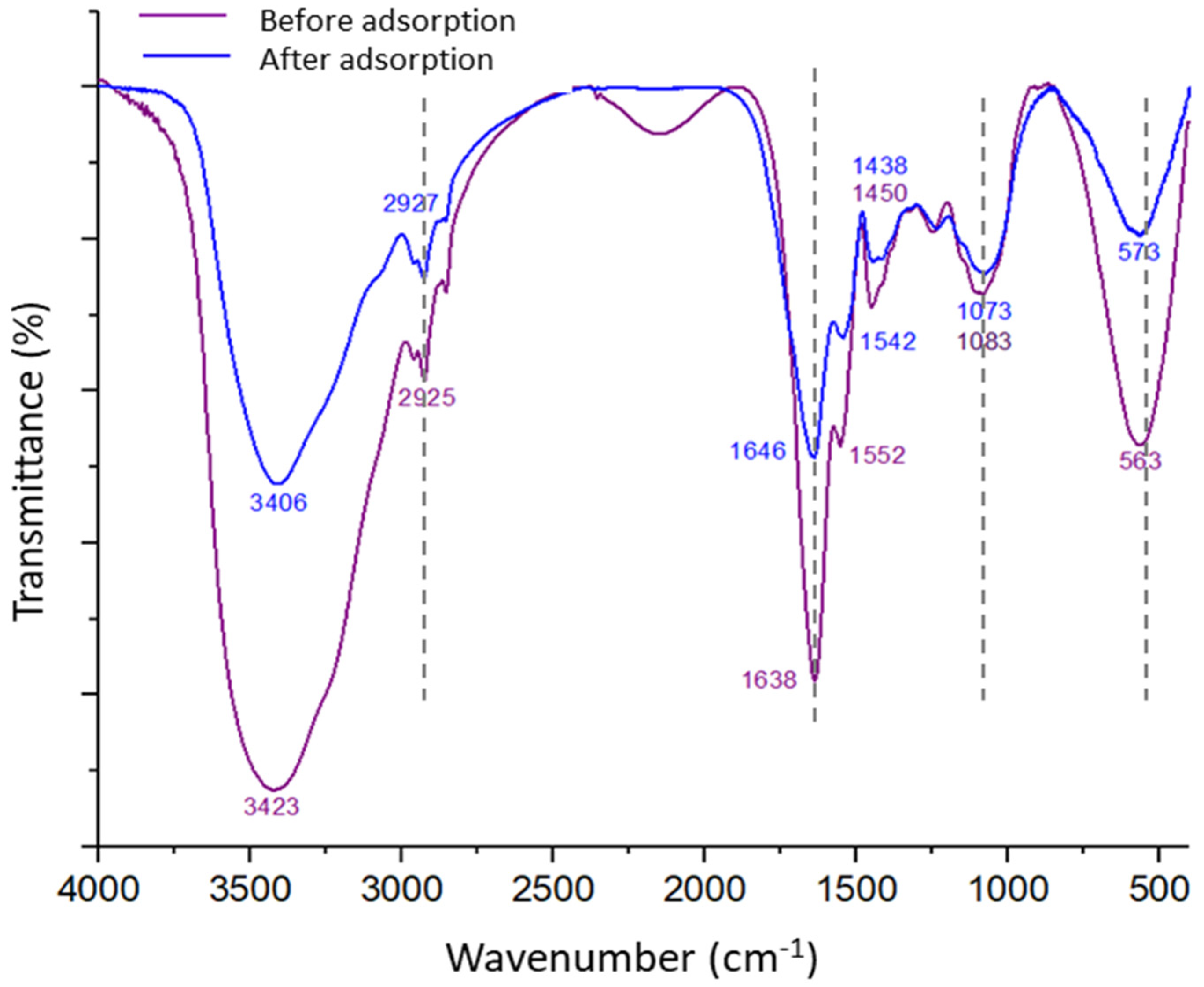
3.2. Phosphorus Removal Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chrispim, M.C.; Scholz, M.; Nolasco, M.A. Phosphorus Recovery from Municipal Wastewater Treatment: Critical Review of Challenges and Opportunities for Developing Countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.; White, S. The Story of Phosphorus: Global Food Security and Food for Thought. Glob. Environ. Change 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.-L.; Chen, X.-F. Recent Advances on Biosorption by Aerobic Granular Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egle, L.; Rechberger, H.; Krampe, J.; Zessner, M. Phosphorus Recovery from Municipal Wastewater: An Integrated Comparative Technological, Environmental and Economic Assessment of P Recovery Technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.O.; Aturagaba, G.; Ntale, M.; Nyakairu, G.W. A Review of Adsorption Techniques for Removal of Phosphates from Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 3113–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lee, Y.-J.; Yuan, T.; Lei, Z.; Adachi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. A Review on Recovery of Extracellular Biopolymers from Flocculent and Granular Activated Sludges: Cognition, Key Influencing Factors, Applications, and Challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A.; Persiani, R.; Dueholm, M.K.; Van Loosdrecht, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.W.; Lin, Y. Rethinking Characterization, Application, and Importance of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Water Technologies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 89, 103192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Little, B.J.; Neu, T.R.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.; Stoodley, P.; Wingender, J.; Wuertz, S. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances in the Environment, Technology and Medicine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Ghaani, M.; Mohamed, A.Y.A.; Gallagher, J.; Saikaly, P.E.; Ali, M. Alginate-like Exopolysaccharides Extracted from Different Waste Sludges Exhibit Varying Physicochemical and Material Properties. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1493782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hao, X.; Persiani, R.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Reinvestigating the Composition of Alginate-Like Exopolymers Extracted from Activated Sludge. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, N.T.; Wilfert, P.; Korving, L.; Van Loosdrecht, M. Integrated Resource Recovery from Aerobic Granular Sludge Plants. Water Res. 2023, 234, 119819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Shi, C.; Zhao, B.-H.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.-Y.; Hao, L.-T.; Wang, X.-Y. Recycling Alginate-like Extracellular Polymers (ALE) from Municipal Sludge: Value-Added Products and External Impact. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.M.; Fiore, F.A.; Saron, A.; Da Silva, G.H.R. Systematic Review of the Last 20 Years of Research on Decentralized Domestic Wastewater Treatment in Brazil: State of the Art and Potentials. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3469–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, A.; Gommersbach, C.; Cavali, M.; Libardi, N.; Costa, R.H.R.D. Biopolymers Recovery from Biological Sludge and Its Use as Phosphorus Biosorbent. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2024, 29, e20230087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felz, S.; Al-Zuhairy, S.; Aarstad, O.A.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y.M. Extraction of Structural Extracellular Polymeric Substances from Aerobic Granular Sludge. JoVE 2016, 115, 54534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewater, L.L.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation (Eds.) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-87553-287-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.M.; Sharma, P.K.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. The Chemical and Mechanical Differences between Alginate-like Exopolysaccharides Isolated from Aerobic Flocculent Sludge and Aerobic Granular Sludge. Water Res. 2013, 47, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schambeck, C.M.; Ribeiro Da Costa, R.H.; Derlon, N. Phosphate Removal from Municipal Wastewater by Alginate-like Exopolymers Hydrogels Recovered from Aerobic Granular Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Wang, P.; Song, B.; Lan, Y.; Ma, W.; Shi, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, P.; Lian, J. Sludge-Derived Alginate-like Extracellular Polymers (ALE) for Preparation of Fe-ALE and FeCaMg-ALE: Application to the Adsorption of Phosphate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 134995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Gusiatin, M.Z.; Zielińska, M.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Kulikowska, D.; Bernat, K. Alginate-like Polymers from Full-Scale Aerobic Granular Sludge: Content, Recovery, Characterization, and Application for Cadmium Adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Eris, S.; Azizian, S. Alginate-Based Hydrogel Beads as a Biocompatible and Efficient Adsorbent for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 15140–15148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lin, X.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Luo, J.; Liao, X.; Cheng, H. Biosorption of Copper Ions through Microalgae from Piggery Digestate: Optimization, Kinetic, Isotherm and Mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, I.A.; Viswanathan, N. Fabrication of Zirconium(IV) Cross-Linked Alginate/Kaolin Hybrid Beads for Nitrate and Phosphate Retention. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 13, 4111–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hao, X.; Gan, W.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Wu, Y. Enhancing Extraction of Alginate like Extracellular Polymers (ALE) from Flocculent Sludge by Surfactants. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, J.; Xue, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Qin, K.; Jiang, J.; Ding, J.; Zhao, Q. Adsorption Behaviors of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ onto Proteins, Humic Acid, and Polysaccharides Extracted from Sludge EPS: Sorption Properties and Mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Dong, Y.; Safferman, S.I. Phosphorus Adsorption and Recovery from Waste Streams Using Biochar: Review of Mechanisms, Modifications, and Agricultural Applications. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.S.; Classen, J.J.; Payne, G.A. Aspergillus Niger Absorbs Copper and Zinc from Swine Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Before Adsorption (mg/kg) | After Adsorption (mg/kg) | Brazilian Legislation (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arsenic | 0.042 | 0.049 | 41 |
| Barium | 0.367 | 0.671 | 1300 |
| Cadmium | 0.002 | 0.006 | 39 |
| Calcium | 7928 | 505 | - |
| Chrome | 0.106 | 0.088 | 1000 |
| Copper | 3.248 | 9.573 | 1500 |
| Lead | 0.098 | 0.037 | 300 |
| Magnesium | 1.710 | 166 | - |
| Molybdenum | 0.396 | 0.191 | 50 |
| Nickel | 0.128 | 0.093 | 420 |
| Nitrate | <3 | <3 | - |
| Nitrite | <3 | <3 | - |
| Phosphorus | 269 | 293 | - |
| Potassium | 5.993 | 58 | - |
| Selenium | 0.016 | <0.010 | 36 |
| Sodium | 307 | 36 | - |
| Sulfur | 43 | 29 | - |
| Zinc | 2.845 | 11 | 2800 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabral, A.; Da Silva, G.P.; Cavali, M.; Junior, N.L.; da Costa, R.H.R. Phosphorus Removal from Piggery Wastewater Using Alginate-like Exopolymers from Activated Sludge. Processes 2025, 13, 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092689
Cabral A, Da Silva GP, Cavali M, Junior NL, da Costa RHR. Phosphorus Removal from Piggery Wastewater Using Alginate-like Exopolymers from Activated Sludge. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092689
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabral, Amábile, Grazieli Pereira Da Silva, Matheus Cavali, Nelson Libardi Junior, and Rejane Helena Ribeiro da Costa. 2025. "Phosphorus Removal from Piggery Wastewater Using Alginate-like Exopolymers from Activated Sludge" Processes 13, no. 9: 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092689
APA StyleCabral, A., Da Silva, G. P., Cavali, M., Junior, N. L., & da Costa, R. H. R. (2025). Phosphorus Removal from Piggery Wastewater Using Alginate-like Exopolymers from Activated Sludge. Processes, 13(9), 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092689







