Gas Sources and Productivity-Influencing Factors of Matrix Reservoirs in Xujiahe Formation—A Case Study of Xin 8-5H Well and Xinsheng 204-1H Well
Abstract
1. Introduction
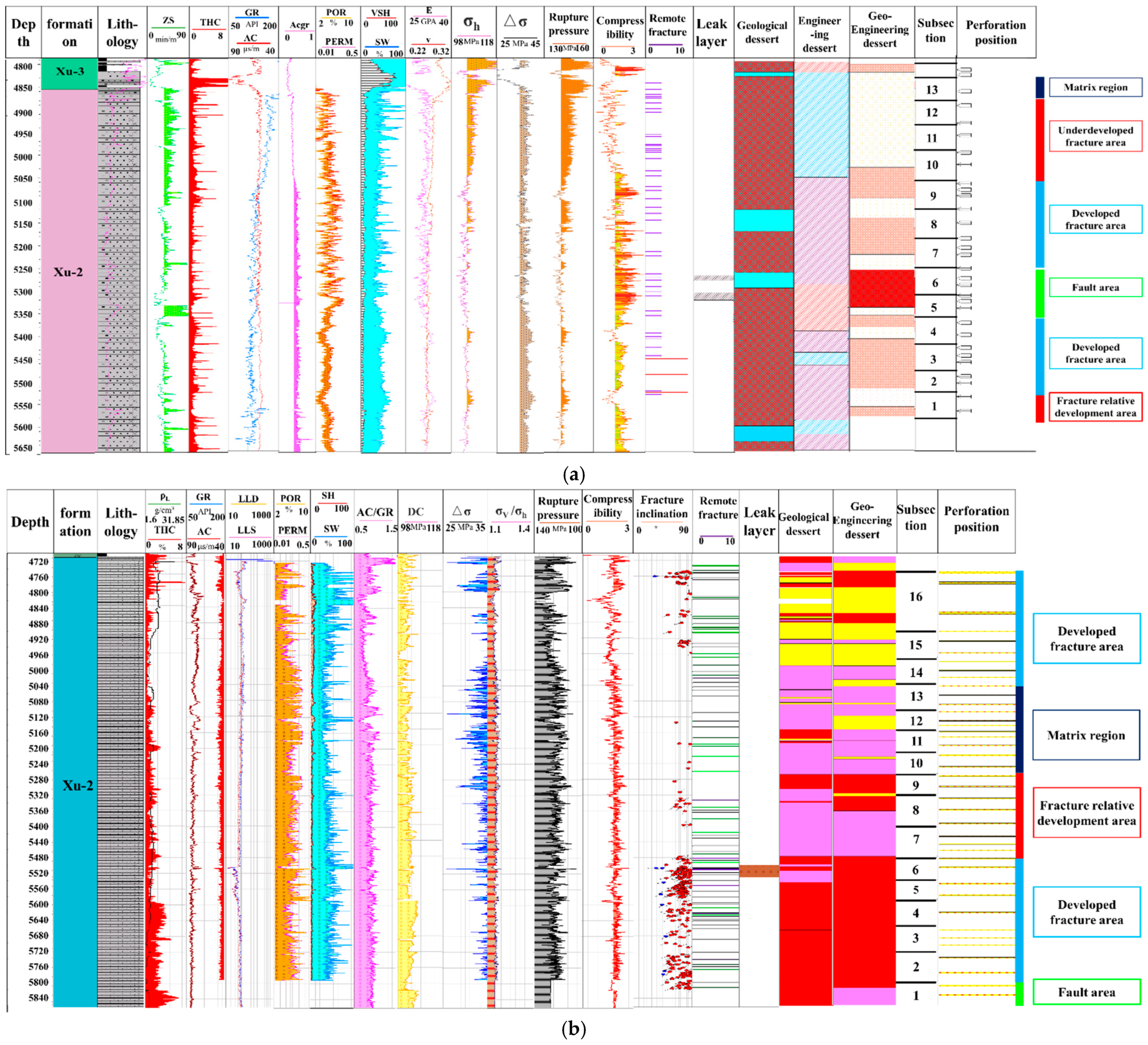
2. Geological Characteristics
3. Analysis of Gas Production Sources for Well Xin 8-5H and Well Xin Sheng 204-1H
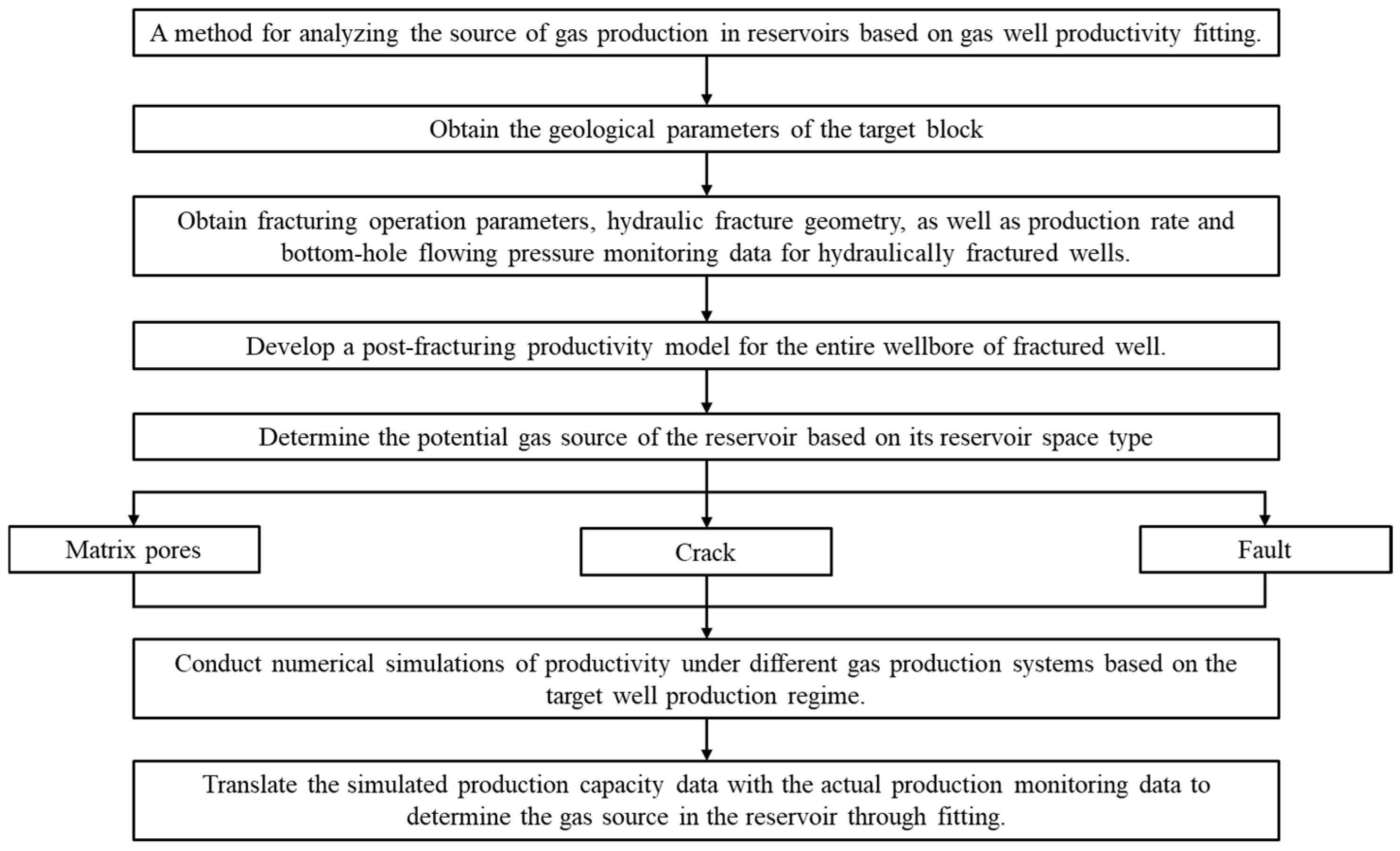
3.1. Methodology
3.2. Post-Pressure Productivity Model for the Entire Well Section
3.2.1. Mathematical Model of Two-Phase Seepage in Tight Sandstone Fracturing
3.2.2. Physical Model
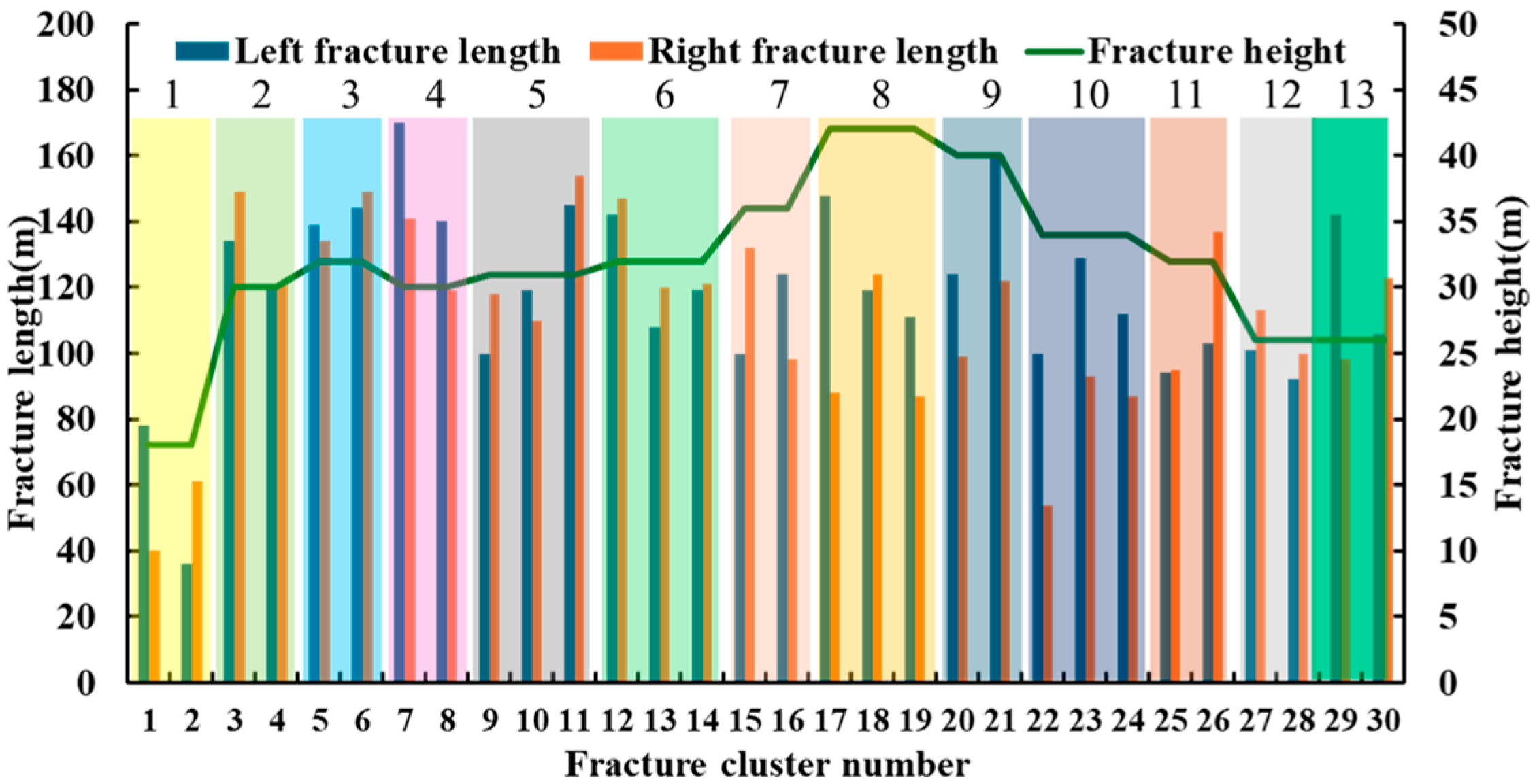
Model Establishment
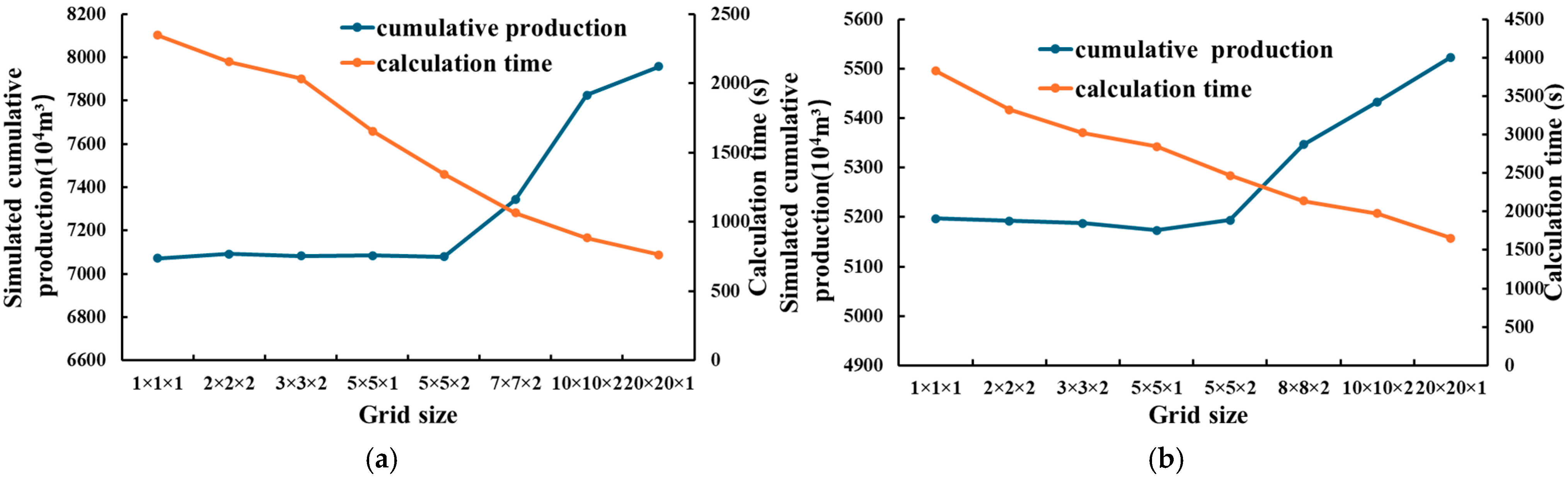
Grid Independence Verification
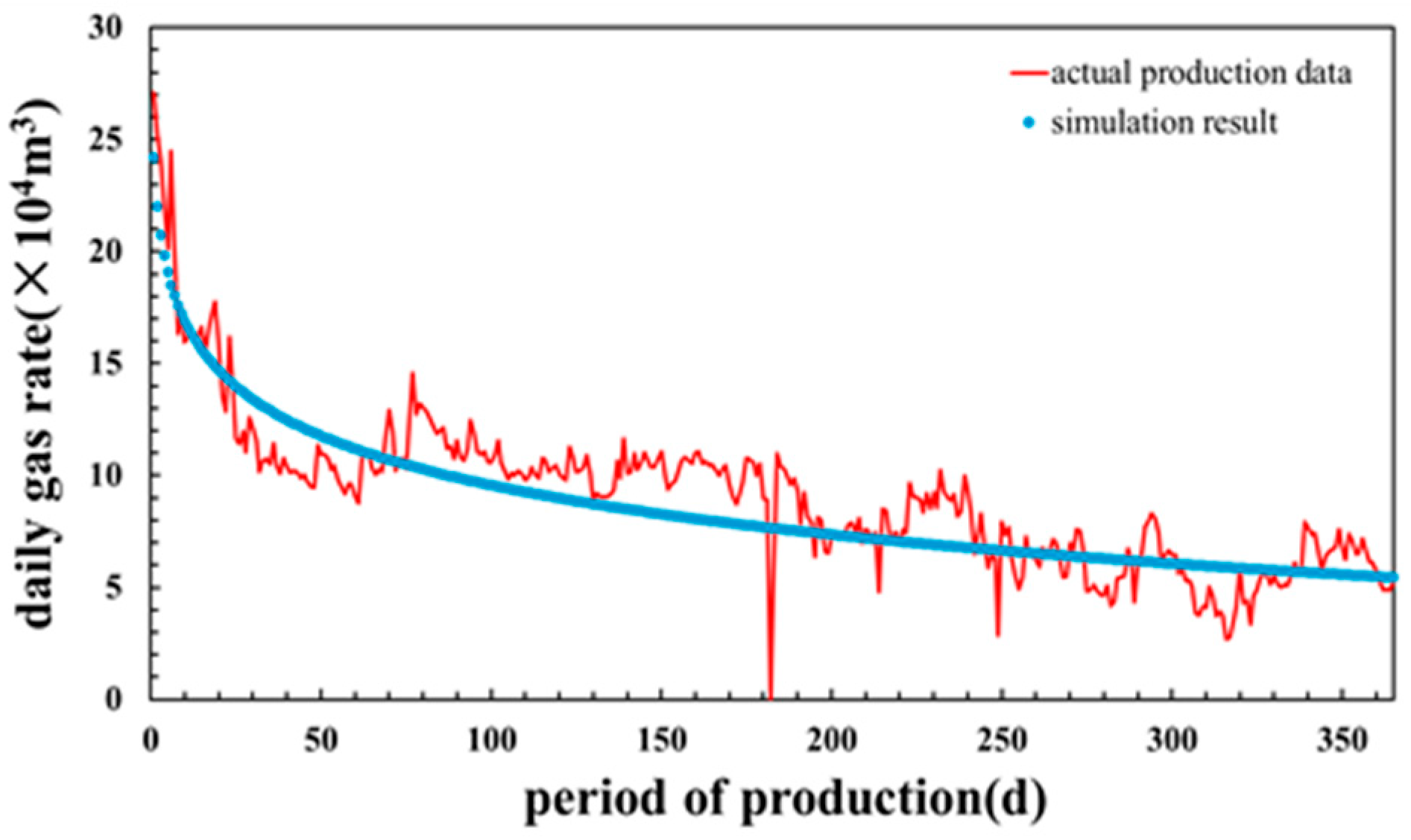
Model Verification
3.3. Production Matching Result
3.3.1. Xin 8-5H Well
3.3.2. Xinsheng 204-1H Well
4. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Productivity
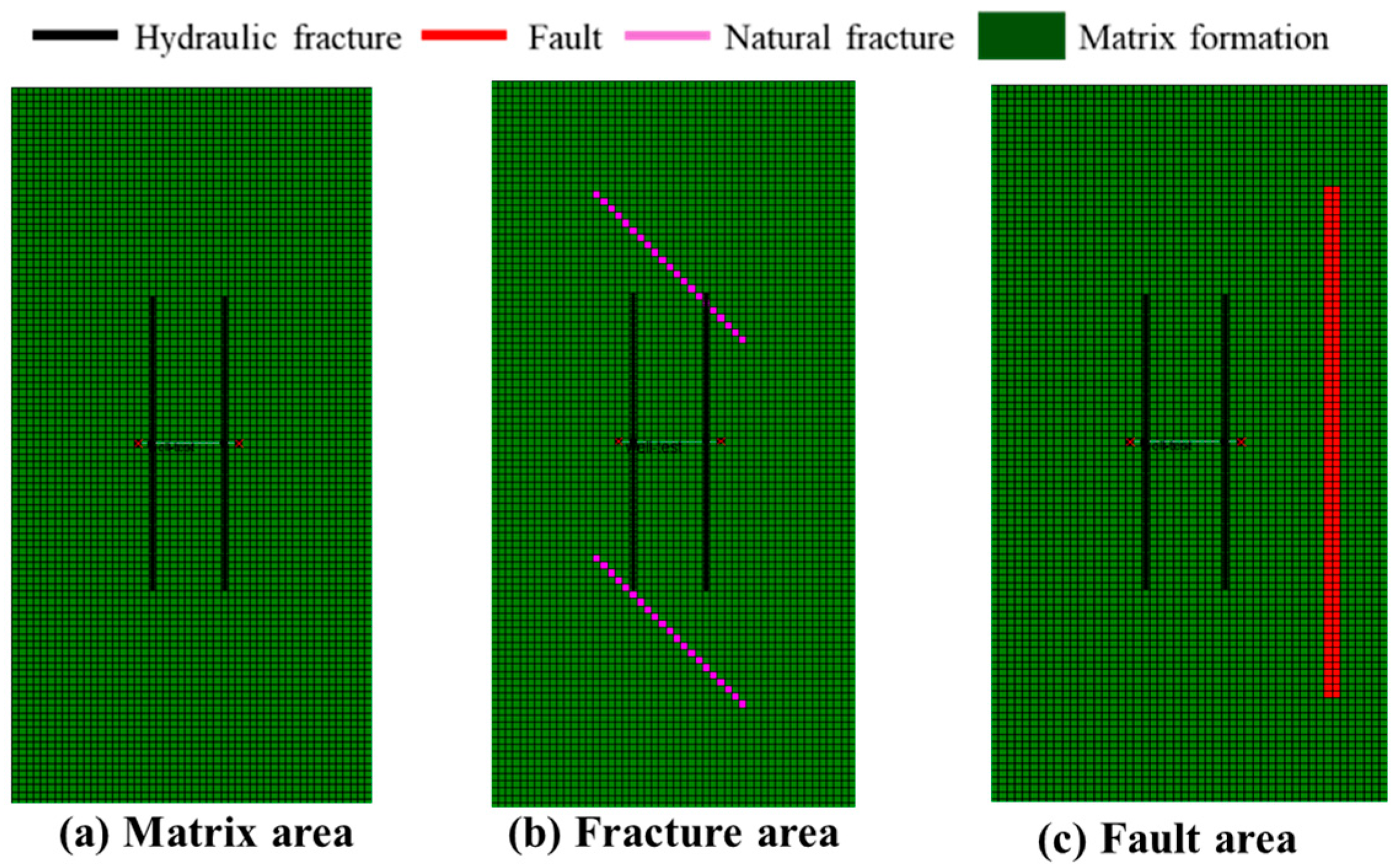
4.1. Physical Model of Post-Fracturing Productivity for a Single Fracturing Section
4.2. Simulation Result
4.2.1. Factors Influencing Productivity in the Matrix Area
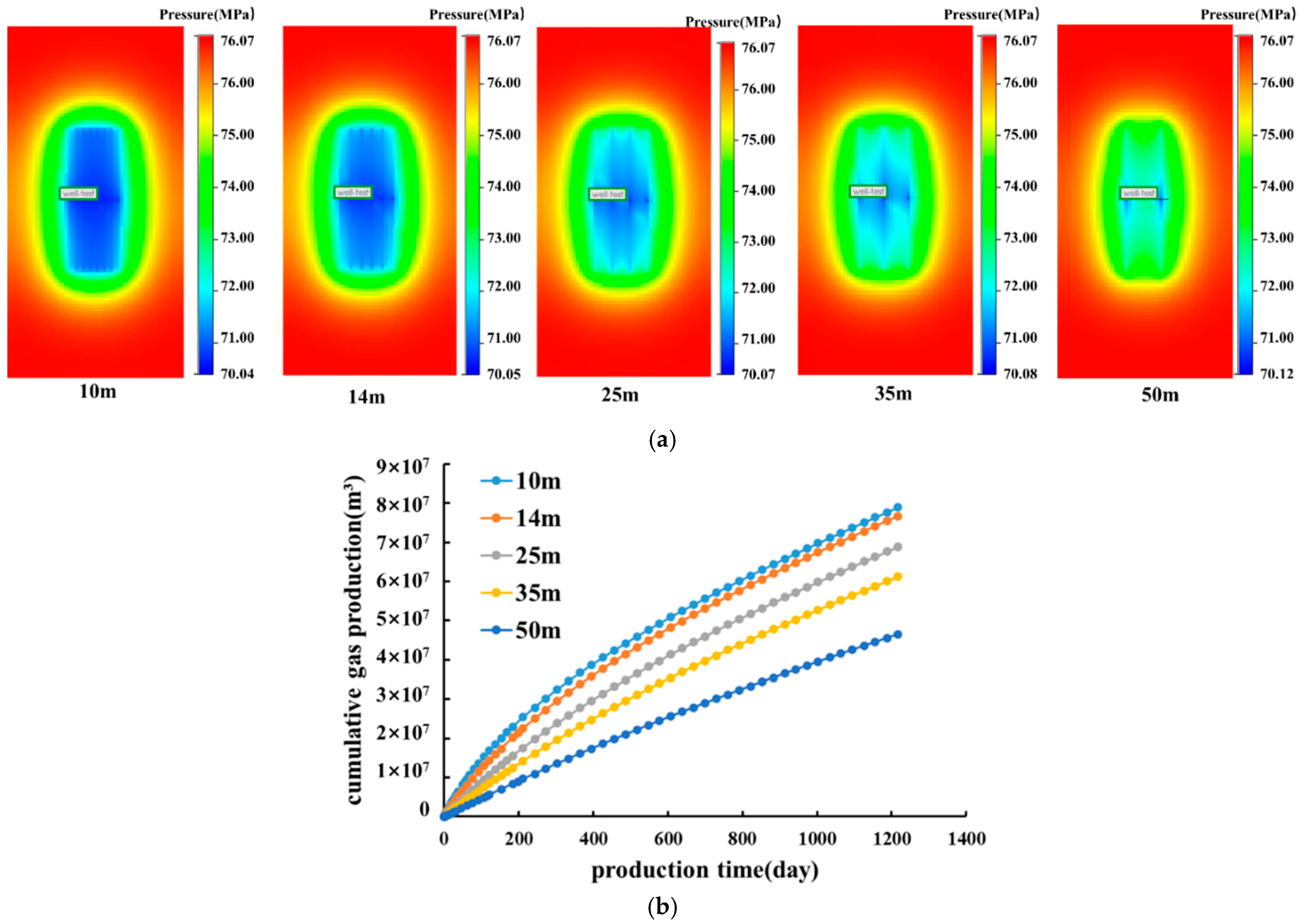
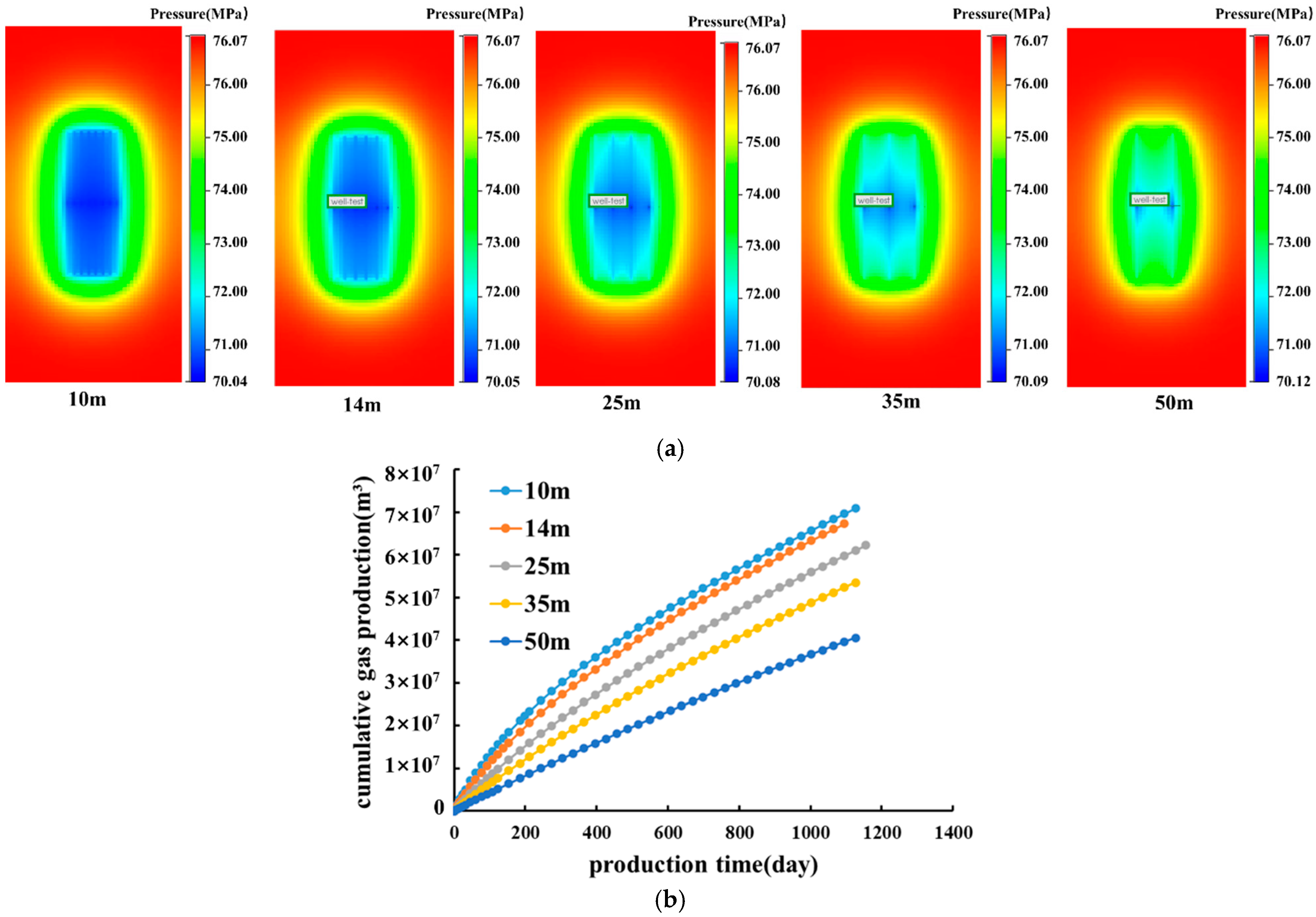
Cluster Spacing
4.2.2. Factors Influencing Productivity in the Fracture Area
Cluster Spacing
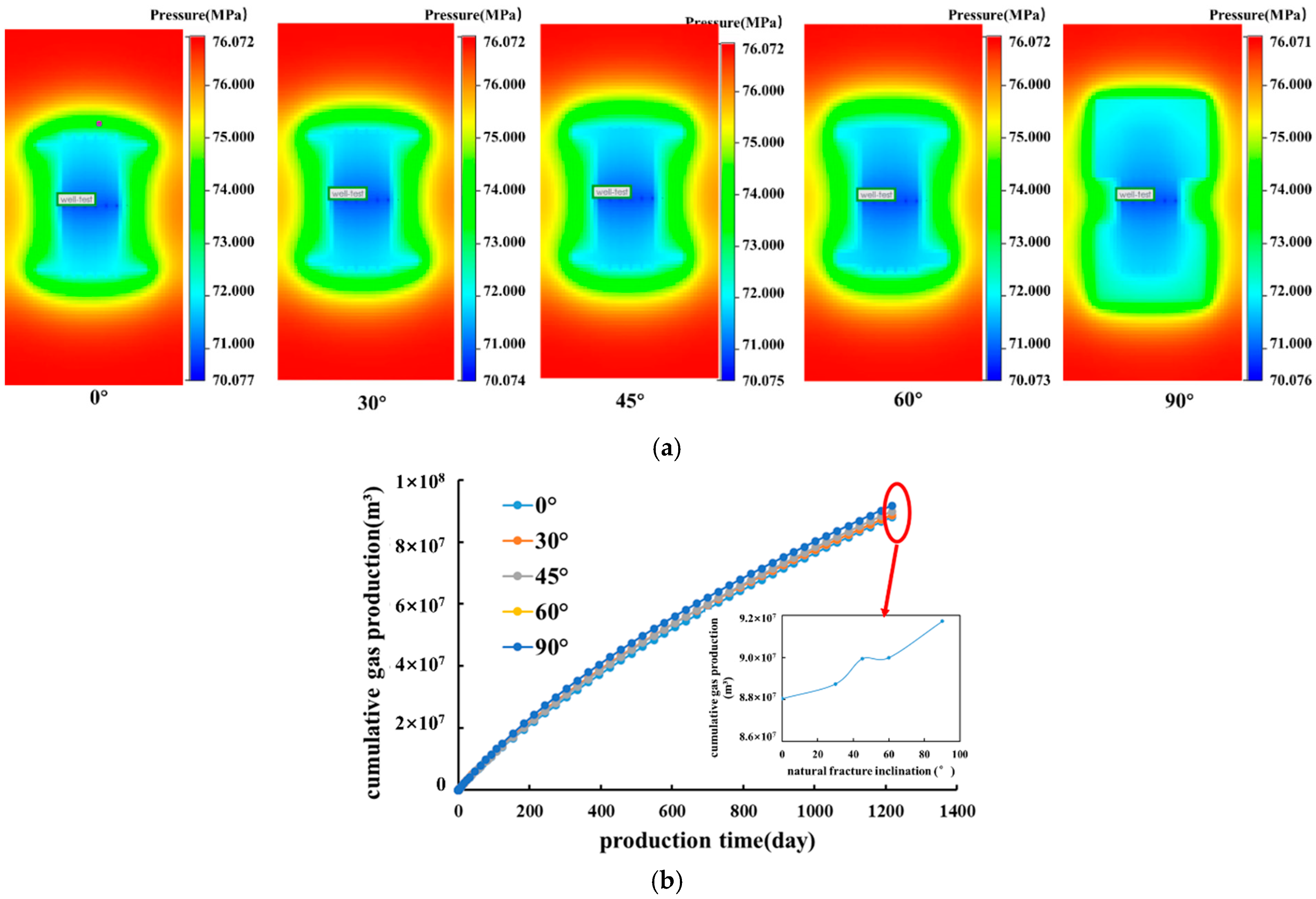
Angle Between Natural Fracture and Wellbore

Natural Fracture Inclination
4.2.3. Factors Influencing Productivity in the Fault Area
Cluster Spacing

Distance Between Fault and Fracturing Section

5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakhmakhchev, A.; Kurz, M.D.; McRae, T.A.; Yu, X.; Abarghani, A.; Schmidt, D.D.; Azzolina, N.A.; Kurz, B.A.; Sorensen, J.A. Investigating H2S Occurrence in Bakken Oil-Producing Wells Using Sulfur Isotopes in Gas, Water, and Rock Samples. In Proceedings of the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 17–19 June 2024; p. D021S036R002. [Google Scholar]
- Almubarak, Z.; Alrowaie, M.; Lu, F.; Algeer, R. Gas Chemical and Carbon Isotope Composition as a Diagnostic Tool for Energy. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 3–5 October 2022; p. D011S011R003. [Google Scholar]
- Hume, G.S. Distribution of Probable Source Rocks in Relation to Natural Gas and Petroleum Production in Alberta, Canada. In Proceedings of the 1st World Petroleum Congress, London, UK, 18–24 July 1933; p. WPC-1015. [Google Scholar]
- Drylie, S.; Pechiney, J.; Villaseñor, R.; Woodroof, R. Determining the Number of Contributing Fractures in Shale Gas Wells with Production Analysis and Proppant Tracer Diagnostics. In Proceedings of the SPE Production and Operations Symposium, Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 1–5 March 2015; p. SPE-173620-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, C.; Pan, K.; Zhang, H.; Cui, H. Controlling factors of gas-water distribution in source-reservoir separated tight sandstone gas reservoirs:a case study of Shaximiao Formation tight sandstone gas in central Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2024, 45, 1187–1201+1218. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P. Microcosmic factor analysis of yielding difference of major pay in east area of Sulige Gas Field. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2012, 19, 756–759. [Google Scholar]
- Hampton, T.J.; Reid, S.A.; McIntyre, J.L.; Querin, E.M. Possible Sources of Gas from the 31S C/D Shale Reservoirs, Monterey Formation, Elk Hills Field, California. In Proceedings of the SPE Western Regional Meeting, Anchorage, AK, USA, 22–24 May 1996; p. SPE-35742-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Feng, Y.; He, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, F. Experimental Methods for Evaluating Productivity Contribution ofDifferent Types of Low Permeability Gas Reservoir. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2014, 36, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, L.; Marmin, N.; Mukha, A. Acoustic-based Methodology of Assessing Zonal Production Contribution, Hydraulic Fracture Productive Height, and Reservoir Fluid Type in Tight Gas Condensate and Oil Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition, Brisbane, Australia, 9–11 November 2015; p. SPE-176863-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, D.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q. Experimental study on fracture contribution to gas reservoir permeability and well capacity. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2019, 41, 769–772. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Natural fractures do not contribute much to shale gas reservoir productivity. Nat. Gas Explor. Dev. 2017, 40, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Alalawi, W.Z.; Alrowaie, M.A.; AlQathami, S.M. Gas geochemical characteristics and thermal maturity of the Type-IIS source rock. In Proceedings of the SEG/AAPG International Meeting for Applied Geoscience & Energy, Houston, TX, USA, 28 August–1 September 2022; p. D011S055R003. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Vo, M.; Jia, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Integrated Gas Source Analysis for Wells with Sustained Casing Pressure: A Case Study from Sour Gas Fields in Sichuan Basin, China. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Virtual, 23 March–1 April 2021; p. D041S020R003. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, X.; Feng, D.; Hao, S.; Wang, K.; Su, E. Gas source and contribution identification for coal measure gas commingled production in Wulihou mining area. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2024, 14, 952–958. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, V.; Ribeiro, A.; Hurter, S. Modelling the Contribution of Individual Seams to Coal Seam Gas Production. In Proceedings of the SPE/AAPG/SEG Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 18–19 November 2019; p. D022S027R002. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, V.; Ribeiro, A.; Hurter, S. Modeling the Contribution of Individual Coal Seams on Commingled Gas Production. SPE Prod. Oper. 2021, 36, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Yan, B.; Liu, Q.; Ren, Z. The Fracture Network Inversion Based on Gas Production Profile. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Beijing, China, 26–28 March 2019; p. D011S013R005. [Google Scholar]
- Gueddoud, A.; Al Hanaee, A.; Khan, R.; Abdelaal, A.; Kurniawan, R.; Al Ameri, A. Dynamic Modeling Workflow for an Unconventional Biogenic Gas Reservoir with Multistage Hydraulic Fracture. A Case Study of Miocene Gachsaran Formation, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. In Proceedings of the SPE Middle East Oil & Gas Show and Conference, Sanabis, Bahrain, 28 November–1 December 2021; p. D041S047R001. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, B. Production Contribution Analyse on Outer Region of Stimulated Reservoir Volume in Condensate Shale Gas Well:Taking Typical Condensate Shale Gas Well in Eagle Ford as an Example. Sci. Technol. Ind. 2024, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zhichong, S.; Dong, W.; Yonggang, J. Analysis on gas hydrate exploitation response between the horizontal and vertical wells at SH2 site in the Shenhu area of the South China Sea. Ocean Eng. 2019, 37, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, D.; Ma, C.; Li, Z. Evaluation on Occluded Hydrocarbon in Deep-ultra Deep Ancient Source Rocks and Its Cracked Gas Resources. In Proceedings of the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 1–3 August 2016; p. URTEC-2460417-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, R.N.; Aghabozorgi, S.; Foroozesh, J. Numerical Simulation of Gas Production From Tight, Ultratight and Shale Gas Reservoirs: Flow Regimes and Geomechanical Effects. In Proceedings of the EUROPEC 2015, Madrid, Spain, 1–4 June 2015; p. SPE-174323-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Peeters, M.; Van Kirk, C.W.; Cloud, T.A. Gas Productivity Related to Cleat Volumes Derived from Focused Resistivity Tools in Coalbed Methane (CBM) Fields. Petrophysics-SPWLA J. 2006, 47, SPWLA-2006-v47n3a5. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Guo, X.; Cui, H.; Lei, K.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L. Research on Production Distribution Law of Multi-layer Gas Wells in Yan’an Gas Field. Liaoning Chem. Ind. 2021, 50, 904–906+928. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenyu, Z.; Hong, L.; Youming, L. Logging Identification And Evaluation of Cambrian-ordovician Source Rock In Tarim Basin. In Proceedings of the 2003 SEG Annual Meeting, Dallas, TX, USA, 26–31 October 2003; p. SEG-2003-0098. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, S.; Omer, S.; Tomor, P.S.; Harilal. Shale Gas Sweet Spot Identification Using Quantitative Seismic Interpretation (QSI) and Neural Network in Krishna-Godavari Basin, India. In Proceedings of the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Virtual, 20–22 July 2020; p. D023S052R001. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, D.M.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Sun, P.C.; Wu, H.G.; Fu, H.; Wang, Z.Q. Multi-scale classification and evaluation of shale reservoirs and ‘sweet spot’ prediction of the second and third members of the Qingshankou Formation in the Songliao Basin based on machine learning. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 216, 110678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, M.; Feng, Y.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Ding, J.; Chen, Q. Intelligent recognition of “geological-engineering” sweet spots in tight sandstone reservoirs—An application to a tight gas reservoir in Ordos Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 13, 1535883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, J.; Musa, I.H.; Mazeli, A.H.; Che Yusoff, M.F.; Jowett, D.; Redpath, D.; Saltman, P. Machine Learning Sweet Spot Identification and Performance Validation Utilising Reservoir and Completion Data from Unconventional Reservoir in British Columbia, Canada. In Proceedings of the SPE/IATMI Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, Jakarta, Indonesia, 10–12 October 2023; p. D021S011R001. [Google Scholar]
- Leem, J.; Mazeli, A.H.; Musa, I.H.; Che Yusoff, M.F. Data Analytics and Machine Learning Predictive Modeling for Unconventional Reservoir Performance Utilizing Geoengineering and Completion Data: Sweet Spot Identification and Completion Design Optimization. In Proceedings of the ADIPEC, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 31 October–3 November 2022; p. D021S062R002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Fan, C.; You, J.; Li, R.; Deng, C.; Li, G. Machine learning-based sweet spot prediction for lacuscrine shale oil in the Weixinan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2025, 179, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, F.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yang, J.; Xie, B. A novel approach for identifying sweet spots in tight reservoir fracturing engineering based on physical-data dual drive. J. Appl. Geophys. 2025, 238, 105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Sun, H.; Qiu, B.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Fang, J. Gray evaluation of layered productivity contribution of gas wells in Sulige Gas Field. Mud Logging Eng. 2022, 33, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Du, X.; Su, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, J. Machine Learning Based Stereoscopic Triple Sweet Spot Evaluation Method for Shale Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 13–15 June 2023; p. D031S073R003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Calculation method for productivity of fractured horizontal Wells in tight gas reservoirs. Lithol. Reserv. 2018, 30, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Z. The Key Technologies for Quantitative Evaluation for the Complex Deep Tight Gas Reservoirs—Taking TX2 Gas Reservoir of the West Sichuan Depression as an Example. Ph.D. Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Jin, L. Fracture competition propagation patterns and induced stress field evolution mechanisms during staged fracturing with mining-induced stress disturbance. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, L.; Wei, C.; Dai, F.; Liu, S.; Wang, W. Analysis on stress shadow of mutual interference of fractures in hydraulic fracturing engineering. Rock Mech. Eng. J. 2017, 36, 2926–2939. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Tian, Y. Capacity of Compact Reservoir Based on Dual Medium Embedded Discrete Crack Model. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 10780–10790. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Productivity analysis of low-permeability gas reservoirs considering the influence of natural fractures. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2020, 47, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Cui, H.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.; Shi, Y. Influence of natural fractures on the productivity of shale gas wells. Nat. Gas Ind. 2021, 41, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, W. Fault distribution characteristics and their impacts on the yield of the Ledong Gas 15-1 Field, Yinggehai Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2013, 33, 56–61. [Google Scholar]





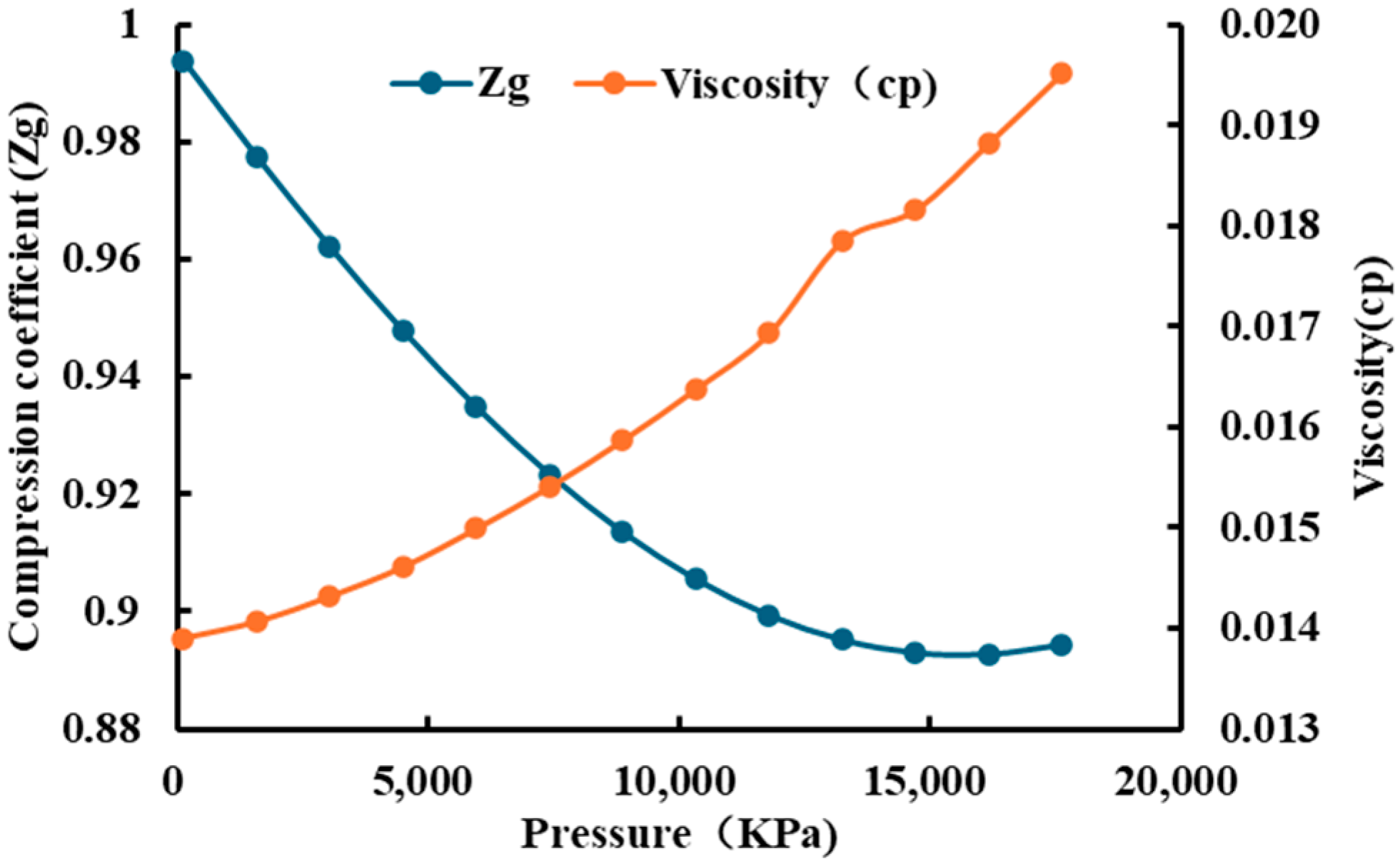
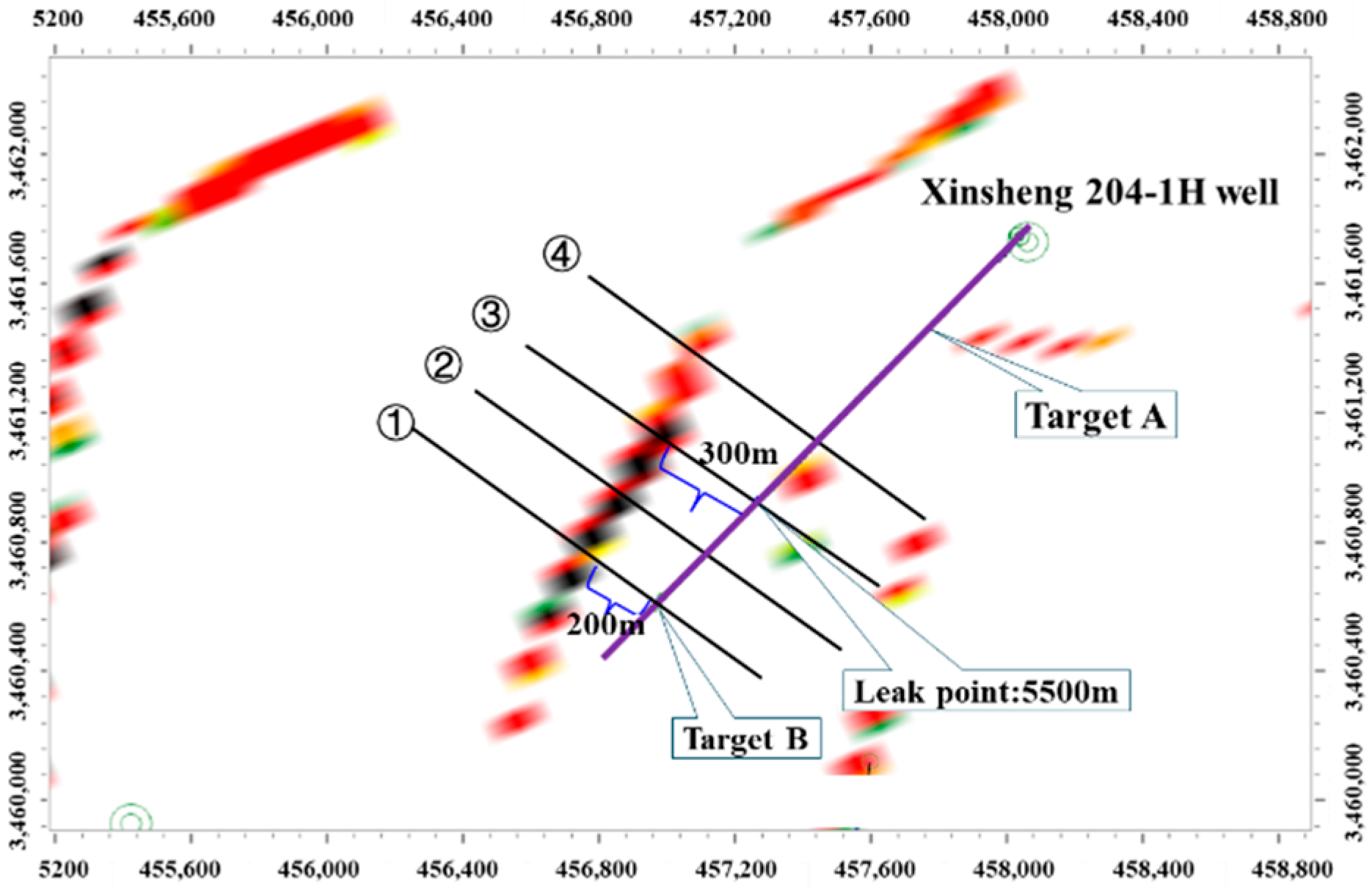

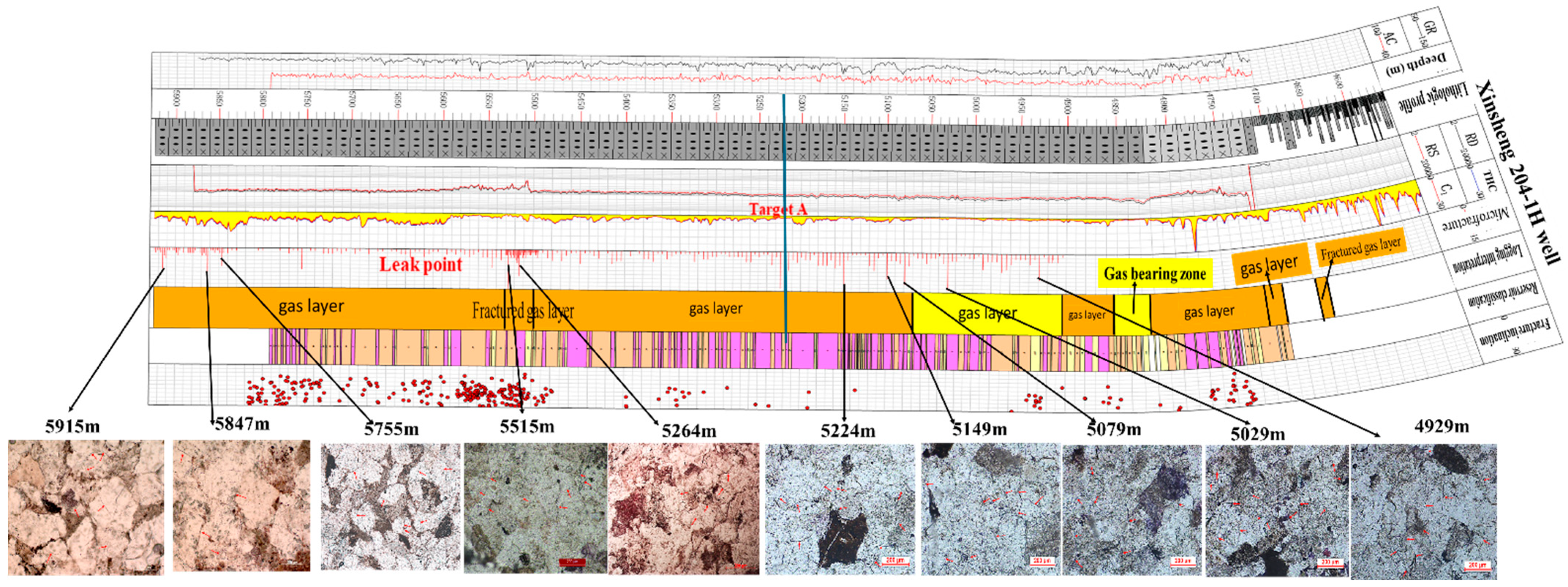
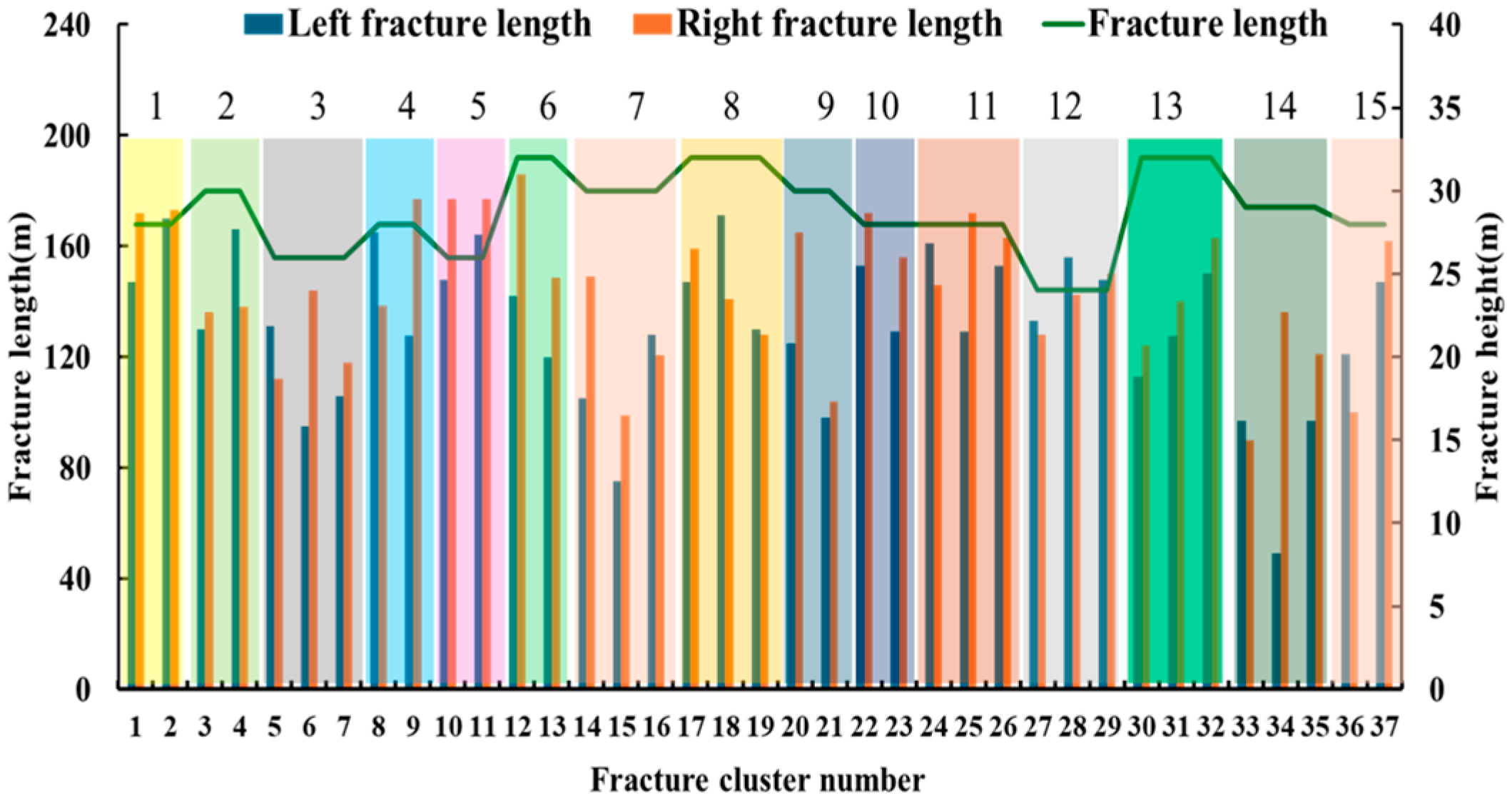





| Layer | Number of Samples | Filler Content /% | Cementing Material | Miscellaneous Base | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcite /% | Quartz /% | Dolomite /% | Siliceous /% | Chlorite /% | Muddy /% | Water Mica /% | Kaolinite /% | |||
| TX22 | 578 | 6.65 | 1.44 | 1.24 | 3.27 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.34 | 0.01 |
| TX23 | 258 | 6.88 | 1.62 | 1.34 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.04 |
| TX24 | 796 | 4.87 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 1.41 | 0.29 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0 |
| TX25 | 311 | 5.14 | 0.8 | 1.81 | 1.56 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0 |
| TX26 | 230 | 5.12 | 1.82 | 1.31 | 1.02 | 0.18 | 0.46 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.01 |
| TX27 | 222 | 7.12 | 3.33 | 0.49 | 2.46 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.08 |
| TX28 | 74 | 4.21 | 2.42 | 0.39 | 1.01 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0 |
| Input Parameter | Value | Input Parameter | Value | Input Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir model dimensions, m3 | 1000 × 1000 × 60 | Reservoir temperature, °C | 128.46 | Fracture zone area length, m | 200 |
| Matrix permeability, mD | 1.2 × 10−2 | Hydraulic fracture height, m | 18~42 | Fracture zone area height, m | 80 |
| Matrix porosity | 0.032 | Fracturing stage length, m | 765 | Natural fracture permeability, mD | 3 |
| Initial water saturation | 0.31 | Hydraulic fracture length, m | 139-311 | Fault location, m | 5308 |
| Fracture width, m | 0.00204 | Hydraulic fracture conductivity, D·cm | 25 | Fault zone permeability, mD | 15 |
| Fracture zone area location | 5036 m, 5136 m, 5186 m, 5236 m, 5386 m, 5486 m | Fault extension length, m | 600 | ||
| Fault throw, m | 10 | Fault height, m | 100 | Formation pressure, MPa | 56.75 |
| Water compressibility, 1/MPa | 5.38 × 10−4 | Rock compressibility, 1/MPa | 2.2 × 10−4 | ||
| Input Parameter | Value | Input Parameter | Value | Input Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir model dimensions, m3 | 1500 × 600 × 60 | Reservoir temperature, °C | 123 | Natural fracture area length, m | 31–333 m |
| Matrix permeability, mD | 2.8 × 10−2 | Hydraulic fracture height, m | 24–32 | Natural fracture area height, m | 200 |
| Matrix porosity | 0.051 | Fracture stage length, m | 962 | Natural fracture zone width, m | 100 |
| Initial water saturation | 0.39 | Hydraulic fracture length, m | 233~345 | Natural fracture permeability, mD | 2.8 |
| Fault length, m | 475 m | Fault permeability, mD | 25 | Fracture zone location, m | 4747–4941 m, 5329–5360 m, 5483–5816 m |
| Fault height, m | 100 | Fracture conductivity, D·cm | 15 | ||
| Fault width, m | 10 | Hydraulic fracture conductivity, D·cm | 22.5 | ||
| Formation pressure, MPa | 75.56 | Water compressibility, 1/MPa | 5.38 × 10−4 | Rock compressibility, 1/MPa | 2.2 × 10−4 |
| Well Xin 8-5H | Well Xinsheng 204-1H | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid Size (m3) | Number of Grids | Simulated Cumulative Production (104 m3) | Calculation Time (s) | Grid Size (m3) | Number of Grids | Simulated Cumulative Production (104 m3) | Calculation Time (s) |
| 1 × 1 × 1 | 113,204,500 | 7071.325 | 2346.8 | 1 × 1 × 1 | 160,688,250 | 5197.35 | 3825.65 |
| 2 × 2 × 2 | 14,151,813 | 7091.256 | 2156.8 | 2 × 2 × 2 | 20,086,031 | 5192.56 | 3325.25 |
| 3 × 3 × 2 | 6,289,695 | 7083.452 | 2035.4 | 3 × 3 × 2 | 8,927,125 | 5187.65 | 3025.69 |
| 5 × 5 × 1 | 4,528,580 | 7085.256 | 1656.2 | 5 × 5 × 1 | 6,427,530 | 5173.5 | 2845.65 |
| 5 × 5 × 2 | 2,264,290 | 7078.538 | 1344.5 | 5 × 5 × 2 | 3,213,765 | 5193.483 | 2468.9 |
| 7 × 7 × 2 | 1,155,250 | 7343.259 | 1065.3 | 8 × 8 × 2 | 1,255,377 | 5346.58 | 2135.8 |
| 10 × 10 × 2 | 566,073 | 7826.45 | 884.2 | 10 × 10 × 2 | 803,442 | 5432.58 | 1975.68 |
| 20 × 20 × 1 | 283,037 | 7958.265 | 762 | 20 × 20 × 1 | 401,721 | 5523.26 | 1654.2 |
| Input Parameter | Value | Input Parameter | Value | Input Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir model dimensions, m3 | 1600 × 600 × 80 | Reservoir temperature, K | 337 | Initial formation pressure, MPa | 64 |
| Matrix permeability, mD | 0.13 | Fracture stage length, m | 1360 | Bottomhole flowing pressure, MPa | 58 |
| Matrix porosity | 0.11 | Fracture length, m | 160~430 | Fracture width, m | 0.003 |
| Initial water saturation | 0.6 | Fracture conductivity, D·cm | 25 |
| Input Parameter | Value | Input Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir temperature, °C | 123 | Original water saturation | 0.35 |
| Matrix permeability, mD | 2.6 × 10−2 | Formation pressure, MPa | 76 |
| Matrix porosity | 0.04 | Fracture height, m | 28 |
| Fracture conductivity, D·cm | 25 | Fracture width, m | 0.00204 |
| Formation pressure, MPa | 66 | Water compressibility, 1/MPa | 5.45 × 10−4 |
| Rock compressibility, 1/MPa | 2.2 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, L.; Lu, Q.; Gong, X. Gas Sources and Productivity-Influencing Factors of Matrix Reservoirs in Xujiahe Formation—A Case Study of Xin 8-5H Well and Xinsheng 204-1H Well. Processes 2025, 13, 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082644
Miao W, Wang X, Zhang W, Qiu L, Lu Q, Gong X. Gas Sources and Productivity-Influencing Factors of Matrix Reservoirs in Xujiahe Formation—A Case Study of Xin 8-5H Well and Xinsheng 204-1H Well. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082644
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Weijie, Xingwen Wang, Wen Zhang, Ling Qiu, Qianli Lu, and Xinwei Gong. 2025. "Gas Sources and Productivity-Influencing Factors of Matrix Reservoirs in Xujiahe Formation—A Case Study of Xin 8-5H Well and Xinsheng 204-1H Well" Processes 13, no. 8: 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082644
APA StyleMiao, W., Wang, X., Zhang, W., Qiu, L., Lu, Q., & Gong, X. (2025). Gas Sources and Productivity-Influencing Factors of Matrix Reservoirs in Xujiahe Formation—A Case Study of Xin 8-5H Well and Xinsheng 204-1H Well. Processes, 13(8), 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082644






