Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Water by Copper–Iron Bioxide-Activated Persulfate System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of CuFe Catalysts
2.3. Characterization Methods of CuFe Catalysts
2.4. Degradation Experiments
2.5. Quenching Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of CuFe Catalysts
3.1.1. SEM Analysis
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
3.2. Research on Influencing Factors
3.2.1. The Impact of the Reaction System
3.2.2. The Impact of pH
3.2.3. The Impact of PMS Concentration
3.2.4. The Impact of Catalyst Dosage
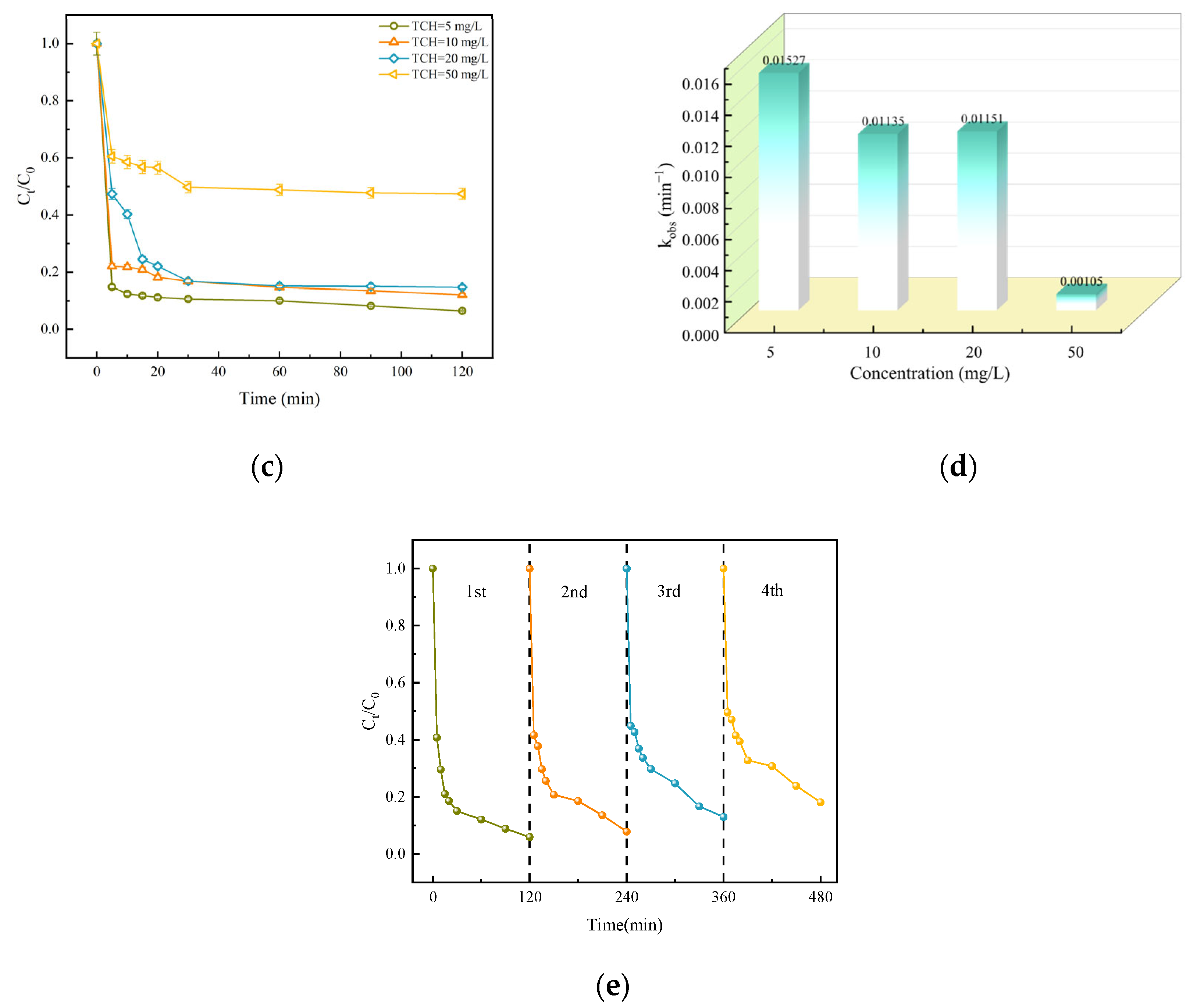
3.2.5. The Impact of TCH Concentration
3.2.6. Reuse of Catalysts
3.3. Identification of Reactive Species
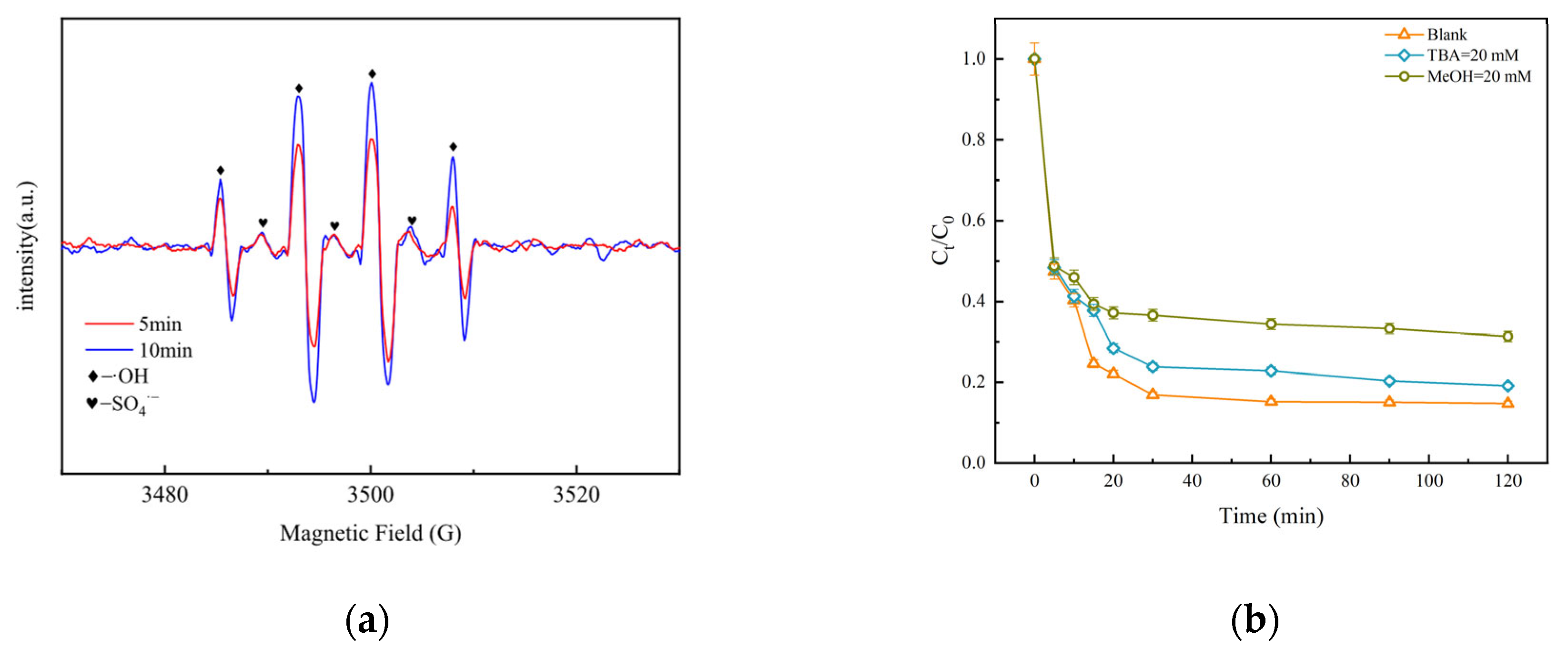
3.3.1. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Analysis
3.3.2. Free Radical Quenching Experiment
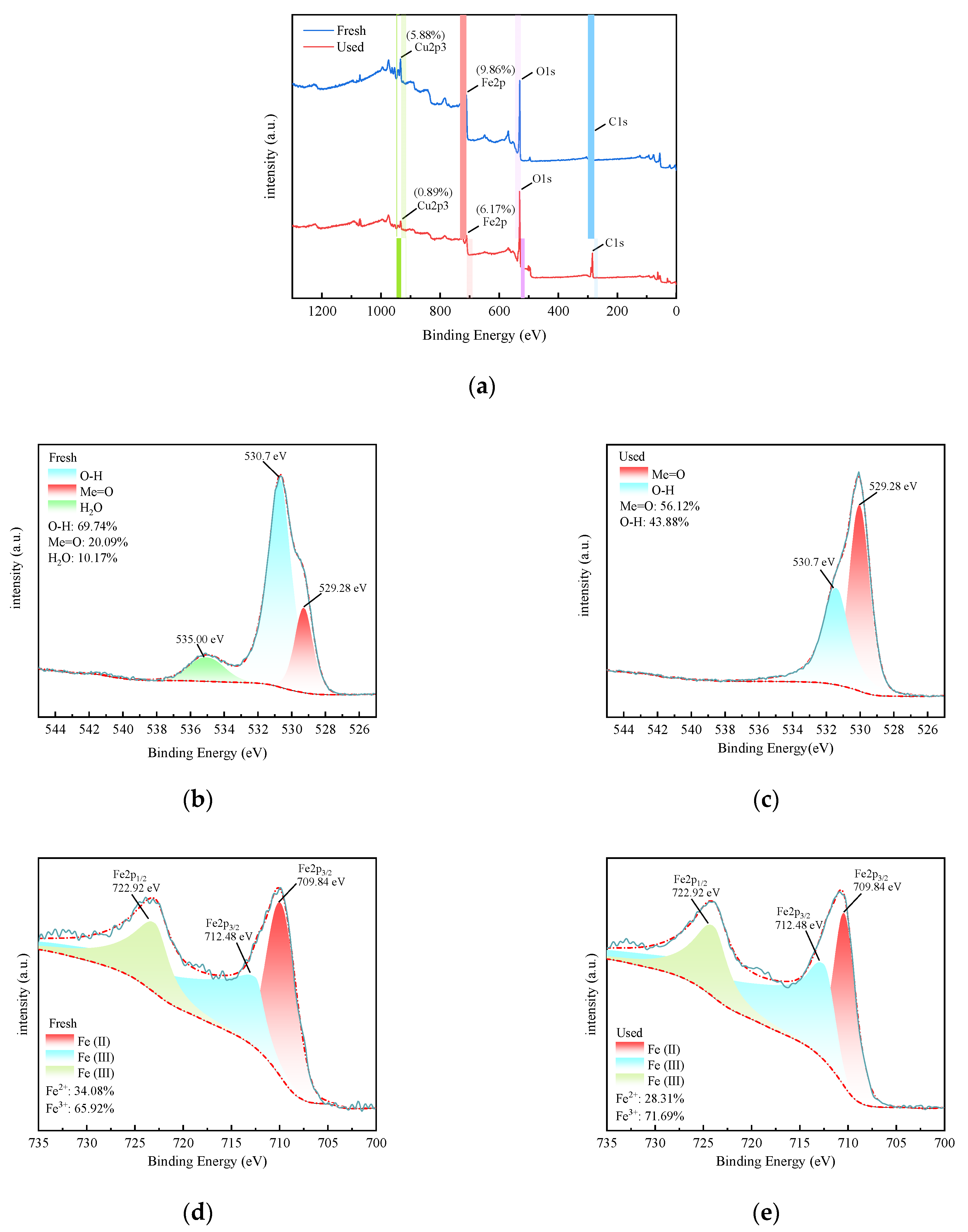
3.4. XPS Analysis
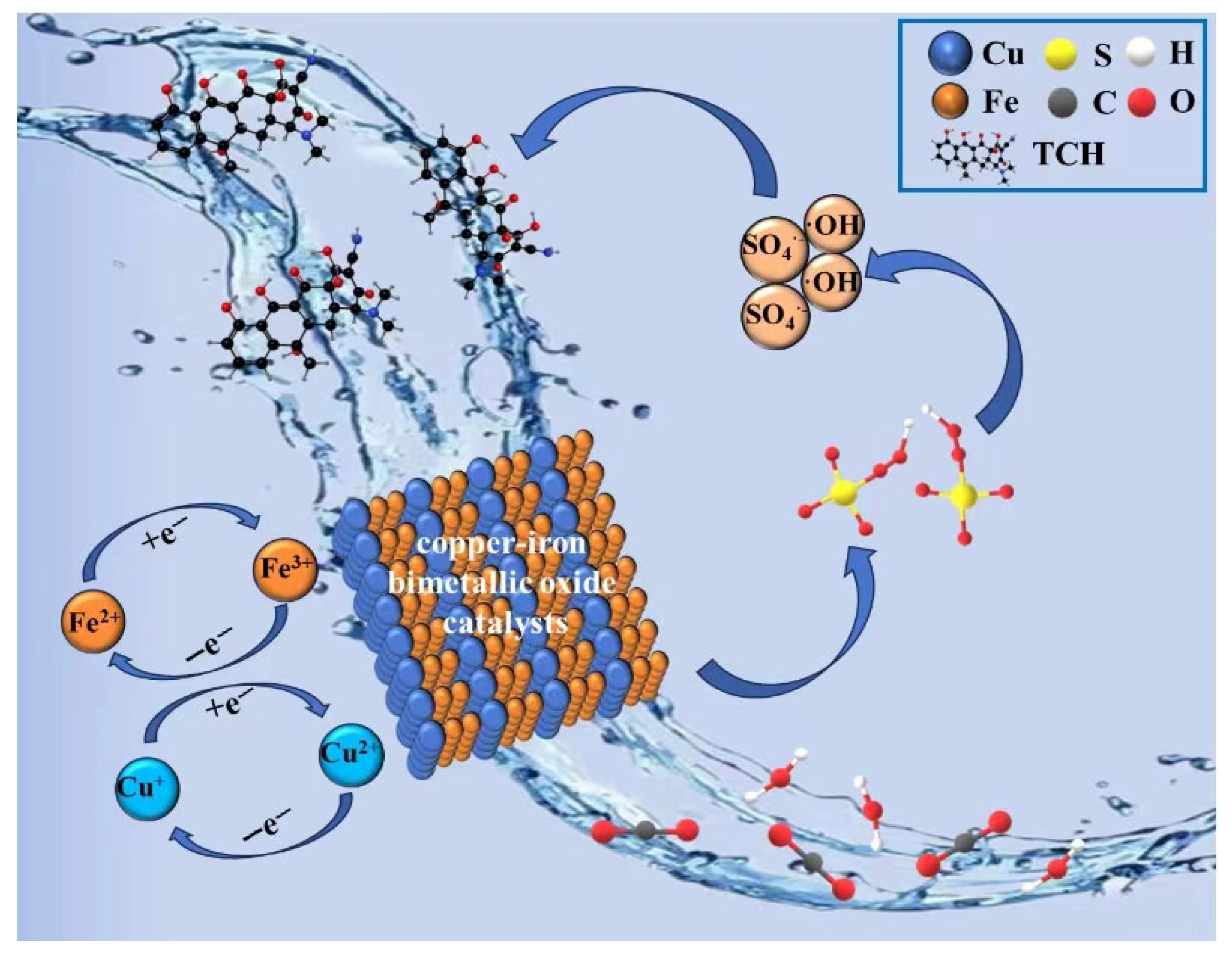
3.5. Persulfate Activation Mechanism
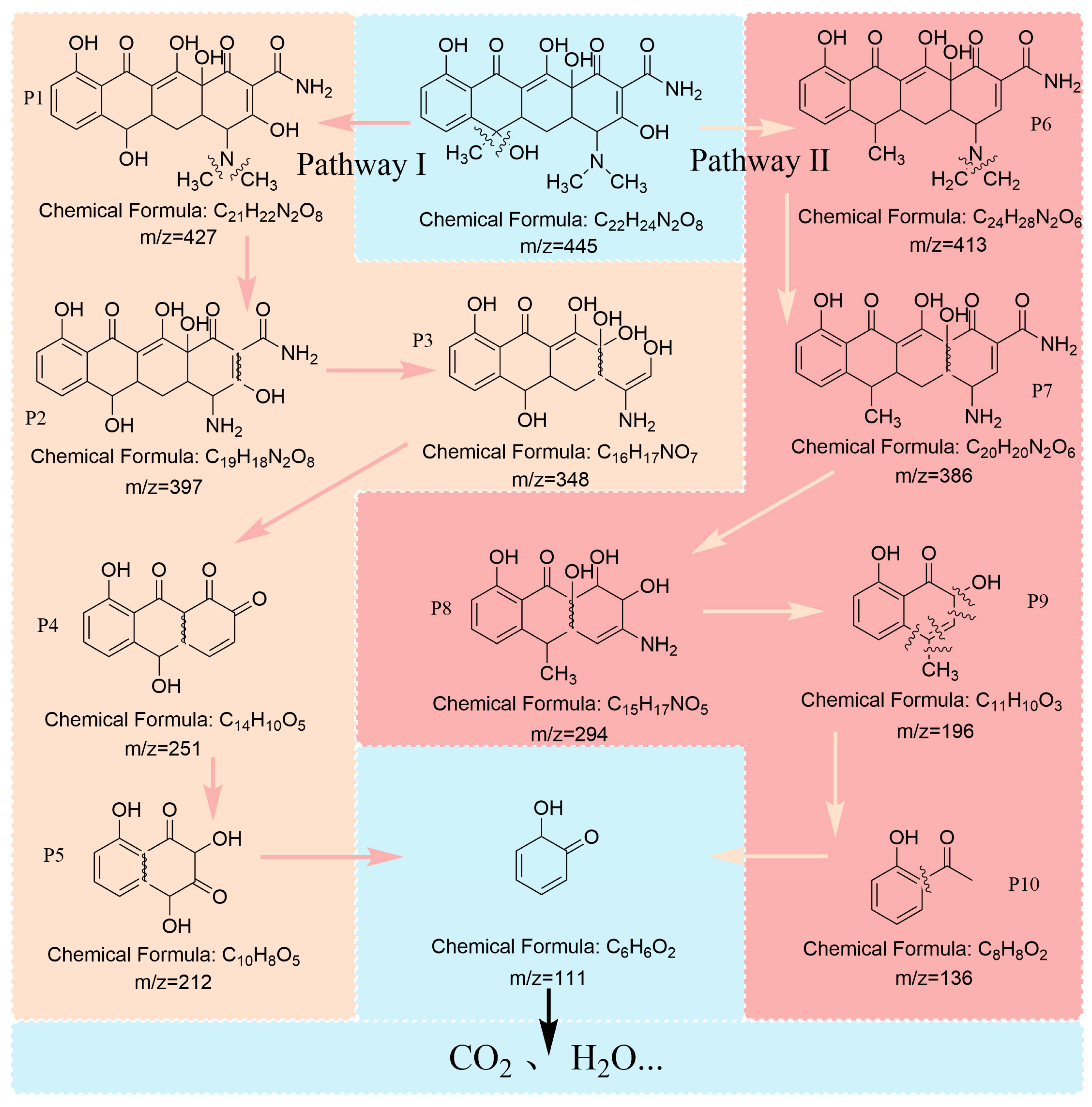
3.6. Possible Degradation Pathways of TCH
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOPs | Advanced oxidation processes |
| PMS | Peroxymonosulfate |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| TCH | Tetracycline hydrochloride |
References
- Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Kang, Z.; Wang, B.; Sun, L.; Yang, D.P.; Du, W. Enhanced Degradation of Aqueous Tetracycline Hydrochloride by Integrating Eggshell-Derived CaCO3/CuS Nanocomposite with Advanced Oxidation Process. Mol. Catal. 2021, 501, 111380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Chinthala, M.; Polagani, R.K.; Vo, D.V.N. Removal of Tetracycline from Wastewater Using G-C3N4 Based Photocatalysts: A Review. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Jing, L.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J. Characterization of Antibiotics in a Large-Scale River System of China: Occurrence Pattern, Spatiotemporal Distribution and Environmental Risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Fang, L.; Liao, P.; Chen, H. Ultrasound-Activated Peracetic Acid to Degrade Tetracycline Hydrochloride: Efficiency and Mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Pang, E.; Zhao, W.J. Photoassisted Activation of Persulfate by Cu2(OH)2 CO3 for the Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct 2024, 19, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, H.; Zhang, S.; Su, X. Non-Metal Activated Peroxydisulfate by Straw Biochar for Tetracycline Hydrochloride Oxidative Degradation: Catalytic Activity and Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 50815–50828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhou, K.; Garcia-Meza, J.V.; Song, S.; Xia, L. Yeast-Derived Biochar to Load CoFe2O4: Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride by Heterogeneous Activation of Peroxymonosulfate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhu, X.; Song, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Mao, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Ouyang, G. The Potential of a Natural Iron Ore Residue Application in the Efficient Removal of Tetracycline Hydrochloride from an Aqueous Solution: Insight into the Degradation Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76782–76792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zheng, X. Synthesis of ZnFe2O4/B,N-Codoped Biochar via Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis for Enhancing Adsorption-Photocatalytic Elimination of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 114066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, S.; Jin, C.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Ji, J.; She, Z. Electrochemical Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Sulfate Solutions on Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode: The Accumulation and Transformation of Persulfate. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.P.; Subudhi, S.; Ray, A.; Behera, P.; Panda, J.; Dash, S.; Parida, K. Hydrolytically Stable Mixed Ditopic Linker Based Zirconium Metal Organic Framework as a Robust Photocatalyst towards Tetracycline Hydrochloride Degradation and Hydrogen Evolution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kang, Y. Underwater Bubbling Plasma Assisted with Persulfate Activation for the Synergistic Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Wei, Y.; He, L.; Lan, B.; He, X.; Wang, J. Effective Mineralization of Quinoline and Bio-Treated Coking Wastewater by Catalytic Ozonation Using CuFe2O4/Sepiolite Catalyst: Efficiency and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, R.; Fierro, V.; Martinez de Yuso, A.; Nabarlatz, D.; Celzard, A. Tetracycline Adsorption onto Activated Carbons Produced by KOH Activation of Tyre Pyrolysis Char. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yue, Q.; Gao, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, X.; Ren, Z.; Jin, Y. Application for Oxytetracycline Wastewater Pretreatment by Fenton Iron Mud Based Cathodic-Anodic-Electrolysis Ceramic Granular Fillers. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, W.; Cui, J.; Feng, Y.; Mei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, W. Degradation of Aniline in Aqueous Solution by Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma: Mechanism and Degradation Pathways. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Xie, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xie, D.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; An, J. Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Aqueous via Combined Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma and Fe–Mn Doped AC. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Shi, M.; Chang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Jiang, L.; Pang, D.; et al. Tetracycline Degradation by the Co3O4/Peroxymonosulfate System: Effect of Calcination Temperature. Chem. Phys. Impact 2024, 8, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F. Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride by Electro-Activated Persulfate Oxidation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 809, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Fang, G.; Chen, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhu, F.; Ma, L.; Zhou, D.; Zhan, J. Efficient Activation of Persulfate Decomposition by Cu2FeSnS4 Nanomaterial for Bisphenol A Degradation: Kinetics, Performance and Mechanism Studies. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 253, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Song, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shang, J.; Cheng, X. CuFe2O4/CuO Magnetic Nano-Composite Activates PMS to Remove Ciprofloxacin: Ecotoxicity and DFT Calculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, P.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; et al. Heterogeneous Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Magnetic Hybrid CuFe2O4@N-RGO for Excellent Sulfamethoxazole Degradation: Interaction of CuFe2O4 with N-RGO and Synergistic Catalytic Mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Niu, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, N.; Long, Z.; Zhi, R. An Efficient CuO-ΓFe2O3 Composite Activates Persulfate for Organic Pollutants Removal: Performance, Advantages and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cong, S.; He, Y.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Yao, B.; Sun, W. Study on the Mechanism of Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride by Microwave-Activated Sodium Persulfate. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, M.R.; Vijay, P.; Tadé, M.O.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Submicron Sized Water-Stable Metal Organic Framework (Bio-MOF-11) for Catalytic Degradation of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cheng, G.; Gao, C.; Chen, C.; Ai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. The Confined Interlayer Growth of Ultrathin Two-Dimensional Fe3O4 Nanosheets with Enriched Oxygen Vacancies for Peroxymonosulfate Activation. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 11256–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.-D.; Dong, Z.; Lim, T.T. Generation of Sulfate Radical through Heterogeneous Catalysis for Organic Contaminants Removal: Current Development, Challenges and Prospects. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 194, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Zou, T.; Liao, X.L.; Chen, Z.F.; Yu, L. Nano Fe3-XCuxO4 as the Heterogeneous Catalyst in an Advanced Oxidation Process for Excellent Peroxymonosulfate Activation toward Climbazole Degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Ma, Y.; Xing, S. Enhanced Superoxide Radical Production for Ofloxacin Removal via Persulfate Activation with Cu-Fe Oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.Q.; Pu, S.Y.; Yang, X. Synergistic Reaction Mechanism of Cu0@Fe3O4 Activated PMS for Degradation of P-Nitrophenol. Huanjing Kexue/Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4615–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Zhou, B.; Chen, S.; Zhu, F.; Chen, B.; Gong, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, D.; He, F.; et al. Preparation of Fe/Cu Bimetals by Ball Milling Iron Powder and Copper Sulfate for Trichloroethylene Degradation: Combined Effect of FeSx and Fe/Cu Alloy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Kumar, A.; Babu, J.N.; Kumar, S. Tetracycline Removal via Three-Way Synergy between Pistachio Shell Powder, Zerovalent Copper or Iron, and Peroxymonosulfate Activation. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 12, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, D.; Du, Q.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, T. Fe3O4–CuO@Lignite Activated Coke Activated Persulfate Advanced Treatment of Phenolic Wastewater from Coal Chemical Industry. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Xia, D.; Li, Q. Orange Peels Biochar Doping with Fe-Cu Bimetal for PMS Activation on the Degradation of Bisphenol A: A Synergy of SO4·−, ·OH, 1O2 and Electron Transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Lv, S.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, P. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Tea Residue Biochar Loaded with Fe3O4 for the Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride: Performance and Reaction Mechanism. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18525–18538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Guo, R.; Cheng, Q.; Cheng, X. Synthesis of Magnetic CuO/MnFe2O4 Nanocompisite and Its High Activity for Degradation of Levofloxacin by Activation of Persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, J. Sulfate Radical Degradation of Acetaminophen by Novel Iron–Copper Bimetallic Oxidation Catalyzed by Persulfate: Mechanism and Degradation Pathways. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.Y.; Hong, J. Oxidation of Bisphenol A by Persulfate via Fe3O4-A-MnO2 Nanoflower-like Catalyst: Mechanism and Efficiency. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, R.; Sun, J.; Ren, H. Magnetic CuO@Fe3O4 Nanocomposite as a Highly Active Heterogeneous Catalyst of Persulfate for 2,4-Dichlorophenol Degradation in Aqueous Solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 57058–57066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, Z.S.; Bruell, C.J. Influence of PH on Persulfate Oxidation of TCE at Ambient Temperatures. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Su, H.W. Identification of Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radicals in Thermally Activated Persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Qu, R.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Sui, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Degradation of Flumequine in Aqueous Solution by Persulfate Activated with Common Methods and Polyhydroquinone-Coated Magnetite/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Catalysts. Water Res. 2015, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y. Efficiently Activate Peroxymonosulfate by Fe3O4@MoS2 for Rapid Degradation of Sulfonamides. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Dong, X.; Sun, Z.; Duan, X.; Ren, B.; Zheng, S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Highly Efficient Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Natural Negatively-Charged Kaolinite with Abundant Hydroxyl Groups for the Degradation of Atrazine. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 247, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Application of Peroxymonosulfate and Its Activation Methods for Degradation of Environmental Organic Pollutants: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, C.; Lyu, J.; Hu, Z.; Ge, M. Tetracycline Degradation by Persulfate Activated with Magnetic Cu/CuFe2O4 Composite: Efficiency, Stability, Mechanism and Degradation Pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Z.; Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Cui, F. Efficient Degradation of P-Arsanilic Acid with Arsenic Adsorption by Magnetic CuO-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles under Visible Light Irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, Z.; Yan, B.; Cao, Z.; Li, H.; Jing, G.L.; Liu, X. Degradation of Rhodamine B by CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles Anchored on Montmorillonite as an Activator of Sodium Persulfate. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 150, 105073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Du, G.; Cheng, X.; Jia, Y. Degradation of Methyl Orange Using Persulfate Activated by Magnetic CuS/Fe3O4 Catalyst: Catalytic Performance and Mechanisms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 618, 156595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Lang, J.; Liao, Z.; Khan, A.; Ifthikar, J.; Lv, Z.; Long, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Activation of Persulfate by CuOx@Co-LDH: A Novel Heterogeneous System for Contaminant Degradation with Broad PH Window and Controlled Leaching. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Zhan, K.; Wang, H.; Shahzad, A.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Ullah, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Tuning of Persulfate Activation from a Free Radical to a Nonradical Pathway through the Incorporation of Non-Redox Magnesium Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2476–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian Tang, X.; Dan Zhang, Y.; Wei Jiang, Z.; Mei Wang, D.; Zhi Huang, C.; Fang Li, Y. Fe3O4 and Metal–Organic Framework MIL-101(Fe) Composites Catalyze Luminol Chemiluminescence for Sensitively Sensing Hydrogen Peroxide and Glucose. Talanta 2018, 179, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Shao, Y.; Kong, X.; Jiang, M.; Lei, X. Hierarchical Carbon-Decorated Fe3O4 on Hollow CuO Nanotube Array: Fabrication and Used as Negative Material for Ultrahigh-Energy Density Hybrid Supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ai, J.; Zhang, H. The Mechanism of Degradation of Bisphenol A Using the Magnetically Separable CuFe2O4/Peroxymonosulfate Heterogeneous Oxidation Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 309, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, F.; Gao, S.; Shi, W.; Cui, F. Development of CuO Coated Ceramic Hollow Fiber Membrane for Peroxymonosulfate Activation: A Highly Efficient Singlet Oxygen-Dominated Oxidation Process for Bisphenol a Degradation. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 256, 117783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; He, J.; Liu, F.; Ding, L. Rapid Synthesis of Cu2O/CuO/RGO with Enhanced Sensitivity for Ascorbic Acid Biosensing. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wen, L.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Tang, J. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by MnFe2O4@BC Composite for Bisphenol A Degradation: The Coexisting of Free-Radical and Non-Radical Pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, A.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Deng, T. Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Water by Copper–Iron Bioxide-Activated Persulfate System. Processes 2025, 13, 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082625
Gao A, Li S, Xu J, Li X, Li Y, Zhang K, Deng T. Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Water by Copper–Iron Bioxide-Activated Persulfate System. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082625
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ang, Shuang Li, Jialu Xu, Xiao Li, Yueran Li, Kuan Zhang, and Tiantian Deng. 2025. "Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Water by Copper–Iron Bioxide-Activated Persulfate System" Processes 13, no. 8: 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082625
APA StyleGao, A., Li, S., Xu, J., Li, X., Li, Y., Zhang, K., & Deng, T. (2025). Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Water by Copper–Iron Bioxide-Activated Persulfate System. Processes, 13(8), 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082625




