Development Characteristics and Distribution Patterns of Natural Fractures in the Tight Reservoirs of the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Tarim Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
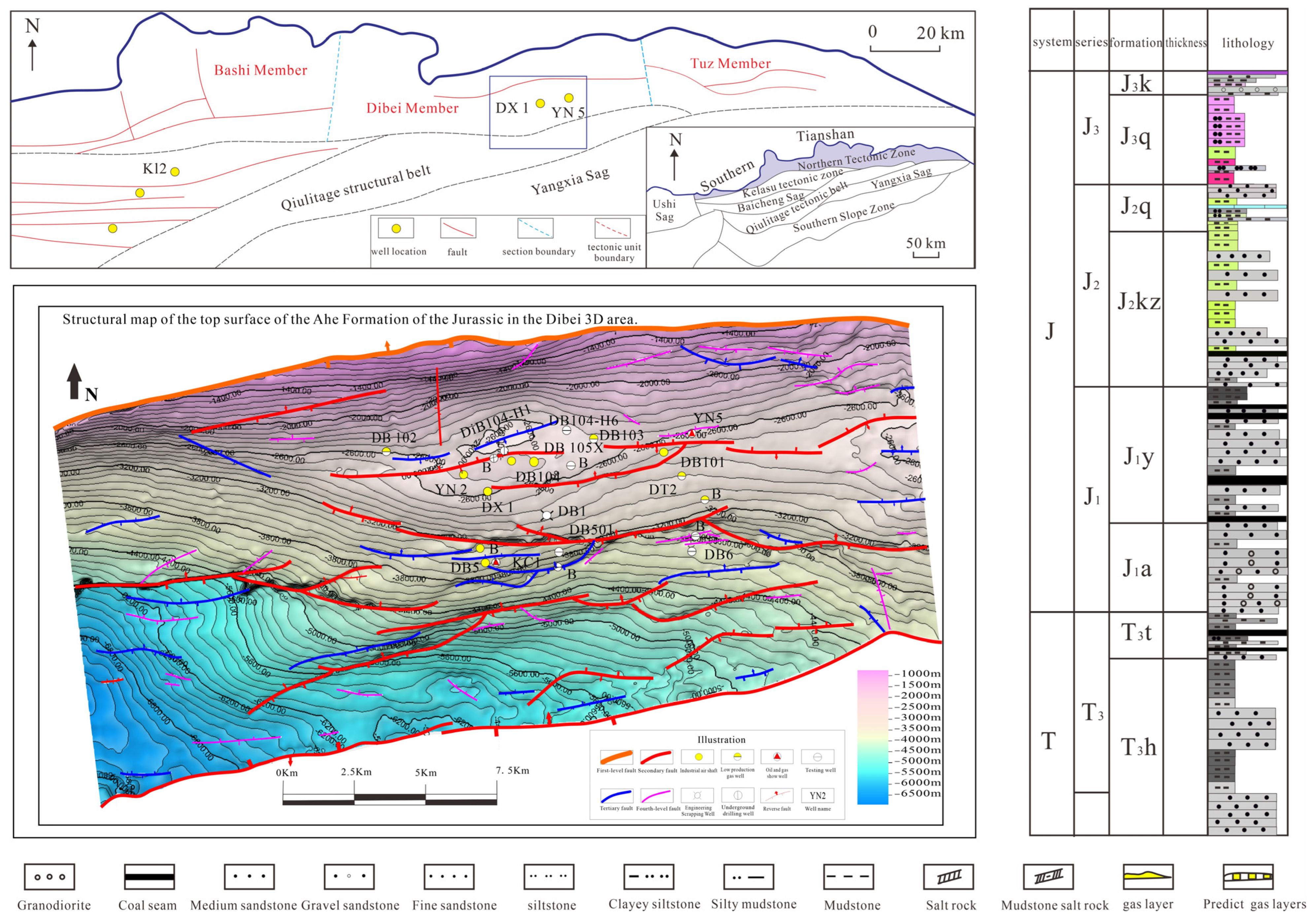
2.1. Regional Geological Overview
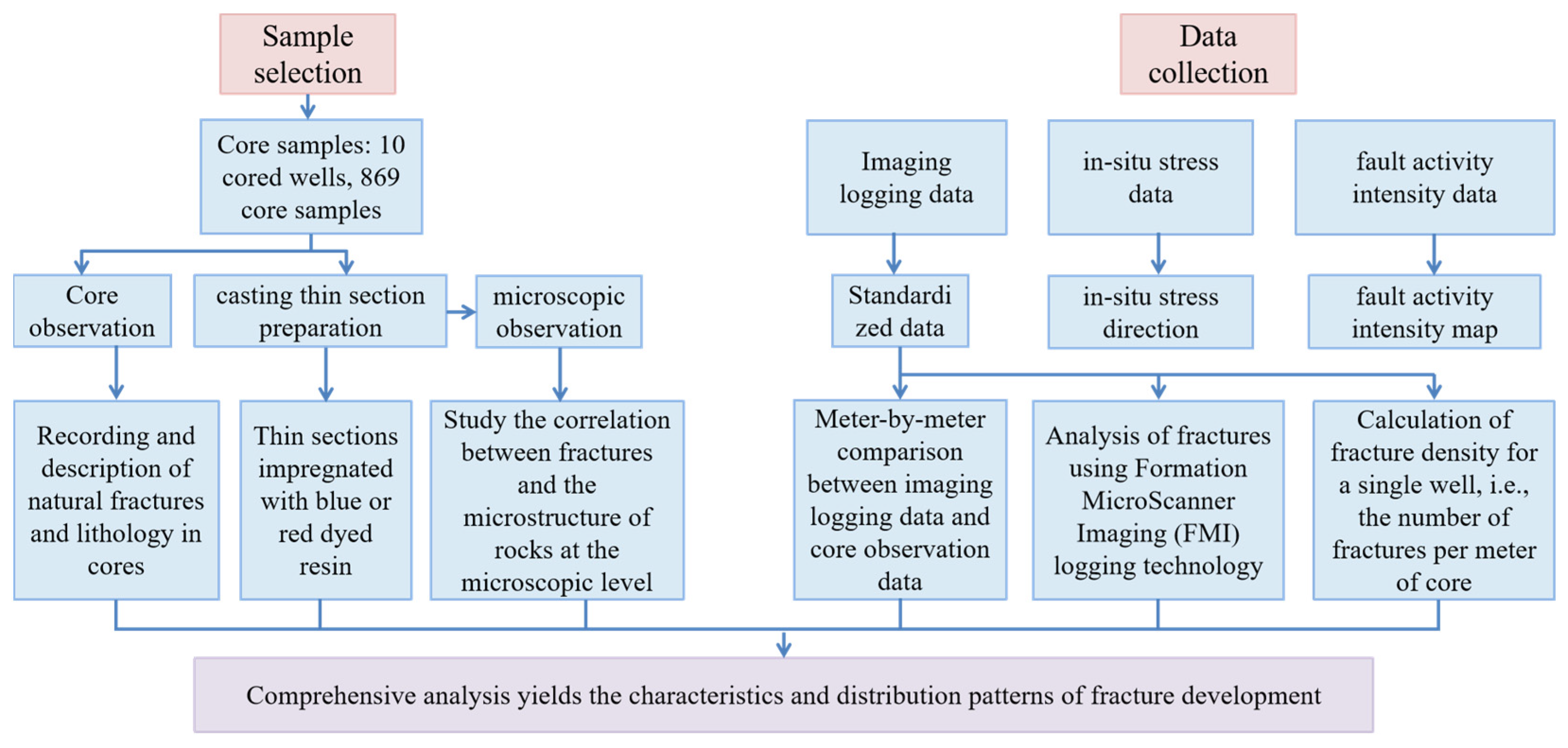
2.2. Samples and Data
2.3. Theory and Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Development and Distribution Characteristics of Natural Fractures
3.1.1. Fracture Origins and Classification
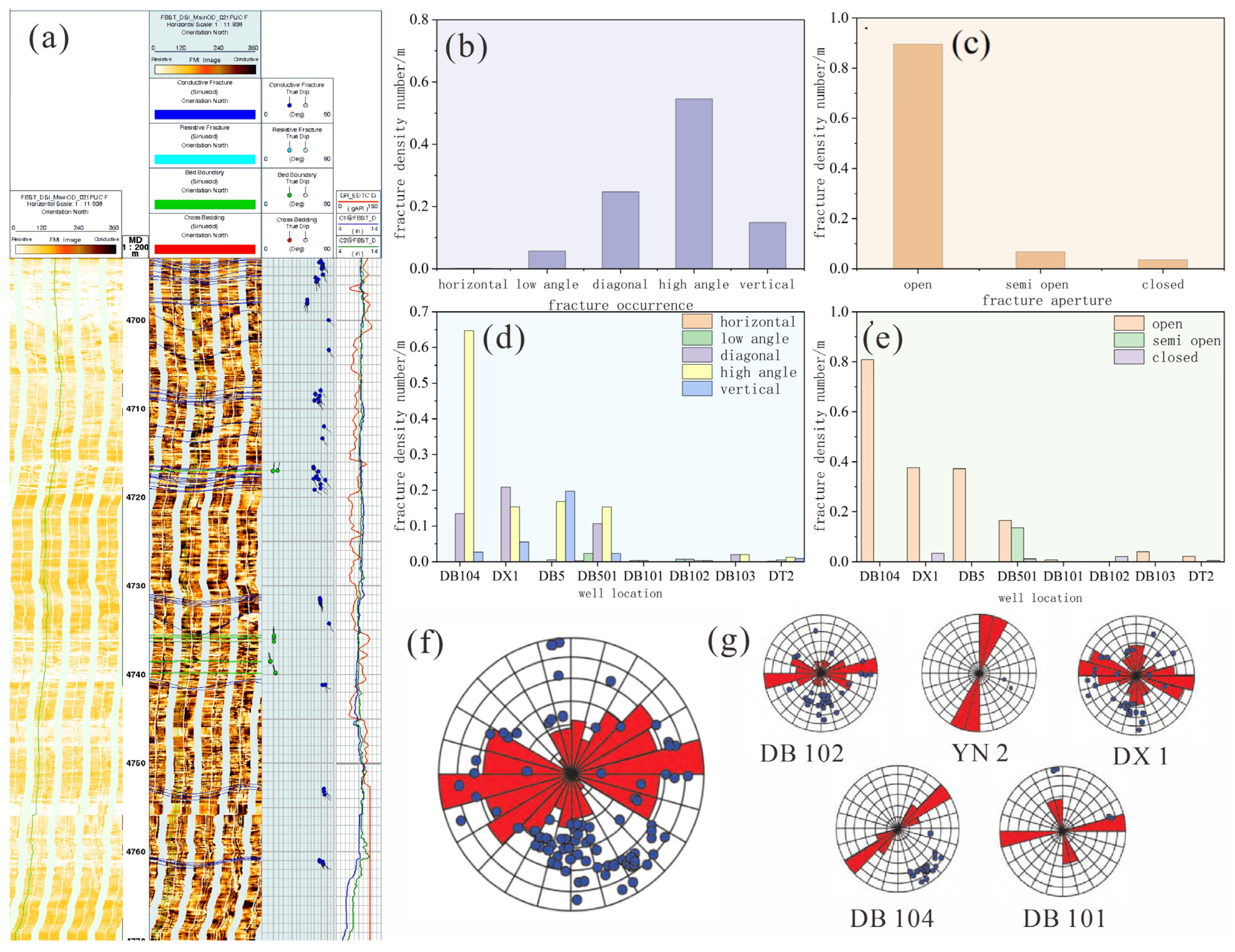
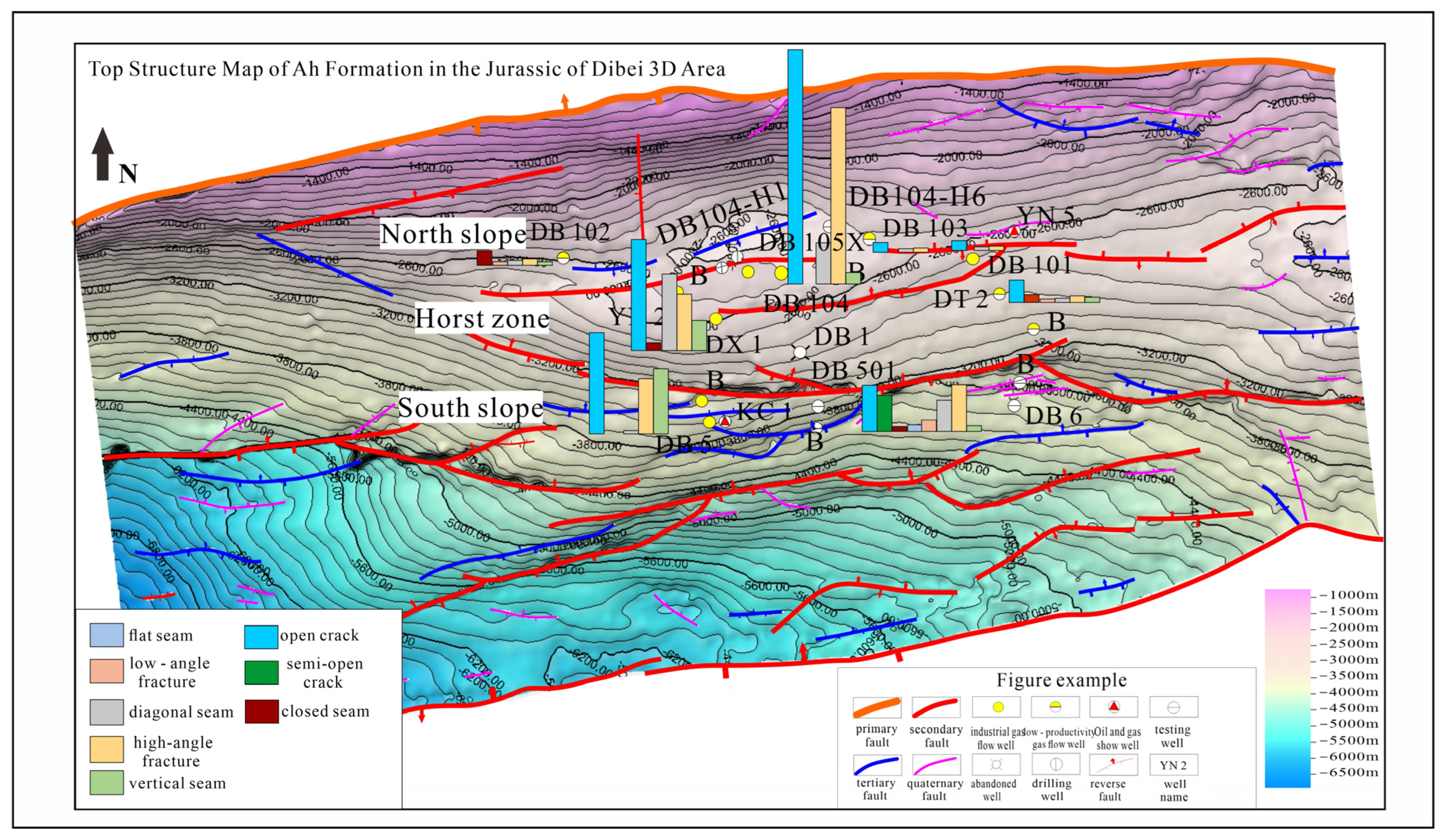
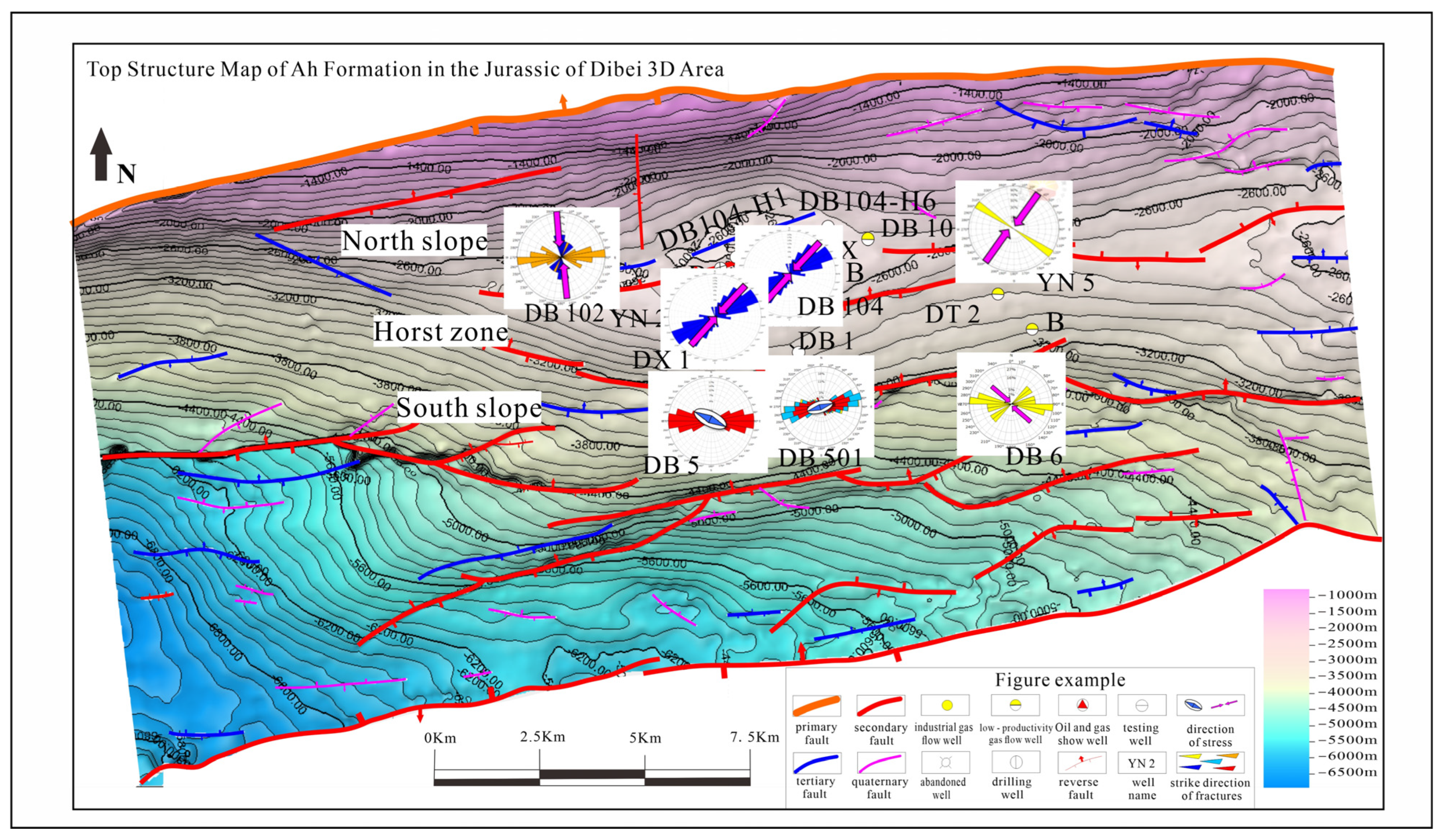
3.1.2. Fracture Distribution Characteristics
- (1)
- Fracture Occurrences and Development Degrees
- (2)
- Distribution Regularities of Fracture Strikes
3.2. Natural Fracture Development Models
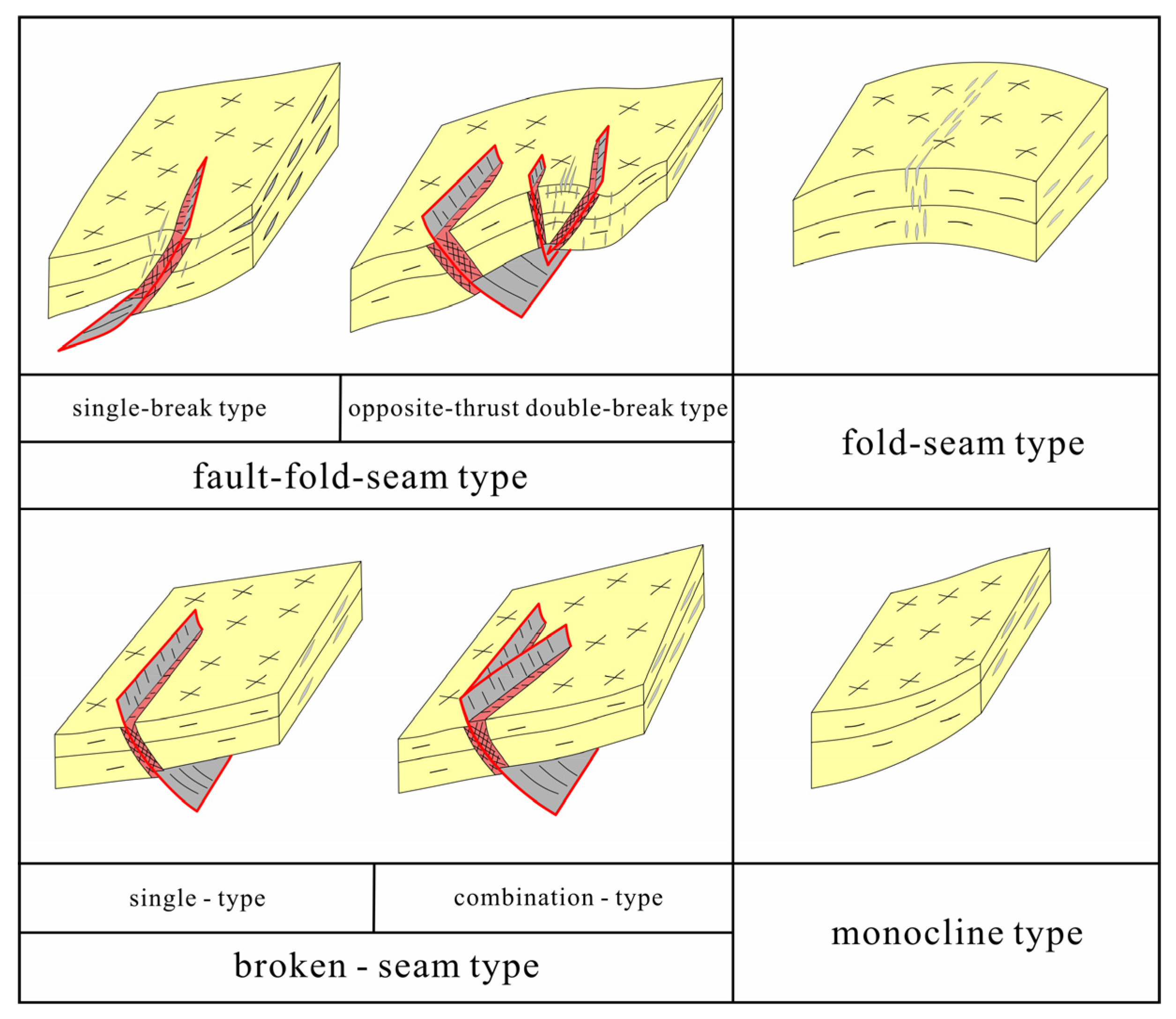
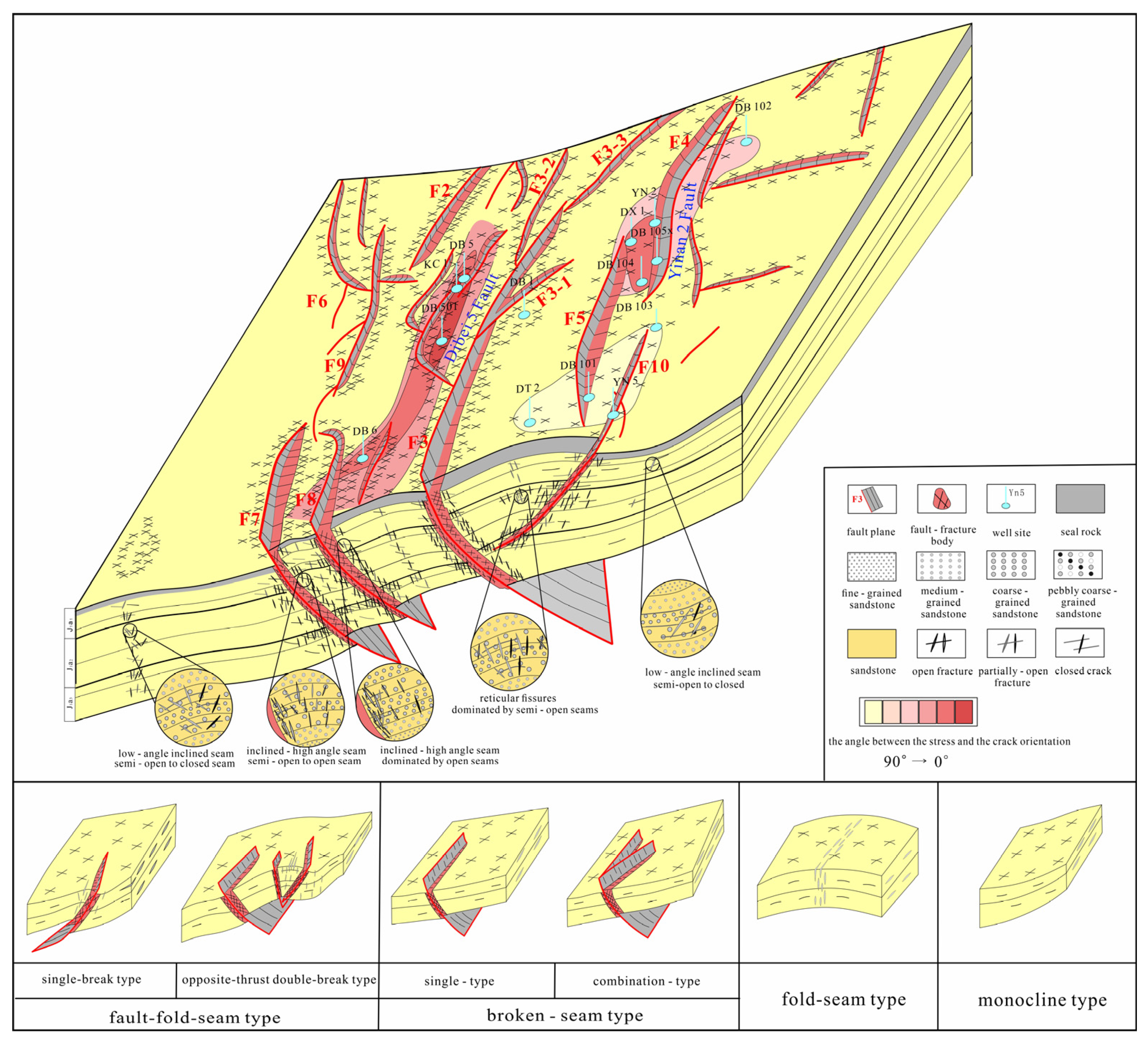
3.2.1. Classification of Tectonic Styles
- (1)
- Fault–Fold–Fracture Type
- (2)
- Fault–Fracture Type
- (3)
- Fold–Fracture Type
- (4)
- Monocline Type
3.2.2. Fracture Development Models
- (1)
- Fault–Fold–Fracture Type
- (2)
- Fault–Fracture Type
- (3)
- Monocline Type
4. Discussion
4.1. The Control Mechanism of Folds on the Development of Natural Fractures
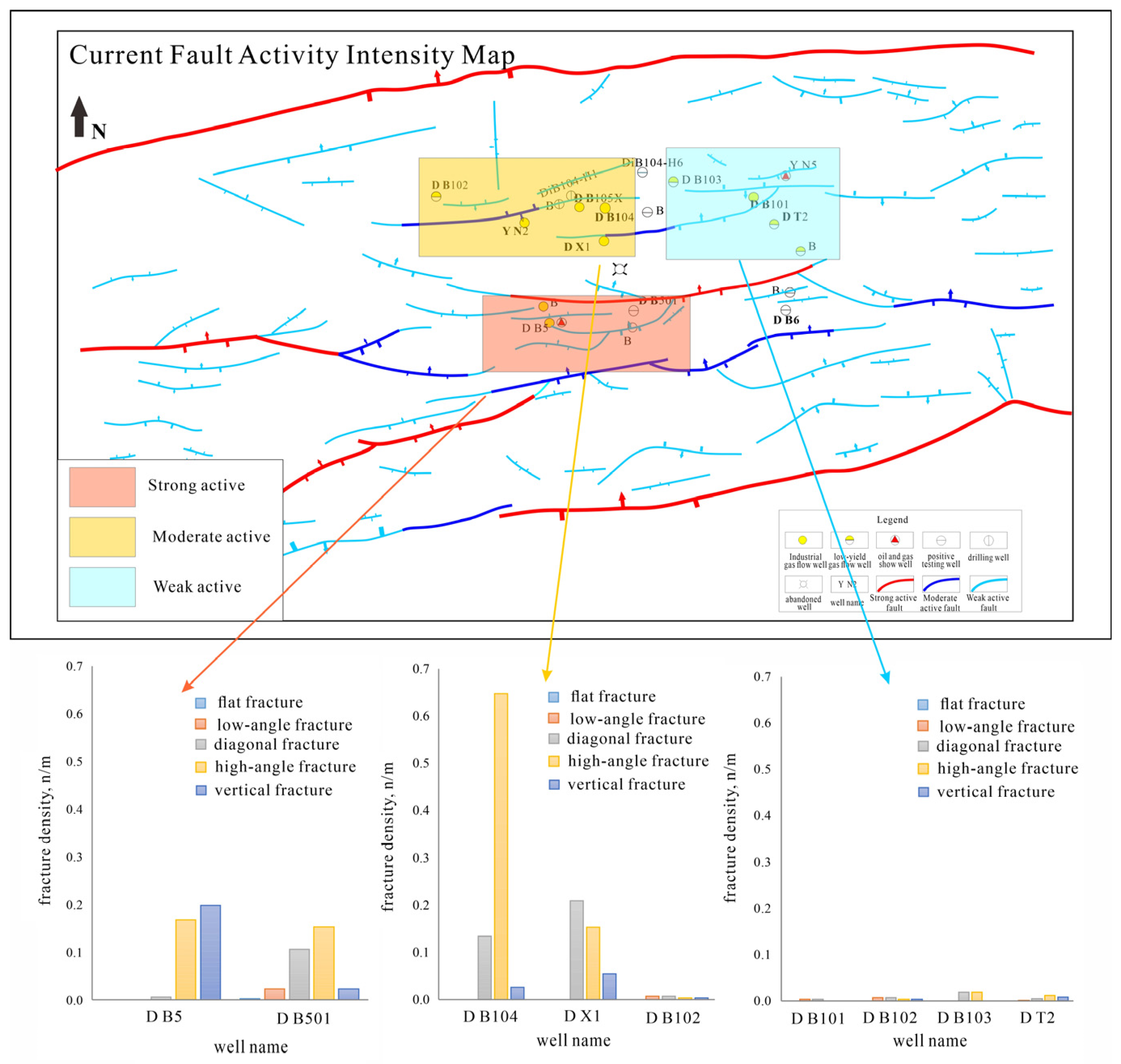
4.2. The Control Mechanism of Faults on the Development of Natural Fractures
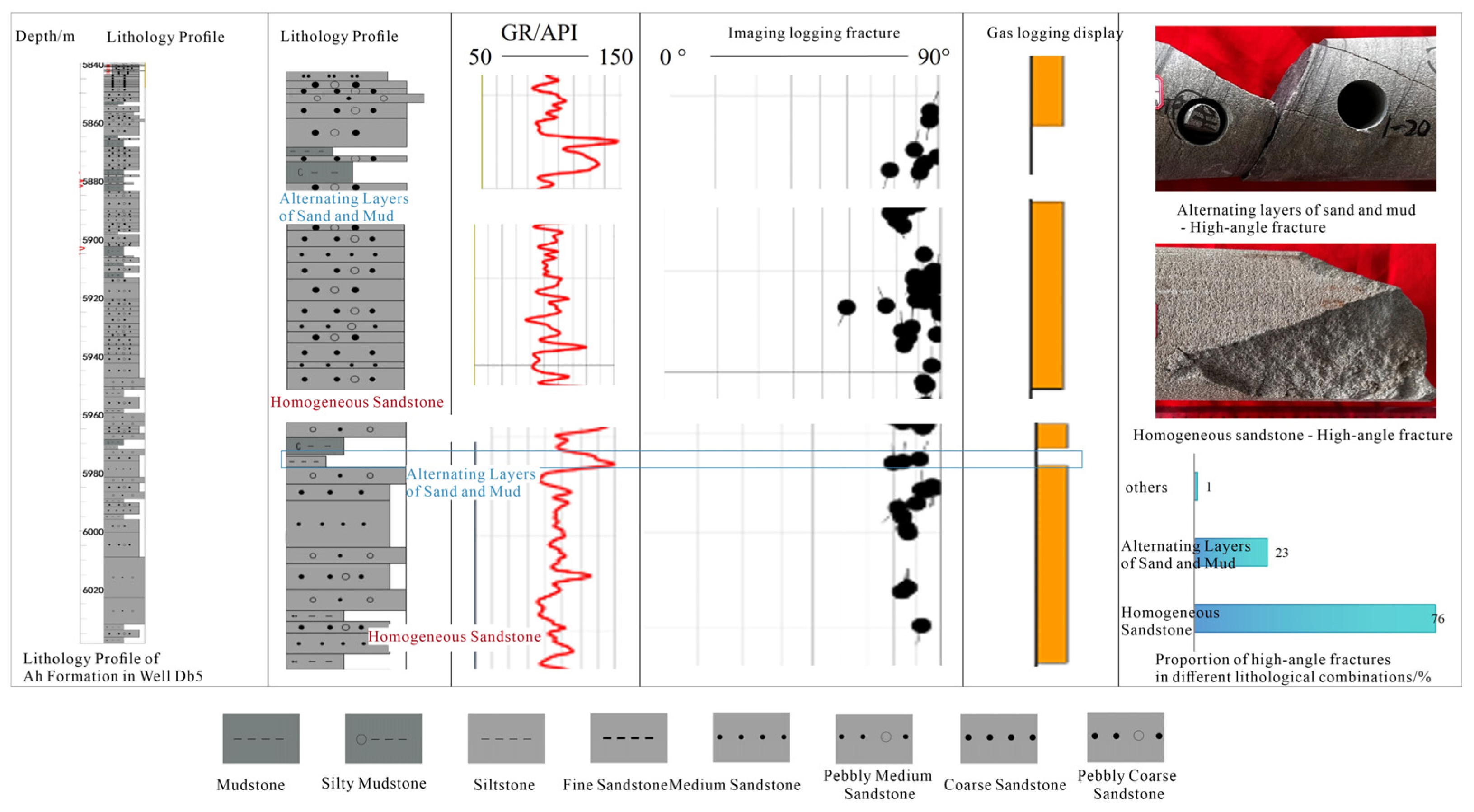
4.3. The Control Mechanism of Lithology on the Development of Natural Fractures
4.4. The Control Mechanism of Stress on the Development of Natural Fractures
4.5. Geological Significance
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the tight reservoirs of the Ahe Formation in the Dibei area of the Tarim Basin, the natural fractures are mainly of tectonic and sedimentary origins, with the tectonic origin being dominant, which is related to multiple tectonic movements. Morphologically, they are dominated by high-angle and open fractures, facilitating the storage and migration of oil and gas. Planar-wise, the high part of the fault block zone has the highest fracture density, being significantly influenced by tectonic stress. The fracture strikes are divided into three systems, namely nearly EW-trending, NE-trending, and nearly SN-trending. The nearly EW-trending fractures are the most widespread, and high-angle fractures are dominant.
- (2)
- In the fault–fold–fracture type, the activities of folds and reverse faults provide the driving force and space for fracture formation. The fault–fracture type is controlled by 2–3-grade faults, with more fractures in favorable rock layers. In the monocline type, due to the stable structure and weak stress, fracture development is scarce. Overall, in the study area, the fault–fold–fracture type has the most fractures, followed by the fault–fracture type, and the monocline type has the least.
- (3)
- The development of natural fractures in the tight reservoirs of the Ahe Formation in the Dibei area is jointly controlled by multiple factors. In the high part of the fold, stress is concentrated, which is conducive to the formation of high-angle open fractures. Fractures are more developed near moderately and strongly active faults, and the closer to the fault, the more obvious this is. When the angle between the stress and the fracture strike is between 0–30°, the fractures are likely to open, facilitating oil and gas migration. Homogeneous sandstone is more conducive to the development of high-angle fractures compared to sand–mud interbeds.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Cui, Y.A.; Liu, J.X. Fluid Discrimination Based on Inclusion-Based Method for Tight Sandstone Reservoirs. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 43, 1469–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqsa, A.; Zhang, H.C.; Umar, A.; Wang, R.; Thanh, H.T.; Radwan, A.E.; Ullah, J.; Abbasi, G.R.; Iqbal, I.; Naffees, A.; et al. Sand-ratio distribution in an unconventional tight sandstone reservoir of Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin: Acoustic impedance inversion-based reservoir quality prediction. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 1018105. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Li, A.H. Pore structure characterization, permeability evaluation and enhanced gas recovery techniques of tight gas sandstones. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 28, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; You, Y.C.; Shang, M.H.; Zhu, Z.P. Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Natural Fractures in Deep Carbonates of the Puguang Area, Sichuan Basin, China. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 16071–16083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.Y.; Jin, Z.J.; Zeng, L.B.; Liu, G.P.; He, W.J.; Mehdi, O.; Liang, X.P.; Yang, S.; Lu, G.P. Characteristics and controlling factors of natural fractures in deep lacustrine shale oil reservoirs of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, China. J. Struct. Geol. 2023, 175, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, T.; Wei, H.X.; Ye, Y. Fluid geochemistry of the Jurassic Ahe Formation and implications for reservoir formation in the Dibei area, Tarim Basin, northwest China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2018, 36, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.G.; Yang, X.Z.; Xie, H.W. Tight gas reservoir characteristics and exploration potential of Jurassic Ahe Formation in Kuqa depression, Tarim Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2021, 26, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.H.; Zeng, Q.L.; Wang, K. New progress in the theory and technology of tectonic diagenesis on reservoir and the geological significance of ultra-deep oil and gas exploration. Acta Pet. Sin. 2020, 41, 1278–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xi, K.L.; Yang, X.Z.; Yu, G.D. Mesozoic Tectonic Setting and Evolution in Kuqa Depression of the Tarim Basin: A Study of Detrital Zircons and Geochemistry. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 13193–13208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.J.; Xu, L.W.; Qi, J.F.; He, P.; Du, J.M.; Sun, T. Structural deformation of the Northern Monocline belt in the Kuqa depression and implications for the Cenozoic uplift history of the South Tianshan Mountains. Tectonophysics 2023, 857, 229840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, M.C.; Dong, C.Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Zhang, J.Z. Reservoir Characteristics of Tight Sandstone and Sweet Spot Prediction of Dibei Gas Field in Eastern Kuqa Depression, Northwest China. Energies 2022, 15, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, D.F.; Zou, H.Y.; Shang, X.Q.; Ren, H.J.; Wang, L.C. Coupling relationship between reservoir diagenesis and gas accumulation in Xujiahe Formation of Yuanba–Tongnanba area, Sichuan Basin. China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 5, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, R.H.; Yang, X.Z. Major Breakthroughs in the Exploration of Tight Sandstone Gas in the Jurassic Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area, Eastern Kuqa Depression and Their Geological Significance. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Li, F.; Yang, H.J.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.F.; Chen, L.; Du, Z.M. Development characteristics of fractures in Jurassic tight reservoir in Dibei area of Kuqa depression and its reservoir-controlling mode. Acta Pet. Sin. 2015, 36, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.Q.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.F.; Jiang, J.; Xie, Y.N.; Zhang, R.H.; Zhou, S.Y.; Lou, H.; Wang, Z.T.; Zhang, H.F.; et al. Characteristics on reservoir architecture and quality of tight sandstone reservoirs: Taking Jurassic Ahe formation in Dibei area of Kuqa foreland basin as an example. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2021, 50, 877–892. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Lu, X.S.; Fan, J.J.; Zhao, M.J.; Wei, H.X.; Zhang, B.S.; Lu, Y.H. Controlling effect of fractures on gas accumulation and production within the tight sandstone: A case study on the Jurassic Dibei gas reservoir in the eastern part of the Kuqa foreland basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 1, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Y.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Li, D.J.; Wu, X.Q.; Miao, W.D.; Zhu, H.H.; Yang, X.L. Lower limits of physical properties and classification evaluation criteria of the tight reservoir in the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Kuqa depression. Open Geosci. 2024, 16, 20220572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.Q.; Wang, K.; Zhang, R.H.; Wang, B.; Yu, C.F. Structural diagenesis and high-quality reservoir prediction of tight sandstones: A case study of the Jurassic Ahe Formation of the Dibei gas reservoir, Kuqa depression, Tarim basin, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 239, 105399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, K.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.L.; Zhou, L.; Ding, X.J. Probing Petroleum Sources Using Geochemistry, Multivariate Analysis, and Basin Modeling: A Case Study from the Dibei Gas Field in the Northern Kuqa Foreland Basin, NW China. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, K. A preliminary study of the present-day in-situ stress state in the Ahe tight gas reservoir, Dibei Gasfield, Kuqa Depression. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 96, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Xiao, A.C.; Cao, T.; Zhang, R.H.; Wei, H.X.; Yu, C.F. Geological structures and petroleum exploration fields of the northern tectonic belt in the Kuqa depression, Tarim basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 368–386. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.D.; Yuan, J.; Liu, K.Y.; Yang, X.Z.; Dong, D.T.; Ma, P.J.; Huang, C.Q. Diagenesis of the Paleogene Sandstones in the DN2 Gas Field, Kuqa Foreland Basin and its Link to Tectonics. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 1538–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.Q.; Peng, J.W.; Jiang, Z.X.; Yang, H.J.; Wang, P.W.; Jiang, F.J.; Wang, K. Hydrocarbon accumulation processes and mechanisms in Lower Jurassic tight sandstone reservoirs in the Kuqa subbasin, Tarim Basin, northwest China: A case study of the Dibei tight gas field. AAPG Bull. 2019, 103, 769–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.L.Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, X.S.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Q. Comprehensive Evaluation of Rock Mechanical Properties and in-situ Stress in Tight Sandstone Oil Reservoirs. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 911504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Jin, Z.J.; Chen, G.; Peng, M.; Huang, L.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Zeng, L.B.; Lu, G.Q.; Du, X.Y.; Liu, G.P. Multi-Scale Natural Fracture Prediction in Continental Shale Oil Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 929467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayeh, T.; Pezhman, S.T.; Meysam, R.; David, A.W.; Shadfar, D.; Hamzeh, G.; Nima, M.; Mehdi, A.A. Optimized machine learning models for natural fractures prediction using conventional well logs. Fuel 2022, 326, 124952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.Q.; Lv, X.X.; Guo, S.; Song, X.; Zhao, J. Effective evaluation of gas migration in deep and ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs of Keshen structural belt, Kuqa depression. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 46, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, S.W.; Qiao, J.C.; Feng, X.; Feng, S. Experimental and theoretical characterization of the natural gas migration and accumulation mechanism in low-permeability (tight) sandstone cores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.R.; Song, M.S.; Liu, H.M.; Feng, Y.C.; Liu, C. Investigating microscopic seepage characteristics and fracture effectiveness of tight sandstones: A digital core approach. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, J.R.; Mao, Z.Q.; Yu, H.Y. A method to evaluate pore structures of fractured tight sandstone reservoirs using borehole electrical image logging. AAPG Bull. 2020, 104, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.Y.; Zeng, L.B.; Liao, Z.H.; Ji, Y.Y.; Lyu, P.; Dong, S.Q. Fault damage zone characterization in tight-oil sandstones of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the southwest Ordos Basin, China: Integrating cores, image logs, and conventional logs. Interpretation 2017, 5, SP27–SP39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, Y.L.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.X.; Wu, J.P.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Tao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; et al. Rock thin-section analysis and identification based on artificial intelligent technique. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Ma, W.; Lin, P.; Hua, Y.L. Deep learning of rock microscopic images for intelligent lithology identification: Neural network comparison and selection. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Hussein, D.; Lawrence, J.A.; Khanaqa, P. Characterization and impact on reservoir quality of fractures in the Cretaceous Qamchuqa Formation, Zagros folded belt. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 113, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.B.; Song, Y.C.; Liu, G.P.; Tan, X.L.; Xu, X.T.; Yao, Y.T.; Mao, Z. Natural fractures in ultra-deep reservoirs of China: A review. J. Struct. Geol. 2023, 175, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Su, X.C.; Gao, S.; Fu, X.F.; Jabbari, H.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, B.; Yue, W.T.; Wang, Z.S.; Gao, A. Characteristics and formation mechanism of natural fractures in the tight gas sandstones of Jiulongshan gas field, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 175, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.B.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Dong, S.Q.; Lyu, W.Y. A review of the genesis, evolution, and prediction of natural fractures in deep tight sandstones of China. AAPG Bull. 2023, 107, 1687–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kong, X. Fine description of natural fractures in the tight sandstone reservoir of the Yanchang reservoirs in the southern Ordos Basin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.F.; Neng, Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhou, L.; Yang, W.J.; Tan, C. Stratification model of an ultra-deep tight sandstone fracture reservoir under tectonic stress: A case study of a Cretaceous reservoir in the Kuqa foreland thrust belt of the Tarim Basin. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 45, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.B. Microfracturing in the Upper Triassic Sichuan Basin tight-gas sandstones: Tectonic, overpressure, and diagenetic origins. AAPG Bull. 2010, 94, 1811–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Tian, T.; Wu, Z.H. Developmental characteristics and distribution law of fractures in a tight sandstone reservoir in a low-amplitude tectonic zone, eastern Ordos Basin, China. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 1546–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, N.D.; Deng, H.C.; Hu, X.F.; Yang, Y.Y.; Feng, X.S.; Du, Y.; et al. Development Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Tectonic Fractures in Ultra—Deep Tight Sandstones: A Case Study of the Lower Cretaceous Reservoirs in the Bozhi—Dabei Area, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 1535–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Yin, G.Q.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, H.Y. High—Efficiency Exploration Technology for Deep Tight Gas Reservoirs Based on Geomechanical Methods: A Case Study of the Dibei Gas Reservoir in the Kuqa Depression. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 621–639. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.B.; Gong, L.; Guan, C.; Zhang, B.J.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zeng, Q.; Lyu, W.Y. Natural fractures and their contribution to tight gas conglomerate reservoirs: A case study in the northwestern Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Cao, H.X.; Deng, H.C.; Yin, C.H.; Zhu, Y.P.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Yin, S. Nature fractures in shales of the Lianggaoshan Formation in northern Sichuan Basin: Fracture development characteristics and fracture formation and evolution model. Earth Sci. Front. 2024, 31, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.Y.; Jin, Z.J.; Zeng, L.B.; Liu, G.P.; He, W.J.; Yang, S.; Liang, X.P.; Lu, G.Q. Development Model of Natural Fractures in Continental Shale of the Pingdiquan Formation in the Shuangjingzi Area. East. Junggar Basin Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, M.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hu, X.Y.; Xiao, K.H.; Liu, G.P. Development Characteristics and Distribution Patterns of Natural Fractures in Continental Reservoirs in the Yuanba Area, Northeast Sichuan. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2022, 29, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hou, G.T.; Hari, K.R.; Neng, Y.; Lei, G.L.; Tang, Y.G.; Zhou, L.; Sun, S.; Zheng, C.F. The model of fracture development in the faulted folds: The role of folding and faulting. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 89, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, H.; Butler, W.R.; Bond, E.C.; Dave, H. Influence of structural position on fracture networks in the Torridon Group, Achnashellach fold and thrust belt, NW Scotland. J. Struct. Geol. 2015, 74, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Wang, K.; Hou, G.T.; Sun, W.T.; Yu, X. Prediction of natural fractures in the Lower Jurassic Ahe Formation of the Dibei Gasfield, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, NW China. Geosci. J. 2018, 22, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Xi, K.L.; Yang, X.Z.; Han, Z.H.; Xu, Z.P.; Zhou, L.; Yu, G.D.; Wang, D.S.; Wang, W.Y. Relationship between Natural Fracture and Structural Style and its Implication for Tight Gas Enrichment: A Case Study of Deep Ahe Formation in the Dibei–Tuzi Area, Kuqa Depression. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2024, 98, 1086–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Gao, L.H.; Zhang, Y.T.; Ning, C.Z.; Xie, E. Fracture attributes in reservoir-scale carbonate fault damage zones and implications for damage zone width and growth in the deep subsurface. J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 118, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maerten, L.; Maerten, F.; Lejri, M. Along fault friction and fluid pressure effects on the spatial distribution of fault-related fractures. J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 108, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Meng, X.X.; Zhao, F.Q.; Wu, S.J.; Guo, X. Sedimentary Characteristics of Fluvial—Dominated Shallow—Water Delta Fronts and Their Control on Lithologic Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Baxigai Formation in the Southern Slope of the Kuqa Depression. Lithol. Reserv. 2021, 33, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.Q.; Zhang, R.H.; Zhi, F.Q.; Wang, K.; Yu, C.F.; Dong, C.Y. Formation Conditions and Exploration Directions of Tectonic—Lithostratigraphic Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in the Mesozoic of the Eastern Kuqa Depression. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.R.; Gao, Z.Y.; Cui, J.G.; Zhou, C.M. Reservoir Porosity Evolution Characteristics and Evaluation of the Jurassic Deep Reservoir from Dibei in Kuqa Depression: Insight from Diagenesis Modeling Experiments Under the Influence of Burial Mode. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 305–320. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Luo, X.R.; Lei, G.L.; Wei, H.X.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhang, L.K.; Lei, Y.H. Effects of early oil emplacement on reservoir quality and gas migration in the Lower Jurassic tight sand reservoirs of Dibei gas field, Kuqa Depression, western China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 50, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Han, H.D.; Xia, Q.S.; Li, B. Fractal characteristic of microscopic pore structure of tight sandstone reservoirs in Kalpintag Formation in Shuntuoguole area, Tarim Basin. Pet. Res. 2020, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.F. Water-sensitive characterization and its controlling factors in clastic reservoir: A case study of Jurassic Ahe Formation in Northern tectonic zone of Kuqa depression. Pet. Res. 2020, 5, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, T.; Wang, G.W.; Xiao, C.W.; Zhou, L.; Deng, L.; Li, R.J. The in situ stress determination from borehole image logs in the Kuqa Depression. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 34, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Zhou, Z.H.; He, C.; Jiang, C.W.; Wang, B.; Li, T.S. Influence of faults on the geo-stress field distribution and damage evolution mechanism of fracture zones. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, R.; Wu, J.F.; Huang, H.Y.; Xu, E.S.; Xu, B. Complex in situ stress states in a deep shale gas reservoir in the southern Sichuan Basin, China: From field stress measurements to in situ stress modeling. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 141, 105702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Tang, H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, K. Natural Fractures in Tight Sandstone Gas Condensate Reservoirs and Their Influence on Production in the Dina 2 Gas Field in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, China. Energies 2024, 17, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, G.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Sun, Q.; Lai, J.; Han, Z.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, K. Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Natural Fractures in Lacustrine Mixed Shale Oil Reservoirs: The Upper Member of the Lower Ganchaigou Formation in the Ganchaigou Area, Qaidam Basin, Western China. Energies 2024, 17, 5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.; Su, X.H.; He, W.Y.; Fu, X.F.; Ai, C.; Xie, K. Intelligent Prediction of Shale Hydraulic Fracturing Network Evaluation Based on Artificial Intelligence Model. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 2. [Google Scholar]

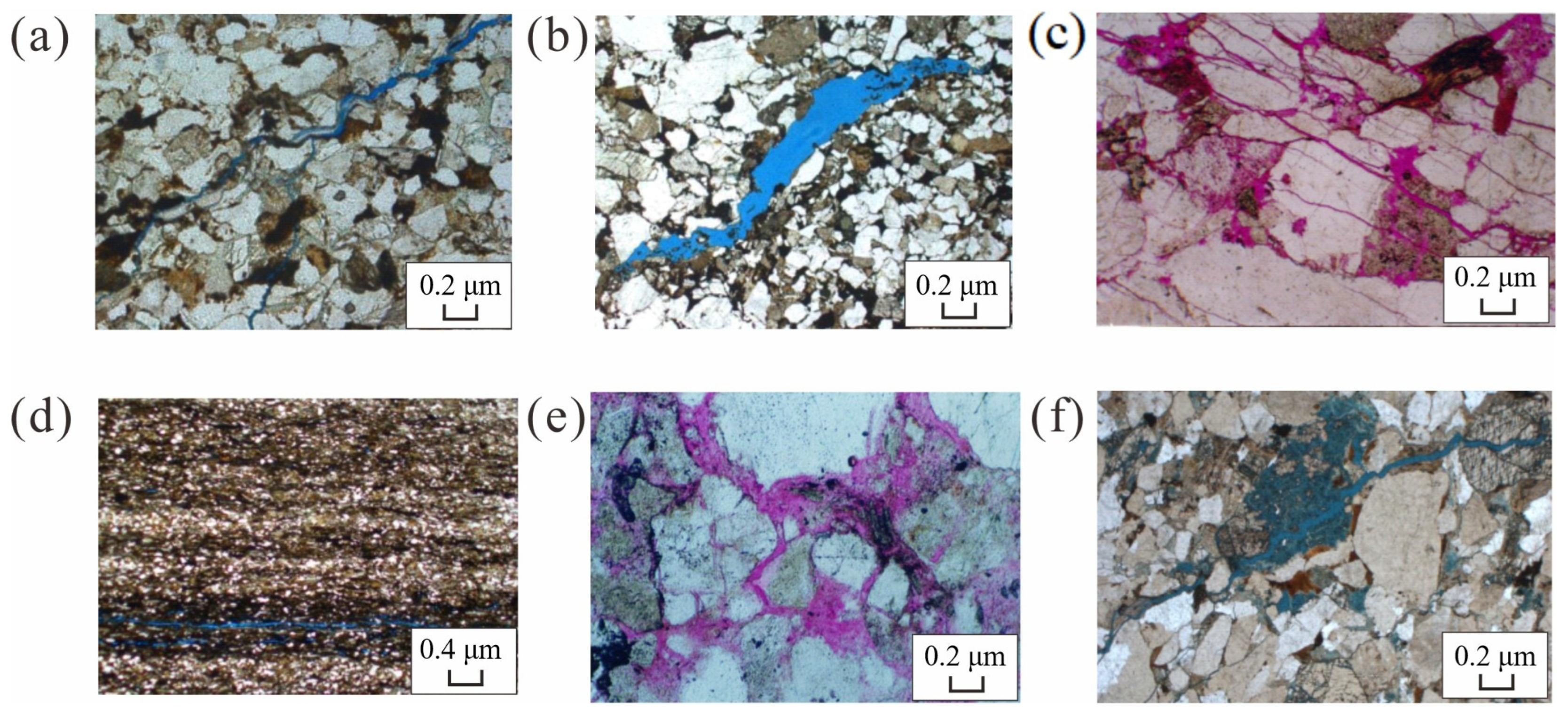
| Fracture Type | Fracture Dip Angle | Core Photos |
|---|---|---|
| Sedimentary origin fractures | 0–10° |  Well YiNan 5 (YN 5), 4842.23 m |
| 10–30° |  Well DiBei 105X (DB105X), 4768.85 m | |
| Tectonic origin fractures | 30–60° |  Well DiTan 2 (DT 2), 5098.50 m |
| 60–80° |  Well DiBei 102 (DB102), 5053.50 m | |
| 80–90° |  Well YiNan 4 (YN 4), 4608.00 m |
| Regional Distribution | Well Name | Fracture Filling Status | Fracture Dip Angle Types | Density | Bedding Fractures | Fracture Development Status | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Fractures | Semi-Open Fractures | Open Fractures | Vertical Fractures | High-Angle Fractures | Inclined Fractures | Low-Angle Fractures | Horizontal Fractures | ||||||
| Fault terrace zone area | High position of the fault terrace zone | DB 104 | 60/0.809 | 2/0.027 | 48/0.547 | 10/0.135 | 0.809 | Good | |||||
| DX1 | 8/0.034 | 88/0.376 | 13/0.056 | 36/0.154 | 47/0.200 | 0.41 | Relatively good | ||||||
| Low position of the fault terrace zone | DB 101 | 2/0.008 | 1/0.004 | 1/0.004 | 0.008 | Poor | |||||||
| DB 102 | 6/0.021 | 1/0.003 | 2/0.007 | 3/0.011 | 0.021 | 5/0.087 | Poor | ||||||
| DB 103 | 2/0.04 | 1/0.02 | 1/0.02 | 0.04 | Poor | ||||||||
| DT 2 | 3/0.006 | 12/0.022 | 5/0.009 | 6/0.012 | 3/0.006 | 1/0.001 | 0.029 | Relatively poor | |||||
| Southern slope | High position of the southern slope | DB 5 | 64/0.372 | 34/0.197 | 29/0.169 | 1/0.006 | 0.372 | 16/0.882 | Relatively good | ||||
| Low position of the southern slope | DB 501 | 8/0.117 | 93/0.135 | 113/0.16 | 16/0.023 | 107/0.153 | 73/0.106 | 16/0.023 | 2/0.002 | 0.31 | 2/0.076 | Relatively good | |
| Regional Distribution | Well Name | Lithologic Combination | Fracture Development Status | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Semi-) Open Fracture | Closed Fracture | Tectonic Fractures | Density | ||||
| Fault terrace zone area | High position of the fault terrace zone | DX1 | Sand–mud interbed | 0.081 | 0.03 | 0.111 | 0.111 |
| Homogeneous sandstone | 0.295 | 0.004 | 0.299 | 0.299 | |||
| Low position of the fault terrace zone | DB 102 | Sand–mud interbed | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.007 | ||
| Homogeneous sandstone | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.011 | ||||
| Southern slope | High position of the southern slope | DB 5 | Sand–mud interbed | 0.111 | 0.111 | 0.111 | |
| Homogeneous sandstone | 0.256 | 0.256 | 0.256 | ||||
| Low position of the southern slope | DB 501 | Sand–mud interbed | 0.221 | 0.009 | 0.227 | 0.23 | |
| Homogeneous sandstone | 0.095 | 0.003 | 0.084 | 0.098 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Pang, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, T.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; et al. Development Characteristics and Distribution Patterns of Natural Fractures in the Tight Reservoirs of the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Tarim Basin. Processes 2025, 13, 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082613
Tang Y, Wang Y, Zhang L, Jiang J, Pang H, Shen L, Zhang G, Zhao T, Li L, Zhou C, et al. Development Characteristics and Distribution Patterns of Natural Fractures in the Tight Reservoirs of the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Tarim Basin. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082613
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yangang, Yuying Wang, Liang Zhang, Jun Jiang, Hong Pang, Lin Shen, Guowei Zhang, Tiantian Zhao, Ling Li, Chang Zhou, and et al. 2025. "Development Characteristics and Distribution Patterns of Natural Fractures in the Tight Reservoirs of the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Tarim Basin" Processes 13, no. 8: 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082613
APA StyleTang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Jiang, J., Pang, H., Shen, L., Zhang, G., Zhao, T., Li, L., Zhou, C., Deng, J., Li, S., & Chen, D. (2025). Development Characteristics and Distribution Patterns of Natural Fractures in the Tight Reservoirs of the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Tarim Basin. Processes, 13(8), 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082613







