Abstract
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) can have high pollutant removal efficiencies and generate electricity; however, the use of selective membranes represents a considerable expense. In this investigation, the performance of a membraneless MFC was evaluated at different hydraulic retention times (HRTs) of 12, 24, 36, and 48 h. The chemical oxygen demand removal efficiencies (CODREs) were 93.5, 90.9, 87.3, and 85.4%, and the biochemical oxygen demand (BODRE) values were 94.5, 91.5, 88.9, and 85.5 at HRTs of 48, 36, 24, and 12 h, respectively. Lower concentrations of solids (suspended solids and total dissolved solids), total nitrogen, phosphorus, fats and oils, and microbiological contamination (helminth eggs and fecal coliforms) were detected when operating the system at a 48 h HRT. At an HRT of 12 h, no decrease in electrical conductivity was detected, whereas at 48 h, it decreased by 19.6%. The oxidation–reduction potential and OCV increased at longer HRTs. The microorganisms detected at the anode were Achromobacter denitrificans, Achromobacter anxifer, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The 48 h HRT improved the chemical, physical, and microbiological quality of the municipal wastewater, favoring voltage generation.
1. Introduction
MFCs are considered an innovative technology that removes contaminants from wastewater and produces renewable energy through anaerobic oxidation carried out by microorganisms, mainly bacteria and archaea, although this activity has also been detected in yeasts [1,2,3]. Among the most commonly reported genera of electroactive microorganisms are Geobacter, Rhodopseudomonas, Shewanella, and Pseudomonas, among others, which enable the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy [4]. Electrochemically active bacteria (EAB) are also referred to as electrogenic bacteria, anode-respiring bacteria, exoelectrogenic bacteria, or electricigens [5]. EAB are divided into electrogenic and electrotrophic bacteria: electrogenic bacteria (which produce electrons) are capable of transferring electrons to electron acceptors that are outside the cell, which are located in the anode, while electrotrophic bacteria (which consume electrons) are bacteria that transfer electrons to the bacterial cell from electron donors that are outside the cell and can be located in the cathode [6]. In addition to the microbial population, MFCs consist of an anode, a cathode, and a selective or proton-exchange membrane (PEM) that separates the anodic compartment from the cathodic one [7,8]. Anaerobic microorganisms biotransform organic contaminants into protons, electrons, and carbon dioxide. The generated electrons are transported to the cathode by the external circuit, where there are electron acceptors such as oxygen, nitrate, and sulfate. Protons pass through the PEM and are transported to the cathode, where they react with oxygen to form water [9,10].
The cost of PEMs is very high. For example, one of the most used membranes is Nafion® 117, composed of perfluorosulfonic acid, but its cost is approximately 60% of the total MFC, which has not allowed us to commercialize the MFC, which is why there is interest in studying membraneless microbial fuel cells (ML-MFCs) that represent a low-cost alternative, have lower internal resistance, decrease or eliminate the use of oxygen (external aeration), increase proton diffusion, have easier operation, and have a simpler design, where the anode and cathode are in the same compartment [9,11,12,13].
Among the disadvantages of ML-MFCs is that by not having a physical barrier (membrane), the components of the anode and cathode can be partially mixed, which reduces the electrochemical efficiency of the system, and another disadvantage is that the distance between the cathode and the anode must be greater, which has a negative impact on anaerobic microorganisms [9,12]. To replace the membranes in ML-MFCs and to separate the anode and cathode, inexpensive materials such as glass, ceramic, and wood have been used, which allow for the diffusion of chemical species [11,14].
Ceramic separators are used due to their porosity, which facilitates the transport of ions. Additionally, other factors, such as the composition of the clays, the wall thickness, and the pore size, are also considered [15]. ML-MFCs have been used for the treatment of various types of wastewater, including domestic, industrial, municipal, and mixtures of these [16]. Municipal wastewater (MWW) is complex, as it contains a diversity of toxic chemical compounds and pathogenic microorganisms [17]. Apart from the type of wastewater (composition and concentration), other factors affect the performance of an MFC, such as reactor design, electrode composition, electron acceptors, pH, temperature, and HRT, among others [18]. In the operation of ML-MFCs, the hydraulic retention time (HRT) is a key parameter that regulates the contact between microorganisms and the substrate(s) in the wastewater. The HRT significantly affects the removal of contaminants and the generated voltage [11]. In an MFC operated in semi-continuous flow at different HRTs in domestic wastewater treatment, the maximum voltages detected were 319 mV and 308 mV using a carbon fiber brush and a graphite rod as the anodes, respectively, at an HRT of 8 h, while the highest COD removal percentages were 80.3% and 73.9% with carbon fiber brush and graphite rod anodes, respectively, at an HRT of 48 h [18]. This trend, where the HRT decreases, the voltage increases, and the COD removal percentage decreases, and vice versa, was also observed when treating wastewater from a fish-canning industry in an MFC using carbon fibers as anodes [11].
When comparing the performance of an ML-MFC with an MFC with different HRTs and different feeding regimes, using urine as a substrate, some researchers observed that in the ML-MFC, the power produced decreased as the HRT increased, while the COD removal efficiency percentage increased with increasing HRT, while in the MFC, the power produced was stable at the different HRTs, which did not occur with the COD removal efficiency percentage, which increased according to the increase in the HRT, concluding that MFCs could be more appropriate to operate with long HRTs and the ML-MFC with short HRTs [19]. The purpose of this research was to evaluate the performance of municipal wastewater treatment with an ML-MFC with graphite felt electrodes (the anode and cathode) at different HRTs of 48, 36, 24, and 12 h. Performance was evaluated by measuring the following parameters: chemical oxygen demand, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), solids (total (TSs), total suspended (TSSs), and total dissolved (TDSs) solids), total nitrogen (TN: NO3−, NO2−, NH4+, and organic nitrogen (ON)), phosphorus (P), fats and oils (F&Os), helminth eggs (HEs), fecal coliforms (FCs), electrical conductivity (EC), oxidation reduction potential (ORP), and open-circuit voltage (OCV).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analytical Techniques, Reagents, and Equipment
The COD was determined using the small-scale sealed tube method [20]. The reagents used were concentrated sulfuric acid (96–98%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), potassium dichromate (96–98%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), mercury sulfate (>98%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), silver sulfate (>98%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), and potassium dichromate (96–98%). The equipment used was a HACH Model Digital Reactor Block 200 thermoreactor (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA) and a HACH Model DR 5000 spectrophotometer (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA).
The OCV was determined by the electrometric method [21]. No reagents were used. The equipment used was graphite rods, graphite felt electrodes, and a STEREN PC LINK brand multimeter (Electrónica Steren S.A de C.V. Azcapotzalco, Mexico City, México).
The pH was determined by the electrometric method [22]. The reagents used were Thermo Scientific Buffer pH 4.01 Orion application solution 910104 (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA), Thermo Scientific Buffer pH 7.00 Orion application solution 910107 (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA), and Thermo Scientific Buffer pH 10.01 Orion application solution 910110 (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA). The equipment used was a Thermo Scientific Orion Star A215 pH/Conductivity meter with an Orion ROSS Combination pH 8102BN electrode (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA).
The ORP was determined by the electrometric method [23]. The reagent used was ORP Standard (420 mV), Orion application solution 967901 (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA). The equipment used was a Thermo Scientific Orion Star A215 pH/Conductivity meter with an Orion Sure-Flow Comb Redox/ORP electrode 9678BNWP (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA).
The EC was determined by the electrometric method [24]. The reagents used were Thermo Scientific Conductivity/TDS Standard (100 µS/cm–47 ppm as NaCl), Orion application solution 011008 (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA), and Thermo Scientific Conductivity/TDS Standard (1413 µS/cm–692 ppm as NaCl), Orion application solution 011007 (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA). The equipment used was a Thermo Scientific Orion Star A215 pH/Conductivity meter with an Orion Conductivity Cell 013005MD electrode (Thermo Fisher Orion, Waltham, MA, USA).
The TSs were determined by the gravimetric method by evaporation [25]. The equipment used was an ARSA brand drying oven (model AR-290) (Proquisur Milpa Alpa, Mexico City, México) and a Joanlab brand analytical balance (model FA3304N) (JoanLab Equipment Co., Huzhou, China).
The TSSs were determined by the gravimetric method by filtration and evaporation [25]. The equipment used was AHLSTROM MUNKSJO brand glass microfiber filters (Ahlstrom Munksjö Helsinki, Uusimaa, Finland), a Millipore brand vacuum pump (model WP6111560), an ARSA brand drying oven (model AR-290) (Proquisur Milpa Alpa, Mexico City, México), and a Joanlab brand analytical balance (model FA3304N) (JoanLab Equipment Co., Huzhou, China).
The TDSs were determined by the gravimetric method by evaporation [25]. The equipment used was an ARSA brand drying oven (model AR-290) (Proquisur Milpa Alpa, Mexico City, México) and a Joanlab brand analytical balance (model FA3304N) (JoanLab Equipment Co., Huzhou, China).
The F&Os were determined by the Soxhlet method [26]. The reagents used were concentrated sulfuric acid (96–98%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), diatomaceous earth MAESA brand (Materiales y Abastos Especializados, S.A. de C.V. Benito Juárez, Mexico City, México), and n-hexane (>65%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León México), and the equipment used was a Soxhlet distillation system (Chemglass Life Sciences, Vineland, NJ, USA), Whatman brand cellulose cartridges for extraction 33 × 80 mm (Whatman plc, Marlborough, MA, USA), a Corning brand magnetic stirring/heating plate (model PC320) (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA), a KAMOER brand peristaltic pump (model KGHM100) (Kamoer Fluid Tech Distrito Songjiang, Shanghai, China), an ARSA brand drying oven (model AR-290) (Proquisur Milpa Alpa, Mexico City, México), and a Joanlab brand analytical balance (model FA3304N) (JoanLab Equipment Co., Huzhou, China).
P was determined by the vanadomolybdophosphoric acid method [27]. The reagents used were phenolphthalein Hycel brand (Hycel de México, S.A. de C.V. Zapopan, Jalisco, México), ethyl alcohol (96%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León México), concentrated sulfuric acid (96–98%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), concentrated nitric acid (64–66%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), ammonium heptamolybdate heptahydrate (>81%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), ammonium metavanadate (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), and concentrated hydrochloric acid (36–38%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México). The equipment used was a Corning PC320 magnetic stirrer/heating plate (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA) and a HACH DR 5000 spectrophotometer (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA).
The TN was determined by adding the following parameters: Nitrates were determined by the chromotropic acid method [28]. The reagents used were sulfamic acid (>99%) Mallinckrodt Chemicals brand (Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, St. Louis, MO, USA), chromotropic acid (>99%) Sigma-Aldrich brand (Sigma-Aldrich, Corporation St. Louis, MO, USA), and concentrated sulfuric acid (96–98%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), and the equipment used was a HACH brand spectrophotometer (model DR 5000) (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA). Nitrites were determined by the colorimetric method with sulfanilamide and NEDA [29]. The reagents used were sodium hydroxide (>97%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), concentrated sulfuric acid (96–98%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), and sulfanilamide (>99%) Sigma-Aldrich brand (Sigma-Aldrich Corporation, St. Louis, MO, USA), and the equipment used was a HACH brand spectrophotometer (model DR 5000) (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA). Ammoniacal nitrogen and organic nitrogen were determined by the Kjeldahl method [30]. The reagents used were sodium hydroxide (>97%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), sodium tetraborate decahydrate (>95%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México),, boric acid (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), methyl red DEQ brand (Desarrollo de Especialidades Químicas, S.A. de C.V. García, Nuevo León, México), methylene blue Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), ethyl alcohol (96%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), potassium sulfate (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), anhydrous copper sulfate (>98%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), concentrated sulfuric acid (96–98%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), and sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate (>99%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México). The equipment used was a LABCONCO brand micro Kjeldahl digester (Labconco Corporation, Kansas City, MO, USA), a distillation system, a KAMOER brand peristaltic pump (model KGHM100) (Kamoer Fluid Tech Distrito Songjiang, Shanghai, China), and a Corning brand magnetic stirrer/heating plate (model PC320) (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA).
The BOD was determined by the seed dilution method [31] and dissolved oxygen measurement [32]. The reagents used were magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (>98%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), anhydrous calcium chloride (>96%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), ferric chloride hexahydrate (>97%) Karal brand (Karal, S.A. de C.V. León, Guanajuato, México), potassium phosphate monobasic (>99%) Analytyka brand (Analytyka reactivos y materias primas especiales Guadalajara, Jalisco, México), potassium phosphate dibasic (>98%) PQM brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate (>99%) Baker´s Analyzed brand (Avantor, Inc., Radnor, PA, USA), ammonium chloride (>99%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), manganese sulfate monohydrate (>98%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), sodium hydroxide (>97%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), potassium hydroxide (>98%) MAESA brand (Materiales y Abastos Especializados, S.A. de C.V. Benito Juárez, Mexico City, México), potassium iodide (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), sodium azide (>98%) CTR brand (CTR Scientific Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), soluble starch (98%) Hycel brand (Hycel de México, S.A. de C.V. Zapopan, Jalisco, México), salicylic acid (>99%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), sodium thiosulfate (>99%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México), and concentrated sulfuric acid (96–98%) FERMONT brand (Productos Químicos Monterrey Monterrey, Nuevo León, México). The equipment used was a Corning brand magnetic stirrer/heating plate model PC320 (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA), and a HACH brand BOD incubator, model 205 (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA).
The FCs were determined by the serial dilution method [33]. The reagents used were sodium lauryl sulfate broth BD brand (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and EC broth BD brand (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). The equipment used was a Corning brand magnetic stirrer/heater, model PC320 (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA), an ALL AMERICAN brand electric pressure sterilizer, model 1930 (Wisconsin Aluminum Foundry Co., Inc. Manitowoc, WI, USA), a SCILOGEX brand vortex stirrer, model MX-S (Scilogex, LLC, Rocky Hill, CT, USA), and an ARSA brand drying oven, model AR-290 (Proquisur Milpa Alpa, Mexico City, México).
The HEs were determined by the modified Bailenger method [34]. The reagents used were Triton X-100 Hycel brand (Hycel de México, S.A. de C.V. Zapopan, Jalisco, México), sodium acetate trihydrate (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), glacial acetic acid (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), ethyl ether (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México), and zinc sulfate heptahydrate (>99%) Jalmek brand (Jalmek Científica, S.A. de C.V. San Nicolás de los Garza, Nuevo León, México). The equipment used was an IEC HN-SII model BM1000 centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Needham Heights, MA, USA), a SCILOGEX model MX-S vortex mixer (Scilogex, LLC, Rocky Hill, CT, USA), a McMaster chamber (Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG Karlsruhe, BW, Germany), and a Prisma model 208 optical microscope (Ingeniería Científica Bionanomolecular, S.A. de C.V., Guadalajara, Jalisco, México).
2.2. Characterization of Municipal Wastewater
The experiment was conducted during May and June, during which time municipal wastewater was collected weekly from the reception module of the Mexican Army Urban Forest treatment plant in Saltillo, Coahuila. After each MWW collection, the parameters presented in Table 1 were analyzed. The average values for all collections performed during the study period are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical and microbiological characterization of municipal wastewater.
2.3. Description and Operation of ML-MFC
The ML-MFC was constructed using transparent acrylic and 3D-printed polylactic acid (PLA) parts, with a working volume of 3.7 L, comprising 1.85 L for the anode and 1.85 L for the cathode. The anode and cathode were separated by a 3D-printed piece with a mesh center, its main function being to contain 430 g of 10 mm diameter ceramic clay (ceramsite). The top and bottom lids, as well as the reactor centerpiece, were also 3D-printed with PLA.
The electrodes for both the anode and cathode consisted of graphite felt, which served as an electron collector (electrical energy) and as a support for the microorganisms. The graphite felt used was 6 mm thick and was cut into 8.5 cm diameter pieces. These pieces, in turn, contained 10 perforations, each 5 mm in diameter, along the surface to improve water flow. Six stacked pieces of graphite felt were used for both the anode and cathode. The stacked graphite felt piece package (anode) was introduced into a solution of MWW and sludge from a municipal wastewater treatment plant (90% MWW—10% sludge), and the corresponding cathode package was immersed in a solution with MWW and the same type of sludge (90% MWW—10% sludge), and aeration was provided (ELITE brand, model 799) for 15 d, which served to promote the formation of microbial biofilms on both electrodes. At the end of this period, the ML-MFC was assembled for operation in continuous flow. The anode and cathode electrodes were in contact with two pieces of graphite rod, 5 cm long by 5 mm wide, to serve as terminals to measure the OCV. The assembled ML-MFC is shown in Figure 1.
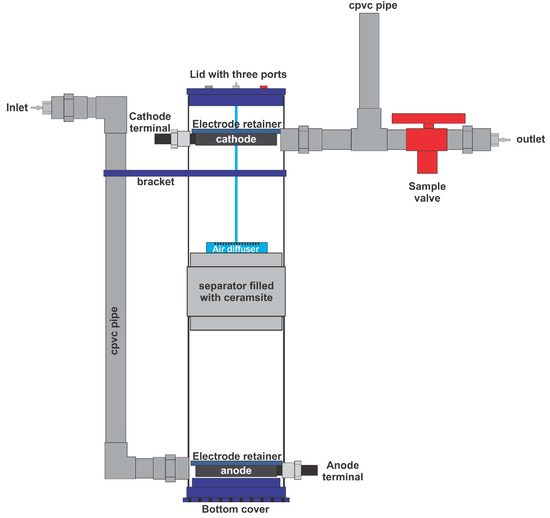
Figure 1.
The design of the ML-MFC used in this research.
The ML-MFC was fed by a Watson-Marlow Limited 101U/R peristaltic pump, which was configured to provide HRTs of 48, 36, 24, and 12 h in each experiment. The MWW moved to the anode located at the bottom, and then the water continued its course toward the cathode situated at the top of the ML-MFC. The air flow to the cathode was administered through an aerator pump (ELITE brand, model 799) at a flow rate of 2 L/min, which entered the system through a silicone hose coupled to a circular diffuser with a diameter of 3.5 cm, a thickness of 1.7 cm, and 217 holes of 1 mm for air outlet, which was 3D-printed with PLA. Each HRT was studied for 168 continuous h (7 d). Parameters such as COD, OCV, pH, ORP, and EC were monitored in the effluent starting at 48 h and then every 24 h thereafter. Parameters such as TSs, TSSs, TDSs, F&Os, P, TN, BOD, FCs, and HEs were measured at the end of 168 h for each HRT.
2.4. Molecular Characterization of Microorganisms on ML-MFC Anode
The sample taken from the anode was homogenized using a SCILOGEX MX-S brand vortex stirrer. Subsequently, 1 mL of the sample was taken, and serial dilutions were made up to 1 × 10−5. From each dilution, 100 μL was seeded on LB agar medium plates (Sigma Aldrich, Cat. L3147, Saint Louis, MO, USA), and the plates were incubated for 48 h at 27 °C. From the resulting colonies, six were selected based on their distinct separation from the others. Genomic DNA was extracted from the resulting colonies using the HotShot method [35]. Briefly, the selected colonies were picked with sterile toothpicks and dissolved in 50 μL of an alkaline lysis solution (25 mM NaOH and 0.2 mM Na2EDTA) in a 0.2 mL sterile microtube and incubated at 95 °C in a thermocycler (Maxigene II, Axygen, Corning Life Sciences, Union City, CA, USA) for one hour. Then, 50 μL of a neutralization solution (40 mM Tris-HCl) was added, and the resulting solution was stored at −20 °C.
Subsequently, a 2 μL sample of each solution was taken to carry out the amplification of the 16S ribosomal fragment, using the commercial GoTaq Green Master Mix kit (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) and the previously documented universal primers 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1429R (5′-GTTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) [36]. The PCR products were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis (1%, TAE1X, 80V), and the resulting products were purified using the Wizard SV Gel and PCR Clean-Up System commercial kit (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA).
The purified products were verified by agarose gel electrophoresis (1%, TAE1X, 80 V), quantified (GelAnalyzer v19.1), and sent for bidirectional sequencing, using the primers 27F and 1429R in each sample, to the Genomic Services Laboratory (Labsergene-Langebio, CINVESTAV, Irapuato, Mexico), following the specifications of the service provider.
The obtained sequences were visualized and manipulated using the SnapGene v8.1.1 program. The bidirectional sequences of each sample were aligned using the MAFFT program. Each alignment was exported in FASTA format and used to obtain the consensus sequence with the EMBOSS Cons program (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/jdispatcher/msa/emboss_cons?stype, accessed on 1 July 2025). The consensus sequence was then used to perform alignment with the BLAST tool (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 1 July 2025). The criteria for species validation were considered to be that the identity percentage was greater than 98% and from 95% for genus validation [37].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Physical, Chemical, and Electrical Parameters of MWW Treatment Using ML-MFC Operated at Different HRTs
3.1.1. COD
The COD removal efficiency percentage obtained in the ML-MFC was highest at the longest HRT, reaching 93.5%, and decreased to 85.4% at the shortest HRT of 12 h, representing an 8.1% decrease (Figure 2). Ullah and Ahmad (2023) [18], when investigating the performance of an MFC at different HRTs (2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h) in the treatment of domestic wastewater using two types of electrodes (a carbon fiber brush and graphite rods), detected a higher COD removal efficiency with increasing HRT and when using a carbon fiber brush as the anode material, reaching COD removal efficiencies of 80% at an HRT of 48 h and 45% at an HRT of 2 h. This directly proportional relationship between the increase in COD removal and the increase in HRT was also detected by Castellano-Hinojosa et al. (2024) [11] when using an MFC to treat wastewater from a fish-canning industry using carbon fibers as the anode at different HRTs of 1, 3, and 6 d, observing COD removal efficiencies of 18, 39, and 59%, respectively. Walter et al. (2022) [19], when operating a stratified ML-MFC and a ceramic MFC at different HRTs of 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 65 h in urine treatment, obtained COD removal efficiencies of less than 10% and greater than 50% at HRTs of 3 and 65 h, respectively, in the ML-MFC, while in the ceramic MFC, the COD removal efficiencies were less than 3% and greater than 20% at HRTs of 3 and 65 h. respectively. By using a dual-chambered membraneless microbial fuel cell with glass wool and glass beads as a replacement for a PEM in dairy wastewater treatment, Sanjay and Udayashankara (2021) [38] obtained high COD removal efficiencies of over 83% using copper and stainless steel electrodes at an HRT of 6 h. An ML-MFC fed with municipal wastewater and different proportions of yeast production wastewater (with a high COD) showed an increase in the CODRE in proportion to the increase in COD [17]. These results confirm that an ML-MFC can have a high removal efficiency for COD contained in different wastewaters.
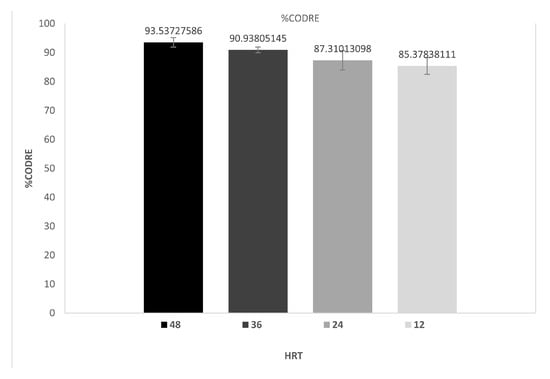
Figure 2.
Percentages of COD removal efficiency in ML-MFC at different hydraulic retention times.
3.1.2. OCV
Table 2 shows the OCV generated by the ML-MFC at different HRTs. Increasing the HRT also increased the OCV generated in the system, with the highest value of 504 mV achieved at an HRT of 48 h. Tahir et al. (2024) [14], when studying the effect of the HRT (24, 48, and 72 h) in an ML-MFC using pine wood as a container and separator (the anode and cathode) fed with sucrose, obtained the highest OCV value of 551 mV and COD removal efficiency of 48% at an HRT of 48 h. This may be attributed to the fact that a decrease in influent inflow favors the contact time between the substrate and biofilm, thereby improving the degradation of organic matter and electron transfer [39]. Also, Ye et al. (2020) [40] indicated that a low HRT promotes microbial leaching and substrate mixing conditions, which significantly reduce the cellular metabolism of the microorganisms present in the system. Likewise, Li et al. (2024) [41] mentioned that high feed flows in bioelectrochemical systems lead to the rapid leaching of organic matter, thereby decreasing its availability to electroactive microorganisms. Despite this, other studies indicate that a lower HRT increases the current, power density, and overall performance of SBEs [11,42], which suggests that the optimal HRT seems to depend on other factors, such as (i) the specific configuration of the system, (ii) the type of substrate, and (iii) the microbial community present, among others.

Table 2.
Effect of HRT on OCV in a pilot-scale microbial fuel cell.
3.1.3. pH, ORP, and EC
The average pH of the MWW was 8.57 after treatment with the ML-MFC at the different HRTs operated. It was observed that by decreasing the HRT, the pH increased slightly but maintained an alkaline pH of higher than 8 units (Table 3). Among the factors that can significantly affect the performance of an MFC is the pH. Tremouli et al. (2017) [43] investigated the behavior of an MFC when operated in batch mode with a synthetic glucose solution at various pH levels, ranging from 6 to 9. They observed that the pH of the effluent tended to increase when the pH was acidic and decrease when the pH was basic. Specifically, the pH rose from 6 to 6.3 and decreased from 9 to 7.7, indicating a tendency toward neutrality. The average ORP of the MWW was −239 mV, and after treatment with the ML-MFC, it was determined that the increase in the HRT increased the ORP (from −69.33 mV at 12 h to 22.5 mV at 48 h). It is known that this parameter is related to microbiological processes and also indicates the quality of the water. A high ORP (650 mV or higher) indicates water free of pathogenic microorganisms [44,45]. The average EC detected in the MWW was 1794 μS/cm, and the increase in the HRT decreased the EC concentration (from 1831 μS/cm at 12 h to 1442.33 μS/cm at 48 h). In the treatment of synthetic wastewater using a bioreactor and electro-bioreactor at different HRTs (from 6 to 75 h), it was detected that the EC decreased to a greater extent in the electro-bioreactor at all the HRTs tested, although no correlation was observed with the increase in the HRT [46], while Rehman et al. (2020) [47] studied the effect of the HRT (24, 48, and 72 h) in the treatment of domestic wastewater using a trickling filter (TF) system consisting of a primary sedimentation tank and a TF with stone as the filter material, obtaining, as a result, a greater decrease of between 14 and 39% of the EC at an HRT of 48 h. In this study, an average decrease percentage of 19.6% was obtained at the same HRT.

Table 3.
Physical and chemical parameters measured daily during the experiment at different HRTs.
3.1.4. Physical Parameters
Table 4 presents the results regarding the presence of solids (TSSs, TDSs, and TSs). Their removal was dependent on the increase in the HRT. The removal of TSSs at different HRTs was detected to be above 80%, with 83% removal at 12 h and 88% at 48 h. In contrast, the removal of TDSs was more dependent on the increase in the HRT, with 54.55% removal at 12 h and 87.37% removal at 48 h. Sanjay and Udayashankara (2021) [38] detected a high removal (76.3%) of TDSs at an HRT of 6 h in the treatment of wastewater from the dairy industry using an ML-MFC. Rehman et al. (2020) [47] detected 22, 39, and 58% TDS removal efficiencies at HRTs of 24, 48, and 72 h in a TF when treating domestic wastewater, which was attributed to the increase in the HRT that allowed the biofilm microorganisms (which, in this case, were found on the electrodes) to have sufficient contact to remove dissolved organic compounds in the wastewater. MFCs can also remove high concentrations of dissolved solids, such as those found in distillery spentwash wastewater, which are typically around 60,000 mg/L [48].

Table 4.
Physical parameters measured at the beginning and end of each HRT.
3.1.5. Chemical Parameters
The TN represents the sum of all types of nitrogen measured in this research (nitrates, nitrites, ammonia, and organic nitrogen). As shown in Table 5, nitrogen removal was dependent on the increase in the HRT, with 31% being removed at 12 h and 87% at 48 h. Ghangrekar and Shinde (2007) [49] studied the performance of an ML-MFC with glass beads and glass wool replacing the PEM, which was fed synthetic wastewater containing different carbon sources, including sucrose, lactose, and dextrose, as well as nitrogen in the form of ammonium at higher concentrations and nitrate at lower concentrations. It showed a nitrogen removal efficiency of 46% at an HRT of 49.8 h. Table 1 presents the composition of the MWW and shows that the highest concentration of nitrogen forms belonged to ammonia, which represented approximately 68% of the TN, followed by NO, which represented 27%, and the remainder was composed of nitrate and nitrite. It can be seen that nitrite increased as a byproduct of the nitrification reaction carried out at the cathode; this was subsequently oxidized to nitrate (Table 5), as evidenced by the increasing values of this ion with increasing HRT, indicating that there was more time for the intermediate compounds to be oxidized. Ghangrekar and Shinde (2007) [49] detected minimal nitrogen removal at the anode; therefore, the highest nitrogen removal occurred at the cathode, which could be attributed to ammonia-stripping, nitrification, and denitrification processes, and, to a lesser extent, to nitrogen assimilation (biosynthesis), in addition to the fact that the anode did not have the expected anoxic conditions due to the displacement of oxygen from the cathode to the anode due to the lack of a PEM. Similar to this research, where the HRT affected nitrogen removal, Rehman et al. (2020) [47] detected 11, 24, and 67% TN removal efficiencies at HRTs of 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively, in a TF when treating domestic wastewater. Castellano-Hinojosa et al. (2024) [11] investigated the effect of the HRT (1, 3, and 6 d) on the treatment of fish-canning industry wastewater using an MFC and found no statistically significant difference in the percentage of nitrogen removal. The MWW used in this research contained a low phosphorus concentration of approximately 4 mg/L. Removal rates greater than 70% were detected across different HRTs, with the rate increasing as the HRT increased, reaching 78.7% at 48 h. Rehman et al. (2020) [47] studied the removal of phosphates from domestic wastewater that contained a similar concentration of phosphates and, like in this research, the increase in the HRT increased the removal, detecting 44, 41, and 82% phosphate removal percentages at HRTs of 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. Another of the chemical parameters measured in this research was the F&O concentration. The MWW contained, on average, 123 mg/L, which decreased as the HRT increased, removing up to 75.6% in 48 h. Valladares-Linares et al. (2019) [50] operated a system for the treatment of domestic wastewater, consisting of a septic tank as the primary treatment (with an HRT of 2 d), an 18-MFC stack system (with an HRT of 3.3 d) (AQUOX®-MFCSS) as the secondary treatment, and calcium hypochlorite as the tertiary treatment. They detected F&O removal percentages of 19, 90, and 93%, respectively, when passing through each of these phases, where a higher removal of 70% was determined in the MFC. Saatci et al. (2003) [51] studied the removal of total lipids and fatty acids from the wastewater of a sunflower oil production industry using an upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor, finding a high removal (above 70%) of these parameters at HRTs of 2 and 2.8 d.

Table 5.
Chemical parameters measured at beginning and end of each HRT.
3.1.6. Microbiological Parameters
The results of the BODRE (Table 6) percentages were very similar to those obtained in the COD, showing a positive effect on removal in proportion to the increase in the HRT. Specifically, values of 85.5% and 94.54% of BODRE were detected at HRTs of 12 and 48 h, respectively. Sanjay and Udayashankara (2021) [38] obtained an average BODRE of 86% at an HRT of 6 h in the treatment of wastewater from the dairy industry using an ML-MFC. Ghangrekar and Shinde (2007) [49], when studying an ML-MFC fed with synthetic wastewater, presented a BODRE of 87% at an HRT of 49.8 h. The FC concentration decreased substantially at all HRTs. The MWW contained, on average, 1 × 1022 MPN/100 mL; this concentration decreased to 99.99 at all HRTs. At 12 h, the ML-MFC influent contained 1 × 1010 MPN/100 mL, while at 48 h, the influent contained 1 × 105 MPN/100 mL (Table 6). In a system for treating domestic wastewater, which included a septic tank, followed by an MFC stack system, and finally, calcium hypochlorite, an HRT of 5 d was operated, achieving 75, 78, and 100% FC removal percentages, respectively. Notably, the septic tank was responsible for the highest removal [50]. In addition to the high concentration of FCs in the MWW, a very high average concentration of HEs of 6458 H/L was detected (Table 6), which was reduced by 26 and 64%, respectively, at HRTs of 12 and 48 h, so the increase in the HRT positively influenced the removal. Liu et al. (2024) [52] studied the removal of fecal coliforms (E. coli) and the removal and inactivation of Ascaris lumbricoides eggs in livestock and poultry manure slurry in an ML-MFC at an HRT of 24 h, obtaining a maximum removal of E. coli of 11.7% and an egg mortality rate of A. lumbricoides of 21.5%.

Table 6.
Microbiological parameters measured at beginning and end of each HRT.
3.1.7. Microorganisms Present on ML-MFC Anode
The microorganisms detected on the anode of the ML-MFC used in this research were A. denitrificans, A. anxifer, and P. aeruginosa. When studying single-chambered air-cathode MFCs operated in batch mode at a temperature of 25 °C with anodes of different compositions (a soybean–potato composite plant powder modified with graphene oxide, polyaniline, and carbon nanotubes) inoculated with activated sludge for biofilm formation, it was found that the anode modified with PANI had a higher relative abundance. Within the ten most recurrent genera within the biofilms of the studied anodes, Pseudomonas and Achromobacter coincided, as in this investigation, as well as Enterobacter, Lactobacillus, Clostridium, Paenibacillus, Stenotrophomonas, Trabulsiella, and Bacillus. Among Pseudomonas, Geobacter, and Shewanella, which are the most common electrogenic microorganisms found in bioelectrochemical systems, Pseudomonas and Geobacter were isolated when the substrate was MWW, as in this investigation [53]. In the removal of Cd and Ni using an MFC inoculated with wetland sediment, the fermenting genus Achromobacter was predominant within the anode biofilm [54]. In the decolorization of azo dyes through five different single-chambered air-cathode MFCs, Achromobacter and Pseudomonas were some of the genera found in the cathode biofilm (composed of graphite carbon cloth and inoculated with activated sludge from a treatment plant of a bakery yeast production company), although the percentage of abundance was higher for Achromobacter. Achromobacter and Pseudomonas were not present in the inoculum, but in the biofilm that formed on the cathode [55]. Achromobacter is a genus capable of biodegrading aromatic or halogenated compounds [55] and industrial thermoplastics, such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride [56]. A. denitrificans and other species of this genus (Achromobacter sp. GAD-3) can perform aerobic denitrification [57]. It is mentioned that some species of Achromobacter and Pseudomonas have the ability to perform oxygen-tolerant aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic nitrification [58].
4. Conclusions
The hydraulic retention time played a very important role in the performance of the ML-MFC, as it influenced the removal of all chemical parameters, such as COD, N, P, and F&Os; physical parameters, such as EC and solids; and microbiological parameters, such as BOD, FCs, and HEs, as well as open-circuit voltage generation. Overall, operating the ML-MFC for an HRT of 48 h provided a longer contact time between the substrate and the microbial biofilm, enhancing biological oxidation, open-circuit voltage generation, and contaminant degradation processes, ultimately resulting in improved effluent quality.
The ML-MFC represents a less expensive alternative to an MFC that requires a PEM, although materials that replace PEMs require further study to prevent air diffusion, especially if the intended removal requires microbial reactions carried out under strictly anaerobic conditions. In this study, the microorganisms found in the anode biofilm were aerobic bacteria. The dominant microbial community identified on the anode consisted of A. denitrificans, A. anxifer, and P. aeruginosa, indicating aerobic conditions within the anode, likely due to the absence of a selective physical barrier between the anode and cathode.
Given the intrinsic variability in the composition of municipal wastewater—resulting from mixed domestic and commercial sources—future long-term studies under dynamic and realistic conditions are recommended to better assess the operational stability, reproducibility, and overall treatment efficiency of ML-MFC systems.
Despite the promising results obtained in terms of contaminant removal efficiency and electricity generation, the ML-MFC system presents several operational limitations that must be considered for its future scaling and implementation. Firstly, the absence of a PEM, while reducing costs and simplifying the reactor design, compromises the establishment of strictly anaerobic conditions in the anode. Secondly, another important limitation is the system’s dependence on the HRT. Although extended HRTs (48 h) favor contaminant removal and biofilm development, they also require larger reactor volumes or lower treatment flow rates, which may restrict economic and technical feasibility in large-scale applications or in contexts requiring high-throughput wastewater treatment. Lastly, the variability in the composition of municipal wastewater may affect the stability of operational parameters (e.g., pH, EC, and ORP) and the microbial selectivity toward electroactive species. This variability could compromise system efficiency if not mitigated by appropriate buffering mechanisms or pretreatment strategies. Taken together, these limitations do not negate the potential of ML-MFC technology but highlight the need for further studies focused on optimizing system design, material selection, and long-term performance evaluation under dynamic and realistic operating conditions, to bring this technology closer to practical application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Y.M.-A. and J.A.R.-D.l.G.; methodology, J.A.R.-D.l.G., S.Y.M.-A., B.V.B.-L., P.P.-R., A.V.R.-A., L.J.R.-G. and M.Á.P.-R.; validation, A.V.R.-A., L.J.R.-G. and P.P.-R.; investigation, S.Y.M.-A. and J.A.R.-D.l.G.; resources, S.Y.M.-A., A.V.R.-A., P.P.-R., M.Á.P.-R. and J.A.R.-D.l.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.A.R.-D.l.G., S.Y.M.-A., B.V.B.-L., P.P.-R. and M.Á.P.-R.; writing—review and editing, J.A.R.-D.l.G., S.Y.M.-A. and J.A.R.-D.l.G.; visualization, S.Y.M.-A.; supervision, B.V.B.-L. and S.Y.M.-A.; project administration, B.V.B.-L. and L.J.R.-G.; funding acquisition, S.Y.M.-A. and J.A.R.-D.l.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Universidad Autónoma Agraria Antonio Narro through research project 2234 and by the Secretariat of Science, Humanities, Technology, and Innovation (SECIHTI), which awarded the BVB-L master’s scholarship.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| BOD | Biochemical oxygen demand |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| EAB | Electrochemically active bacteria |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| F&Os | Fats and oils |
| FCs | Fecal coliforms |
| HEs | Helminth eggs |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| ML-MFC | Membraneless microbial fuel cell |
| MWW | Municipal wastewater |
| OCV | Open-circuit voltage |
| ON | Organic nitrogen |
| ORP | Oxidation reduction potential |
| P | Phosphorus |
| PEM | Proton-exchange membrane |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| TDSs | Total dissolved solids |
| TF | Trickling filter |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TSSs | Total suspended solids |
References
- Thung, W.E.; Ong, S.A.; Ho, L.N.; Wong, Y.S.; Ridwan, F.; Oon, Y.L.; Oon, S.Y.; Lehl, H.K. Sustainable green technology on wastewater treatment: The evaluation of enhanced single chambered up-flow membrane-less microbial fuel cell. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 66, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suransh, J.; Jadhav, D.A.; Nguyen, D.D.; Mungray, A.K. Scalable architecture of low-cost household microbial fuel cell for domestic wastewater treatment and simultaneous energy recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo-Escobar, L.M.; Cabrera, S.E. Microorganisms and microbial communities in bioelectrochemical systems for wastewater bioremediation and energy generation. In Water Purification-Present and Future; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, M.; Kiros, Y.; Farooq, R.; Lindström, R.W. Low-cost single chamber MFC integrated with novel lignin-based carbon fiber felt bioanode for treatment of recalcitrant azo dye. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 672817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, B.; He, Y. Microbial electro-Fenton: An emerging and energy-efficient platform for environmental remediation. J. Power Sources 2019, 424, 220–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsena, M.T.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Advances in microbial fuel cell technology for zero carbon emission energy generation from waste. In Biofuels and Bioenergy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 321–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.E.; Hemdan, B.A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; El-Liethy, M.A.; Jadhav, D.A.; El-Hendawy, H.H.; Ali, M.; El-Taweel, G.E. Harnessing the power of microbial fuel cells as pioneering green technology: Advancing sustainable energy and wastewater treatment through innovative nanotechnology. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2025, 48, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gelel, I.Y.; Abdel-Mongy, M.; Hamza, H.A.; Abbas, R.N.; Abdelgelel, I.Y. Bioelectricity production from different types of bacteria using MFC under optimizing factors and new bacterial strain bioelectricity production isolated from milk sample in Egypt. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 20377–20391. [Google Scholar]
- Jenani, R.; Karishmaa, M.; Babu-Ponnusami, A.; Senthil-Kumar, P.; Rangasamy, G. A recent development of low-cost membranes for microbial fuel cell applications. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, P.; Ala, A.; Nazari, P.; Jalili, B.; Ganji, D.D. A comprehensive review of microbial fuel cells considering materials, methods, structures, and microorganisms. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; Gallardo-Altamirano, M.J.; Pozo, C.; González-Martínez, A.; González-López, J. Hydraulic retention time drives changes in energy production and the anodic microbiome of a microbial fuel cell (MFC). J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.; Haghighi, M.; Behvand Usefi, M.M.; Ghasemi, M. Overview of Sustainable Water Treatment Using Microbial Fuel Cells and Microbial Desalination Cells. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Nava, J.; Martínez-Castrejón, M.; García-Mesino, R.L.; López-Díaz, J.A.; Talavera-Mendoza, O.; Sarmiento-Villagrana, A.; Rojano, F.; Hernández-Flores, G. The implications of membranes used as separators in microbial fuel cells. Membranes 2021, 11, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, C.A.; Agarwal, C.; Pásztory, Z.; Csóka, L. A novel membrane-less microbial fuel cell reactor using wood as container and separator to prevent air–cathode deterioration and biofouling. Discov. Water 2024, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Wallis, L.; Radisavljevic, N.; Pasternak, G.; Sglavo, V.M.; Hanczyc, M.M.; Greenman, J.; Ieropoulos, I. A comprehensive study of custom-made ceramic separators for microbial fuel cells: Towards “living” bricks. Energies 2019, 12, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk, B.; Włodarczyk, P.P. The membrane-less microbial fuel cell (ML-MFC) with Ni-Co and Cu-B cathode powered by the process wastewater from yeast production. Energies 2020, 13, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk, B.; Włodarczyk, P. Feeding a membrane-less microbial fuel cell by mixed municipal and industrial wastewater. Civ. Environ. Eng. Rep. 2023, 33, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Ahmad, I. Effect of hydraulic retention time and electrode type on the performance of semi-continuous flow microbial fuel cell. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, X.A.; Madrid, E.; Gajda, I.; Greenman, J.; Ieropoulos, I. Microbial fuel cell scale-up options: Performance evaluation of membrane (c-MFC) and membrane-less (s-MFC) systems under different feeding regimes. J. Power Sources 2022, 520, 230875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-030/2-SCFI-2011. Análisis de Agua—Determinación de la Demanda Química de Oxígeno en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba—Parte 2—Determinación del Índice de la Demanda Química de Oxígeno—Método de Tubo Sellado a Pequeña Escala. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166775/NMX-AA-030-2-SCFI-2011.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Tabish, A.N.; Farhat, I.; Irshad, M.; Hussain, M.A.; Usman, M.; Chaudhary, T.N.; Fouad, Y.; Raza, S.; Ashraf, W.M.; Krzywanski, J. Electrochemical Insight into the Use of Microbial Fuel Cells for Bioelectricity Generation and Wastewater Treatment. Energies 2023, 16, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2018. Análisis de Agua—Medición del pH en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166767/NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2016.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Oxidation-Reduction Potential of Water (ASTM D1498-14). ASTM International. 2014. Available online: https://www.astm.org/D1498-14.html (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-093-SCFI-2000. Análisis de Agua—Determinación de la Conductividad Electrolítica—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166800/NMX-AA-093-SCFI-2000.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-034-SCFI-2015. Análisis de Agua—Medición de Sólidos y Sales Disueltas en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166146/nmx-aa-034-scfi-2015.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-005-SCFI-2013. Análisis de Agua—Medición de Grasas y Aceites Recuperables en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166764/nmx-aa-005-scfi-2013.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-029-SCFI-2001. Análisis de Aguas—Determinación de Fósforo Total en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166773/NMX-AA-029-SCFI-2001.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Santos, A.C.O.; Matoso, E. Validation of Nitrogen-Nitrate Analysis by the Chromotropic Acid Method; No. INIS-BR--19677; Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear (ABEN): Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 2017; Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/records/vgq4c-ekk44 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-099-SCFI-2006. Análisis de Agua—Determinación de Nitrógeno de Nitritos en Aguas Naturales y Residuales—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://biblioteca.semarnat.gob.mx/janium/Documentos/Ciga/agenda/PPD1/DO3046.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-026-SCFI-2010. Análisis de Agua—Medición de Nitrógeno Total Kjeldahl en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166772/NMX-AA-026-SCFI-2010.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-028-SCFI-2021. Análisis de Agua—Medición de Demanda Bioquímica de Oxígeno (DBO5) en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Dilución y Método de Siembra—Método de Prueba. Available online: http://www.economia-nmx.gob.mx/normas/nmx/2001/nmx-aa-028-scfi-2001.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-012-SCFI-2001. Análisis de Agua—Determinación de Oxígeno Disuelto en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas—Método de Prueba. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166768/NMX-AA-012-SCFI-2001.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Norma Mexicana. NMX-AA-042-SCFI-2015. Análisis de Agua—Enumeración de Organismos Coliformes Totales, Organismos Coliformes Fecales (Termotolerantes) y Escherichia coli—Método del Número Más Probable en Tubos Múltiples. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166147/nmx-aa-042-scfi-2015.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Ayres, R.M.; Mara, D.D. Análisis de Aguas Residuales para Su Uso en Agricultura: Manual de Técnicas Parasitológicas y Bacteriológicas de Laboratorio; Organización Mundial de la Salud: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/41996 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Truett, G.E.; Heeger, P.; Mynatt, R.L.; Truett, A.A.; Walker, J.A.; Warman, M.L. Preparation of PCR-quality mouse genomic DNA with hot sodium hydroxide and tris (HotSHOT). Biotechniques 2000, 29, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H.; Whitman, W.B.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, S.; Udayashankara, T.H. Dairy wastewater treatment with bio-electricity generation using dual chambered membrane-less microbial fuel cell. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 35, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli, N.; Mutamim, N.S.A.; Jafri, N.M.A.; Ramli, N.A.M. Microbial fuel cell (MFC) in treating spent caustic wastewater: Varies in hydraulic retention time (HRT) and mixed liquor suspended solid (MLSS). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4339–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Zhang, X.; Luo, G.; Liu, Y. Impacts of hydraulic retention time on a continuous flow mode dual-chamber microbial fuel cell for recovering nutrients from municipal wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, P.; Yan, J.; Chen, M.; You, S.; Bai, J.; You, G.; Ullah, H.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Effects of hydraulic retention time on removal of Cr (VI) and p-chlorophenol and electricity generation in L. hexandra-planted constructed wetland–microbial fuel cell. Molecules 2024, 29, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akman, D.; Cirik, K.; Ozdemir, S.; Ozkaya, B.; Cinar, O. Bioelectricity generation in continuously-fed microbial fuel cell: Effects of anode electrode material and hydraulic retention time. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremouli, A.; Martinos, M.; Lyberatos, G. The effects of salinity, pH and temperature on the performance of a microbial fuel cell. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.Y.; Lee, C.C.; Jian, Z.R.; Chen, J.C.; Lin, C.H. The potential of using microbial fuel cells as a “quality” monitor for ornamental seawater aquarium. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 9, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslow, T.V. Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) for Water Disinfection Monitoring, Control, and Documentation; University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources (UC ANR): Davis, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElNaker, N.A.; Yousef, A.F.; Hasan, S.W. Effect of hydraulic retention time on microbial community structure in wastewater treatment electro-bioreactors. MicrobiologyOpen 2018, 7, e00590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Ayub, N.; Naz, I.; Perveen, I.; Ahmed, S. Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) on the performance of a pilot-scale trickling filter system treating low-strength domestic wastewater. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, S.; Pradeep, N.V.; Hampannavar, U.S. Anaerobic followed by aerobic treatment approaches for Spentwash using MFC and RBC. Sugar Tech 2013, 15, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghangrekar, M.M.; Shinde, V.B. Performance of membrane-less microbial fuel cell treating wastewater and effect of electrode distance and area on electricity production. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2879–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares-Linares, R.; Domínguez-Maldonado, J.; Rodríguez-Leal, E.; Patrón, G.; Castillo-Hernández, A.; Miranda, A.; Romero, D.D.; Moreno-Cervera, R.; Camara-Chale, G.; Borroto, C.G.; et al. Scale up of Microbial Fuel Cell Stack System for Residential Wastewater Treatment in Continuous Mode Operation. Water 2019, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatci, Y.; Arslan, E.I.; Konar, V. Removal of total lipids and fatty acids from sunflower oil factory effluent by UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Chen, D.; Mahmood, A.; Yang, S.J. Study on the synergistic effect of microbial fuel cell on the treatment of livestock and poultry manure slurry. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2024, 22, 3797–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdan, B.A.; El-Taweel, G.E.; Naha, S.; Goswami, P. Bacterial community structure of electrogenic biofilm developed on modified graphite anode in microbial fuel cell. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kaushik, A. Removal of Cd and Ni with enhanced energy generation using biocathode microbial fuel cell: Insights from molecular characterization of biofilm communities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 127940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumru, M.; Eren, H.; Catal, T.; Bermek, H.; Akarsubaşı, A.T. Study of azo dye decolorization and determination of cathode microorganism profile in air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, M.M.; Moghimi, H.; Azin, E. Biodegradation of thermo-oxidative pretreated low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) microplastics by Achromobacter denitrificans Ebl13. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Effect of NaCl on aerobic denitrification by strain Achromobacter sp. GAD-3. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5139–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathiravan, V.; Krishnani, K.K. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Achromobacter sp.: Nitrifying aerobic denitrifiers have a plasmid encoding for denitrifying functional genes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).