Investigation into the Dynamic Evolution Characteristics of Gear Injection Lubrication Based on the CFD-VOF Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model of the Gear Reducer
2.1. Continuity and Momentum Equations for Oil–Air Multiphase Flow
2.2. VOF-Based Interface Tracking for Oil–Air Interaction
2.3. Dynamic Mesh Technique for Gear Rotation Modeling
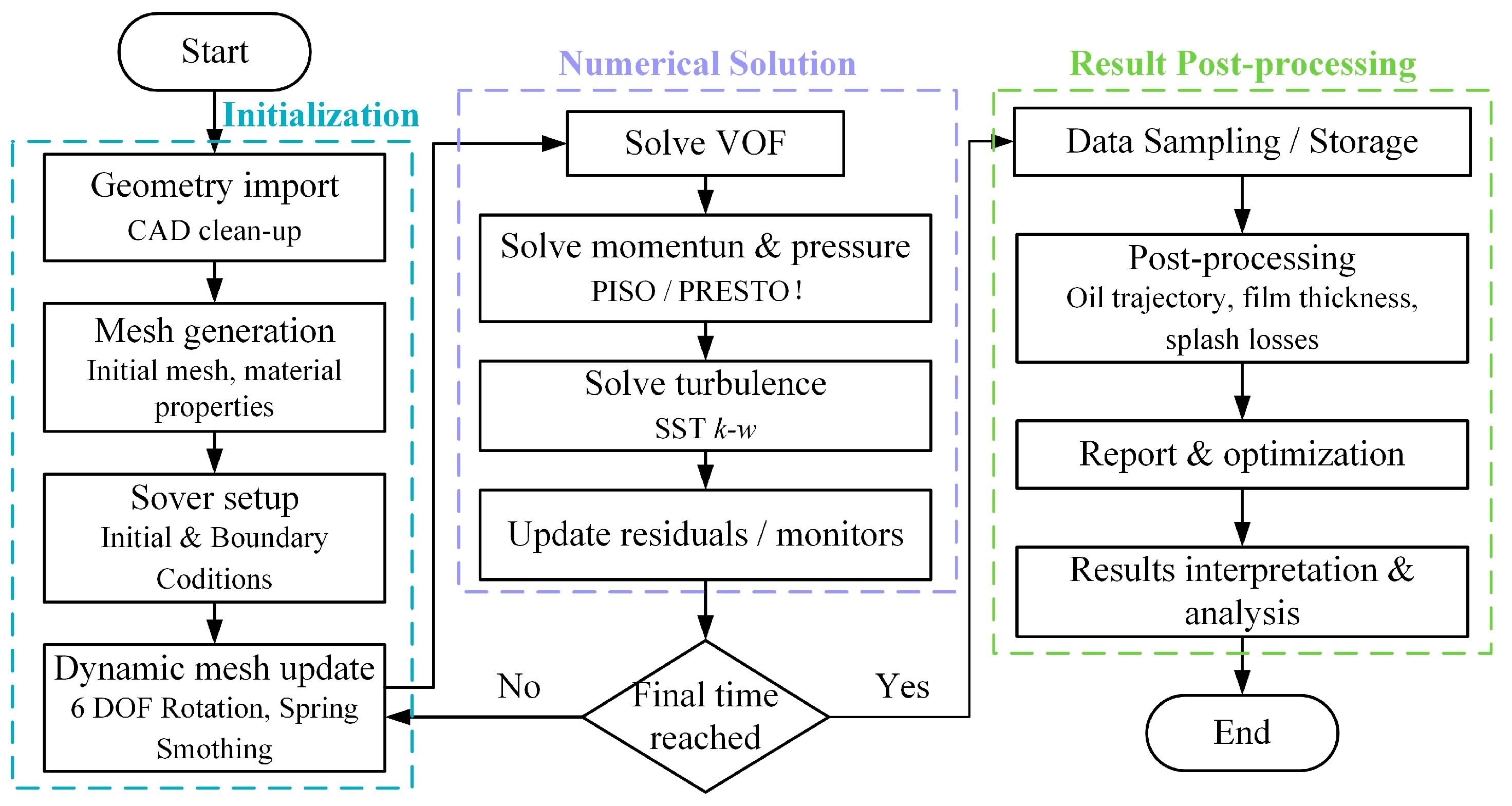
2.4. Integrated CFD Workflow and Numerical Implementation
3. Gearbox Numerical Model
3.1. Geometry and Computational Domain
3.2. Initial and Boundary Conditions
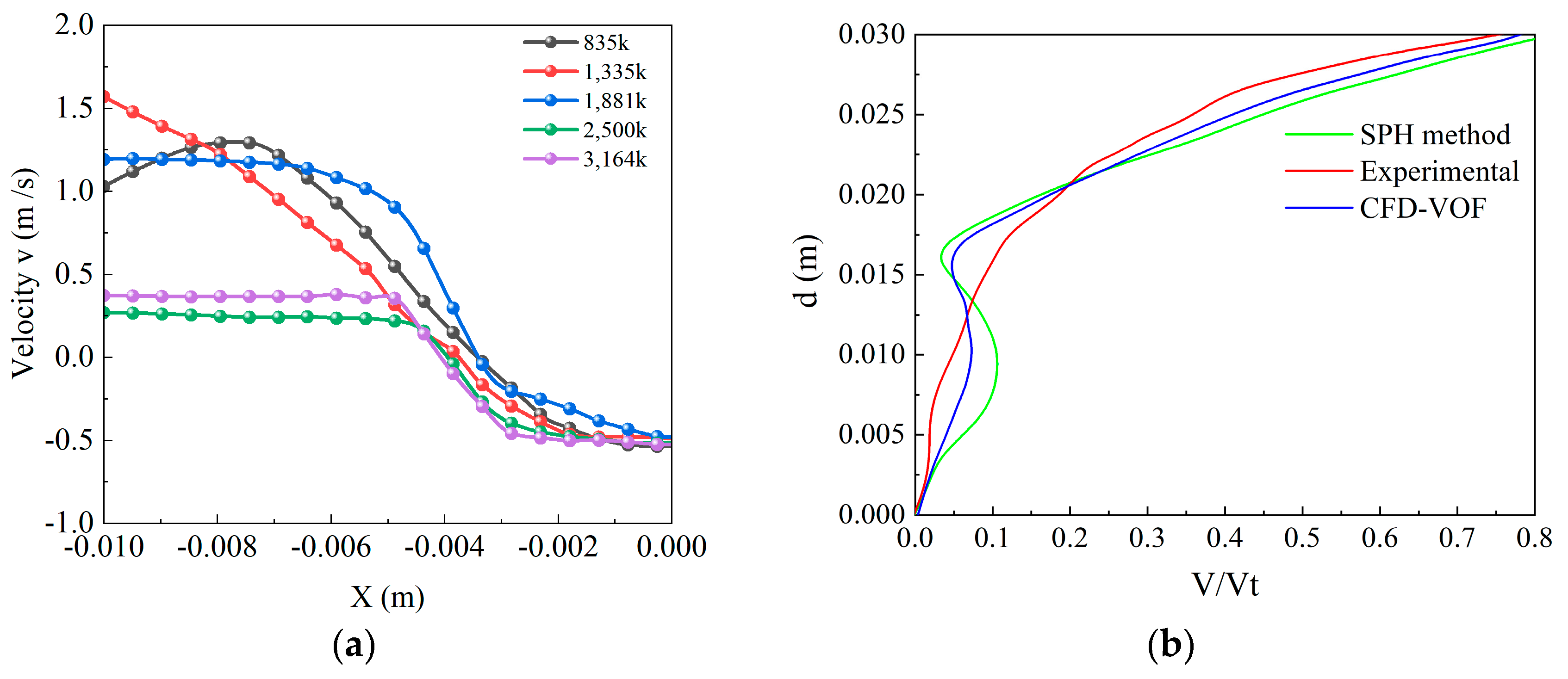
3.3. Independence and Accuracy Verification
4. Numerical Results and Discussion
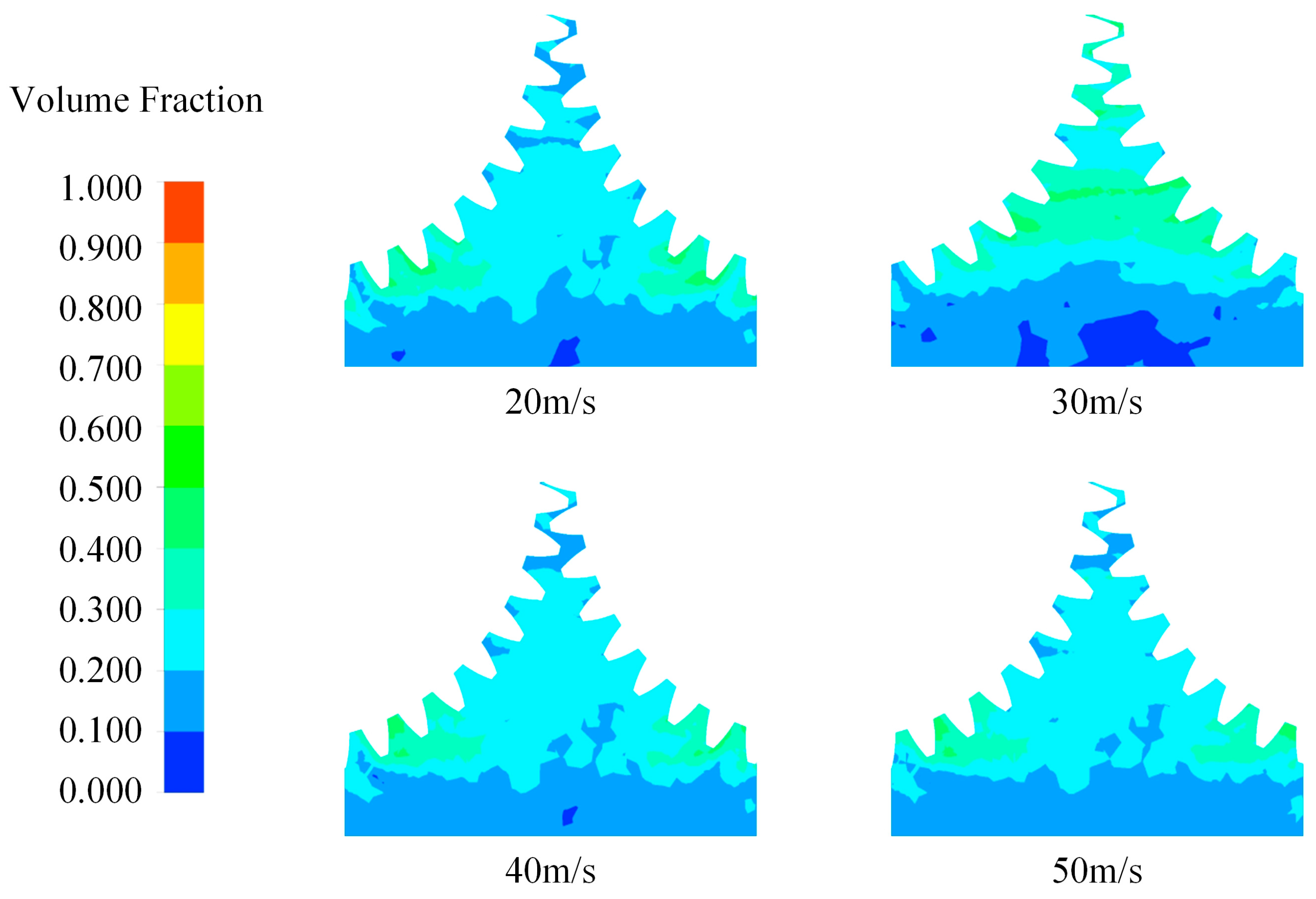
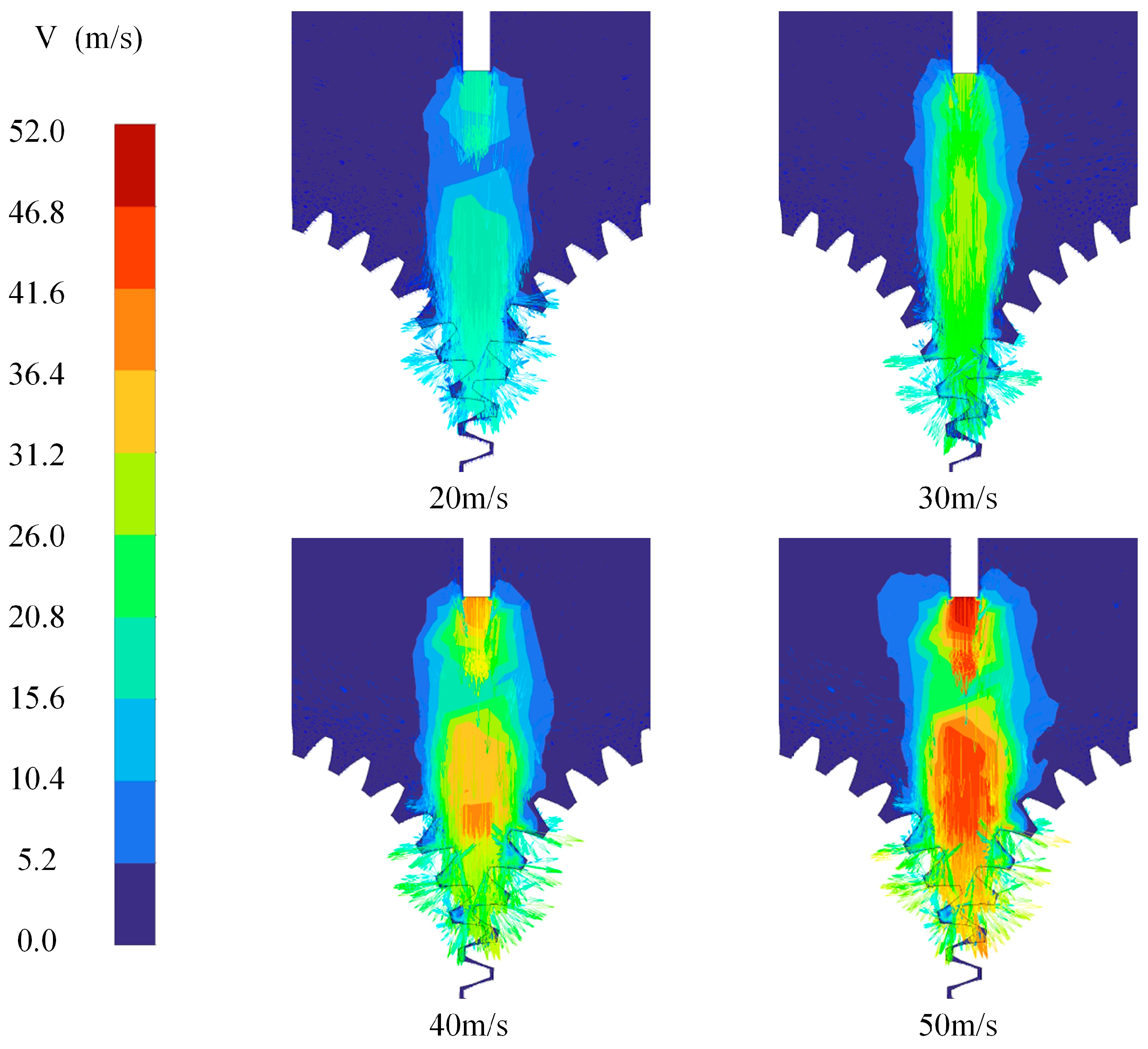
4.1. Influence of Injection Velocity on Tooth-Surface Lubrication
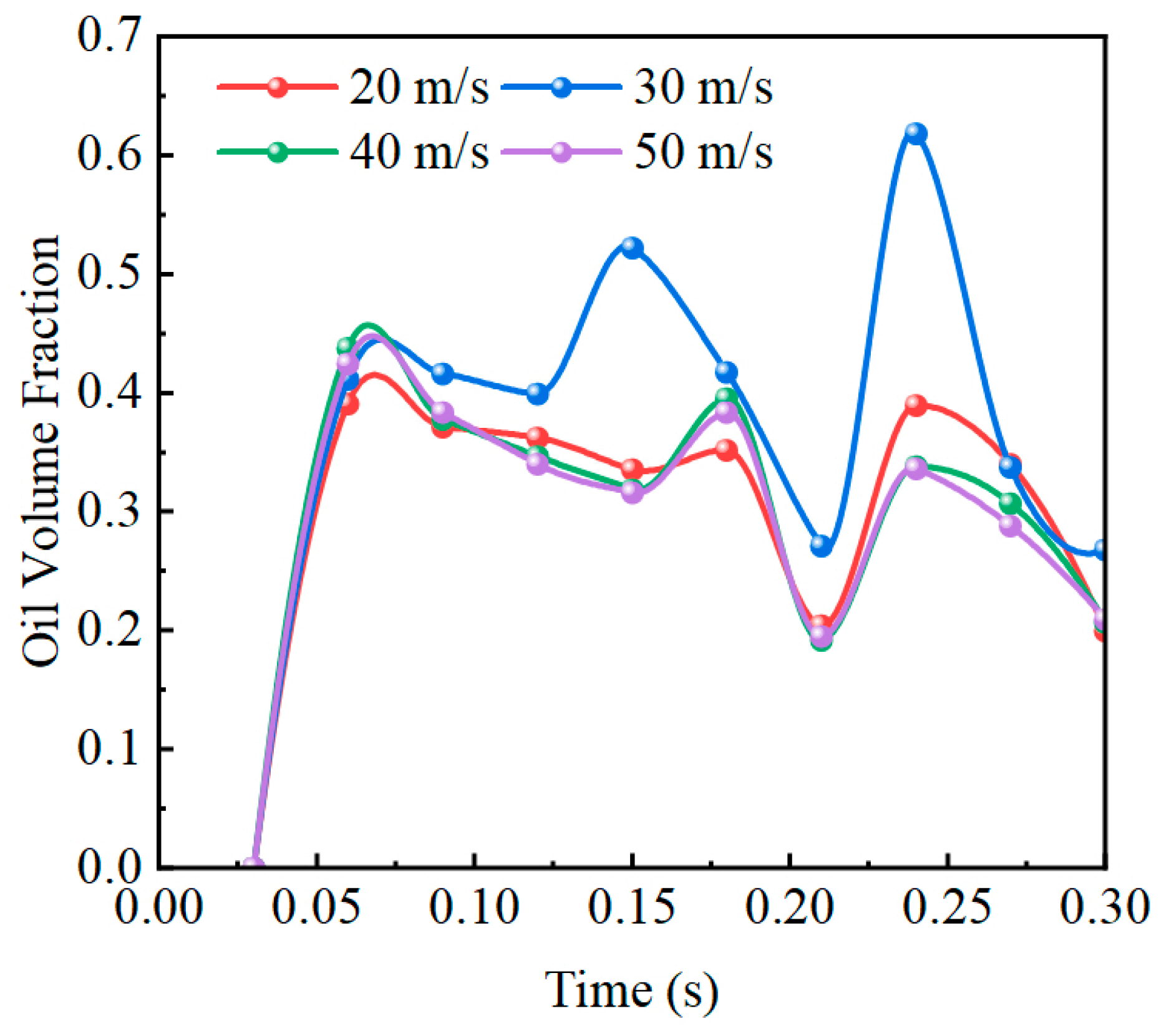
4.2. Influence of Injection Velocity on Oil-Phase Volume Fraction
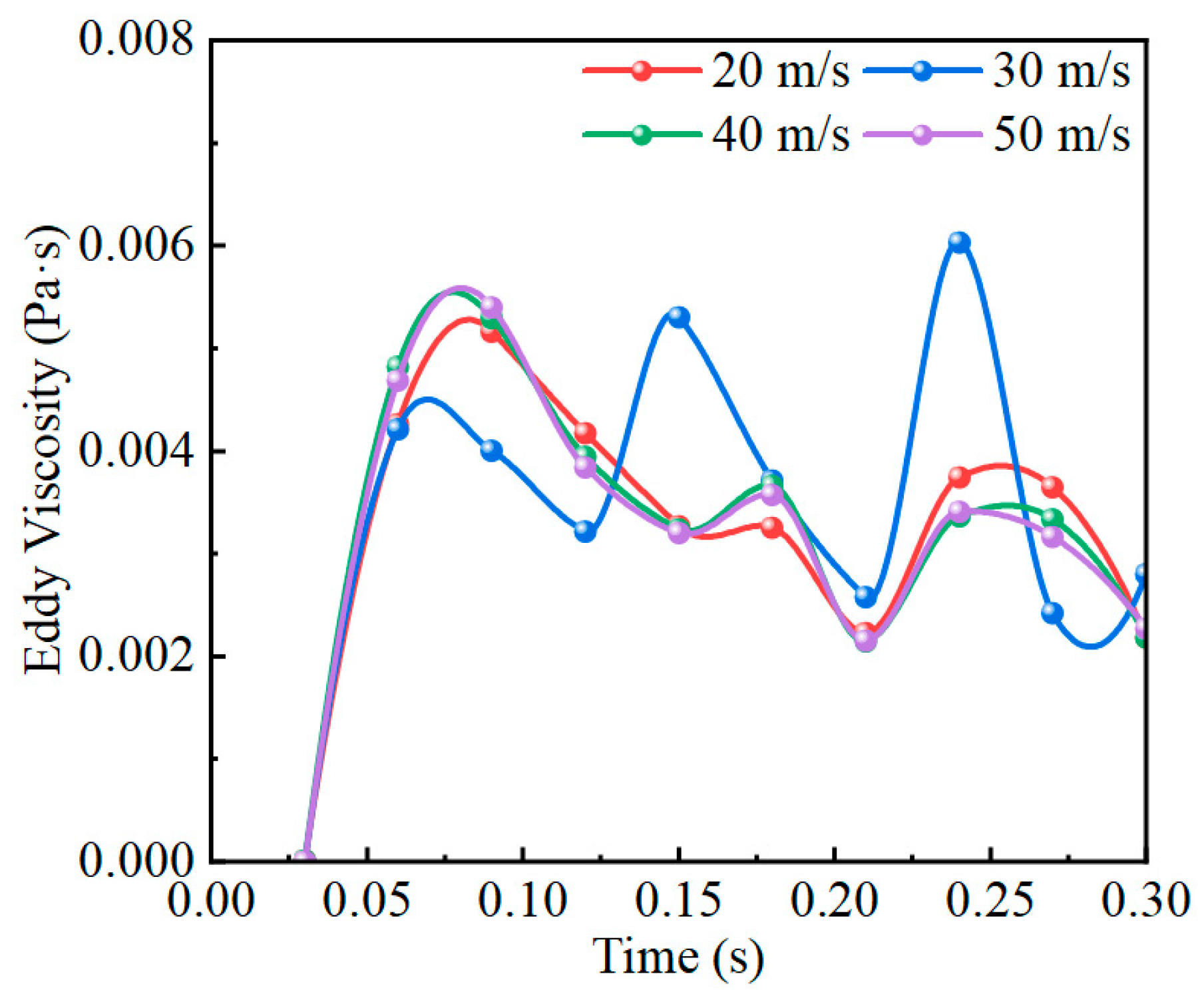
4.3. Influence of Injection Velocity on Oil-Phase Viscosity
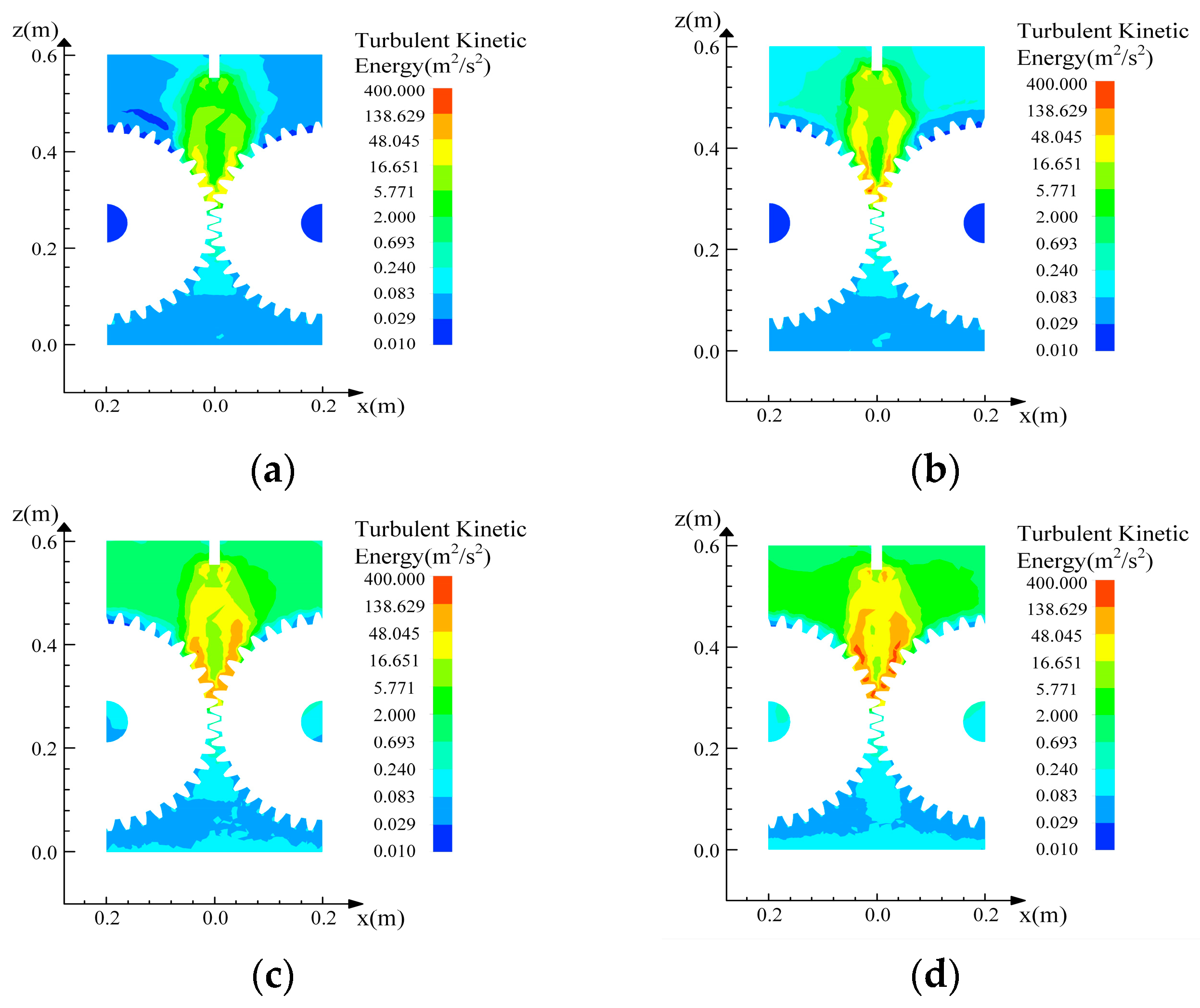
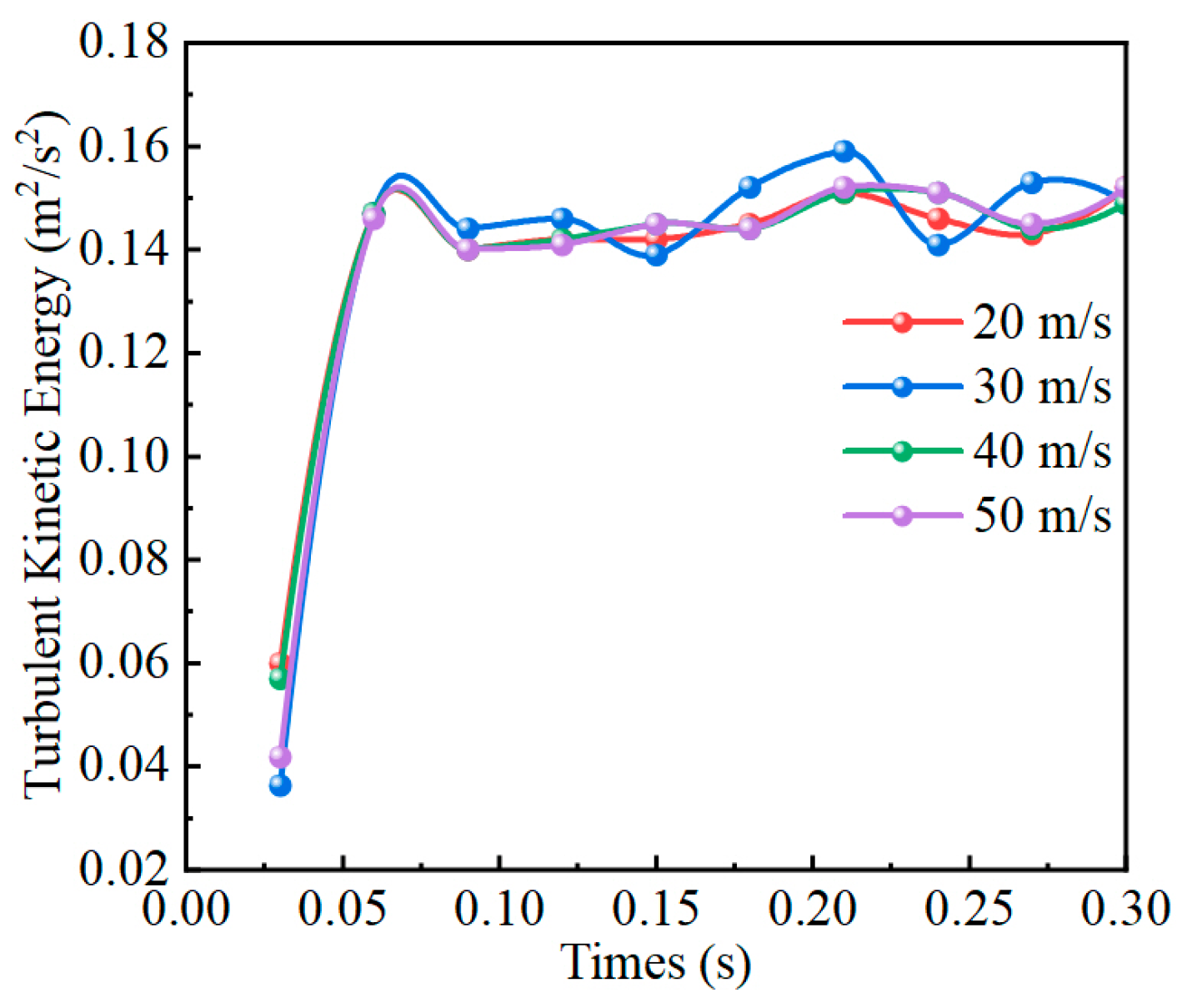
4.4. Influence of Injection Velocity on Turbulent Kinetic Energy
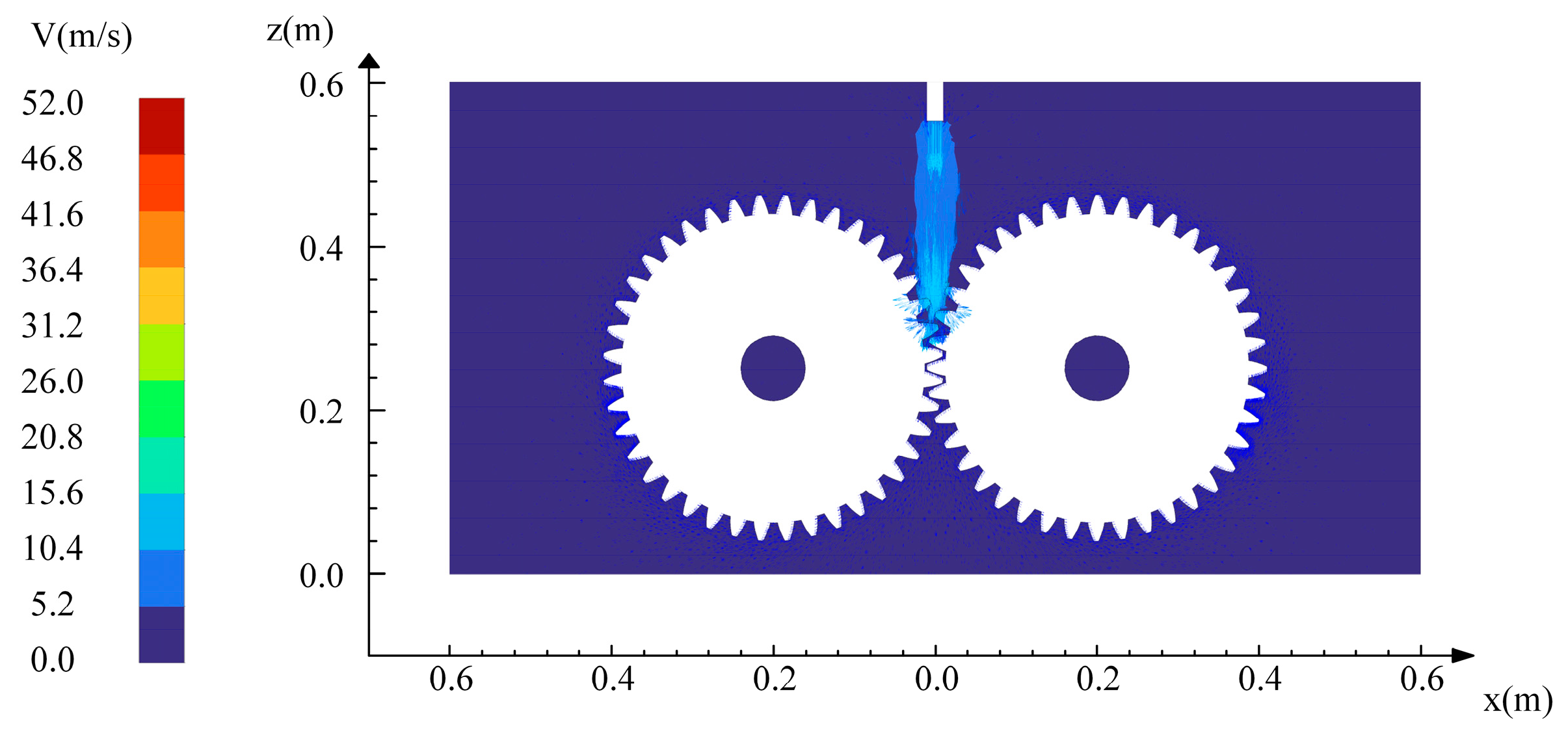
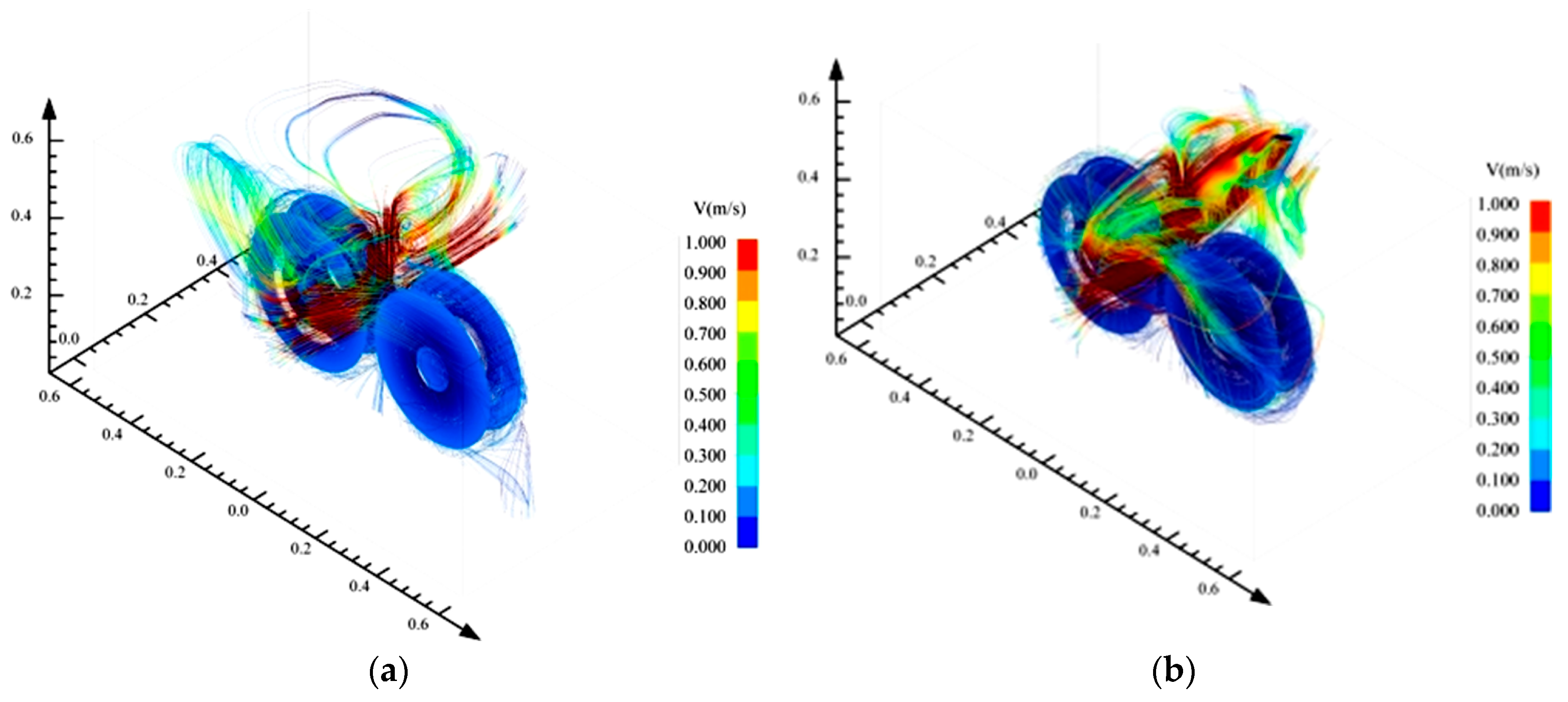
4.5. Influence of Injection Velocity on Oil Velocity
5. Conclusions
- A transient multiphase flow model of gear lubrication is established based on the CFD-VOF coupled approach. Combined with dynamic mesh and adaptive refinement technologies, the model accurately captures key physical phenomena, including oil film formation, jet impingement, turbulent interactions, and phase interface evolution, thereby revealing the dynamic coupling mechanisms of lubricant transport at varying injection velocities.
- With increasing injection velocity, lubrication effectiveness first enhances and then deteriorates, exhibiting a clear optimal range of approximately 30 m/s. Lower injection velocities fail to generate sufficient kinetic energy, resulting in discontinuous lubrication films. Moderate velocities enable stable and continuous oil film coverage, achieving optimal lubrication. Higher velocities, however, induce pronounced oil splashing and film detachment, resulting in decreased lubrication efficiency.
- Turbulence characteristics and oil transport patterns exhibit significant velocity-dependent variability. As jet velocity increases, turbulence kinetic energy and eddy viscosity intensify, reaching peak local shear and turbulence effects around 30 m/s. Beyond this range, excessive turbulence exacerbates oil flow instability, causing substantial fluctuations in both oil velocity and phase distribution. Consequently, excessively high velocities diminish lubricant adhesion and amplify energy losses.
- Flow visualization reveals distinct modes of oil transport under varying injection velocities. At lower velocities, the lubricant flow is dispersed and significantly rebounds, impeding effective lubrication. At moderate velocity (30 m/s), coherent, adequate lubricant transport occurs, effectively penetrating gear teeth clearances and enhancing lubrication. Although high velocity (50 m/s) concentrates oil transport, the increased risks of splash and energy loss significantly compromise the effectiveness of lubrication.
6. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, J.F.; Yin, Z.C.; Tan, D.P. Numerical investigation of mesoscale multiphase mass transport mechanism in fibrous porous media. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2024, 18, 2363246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Song, F.; Yao, X.; Xiao, B.; Lin, P.; Qi, H.; Liu, S.; Tang, H. Multi-build orientation effects on microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior of truly as-built selective laser melting Ti6Al4V alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, Y.; Xu, W.; Ni, Y.; Yang, J.; Tan, D. Fluid-induced transport dynamics and vibration patterns of multiphase vortex in the critical transition states. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 252, 108376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wan, H.; Hong, B.; Hang, W.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, R.; Han, X.; et al. A novel liquid film shearing polishing technique for silicon carbide and its processing damage mechanisms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 688, 162317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, B.; Xu, W.X.; Gu, Z.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Tan, D.P. Mechanism of multiphase coupling transport evolution of free sink vortex. Acta Phys. Sin. 2023, 72, 034702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Transport Mechanism and Optimization Design of LBM-LES Coupling-Based Two-Phase Flow in Static Mixers. Processes 2025, 130, 1666. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xu, W.X.; Tan, Y.F.; Yang, Y.S.; Yang, J.G.; Tan, D.P. Fluid-induced vibration evolution mechanism of multiphase free sink vortex and the multi-source vibration sensing method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 189, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, H. Research on dynamic behavior of multistage gears-bearings and box coupling system. Measurement 2020, 150, 107096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Xu, P.; Zheng, R.Y.; Yin, Z.C.; Bao, J.J.; Yang, Y.S.; Tan, D.P. Multiscale heat transfer mechanism and dynamic regulation of free-surface swirling flow based on LBM-LES coupling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 150, 107096. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xu, P.; Li, Q.H.; Zheng, R.Y.; Xu, X.M.; Wu, J.F.; He, B.Y.; Bao, J.J.; Tan, D.P. A coupled LBM-LES-DEM particle flow modeling for microfluidic chip and ultrasonic-based particle aggregation control method. Appl. Math. Model. 2025, 143, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morhard, B.; Paschold, C.; Lohner, T.; Stahl, K. Power loss and damage behavior of gears operating under loss of lubrication. J. Tribol. 2024, 146, 072201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, P.; Li, Q.H.; Yin, Z.C.; Zheng, R.Y.; Wu, J.F.; Bao, J.J.; Qi, H.; Tan, D.P. Multi-field coupling particle flow dynamic behaviors of the microreactor and ultrasonic control method. Powder Technol. 2025, 454, 120731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Tang, W.; Huang, Q.; Xie, J. An improved load distribution model for gear transmission in thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Lubricants 2023, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zheng, G. Study on the dynamic characteristics of the gear lubrication flow field with baffles and optimization design strategies. Lubricants 2025, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B. Thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication of herringbone gear considering the effect of oil gas mixture. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2023, 15, 061003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, X.; Yan, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Qi, D. Tribological characteristics evaluation of a helical gear pair based on the tribo-dynamic model. Lubr. Sci. 2023, 35, 616–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Fan, X.H.; Li, L.; Zheng, G.A. Investigations of the Mass Transfer and Flow Field Disturbance Regulation of the Gas-Liquid-Solid Flow of Hydropower Stations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.J. Analysis of Flow Field and Machining Parameters in RUREMM for High-precision Micro-texture Fabrication on SS304 Surfaces. Processes 2025, 13, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.F.; Ni, Y.S.; Xu, W.X.; Xie, Y.S.; Tan, D.P. Key technologies and development trends of the soft abrasive flow finishing method. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2023, 24, 1043–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, P.; Hou, Y.Q.; Tan, D.P. Collision modelling approach and transient response mechanism of ring-ribbed cylindric shells for underwater vehicles. Appl. Math. Model. 2025, 141, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hong, B.; Chen, H.; Qi, H.; Zhang, J.; Hang, W.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, K.; Lyu, B. Enhancing Tungsten Machinability via Laser Pretreatment for Abrasive Particles-based Shear Rheological Polishing. Powder Technol. 2025, 455, 120758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.A.; Xu, P. Investigate on the Fluid Dynamics and Heat Transfer Behavior in an Automobile Gearbox Based on the LBM-LES Model. Lubricants 2025, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Xie, Y.; Tan, D. Mechanism of multiphase flow transport in laterally-compressed cathode channels with fin-type obstacles for PEMFC. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Li, Q.; Tan, Y.; Yu, J.; Yuan, J.; Tan, D. Multi-physical coupling modeling and ultrasonic crack detection mechanism analysis for underwater steel structures. Ocean. Eng. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shao, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Wen, Y. Multi-physics field coupling interface lubrication contact analysis for gear transmission under various finishing processes. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 165, 108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, X.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y. Simulation study of oil-jet lubrication for high-speed gears. Lubr. Eng. 2019, 44, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, M.; Kromer, C.; Cordes, L.; Schwitzke, C.; Bauer, H.-J. CFD study of oil-jet gear interaction flow phenomena in spur gears. Aeronaut. J. 2020, 124, 1301–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ma, F.; Zhu, X.; Su, Q.; Hu, X. Evaluation and optimization of the oil jet lubrication performance for orthogonal face gear drive: Modelling, simulation and experimental validation. Energies 2019, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Niu, W.; Chen, Y. Influence of oil injection methods on the lubrication process of high-speed spur gears. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, C.; Su, J.; Jin, G.; Shen, R. Injection parameter design to improve the high-speed gear heat dissipation: CFD simulation and regression orthogonal experiment. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2023, 128, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, P.; Quan, C.; Wang, J. CFD investigation on oil injection lubrication of meshing spur gears via lattice Boltzmann method. Lubricants 2022, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wei, C.; Yuan, S. Numerical simulation of ball bearing flow field using the moving particle semi-implicit method. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2022, 16, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, C.; Feng, L.; Dai, Y. Churning power losses of a gearbox with spiral bevel geared transmission. Tribol. Int. 2019, 129, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, J.-B.; Neurouth, A.; Changenet, C.; Ville, F. Experimental investigations on churning power losses generated in a planetary gear set. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2017, 11, 00196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.; Hong, S.; Li, P.; Wu, M. Influences of an oil guide device on splash lubrication performance in a spiral bevel gearbox. Tribol. Int. 2019, 136, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concli, F.; Mastrone, M.N. Advanced lubrication simulations of an entire test rig: Optimization of the nozzle orientation to maximize the lubrication capability. Lubricants 2023, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, P.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Tan, D. Investigation on the Lubrication Heat Transfer Mechanism of the Multilevel Gearbox by the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Processes 2024, 12, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Hou, X.; Ma, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, R.; Zhu, R. Transient simulation analysis of needle roller bearing in oil jet lubrication and planetary gearbox lubrication conditions based on computational fluid dynamics. Lubricants 2024, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Xu, W.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, J.F.; Tan, D.P. Dynamic behaviors of multiphase vortex-induced vibration for hydropower energy conversion. Energy 2024, 308, 132897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S.; Tan, D.P.; Xu, S.C.; HU, T.C.; Qi, H.; Li, L. Investigation of Crack Propagation and Failure of Liquid-Filled Cylindrical Shells Damaged in High-Pressure Environments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, A.; Ding, S.; Han, S.; Li, F.; Kujala, P. Numerical Study of the Cavitation Performance of an Ice-Blocked Propeller Considering the Free Surface Effect. Water 2024, 16, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yao, Q.; Jin, H.; Xu, Y.; Hang, W.; Chen, H.; Li, K.; Shi, L.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A novel in-situ sensor calibration method for building thermal systems based on virtual samples and autoencoder. Energy 2024, 297, 131314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-W.; Song, J.; Chen, Z.-D.; Lv, Z.-H.; Li, B.; Yang, H.-F.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, F.-Y. Two-phase closed thermosiphon with grooved the evaporator section applied for low-grade energy recovery: Thermo-hydrodynamic performance and potentials. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2025, 208, 109416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, P.; Xu, W.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Tan, D.P. Multi-field coupling vibration patterns of the multiphase sink vortex and distortion recognition method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 219, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Li, Q.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Tan, D.P.; Wu, H.P. Interlayer healing mechanism of multipath deposition 3D printing models and interlayer strength regulation method. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 141, 1031–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.C.; Lu, J.F.; Wang, T.; Wang, R.H.; Fan, X.H.; Lin, H.K.; Huang, Y.S.; Tan, D.P. Optimized Scheme for Accelerating the Slagging Reaction and Slag-Metal-Gas Emulsification in a Basic Oxygen Furnace. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Jiang, X.; Su, J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, S. Injection lubrication for high-speed helical gears using the overset mesh method and experimental verification. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yin, Z.; Wang, T.; Fan, X.; Wang, R. Investigation on the multiphase vortex and its fluid-solid vibration characters for sustainability production. Renew. Energy 2021, 175, 887–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, A.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Influence of dynamic attitudes on oil supply for bearings and churning power losses in a splash lubricated spiral bevel gearbox. Tribol. Int. 2021, 159, 106951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, C.; Yang, X.; Schlautman, J.; Wang, D.; Gangaraj, S. Conjugate heat transfer CFD analysis of an oil cooled automotive electrical motor. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2020, 2, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gu, Z.H.; Xu, W.X.; Tan, Y.F.; Fan, X.H.; Tan, D.P. Mixing mass transfer mechanism and dynamic control of gas-liquid-solid multiphase flow based on VOF-DEM coupling. Energy 2023, 272, 127015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Yu, W. Gear dynamic modelling based on the concept of dynamic mesh stiffness: Theoretical study and experimental verification. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 4953–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hou, X. Analysis of two-phase flow fields and spray lubrication characteristics of high-speed gears. J. Mech. Transm. 2024, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- de Bie, V.G.; Spanjaards, M.M.; Hulsen, M.A.; Anderson, P.D. The extrusion of EPDM using an external gear pump: Experiments and simulations. Int. Polym. Process. J. Polym. Process. Soc. 2022, 37, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Ni, Y.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Tan, Y.F.; Tan, D.P. Critical penetrating vibration evolution behaviors of the gas-liquid coupled vortex flow. Energy 2024, 292, 130236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lian, X.; Savari, C.; Barigou, M. Evaluating the effectiveness of CFD-DEM and SPH-DEM for complex pipe flow simulations with and without particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 288, 119788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondelli, T.; Andreini, A.; Da Soghe, R.; Facchini, B.; Cipolla, L. Numerical simulation of oil jet lubrication for high speed gears. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2015, 2015, 752457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Tan, Y.F.; Tan, D.P. Mass transfer mechanism of multiphase shear flows and interphase optimization solving method. Energy 2024, 292, 130475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pei, C.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. Assessment of cavitation erosion risk by Eulerian–Lagrangian multiscale modeling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 262, 108735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Jin, P.; Qi, Y.; Cai, G. Effect of inlet mass flow rate oscillation on simplex swirl injector flow based on VOF-to-DPM model. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 211, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ning, B.; Chen, X.B.; Lv, H.M. Research progress of stirring power loss in gear transmission. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 56, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsukova, E.; Morvan, H. Computational Fluid Dynamics Study of Oil Behavior in a Scoop, and Factors Affecting Scoop Capture Efficiency. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power Trans. ASME 2020, 142, 051008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laruelle, S.; Fossier, C.; Changenet, C.; Ville, F.; Koechlin, S. Experimental investigations and analysis on churning losses of splash lubricated spiral bevel gears. Mech. Ind. 2017, 18, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, J.F.; Xie, Y.S.; Yin, Z.C.; Tan, D.P. Deposition Mechanism of Microscopic Impacting Droplets on Flexible Porous Substrates. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 288, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yao, Q.; Shi, L.; Jin, H.; Xu, Y.; Yang, P.; Xiao, H.; Chen, D.; Zhao, P.; Shen, X. A virtual sample diffusion generation method guided by LLM-generated knowledge for enhancing information completeness and zero-shot fault diagnosis in building thermal systems. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Uerlich, R.; Koch, T.; Theising, H.; Eckstein, L. Method for thermal evaluation of automotive gearbox packages taking into account load point-dependent oil distribution. Automot. Engine Technol. 2022, 7, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Stanic, M.; Hartono, E.A.; Chernoray, V. Numerical simulations of oil flow inside a gearbox by Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method. Tribol. Int. 2018, 127, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Yan, Q. Investigation into the Dynamic Evolution Characteristics of Gear Injection Lubrication Based on the CFD-VOF Model. Processes 2025, 13, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082540
Gu Y, Zhang X, Li L, Yan Q. Investigation into the Dynamic Evolution Characteristics of Gear Injection Lubrication Based on the CFD-VOF Model. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082540
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Yihong, Xinxing Zhang, Lin Li, and Qing Yan. 2025. "Investigation into the Dynamic Evolution Characteristics of Gear Injection Lubrication Based on the CFD-VOF Model" Processes 13, no. 8: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082540
APA StyleGu, Y., Zhang, X., Li, L., & Yan, Q. (2025). Investigation into the Dynamic Evolution Characteristics of Gear Injection Lubrication Based on the CFD-VOF Model. Processes, 13(8), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082540




