A Comparative Evaluation of Ulothrix sp. and Spirogyra sp. as Eco-Friendly Biosorbents for Methylene Blue Removal: Mechanistic Insights from Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Adsorbent Preparation
2.3. Characterization of Algae
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
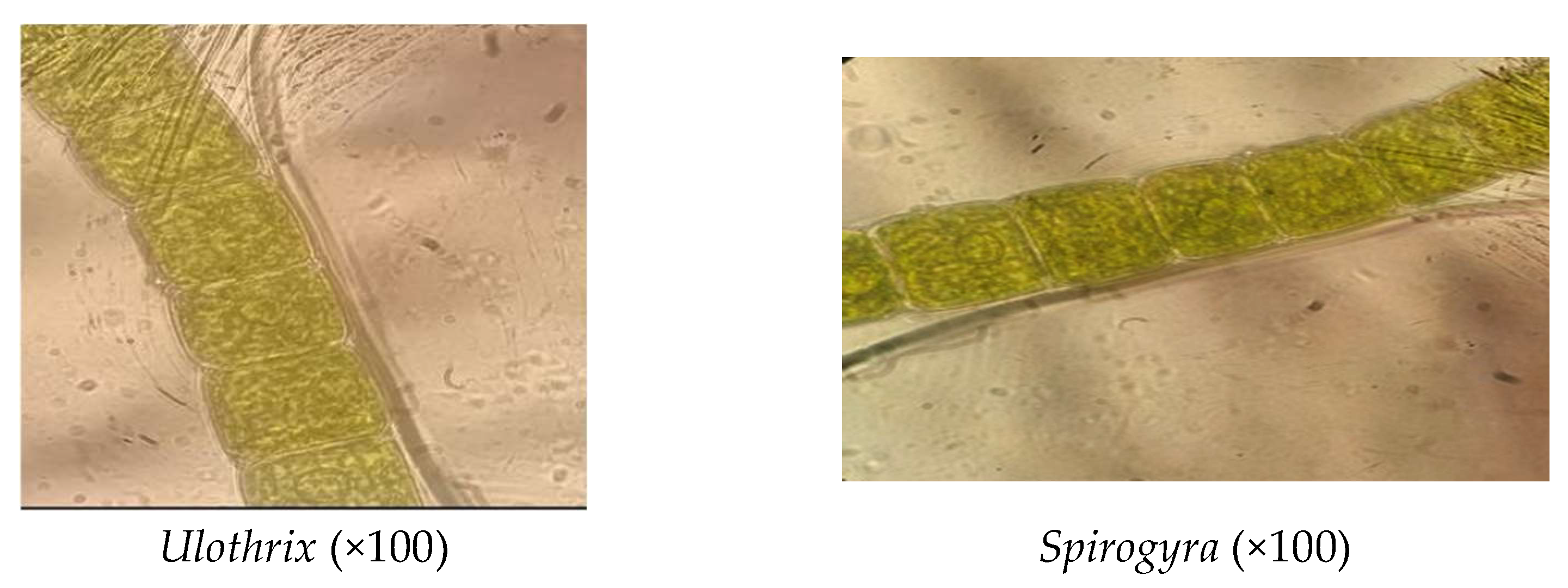
3.1. Material Characterization
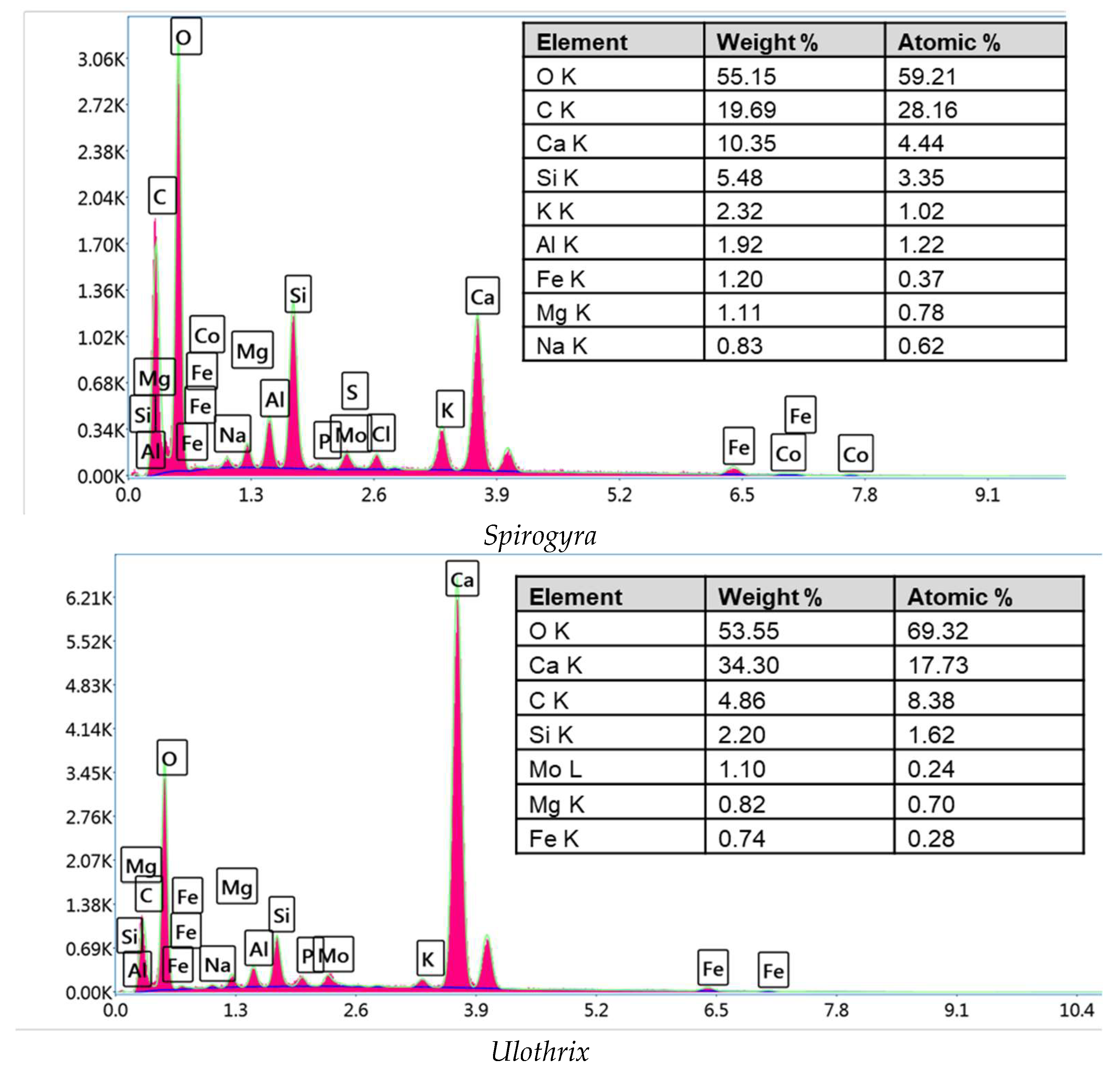
3.1.1. EDS Analysis
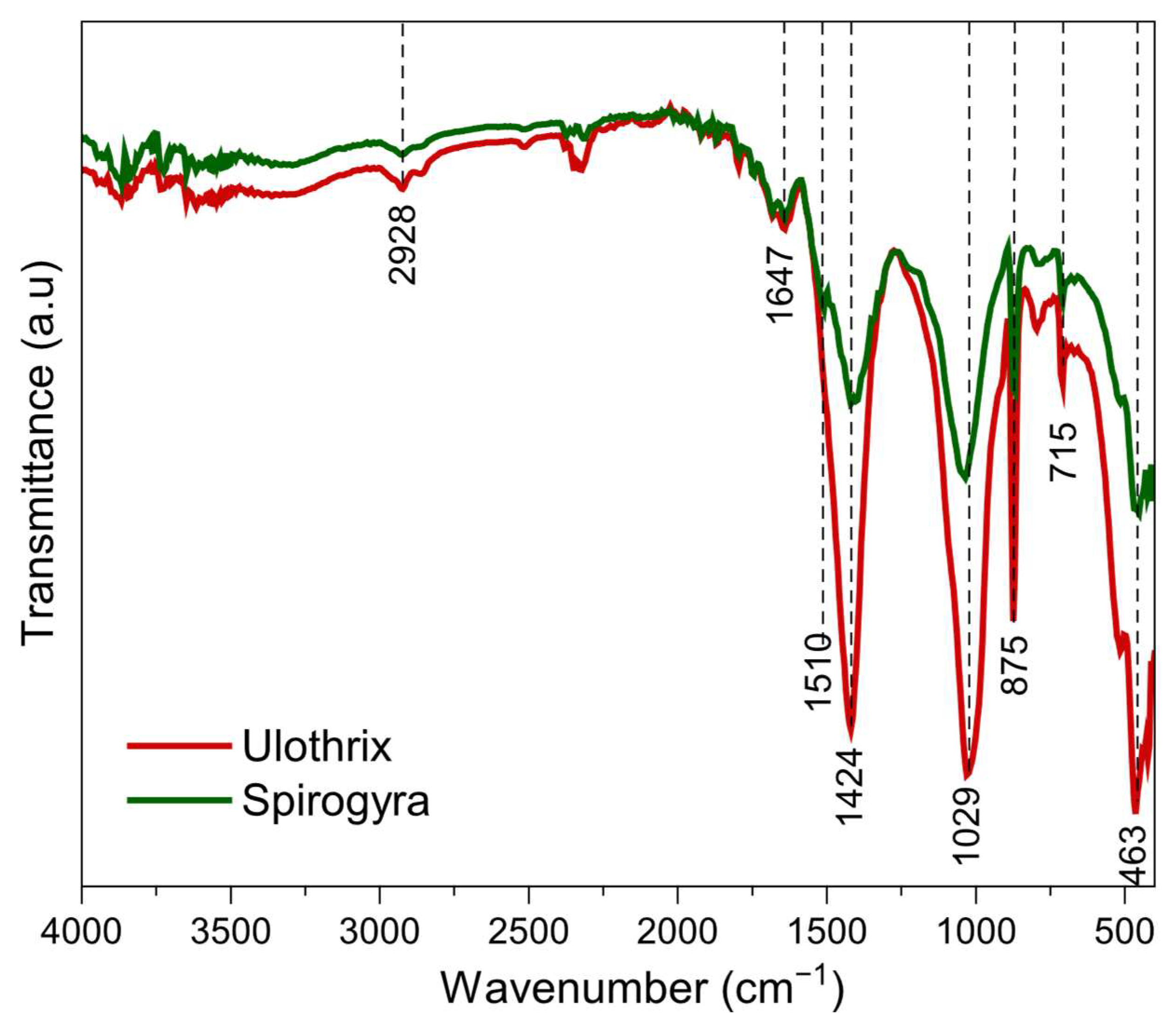
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
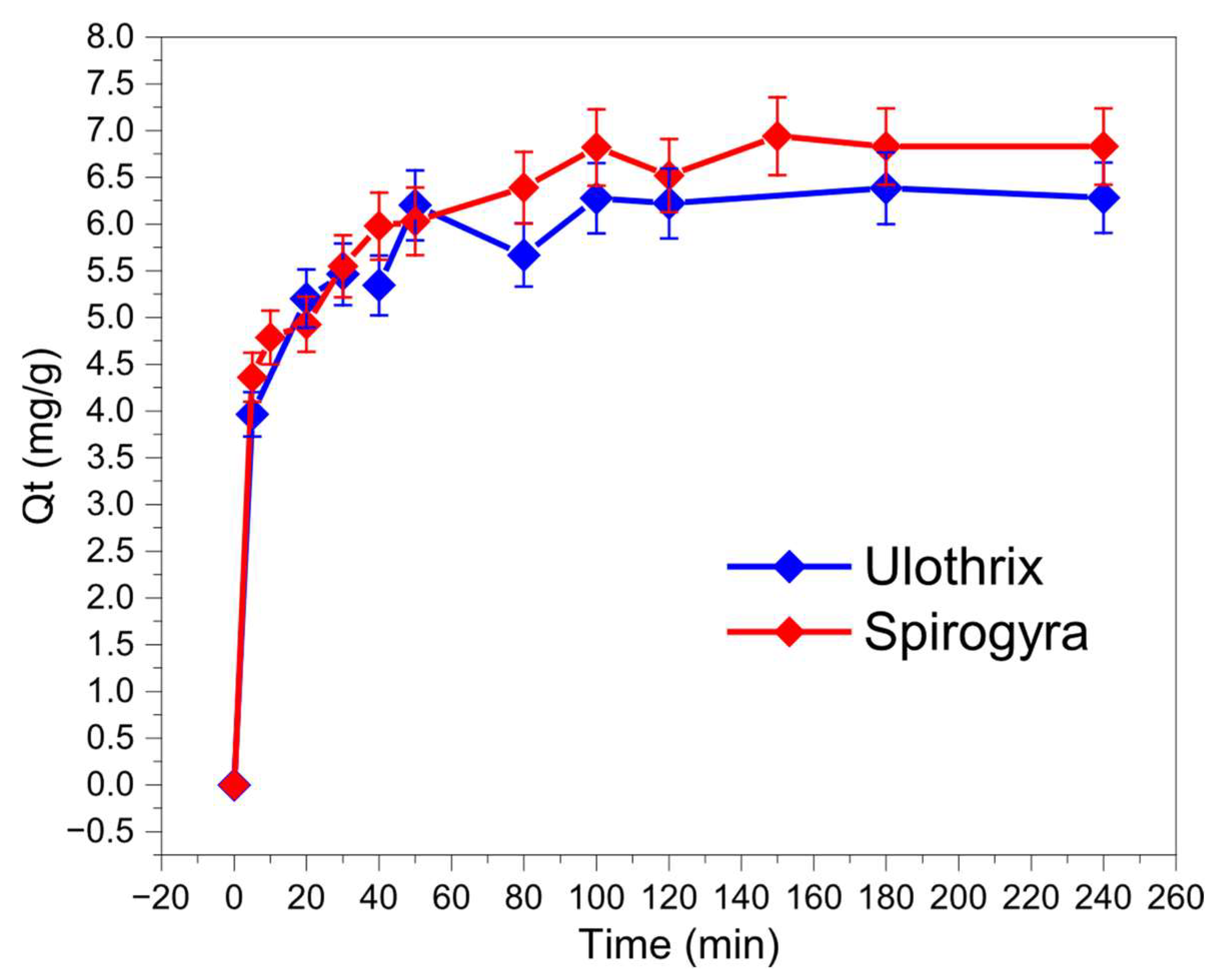
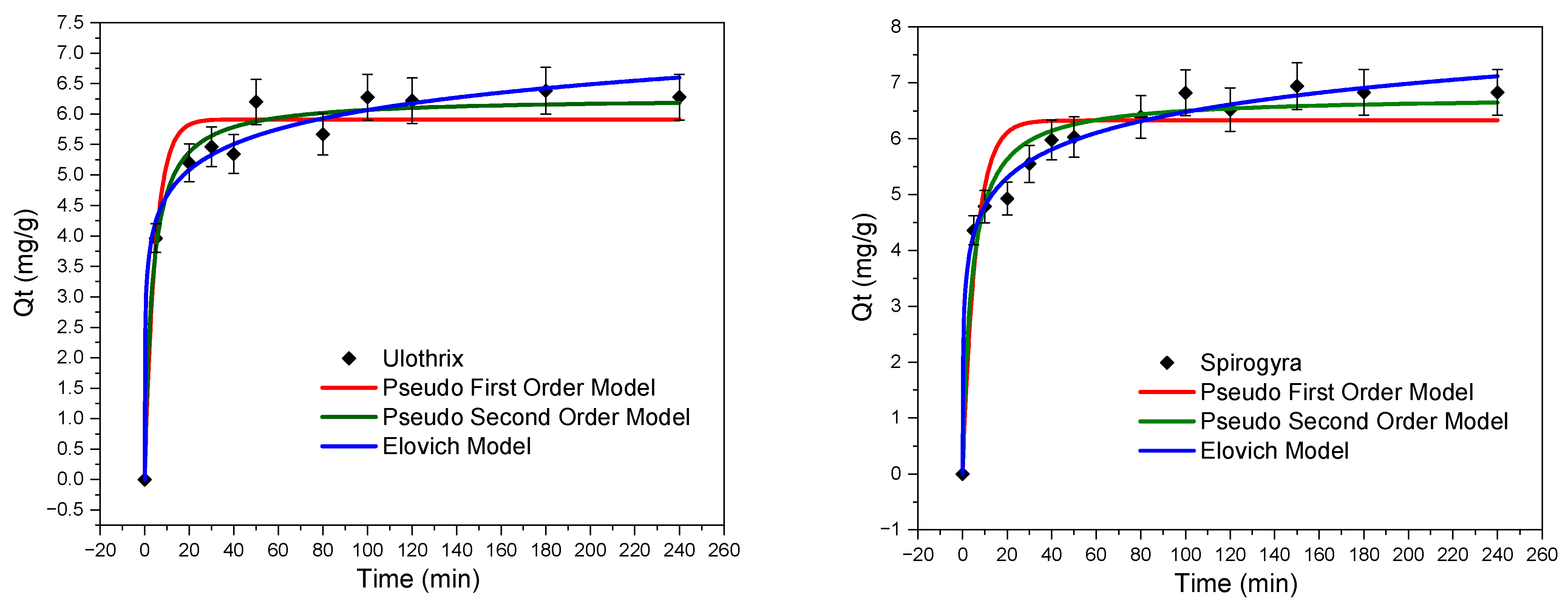
3.2. Contact Time Effect—Adsorption Kinetics Study
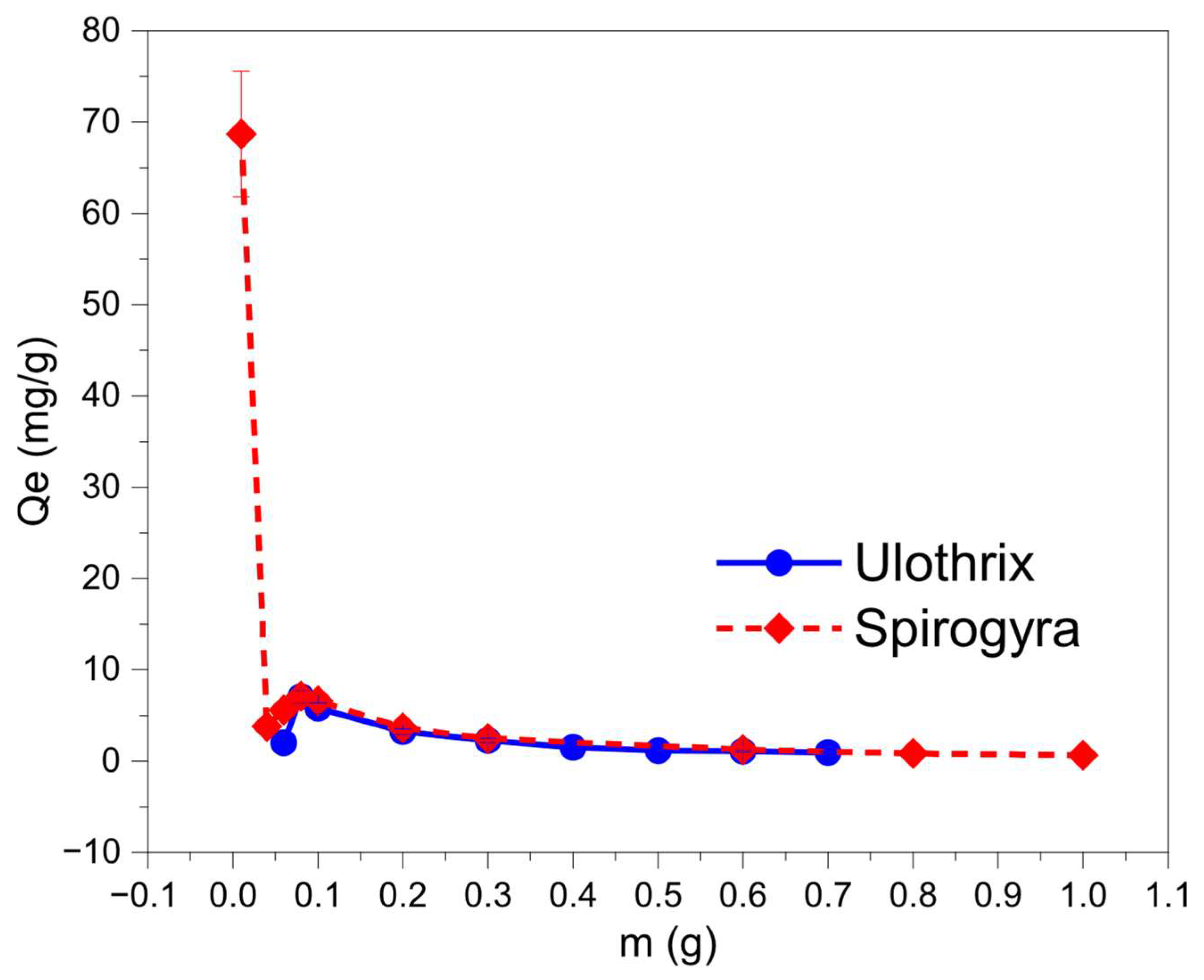
3.3. Effect of Adsorbent Type and Dosage
3.4. Effect of pH
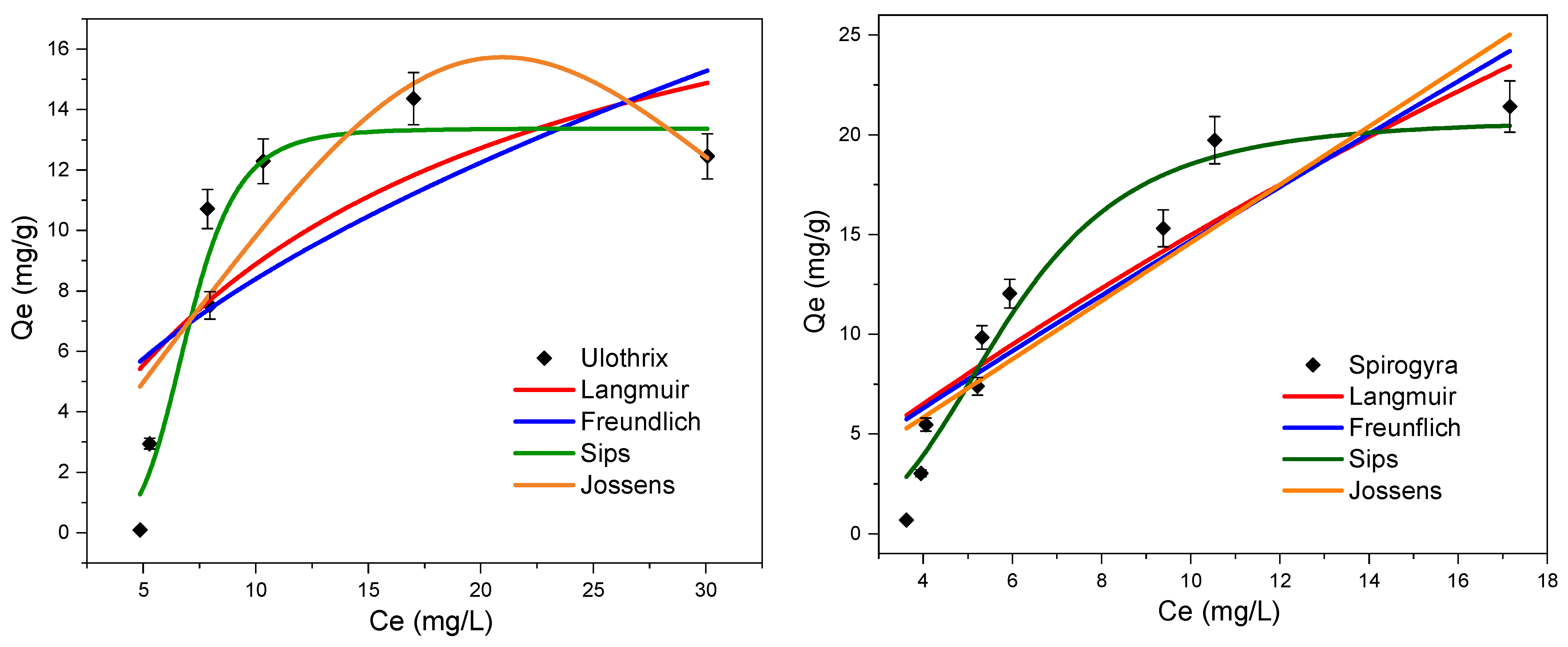
3.5. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5.1. Sips Model
3.5.2. Jossens Model
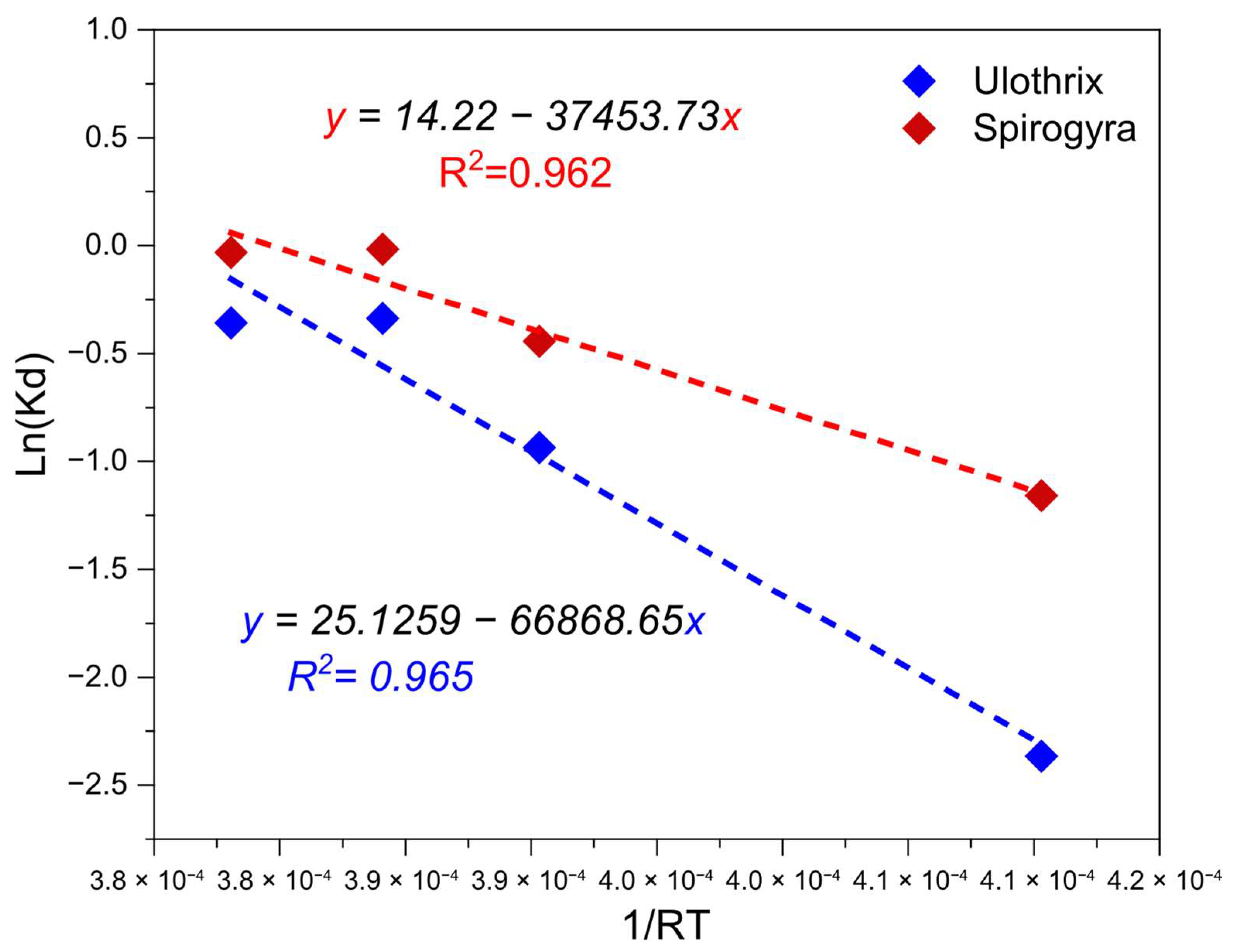
3.6. Adsorption Thermodynamics
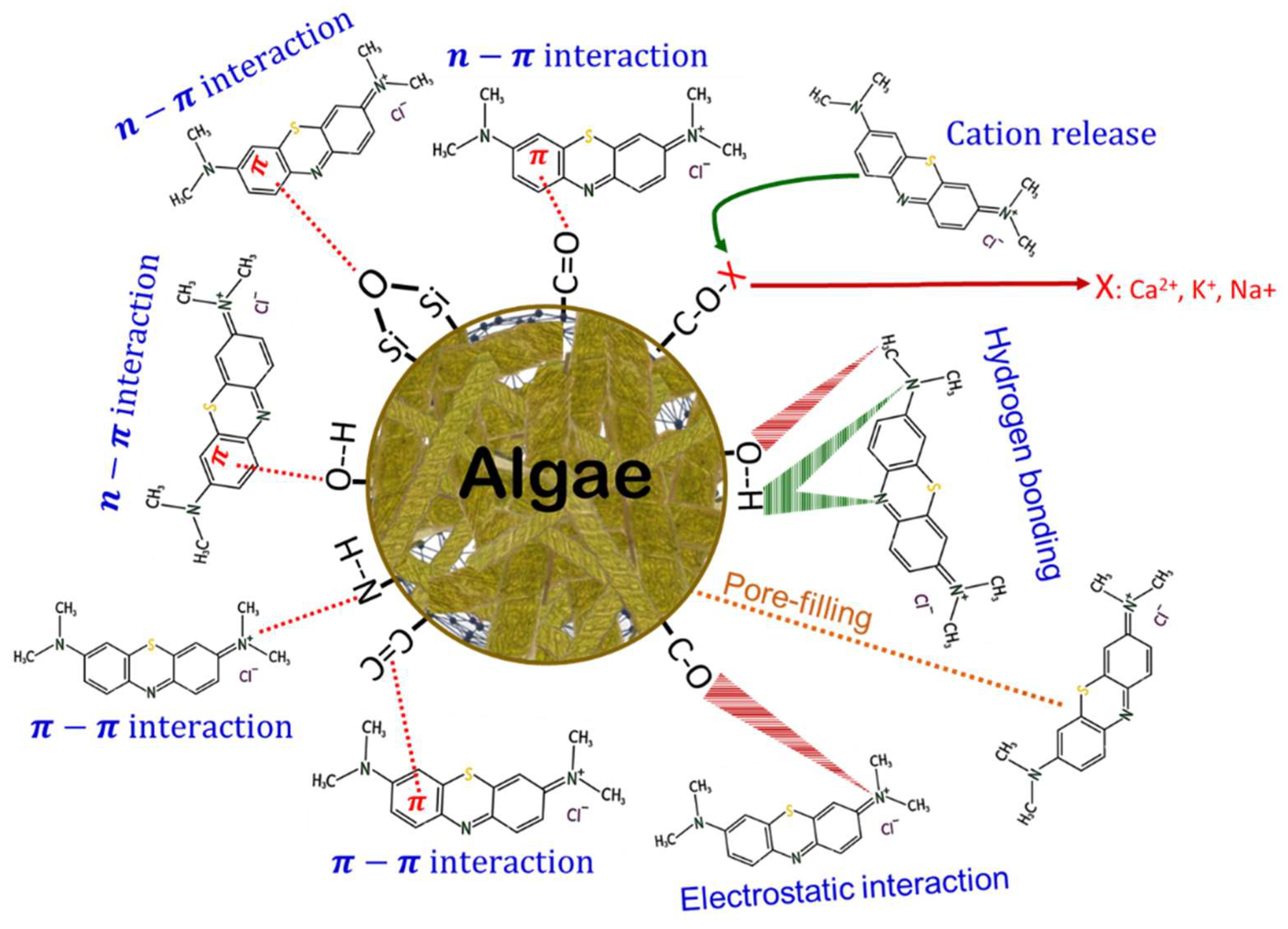
3.7. Adsorption Mechanism
3.8. Comparative Analysis of Adsorption Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Couillard, D. Évaluation De La Pollution Et Des Répercussions Des Rejets Des Industries Des Pâtes Et Papiers Sur La Vie Aquatique. Sci. Total Environ. 1980, 14, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, I.; Guesmi, A.; Baaloudj, O.; Zeghioud, H.; Elfalleh, W.; Benhammadi, N.; Khezami, L.; Assadi, A.A. Review on Inactivation of Airborne Viruses Using Non-Thermal Plasma Technologies: From MS2 to Coronavirus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4880–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourthuraj, A.A.; Hatshan, M.R.; Hussein, D.S. Biocatalytic Degradation of Organophosphate Pesticide from the Wastewater and Hydrolytic Enzyme Properties of Consortium Isolated from the Pesticide Contaminated Water. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.B.; Rodrigues, F.H.A.; Paulino, A.T.; Martins, A.F.; Fajardo, A.R. Recent Advances on Composite Hydrogels Designed for the Remediation of Dye-Contaminated Water and Wastewater: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jubouri, S.M.; Al-Jendeel, H.A.; Rashid, S.A.; Al-Batty, S. Antibiotics Adsorption from Contaminated Water by Composites of ZSM-5 Zeolite Nanocrystals Coated Carbon. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghioud, H.; Fryda, L.; Djelal, H.; Assadi, A.; Kane, A. A Comprehensive Review of Biochar in Removal of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater: Characterization, Toxicity, Activation/Functionalization and Influencing Treatment Factors. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, E.S.; Abdallah, H.; Shaban, A.M. Fabrication of High Selectivity Blend Membranes Based on Poly Vinyl Alcohol for Crystal Violet Dye Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagga, U.; Brown, D. The Degradation of Dyestuffs: Part II Behaviour of Dyestuffs in Aerobic Biodegradation Tests. Chemosphere 1986, 15, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.B.; Mounir, B.; Hachkar, M.; Bakasse, M. Revue Des Sciences de l’Eau Solution Aqueuse Par l’Argile de Safi “Bleu de Méthylène” En Solution Aqueuse Par l’Argile de Safi. Removal of Basic Dye “Methylene Blue” in Aqueous Solution by Safi Clay Élimination Du Colorant Basique. J. Water Sci. 2020, 23, 375–388. [Google Scholar]
- Dardouri, S.; Sghaier, J. Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Different Agricultural Wastes as Adsorbents. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladjal, N.; Terchi, S.; Debih, H. Haute Efficacité d’Adsorption Du Colorant Basique (Cristal Violet) Sur La Montmorillonite Algérienne. Sci. Study Res. Chem. Chem. Eng. Biotechnol. Food Ind. 2024, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Low-Cost Adsorbents: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benazouz, K.; Bouchelkia, N.; Imessaoudene, A.; Bollinger, J.C.; Amrane, A.; Assadi, A.A.; Zeghioud, H.; Mouni, L. Efficient and Low-Cost Water Remediation for Chitosan Derived from Shrimp Waste, an Ecofriendly Material: Kinetics Modeling, Response Surface Methodology Optimization, and Mechanism. Water 2023, 15, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadyrbaeva, T.Z. Removal of Chromium(VI) from Aqueous Solutions Using a Novel Hybrid Liquid Membrane—Electrodialysis Process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 99, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golder, A.K.; Samanta, A.N.; Ray, S. Removal of Chromium and Organic Pollutants from Industrial Chrome Tanning Effluents by Electrocoagulation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, B. Hexavalent Chromium Reduction From Real Electroplating. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2020, 34, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Sukla, L.B.; Sawyer, M.; Rahman, P.K.S.M. Recent Bioreduction of Hexavalent Chromium in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, D.C.; Riotte, J.; Subramanian, S. Bioremediation of Hexavalent and Trivalent Chromium Using Citrobacter Freundii: A Mechanistic Study. Nat. Resour. Eng. 2016, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Duque, F.; Pétrier, C.; Pulgarin, C.; Peñuela, G.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Effects of Sonochemical Parameters and Inorganic Ions during the Sonochemical Degradation of Crystal Violet in Water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popli, S.; Patel, U.D. Destruction of Azo Dyes by Anaerobic–Aerobic Sequential Biological Treatment: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Anu, N.; Selvaraju, N. Sequestration of Dye from Textile Industry Wastewater Using Agricultural Waste Products as Adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbes, M.; Assadi, A.A.; Bouguerra, W.; Khezami, L.; Amrane, A.; Kane, A.; Mouni, L.; Elaloui, E.; Hjiri, M.; Zeghioud, H. Remediation of Water Contamination Using a Synergetic System of Biochar and Photocatalyst: Complete Mineralization in Simulated Real Condition. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2024, 9, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Nam, S.N.; Jang, A.; Jang, M.; Park, C.M.; Son, A.; Her, N.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Review of Adsorption–Membrane Hybrid Systems for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errais, E. Réactivité de Surface d’Argiles Naturelles Etude de l’Adsorption de Colorants Anioniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite de Strasbourg, Strasbourg, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mazet, M.; Dusart, O.; Dussoubs-marmier, M.R.D. Elimination de Colorants de l’ Industrie Textile Par Des Sciures de Bois. Elimination de Colorants de l’ Industrie Textile Par Des Sciures de Bois Dyes Removal from Textile Effluents by Wood Sawdusts. Rev. Des Sci. De L’eau 2012, 3, 129–149. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshvar, E.; Kousha, M.; Jokar, M.; Koutahzadeh, N.; Guibal, E. Acidic Dye Biosorption onto Marine Brown Macroalgae: Isotherms, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 204–206, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncibi, M.C.; Mahjoub, B.; Seffen, M. Étude de La Biosorption Du Chrome (VI) Par Une Biomasse Méditerranéenne: Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Rev. Sci. L’Eau 2008, 21, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamba, R.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K.; Kumar Kansal, S. Well-Crystalline Porous ZnO–SnO2 Nanosheets: An Effective Visible-Light Driven Photocatalyst and Highly Sensitive Smart Sensor Material. Talanta 2015, 131, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, E.; Vazirzadeh, A.; Niazi, A.; Kousha, M.; Naushad, M.; Bhatnagar, A. Desorption of Methylene Blue Dye from Brown Macroalga: Effects of Operating Parameters, Isotherm Study and Kinetic Modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, V.J.P.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Methylene Blue Adsorption by Algal Biomass Based Materials: Biosorbents Characterization and Process Behaviour. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.V.; Porkodi, K.; Rocha, F. Isotherms and Thermodynamics by Linear and Non-Linear Regression Analysis for the Sorption of Methylene Blue onto Activated Carbon: Comparison of Various Error Functions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, U.A.; Sarioglu, M. Single and Binary Biosorption of Cu(II), Ni(II) and Methylene Blue by Raw and Pretreated spirogyra sp.: Equilibrium and Kinetic Modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, M.; Worth, A.P. Review of Estimation Models for Biodegradation. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2008, 27, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A.; Tamjidi, S.; Dehghankhalili, F.; Farhadi, A.; Saati, M.A. Application of Algae as Low Cost and Effective Bio-Adsorbent for Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater: A Review Study. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2020, 9, 85–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motik, C.; Chegdani, F.; Blaghen, M. The Biosorption Potential of Plocamium Cartilagineum Algal Biomass for the Elimination of the Synthetic Dye Cibacron Blue. AACL Bioflux 2022, 15, 544–556. [Google Scholar]
- Jegan, J.; Vijayaraghavan, J.; Bhagavathi Pushpa, T.; Sardhar Basha, S.J. Application of Seaweeds for the Removal of Cationic Dye from Aqueous Solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 25812–25821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, B.; Saravanan, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Thamarai, P.; Shaji, A.; Rangasamy, G. A Review on Algae Biosorption for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants from Wastewater: Limiting Factors, Prospects and Recommendations. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukaram Bai, M.; Anudeep, Y.V.; Raju, C.A.I.; Venkata Rao, P.; Chittibabu, N. Decolourization of Eosin Yellow (EY) Dye Using a Variety of Brown Algae. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, A.G.M.; Van, H.T.; Tran, D.T.; El Sikaily, A.; Hassaan, M.A.; El Nemr, A. Green Algae Ulva Lactuca-Derived Biochar-Sulfur Improves the Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Water. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğar, Ç.; Gürses, A.; Açıkyıldız, M.; Özkan, E. Thermodynamics and Kinetic Studies of Biosorption of a Basic Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Green Algae Ulothrix Sp. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordóñez, J.I.; Cortés, S.; Maluenda, P.; Soto, I. Biosorption of Heavy Metals with Algae: Critical Review of Its Application in Real Effluents. Sustainability. 2023, 15, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Kinetic Models: Physical Meanings, Applications, and Solving Methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampranpiboon, P.; Feng, X. Kinetic Models on Chromium (VI) Adsorption onto Carbonized Oil Palm Kernel with Potassium Hydroxide Activation. Int. J. Adv. Chem. Eng. Biol. Sci. 2016, 3, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffari Majd, M.; Kordzadeh-Kermani, V.; Ghalandari, V.; Askari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Comprehensive and Systematic Review (2010–2020). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperatures and Times on the Adsorption of Cadmium onto Orange Peel Derived Biochar. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Alprol, A.E.; Khedawy, M.; Abualnaja, K.M.; Mansour, A.T. Equilibrium and Kinetic Modeling of Crystal Violet Dye Adsorption by a Marine Diatom, Skeletonema Costatum. Materials 2022, 15, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saeedi, S.I.; Ashour, M.; Alprol, A.E. Adsorption of Toxic Dye Using Red Seaweeds from Synthetic Aqueous Solution and Its Application to Industrial Wastewater Effluents. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1202362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidi, D.S.; Alwared, A.I. Role of Immobilised Chlorophyta Algae in Form of Calcium Alginate Beads for the Removal of Phenol: Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xia, J.; Long, J. Biosorption of Methylene Blue by Nonliving Biomass of the Brown Macroalga Sargassum Hemiphyllum. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, B.D. A Handbook of Spectroscopic Data CHEMISTRY (UV, IR, PMR, 13CNMR and Mass Spectroscopy); Oxford Book Company: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, B. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha, A.K.; Gupta, N.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Removal of Cationic Methylene Blue and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Waste Materials of Daucus Carota. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertugay, N.; Malkoc, E. Adsorption Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies for Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by Needles of Pinus sylvestris L. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Rastogi, A.; Nayak, A. Biosorption of Nickel onto Treated Alga (Oedogonium hatei): Application of Isotherm and Kinetic Models. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plazinski, W.; Rudzinski, W.; Plazinska, A. Theoretical Models of Sorption Kinetics Including a Surface Reaction Mechanism: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, Q.-B.; Yu, H.-Q. Isotherms, Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Dye Biosorption by Anaerobic Sludge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z. Application of Biochar for the Removal of Pollutants from Aqueous Solutions. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenvi, S.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Shilton, S.J.; Al Ahmed, A. Humic Acid Based Biopolymeric Membrane for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4965–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Najafi, F.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Malachite Green Dye Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions on Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Li, X. Characterization and Ciprofloxacin Adsorption Properties of Activated Carbons Prepared from Biomass Wastes by H3PO4 Activation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 217, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.K.; Gupta, R.; Bala Yadav, A.; Kumar, R. Dye Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption on Treated Sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, B.H.; El-Khaiary, M.I. Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies of Malachite Green Adsorption on Rice Straw-Derived Char. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, B.; Sorial, G.A.; Bahrami, H.; Arami, M. Equilibrium and Kinetic Adsorption Study of a Cationic Dye by a Natural Adsorbent—Silkworm Pupa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, B.; Liu, Q.; Wu, C.; Li, Z. Preparation of Porous Biochar from Heavy Bio-Oil for Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Wastewater. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 238, 107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Rabago, J.J.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Ocampo-Perez, R.; Cerino-Cordova, F.J. Biosorption Mechanism of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution onto White Pine (Pinus durangensis) Sawdust: Effect of Operating Conditions. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, T.M.; Aigbe, U.O.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; Onyancha, R.B.; El-Nemr, M.A.; Hassaan, M.A.; Ragab, S.; Osibote, O.A.; El Nemr, A. Adsorption of Methylene Blue (MB) Dye on Ozone, Purified and Sonicated Sawdust Biochars. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 9361–9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Mohammad, M.; Emdadi, Z.; Asim, N.; Azizi, M.; Safaei, J. Adsorbent Materials Based on a Geopolymer Paste for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3017–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, M.A.H.; Luukkonen, T. Adsorption of Methylene Blue by Composite Foams Containing Alkali-Activated Blast Furnace Slag and Lignin. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 3789–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qin, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Hou, H.; Zhou, M. Study on the Adsorption of Dyestuffs with Different Properties by Sludge-Rice Husk Biochar: Adsorption Capacity, Isotherm, Kinetic, Thermodynamics and Mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, M.; Özdemir, Y.; Alkan, M. Adsorption Kinetics and Mechanism of Cationic Methyl Violet and Methylene Blue Dyes onto Sepiolite. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 75, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Angaye, S.S.; Wankasi, D.; Dikio, E.D. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxide for the Degradation of Congo Red in Aqueous Solution. Open J. Phys. Chem. 2015, 5, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C.; Pezoti, O.; Cazetta, A.L.; Bedin, K.C.; Yamazaki, D.A.S.; Bandoch, G.F.G.; Asefa, T.; Visentainer, J.V.; Almeida, V.C. Removal of Tetracycline by NaOH-Activated Carbon Produced from Macadamia Nut Shells: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.R.; Eagleton, L.C.; Acrivos, A.; Vermeulen, T. Pore- and Solid-Diffusion Kinetics in Fixed-Bed Adsorption under Constant-Pattern Conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1966, 5, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G.; Al Duri, B. Simplified Model for the Equilibrium Adsorption of Dyes from Mixtures Using Activated Carbon. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 1987, 22, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethaji, S.; Sivasamy, A.; Mandal, A.B. Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics and Mechanism for the Adsorption of Cationic and Anionic Dyes onto Carbonaceous Particles Prepared from Juglans Regia Shell Biomass. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, I. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Clinoptilolite: Determination of Isotherm and Thermodynamic Parameters and Comparison of Kinetics by the Double Exponential Model and Conventional Kinetic Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 970–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheper, T. New Trends and Developments in Biochemical Engineering. In Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lesage, G. Etude de l’Élimination de Substances Aromatiques Dangereuses Dans Un Procédé Couplant Adsorption et Biodégradation. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Ma, H. NaOH-Modified Mesoporous Biochar Derived from Tea Residue for Methylene Blue and Orange II Removal. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 167, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.; Mayer, S.; Rehmann, D.; Hofmann, T.; Glas, K. Equilibrium Data and Its Analysis with the Freundlich Model in the Adsorption of Arsenic(V) on Granular Ferric Hydroxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 243, 116704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, F.; Atar, N.; Olgun, A. Biosorption of Acidic Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Paenibacillus Macerans: Kinetic, Thermodynamic and Equilibrium Studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qi, Y.; Lu, T.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Cui, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z. Highly Efficient Removal of Imidacloprid Using Potassium Hydroxide Activated Magnetic Microporous Loofah Sponge Biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, A.; Foroutan, R.; Esmaeili, H.; Tamjidi, S. The Role of Bentonite Clay and Bentonite Clay@MnFe2O4 Composite and Their Physico-Chemical Properties on the Removal of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) from Aqueous Media. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14044–14057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, K.P.; Sankar, J.; Sankar, M.J.; Gupta, A.; Dadhich, J.P.; Gupta, Y.P.; Bhatt, G.C.; Ansari, D.A.; Sharma, B. Effect of Peer Counselling by Mother Support Groups on Infant and Young Child Feeding Practices: The Lalitpur Experience. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumchita, S.; Lahrichi, A.; Benjelloun, Y.; Lairini, S.; Nenov, V.; Zerrouq, F. Elimination d’un Colorant Cationique Dans Une Solution Aqueuse Par Un Déchet Alimentaire: Epluchure de Pomme de Terre. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. Bio/Hydrochar Sorbents for Environmental Remediation. Energy Environ. Mater. 2020, 3, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Gao, B.; He, F.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Ding, C.; Tang, J.; Crittenden, J.C. Experimental and Modeling Investigations of Ball-Milled Biochar for the Removal of Aqueous Methylene Blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghioud, H.; Fryda, L.; Mahieu, A.; Visser, R.; Kane, A. Potential of Flax Shives and Beech Wood-Derived Biochar in Methylene Blue and Carbamazepine Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2022, 15, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, E.E.; Beshay, B.Y.; Tonbol, K.; Makled, S.O. Biological Activities and Biosorption Potential of Red Algae (Corallina officinalis) to Remove Toxic Malachite Green Dye. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motik, C.; Chegdani, F.; Blaghen, M. The Biosorption Potential of the Algal Biomass from Plocamium Cartilagineum for the Removal of the Reactive Red Dye. AACL Bioflux 2023, 16, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Jayganesh, D.; Tamilarasan, R.; Kumar, M.; Murugavelu, M.; Sivakumar, V. Equilibrium and Modelling Studies for the Removal of Crystal Violet Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Eco-Friendly Activated Carbon Prepared from Sargassm Wightii Seaweeds. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 2122–2131. [Google Scholar]




| Non-Linear Kinetic Equations | Parameters | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | ||
| qt: sorption capacity (mg/g) time t K1: rate constant (min−1) | [42] | |
| Pseudo-second-order | ||
| qt : equilibrium concentration (mg/g). k2 : rate constant (g mg−1 min−1) | [42] | |
| Elovich | ||
| α: initial adsorption rate constant (mg/(g.min)) β: the ratio between surface coverage and activation energy constant of chemisorption (g/mg) | [22] | |
| Intraparticle diffusion (ID) | ||
| Kint: the rate constant for intraparticle diffusion (mg.g−1.min−1/2). C: the intercept relating to the amount of MB removed by rapid initial adsorption and/or the boundary layer thickness. (mg/g) | [43] | |
| Non-Linear Isotherm Equations | Parameters | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | ||
| qmax: maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g) bL: Langmuir coefficient (L/mg) Ce: equilibrium concentration (mg/L) | [44] | |
| Freundlich | ||
| Kf: Freundlich adsorption coefficient (L/g) n: Freundlich isotherm exponent reflects adsorption intensity. | [44] | |
| Sips | ||
| Ks: is the Sips adsorption constant (L/mg) βs: describes the surface heterogeneity as: Sips’ isotherm model constant (L/g) | [45] | |
| Jossens | ||
| Kj: Jossens constant, L/g βj: Jossens constant, L/g nj: dimensionless Jossens constant | [45] | |
| Samples | SBET (m2/g) | Smic [a] (m2/g) | Dave [b] (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spirogyra | 3.4715 ± 0.1313 | 2.67 | 20.97 | 0.0095 | This study |
| Ulothrix | 5.3508 ± 0.0337 | 4.84 | 32.77 | 0.0252 | This study |
| S. costatum | 87.17 | - | 3.131 | 0.103 | [47] |
| P. capillacea | 87.1721 | - | 1.564 | 0.10368 | [48] |
| Mougeotia robusta | 3.1806 | - | 24.733 | 0.019666 | [49] |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment | Implication Adsorption |
|---|---|---|
| 2928 | C-H stretching vibration (alkyl groups) [51] | Not directly involved in adsorption |
| 1647 | C=O stretching vibration (carbonyls in proteins, amides) [6] | Interaction with MB via hydrogen bonds or electrostatic forces |
| 1510 | C=C aromatic or N-H bending (secondary amines) [52] | Possible interaction with MB through electrostatic attraction |
| 1424 and 1418 | Carboxylate(-COO-) bending vibration [51] | Involved in electrostatic interactions with MB |
| 1035 and 1029 | C-O stretching vibration (polysaccharides alcohols) [52] | Possible hydrogen bonding with MB |
| 875, 709, 715 and 463 | Out of plane deformation modes (aromatic or silicates) [51] | Changes after adsorption suggest interaction with MB |
| Concentration | qexp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Elovich | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | qm | k1 | R2 | qm | k2 | R2 | Ɓ | α | ||
| Ulothrix | 6.38 | 0.95 | 5.92 | 0.21 | 0.98 | 6.27 | 0.048 | 0.98 | 1.64 | 126.23 |
| Spirogyra | 6.94 | 0.90 | 6.33 | 0.17 | 0.97 | 6.76 | 0.037 | 0.99 | 1.37 | 51.14 |
| Calculated Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent: Ulothrix | |||||||||
| Langmuir | qexp (mg/g): 14.36 | qm: | 22.43 | KL: | 0.065 | R2: | 0.60 | ||
| Freundlich | KF: | 2.39 | n: | 1.83 | R2: | 0.51 | |||
| Sips | KS: | 7.2 × 10−5 | βS: | 6.24 | aS: | 5.4 × 10−6 | R2: | 0.94 | |
| Jossens | Kj: | 0.996 | Bj: | 1.41 × 10−6 | nj: | 4.06 | R2: | 0.76 | |
| Calculated Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent: Spirogyra | |||||||||
| Langmuir | qexp (mg/g): 21.42 | qm: | 112.03 | KL: | 0.015 | R2: | 0.83 | ||
| Freundlich | KF: | 1.75 | n: | 1.08 | R2: | 0.82 | |||
| Sips | KS: | 0.022 | βS: | 3.89 | aS: | 0.001 | R2: | 0.95 | |
| Jossens | Kj: | 1.46 | Bj: | 1 × 10−14 | nj: | 1 × 10−8 | R2: | 0.81 | |
| Adsorbents | T (K) | ∆G° (kJ/mol) | ∆H° (kJ/mol) | ∆S° (kJ/mol.K) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ulothrix | 293.15 | −27.90541662 | 66.86865 | 0.20889673 | 0.965 |
| 308.15 | −33.00104698 | ||||
| 313.15 | −35.09378418 | ||||
| 318.15 | −35.59752841 | ||||
| Spirogyra | 293.15 | −30.85305612 | 37.45373 | 0.11822508 | 0.962 |
| 308.15 | −34.2596712 | ||||
| 313.15 | −35.9287893 | ||||
| 318.15 | −36.46073148 |
| Adsorbent | Pollutant (Concentration) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algae | |||
| Spirogyra | Methylene blue (20 mg/L) | 6.94 | This study |
| Ulothrix | Methylene blue (20 mg/L) | 6.38 | This study |
| Skeletonema costatum | Crystal Violet Dye | 6.410 | [47] |
| Corallina officinalis | Malachite green dye (20 mg/L) | 101.30 | [90] |
| Red seaweed, Gracilaria corticata | Crystal Violet Dye (100 mg/L) | 181.0 | [36] |
| Red seaweed, Pterocladia capillacea | Crystal Violet Dye (0.3 g/L) | 5.714 | [48] |
| Sargassum Tenerrimum | Eosin yellow | 5.18 | [47] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | Reactive red | 34.72 | [91] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | Cibacron blue | 25.83 | [35] |
| Other adsorbents (activated carbon, biochar, etc.) | |||
| Sargassum weightii Activated Carbon | Crystal Violet Dye (80 mg/L) | 3.306 | [92] |
| green algae Ulva lactuca biochar-sulfur | Methylene blue (200 mg/L) | 303.78 | [39] |
| Yellow passion fruit waste | Methylene blue | 44.7 | [33] |
| Beech Biochar Flax Biochar Citric acid-treated Beech Biochar | Methylene blue | 81.06 24.74 117.33 | [89] |
| Shrimp carapace-derived chitosan | Orange G dye | 34.63 | [13] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dehbi, M.; Zeghioud, H.; Smail, D.; Dehbi, F. A Comparative Evaluation of Ulothrix sp. and Spirogyra sp. as Eco-Friendly Biosorbents for Methylene Blue Removal: Mechanistic Insights from Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Analyses. Processes 2025, 13, 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082408
Dehbi M, Zeghioud H, Smail D, Dehbi F. A Comparative Evaluation of Ulothrix sp. and Spirogyra sp. as Eco-Friendly Biosorbents for Methylene Blue Removal: Mechanistic Insights from Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Analyses. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082408
Chicago/Turabian StyleDehbi, Meriem, Hicham Zeghioud, Dalila Smail, and Faouzia Dehbi. 2025. "A Comparative Evaluation of Ulothrix sp. and Spirogyra sp. as Eco-Friendly Biosorbents for Methylene Blue Removal: Mechanistic Insights from Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Analyses" Processes 13, no. 8: 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082408
APA StyleDehbi, M., Zeghioud, H., Smail, D., & Dehbi, F. (2025). A Comparative Evaluation of Ulothrix sp. and Spirogyra sp. as Eco-Friendly Biosorbents for Methylene Blue Removal: Mechanistic Insights from Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Analyses. Processes, 13(8), 2408. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082408







