TPG Conversion and Residual Oil Simulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
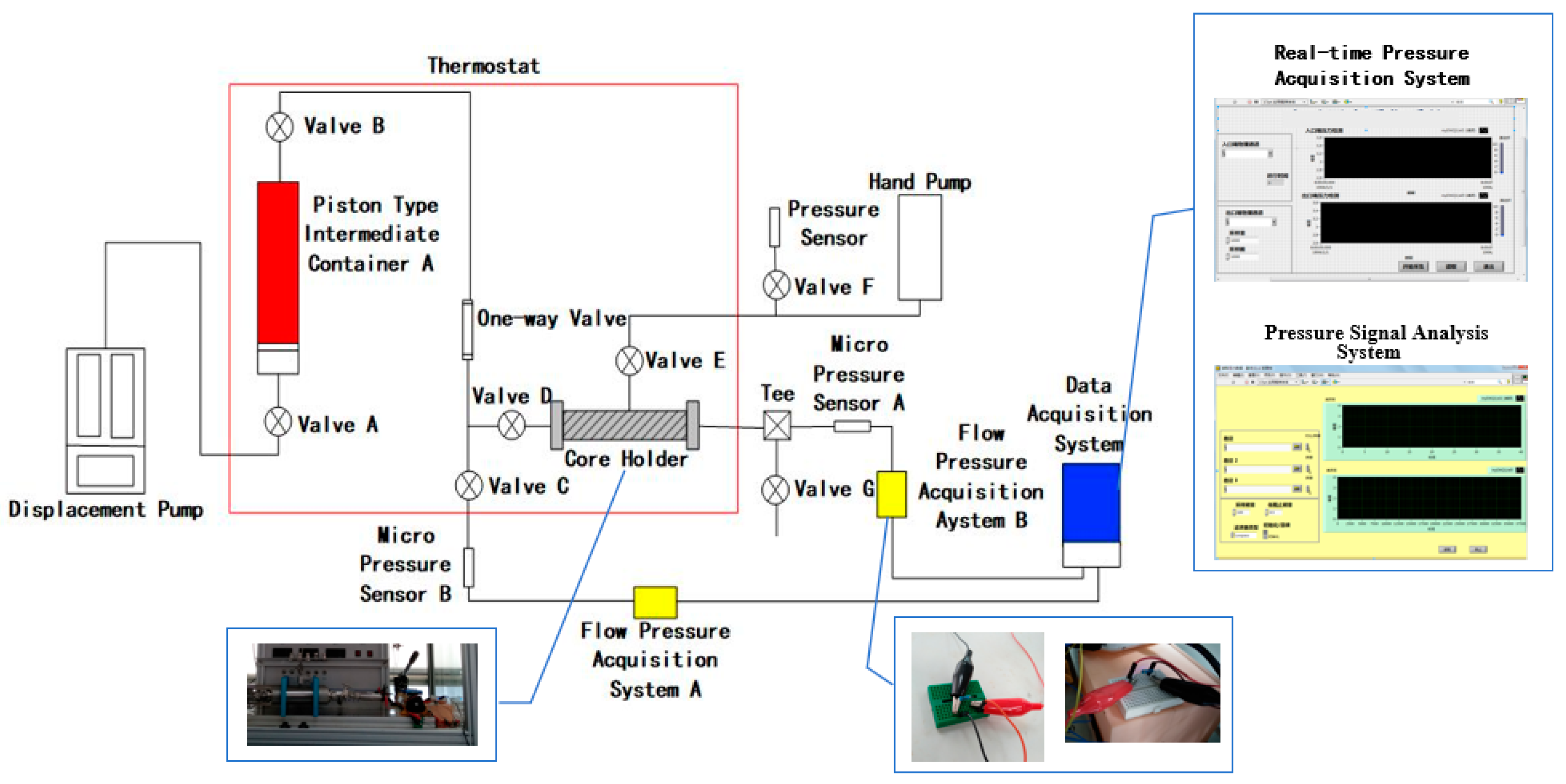
2.2.1. The Method for Measuring True Threshold Pressure Gradient (TTPG)
2.2.2. The Method for Measuring Pseudo-Threshold Pressure Gradient (PTPG)
2.2.3. Conversion Methods Between TTPG and TPTG
3. Numerical Method
3.1. Nonlinear Seepage
3.2. Flow Model
3.3. IMPES
3.4. The Nonlinear Seepage Simulator (NRSNL)
3.5. Establishment of Mechanistic Model
4. Results and Discussion
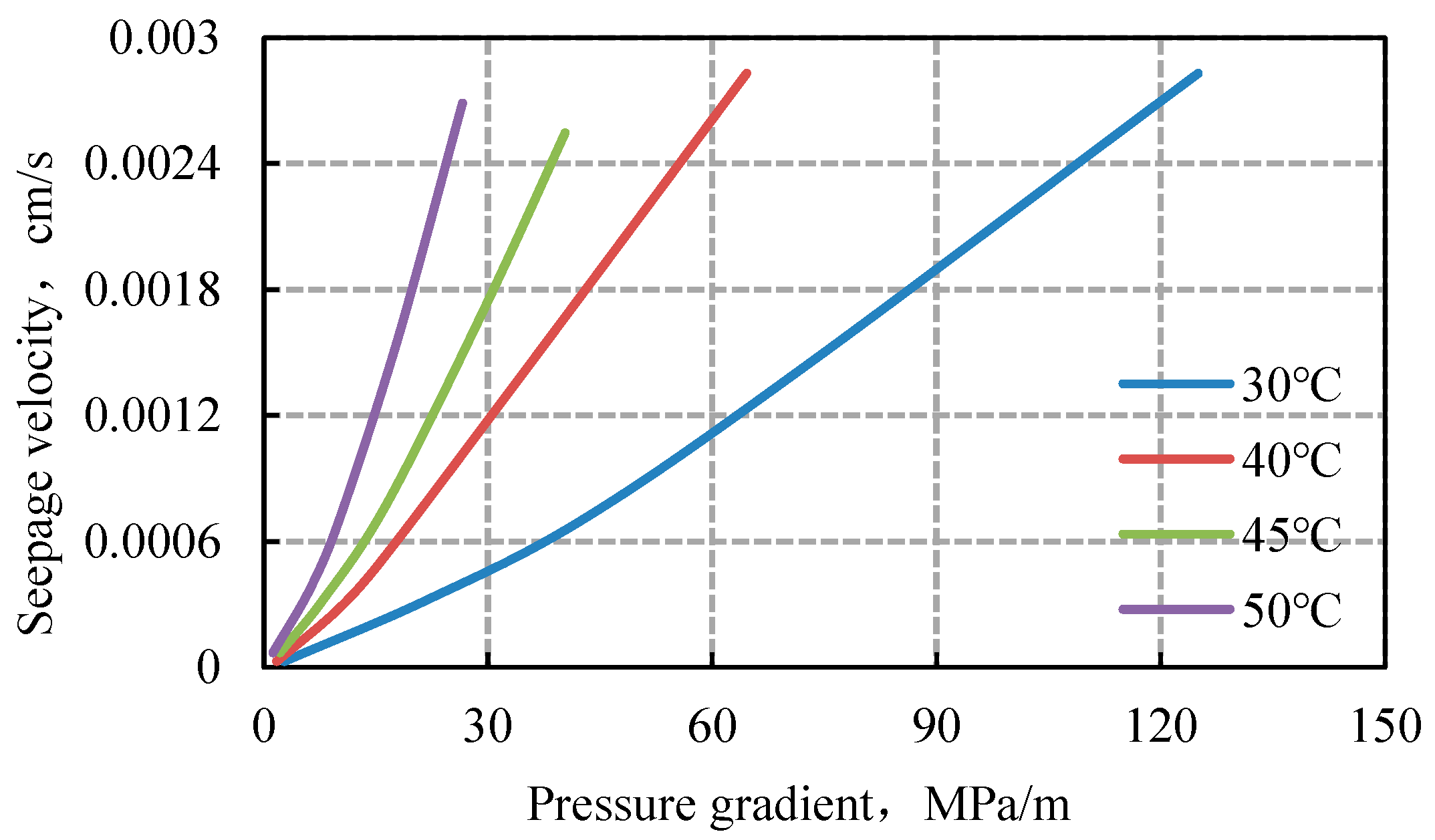
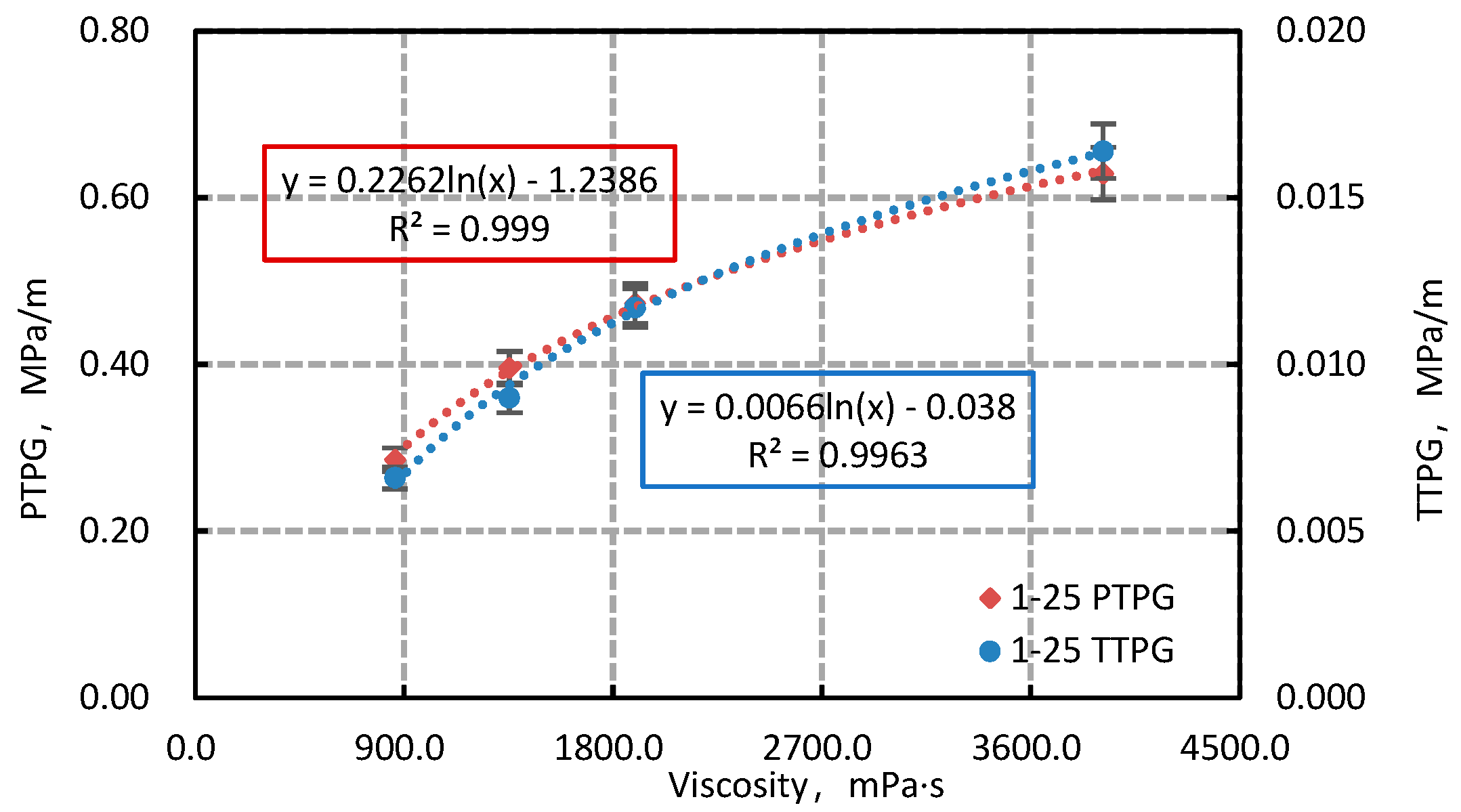
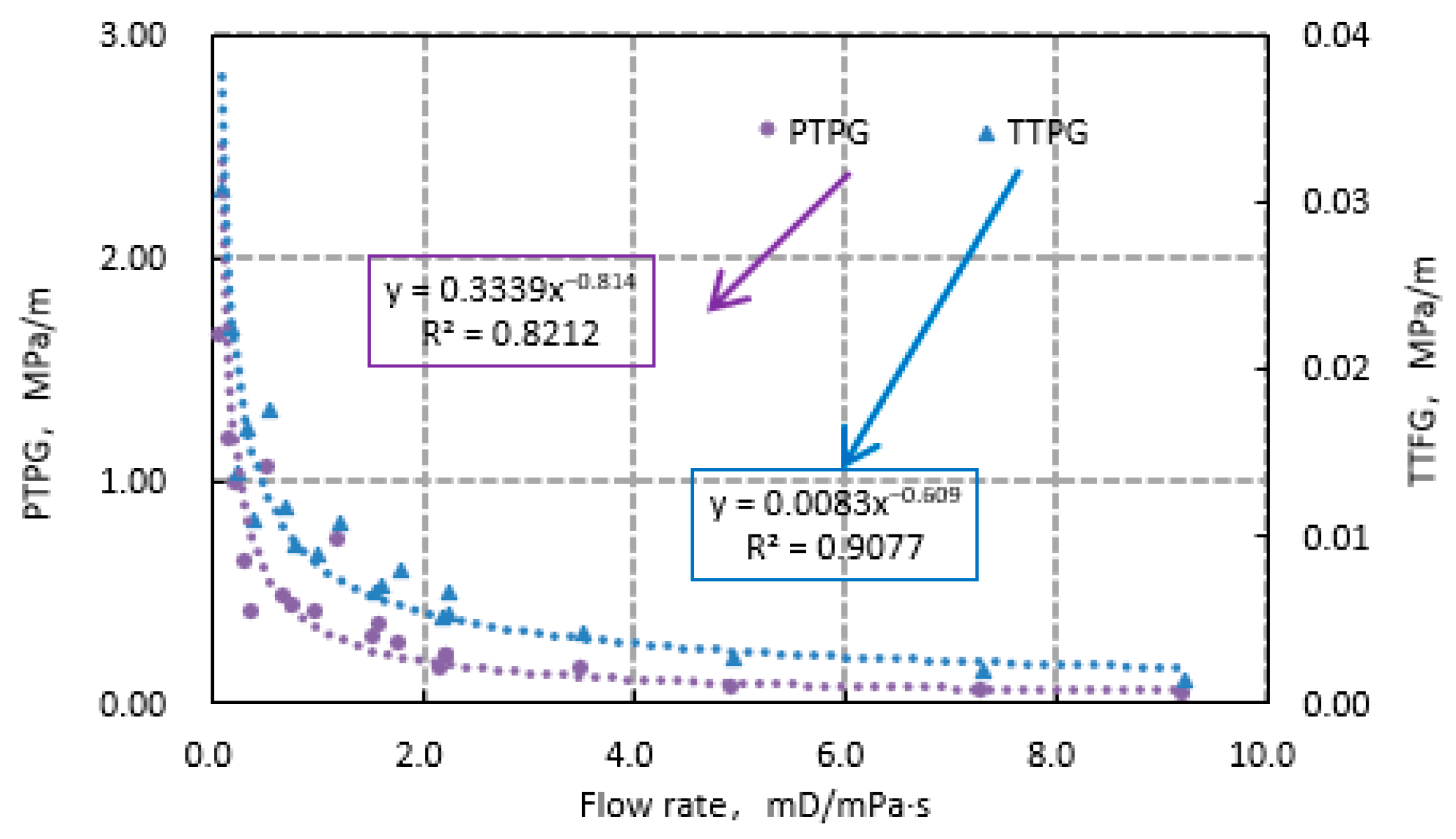
4.1. Conversion Relationship Between TTPG and PTPG
| Core Numbering | Heavy Oil Sample | Temperature, °C | Seepage Curve Fitting Equation | Correlation Coefficient | PTPG, MPa·m−1 | TTPG, MPa·m−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–8 | 2# | 30 | y = 0.0000170x − 0.0000280 | 0.9974 | 1.6471 | 0.0307 |
| 40 | y = 0.0000344x − 0.0000403 | 0.9928 | 1.1715 | 0.0225 | ||
| 45 | y = 0.0000498x − 0.0000488 | 0.9969 | 0.9799 | 0.0137 | ||
| 50 | y = 0.0000710x − 0.0000286 | 0.9917 | 0.4028 | 0.0110 | ||
| 1–25 | 2# | 30 | y = 0.0001103x − 0.0000694 | 0.9998 | 0.6292 | 0.0164 |
| 40 | y = 0.0002851x − 0.0001349 | 0.9992 | 0.4732 | 0.0117 | ||
| 45 | y = 0.0003876x − 0.0001534 | 0.9999 | 0.3958 | 0.0090 | ||
| 50 | y = 0.0005315x − 0.0001518 | 0.9999 | 0.2856 | 0.0066 | ||
| 1–49 | 2# | 30 | y = 0.0002901x − 0.0001241 | 0.9998 | 0.4278 | 0.0095 |
| 40 | y = 0.0005861x − 0.0001666 | 0.9999 | 0.3413 | 0.0070 | ||
| 45 | y = 0.0006855x − 0.0001408 | 0.9992 | 0.2054 | 0.0052 | ||
| 50 | y = 0.0008938x − 0.0001357 | 0.9997 | 0.1518 | 0.0042 | ||
| 1–7 | 1# | 30 | y = 0.0001786x − 0.0001866 | 0.9994 | 1.0441 | 0.0177 |
| 40 | y = 0.0003132x − 0.0002267 | 0.9994 | 0.7238 | 0.0108 | ||
| 45 | y = 0.0004536x − 0.0001151 | 0.9985 | 0.2537 | 0.0079 | ||
| 50 | y = 0.0006263x − 0.0001257 | 0.9998 | 0.2007 | 0.0067 | ||
| 1–24 | 1# | 30 | y = 0.0009229x − 0.0001312 | 0.9986 | 0.1422 | 0.0052 |
| 40 | y = 0.0015222x − 0.0000880 | 0.9991 | 0.0578 | 0.0027 | ||
| 45 | y = 0.0018016x − 0.0000759 | 0.9995 | 0.0421 | 0.0019 | ||
| 50 | y = 0.0021171x − 0.0000683 | 1.0000 | 0.0323 | 0.0014 |
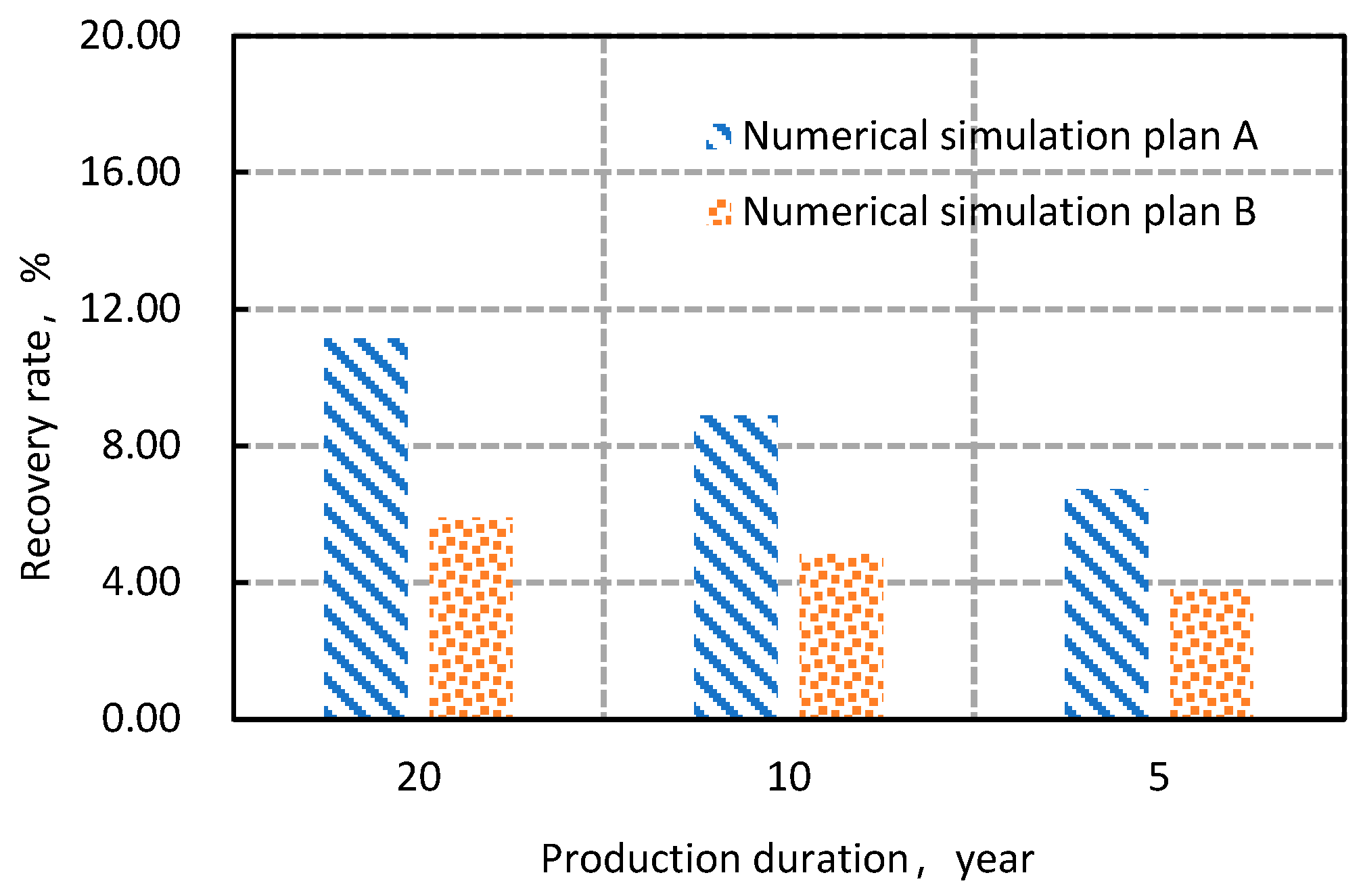
4.2. Numerical Simulation of Residual Oil in Heavy Oil Reservoirs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, C.; Gong, S.; Lai, J.; Huang, S.; Li, B.; Li, Y. Experimental analysis and research on physical properties of heavy oil in offshore oilfields. Petrochem. Technol. 2009, 26, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiecker, P.M.; Gawrys, K.L.; Trail, C.B.; Kilpatrick, P.K. Effects of petroleum resins on asphaltene aggregation and water-in-oil emulsion formation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 220, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K. Study on Cold—Production Technology for Heavy-Oil Reservoirs with Strong Edge and Bottom Water in Zhan29 Block of Taiping Oilfield. Petrochem. Technol. 2019, 26, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, M.; Fieldhouse, B. Studies on crude oil and petroleum product emulsions: Water resolution and rheology. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 333, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balhoff, M.T.; Thompson, K.E. Modeling the steady flow of yield stress fluids in packed beds. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 3034–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, A.R.; Radilla, G. Flow of yield stress and C arreau fluids through rough-walled rock fractures: Prediction and experiments. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 6197–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichting, H. Boundary Layer Theory; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, W.L.; Wang, W.Y.; You, Y.; Ouyang, Y.L.; Yang, L.J.; Li, Q.H. Research on determination method of start-up pressure gradient for nonlinear seepage. Petrochem. Ind. Appl. 2013, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dai, J.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Tu, Y. Experimental study on enhanced oil recovery of offshore heavy oil reservoirs in high-ultra-high water cut stage. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Yu, G.M.; Ke, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Ge, Y. Experimental study of nonlinear seepage for heavy oil. Pet. Exp. Geol. 2013, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.M. Porous Flow Mechanics for Low Permeability Reservoirs and Its Application. Grad. Sch. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2007, 22, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, P.F. Research on Petrosite heavy oil module algorithm. China New Technol. Prod. 2013, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L. The Numerical Simulation Applied Technological Research of Chang 7 Super-Low Permeability Reservoir Water Injection Development. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an Petroleum University, Xi’an, China, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, M. Nonlinear Seepage Behaviors of Pore-Fracture Sandstone under Hydro-Mechanical Coupling. Crystals 2022, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.M.; Yu, R.Z.; Su, Z.X. Numerical simulation of the nonlinear flow in ultra-low permeability reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2010, 37, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Qi, Z.L.; Tian, J.; Yan, W.D.; Huang, X.L.; Huang, S.W. Change law of reservoir property during multi-cycle steam stimulation in heavy oil reservoir: A case study of HJ Oilfield. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2022, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.L. Research on Nonlinear Percolation Law of Heavy Oil. Diploma Thesis, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Orgéas, L.; Idris, Z.; Geindreau, C.; Bloch, J.-F.; Auriault, J.-L. Modelling the flow of power-law fluids anisotropic porous media at low-pore reynolds number. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 4490–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, Z.; Sun, Z. A nonlinear seepage theory model is developed using nuclear magnetic experiment and fractal theory. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, H.L.; Zhao, W.; Luo, Q.S. A new nonlinear seepage model for clay soil considering the initial hydraulic gradient of microscopic seepage channels. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 154, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NB/SH/T 0509; Test Method for Separation of Asphalt into Four Fractions. National Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Ning, L.H. Experimental method and application of pressure gradient determination of heavy oil to be started. J. Coll. Univ. Petrochem. Ind. 2011, 24, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Xu, J.F.; Cheng, L.S. Characterization and physical simulation method of starting pressure gradient for common heavy oil. J. Southwest Univ. Pet. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2009, 31, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.K.; Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ke, W.; Kong, D.; Wu, K.; Chen, Z. Non-Newtonian Flow Characteristics of Heavy Oil in the Bohai Bay Oilfield: Experimental and Simulation Studies. Energies 2017, 10, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Study and Application of Numerical Simulation of Nonlinear Percolation of Heavy Oil in Water Drive. Master’s Thesis, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- You, X.; Li, S.; Kang, L.; Cheng, L. A Study of the Non-Linear Seepage Problem in Porous Media via the Homotopy Analysis Method. Energies 2023, 16, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Li, Z.C.; Yu, C.M.; Han, H.Y.; Wang, K.C.; Guo, L.Q.; Wang, K.; Yang, X. Threshold pressure gradient characteristics and drainage radius determination of low-permeability reservoirs. Oil Gas Geol. 2025, 46, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.T. Research status of threshold pressure gradient in low-permeability reservoirs. Neijiang Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Liu, R.; Meng, X.; Zhang, D.; Hu, Y. Evolution of the permeability and pore structure of transversely isotropic calcareous oil-bearing sediments subjected to triaxial pressure and high temperature. Eng. Geol. 2019, 253, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, Q.S.; Li, C.L.; Wu, S.; Yang, J.W. Study on occurrence state of oil and water in low permeability reservoir. Zhongzhou Coal 2021, 43, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.Q.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wang, X.R.; Zhu, X.L.; Wen, J.T. Research on Remaining Oil Distribution and Potential Tapping Limit of Offshore Thin Oil Reservoirs Considering Starting Pressure Gradient. J. Chongqing Univ. Technol. 2021, 23, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Luyu, W.; Chen, W.Z.; Sui, Q. Study of hydro-mechanical behaviours of rough rock fracture with shear dilatancy and asperities using shear-flow model. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 16, 4004–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














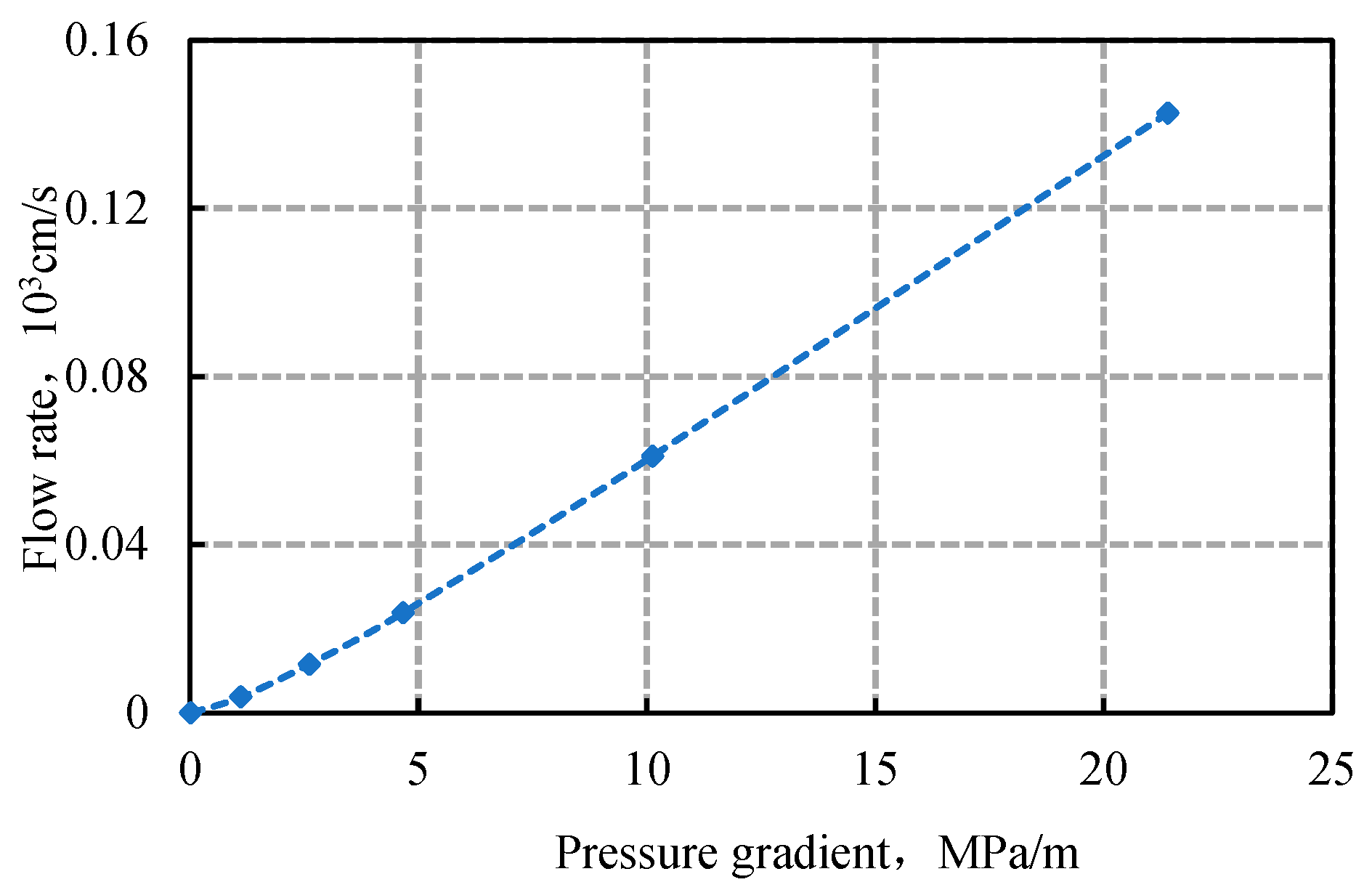



| Heavy Oil Sample Number | Saturate, % | Aromatic, % | Resin, % | Asphaltene, % | Viscosity at 30 °C, mPa·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 47.35 | 31.13 | 16.23 | 5.30 | 612.10 |
| 2# | 38.76 | 23.13 | 30.75 | 7.36 | 3912.65 |
| Core Number | Heavy Oil Sample | Length, cm | Diameter, cm | Porosity, % | Permeability, mD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–7 | 1# | 9.65 | 2.41 | 26.15 | 325.50 |
| 1–24 | 1# | 9.49 | 2.49 | 31.52 | 1331.32 |
| 1–8 | 2# | 9.04 | 2.50 | 24.80 | 328.07 |
| 1–25 | 2# | 9.47 | 2.48 | 31.23 | 1336.83 |
| 1–49 | 2# | 9.00 | 2.50 | 34.90 | 3021.33 |
| Numerical Simulation Plan | Application Model | Number of Layers | Permeability, mD | TTPG, MPa·m−1 | PTPG, MPa·m−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Model (1), Equation (1) | 1 | 300 | 0.0058 | 0.2121 |
| 2 | 600 | 0.0037 | 0.0963 | ||
| 3 | 900 | 0.0029 | 0.0546 | ||
| B | Model (2), Equation (2) | 1 | 300 | / | 0.2121 |
| 2 | 600 | / | 0.0963 | ||
| 3 | 900 | / | 0.0546 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q. TPG Conversion and Residual Oil Simulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Processes 2025, 13, 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082403
Ke W, Li Z, Liu Q. TPG Conversion and Residual Oil Simulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082403
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Wenli, Zonglun Li, and Qian Liu. 2025. "TPG Conversion and Residual Oil Simulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs" Processes 13, no. 8: 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082403
APA StyleKe, W., Li, Z., & Liu, Q. (2025). TPG Conversion and Residual Oil Simulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Processes, 13(8), 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082403






