Abstract
Despite notable advancements in smart home technologies, residential energy management continues to face critical challenges. These include the complex integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, issues related to data latency, interoperability, and standardization across diverse systems, the inflexibility of centralized control architectures in dynamic environments, and the difficulty of accurately modeling and influencing occupant behavior. To address these challenges, this study proposes an intelligent multi-agent system designed to accurately estimate and control energy consumption in residential buildings, with the overarching objective of optimizing energy usage while maintaining occupant comfort and satisfaction. The methodological approach employed is a hybrid framework, integrating multi-agent system architecture with system dynamics modeling and agent-based modeling. This integration enables decentralized and intelligent control while simultaneously simulating physical processes such as heat exchange, insulation performance, and energy consumption, alongside behavioral interactions and real-time adaptive responses. The system is tested under varying conditions, including changes in building insulation quality and external temperature profiles, to assess its capability for accurate control and estimation of energy use. The proposed tool offers significant added value by supporting real-time responsiveness, behavioral adaptability, and decentralized coordination. It serves as a risk-free simulation platform to test energy-saving strategies, evaluate cost-effective insulation configurations, and fine-tune thermostat settings without incurring additional cost or real-world disruption. The high fidelity and predictive accuracy of the system have important implications for policymakers, building designers, and homeowners, offering a practical foundation for informed decision making and the promotion of sustainable residential energy practices.
1. Introduction
1.1. Context
The accurate estimation and effective control of energy consumption in residential buildings have emerged as critical areas of study, driven by escalating energy costs, growing environmental concerns, and the increasing demand for intelligent, user-centric building solutions. Despite technological advancements, several persistent challenges remain unresolved. These include the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, issues surrounding data latency, interoperability and standardization across heterogeneous systems, and the limitations of centralized control systems in dynamic and multi-variable environments. Additionally, modeling and influencing occupant behavior present substantial complexity. This paper identifies a fundamental gap in the current approaches: while many models address specific aspects of the energy management problem, few offer a comprehensive, decentralized, and adaptive framework that integrates user behavior, thermodynamic modeling, and intelligent control mechanisms. To address this gap, the present paper proposes a hybrid framework that combines Multi-Agent Systems (MASs) with System Dynamics Modeling (SDM) and Agent-Based Modeling (ABM). The main goal is to develop a system to optimize energy consumption in residential buildings while ensuring user comfort and responsiveness to environmental changes.
The paper is structured as follows. The next section presents a literature review outlining the key developments and gaps in existing energy management strategies. This is followed by a detailed description of the proposed methodology. It provides a background on MASs and the Net Logo simulation environment. This section establishes the theoretical and technical foundations for the proposed model. Thereafter, the architectural design and simulation framework are discussed. This section outlines the key components of the model, such as the agents representing building elements and the functions used to calculate energy consumption, leading into the results and validation section.
This section presents the results of five test scenarios designed to evaluate the performance of the MAS model under various conditions, highlighting the model’s ability to simulate energy consumption patterns and identify optimal energy-saving strategies accurately. The paper concludes with a summary of the findings, discussing the practical implications for policymakers, building designers, and homeowners. This section emphasizes the contribution of the research to the field of building energy optimization and suggests future research directions.
1.2. Literature Review
The estimation and control of energy consumption in residential buildings have attracted increasing attention due to growing environmental concerns, rising energy costs, and the push for smarter, user-centric building technologies. Despite significant advancements, several challenges persist in developing efficient, adaptive, and scalable energy management systems. One of the foremost challenges is the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into residential energy systems. The variability of these sources makes it difficult to maintain a stable balance between supply and demand. This calls for the development of advanced forecasting models and adaptive control algorithms capable of optimizing energy usage without compromising grid stability. Li et al. [1] emphasize the importance of smart energy systems that coordinate renewable energy integration through coherent infrastructure and dynamic control. Similarly, Lund et al. [2] proposes the use of deep reinforcement learning for responsive and resilient smart grid energy management. Recent developments in deep reinforcement learning (DRL) have demonstrated enhanced capabilities for real-time residential energy optimization. For instance, multi-agent DRL frameworks using proximal policy optimization (PPO) and soft actor–critic (SAC) has shown promise in controlling HVAC systems while learning occupant preferences over time [3,4]. Integrating such approaches could augment the intelligence and adaptability of MAS frameworks.
Modern smart homes rely on dense sensor networks and IoT devices to monitor and control energy usage in real time. However, challenges related to data latency, interoperability, and standardization hinder the seamless operation of such systems. Gungor [5] identifies the need for robust communication protocols and scalable infrastructure to manage large volumes of heterogeneous data. The lack of uniform standards often results in bottlenecks, as highlighted by Mourshed’s [6] integration. For example, different vendors may use incompatible data formats or communication protocols, making it difficult for devices to share information or operate in a coordinated manner. This fragmentation can degrade the performance of learning-based models, as inconsistent or incomplete data reduces the accuracy of demand forecasts and undermines control optimization. In effect, without standardized inputs, intelligent systems struggle to adapt across various smart home configurations, leading to suboptimal energy management.
Centralized control systems are often inadequate for managing complex residential energy environments, especially when scaling to multi-zone or community-level scenarios. Decentralized control mechanisms, such as those enabled by hierarchical or distributed multi-agent system (MAS) architectures, offer improved fault tolerance and responsiveness. Lo [7] and Xu [8] demonstrate that decentralized and hierarchical multi-agent systems can significantly enhance the efficiency of energy management in large-scale and dynamic environments. Estimating energy consumption accurately requires understanding and predicting occupant behavior, which is inherently variable and context dependent. Standard rule-based models often fail to reflect the nuances of human behavior. Dragomir [9] and Patel [10] introduce adaptive learning models and smart sensors that collect data on occupant activities and preferences to dynamically adjust environmental parameters such as temperature and lighting, ensuring both energy efficiency and comfort. This focus on behavioral variability directly ties into the relevance of MASs, which offers a flexible framework to model and manage these dynamic and decentralized interactions. Since these tools can represent both the physical infrastructure and human agents, they are particularly suited for capturing the relations between occupant behavior and energy consumption, enabling more accurate energy estimation and adaptive control. User behavior plays a critical role in residential energy consumption. Therefore, systems must engage occupants meaningfully to encourage sustainable energy practices. Bahman [11] and Ahmed [12] show that gamification, personalized feedback, and real-time consumption dashboards can effectively promote energy-saving behavior. Additionally, Sun [13] applies data-driven behavioral analytics to personalize energy interventions and foster long-term engagement. The widespread adoption of interconnected energy management systems has heightened concerns around cybersecurity and data privacy. Gomez [14] highlights the risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access in smart grids, advocating for strong encryption, anonymization, and regulatory compliance to protect user data.
Building on this, multi-agent systems represent a promising architecture for managing complex residential systems due to their distributed decision-making capabilities. MASs can simulate and predict energy consumption through the collaboration of autonomous agents. Wooldridge [15] provides a foundational overview of MASs, underscoring their utility in distributed control settings. Practical implementations, such as those by Dragomir [16] and Santos [17], demonstrate the ability of MAS-based platforms to simulate demand–response programs and optimize energy flows within residential environments. Furthermore, Tang [18] and Prouzeau [19] highlight how MASs can incorporate adaptive learning, behavioral modeling, and user feedback to refine control strategies over time.
However, despite the growing number of real-world smart building deployments post-2022, such as the EU Smart Readiness Indicator pilot projects and DOE-funded trials in the U.S., these empirical data sources remain underutilized in MAS validation. Future work should leverage these field-tested datasets to better assess system reliability and generalizability. Recent studies conducted by Dragomir and Wang [3,20] have explored hybrid AI models and real-time demand-response applications, highlighting the growing complexity of residential energy systems. However, few have adopted an integrated MAS-SDM-ABM framework as proposed in this study. Furthermore, validations often rely solely on simulated benchmarks without real-world data comparison. Our approach seeks to bridge this gap by offering cross-validation with empirical profiles in future work.
Given the complexity and interdependence of modern residential energy systems, a MAS-based tool specifically designed for energy estimation and control offers a compelling approach. Such a system would enable real-time responsiveness, behavioral adaptation, decentralized coordination, and enhanced user engagement, addressing the core challenges identified in current research. Building upon these existing methodologies, the present paper adapts a systematic agent role design approach, originally proposed in previous works, to define agent behaviors and interactions in residential energy systems. However, unlike prior models, this framework integrates thermodynamic and behavioral simulations in a unified platform.
The contribution of this paper is to address a critical gap in literature: the lack of integrated frameworks that simultaneously model physical system dynamics, user behavior, and intelligent control. The specific objectives addressed in this research are to develop an intelligent, decentralized energy management system; to integrate behavioral and thermodynamic modeling into a coherent framework; and to validate the system across a range of building types and environmental conditions.
2. Methodology
Enhancing energy efficiency in residential buildings requires not only technological integration but also advanced computational tools capable of modeling dynamic and heterogeneous consumption behaviors. In response to this demand, the present paper proposes a methodologically based MAS designed to simulate, control, and estimate energy consumption in a residential environment.
The MAS model was developed using NetLogo v 6.3.1 [21]. Parameters such as house size (m2), insulation factor (leakage percentage), and thermostat settings were varied using sliders. Agents were designed to represent HVAC components, walls, sensors, and occupant profiles. Each scenario ran for 5000 ticks, simulating a 24 h cycle, with results collected at 10 min intervals. The hardware used was Intel i8/i4 processors. Energy consumption was calculated using thermodynamic functions as outlined in Equations (1)–(5).
Given the complexity of residential energy ecosystems, where multiple, interdependent components interact under varying environmental and behavioral conditions, traditional modeling techniques often fall short. The MAS paradigm offers a robust computational framework for representing such systems. Each agent within a MAS operates as an autonomous software entity capable of perceiving, reasoning, and acting based on localized knowledge and shared goals. This autonomy and distributed intelligence make MASs particularly well-suited for energy management scenarios characterized by decentralized control and dynamic adaptation.
Dragomir et. Al have proposed in [22] a general framework for intelligent behavior, precisely a general cognitive agent architecture based on the BDI (Belief–Desire–Intention) model, designed to support autonomous decision making in a wide range of intelligent systems. It includes abstract components such as beliefs, desires, intentions, reasoning mechanisms, and effectors, making it suitable for modeling complex agent behavior across various domains. This architecture emphasizes goal-oriented reasoning and adaptive planning, with no specific application context.
The methodological approach followed in this article (see Figure 1) is a systematic one and relies on identifying the energy system’s functional and non-functional requirements, including energy estimation accuracy, adaptability, and user comfort, and assigning specific roles and responsibilities to each agent. For example, individual agents may represent HVAC units, lighting systems, appliances, or even occupants. Each intelligent agent is autonomous, uniquely identifiable, and self-contained. Agents operate independently but adjust behaviors based on real-time interactions with other agents and their environment. Their decisions are driven by specific goals and evaluated using utility functions, which balance comfort and energy efficiency. Each intelligent agent in the system is self-contained, uniquely identifiable, and autonomous in its decision making. Agents operate autonomously, yet their behavior is continuously changed by real-time interactions with both other agents and their surroundings. Driven by specific objectives, these agents rely on utility functions to evaluate outcomes, aiming to balance energy efficiency with comfort preservation. Agents demonstrate four essential capabilities: autonomy, making independent decisions without centralized control; reactivity, meaning responding to environmental changes such as occupancy or weather conditions; proactivity, proved by anticipating future states and taking initiative, e.g., pre-cooling a room based on forecasted occupancy; and social ability, composed of cooperating, negotiating, or competing with other agents to optimize collective outcomes.
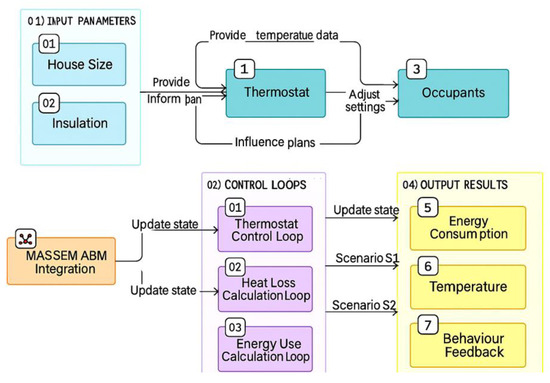
Figure 1.
Systematic methodological approach adapted from [22].
In the proposed system, each agent models a distinct energy-consuming or environmental element in a residential building. These include appliances, thermostats, occupancy sensors, and even user behavior profiles. Agents operate within a shared virtual environment, exchanging data to collectively estimate total energy consumption and to make localized control decisions. This interaction mirrors real-world interdependencies between systems (e.g., heating affected by occupancy and insulation quality). Through ongoing communication and feedback, agents continuously refine their internal models, enabling the system to learn and adapt to changing conditions over time. This adaptability supports real-time energy estimation and the implementation of optimized control strategies, such as load-shifting, demand-response, and behavioral nudges.
While the referenced approach offers a flexible, general framework for intelligent behavior, Figure 1 illustrates the structured design process guiding the MAS implementation, being tailored for detailed analysis and evaluation of system performance within a specific, practical application. The approach has been expanded to include additional agent behaviors and interaction flows that reflect the specific objectives of this study.
The methodology emphasizes the systemic decomposition of a building’s energy context into intelligent, interactive components, allowing for fine-grained control, transparent estimation, and scalable deployment across diverse residential scenarios.
In conclusion, this methodological framework leverages the core strengths of MAS: modularity, adaptability, and decentralized intelligence to develop a tool capable of accurately estimating and managing energy consumption in residential buildings. It provides a foundation not only for simulation but also for real-world implementation in smart home environments. Following the design principles of the GAIA methodology [23] and aligned with contemporary MAS development strategies [22], the implementation emphasizes autonomy, interactivity, and adaptability of agents within a structured decision-making environment.
Thus, the next section describes in detail the development of the system architecture, the modeling framework, and the functional design of control loops and estimation formulas, serving as a bridge between the conceptual foundation and the simulation-based validation.
3. Model Architecture
The increasing complexity of residential energy systems, coupled with the need for personalized, adaptive control strategies, demands a methodological framework that is both modular and dynamic. Specifically, the system aims to control indoor temperature based on user-defined comfort levels, to simulate and analyze various insulation and usage scenarios, and to dynamically adapt system parameters in real-time to reduce unnecessary energy use. While the model incorporates occupant profiles via agents, it currently assumes static behavior. Enhanced modeling of dynamic behavioral routines, such as daily schedules, adaptive comfort preferences, and response to pricing signals, could be achieved using probabilistic rule sets or machine learning-based pattern recognition.
To address these requirements, this paper proposes a hybrid methodological approach, combining MAS architecture with system dynamics modeling (SDM) and agent-based modeling (ABM) techniques. The MAS enables decentralized, intelligent control of building subsystems, while the SDM and ABM components allow for detailed simulation of physical processes and behavioral interactions. The integration of MAS with SDM and ABM results in a comprehensive model capable of capturing macro-level system behavior (SDM), micro-level agent interactions (ABM), and distributed decision making (MAS). This layered architecture allows for both high-level policy testing and low-level operational adjustments, enhancing system robustness and realism.
The system architecture integrates agent-based modeling for user behavior and control logic and system dynamics modeling for physical processes such as heat exchange, insulation performance, and energy consumption. Agents are responsible for managing localized tasks (e.g., thermostat control, sensor interpretation) and operate in a shared environment informed by SDM components. This hybrid framework supports both real-time feedback and predictive scenario testing.
MASs can maintain house temperature across varying conditions related to the outside temperature (), inside temperature (, reference temperature in the house (), house insulation (, the house size , with a certain amount of energy consumed (see Figure 2).
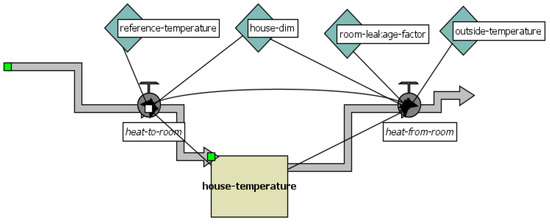
Figure 2.
SDM model workflow.
The SDM model is correlated with the ABM to highlight the interactions between parameters and variables. Three primary control loops are integrated in the thermal management dynamics: thermostat control loop activates the furnace when the indoor temperature falls below the target threshold, increasing the temperature until it stabilizes. Heat Loss Loop models the inverse relationship between temperature increase and heat dissipation to the external environment. The energy consumption loop captures the trade-off between thermal gains and increased energy use, particularly under poor insulation conditions. These interrelated loops are influenced by external weather conditions and internal building characteristics, which the system continuously monitors and adjusts through agent decisions (see Figure 3).
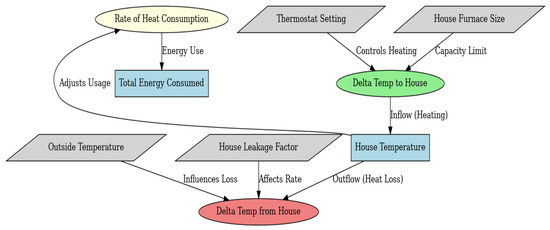
Figure 3.
ABM model.
Three control loops have been identified in the house dynamics: the thermostat one increases the furnace heat output when the house temperature is lower than the thermostat setting. This raises the house temperature, eventually stabilizing near the thermostat setting. The second one is related to heat loss. As house temperature increases, heat loss to the environment also increases. It acts as a balancing force, reducing the temperature. The energy consumption loop increases furnace heat output leading to higher energy consumption. If it is not managed properly, this can lead to excessive energy use. These three loops work in concert to maintain comfort while minimizing energy expenditure. By dynamically adjusting based on both internal state and external environment, the system ensures efficient load management, especially under extreme weather or poor insulation conditions. Thus, the variables are incorporated into the model’s calculations through functions (inside and outside flows) and then are used to evaluate the system’s estimation and control performances (1).
Delta-temperature () computes the heating requirement to achieve the target indoor temperature (2):
Delta temperature-to-house () determines the adjustment to the indoor temperature needed to offset heat loss to the outside environment. It modifies the value calculated by to account for heat loss due to the temperature difference between inside and outside (3).
Delta temperature-from-room () calculates the heat loss from the room to the outside considering the room leakage factor and the temperature difference between inside and outside (4).
The rate-of-heat-consumption () is used to compute the energy consumption rate required to maintain the desired indoor temperature, considering the adjustments for heat loss (5).
The equations assume constant thermal transmittance, linear heat exchange, and stable occupancy, which simplifies computation but may reduce fidelity under rapid occupancy changes or nonlinear material responses. Sensitivity analysis and stochastic modeling could improve robustness. These equations are adapted from standard thermodynamic models, proposed by American Society of Heating is [24], used in building energy simulations. They model temperature differentials, insulation performance, and heat flow, enabling the MAS agents to estimate real-time energy consumption accurately.
The agent-based model dynamically visualizes indoor and outdoor temperatures, thermostat behavior, and cumulative energy consumption over time. Each agent, representing a control element, evaluates its actions based on system feedback and interacts with others to coordinate decisions. For instance, an HVAC agent may reduce output in response to favorable weather, while an insulation agent may adjust parameters to minimize loss. This behavioral modeling not only supports operational control but also enables real-time simulation analysis. Users can observe how temperature, insulation quality, and energy usage evolve under different configurations. The system can be used to test multiple strategies, identify cost-effective insulation levels, and refine thermostat schedules. By integrating dynamic system modeling with intelligent, decentralized control, the MAS-based tool can replicate real-world residential scenarios with high fidelity.
The following section presents a series of simulations that evaluate the system’s performance under varying insulation levels, temperature profiles, and user-defined comfort settings. These simulations validate the model’s accuracy, responsiveness, and potential for real-world application.
4. Simulation Framework
The simulation approach relies on NetLogo v 6.3.1. [21], a programming and simulation environment suitable for modeling complex systems, especially agent-based simulations. This software platform has open user access and provides a flexible virtual environment for testing different scenarios and optimization strategies. NetLogo provides accessibility, visual feedback, and agent interaction tools, making it ideal for prototyping. However, it lacks native support for high-fidelity thermodynamic modeling or real-time data integration.
The MAS consists of four primary agent types that collectively manage residential energy dynamics. The Thermostat Agent regulates heating by activating or deactivating the system based on target temperatures. The Sensor Agent continuously monitors both indoor and outdoor thermal conditions. The Energy Tracker Agent calculates cumulative and daily energy consumption, while the Occupant Agent models user interactions, such as adjusting thermostat settings or opening windows. These agents operate through three interconnected feedback loops: the thermal control loop, which maintains indoor temperature stability; the heat loss loop, which captures thermal dissipation to the environment; and the energy loop, which monitors energy usage and cost, subsequently informing agent decision making. This structure enables adaptive, responsive energy control within the designed environment. Although NetLogo v 6.3.1. offers accessibility and ease of use for agent-based modeling, it lacks integration with advanced energy simulation engines such as EnergyPlus, Modelica, or UrbanOpt. These platforms enable high-resolution thermodynamic modeling and facilitate co-simulation with building energy performance tools. Future extensions could consider hybrid approaches leveraging NetLogo v 6.3.1. for agent logic and EnergyPlus for physics-based validation.
The MAS-based application simulated in Net Logo v 6.3.1. consists of a series of objects placed on a graphical user interface (see Figure 4). The user can set the indoor temperature to satisfy his comfort needs. For example, 22 °C, as shown in Figure 4. The environmental conditions represented by the outdoor temperature, the size of the house, the thermostat setting slider, and the room leakage factor associated with the degree of insulation of the house are integrated as object-oriented sliders. The monitors in the model are integrated to visualize the variation in inside temperature and the rate of heat consumption.
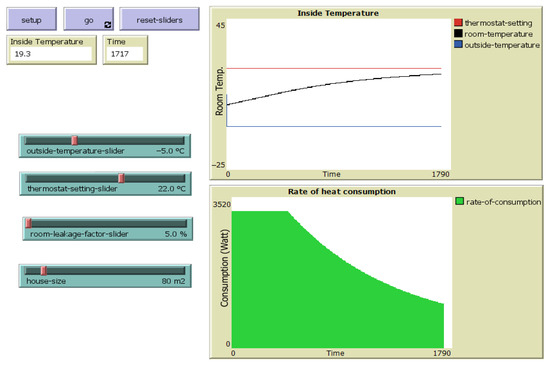
Figure 4.
House heating system simulation interface.
The information flow behind these object-oriented agents is assigned using procedural programming. The model, as shown in Figure 4, based on an initial house and outside temperature, thermostat, and furnace settings, determines the heat consumption of distinct types of houses. It can update dynamically, tracking energy consumption and temperature changes over time. Furthermore, the users have the possibility, due to the software environment, to plan different scenarios and to simulate them using the trial-and-error method, with no risk or extra cost. Thus, it removes the user from a potentially hazardous environment. By varying parameters like house size, thermostat settings, and insulation levels, the model simulates a broad spectrum of use cases. This enables designers and policymakers to perform comparative analysis and identify cost-effective configurations tailored to specific climates.
The simulation scenarios were deployed to ensure that the MAS architecture and interactions effectively address the complexity of the building characteristics. The scenarios were defined based on thermal modeling standards from ISO 13790 [25] and reflect seasonal temperature profiles and typical European housing sizes. The insulation quality and external temperatures were varied to simulate real-world conditions. The validation of the MAS behavior and the verification that meets the desired performance criteria represented the main challenges of the simulation.
4.1. Scenario 1
This is considered a well-insulated house (Low-E), having a heat loss rate of 15%. The simulation conditions are the outside temperature of −25 °C (in the winter season), thermostat setting of 22 °C, and house size of 83 m2. The simulation results (Figure 5) show that the system successfully maintained the indoor temperature at 22 °C, as expected, with a high energy consumption of approximately 46.4 kW per day, translating to 1.4 MW per winter month and a consumption rate of 16.85 kW/m2/per winter month. The high energy usage results from the substantial temperature difference between the interior and exterior environments.
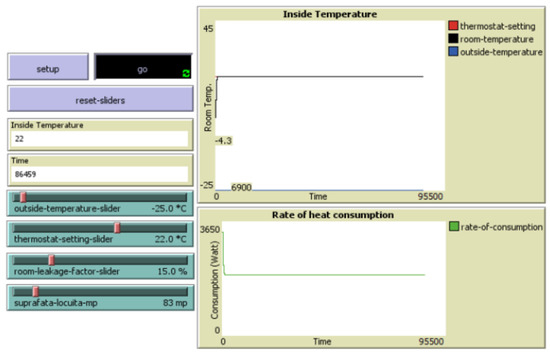
Figure 5.
Well-insulated house (Low-E) in cold winter conditions.
4.2. Scenario 2
The hypothesis for scenario 2 is that the outside temperature is 10 °C, the thermostat setting is 22 °C, there is a heat loss of 15%, and the building size is 83 m2 (Figure 6). Low energy consumption was expected due to the slight temperature difference between inside and outside. As anticipated, the system maintained the indoor temperature at 22 °C with a low energy consumption of about 12 kW per day (360 kW per spring or autumn month), resulting in a consumption rate of 4.33 kW/m2 per spring or autumn month. The results demonstrate a direct correlation between outside temperature and energy consumption. And highlight the importance of considering local climate conditions when designing energy-efficient buildings.
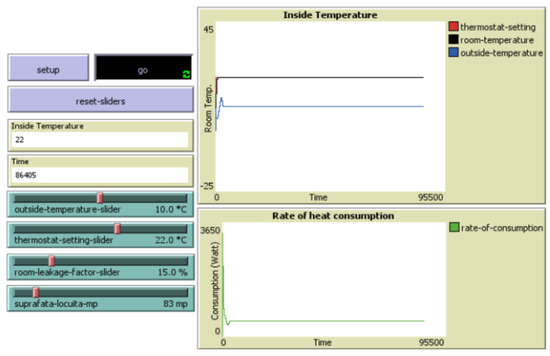
Figure 6.
Well-insulated house (Low-E) in mild conditions (spring or autumn seasons).
4.3. Scenario 3
Scenario 3 considered a passive house design in the hypothesis of an outside temperature of −30 °C (in winter season), a thermostat setting of 22 °C, a heat loss of 5%, and a building size of 100 m2. The system maintained the indoor temperature at 22 °C with a moderate energy consumption of approximately 20.85 kW per day (625.5 kW per winter month), resulting in a consumption rate of 6.25 kW/m2 per winter month. This outcome is notable for achieving a low energy consumption despite a substantial temperature difference of 52 °C, highlighting the effectiveness of passive house design in reducing energy needs (Figure 7).
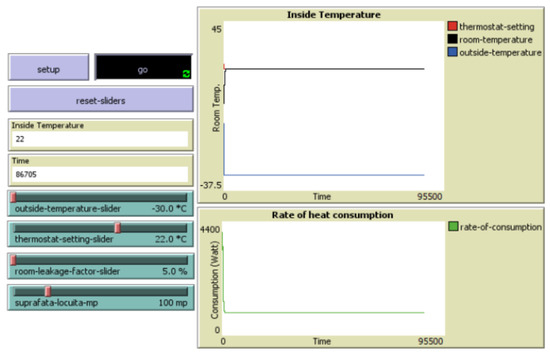
Figure 7.
Passive house in icy winter conditions.
Passive houses achieve superior energy efficiency through airtight construction, high-performance insulation, triple-glazed windows, and heat recovery ventilation. These features drastically reduce heat loss, which is reflected in the lower simulated energy consumption across scenarios.
4.4. Scenario 4
Scenario 4 initially sets the outside temperature to 0.5 °C, the thermostat setting to 22 °C, the heat loss to 5%, and the building size to 100 m2. In this context, the system maintained the indoor temperature at 22 °C with the lowest energy consumption among all scenarios, at approximately 8.8 kW per day (256 kW per spring or autumn month) and a consumption rate of 2.64 kW/m2 per spring or autumn month (Figure 8). Low energy consumption due to the slight temperature difference and the efficient insulation of the passive house was expected as an outcome.
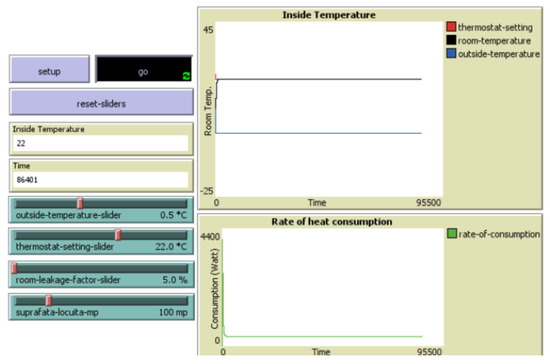
Figure 8.
Passive house in mild spring or autumn conditions.
Scenario 5: Low-E house at −20 °C and Scenario 6: Passive house at −25 °C simulate more extreme winter conditions (−20 °C and −25 °C, respectively) to evaluate the MAS system’s robustness under high-demand environments. These cases further validate the model’s accuracy and scalability under severe external conditions.
Overall, all these scenarios have validated the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed Net Logo MAS system in simulating different energy consumption patterns. The model’s ability to accurately reflect the impact of several factors, including house insulation, outside temperature, and thermostat settings, makes it valuable for understanding energy use dynamics and exploring energy-saving strategies.
Future extensions of the proposed work could consider hybrid approaches leveraging NetLogo for agent logic and EnergyPlus for physics-based validation because these platforms (e.g., EnergyPlus [26], Modelica [27], or UrbanOpt [28]) enable high-resolution thermodynamic modeling and facilitate co-simulation with building energy performance tools.
5. Tests and Validation
To evaluate the performance of the MAS, this paper considered four case studies. The simulation environment replicates a temperate-climate residential zone representative of Central European housing stock. This choice reflects the relevance of insulation and seasonal variation in energy use. The house sizes and leakage factors are based on EU building energy guidelines. Each one focuses on a specific combination of parameters, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of the instant heating energy consumption [W] (case study 1—CS1), average daily heating energy consumption [kW] (case study 2—CS2), monthly heating energy consumption [kWh/m2/month] (case study 3—CS3), and annual heating energy consumption (case study 4—CS4) of Low-E and passive house types. In every case study, the values of inside desired reference temperature [°C] were considered as 22 °C.
Case study 1: The outcomes of MAS, in case study 1—CS 1, presented in Table 1, have aligned well with the estimated values for instant heating energy consumption data [W] (Figure 9). The correlation between them, measured with R2, is 0.9353 for passive houses, better than in the case of well-insulated houses 0.5251.

Table 1.
MAS tests in case studies 1 and 2 (CS1 and CS2).
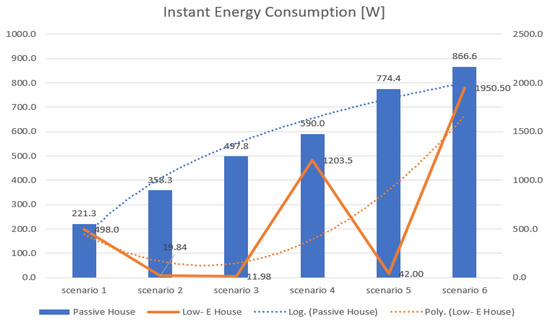
Figure 9.
Instant heating energy consumption for passive houses (blue) and Low-E houses (orange).
Case study 2: Average daily heating energy consumption [kW]
The relative efficiency for evaluating the accuracy of the MAS predictor feature is confirmed in CS2 by the correlation coefficient R. Furthermore, the accuracy of the implemented formulas in the proposed MAS system is presented in Figure 10. The outcomes underscore the importance of investing in high-quality insulation of the houses to minimize heat loss and reduce energy needs and carbon footprints.
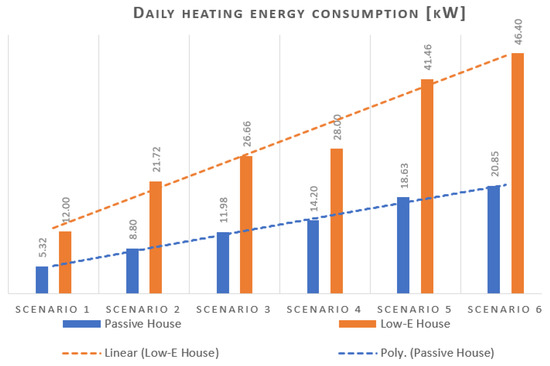
Figure 10.
Average daily heating energy consumption for passive houses (blue) and Low-E houses (orange).
Case study 3: Monthly heating energy consumption [kWh/m2/month].
Figure 11 indicate the errors in both cases, between monthly heating energy consumption (for the winter months) estimated by MAS (blue) and the reference values in the scientific literature (orange): less than 3 [kWh/m2/winter month] monthly heating energy consumption in the case of passive house and above 10 [kWh/m2/winter month] monthly heating energy consumption in case of Low-E houses. The error in the testing process increases with the time prediction horizon.
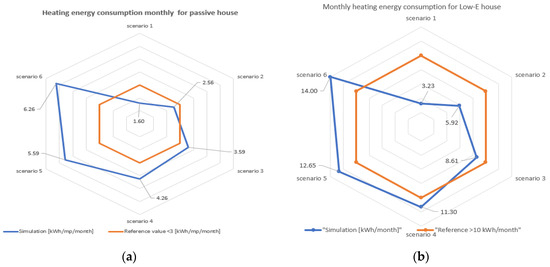
Figure 11.
(a) Monthly heating energy consumption for passive house in the winter; (b) monthly heating energy consumption for Low-E houses in the winter.
On the other hand, Figure 12 shows how closely correlated the values R2 = 0.9975 (Low-E house) and R2 = 0.9943 (passive house) are.
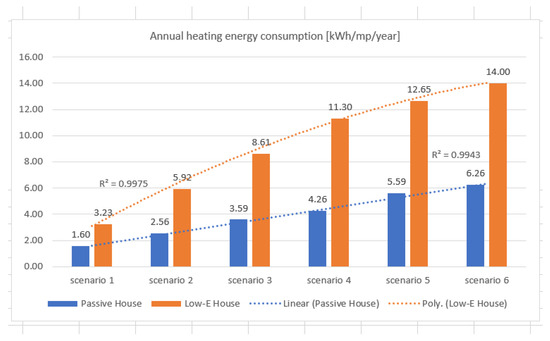
Figure 12.
Annual heating energy consumption for passive houses (blue) Low-E houses (orange).
NetLogo v 6.3.1. allowed us to perform experiments with the MAS model by systematically varying the model’s settings and recording the results of each model run. We have run each of the proposed case studies presented above on two different computer hardware architectures, i8 and i4, for 5000 ticks. Case study 1, simulated on a computer with four cores, had a total elapsed time of 4 min and 14 s, compared with 3 min and 8 s in the case of i8 architecture. The number of processor cores influenced the computational time of our model but not significantly, meaning that the proposed tool is a robust one. While this model currently focuses on thermal energy management, integration of emerging technologies such as residential battery storage and EV charging systems is critical. These systems present unique demand peaks and bidirectional energy flow scenarios, which MAS could manage effectively with priority-based or negotiation-based agent logic [29]. The current model uses synthetic input parameters, but publicly available datasets such as REFIT [30], OpenEI [31], and Pecan Street [32] provide real-time smart meter data from residential buildings. Integrating such datasets would allow for calibration, benchmarking, and testing under real consumption variability.
Statistical correlation coefficients (R2) between simulated and reference energy consumption values: passive house (instant power): R2 = 0.935; Low-E house (instant power): R2 = 0.525; monthly energy consumption: R2 > 0.99 in both cases. These support the model’s predictive accuracy. Although the model shows strong internal consistency, external validation against real-world smart home data is necessary. Future work should include calibration using smart meter data and experimental studies to increase confidence in predictions.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
This paper proposes and validates an intelligent, hybrid framework for residential energy management by integrating Multi-Agent Systems (MASs), System Dynamics Modeling (SDM), and Agent-Based Modeling (ABM). The approach addresses critical challenges in the field, including the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, the inflexibility of centralized control systems in dynamic environments, the complexity of modeling occupant behavior, and issues related to data interoperability in smart home infrastructures. Through a modular, decentralized architecture, the system simulates interactions between physical subsystems and occupant behaviors, enabling adaptive control that maintains thermal comfort while minimizing energy consumption. Passive houses, in particular, demonstrate superior energy efficiency under all simulated conditions.
The framework exhibits strong predictive performance, achieving an R2 > 0.99 in annual simulations. Scenario testing confirms its utility for informing energy-saving strategies in both retrofitted and newly constructed homes. NetLogo serves as a robust simulation environment for validation, although future iterations should incorporate real-time sensor data and machine learning (ML) integration for improved responsiveness and adaptability. Specifically, ML techniques such as reinforcement learning (e.g., Q-learning, Deep Q-Networks), LSTMs for temporal pattern recognition, and clustering algorithms (e.g., K-means, DBSCAN) for occupant profiling can enhance the system’s intelligence and personalization. Methodologically, the tri-layer integration leverages MAS for decentralized control through autonomous agents, SDM for accurate modeling of thermodynamic and energy flow processes, and ABM for capturing the variability in occupant behaviors. This synergy enables high-resolution, context-aware simulations that mirror real-world residential dynamics. The decentralized nature of MAS overcomes the rigidity of traditional control schemes, while ABM and SDM ensure behavioral responsiveness and physical accuracy, respectively. The abstract and interoperable model design supports integration with various IoT devices and communication protocols, promoting practical implementation. Future research directions include extending scalability to multi-unit buildings or community-level energy systems, integrating dynamic pricing and weather forecasts, incorporating renewable generation, battery storage, and EV infrastructure, and developing user-centric interfaces to support human-in-the-loop control. Ensuring data security and privacy through encryption and governance frameworks is also essential.
In conclusion, this work presents a flexible, high-fidelity framework that unites behavioral adaptability with technical precision, offering a powerful tool for energy optimization in smart residential environments. It supports informed decision making for designers, policymakers, and occupants alike, with significant implications for advancing sustainable building practices. The findings advocate for the adoption of MAS-based control architectures, the promotion of passive house standards, and the integration of behavioral feedback mechanisms to drive energy efficiency and user engagement.
Author Contributions
O.E.D. and F.D. conceived the idea of the research, implemented the research, performed the analysis, and authored the paper. All authors have contributed significantly to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Shahidehpour, M.; Yang, T.; Zeng, Z.; Chai, T. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Smart Grid Operations: Algorithms, Applications, and Prospects. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 1055–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Østergaard, P.A.; Connolly, D.; Mathiesen, B.V. Smart energy and smart energy systems. Energy 2017, 137, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, O.E.; Dragomir, F.; Păun, M.; Duca, O.; Gurgu, I.V.; Drăgoi, I.-C. Application of Neuro-Fuzzy Techniques for Energy Scheduling in Smart Grids Integrating Photovoltaic Panels. Processes 2023, 11, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um-e-Habiba; Ahmed, I.; Asif, M.; Alhelou, H.H.; Khalid, M. A review on enhancing energy efficiency and adaptability through system integration for smart buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, V.C.; Sahin, D.; Kocak, T.; Ergüt, S.; Buccella, C. Smart grid technologies: Communication technologies and standards. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2011, 9, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourshed, M.; Robert, S.; Ranalli, A.; Messervey, T.; Reforgiato, D.; Contreau, R.; Becue, A.; Quinn, K.; Rezgui, Y.; Lennard, Z. Smart grid futures: Perspectives on the integration of energy and ICT services. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.; Ansari, N. Decentralized Controls and Communications for Autonomous Distribution Networks in Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 4, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jia, H.; Wang, D.; Yu, D.C.; Chiang, H.D. Hierarchical energy management system for multi-source multi-product microgrids. Renew. Energy 2015, 78, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, O.E.; Dragomir, F. A Decentralized Hierarchical Multi-Agent Framework for Smart Grid Sustainable Energy Management. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Jigarkumar, S. Sensor-based activity recognition in the context of ambient assisted living systems: A review. J. Ambient. Intell. Smart Environ. 2019, 11, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahman, H. Gamification in Energy Consumption: A Model for Consumers’ Energy Saving. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2024, 14, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, X.; Xia, Y.; Bai, Y.; Kong, Y. Analysis of user behavior and energy-saving potential of electric water heaters. Energy Inform. 2024, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Weituo, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B. Data-driven occupant-behaviour analytics for residential buildings. Energy 2020, 206, 118100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Faria, P.; Morais, H.; Vale, Z.; Ramos, C. Distributed, agent-based intelligent system for demand response program simulation in smart grids. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2014, 29, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, M. An Introduction to Multi-Agent Systems, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 221–253. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomir, O.E. Modelling and simulation of distributed systems using intelligent multi-agents. J. Sci. Arts 2022, 22, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.; Pinto, T.; Praça, I.; Vale, Z. Mascem: Optimizing the performance of a multi-agent system. Energy 2016, 111, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Cao, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Xia, Y.; Huo, W.; Shi, G.; Fan, Q. Adaptive multi-task ensemble framework for smart home automation. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouzeau, A.; Dharshini, M.B.; Balasubramaniam, M.; Henry, J.; Hoang, N.; Dwyer, T. Visual Analytics in Energy Monitoring in the Context of Building Management. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Big Data Visual and Immersive Analytics (BDVA), Konstanz, Germany, 17–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, F.; Ran, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Scalable energy management approach of residential hybrid energy system using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Appl. Energy 2024, 367, 123414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilensky, U. NetLogo 6.3.1; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 1999; Available online: http://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/ (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Dragomir, O.E.; Dragomir, F. Application of Scheduling Techniques for Load-Shifting in Smart Homes with Renewable-Energy-Sources Integration. Buildings 2023, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, M.; Jennings, N.R.; Kinny, D. The Gaia Methodology for Agent-Oriented Analysis and Design. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2000, 3, 285–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. ASHRAE Resources Available to Address COVID-19 Concerns; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 52016-1:2017; Energy Performance of Buildings—Energy Needs for Heating and Cooling, Internal Temperatures and Sensible and Latent Heat Loads. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- U.S. Department of Energy. EnergyPlus Version 25.1.0. 2025. Available online: https://energyplus.net (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Wetter, M.; Zuo, W.; Nouidui, T.S.; Pang, X. Modelica Buildings Library. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2014, 7, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). URBANopt SDK Documentation. U.S. Department of Energy. 2025. Available online: https://docs.urbanopt.net (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Lee, J.; Smith, A.; Kumar, R. Bioenergy generation from thermochemical conversion of lignocellulosic biomass-based integrated renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 176, 113213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.; Stankovic, L.; Stankovic, V. An electrical load measurements dataset of United Kingdom households from the REFIT smart home study. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 160122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenEI. Open Energy Data Initiative (OEDI) Data Lake. U.S. Department of Energy. 2025. Available online: https://data.openei.org (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Pecan Street Inc. Dataport Residential Energy Data Overview [Data Sheet]. 2025. Available online: https://www.pecanstreet.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Pecan-Street-Data-Sheet-Feb-2025.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).