Effect Mechanism of Phosphorus-Containing Flame Retardants with Different Phosphorus Valence States on the Safety and Electrochemical Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Experimental Materials and Instruments
2.2. Experimental Method
2.2.1. Thermal Stability Experiment of Electrolyte
2.2.2. Battery Electrochemical Performance Experiment
2.2.3. SEM and XPS Experimental Equipment and Methods
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of Phosphorus-Based Flame Retardants on the Thermal Stability of the Electrolyte
3.2. The Impact of Phosphorus-Based Flame Retardants on the Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4|Li Half-Cells
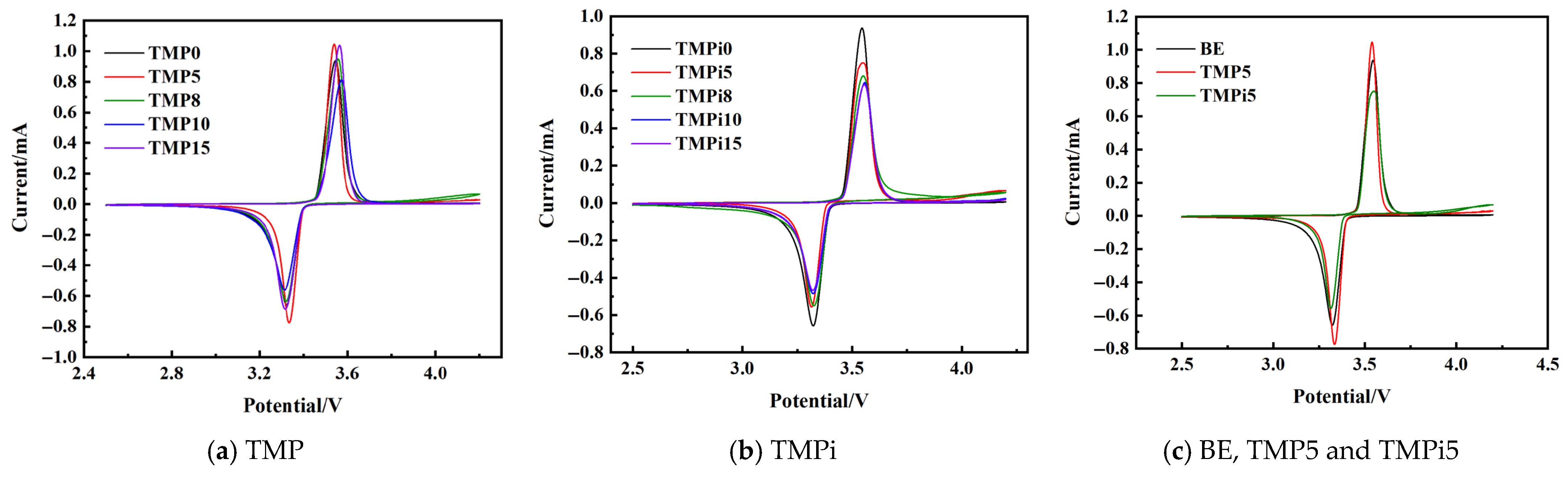
3.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry Testing of LiFePO4|Li Half-Cells
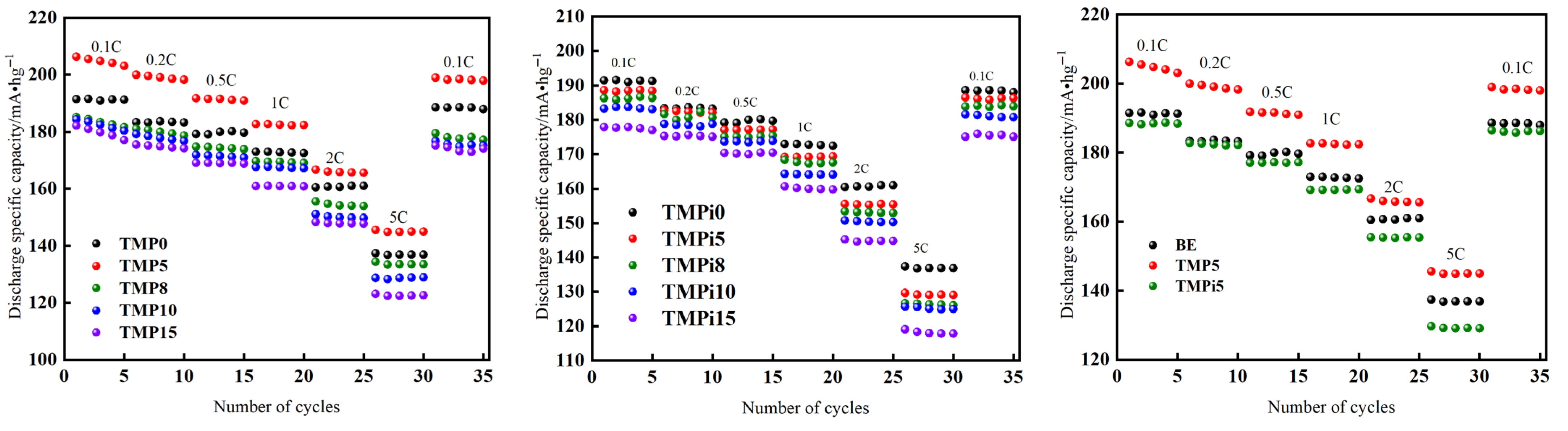
3.2.2. Discharge Specific Capacity of LiFePO4|Li Half-Cells
3.2.3. Rate Performance of LiFePO4|Li Half-Cells
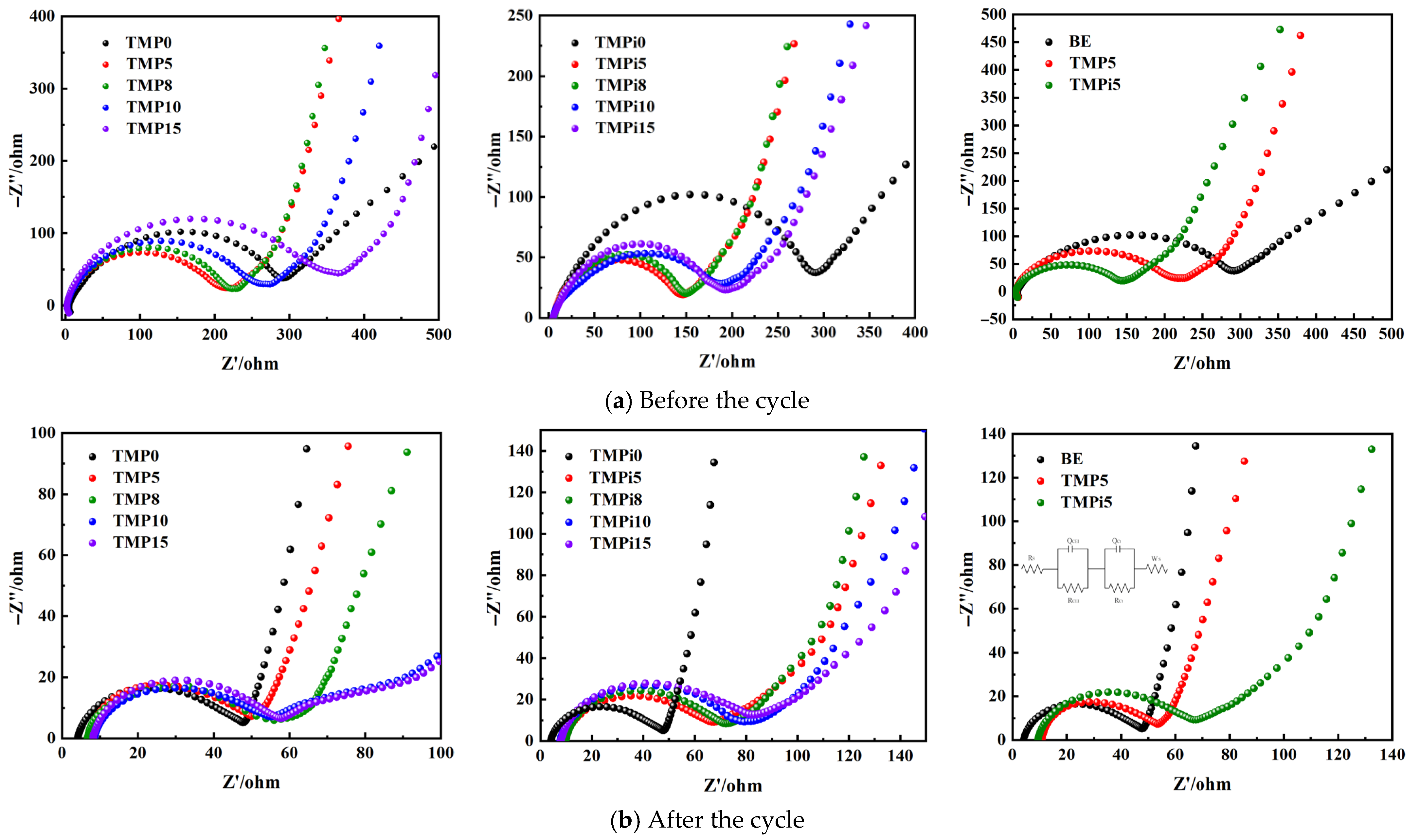
3.2.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of LiFePO4|Li Half-Cells Before and After Cycling
3.3. Mechanism of Action
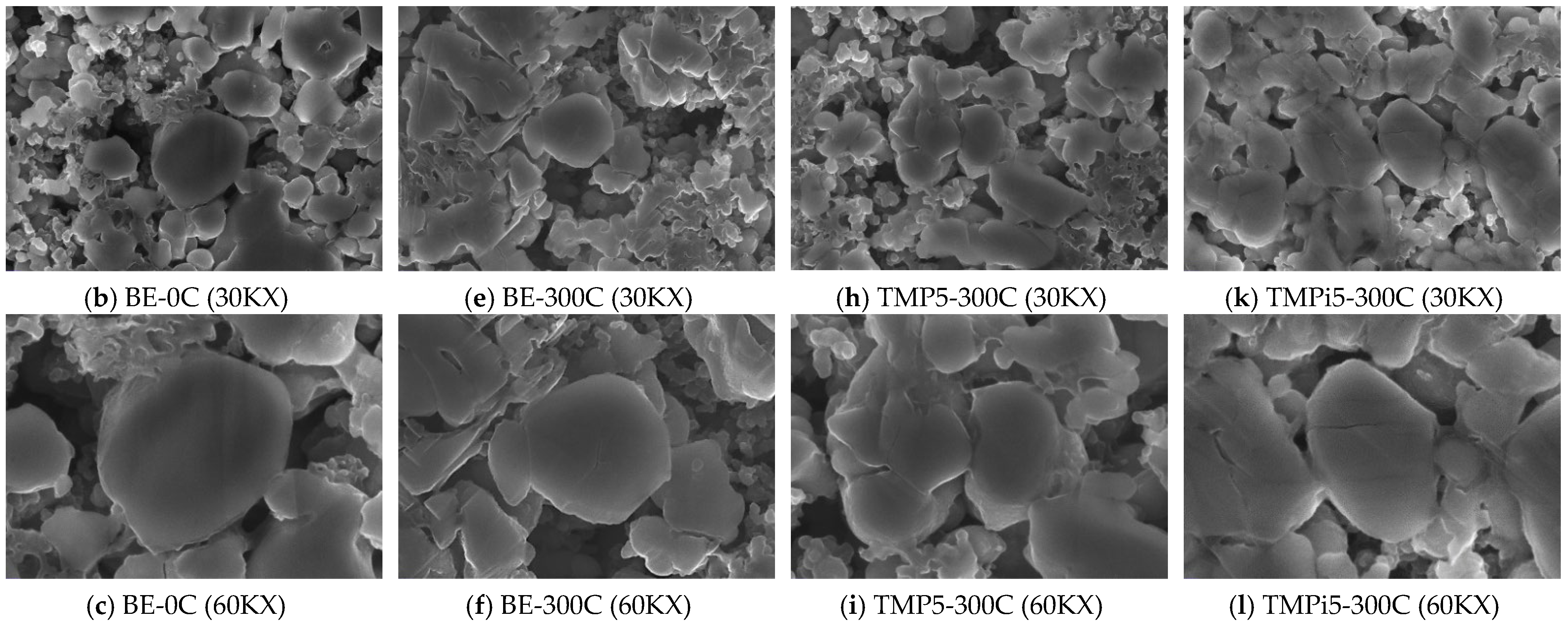
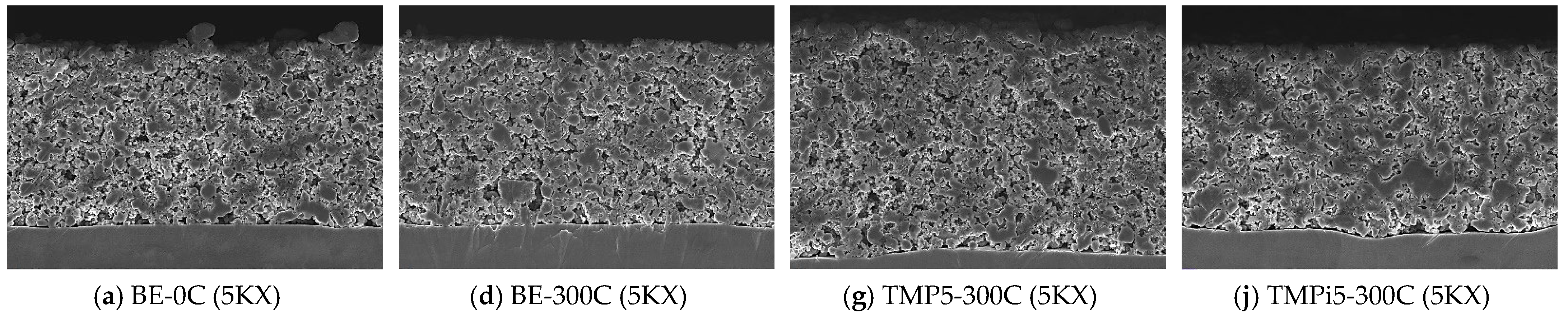
3.3.1. Analysis of Electrode Surface Morphology
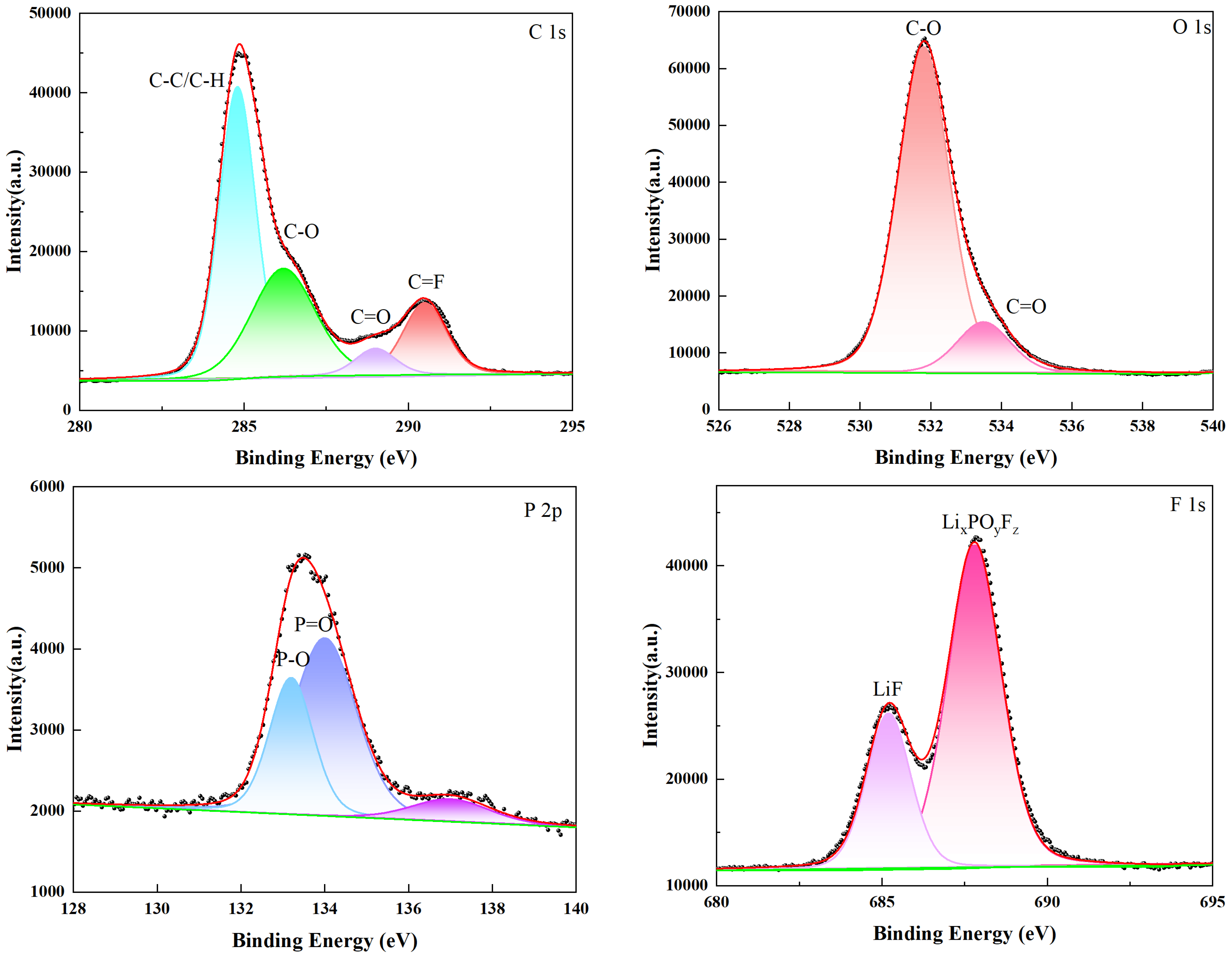
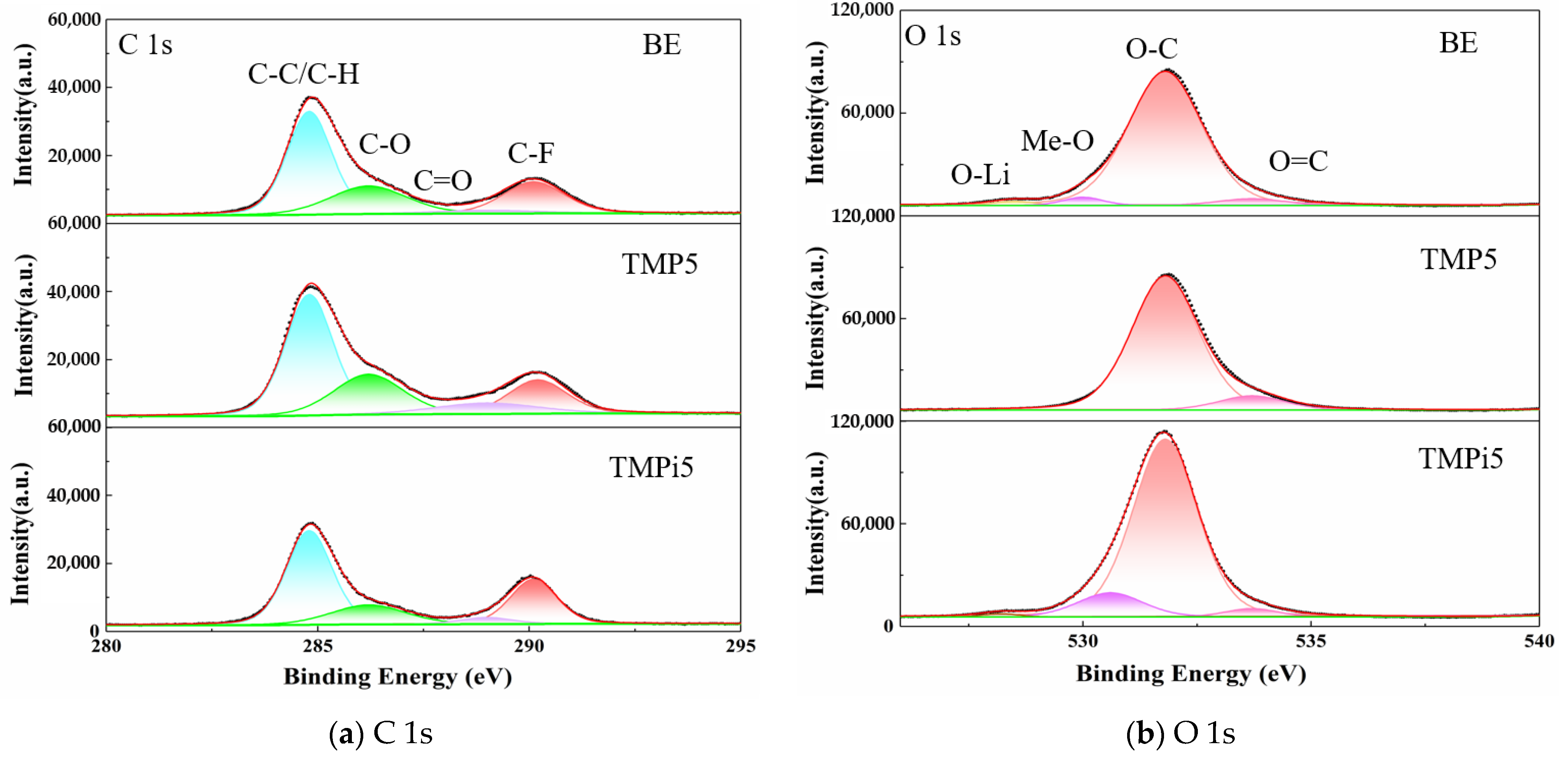
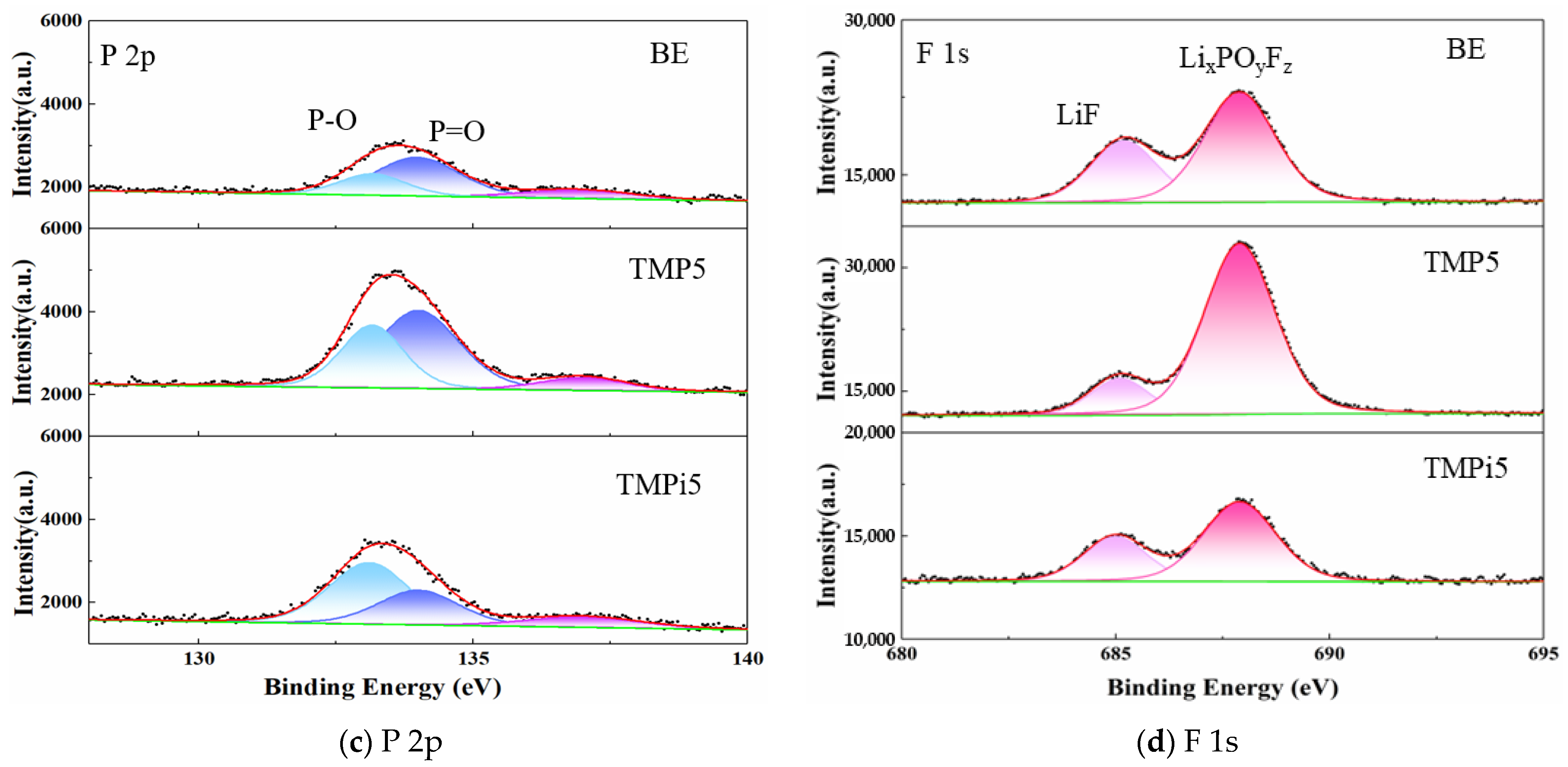
3.3.2. Analysis of Electrode Surface Composition and Elements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konarova, M.; Taniguchi, I. Preparation of carbon coated LiFePO4 by a combination of spray pyrolysis with planetary ball-milling followed by heat treatment and their electrochemical properties. Powder Technol. 2009, 191, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumai, K.; Miyashiro, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takei, K.; Ishikawa, R. Gas generation mechanism due to electrolyte decomposition in commercial lithium-ion cell. J. Power Sources 1999, 81, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, H.; Luan, H.; Chen, L. A novel flame retardant and film-forming electrolyte additive for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Xia, Y.G.; Liu, Z.P. A novel fluorocyclophosphazene as bifunctional additive for safer lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 278, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, X.; Ai, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y. Bis(2,2,2-Trifluoroethyl) ethylphosphonate as novel high-efficient flame retardant additive for safer lithium-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 165, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.P.; Nadimpalli, S.P.V.; Guduru, P.; Lucht, B.L. Flame retardant co-solvent in-corporation into lithium-ion coin cells with thin-film Si anodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 161, A176–A182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Xu, J.B.; Lin, M.; Xu, Q.; Ma, C.F.; Xiang, H.F. Ethylene ethyl phosphate as a multifunctional electrolyte additive for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17566–17571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wei, O. Polyfluorinated electrolyte solutions and additives for high voltage non-flammable lithium batteries. ECS Trans. 2013, 50, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoi, K.; Iwama, E.; Honda, Y. Discharge behavior and rate performances of lithium-ion batteries in nonflammable hydrofluoroethers (II). J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Dan, K.-I.; Koh, M.; Ino, T.; Shimizu, T. Effect of addition of fluoroethers to organic solvents for lithium ion secondary batteries. J. Fluor. Chem. 2001, 111, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Pei, F.; Wu, Y.; Mao, R.; Ai, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y. An electrochemically compatible and flame-retardant electrolyte additive for safe lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 227, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zhan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z. A new phosphonamidate as flame retardant additive in electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 197, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Gao, H.; Kong, C.; Zhan, H.; Li, Z. A novel phosphate-based flame retardant and film-forming electrolyte additive for lithium ion batteries. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2013, 2, A66–A68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, S.; Xiong, S.; Scheers, J.; Jacobsson, P.; Johansson, P. Ionic liquids in lithium battery electrolytes: Composition versus safety and physical properties. J. Power Sources 2015, 283, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Brutti, S.; Navarra, M.A.; Panero, S.; Reale, P. Mixtures of ionic liquid-alkyl carbonates as electrolytes for safe lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 227, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Yasukawa, E.; Kasuya, S. Nonflammable Trimethyl Phosphate Solvent-Containing Electrolytes for Lithium Ion Batteries: I. Fundamental Properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A1058–A1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P. Study on Phosphorus Containing Flame Retardant Additives of Lithium Iron Battery Electrolyte. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Campion, C.L.; Li, W.; Lucht, B.L. Thermal decomposition of LiPF6-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-H.; Huang, A.-C.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.-P.; Liu, Y.-C.; Li, Z.-P.; Zhou, H.-L.; Huang, C.-F.; Xing, Z.-X.; Shu, C.-M.; et al. Thermal Effect and Mechanism Analysis of Flame-Retardant Modified Polymer Electrolyte for Lithium-Ion Battery. Polymers 2021, 13, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Du, H.; Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Qiang, Q.; Lu, H. Designing ionic liquid electrolytes for a rigid and Li+-conductive solid electrolyte interface in high performance lithium metal batteries. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2025, 866, 141959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, A.; Kumar, A.; Alam, K.; Lohani, H.; Sengupta, A.; Kumari, P.; Thapliyal, K.; Major, D.T.; Mitra, S. Enhancing High-Voltage LNMO Cathode Performance in Li-Metal Batteries Via Anionic Electrolyte Additive-Integrated CEI Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2416634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Yang, J.; Pan, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Fan, X.; Zheng, F.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. Optimizing interphase structure to enhance electrochemical performance of high voltage LiNi5Mn1.5O4 cathode via anhydride additives. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Song, W.; Liu, W.; Long, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, H.; Feng, C.; et al. Fluorinated phosphazene derivative–A promising electrolyte additive for high voltage lithium ion batteries: From electrochemical performance to corrosion mechanism. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L. Performance Investigation of Electrolyte Containing Flame-Retardants of Phosphate for Lithium Batteries. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, A.; Avvaru, V.S.; De la Vega, J.; Zhang, M.; Molleja, J.G.; Wang, D.-Y. Unveiling the structure, chemistry and formation mechanism of an in-situ phosphazene flame retardant-derived interphase layer in LiFePO4 cathode. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 455, 140678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kang, J.; Kim, C.; Jung, C.; Lee, R.; Park, M.; Park, M. Design Strategies and Performance Enhancement Techniques for LiFePO4-Based Li Metal Battery Systems. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 42, 1427–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
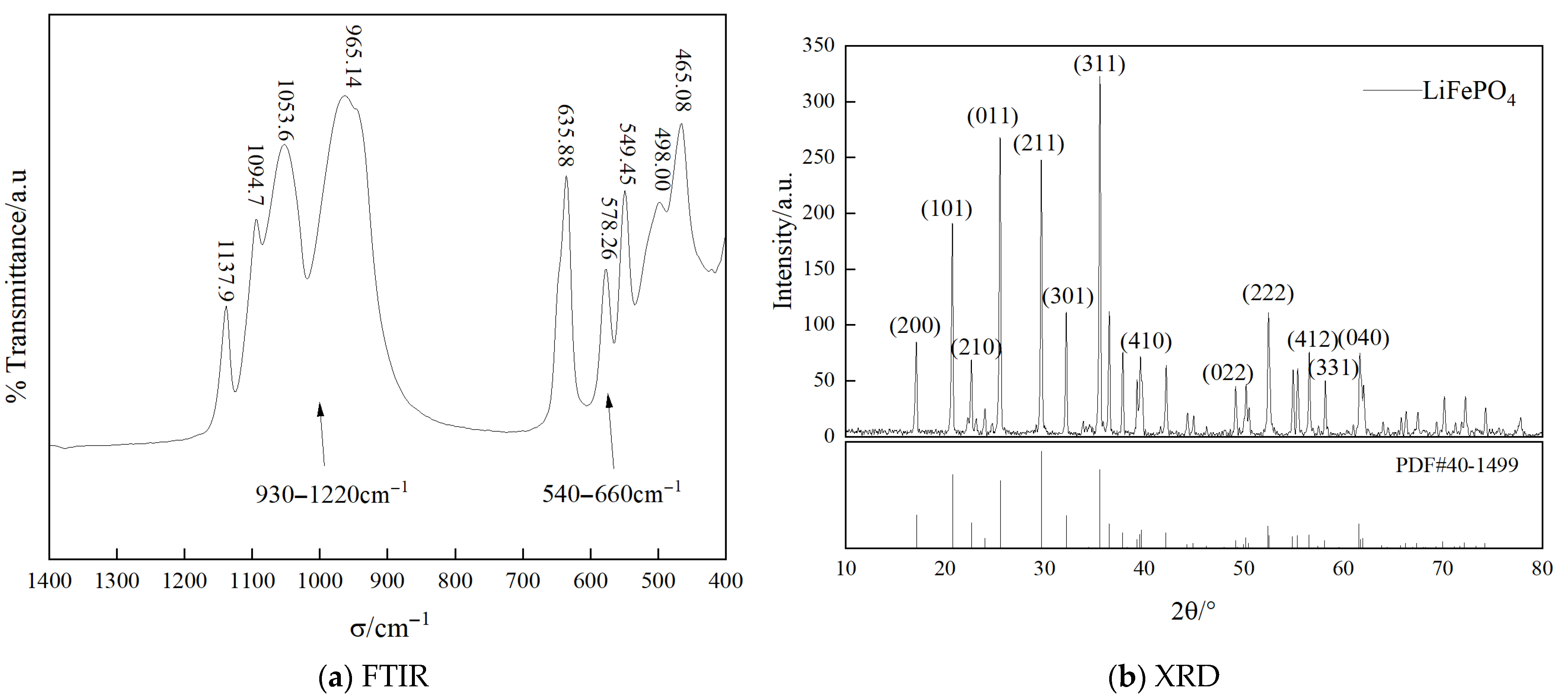






| Material Name | Grade/Model | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Argon gas | High purity | / |
| Lithium iron phosphate | Battery grade | Shenzhen Tianchenghe Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China |
| Acetylene black | Battery grade | Shenzhen Tianchenghe Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride | PVDF5130 | Guangdong Canrd New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China |
| N-methylpyrrolidone | Analytical grade | Tianjin Yongda Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China |
| Trimethyl phosphate | Analytical grade | Tianjin Yongda Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China |
| Trimethyl phosphite | Analytical grade | Adamas Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Electrolyte | 1 M LiPF6/EC: DMC: EMC (1:1:1 wt.%) | Guangdong Canrd New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China |
| Separator | Domestic PP | Shenzhen Tianchenghe Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China |
| Lithium metal sheet | / | Nanjing Wanqing Chemical Glass Instrument Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China |
| Aluminum foil | Battery grade | Shenzhen Tianchenghe Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China |
| Copper foil | Battery grade | Hefei Kejing Materials Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei, China |
| Ceramic fiber paper | 1 mm × 0.61 m × 1 m | / |
| Number | Basic Electrolyte Composition | Flame-Retardant Volume Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|
| BE (TMP0/TMPi0) | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 0 |
| TMP5 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 5 |
| TMP8 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 8 |
| TMP10 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 10 |
| TMP15 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 15 |
| TMPi5 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 5 |
| TMPi8 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 8 |
| TMPi10 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 10 |
| TMPi15 | LiPF6 molar concentration: 1.0 mol L−1 EC:DMC:EMC mass ratio = 1:1:1 | 15 |
| Electrolyte | m1/g | m2/g | t/s | m1−m2 | SET/s g−1 | Average Value of SET/s g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE | 22.55 | 21.91 | 30.76 | 0.64 | 48.063 | 46.67 |
| 21.21 | 33.50 | 0.70 | 47.859 | |||
| 20.53 | 29.98 | 0.68 | 44.088 | |||
| TMP5 | 28.48 | 27.80 | 18.69 | 0.68 | 27.485 | 27.925 |
| 27.14 | 18.72 | 0.66 | 28.364 | |||
| 26.53 | 17.03 | 0.61 | 27.926 | |||
| TMP8 | 29.54 | 28.92 | 15.18 | 0.62 | 24.484 | 26.472 |
| 28.31 | 16.81 | 0.61 | 27.557 | |||
| 27.67 | 17.52 | 0.64 | 27.375 | |||
| TMP10 | 30.74 | 30.09 | 16.78 | 0.65 | 25.815 | 25.078 |
| 29.39 | 17.4 | 0.70 | 24.857 | |||
| 28.75 | 15.72 | 0.64 | 24.563 | |||
| TMP15 | 30.56 | 29.91 | 15.47 | 0.65 | 23.8 | 23.637 |
| 29.26 | 15.28 | 0.65 | 23.508 | |||
| 28.68 | 13.69 | 0.58 | 23.603 | |||
| TMPi5 | 22.67 | 22.06 | 17.54 | 0.61 | 28.754 | 28.795 |
| 21.44 | 17.73 | 0.62 | 28.60 | |||
| 20.8 | 18.58 | 0.64 | 29.031 | |||
| TMPi8 | 22.94 | 22.27 | 15.85 | 0.67 | 23.671 | 23.43 |
| 21.62 | 14.94 | 0.65 | 22.985 | |||
| 20.93 | 16.31 | 0.69 | 23.638 | |||
| TMPi10 | 23.45 | 22.75 | 16.28 | 0.70 | 23.257 | 23.16 |
| 22.08 | 15.57 | 0.67 | 23.239 | |||
| 21.43 | 14.94 | 0.65 | 22.985 | |||
| TMPi15 | 24.16 | 23.51 | 14.94 | 0.65 | 22.985 | 23.01 |
| 22.87 | 14.65 | 0.64 | 22.891 | |||
| 22.19 | 15.74 | 0.68 | 23.147 |
| Electrolyte | Initial Reaction Temperature/°C | The First Peak Temperature/°C | The Second Peak Temperature/°C | The Total Heat Absorbed J g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE | 96.8 | 119.96 | 270.79 | 398.2 |
| TMP5 | 94.87 | 121.56 | 259.61 | 357.7 |
| TMPi5 | 110.90 | 111.53 | 259.69 | 389.8 |
| Electrolyte Solution | Oxidation Peak Potential/V | Reduction Peak Potential/V | Peak Potential Difference/V |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMP0 (BE) | 3.545 | 3.323 | 0.222 |
| TMP5 | 3.539 | 3.334 | 0.205 |
| TMP8 | 3.557 | 3.32 | 0.237 |
| TMP10 | 3.572 | 3.313 | 0.259 |
| TMP15 | 3.563 | 3.316 | 0.247 |
| TMPi0 (BE) | 3.545 | 3.323 | 0.222 |
| TMPi5 | 3.551 | 3.328 | 0.223 |
| TMPi8 | 3.551 | 3.326 | 0.225 |
| TMPi10 | 3.562 | 3.332 | 0.230 |
| TMPi15 | 3.555 | 3.322 | 0.233 |
| LiFePO4|Li Half-Cell Containing TMP and TMPi | Discharge Specific Capacity After the First Cycle/mAh g−1 | Discharge Specific Capacity After 300 Cycles/mAh g−1 | Capacity Retention Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMPi0 (BE) | 180.7 | 175.2 | 97.0 |
| TMP5 | 182.3 | 181.4 | 99.5 |
| TMP8 | 183.3 | 173.9 | 94.9 |
| TMP10 | 189.6 | 172.7 | 91.1 |
| TMP15 | 182.3 | 162.9 | 92.8 |
| TMPi0 (BE) | 180.7 | 175.2 | 97.0 |
| TMPi 5 | 174.7 | 168.2 | 96.3 |
| TMPi 8 | 163.2 | 165.8 | 101.6 |
| TMPi 10 | 160.2 | 161.0 | 100.5 |
| TMPi 15 | 157.8 | 147.0 | 93.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, P.; Sun, F.; Tang, X.; Fan, X.; Cong, G.; Lu, Z.; Zhuo, Q. Effect Mechanism of Phosphorus-Containing Flame Retardants with Different Phosphorus Valence States on the Safety and Electrochemical Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Processes 2025, 13, 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072248
Xi P, Sun F, Tang X, Fan X, Cong G, Lu Z, Zhuo Q. Effect Mechanism of Phosphorus-Containing Flame Retardants with Different Phosphorus Valence States on the Safety and Electrochemical Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072248
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Peng, Fengling Sun, Xiaoyu Tang, Xiaoping Fan, Guangpei Cong, Ziyang Lu, and Qiming Zhuo. 2025. "Effect Mechanism of Phosphorus-Containing Flame Retardants with Different Phosphorus Valence States on the Safety and Electrochemical Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries" Processes 13, no. 7: 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072248
APA StyleXi, P., Sun, F., Tang, X., Fan, X., Cong, G., Lu, Z., & Zhuo, Q. (2025). Effect Mechanism of Phosphorus-Containing Flame Retardants with Different Phosphorus Valence States on the Safety and Electrochemical Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Processes, 13(7), 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072248







