Abstract
Rapid growth in the alumina industry generates vast amounts of highly alkaline red mud (RM), posing significant environmental risks. However, RM shows great promise as a resource for environmental remediation, particularly through its conversion into effective adsorbents. This research reviews recent advancements in developing RM-based adsorbents for sustainable wastewater treatment, especially targeting heavy metal(loid)s (HMs). We examine key modification mechanisms to enhance RM’s properties, summarize synthesis methods for various RM- based adsorbents, and evaluate their performance in removing HMs from water, guiding the design of subsequent new materials. Crucially, this review highlights studies on adsorbent reusability, HM leaching, and economic feasibility to address economic and safety concerns. Finally, we discuss adsorption mechanisms and prospects for these materials.
1. Introduction
In trace amounts, heavy metal(loid)s (HMs) are poisonous and non-biodegradable, harming the ecosystem [1,2]. HM poisoning causes cancer, neurological disabilities, organ failure, growth delays, and gastrointestinal disorders [3,4]. Battery and mining effluents increase metal(loid) concentrations in the environment [5,6]. As(III) [7], Cd(II) [8], Cr(VI) [9], Hg(II) [10], Pb(II) [11,12], Cu(II) [13], Ni(II) [14], Mn(II) [13], Sb(III, V) [15,16,17,18,19,20,21] and other hazardous ions are found in wastewater. Species, concentration, pH, wastewater type, and HM ion solubility affect HMs’ toxicity [22].
Many water treatment methods have been developed to purify HMs in wastewater, including ion exchange [23], chemical precipitation [24], adsorption [25,26], membrane separation [27], etc. These technologies have advantages and disadvantages in practice. Adsorption is optimal for removal capacity, energy consumption, operating conditions, and secondary pollutants. Adsorption is simple to handle, regenerable, and non-toxic [28,29], making it a promising method for HMs’ removal from water. However, conventional adsorbents (e.g., activated carbon, zeolites, molecular sieves, and resins) are cost prohibitive. Thus, developing low-cost, efficient adsorbents has garnered interest. Red mud (RM), a porous structural material, is frequently used to remove heavy metal cations (Pb, Cu, Zn), inorganic anions (phosphate, nitrate, fluoride), and organic contaminants (dyes and antibiotics) [30].
RM is an aluminum smelting byproduct. It may be Bayer RM, sintered RM, or mixed RM, depending on the manufacturing technique. RM’s chemical composition is globally similar, but its specific content varies. Bayer RM has high quantities of alumina, iron oxide, and alkali because alumina is reacted with caustic soda to make aluminum salts [31], whereas sintered RM has high CaO and little iron and alkali [32]. Bauxite composition, alumina production, RM storage technique, and storage period impact RM form and composition. RM typically comprises Fe, Al, Na, and Ti oxides [33].
The application scope of red mud encompasses construction materials [34,35,36,37], ceramics [38], environmental remediation [39], acid mine drainage (AMD) treatment [13], catalysis [38,40], neutralizers [41], and soil rehabilitation [42,43,44,45]. However, RM’s high alkalinity and massive stockpiles pose severe environmental risks to soil and groundwater [46,47]. It has been utilized as an adsorbent for HM ions to improve red mud treatment, which is efficient in removing Pb [11], Cu [48,49], Zn [50,51], Ni [52], Cd [52,53], and Cr [54]. O-H, C-O-C, Si-C, and Si-O surface chemical groups play a crucial role [55].
Red mud’s tiny particle size, huge specific surface area, and rich pore structure make it ideal for HMs’ removal. In practice, strong alkalinity, tendency for particle agglomeration, weak selective adsorption capacity when multiple HMs coexist, and other issues must be addressed to meet water quality standards [56,57,58]. Many modifications have been devised to improve HMs’ removal, resulting in a variety of tailored red mud-based adsorbents.
Previous research has reviewed the application of red mud and red mud-based adsorbents in the removal of HMs, inorganic anions, and organic compounds; however, there is a lack of guiding principles for modified synthesis processes and specialized analyses of the removal mechanisms for individual target pollutants. This study aims to summarize the application of red mud adsorbents in heavy metal removal to further advance sustainable remediation research. Additionally, it emphasizes the need to consider economic feasibility and production processes when designing new adsorbents, with the goal of providing guidance for establishing a comprehensive standard framework.
The primary aim of this review is to present the latest advancements in the application of red mud-based adsorbents in the field of water and wastewater treatment. Firstly, this review provides the modification processes of red mud, along with the synthesis techniques, advantages, and disadvantages of several red mud-based adsorbents. Secondly, the adsorption mechanisms of HMs by red mud-based adsorbents are elucidated, with emphasis on their reusability, potential metal leaching, and economic feasibility. Thirdly, this review examines the possible use of red mud-based adsorbents in water treatment and future research paths based on the literature to give theoretical justification and practical evidence for enhancing their performance and sustainable treatment. Subsequently, this review covers the mechanism, limits, and future developments of HM ions’ adsorption.
2. Modification of Red Mud
Red mud requires processing to diminish its toxicity and enhance its physicochemical qualities before its use as a wastewater adsorbent, owing to its elevated alkalinity, potential leaching toxicity, and inadequate adsorption capacity. Heat treatment [59], neutralization [60], organic modification [61], and metal compound modification [62] are common practices. These modification approaches are systematically compared in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of different modification methods.
2.1. Heat Treatment
At high temperatures (300–1000 °C), heat treatment optimizes red mud’s adsorption ability by reorganizing its physical structure and changing its chemical phase [59]. At the physical level, thermal processes contribute to the grain size adjustment and pore morphology evolution of hematite: dewatering (removal of structural water, bound water) reduces the adsorption resistance before 500 °C, while carbonate decomposition releases CO2 to form a rough surface, and the specific surface area and porosity are significantly increased; however, after the temperature exceeds 600 °C, the enhanced crystallinity of hematite leads to the sintering shrinkage of the material, and a sharp decrease in the specific surface area above 700 °C triggers a decline in adsorption efficiency [63,64,65]. At the chemical level, the phase transition sequence dominates component activation: dehydration of alumina trihydrate to produce Al2O3 at 300–550 °C, decomposition of calcite to CaO with CO2 at 600–800 °C, and formation of new phases, such as tricalcium aluminate, at 800–900 °C, where 700 °C may be the critical threshold temperature [66]. Although heat treatment at 700 °C reduces specific surface area, it has been shown that 700 °C annealed red mud (ARM700) exhibits optimal adsorption properties compared to other annealing temperature conditions due to the simultaneous activation of the multicomponent synergistic effects of Fe2O3, Al2O3, SiO2, and sodium–aluminum–silicon carbonate (Equations (1) and (2)), which is attributed to the high-temperature-stimulated directional generation of reactive phases, such as CaO, Al2O3, and Fe3O4, resulting in a highly reactive crystalline composite structure [67,68]. The temperature of heat treatment is a crucial control parameter that profoundly influences the efficacy of red mud-based adsorbents: moderate heat treatment can enhance the physicochemical properties of the materials, whereas elevated temperatures tend to compromise the pore structure and diminish adsorption capacity, while high energy consumption restricts scalability [59,69]. Therefore, future research should prioritize low-temperature synergistic modification approaches (e.g., coupled chemical activation) to simultaneously optimize structural stability, adsorption performance, and cost-effectiveness.
2.2. Neutralization
RM neutralization treatment is a high-quality solution for reducing environmental damage. Neutralization works by adding gypsum or phosphogypsum, acid activation, CO2, or seawater to decrease the material’s pH and change its micromorphology to enhance its specific surface area [70,71,72,73,74]. Amorphous material in the RM portion may be increased to promote HMs’ binding. pH neutralization makes red mud useful for cleanup [60].
- (1)
- Acid activation. Through acid solution and RM reaction, acid treatment modulates surface properties and component activities to improve pollutant adsorption, dissolve/reconstruct mineral phases, and functionalize surfaces and surface functionalization [75]. Existing studies have mostly used inorganic acids like HCl, HNO3, and H2SO4 (0.05–1.0 M concentration range) to modify samples. Two typical processes are acid solution reflux followed by liquid ammonia precipitation and drying [76] and direct acid leaching followed by washing and drying [77,78,79]. Both methods effectively remove alkali metal and impurity phases, expose fresh active surfaces, and optimize pore structure [80]. Acid treatment increased the specific surface area of red mud (e.g., from 13.15 to 23.80 m2/g [75], or from 33.5 to 67.10 m2/g [81]), dissolved mineral phases like hematite and gibbsite [82], and increased Fe2O3 content by 3–4% [75,83,84]. Additionally, surface hydroxyl and metal–oxygen group density increased, forming high-affinity metal binding [75,85]. Acid treatment increases electrostatic adsorption capacity by modulating surface charge characteristics (e.g., pH decreased from 11.00 to 2.12, isoelectric PZC decreased), but the acid concentration and reaction time must be tightly controlled to avoid the over-dissolution of Fe/Al oxides [85]. Moreover, the buffering capacity of red mud is intrinsically linked to its alkaline constituents (e.g., calcium hydroxide, carbonates, etc.). However, some studies have shown that specific surface area is not necessarily correlated with cation adsorption efficiency, emphasizing the importance of surface chemical properties (e.g., functional group type and charge distribution) [70]. In conclusion, acid treatment optimizes adsorption performance through physical–chemical synergistic modification, but the source and mineral composition of red mud affect its effect, which must be combined with the surface reaction mechanism for targeted process design. Acid neutralization of red mud has the potential for low cost and “waste for waste,” but is limited by location dependence, the risk of dilute salt contamination, and transportation costs. Its adsorption efficiency is regulated by chemical composition, specific surface area, etc., but the correlation between the latter and cation adsorption is still controversial.
- (2)
- Neutralization with seawater. Seawater neutralization reduces pH to 8.5–8.8 by replacing Na+ in red mud with Ca2+ and Mg2+ while maintaining residual neutralization potential and also converts soluble wastes to solids (such as hydrotalcite, calcite, and brucite; Equation (3)) and increases the surface area [86,87,88,89]. Rai et al. [90] demonstrated that pH is mainly controlled by seawater dosage and that the technique is very efficient and cost-effective but is limited by geographical location.
- (3)
- Neutralization with gypsum. Gypsum neutralization of red mud induces the precipitation of Ca(OH)2, tricalcium aluminate, and CaCO3, and the addition of 5–8% gypsum releases Ca2+ and reduces pH to 8.6 [80,91] via the mechanism that Ca2+ reacts with carbonate to form calcite to improve buffering capacity (Equation (4)) [92,93,94]. At the same time, carbonate precipitation provides adsorption sites for the immobilization of toxic elements [95], and excess Ca2+ may react directly with aluminate to form phases such as hydrocalumite Ca2Al(OH)7·2H2O (Equation (5)) [96]. Although this method is limited by the efficiency of carbonate precipitation in the presence of Ca2+/Mg2+ deficiency [97], it has been popularized in the field of construction materials and soil remediation due to its ease of operation.
- (4)
- Neutralization with carbon dioxide. CO2-neutralized red mud lowers pH via liquid-phase carbonation, where CO2 dissolution produces carbonic acid that interacts with alkaline components. However, a pH rebound occurs due to the ongoing dissolution of solid-phase alkalinity, such as tricalcium aluminate (TCA), which releases OH- ions [80,98,99,100]. Equations (6) and (7) represent interactions between CO2 and hydroxide ions in the caustic solution, whereas Equations (8)–(10) depict the dissolution of TCA in CO2. TCA interacts with CO2 to produce calcite and aluminum hydroxide; however, the kinetics are sluggish, and the reaction is reversible. Additionally, residual alkaline minerals, such as kaolinite, present in the solid phase after incomplete conversion, elevate the pH back to the alkaline range by dissolution [98,101]. Yadav et al. [102] determined that a particle size of 30 μm for red mud maximized carbonation efficiency owing to a substantial proportion of the active phase, but larger particles hindered full neutralization due to inadequate solid–liquid interaction. This method sequesters CO2 and diminishes the necessity for subsequent acid leaching [99]; however, the solid-phase alkalinity buffering effect renders the neutralization effect transient, necessitating the integration of subsequent stabilization treatments (e.g., calcium carbonate generation) to mitigate pH fluctuations [101]. Therefore, it is critical to elucidate the mechanisms of solid-phase alkalinity conversion and develop sustainable neutralization technologies for red mud, which could effectively remediate its persistent high alkalinity [103].
2.3. Organic and Metal Compound Modification
Organic modification may increase functional groups (hydroxyl groups, amino groups, etc.) and specific surface area to improve metal ion adsorption in red mud (RM), which tends to agglomerate [104,105,106]: The modification (RM/CS) increased the specific surface area from 68.6 to 105.7 m2/g and the maximum adsorption capacities for nickel (II) and lead (II) reached 31.66 mg/g and 208.48 mg/g, respectively [107,108]. A new method of in situ graft polymerization was used in a reverse suspension system to synthesize red mud/polyacrylic acid (RM/PAA) composite materials. The maximum adsorption capacity reached 96.15 mg/g, which is much higher than that of RM (21.70) [109]. Red mud activated with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) can greatly improve the removal ratio of Cr(VI) up to four-times higher than that of original red mud [61]. Organic matter agglomeration reduces the specific surface area, which must be adjusted. In addition, metal compound modification has improved RM adsorption capability significantly. MnO2 can complex and remove HMs ions like Cd(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Pb(II) due to its excellent specific surface area, high surface activity, and chemical stability [62], but its poor dispersibility and tendency to agglomerate limit its use [110]. Loading it onto red mud carriers improves its dispersibility and adsorption efficiency [111]. MnO2 alteration increased RM’s specific surface area, pore volume, and surface functional groups [11]. Fe2O3 has also been utilized to modify red mud because of its superior adsorption ability and selective removal of numerous HM ions [112]. In research findings, Fe2O3-coated red mud adsorbent removed 91.74% of As(III) [113]. Some investigations employed FeCl3-modified RM to create MRM with variable arsenate adsorption at various pH levels [114]. La-RM, made by loading rare earth element lanthanum (La) over red mud, adsorbs Cr(VI) at 17.35 mg/g [115]. The L-PR composites made by combining phosphogypsum and red mud and modified via La impregnation optimized the structure and composition of the raw materials and significantly increased the specific surface area and pore volume with a uniform pore size distribution. The La-associated oxygen-containing functional groups may be involved in As(V) adsorption, which improve performance [7,116]. In summary, while organic functionalization and metal composite modification markedly improve red mud’s adsorption capacity, their practical application is constrained by material agglomeration, cost-effectiveness, and pollutant selectivity, necessitating the future development of aggregation-resistant composite architectures and integrated optimization frameworks to simultaneously enhance performance, economic viability, and environmental sustainability.
3. Preparation Method of Red Mud-Based Adsorbent
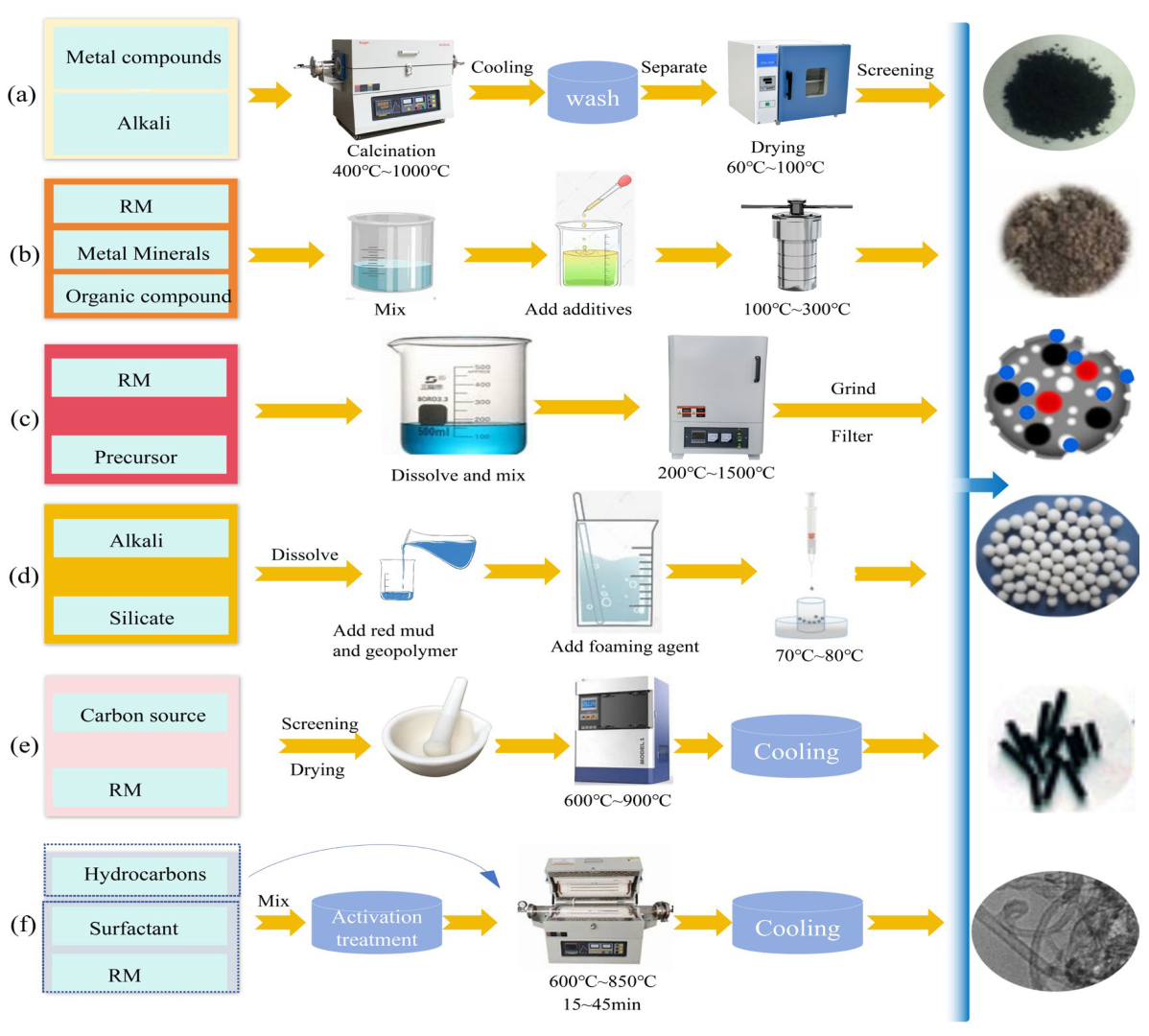
Red mud-based adsorbent synthesis techniques vary depending on the method, from a single hydrothermal approach, alkali fusion, pyrolysis, etc. to a diversity of processes. Table 2 lists the advantages and disadvantages of several preparation procedures, and Figure 1 shows their process parameters.

Table 2.
Advantages and disadvantages of various preparation techniques.
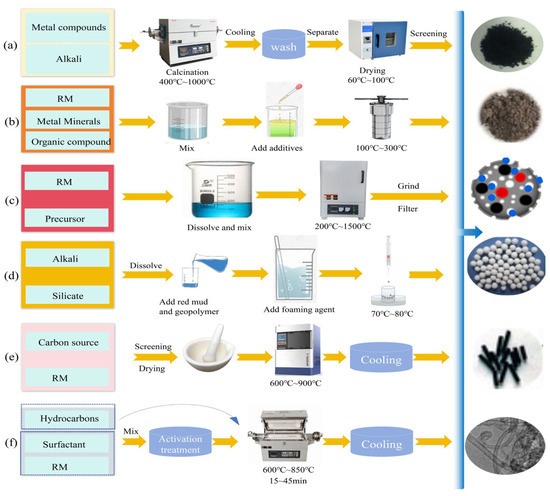
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the preparation method of red mud-based adsorbent ((a) alkali fusion, (b) hydrothermal, (c) pyrolysis, (d) cured foam method, (e) carbothermal reduction, (f) CVD method).
3.1. Alkali Fusion
High-temperature melting with alkali fusion may react with alumina and other metal oxides in red mud to create corrosion-resistant aluminate crystals, Figure 1a. Coal fly ash (CFA) is a powdery mineral residue formed as a byproduct of coal combustion. In the past several years, RM and CFA have often been used as adsorbents to remove HMs. Al2O3 and SiO2 are the primary active ingredients in both CFA and RM; different proportions of these two ingredients combined can produce the diverse radioactivity of Si and Al [123]. Zhao et al. [123] adjusted the ratio of CFA to RM and the ratio of silica–alumina synthesis in conjunction with NaOH calcination at 300 °C to create composite C1R4 with a high specific surface area, adsorption capacity, and magnetic characteristics to improve adsorption efficiency and economics. Xie et al. [117] demonstrated that optimal magnetic 4A zeolite synthesis—achieving maximum SiO2 and Al2O3 solubility and high adsorption efficiency—was obtained at a red mud/NaOH mass ratio of 1:2, an alkali fusion temperature of 800 °C, and a reaction duration of 90 min. The alkali fusion method’s essential process parameters (temperature, percentage of alkali, melting duration, etc.) require optimization to achieve the synthesis reaction and maintain the balance between melting conditions and material activity for the optimum benign adsorbent.
3.2. Hydrothermal
Hydrothermal technique: Creating a high-temperature and high-pressure environment promotes the transformation of mineral phases in red mud, Figure 1b, especially the synthesis of zeolite-like (tetrahedral unit framework composed of SiO4 and AlO4) adsorbent materials, which have a strong affinity for HM ions due to their excellent ion-exchange capacity and large specific surface area. Researchers found that acid-leaching pretreatment and hydrothermal modification dissolved and recrystallized red mud alumina and silica into a zeolite structure, improving adsorption performance [14,118]. Low-temperature hydrothermal zeolites were synthesized by Belviso et al. [124] to remove HM ions. Other substances can be loaded onto red mud using the hydrothermal method, such as Bai et al.’s manganese dioxide-modified red mud [11], which showed enhanced adsorption effects. Mg-Fe-Al LDHs were prepared by Chai et al. [125], expanding the utilization of red mud-based adsorbents. Optimal preparation conditions were the pH of the reaction precursor (10.0), 4:1 molar ratio (Mg2+: (Fe3+ + Al3+)), 100 °C crystallization temperature, and 12 h crystallization duration. Wang et al. [126] prepared integrated microelectrolytic functional materials (IMCs) by combining hydrothermal and co-pyrolysis processes, and red mud’s high iron content (>30 wt%) can be used to make IMCs [32], suggesting that hydrothermal methods can be enhanced by other methods. They prepared red mud/black liquor (RM/BL) for Cr(VI) removal beforehand [9]. RM/BL had average pore volumes of 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15 cm3/g at 350, 650, and 850 °C, demonstrating that higher water bath temperatures promote porous structures. In addition, Yan et al. [127] produced magnetic zeolites from red mud and coal gangue (CG) using the alkali calcination–hydrothermal technique. Alkali calcination has been used as a pretreatment to improve feedstock aluminum and silicon conversion, and iron in RM can be reduced by carbon in CG under a non-oxidizing atmosphere to form the magnetic phase. Zeolite A diffraction peaks rose at 90 °C hydrothermal temperature. Zeolite A and magnetite diffraction peaks developed simultaneously at 3 h. These diffraction peaks rose steadily with hydrothermal time and peaked at 9 h. Zeolite A and magnetite diffraction peaks increased with increasing hydrothermal time [128]. Liu et al. [129] produced pure single-crystal four molecular sieves from red mud utilizing alkali–melt–hydrothermal crystallization. Hydrothermal methods can produce uniform and defect-free crystals and nanostructures, but the pore structure and morphology of red mud-based hydrothermal products are sensitive to many factors, so the parameters must be finely tuned for high-performance design. Additionally, the synthesis cycle, reaction condition constraints, and solvent selection must be addressed. Thus, future studies should investigate ways for technological integration to increase preparation efficiency and material attributes.
3.3. Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis converts biowaste to biochar through anaerobic high temperature and the co-pyrolysis modification of transition metals (Fe, Al, etc.) in red mud to enhance adsorption performance, Figure 1c. Biochar removes dyes/HMs and recovers energy (pyrolysis of oil, syngas) [119,130,131]. Surface modification using transition metal ion (Fe, Al, and Co) precipitation or co-pyrolysis with metal oxides improves biochar adsorption [119]. As a reaction medium, CO2 accelerates the cleavage of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) through the thermal degradation of the feedstock, generating high volumes of synthesis gases (particularly CO) [132]. This process provides ideas for the application of Fe in combination with biochar. As mentioned above, adding transition metal oxides from red mud to CO2 changes pyrolysis and liquid/gas product characteristics, which makes the combined use of iron and biochar more feasible [133]. Furthermore, CO2 intervention controls Fe phase formation [134], since CO2 pyrolysis only creates magnetite, whereas N2 pyrolysis produces both magnetite and Fe0 (reason: hematite reduces to magnetite [132]). Other favored redox processes, including CO2, may potentially lead to the creation of various Fe compounds. For instance, CO2 with FeO creates CO and Fe3O4 [135]. Pyrolysis temperature impacts the material structure, with 700 °C promoting Fe0 formation and pore development (e.g., MMBC specific surface area increases with temperature [136,137]; SRMBC pore structure changes from microporous to dense at 600–900 °C [138]). Pyrolysis can produce high-purity, evenly dispersed materials by choosing precursors and managing reaction conditions. Pyrolysis processes are unsuitable for heat-sensitive materials because they may destabilize the material structure by causing excessive crystal growth or disintegration [139,140]. Novel precursors and reaction mechanisms to lower reaction temperature and increase pyrolysis’ application are still needed.
3.4. Cured Foam Method
The cured foaming approach enhances the pore structure and mechanical characteristics of the material, as seen in Figure 1d, by meticulously controlling the foaming parameters, namely the dose of the foaming agent. Geopolymers possess inherent mesoporosity and are capable of adsorbing HMs [141,142]. Porous adsorbent materials were synthesized through integrating red mud and geopolymer. For instance, Yan et al. [120] employed red mud/slag as the precursor, utilizing H2O2 foaming to create a microcracked structure that augmented the adsorption sites. Gonçalves et al. [143] achieved a controllable enhancement in pore quantity and size by varying the sodium dodecyl sulfate blowing agent content (1.2–1.7 wt%), although an excessive concentration (2.2 wt%) resulted in phase separation and diminishing porosity [144]. Carvalheiras et al. [145] produced mechanically stable foams with a peak lead adsorption capacity of 30.96 mg/g by optimizing the metakaolin/red mud ratio relative to the blowing agent. In summary, some recent research has concentrated on the impact of blowing agent dose on the material’s adsorption characteristics; however, the challenging management of the material’s internal void structure presents many issues, rendering the foaming technique acceptable only for systems with high mechanical strength. Further optimization of the process is necessary for general use.
3.5. Carbothermal Reduction
The carbothermal reduction process converts Fe2O3 in red mud to zero-valent iron (ZVI) using a high-temperature carbon source, such as biomass, while offering the benefits of low cost and environmental sustainability, as seen in Figure 1e. Du et al. [121] synthesized a granular red mud adsorbent (ZVI@GRM) under anoxic conditions at 900 °C, employing corn stover as a pore-forming agent and carbon source, along with a biochar framework to mitigate iron agglomeration and enhance specific surface area. Concurrently, Li et al. [146] implemented carbothermal regeneration at 800 °C to convert Fe2O3 into nanozero-valent iron (nZVI), utilizing Al2O3/SiO2 as a dispersant to stabilize nZVI, thereby enabling the regenerated material to effectively remove and immobilize Cr(VI) through the formation of FeCr2O4. This method lowers production costs by substituting graphite with biomass; however, the carbon/red mud ratio and temperature must be meticulously controlled to prevent excessive reduction or product inactivation, and the process conditions require optimization to improve stability and application potential.
3.6. CVD Method
In carbon nanotube (CNT) synthesis, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) demonstrates simplicity and cost-effectiveness compared to arc discharge and laser ablation, enabling operation at low temperatures and ambient pressure while achieving high purity, yield, and precise control over growth parameters and structures (Figure 1f). Utilizing CVD for CNT synthesis from red mud, thermally stable oxides (e.g., Al2O3, SiO2, TiO2) in red mud disperse Fe phases during CVD reactions and promote amphiphilic characteristics in products [147]. Mesgari Abbasi et al. [122] synthesized RM/CNT composites via methane (CH4) decomposition catalyzed by red mud at 650 °C and 750 °C. The enhanced specific surface area was attributed to irregular CNTs, with optimal growth observed at 750 °C, accompanied by sequential Fe2O3→Fe3O4→Fe3C phase transitions and carbon formation [148]. Researchers further explored CNT synthesis on alkali-activated materials (AAMs) derived from red mud, where AAMs (formed by alkali activation of alumina/silica precursors) enhance geopolymers’ mechanical properties [149,150,151]. XRD analysis revealed hematite-to-magnetite/metallic iron transformations, iron carbide phases, and graphite carbon, confirming metallic iron in red mud as catalytic sites for CNT growth [122,151]. While CVD demonstrates potential for synthesizing CNTs from red mud, its large-scale application for producing red mud-derived adsorbents necessitates overcoming key challenges, particularly in process simplification and the development of continuous deposition technologies.
3.7. Comparison and Prospects
Beyond conventional approaches, red mud-based adsorbent preparation encompasses several specialized methods: (1) enhanced precipitation techniques for Fe nanoparticle loading [152]; (2) synthesis of porous geopolymers through alkali-activated red mud-coal gangue systems, utilizing negatively charged aluminosilicate networks for metal ion adsorption [153]; (3) reverse suspension polymerization incorporating carboxyl groups to boost adsorption capacity [109]; and (4) sol–gel-derived red mud/MCM-41 composites exhibiting exceptional Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction capabilities, attributed to their high specific surface area (465 m2/g) [154]. Each synthesis method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the appropriate process should be selected based on the characteristics of the target material and practical application requirements. The solidification foaming method is suitable for low-cost large-scale applications; hydrothermal or CVD methods are suitable for the synthesis of high-precision functional materials; hydrothermal, alkali fusion, or carbon thermal reduction methods are more suitable for preparing materials with high crystallinity and complex structures. In the future, leaching risks can be reduced through functional ligand modification, waste co-utilization, and encapsulation methods such as phosphate solidification or silane coupling agents. Combined with carbon thermal reduction, metal recovery, and machine learning-guided optimization, an “adsorption regeneration” closed-loop, and green sustainable development can be achieved.
4. Key Parameters Impacting HMs’ Removal
pH, coexisting ions, reaction temperature, starting concentration, adsorbent dose, and contact duration impact red mud-based adsorbent adsorption equilibrium. In addition, HMs leaching from the adsorbent, the adsorption–desorption cycle time, and the adsorbent type dose might affect red mud-based adsorbent performance on target pollutants. These and other factors affect the selectivity, adsorption capacity, and adsorption rate of red mud-based adsorbents for specific HMs as well as their stability and competitive adsorption behaviors in complex environments. Understanding these influences is crucial for optimizing the practical application effects of these adsorbents, especially in the process of treating complex wastewater. Researchers and practitioners may customize red mud-based adsorbents to increase their efficiency and efficacy in real-world situations, improving HM pollution mitigation in industrial and environmental settings, as shown in Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials. Utilizing these findings may hasten the development of breakthrough treatment solutions, guaranteeing safer water supplies for HM-polluted areas.
4.1. pH
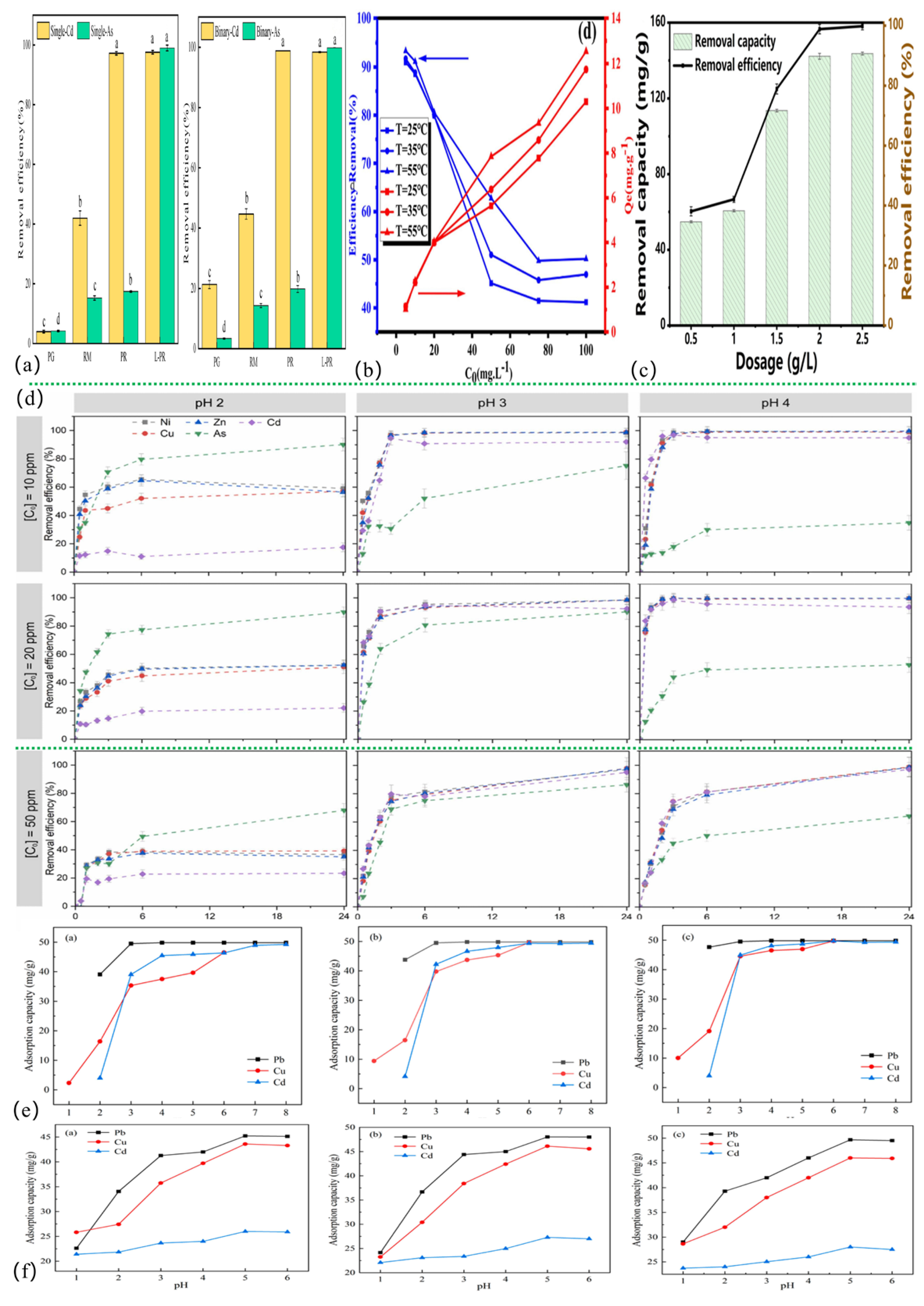
The pH is a critical factor influencing the efficacy of red mud-based adsorbents [155]. The pH of the solution markedly influences the adsorption efficacy of red mud-based adsorbents by altering their surface charge and the shape of HM ions; the transition between protonated and deprotonated states impacts electrostatic interactions [156]. Various red mud-based materials exhibit distinct pHpzc values, defined as the pH at which the zeta potential of the adsorbent equals zero [157], as shown in Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials. Under acidic conditions (pH < pHpzc), protonation results in an augmented surface positive charge, leading to electrostatic repulsion with cations (e.g., Pb2+, Cd2+) and competition for adsorption sites with H+ [123,158]. Consequently, the adsorption of heavy metal cations in water diminishes, obstructing their binding to the material [7]. Conversely, under alkaline conditions (pH > pHpzc), deprotonation increases the negative surface charge, facilitating the electrostatic attraction of cations; however, OH− can induce the precipitation of metal hydroxides [155,159]. Additionally, anionic contaminants (e.g., CrO42- from Cr(VI)) are not adsorbed in water at pH > pHPZC due to blocked electrostatic repulsive adsorption, necessitating chemical reduction (e.g., Cr(VI) → Cr(III)) to improve the removal rate [160]. The variations in pHZC among various materials dictate the suitable pH range, as seen in Figure 2e. Zhao et al. [123] discovered that Pb/Cu/Cd adsorption reached saturation at pH 6–7, whereas optimum Cr(VI) adsorption mostly occurred under acidic circumstances to avoid electrostatic repulsion. Moreover, variations in the affinity of ionic species for functional groups (e.g., the extent of COOH ionization escalates with pH [109]) and the potential for material component dissolution (e.g., under low-pH conditions, the adsorption capacity of arsenic (V) is relatively low, which may be related to the dissolution of magnetite/Fe0 under highly acidic conditions, resulting in the elimination of adsorption sites for arsenic (V) in the adsorption material [134]) further limit adsorption efficacy. Therefore, it is imperative to optimize pH conditions according to the properties of the target pollutants to attain effective adsorption.
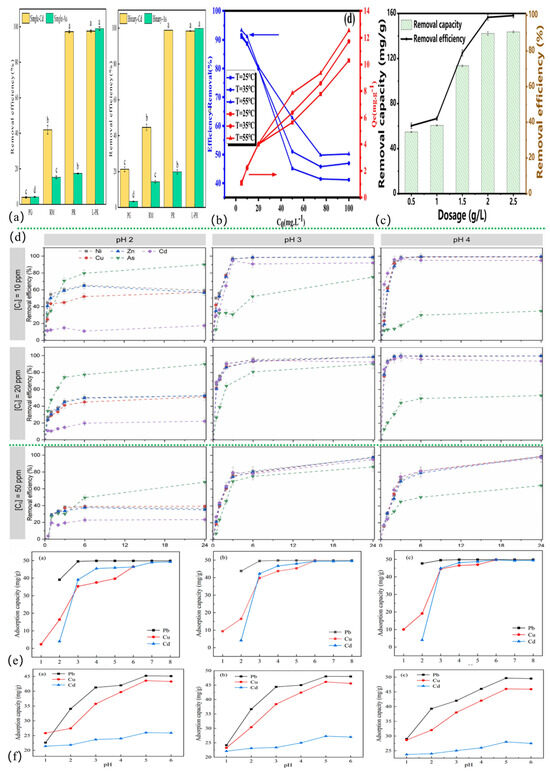
Figure 2.
Comparison of the adsorption effect of red mud-based adsorbents under different influencing factors. (a) Adsorbent type [7], (b) temperature [161], (c) dosage [8], (d) contact time [162], (e) pH [123], (f) coexisting ion [123].
4.2. Coexisting Ion
Through the complex formation of coexisting ions and competitive adsorption, ionic strength has a significant impact on the performance of red mud-based adsorbents. The authors comment on the results from 15 references. For example, Cu2+ and Mn2+ compete for adsorption sites based on differences in hydration radii (0.419 nm and 0.438 nm) and hydration energies (Cu2+: 2121 kJ/mol and Mn2+: 1862 kJ/mol) [163]; the actual adsorption may be related to the electronegativity and hydrated ionic radius of Cu2+ and Mn2+. In addition to having a smaller hydrated radius and a charge center that is closer to the material’s surface, Cu2+ has a greater electronegativity (1.90) than Mn2+ (1.55). This gives the surface of the adsorbent based on red mud more affinity for Cu2+ than for Mn2+. The efficacy of heavy metal adsorption is further reduced by high quantities of K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ in the water column, which compete with heavy metal cations [164]. Among these, highly charged/small-radius ions (e.g., Ca2+) demonstrate stronger competitiveness [11,123,165], while anions modify adsorption mechanisms through complexation—As(V)-Ni(II) complexes synergistically enhance adsorption [166], and specific anions like HCO3− improve Sb(III) uptake via surface coordination [167]. Through competition or inhibition of reduction, SO42−/PO43−, etc., lower the removal of Cr(VI)/Sb(III) [152,168,169,170,171]. However, the adsorption capacity or removal efficiency of the adsorbent reduces when the system comprises two or more cations compared to a single system [129]. As illustrated in Figure 2f, the order of adsorption inhibition is associated with the ionic charge/hydration characteristics under multi-ion systems (e.g., Pb-Cu-Cd coexistence) [123]. To reduce the interference of the coexisting ions in the practical application, this must be combined with pHpzc modulation and the optimization of the adsorbent selectivity.
4.3. Temperature
The adsorption of HMs by the red mud-based adsorbent was mostly negative ΔG°, positive ΔH°, and positive ΔS°, as shown in Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials. This suggests that the adsorption process was spontaneous. The capacity of the adsorbent is strongly influenced by the adsorption temperature. Adsorption is improved by moderate heating because it raises the collision between the adsorbent and the pollutant and improves molecular thermal activity [172]. Within a certain range, the adsorption capacity rises as the temperature rises [121]. The authors comment on the results from five references. FexOy-BC(RM) was prepared by Qi et al. [161] for the adsorption of Cd(II), as shown in Figure 2b. At the same concentration, the adsorbent’s adsorption capacity rose as the temperature rose. Cui et al. [8] showed that under ΔG° < 0, ΔH° > 0, and ΔS° > 0 circumstances, the adsorption of Cd(II) by RM@HC was enhanced by the temperature rise. Yao et al. [173] demonstrated that elevated temperatures promote both the dispersion and mass transfer of Cd(II) in aqueous solutions, while simultaneously enhancing its adsorption and immobilization onto the adsorbent surface. Furthermore, Awual et al. [174] proposed that adsorbate ions diffuse from the outer layer to the adsorbent active sites more quickly at higher temperatures due to increased kinetic energy. A higher temperature may result in more surface active sites, which would improve the adsorbent’s adsorption capacity [175]. Despite enhanced adsorption at elevated temperatures, practical applications should prioritize energy efficiency by minimizing temperature variations.
4.4. Initial Concentration and Adsorbent Dosage
Some researchers posit that the initial concentration and adsorbent dosage significantly influence the adsorption and removal of HMs by red mud-based adsorbents. When the red mud-based adsorbent is not saturated, HM adsorption rises with the starting concentration [138]. Concentration gradients cause pollutants to interact with adsorbent active sites [176]. Higher initial concentrations of HMs enhance mass transfer but saturate adsorption sites [11], reducing efficiency. Excessive initial concentrations of HM coverage inhibit further adsorption on red mud-based materials. Rising concentrations also shift adsorption from monolayer to multilayer, affecting isotherm model fitting. An alternative approach for HMs’ removal involves optimizing the dosage of red mud-based adsorbents. Cui et al. [8] demonstrated that RM@HC achieved maximum Cd(II) adsorption capacity of 113.55 mg/g at an optimal dose of 1.5 g/L (Figure 2c). Due to strong reactive sites in solution, adsorption saturated at 2 g/L with a reduction efficiency of 99.82% (143.68 mg/g) [177]. Due to the adsorbent cost and high metal ion removal, high dosages are required.
4.5. Contact Time
Concerning the effect of contact time, the authors comment on the results from one reference. Red mud-based adsorbents’ adsorption capacity and active site count determine their equilibrium adsorption time. Adsorption begins with HM ions binding quickly to the adsorbent active sites. Adsorption decreases over time due to site saturation. Gonçalves et al. [162] created 3D-printed lattices for Ni, Cu, Cd, Zn, and As adsorption and found equilibrium after 24 h (Figure 2d). High-concentration gradients and abundant active sites promote rapid initial adsorption, which slows as binding sites become saturated. Other modifiers may raise the specific surface area and negative charge density of the red mud-based adsorbent to boost its affinity for HM ions.
4.6. Types of Adsorbents
Concerning the effect of types of adsorbents, the authors comment on the results from one reference. Different adsorbents have different structural characteristics and functional groups that impact adsorption. Adsorbents with oxygen-containing groups (e.g., -COOH, -OH) have more adsorption active sites, improving adsorption. Adsorbents with smaller particle sizes and larger specific surface areas have more interaction with contaminants, improving adsorption. As illustrated in Figure 2a, Shang et al. [7] observed that PG, RM, PR, and L-PR had varied clearance rates in individual and binary Cd(II)/As(V). Functional groups (La-O) formed complexes with Cd(II)/As(V) in monoadsorption and ternary complexes in coadsorption after lanthanum (La) alteration. Specific surface area, pore volume, and pore size rose increase adsorption.
4.7. Reusability and Regeneration
Recovery and reuse are crucial to cost-effective and appealing adsorbents. Recycling adsorption performance is an important parameter since it affects treatment cost. Red mud-based adsorbents typically exhibit declining efficiency after multiple regeneration cycles due to permanent site occupation and loss of unstable functional groups (e.g., carboxyl and hydroxyl) during adsorption–desorption processes [138,178].
The commonly used desorbents primarily include NaCl, NaOH, HCl, HNO3, EDTA, etc. The binding mechanism between different desorbents and HMs affects the regeneration of red mud-based adsorbents. Firstly, NaCl desorbs cations (e.g., Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+) through ion exchange, but the active site loses its activity after multiple cycles, reducing the adsorption capacity (e.g., MZ material maintains 52.89–82.87 mg/g after five cycles [127], porous sphere three cycles, removal efficiency at 54.60% [120]). Secondly, NaOH can desorb As(V) [134], but strong alkaline conditions (pH > 12) deteriorate the adsorbent [179]. Thirdly, strong acids (HCl, HNO3) dissolve metal precipitates but damage adsorbent pores and cause contamination. HNO3-desorbed NaSi-MGP lost 60% Pb2+/Cu2+ capacity after five cycles [153], while solid–liquid separation incurs recovery losses [152]. H ions have a considerable affinity for the active sites on the adsorbent surface [180]; therefore, large amounts will compete with metal ions for active sites. Fourth, EDTA gently desorbs HMs (e.g., Pb2+, Hg2+) under its chelating effect [153], and regeneration efficiencies outperform acids/bases (e.g., RM-nZVI maintains high regeneration for Hg after EDTA desorption [10]). Therefore, optimizing the adsorbent to balance desorption efficiency, material stability, and environmental risks and exploring the multi-cycle regeneration strategy to mitigate functional group loss and structural collapse are needed in the future.
4.8. Leaching of HMs and Economic Viability
Existing studies show that red mud-based adsorbents’ leaching concentrations are usually below the national safety standard (GB5085.3-2007) [181], and geopolymers can further inhibit leaching by encapsulating HMs through dense calcium carbonate hydrates [182]. However, most studies lacked systematic leaching tests, and only a few studies verified their results. Most studies lacked comprehensive leaching testing, and few proved their safety (Table 3). Gonçalves et al. [143] found that Na, Ca, and Si were significantly released in the first 24 h at pH 3, for 28 days, and slowly accumulated, while K, Al, and Fe were released in lower amounts and posed little risk of leaching trace HMs like Mn, Zn, and Ni. Nevertheless, the environmental risks of long-term release behaviors in complex systems require rigorous assessment. Ensuring ecological safety demands standardized leaching protocols and advanced adsorbent encapsulation technologies.

Table 3.
Leaching of HMs in red mud-based adsorbents (mg/L−1).
Economic feasibility is a primary consideration in adsorbent design for large-scale applications. Red mud, as a solid waste material with readily available characteristics, has led to the development of a series of red mud-based adsorbents. However, to date, summaries and analyses of red mud-based adsorbents have primarily focused on their removal efficiency for target pollutants, with limited detailed analysis from an economic feasibility perspective. Given the diversity in raw material selection and production processes for red mud-based adsorbents, calculating costs presents challenges. Therefore, this section summarizes the wholesale prices and advantages/disadvantages of red mud compared to several low-cost commercial adsorbents through Table 4 and Table 5. The aim is to provide insights for designing new materials by combining red mud with these low-cost adsorbents. As shown in Table 5, the wholesale price of red mud (0.0012–0.08) increases with the increase in iron oxide content, but it is still lower than the prices of several adsorbents in Table 4. Red mud, rich in aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, and iron oxide, can be used as raw material for synthetic zeolite and zero-valent iron. In addition, appropriate synthesis processes can be selected based on material characteristics. This content was discussed in previous sections.

Table 4.
The unit chemical cost, and the advantages and disadvantages of using low-cost adsorbents.

Table 5.
Overview of current wholesale prices for red mud in several public markets.
5. Mechanism of HMs’ Removal
HMs are highly toxic environmental pollutants that pose significant health risks, including acute poisoning and chronic diseases, even at minimal concentrations. HMs are always present in different forms, such as cations and anions, when they enter water bodies. Research on red mud is becoming more and more comprehensive, ranging from single materials to composites, and many studies have shown that various red mud-based adsorbents are effective in removing HMs from wastewater (Table S1). So, the differences in the removal mechanisms of HMs will be specifically analyzed in terms of adsorption models, adsorption kinetics, and adsorption mechanisms.
5.1. Sorption Isotherm Model
Adsorption equilibrium occurs when adsorption and desorption rates balance. Researchers utilize adsorption isotherms and kinetic models to describe adsorption [183,184]. Temperature governs the distribution ratio of adsorbed versus free-phase contaminants in aqueous adsorption systems [185]. HM adsorption on red mud-based adsorbents is studied using the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. Supplementary Table S4 shows that the HM adsorption study using terracotta-based materials uses the Langmuir isotherm, indicating chemical monolayer adsorption with consistent surface adsorption [123], homogeneous monolayer adsorption on the adsorbent surface with a few adsorption sites. Adsorption capacity is maximized when all adsorption sites are monolayers [19]. The Freundlich isotherm is an empirical equation for multilayer adsorption without assumptions [185]. Freundlich isotherm analysis reveals three adsorption regimes: ① physisorption (n > 1) dominates in MZ-Cu2+ (n = 6.47), Fe-C-CO2-As(V) (n = 2.88), and SRMBC-750 systems [138]; ② chemisorption occurs when n ≤ 1, as demonstrated by L-PR (1/n = 0.141) [7]; ③ adsorption becomes unfavorable when n < 0.5 [186]. Notably, Cu2+/Cd2+/Pb2+ adsorption shifts from multilayer to monolayer with increasing ionic radius, while Fe-C-CO2 shows metal-specific n values (Ni(II): 6.05) [134]. Ni(II) absorption by RM/CS supports the Sips theory. As temperatures rise, αs remains non-zero, indicating adsorption via monolayer and multilayer processes. The weaker van der Waals interactions of Ni(II) ions promote a transition from multilayer to monolayer adsorption [107].
5.2. Adsorption Kinetic Model
To understand adsorption kinetics, it is necessary to study changes in adsorption quantities or rates. The adsorption of HMs onto red mud-based adsorbents follows both pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models, with the latter being predominant (Table S4). This prevalence indicates that chemisorption is the dominant adsorption mechanism. The pseudo-first-order model implies that the adsorption process is mainly driven by the adsorbent concentration, while the pseudo-second-order model represents the rate of chemical reaction between the adsorbent and the adsorbate [187]. To better understand the adsorption mechanism of red mud-based adsorbents, several studies have used the intraparticle diffusion model, the Elovich kinetic model, and the Boyd equation, which suggest that film diffusion also controls the adsorption rate [120,153,188]. The intraparticle diffusion model describes the kinetic process as three stages: transient boundary diffusion, inner-surface diffusion, and equilibrium adsorption [153]. In these kinetic models, the contact time certainly affects adsorption. Since various HMs reach equilibrium at different times, the contact time should be considered, especially in binary or polymeric heavy metal systems.
5.3. Adsorption Mechanism
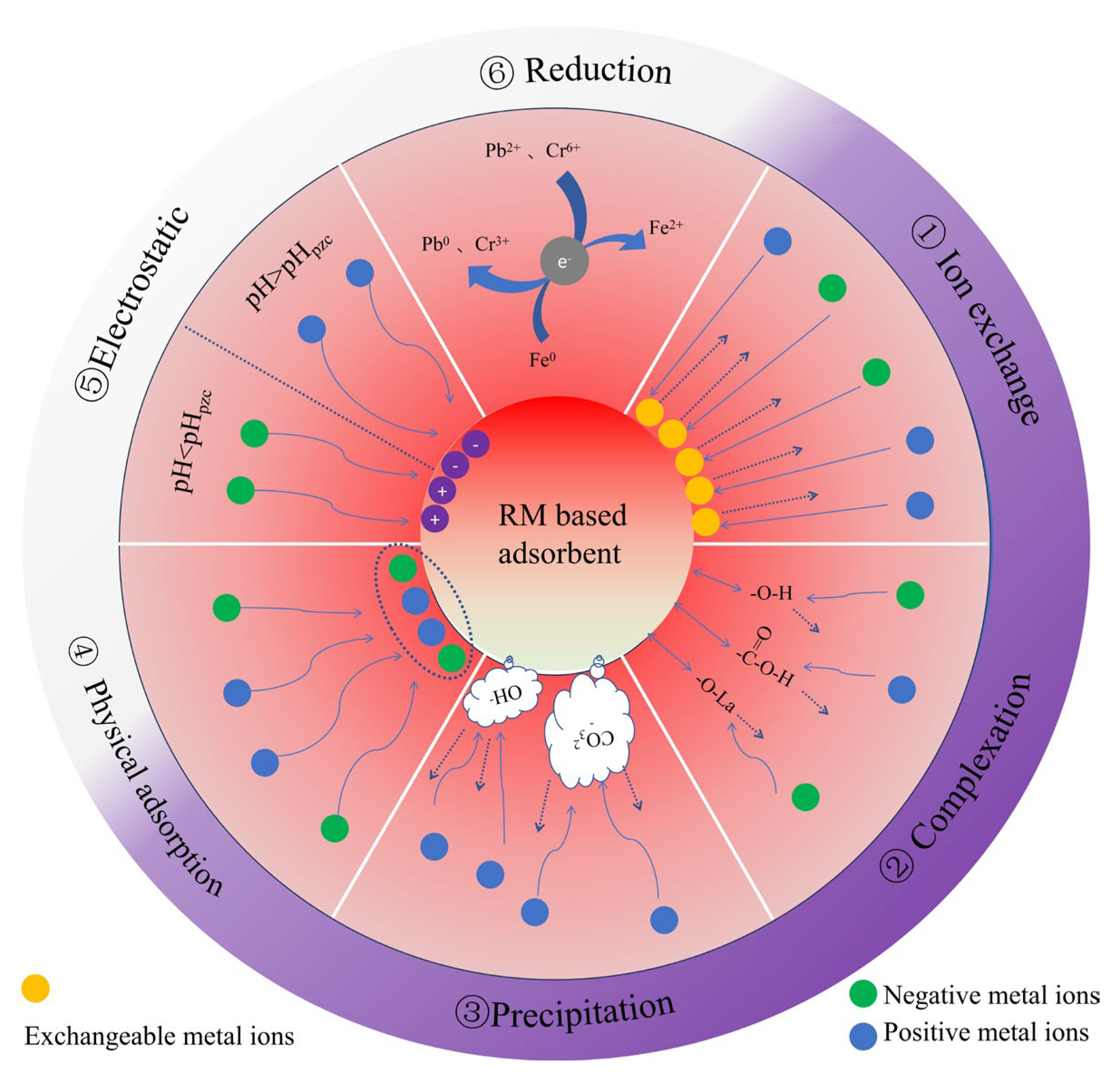
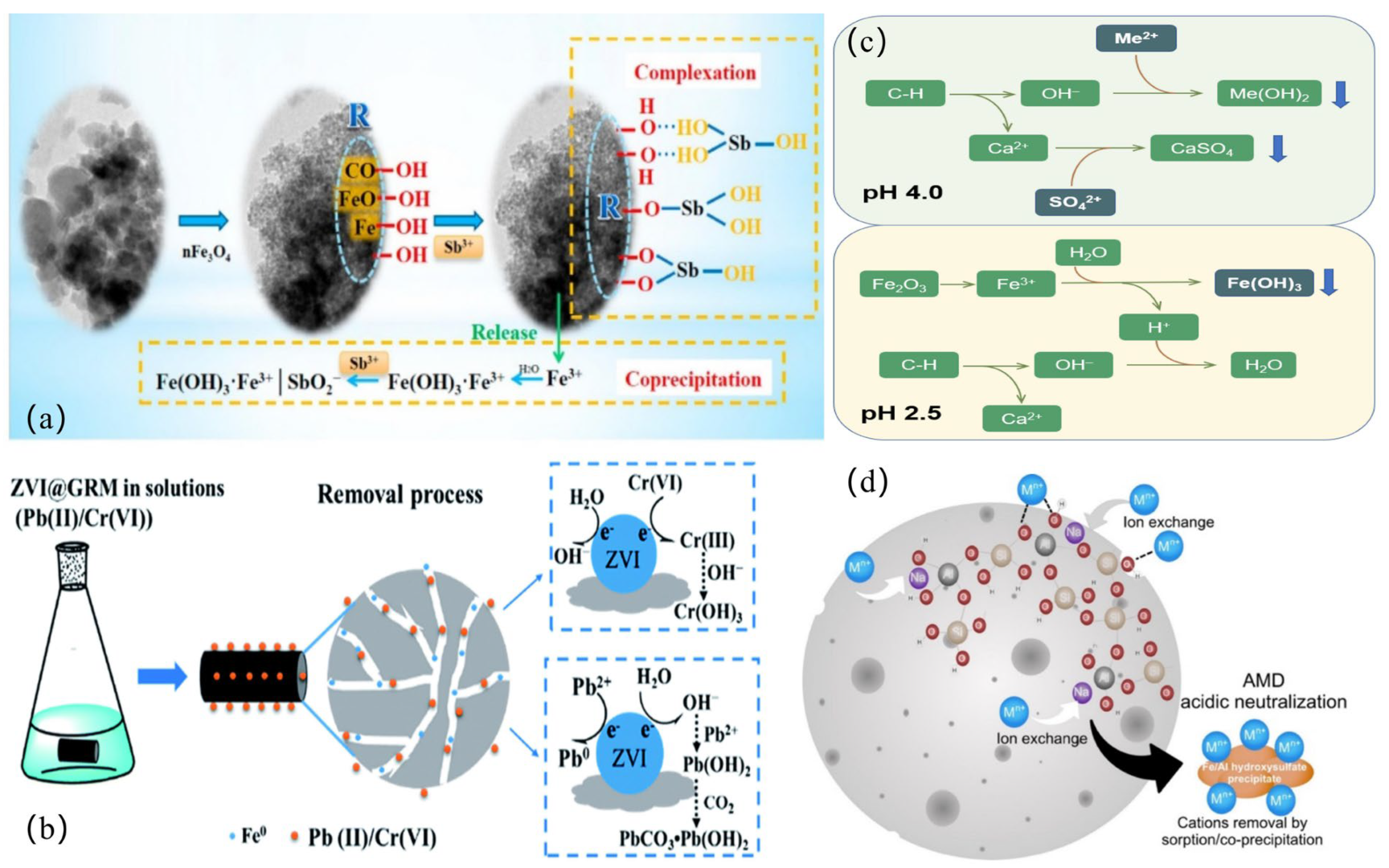
Heavy metal(loid) adsorption by red mud-based adsorbents has several mechanisms (Figure 3). ① Ion exchange: K, Na, Ca2+, and Mg2+ are exchanged with heavy metal cations thanks to numerous adsorption sites [14] (Figure 4d). ② Complexation: Surface oxygen-containing functional groups complex with Pb2+ [137], surface complexation of amorphous iron oxides (nFe3O4 and its byproducts FeO(OH) and Fe(OH)3) with Sb3+ [152], and hydrogen bonding between hydroxyls and antimony molecules remove Sb(III) (Figure 4a). Metal ions may form inner-sphere ternary complexes with sulfate and mineral surface hydroxyl groups to increase adsorption [189,190,191]. ③ Chemical precipitation: Precipitation of metal ions as hydroxides or carbonates occurs. The oxidation of Fe0 produces OH− by reacting with water, and the generated OH− reacts with Pb ions in the solution to form hydroxide precipitates (Pb(OH)2). Subsequently, Pb(OH)2 reacts with Pb2+ and CO32− to form Pb(CO3)·Pb(OH)2 [137], and C-H hydrolysis releases Ca2+ and OH- into the water [13] (Figure 4c). ④ Adsorbent pore size distribution and surface area determine physical adsorption [10,192,193]. Jiang et al. [138] used adsorption isotherms and kinetic experiments. First, zeta potential analysis was used to determine the material’s surface charge distribution under different pH conditions. The Freundlich constant n values were all greater than 1, indicating that physical adsorption was dominant. The negatively charged surface of SRMBC-750 is ideal for Cu2+ adsorption at pH > 3. Electrostatic adsorption has a potential influence throughout [194]. FTIR and XRD spectra showed that oxygen-containing functional groups complexed to modify the C-O peaks from the O-H peaks [195]; these changes reflect the stretching vibrations of -OH and C-O, indicating that the functional groups on SRMBC-750 effectively adsorbed Cu2+. The presence of C-C/C=C in C1s spectra shows that the ‘cation-π’ may also be engaged in Cu2+ adsorption. ⑤ Electrostatic attraction: solution pH and adsorbent pHPZC alter electrostatic interactions [194]. FTIR study showed that Cd(II)/As(V) adsorption on L-PR includes alkoxy C=H groups, indicating electrostatic attraction [7]. ⑥ Reduction converts hazardous high-valence metal ions to low-valence states. Fe0 reduces Pb(II) and Cr(VI) in redox processes (Figure 4b), according to XRD, SEM, and XPS [9,10,121].
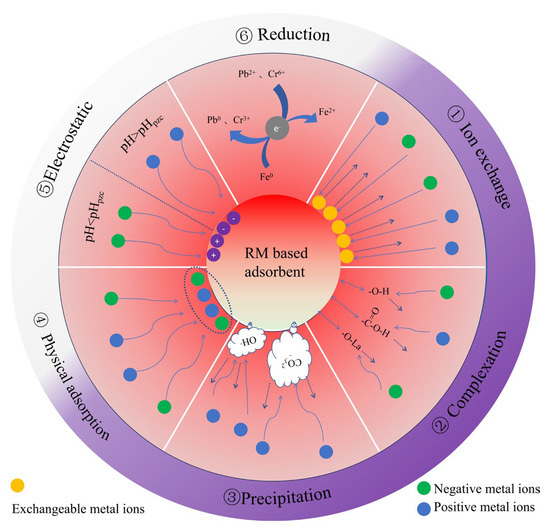
Figure 3.
Red mud-based adsorbent HMs’ removal mechanism.
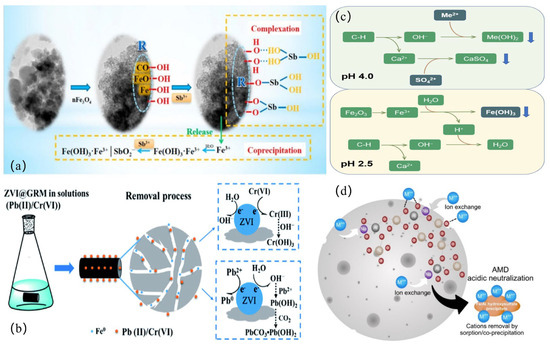
Figure 4.
Application of different adsorbents (a) HRM@nFe3O4 removes Sb(III) from the aqueous phase; (b) ZVI@GRM for the removal of Pb(II) and Cr(VI); (c) the mechanisms for removing HMs by RMPC from acid mine drainage; (d) porous red mud/fly ash-based geopolymeric spheres in fixed bed columns for the repair of true AMD.
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Due to its porous structure, elevated specific surface area, and abundant Fe/Al/Si oxides, the red mud-based adsorbent effectively eliminates HMs from wastewater through ion exchange, chemical precipitation, and complexation, with the adsorption process primarily aligning with pseudo-second-order kinetics and the Langmuir model. It can be combined with industrial/biological wastes (e.g., gangue, phosphogypsum, biochar) and technologies such as hydrothermal and co-precipitation to make composites with high adsorption capacity and regenerability, such as zeolites, magnetic materials, geopolymers, and so on. Practical applications still face problems, such as high preparation costs, poor scale-up practicality, and environmental hazards (e.g., leaching of modifiers). Future goals include the following: pore/group optimization for enhanced adsorption, low-energy synthesis, resource diversification, improved risk assessment, and scalable wastewater treatment validation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13072249/s1; Table S1. Performance characteristics and adsorption mechanisms of red mud-based adsorbents for heavy metal removal from water: conditions and efficacy; Table S2. Red mud-based adsorbent for pHPZC; Table S3. Thermodynamic parameters of red mud-based adsorbents; Table S4. Isothermal and kinetic modeling of red mud-based adsorbents. References [196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
F.L.: Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing original draft. R.D.: Validation, writing review and editing, funding acquisition. B.H.: Validation, writing review and editing, and funding acquisition. L.P.: Investigation, data curation. X.K.: Data curation, funding acquisition. B.Z.: Resources, supervision. B.R.: Validation, writing review and editing. A.H.: Writing review and editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundations of China (2025JJ50181, 2023JJ40288, 2023JJ30244, and 2024JJ8319), the Ministry of Education in China Project of Humanities and Social Science (23YJAZH224), and National Natural Science Foundations of China (52204185 and 41973078). The APC was funded by the corresponding author.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C.; Sharma, S.K. Biosorption of Heavy Metals: Recent Trends and Challenges. In Wastewater Reuse and Management; Sharma, S.K., Sanghi, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 305–322. ISBN 978-94-007-4941-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyappan, R.; Sophia, A.C.; Swaminathan, K.; Sandhya, S. Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Carbon Derived from Agricultural Wastes. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-C.; Son, Y.-O.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; Shi, X. Oxidative Stress and Metal Carcinogenesis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 742–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy Metals, Occurrence and Toxicity for Plants: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, Q.; Nadeem, R.; Iqbal, M.; Saeed, R.; Ansari, T.M. Organic Acids Pretreatment Effect on Rosa Bourbonia Phyto-Biomass for Removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) from Aqueous Media. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasinakis, A.S.; Thomaidis, N.S. Fate and Biotransformation of Metal and Metalloid Species in Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 307–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Geng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Che, D.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, T.; Tang, M.; Huo, L. Lanthanum-Modified Phosphogypsum Red Mud Composite for the Co-Adsorption of Cadmium and Arsenic: Mechanism Study and Soil Remediation. Agriculture 2024, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Chen, D.; Duan, R.; Yang, F.; Li, D.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, R. Taloring Sawdust Derived Hydrochar via Red Mud for Cadmium Removal: Electron Transfer Insight and Recyclability Assessment. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cai, J.; Liao, Z.; Jawad, A.; Ifthikar, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Black Liquor as Biomass Feedstock to Prepare Zero-Valent Iron Embedded Biochar with Red Mud for Cr(VI) Removal: Mechanisms Insights and Engineering Practicality. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.K.; Patel, R.K.; Kurwadkar, S. Mechanistic Insight into the Adsorption of Mercury (II) on the Surface of Red Mud Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Composite. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 246, 103959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Jing, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z. Adsorption of Lead from Water Using MnO2-Modified Red Mud: Performance, Mechanism, and Environmental Risk. Water 2023, 15, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Deng, R. Removal of Pb(II) by Adsorption of HCO–(Fe3O4)x Composite Adsorbent: Efficacy and Mechanism. Water 2023, 15, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Mao, Q.; Luo, L.; Deng, Y. Removal of Heavy Metals from Acid Mine Drainage by Red Mud–Based Geopolymer Pervious Concrete: Batch and Long–Term Column Studies. Polymers 2022, 14, 5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhong, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, S. Transferring Red Mud to Efficient Adsorbent for the Adsorption and Immobilization of Ni(Ⅱ) from Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surf. C Environ. Asp. 2024, 2, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Deng, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Hou, B.; Zhou, S.; Hursthouse, A. New Insights into Adsorption of As(V) and Sb(V) from Aqueous by HCO–(Fe3O4)x Adsorbent: Adsorption Behaviors, Competition and Mechanisms. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, R.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Hou, B.; Zhou, S.; Huang, W.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A. Novel Ce(III) Based Ce-Oxide/Fe3O4 Composite for High-Efficiency Removal of Sb(V) and Sb(III) from Wastewater at Wide pH Range. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, R.; Tang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, X.; Wang, J.; Hursthouse, A. A Study of the Adsorption and Removal of Sb(III) from Aqueous Solution by Fe(III) Modified Proteus Cibarius with Mechanistic Insights Using Response Surface Methodology. Processes 2021, 9, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, R.; Ren, B.; Yaseen, M.; Hursthouse, A. Enhancing the Removal of Sb (III) from Water: A Fe3O4@HCO Composite Adsorbent Caged in Sodium Alginate Microbeads. Processes 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, R.; Ren, B.; Hou, B.; Hursthouse, A. Preparation of a Novel Fe3O4/HCO Composite Adsorbent and the Mechanism for the Removal of Antimony (III) from Aqueous Solution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.-J.; Jin, C.-S.; Ren, B.-Z.; Hou, B.-L.; Hursthouse, A. The Potential for the Treatment of Antimony-Containing Wastewater by Iron-Based Adsorbents. Water 2017, 9, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.-J.; Shao, R.; Ren, B.-Z.; Hou, B.; Tang, Z.-E.; Hursthouse, A. Adsorption of Antimony(III) onto Fe(III)-TreatedHumus Sludge Adsorbent: Behaviorand Mechanism Insights. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 28, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipasa, K.B. Accumulation and Fate of Selected Heavy Metals in a Biological Wastewater Treatment System. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyüz, B.; Veli, S. Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies for the Removal of Nickel and Zinc from Aqueous Solutions by Ion Exchange Resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, M.M.; Howerton, B.S.; Atwood, D.A. Chemical Precipitation of Heavy Metals from Acid Mine Drainage. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.E.; Pereira, M.S.; Jorgetto, A.O.; Martines, M.A.U.; Silva, R.I.V.; Saeki, M.J.; Castro, G.R. The Reactive Surface of Castor Leaf [Ricinus communis L.] Powder as a Green Adsorbent for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Natural River Water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater by Chemically Modified Plant Wastes as Adsorbents: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3935–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaalan, H.F.; Sorour, M.H.; Tewfik, S.R. Simulation and Optimization of a Membrane System for Chromium Recovery from Tanning Wastes. Desalination 2001, 141, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asere, T.G.; Stevens, C.V.; Du Laing, G. Use of (Modified) Natural Adsorbents for Arsenic Remediation: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Lu, J.; Yu, G.; Möslang, M.; Zhou, Y. Superior Adsorption Capacity of Functionalised Straw Adsorbent for Dyes and Heavy-Metal Ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Yi, L.; Wu, Q.; Xia, J.; Zhang, B. A Review of Comprehensive Utilization of Red Mud. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairul, M.A.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. The Composition, Recycling and Utilisation of Bayer Red Mud. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X. Applications of Red Mud as an Environmental Remediation Material: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Xiao, B.; Huang, Q. Synthesis and Strength Optimization of One-Part Geopolymer Based on Red Mud. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Park, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, H. Red Mud-Amended Soil as Highly Adsorptive Hybrid-Fill Materials for Controlling Heavy Metal Sewage Seepage in Industrial Zone. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen, Ö.; Günaydın, H.İ. Preparation and Characterization of Red Mud/Polysulfone Composite Geosynthetic Barrier. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 54, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. Feasibility Study on Grouting Material Prepared from Red Mud and Metallurgical Wastewater Based on Synergistic Theory. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevgili, İ.; Dilmaç, Ö.F.; Şimşek, B. An Environmentally Sustainable Way for Effective Water Purification by Adsorptive Red Mud Cementitious Composite Cubes Modified with Bentonite and Activated Carbon. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, N.; Lini Dev, K. Sustainable Utilization of Red Mud as Recycled Waste: A Critical Review and Future Research Directions. Indian Geotech. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yao, W.; Zheng, K.; Cui, N.; Xie, N. Synergistically Using Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) and Other Solid Wastes to Manufacture Eco-Friendly Cementitious Materials. Buildings 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Lee, J.; Reddy Kannapu, H.P.; Jang, S.-H.; Kim, Y.; Jang, H.; Ha, J.-M.; Jung, S.-C.; Park, Y.-K. Acid-Treated Waste Red Mud as an Efficient Catalyst for Catalytic Fast Copyrolysis of Lignin and Polyproylene and Ozone-Catalytic Conversion of Toluene. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Integration of Lactic Acid Biorefinery with Treatment of Red Mud from Alumina Refinery: Win–Win Paradigm for Waste Valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 401, 130743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, P.; Ni, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Deng, W.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Pei, F.; Du, L.; et al. A Review of Solid Wastes-Based Stabilizers for Remediating Heavy Metals Co-Contaminated Soil: Applications and Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlögl, S.; Diendorfer, P.; Baldermann, A.; Vollprecht, D. Use of Industrial Residues for Heavy Metals Immobilization in Contaminated Site Remediation: A Brief Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 2313–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wang, X.; Deng, M.; Li, H.; Lin, C. Red Mud-Biochar Composites (Co-Pyrolyzed Red Mud-Plant Materials): Characteristics and Improved Efficacy on the Treatment of Acidic Mine Water and Trace Element-Contaminated Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golia, E.E.; Chartodiplomenou, M.-A.; Papadimou, S.G.; Kantzou, O.-D.; Tsiropoulos, N.G. Influence of Soil Inorganic Amendments on Heavy Metal Accumulation by Leafy Vegetables. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 30, 8617–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.; Clark, M.W.; McMahon, P.; Ward, N. Alkalinity Conversion of Bauxite Refinery Residues by Neutralization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.B.; Wasewar, K.L.; Mishra, R.S.; Mahindran, P.; Chaddha, M.J.; Mukhopadhyay, J.; Yoo, C.K. Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide in Red Mud. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoruh, S.; Ergun, O.N. Copper Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions by Usıng Red Mud—An Aluminium Industry Waste. In Survival and Sustainability; Gökçekus, H., Türker, U., LaMoreaux, J.W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1275–1282. ISBN 978-3-540-95990-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nadaroglu, H.; Kalkan, E.; Demir, N. Removal of Copper from Aqueous Solution Using Red Mud. Desalination 2010, 251, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoruh, S.; Ergun, O.N. Use of Fly Ash, Phosphogypsum and Red Mud as a Liner Material for the Disposal of Hazardous Zinc Leach Residue Waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, J.; Fernández, B. Treatment from Abandoned Mine Landfill Leachates. Adsorption Technology. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2732–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoumis, T.; Calmano, W.; Förstner, U. Demobilization of Heavy Metals from Mine Waters. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2000, 28, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Fischel, M.; Lin, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Yan, J. Applying Red Mud in Cadmium Contamination Remediation: A Scoping Review. Toxics 2024, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Thakur, A. Red Mud Based Binder: A Sustainable Material for Removal of Chromium (VI) from Water. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 2955–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, C.; Ma, W.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; Zhang, L.; Mao, A. Study on the Adsorption Performance of Cu2+ in Wastewater by Red Mud. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Liu, X.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, A.; Tang, L.; Wu, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Remediation of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd-Contaminated Agricultural Soil Using a Combined Red Mud and Compost Amendment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 118, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Z. Frontier Research and Prospect of Phosphate Adsorption in Wastewater by Red Mud: A Review. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 310, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Heal, K.V.; Friesl-Hanl, W. The Use of Red Mud as an Immobiliser for Metal/Metalloid-Contaminated Soil: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, S.; Smičiklas, I.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Lončar, B.; Mitrić, M. Rinsed and Thermally Treated Red Mud Sorbents for Aqueous Ni2+ Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O. Novel Applications of Red Mud as Coagulant, Adsorbent and Catalyst for Environmentally Benign Processes. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1621–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Li, L.; Chang, Z.; Rao, Z.; Lu, L. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium by Using Red Mud Activated with Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Xie, F. Adsorption Behavior of Manganese Dioxide Towards Heavy Metal Ions: Surface Zeta Potential Effect. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, S.; Smičiklas, I.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Šljivić, M.; Đukić, B.; Lončar, B. Study of Factors Affecting Ni2+ Immobilization Efficiency by Temperature Activated Red Mud. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Luan, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.; Jia, Z. Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Raw and Activated Red Mud and Fly Ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genç-Fuhrman, H.; Tjell, J.C.; McConchie, D. Increasing the Arsenate Adsorption Capacity of Neutralized Red Mud (Bauxsol). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 271, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X.; Rudolph, V.; Haghseresht, F. Phosphate Removal from Wastewater Using Red Mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Long, Q.; Zhang, Q. Application of Annealed Red Mud to Mn2+ Ion Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 2761–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, K.; Shanmugapriya, T. Investigation on Properties and Heavy MetalIon Extraction of Thermally Activated RedMud Incorporated Cement Mortar. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 3959–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.L.P.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Da Conceição, F.T.; Costa De Jesus, C.P.; Kiyohara, P.K.; Coelho, A.C.V.; Frost, R.L. Red Mud from Brazil: Thermal Behavior and Physical Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santona, L.; Castaldi, P.; Melis, P. Evaluation of the Interaction Mechanisms between Red Muds and Heavy Metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.C.; Patel, R.; Ray, B.C. Utilization of Activated CO2-Neutralized Red Mud for Removal of Arsenate from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Costa, E.T.S.; Curi, N.; Penha, H.G.V. Increasing Arsenic Sorption on Red Mud by Phosphogypsum Addition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, P.; Reddy, M.S.; Patnaik, S.K. Aspergillus Tubingensis Reduces the pH of the Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) Amended Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 2005, 167, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç-Fuhrman, H.; Tjell, J.C.; McConchie, D. Adsorption of Arsenic from Water Using Activated Neutralized Red Mud. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamo, C.; Djomou Djonga, P.N.; Dangwang Dikdim, J.M.; Kamga, R. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Pb(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Red Mud, a Low-Cost Adsorbent. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 2353–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Luan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z. Adsorption Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by Active Red Mud. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.; Tütem, E.; Hügül, M.; Hizal, J. Heavy Metal Cation Retention by Unconventional Sorbents (Red Muds and Fly Ashes). Water Res. 1998, 32, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altundoǧan, H.S.; Tümen, F. Removal of Phosphates from Aqueous Solutions by Using Bauxite II: The Activation Study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altundoğan, H.S.; Altundoğan, S.; Tümen, F.; Bildik, M. Arsenic Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions by Activated Red Mud. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, L.J.; Hartshorn, A.; McMonagle, J.B.; Fleming, L.; Funnell, D. Chemistry of Bauxite Residue Neutralisation and Aspects to Implementation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 119, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.K.; Mandal, S.; Dash, S.S.; Badhai, P.; Patel, R.K. Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution by Acid Activated Red Mud. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Kaur, G.; Yan, C.; Johnstone, D.W.; Millar, G.J. Effect of Strong Acids on Red Mud Structural and Fluoride Adsorption Properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 423, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snars, K.; Gilkes, R.J. Evaluation of Bauxite Residues (Red Muds) of Different Origins for Environmental Applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, M.; Power, G.; Klauber, C. Bauxite Residue Issues: III. Alkalinity and Associated Chemistry. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smičiklas, I.; Smiljanić, S.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Šljivić-Ivanović, M.; Mitrić, M.; Antonović, D. Effect of Acid Treatment on Red Mud Properties with Implications on Ni(II) Sorption and Stability. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, C.; McConchie, D.; Pohl, J.; Creelman, R.; Clark, M.; Stocksiek, C. Chemistry of Seawater Neutralization of Bauxite Refinery Residues (Red Mud). Environ. Eng. Sci. 2004, 21, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.; Frost, R.; Nguyen, T. Hydrotalcites and Their Role in Coordination of Anions in Bayer Liquors: Anion Binding in Layered Double Hydroxides. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, H.; Tjell, J.C.; McConchie, D.; Schuiling, O. Adsorption of Arsenate from Water Using Neutralized Red Mud. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, N.W.; Fulton, I.M.; Morrell, W.J. Seawater Neutralization of Alkaline Bauxite Residue and Implications for Revegetation. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Wasewar, K.L.; Lataye, D.H.; Mukhopadhyay, J.; Yoo, C.K. Feasibility of Red Mud Neutralization with Seawater Using Taguchi’s Methodology. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, I.T.; Peacock, C.L.; Lockwood, C.L.; Stewart, D.I.; Mortimer, R.J.G.; Ward, M.B.; Renforth, P.; Gruiz, K.; Mayes, W.M. Behavior of Aluminum, Arsenic, and Vanadium during the Neutralization of Red Mud Leachate by HCl, Gypsum, or Seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6527–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renforth, P.; Mayes, W.M.; Jarvis, A.P.; Burke, I.T.; Manning, D.A.C.; Gruiz, K. Contaminant Mobility and Carbon Sequestration Downstream of the Ajka (Hungary) Red Mud Spill: The Effects of Gypsum Dosing. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renforth, P.; Manning, D.A.C.; Lopez-Capel, E. Carbonate Precipitation in Artificial Soils as a Sink for Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, I.T.; Mortimer, R.J.G.; Palaniyandi, S.; Whittleston, R.A.; Lockwood, C.L.; Ashley, D.J.; Stewart, D.I. Biogeochemical Reduction Processes in a Hyper-Alkaline Leachate Affected Soil Profile. Geomicrobiol. J. 2012, 29, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandratos, V.G.; Elzinga, E.J.; Reeder, R.J. Arsenate Uptake by Calcite: Macroscopic and Spectroscopic Characterization of Adsorption and Incorporation Mechanisms. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 4172–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, R.; Kirwan, L. Gypsum Amendment of Alkaline Bauxite Residue—Plant Available Aluminium and Implications for Grassland Restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, W.M.; Jarvis, A.P.; Burke, I.T.; Walton, M.; Feigl, V.; Klebercz, O.; Gruiz, K. Dispersal and Attenuation of Trace Contaminants Downstream of the Ajka Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) Depository Failure, Hungary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5147–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.G.; Pennifold, R.M.; Davies, M.G.; Jamieson, E.J. Reactions of Carbon Dioxide with Tri-Calcium Aluminate. In Electrometallurgy and Environmental Hydrometallurgy; Young, C., Alfantazi, A., Anderson, C., James, A., Dreisinger, D., Harris, B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 1705–1715. ISBN 978-1-118-82060-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, R.M.; Ounoughene, G.; Borra, C.R.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Neutralisation of Bauxite Residue by Carbon Dioxide Prior to Acidic Leaching for Metal Recovery. Miner. Eng. 2017, 112, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.C.; Patel, R.K.; Ray, B.C. Neutralization of Red Mud Using CO2 Sequestration Cycle. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archambo, M.; Kawatra, S.K. Red Mud: Fundamentals and New Avenues for Utilization. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.S.; Prasad, M.; Khan, J.; Amritphale, S.S.; Singh, M.; Raju, C.B. Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Using Red Mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-S.; Ji, S.; Lee, P.-K.; Oh, C. Bauxite Residue Neutralization with Simultaneous Mineral Carbonation Using Atmospheric CO2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, X.; Yang, G. Preparation of Nanochitin-Contained Magnetic Chitosan Microfibers via Continuous Injection Gelation Method for Removal of Ni(II) Ion from Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, G.; Naushad, M.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; García-Peñas, A.; Mola, G.T.; Si, C.; Stadler, F.J. Bio-Inspired and Biomaterials-Based Hybrid Photocatalysts for Environmental Detoxification: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.; Kongot, M.; Saini, V.K.; Kumar, A. Removal of Pentachlorophenol Pesticide from Aqueous Solutions Using Modified Chitosan. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.-T.; Nguyen, D.-K.; Nguyen, T.T.P.; Ho, T.-H.; Dinh, V.-P.; Kiet, H.A.T. The Effective Ni(II) Removal of Red Mud Modified Chitosan from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, T.-T.; Dinh, V.-P.; Nguyen, Q.-H.; Tran, N.-Q.; Nguyen, D.-K.; Ho, T.-H.; Nguyen, V.-D.; Tran, D.X.; Kiet, H.A.T. Pb(II) Adsorption Mechanism and Capability from Aqueous Solution Using Red Mud Modified by Chitosan. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, C.; Fang, G.; Chen, Q.; Ao, X. Novel Red Mud/Polyacrylic Composites Synthesized from Red Mud and Its Performance on Cadmium Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, P.; Meng, K.; Lv, F.; Tong, W.; Chu, P.K. Dealkalization of Red Mud by Carbide Slag and Flue Gas. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayazi, M.; Afzali, D.; Ghanei-Motlagh, R.; Iraji, A. Synthesis of Novel Sepiolite–Iron Oxide–Manganese Dioxide Nanocomposite and Application for Lead(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18893–18903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Ali, I. Equilibrium Uptake, Isotherm and Kinetic Studies of Cd(II) Adsorption onto Iron Oxide Activated Red Mud from Aqueous Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 202, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, G.; Narayanan, S.L. Synthesis of Fe2O3-Coated and HCl-Treated Bauxite Ore Waste for the Adsorption of Arsenic (III) from Aqueous Solution: Isotherm and Kinetic Models. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Luan, Z.; Peng, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, J. Arsenate Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Modified Red Mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.-W.; Li, J.; Du, Z.-F.; Peng, Y.-Z. Cr(VI) Adsorption on Red Mud Modified by Lanthanum: Performance, Kinetics and Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zu, Y.-Q.; Li, G.; Sun, G.-X. [Mechanism of As(V)Removal from Water by Lanthanum and Cerium Modified Biochars]. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2018, 39, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.-M.; Zhou, F.-P.; Bi, X.-L.; Chen, D.-D.; Li, J.; Sun, S.-Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Chen, X.-Q. Accelerated Crystallization of Magnetic 4A-Zeolite Synthesized from Red Mud for Application in Removal of Mixed Heavy Metal Ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, F.; Niu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Sun, W.; He, D. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Modified Red Mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of Metal Sorption by Biochars: Biochar Characteristics and Modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, M.; He, C.; Zhai, X.; Wang, S. Synthesis of Porous Red Mud/Slag-Based Spherical Geopolymers for Efficient Methylene Blue and Ni2+ Removal from Water. Langmuir 2024, 40, 23882–23894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Dai, M.; Cao, J.; Peng, C. Fabrication of a Low-Cost Adsorbent Supported Zero-Valent Iron by Using Red Mud for Removing Pb(ii) and Cr(vi) from Aqueous Solutions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 33486–33496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesgari Abbasi, S.; Rashidi, A.; Ghorbani, A.; Khalaj, G. Synthesis, Processing, Characterization, and Applications of Red Mud/Carbon Nanotube Composites. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 16738–16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Luan, H.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Song, M.; Li, B.; Tang, X. Adsorption of Pb, Cu and Cd from Water on Coal Fly Ash-Red Mud Modified Composite Material: Characterization and Mechanism. Water 2023, 15, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C.; Lucini, P.; Mancinelli, M.; Abdolrahimi, M.; Martucci, A.; Peddis, D.; Maraschi, F.; Cavalcante, F.; Sturini, M. Lead, Zinc, Nickel and Chromium Ions Removal from Polluted Waters Using Zeolite Formed from Bauxite, Obsidian and Their Combination with Red Mud: Behaviour and Mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, A.; Ding, S.; Yu, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, D.; Wu, Y. Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu Contaminated Soil with Mg-Fe-Al Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs) Synthesized from Waste Red Mud. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, T.; Chen, D.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J.; Sun, R.; Zi, W.; Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Hexavalent Chromium Elimination from Wastewater by Integrated Micro-Electrolysis Composites Synthesized from Red Mud and Rice Straw via a Facile One-Pot Method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Meng, X.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, F. Feasible Synthesis of Magnetic Zeolite from Red Mud and Coal Gangue: Preparation, Transformation and Application. Powder Technol. 2023, 423, 118495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C.; Cannas, C.; Pinna, N.; Cavalcante, F.; Lettino, A.; Lotti, P.; Gatta, G.D. Effect of Red Mud Added to Zeolite LTA Synthesis: Where Is Fe in the Newly-Formed Material? Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 298, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, C.; Han, L.; Liang, M. Synthesis of 4A Zeolite from Red Mud and Mechanism of Adsorption Removal of Cu2+ and Mn2+ from Water. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2023, 43, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T.K.; Phan, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Slow Pyrolysis Pine Cone Bio-Char in the Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption: Kinetic, Equilibrium, Mechanism and Thermodynamic. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Duan, S.; Wang, Y.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Wang, C.; Li, J. A Valuable Biochar from Poplar Catkins with High Adsorption Capacity for Both Organic Pollutants and Inorganic Heavy Metal Ions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ma, D.; Ge, X. CO2 -Looping in Biomass Pyrolysis or Gasification. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 1700–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Sahu, J.N.; Ganesan, P. Effect of Process Parameters on Production of Biochar from Biomass Waste through Pyrolysis: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Cho, D.-W.; Bhatnagar, A.; Song, H. Adsorption of As(V) and Ni(II) by Fe-Biochar Composite Fabricated by Co-Pyrolysis of Orange Peel and Red Mud. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Z.; Cao, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, F. Thermodynamic Analysis on the Parametric Optimization of a Novel Chemical Looping Methane Reforming in the Separated Productions of H2 and CO. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 192, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.-W.; Yoon, K.; Ahn, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hou, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Song, H. Fabrication and Environmental Applications of Multifunctional Mixed Metal-Biochar Composites (MMBC) from Red Mud and Lignin Wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-I.; Choi, D.; Kim, S.; Park, S.-J.; Kwon, E.E. Fabrication of Fe-Doped Biochar for Pb Adsorption through Pyrolysis of Agricultural Waste with Red Mud. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Li, H.; Cheng, T.; Tian, Y.; Liu, P.; Guo, J.; Cui, K.; Ma, R.; Ma, X.; Cui, F.; et al. Novel Preparation of Sludge-Based Spontaneous Magnetic Biochar Combination with Red Mud for the Removal of Cu2+ from Wastewater. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 806, 139993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee Abyaneh, M.; Aliasghar, A.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Daryabeigi Zand, A.; Moazeni, K. Importance of Pyrolysis Temperature and Particle Size on Physicochemical and Adsorptive Properties of Urban Wood-Derived Biochar. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 40, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. Effects of Pyrolysis Temperature on Biochar’s Characteristics and Speciation and Environmental Risks of Heavy Metals in Sewage Sludge Biochars. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, X.; Liu, C.; Dai, H.; Bai, Z. Steel Slag Base Geopolymer for Efficient Removal of Zn and Ni Ions from Aqueous Solutions: Preparation and Characterization. Mater. Lett. 2023, 340, 134173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onutai, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Thavorniti, P.; Jiemsirilers, S. Removal of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Cd2+ from Wastewater Using Fly Ash Based Geopolymer as an Adsorbent. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 773, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, N.P.F.; Almeida, M.M.; Labrincha, J.A.; Novais, R.M. Effective Acid Mine Drainage Remediation in Fixed Bed Column Using Porous Red Mud/Fly Ash-Containing Geopolymer Spheres. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 940, 173633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korat, L.; Ducman, V. The Influence of the Stabilizing Agent SDS on Porosity Development in Alkali-Activated Fly-Ash Based Foams. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiras, J.; Novais, R.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Metakaolin/Red Mud-Derived Geopolymer Monoliths: Novel Bulk-Type Sorbents for Lead Removal from Wastewaters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 232, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; He, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, D.; Gao, S. Immobilization, Enrichment and Recycling of Cr(VI) from Wastewater Using a Red Mud/Carbon Material to Produce the Valuable Chromite (FeCr2O4). Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Han, Y.; Qu, J.; Guo, Z. The Influence of Carbon Nanotubes/Silica Fume on the Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Composites. Rom. J. Mater. 2015, 45, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzel, C.; Neville, T.P.; Donatello, S.; Vandeperre, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Cheeseman, C.R. Influence of Metakaolin Characteristics on the Mechanical Properties of Geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83–84, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Geopolymer Foams: An Overview of Recent Advancements. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Lu, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S. Multi-Scale Reinforcement of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes / Polyvinyl Alcohol Fibers on Lightweight Engineered Geopolymer Composites. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiras, J.; Oliveira, I.E.; Silva, R.M.; Silva, R.F.; Novais, R.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Catalyst-Free CNTs Growth on Red Mud-Based Alkali Activated Adsorbents: Innovative Route to Boost Heavy Metals Adsorption from Wastewaters. Mater. Lett. 2023, 353, 135246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Luo, L.; Luo, S.; Peng, K.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Q.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y. Efficient Removal of Antimony(III) in Aqueous Phase by Nano-Fe3O4 Modified High-Iron Red Mud: Study on Its Performance and Mechanism. Water 2021, 13, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, M.; Gan, T.; Bao, B. Quantifying Gel Properties of Industrial Waste-Based Geopolymers and Their Application in Pb2+ and Cu2+ Removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, D.; Nanda, B.; Parida, K. Sustainable Nano Composite of Mesoporous Silica Supported Red Mud for Solar Powered Degradation of Aquatic Pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6137–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Deng, T.; Qiu, W.; Hu, T.; Zheng, X.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H.; et al. One Stone, Two Birds: An Eco-Friendly Aerogel Based on Waste Pomelo Peel Cellulose for the Efficient Adsorption of Dyes and Heavy Metal Ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Hong, W.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Duan, X. A Novel Mesoporous Fe-Silica Aerogel Composite with Phenomenal Adsorption Capacity for Malachite Green. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A.M.; Makhlouf, A.S.H.; Chong, K.F.; Alharbi, N.S.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. MWCNTs-Fe3O4 Nanocomposite for Hg(II) High Adsorption Efficiency. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 258, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gou, S.; He, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhou, L.; Gou, G.; Liu, L. N-Methylene Phosphonic Chitosan Aerogels for Efficient Capture of Cu2+ and Pb2+ from Aqueous Environment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Kong, L.; Cai, G.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Tian, Y. Compressible Amino-Modified Carboxymethyl Chitosan Aerogel for Efficient Cu(II) Adsorption from Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Deng, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, K.; Zeng, G. Stabilization of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) with Modified Biochar for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, E.R. Phenomenological Theory of Ion Solvation. Effective Radii of Hydrated Ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Pan, B.; Wan, S.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L. Use of Hydrous Manganese Dioxide as a Potential Sorbent for Selective Removal of Lead, Cadmium, and Zinc Ions from Water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.R.; Zhao, H.H.; Zhang, G.B.; Li, J.T.; Ji, P.H. [Adsorption of Cd2+ from wastewater by modified fly ash]. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2019, 30, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Cai, W. Micro/Nanostructured Porous Fe–Ni Binary Oxide and Its Enhanced Arsenic Adsorption Performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, E.; Izquierdo, M.; Gómez, A.; Mingot, J.; Barrio-Parra, F. Risk Assessment from Exposure to Arsenic, Antimony, and Selenium in Urban Gardens (Madrid, Spain). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 36, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, R.; Liang, X.; Ma, L.; Lin, X.; Zhu, J.; He, H.; Parker, S.C.; Molinari, M. Synergistic Adsorption of Cd(II) with Sulfate/Phosphate on Ferrihydrite: An in Situ ATR-FTIR/2D-COS Study. Chem. Geol. 2018, 477, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Remediation of As(III) and Cd(II) Co-Contamination and Its Mechanism in Aqueous Systems by a Novel Calcium-Based Magnetic Biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H. Simultaneous Adsorption and Oxidation of Antimonite onto Nano Zero-Valent Iron Sludge-Based Biochar: Indispensable Role of Reactive Oxygen Species and Redox-Active Moieties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Li, F.; An, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Shen, C.; Sand, W. Electroactive Modified Carbon Nanotube Filter for Simultaneous Detoxification and Sequestration of Sb(III). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Shou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J. A Functional Lignin for Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption and Wound Care Dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lei, X.; Li, B.; Qian, W. Biomass-Derived Carbon/Iron Composite (FexOy-BC (RM)) with Excellent Cd(II) Adsorption from Wastewater—Red Mud Resource Utilization. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Lai, L.; Liu, F.; Wei, L.; Chen, Y. Bifunctional Catalysts for Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Processes: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3837–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Yaita, T.; Okamoto, Y. A Novel Ligand Based Dual Conjugate Adsorbent for Cobalt(II) and Copper(II) Ions Capturing from Water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Awual, M.R.; Angove, M.J. A Review on Nickel(II) Adsorption in Single and Binary Component Systems and Future Path. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, D.; Zheng, H. Adsorption Behaviors of Paper Mill Sludge Biochar to Remove Cu, Zn and As in Wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Sun, Y. Enhanced Immobilization of Lead, Cadmium, and Arsenic in Smelter-Contaminated Soil by Sulfidated Zero-Valent Iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, N.P.F.; Da Silva, E.F.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Labrincha, J.A.; Novais, R.M. Simultaneous Removal of Multiple Metal(Loid)s and Neutralization of Acid Mine Drainage Using 3D-Printed Bauxite-Containing Geopolymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Yang, Y.; Jin, J.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, F.; Shao, M.; Wan, Y. Characterization of Phosphate Modified Red Mud–Based Composite Materials and Study on Heavy Metal Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 43687–43703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Kang, Y.; Li, L. Aqueous Arsenic (As) and Antimony (Sb) Removal by Potassium Ferrate. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shao, L.; Ruan, Z.; Hu, W.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y. Converting Untreated Waste Office Paper and Chitosan into Aerogel Adsorbent for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5085.3-2007; Hazardous Waste Identification Criteria: Leaching Toxicity Identification Standards. State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Zhao, S.; Xia, M.; Yu, L.; Huang, X.; Jiao, B.; Li, D. Optimization for the Preparation of Composite Geopolymer Using Response Surface Methodology and Its Application in Lead-Zinc Tailings Solidification. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 120969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, P.; Lu, J. Application of Natural Biosorbent and Modified Peat for Bisphenol a Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhang, R.; Lu, J. Removal of Aniline from Aqueous Solution Using Pine Sawdust Modified with Citric Acid and β-Cyclodextrin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, F.; Mollahosseini, A.; Khadir, A.; Milani Hosseini, M. Enhanced Adsorption of Dyes on Microwave-Assisted Synthesized Magnetic Zeolite-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Ren, L.-F.; Lin, Y.; Shao, J.; He, Y.; Gao, X.; Shen, Z. Adsorption of Antimonite and Antimonate from Aqueous Solution Using Modified Polyacrylonitrile with an Ultrahigh Percentage of Amidoxime Groups. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuh-Shan, H. Citation Review of Lagergren Kinetic Rate Equation on Adsorption Reactions. Scientometrics 2004, 59, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, O.; Tor, A. In Situ Preparation of Magnetic Hydrochar by Co-Hydrothermal Treatment of Waste Vinasse with Red Mud and Its Adsorption Property for Pb(II) in Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Yi, X.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z. Chemical Speciation and Distribution of Adsorbed Cd(ii) on Goethite: Influence of pH and Sulfate. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 2500–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Fu, H.; Fu, J. Distinct Effects of Fe3+ on the Adsorption of Chromate and Arsenate: A Comparison of Iron-Bearing Ferrihydrite and Nano-TiO2 Absorbents. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocik, E.M.; Kim, A.; Aiken, M.L.; Smith, L.; Kim, C.S. Sulfate Enhances the Adsorption and Retention of Cu(II) and Zn(II) to Dispersed and Aggregated Iron Oxyhydroxide Nanoparticles. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 162, 105929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, F.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, B. Surface Functional Groups of Carbon-Based Adsorbents and Their Roles in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions: A Critical Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzum, C.; Shahwan, T.; Eroglu, A.; Hallam, K.; Scott, T.; Lieberwirth, I. Synthesis and Characterization of Kaolinite-Supported Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles and Their Application for the Removal of Aqueous Cu2+ and Co2+ Ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifthikar, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Khan, A.; Jawad, A.; Sun, T.; Jiao, X.; Chen, Z. Highly Efficient Lead Distribution by Magnetic Sewage Sludge Biochar: Sorption Mechanisms and Bench Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zheng, H.; Li, F.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Xing, B. Investigating the Mechanisms of Biochar’s Removal of Lead from Solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.; Lyu, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Yan, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Magnetic Zeolite A from Red Mud and Coal Gasification Slag for the Removal of Pb2+ and Cu2+. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Mehmood, S.; Mahmood, M.; Ali, S.; Shakoor, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Asghar, R.M.A.; Zhao, H.; Liu, W.; Li, W. Adsorption of Pb(II) from Wastewater Using a Red Mud Modified Rice-Straw Biochar: Influencing Factors and Reusability. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 326, 121405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, D.K.; Hasan, S.H. Effective Removal of Lead Ions Using Graphene Oxide-MgO Nanohybrid from Aqueous Solution: Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Modeling of Adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2259–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, B.-M.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Her, N.; Heo, J.; Han, J.; Jang, M.; Park, C.M.; Yoon, Y. Comprehensive Evaluation on Removal of Lead by Graphene Oxide and Metal Organic Framework. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Ali Mohamed, H.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; El-Subruiti, G.M. Mesoporous Magnetic Biochar Composite for Enhanced Adsorption of Malachite Green Dye: Characterization, Adsorption Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Isotherms. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Feasible Low-Cost Conversion of Red Mud into Magnetically Separated and Recycled Hybrid SrFe12O19@NaP1 Zeolite as a Novel Wastewater Adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; He, Y.; Peng, X. Efficient Removal of Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) Using Sewage Sludge-Derived Biochar: Adsorptive Effect and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-R.; Chen, H.-R.; Zhao, X.-J.; Xia, J.-L.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, R.; Shu, W.-S.; Pakostova, E. Fe(II) Bio-Oxidation Mediates Red Mud Transformations to Form Fe(III)/Al (Hydr)Oxide Adsorbent for Efficient As(V) Removal under Acidic Conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).