Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Wastewater by Tetravalent Tin-Based Novel Coagulants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Coagulants
2.2.1. Preparation of SnCl4 Solution
2.2.2. Preparation of Cs Solution
2.2.3. Preparation of Hybrid Cs@Sn Coagulants
2.3. Coagulation Performance
2.3.1. Jar Tests
2.3.2. Analytical Determinations
2.3.3. Dye Removal (R (%))
2.4. Characterization of Coagulants
3. Results and Discussion
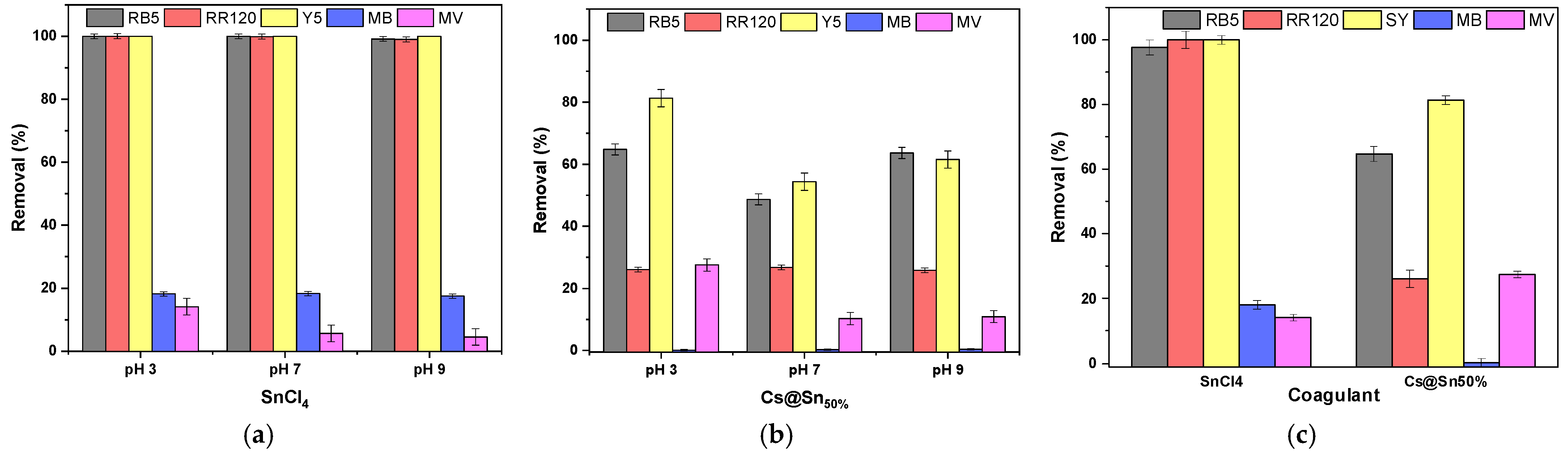
3.1. Effect of pH
3.2. Effect of Dosage
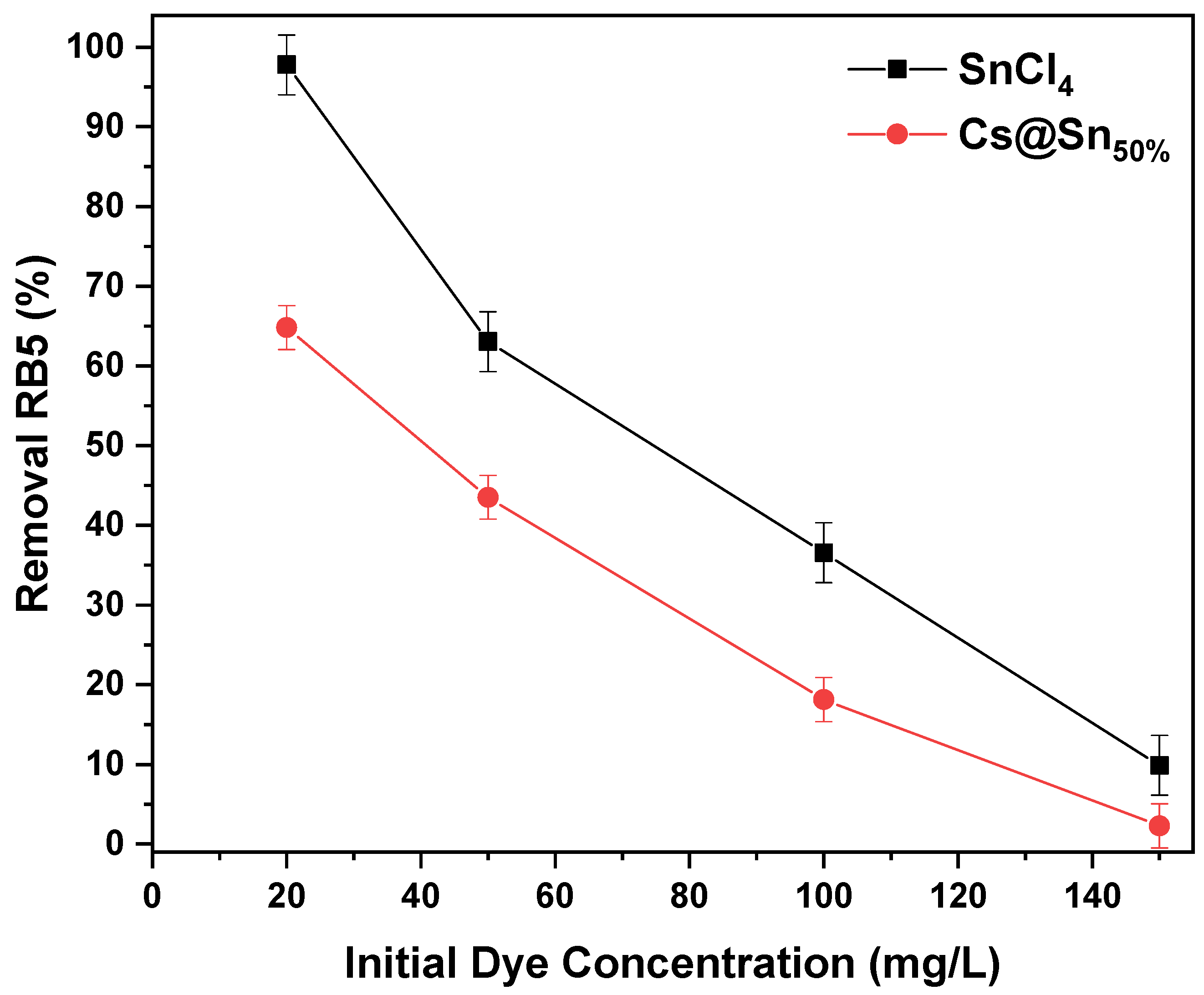
3.3. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
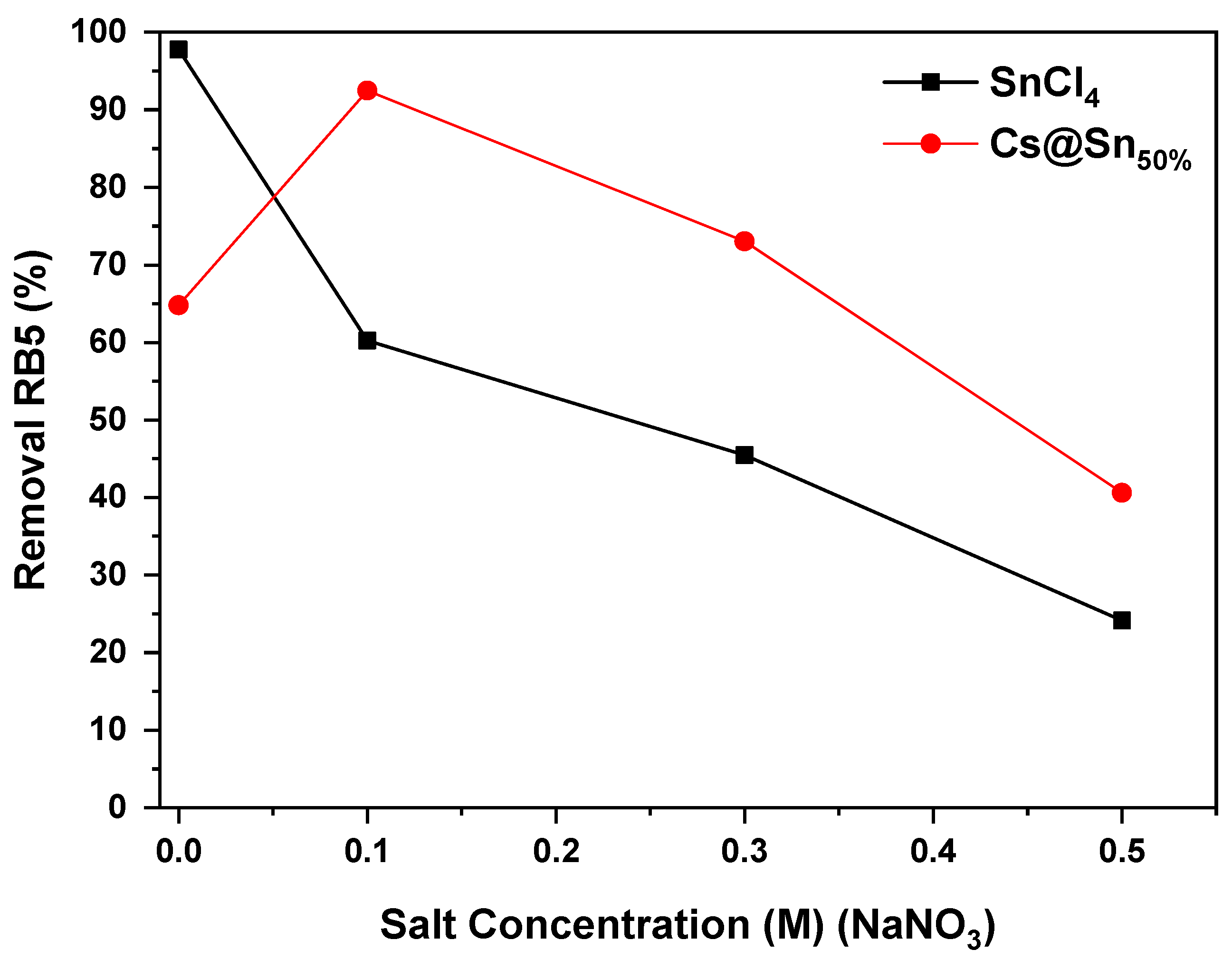
3.4. Effect of Ionic Strength
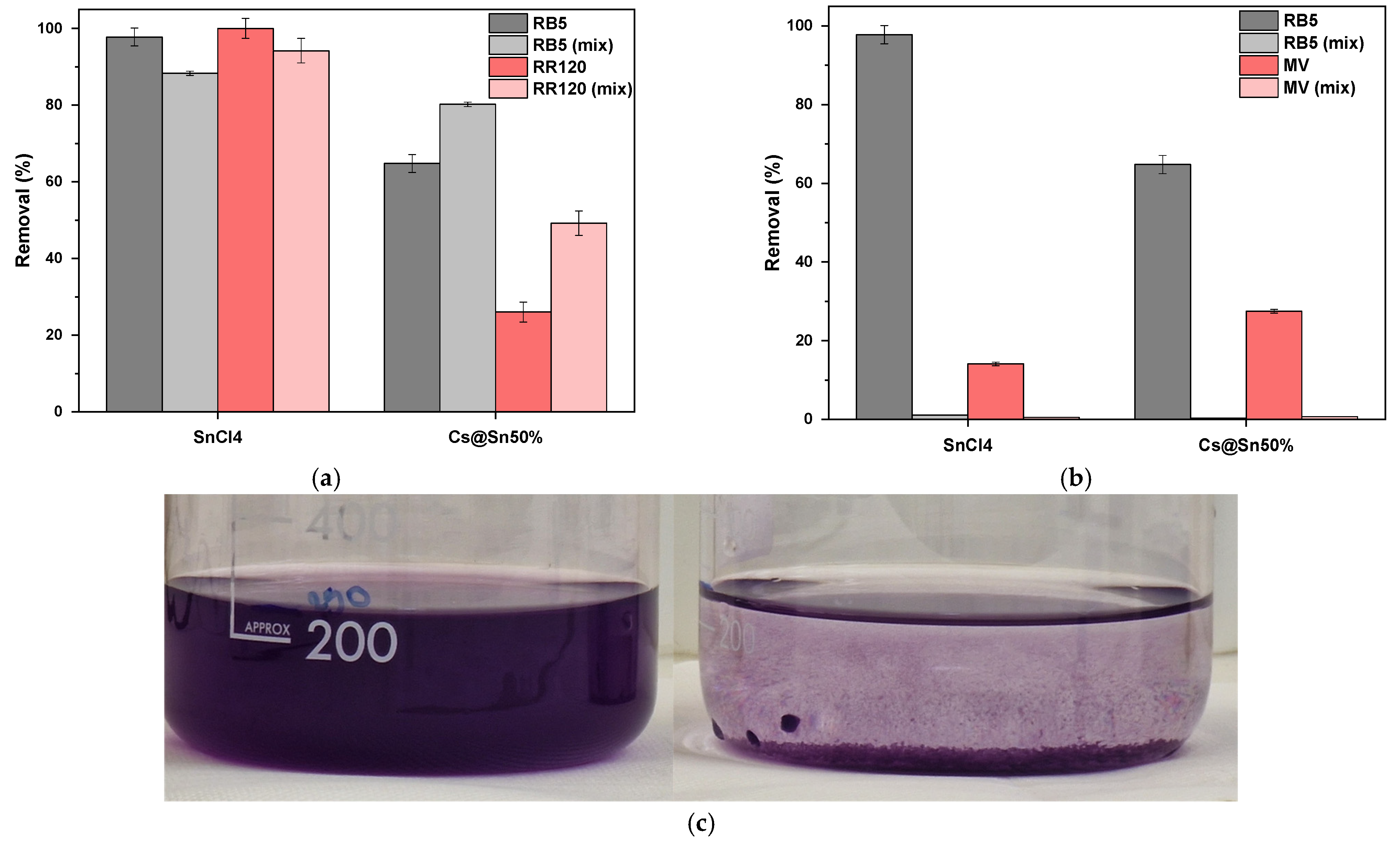
3.5. Single Dye Solutions
3.6. Mixed-Dye Solutions
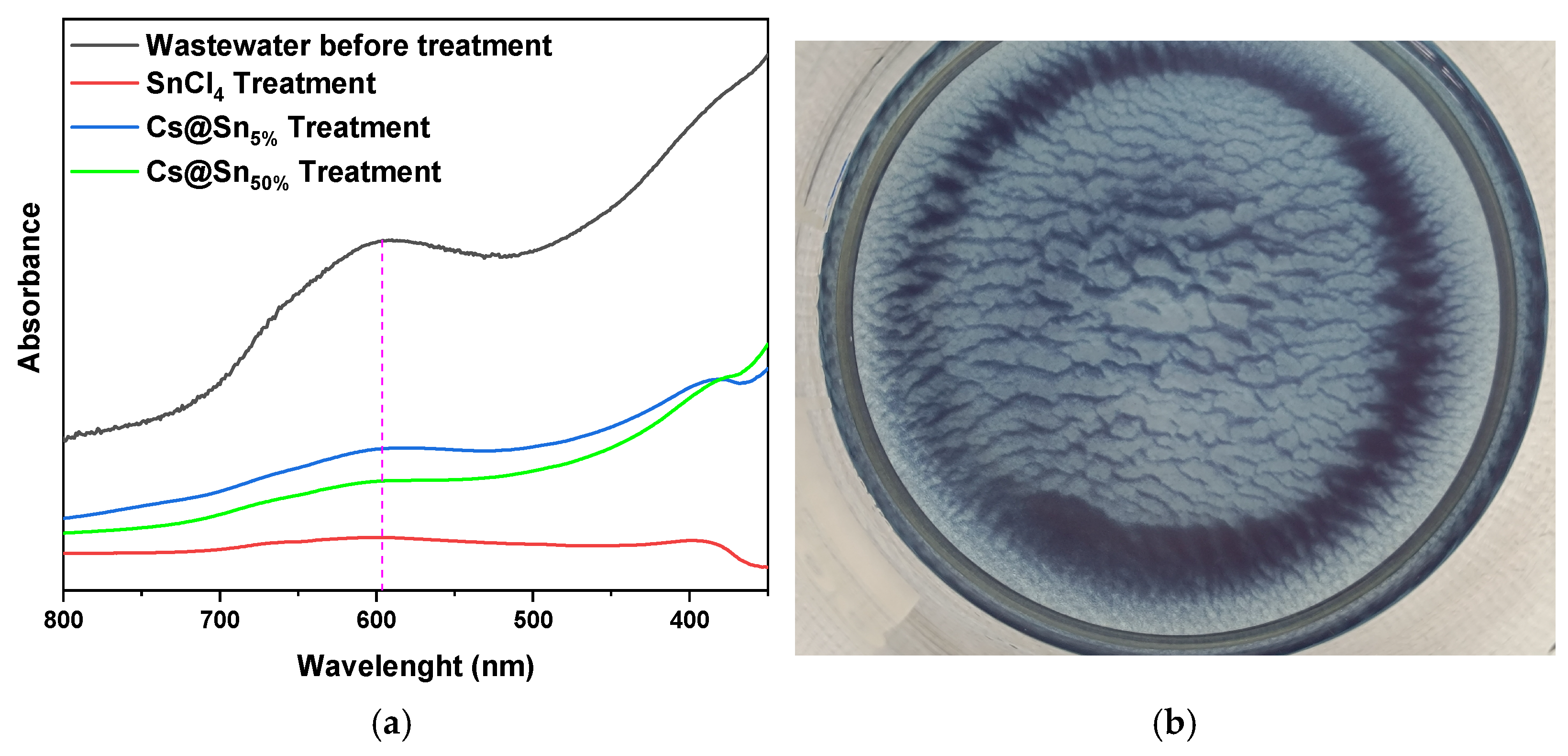
3.7. Real Wastewater Samples
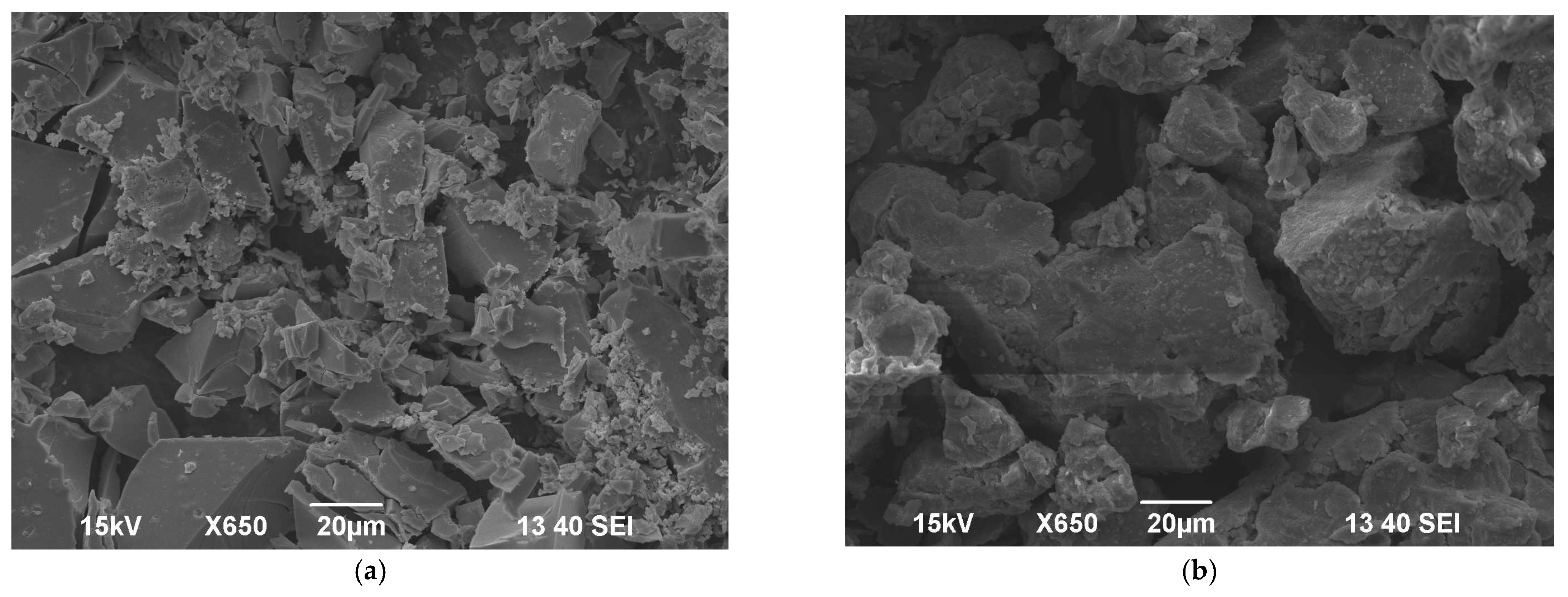
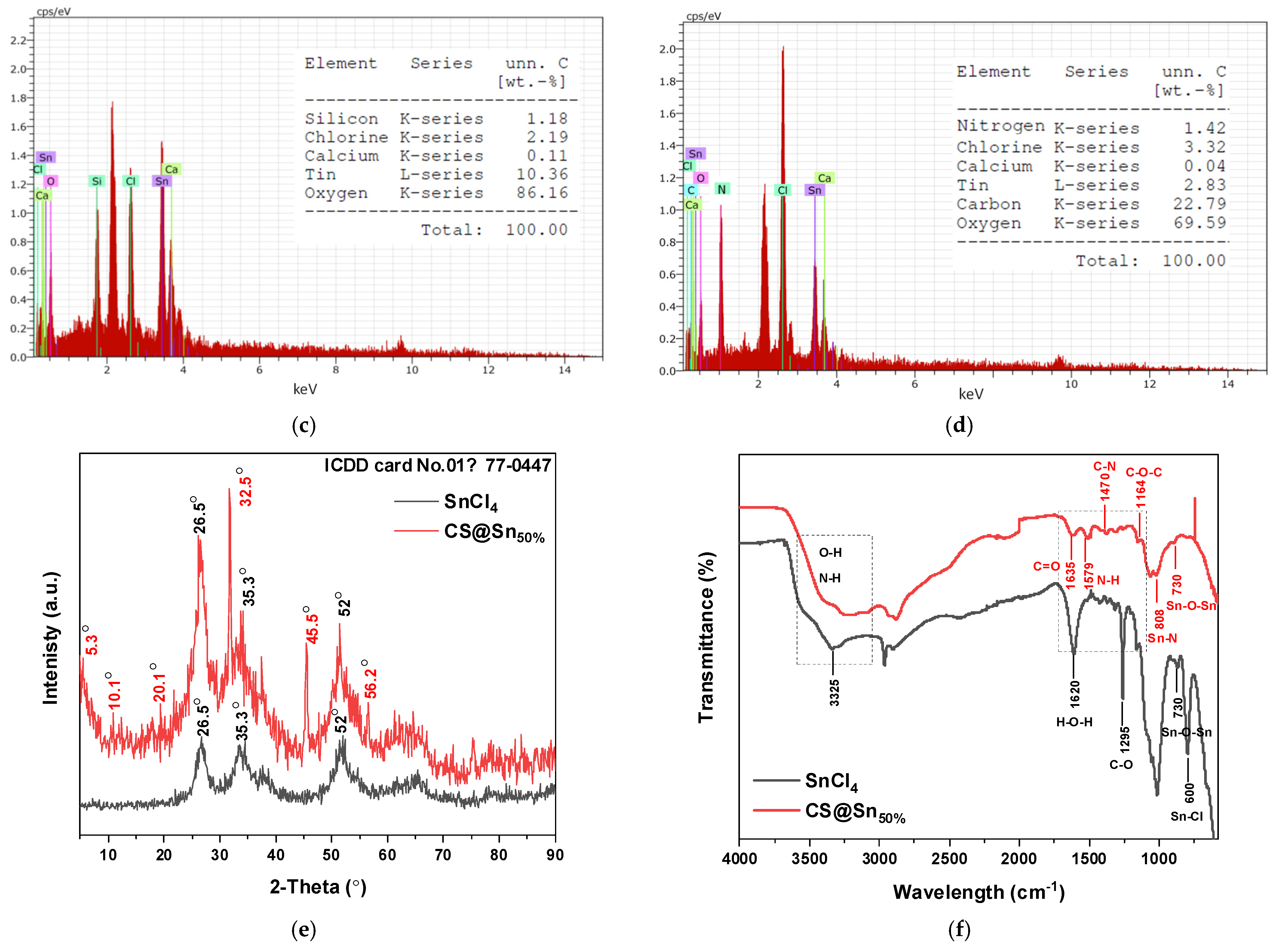
3.8. Characterization of the Coagulants
3.9. Comparison with Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsukaibi, A.K.D. Various Approaches for the Detoxification of Toxic Dyes in Wastewater. Processes 2022, 10, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of Textile Dyes on Health and the Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living Organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiku, M.; Selimi, T.; Berisha, A.; Maloku, A.; Mehmeti, V.; Thaçi, V.; Hasani, N. Removal of Methyl Violet from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption onto Halloysite Nanoclay: Experiment and Theory. Toxics 2022, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, D.H.; da Silva Andrade, J.G.; Porto, C.E.; Alves, B.H.M.; de Carvalho, F.R.; Sakai, O.A.; Batistela, V.R. A Review of Adsorbents for Removal of Yellow Tartrazine Dye from Water and Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 24, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhalim, M.A.A.; Mohtar, S.S.; Mohammed, A.M.; Aziz, F.; Sokri, M.N.M.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Yusof, N.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Aziz, M.; et al. Enhanced Performance of Lanthanum Orthoferrite/Chitosan Nanocomposites for Adsorptive Photocatalytic Removal of Reactive Black. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouraie, M.; El Din, W.S. Biodegradation of Reactive Black 5 by Aeromonas Hydrophila Strain Isolated from Dye-Contaminated Textile Wastewater. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.P.P.; Lai, C.W.; Lee, K.M.; Abd Hamid, S.B. Advanced Chemical Reduction of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Photocatalytic Activity in Degrading Reactive Black. Materials 2015, 8, 7118–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soran, M.L.; Bocșa, M.; Pintea, S.; Stegarescu, A.; Lung, I.; Opriş, O. Commercially Biochar Applied for Tartrazine Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuhybani, M.; Aleid, M.; Alzidan, R.; Bin Bander, K.; Alrehaili, A. High Removal of Methylene Blue and Methyl Violet Dyes from Aqueous Solutions Using Efficient Biomaterial Byproduct. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amode, J.O.; Santos, J.H.; Alam, Z.M.; Mirza, A.H.; Mei, C.C. Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Untreated and Treated (Metroxylon Spp.) Waste Adsorbent: Equilibrium and Kinetics Studies. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2016, 7, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabar, S.; Abdul Aziz, H.; Yusof, N.H.; Subramaniam, S.; Foo, K.Y.; Wilson, L.D.; Lee, H.K. Preparation of Sulfonated Chitosan for Enhanced Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 151, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Pan, C. Photocatalytic and Degradation Mechanisms of Anatase TiO2: A HRTEM Study. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. Role of Fly Ash in the Removal of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 1494–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Khan, M.R.; Ng, K.H.; Wongsakulphasatch, S.; Cheng, C.K. Harnessing Renewable Hydrogen-Rich Syngas from Valorization of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) Using Steam Reforming Technique. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, J. Alkaline-Induced Superhydrophilic/Underwater Superoleophobic Polyacrylonitrile Membranes with Ultralow Oil-Adhesion for High-Efficient Oil/Water Separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 513, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiman, P.M.; Wu, T.Y. Ultrasonication Pre-Treatment of Combined Effluents from Palm Oil, Pulp and Paper Mills for Improving Photofermentative Biohydrogen Production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 119, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, N.; Mustafa, M.; Bakri, A.; Remy, M.; Mohd, R.; Zaino, A.; Murshed, M.F.; Faris, M.A. Review on Adsorption of Heavy Metal in Wastewater by Using Geopolymer. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 97, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabar, J.M.; Adebayo, M.A.; Taleat, T.A.A.; Yılmaz, M.; Rangabhashiyam, S. Ipoma Batatas (Sweet Potato) Leaf and Leaf-Based Biochar as Potential Adsorbents for Procion Orange MX-2R Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2025, 185, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of Various Recent Wastewater Dye Removal Methods: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W. State of the Art and Sustainability of Natural Coagulants in Water and Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Feng, N. Removal of Reactive Dyes from Wastewater Assisted with Kaolin Clay by Magnesium Hydroxide Coagulation Process. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 494, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmana, H.; Bellahsen, N.; Pantoja, F.; Hodur, C. Adsorption and Coagulation in Wastewater Treatment—Review. Prog. Agric. Eng. Sci. 2021, 17, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E.; Roussy, J. Coagulation and Flocculation of Dye-Containing Solutions Using a Biopolymer (Chitosan). React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcyotto, F.; Wei, Q.; Macharia, D.K.; Huang, M.; Shen, C.; Chow, C.W.K. Effect of Dye Structure on Color Removal Efficiency by Coagulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahnasawi, A. Removal of Reactive Red 141 and Disperse Red 13 Dyes from Aqueous Solutions Using Different Coagulants: An Optimization and Comparison Study. Düzce Üniv. Bilim Teknol. Derg. 2023, 11, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, G.; Abbas, N.; Deeba, F.; Butt, T.; Jilal, S.; Sarfraz, S. Efficient Removal of Dyes in Textile Effluents Using Aluminum-Based Coagulant. Chem. Int. 2021, 7, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Mwasiagi, J.I.; Zhao, X.; Chow, C.W.K.; Tang, R. Removal of Direct Dyes by Coagulation: Adaptability and Mechanism Related to the Molecular Structure. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 1850–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyakoub, A.Z.; Lartiges, B.S.; Ouhib, R.; Kacha, S.; El Samrani, A.G.; Ghanbaja, J.; Barres, O. MnCl2 and MgCl2 for the Removal of Reactive Dye Levafix Brilliant Blue EBRA from Synthetic Textile Wastewaters: An Adsorption/Aggregation Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, S.F.; Aziz, H.A. Potential Use of Tin Tetrachloride and Polyacrylamide as a Coagulant-Coagulant Aid in the Treatment of Highly Coloured and Turbid Matured Landfill Leachate. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dago-Serry, Y.; Maroulas, K.N.; Tolkou, A.K.; AbdelAll, N.; Alodhayb, A.N.; Khouqeer, G.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Composite Super-Adsorbents of Chitosan/Activated Carbon for the Removal of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug from Wastewaters. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1298, 137044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. APHA Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmulski, M. The PH Dependent Surface Charging and Points of Zero Charge. X. Update. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 319, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzoutzoglou-Efremidou, A.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; Maroulas, K.N.; Kosheleva, R.I.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Interfacial Adsorption Interactions of Dyes and Chitosan/Activated Carbon@Curcumin Derivatives in Single-Component and Binary Solutions. Langmuir 2025, 41, 3603–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadri, S.; Alavi, M.R.; Arami, M. Decolorization of an Acidic Dye from Synthetic Wastewater by Sludge of Water Treatment Plant. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Xin, H.; Li, T.; Duan, J.; Mulcahy, D. Determination of Cost-Effective Optimum Coagulant Dosage for Removal of Disinfection by-Product Precursors in Water Treatment Based on the Theory of Elasticity. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Kumar, P.; Hira, S.K.; Manna, P.P. Evaluation of Carbofuran-Mediated Toxicity against Human Lymphocytes and Red Blood Cells in Simulated Wastewater Degraded by Coagulation–Flocculation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15315–15324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Choi, S.P.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Shim, W.G.; Moon, H. Evaluation of the Performance of Adsorption and Coagulation Processes for the Maximum Removal of Reactive Dyes. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 69, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvand, A.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Mokhtari, M.; Ebrahimi, A.A.; Ahmadi, R.M.; Mahvi, A.H. Application of Chemical Coagulation Process for Direct Dye Removal from Textile Wastewater. J. Environ. Health Sustain. Dev. 2017, 2, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Degs, Y.S.; El-Barghouthi, M.I.; El-Sheikh, A.H.; Walker, G.M. Effect of Solution PH, Ionic Strength, and Temperature on Adsorption Behavior of Reactive Dyes on Activated Carbon. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 77, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguedach, A.; Brosillon, S.; Morvan, J.; Lhadi, E.K. Influence of Ionic Strength in the Adsorption and during Photocatalysis of Reactive Black 5 Azo Dye on TiO2 Coated on Non Woven Paper with SiO2 as a Binder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeHoux, J.G.; Dupuis, G. Recovery of Chitosan from Aqueous Acidic Solutions by Salting-out: Part Use of Inorganic Salts. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.X.; Cai, X.L.; Feng, L.Y.; Xiong, W.L.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chi, R.A. Synergistic and Competitive Adsorption of Cationic and Anionic Dyes on Polymer Modified Yeast Prepared at Room Temperature. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 57, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, E.K.; Metzger, J.W.; Fischer, K.; Hassani, A.H. Simultaneous Removal of a Cationic and an Anionic Textile Dye from Water by a Mixed Sorbent of Vermicompost and Persian Charred Dolomite. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Tsoutsa, E.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Katsoyiannis, I.A. Sustainable Use of Low-Cost Adsorbents Prepared from Waste Fruit Peels for the Removal of Selected Reactive and Basic Dyes Found in Wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14662–14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Chauhan, S.; Kumar, K.; Singh, S.; Chauhan, G.S. Simultaneous Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes from a Complex Mixture Using a Novel Composite Hydrogel Based on Pine Needles, Chitosan, and Gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 141447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Tsoutsa, E.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Simultaneous Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes on Quaternary Mixtures by Adsorption onto Banana, Orange and Pomegranate Peels. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 685, 133176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.F.B.; Silvestrin, G.; Soares, E.P.; Fasioli, B.; Urano, d.C.E.F.; Genezini, F.A.; da Silva, P.S.C.; Neto, A.O.; Andrade, D.A. Structural Evolution in Tin Chloride through Neutron Irradiation: Toward Indium-Doped Tin. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 20701–20704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadjia, L.; Abdelkader, E.; Mohamed, T. Investigation of Microstructural, Optical, and Photocatalytic Properties of Sol–Gel Synthesized Pristine SnO2 Nanoscale Particles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2025, 131, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, N.; et al. One-Pot Synthesis and Gas Sensitivity of SnO2 Nanoparticles Prepared Using Two Sn Salts of SnCl4·5H2O and SnCl2·2H2O. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2020, 126, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihui, J.; Chun, Y.; Fangnan, Z.; Xiaolian, C.; Yuhi, L.; Huiping, X. One-Step Reinforcement and Deacidification of Paper. Coatings 2020, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamilarasan, V.; Sethuraman, V.; Gopinath, K.; Balalakshmi, C.; Govindarajan, M.; Mothana, R.A.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Khaled, J.M.; Benelli, G. Single Step Fabrication of Chitosan Nanocrystals Using Penaeus Semisulcatus: Potential as New Insecticides, Antimicrobials and Plant Growth Promoters. J. Clust. Sci. 2018, 29, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustriane, C.; Dwivany, F.M.; Suendo, V.; Reza, M. Effect of Chitosan and Chitosan-Nanoparticles on Post Harvest Quality of Banana Fruits. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limwanich, W.; Phetsuk, S.; Dumklang, M.; Cheechana, N.; Meepowpan, P.; Punyodom, W. Development of the Effective Tin(II)-Macroinitiators from the Ring-Opening Polymerization of Cyclic Esters for Utilizing in the Production of the Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyester. Polym. Bull. 2024, 82, 1085–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, S.A.; Peña-Solórzano, D.; Bejarano, O.R.; Ochoa-Puentes, C. Tin(Ii) Chloride Dihydrate/Choline Chloride Deep Eutectic Solvent: Redox Properties in the Fast Synthesis of: N -Arylacetamides and Indolo(Pyrrolo)[1,2- a] Quinoxalines. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 40552–40561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoj, K.P.; Elangovan, N.; Sowrirajan, S.; Chandrasekar, S.; Arumugam, N.; Almansour, A.I.; Altaf, M.; Mahalingam, S.M. Crystal Structure, Hirshfeld Analysis and Computational Study on Tin (IV) Complex: Insights from Synthesis, Spectroscopic, Anticancer Activity and Molecular Docking Studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1301, 137276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyguła, A.; Guibal, E.; Ruiz, M.; Sastre, A.M. The Removal of Sulphonated Azo-Dyes by Coagulation with Chitosan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 330, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlaiaa, Y.S.; Naser, Z.A.R.; Ali, A.H. Comparison between Coagulation and Electrocoagulation Processes for the Removal of Reactive Black Dye RB-5 and Cod Reduction. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 195, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, A.; Soudavari, A.; Mohammadian, M. Comparison of Electrocoagulation and Chemical Coagulation Processes in Removing Reactive Red 196 from Aqueous Solution. J. Hum. Environ. Health Promot. 2016, 1, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudra Paul, S.; Singh, N.H.; Debnath, A. Quick and Enhanced Separation of Eosin Yellow Dye from Aqueous Solution by FeCl3 Interaction: Thermodynamic Study and Treatment Cost Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 2874–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, C.; Yang, J.; Kim, S. Comparison of Disperse and Reactive Dye Removals by Chemical Coagulation and Fenton Oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 112, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Vashi, R.T. Removal of Congo Red Dye from Its Aqueous Solution Using Natural Coagulants. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2012, 16, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudjil, S.; Guergazi, S.; Ghernaout, D.; Temim, D.; Masmoudi, T. Brilliant Green and Methyl Violet 2B Dyes Removal Using Aluminium Sulfate (AS) in Single and Binary Systems. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalia, A.; Derbal, K.; Baatache, O.; Lehchili, C.; Khalfaoui, A.; Pizzi, A. Removal of Dyes from Water Using Aluminum-Based Water Treatment Sludge as a Low-Cost Coagulant: Use of Response Surface Methodology. Water 2024, 16, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
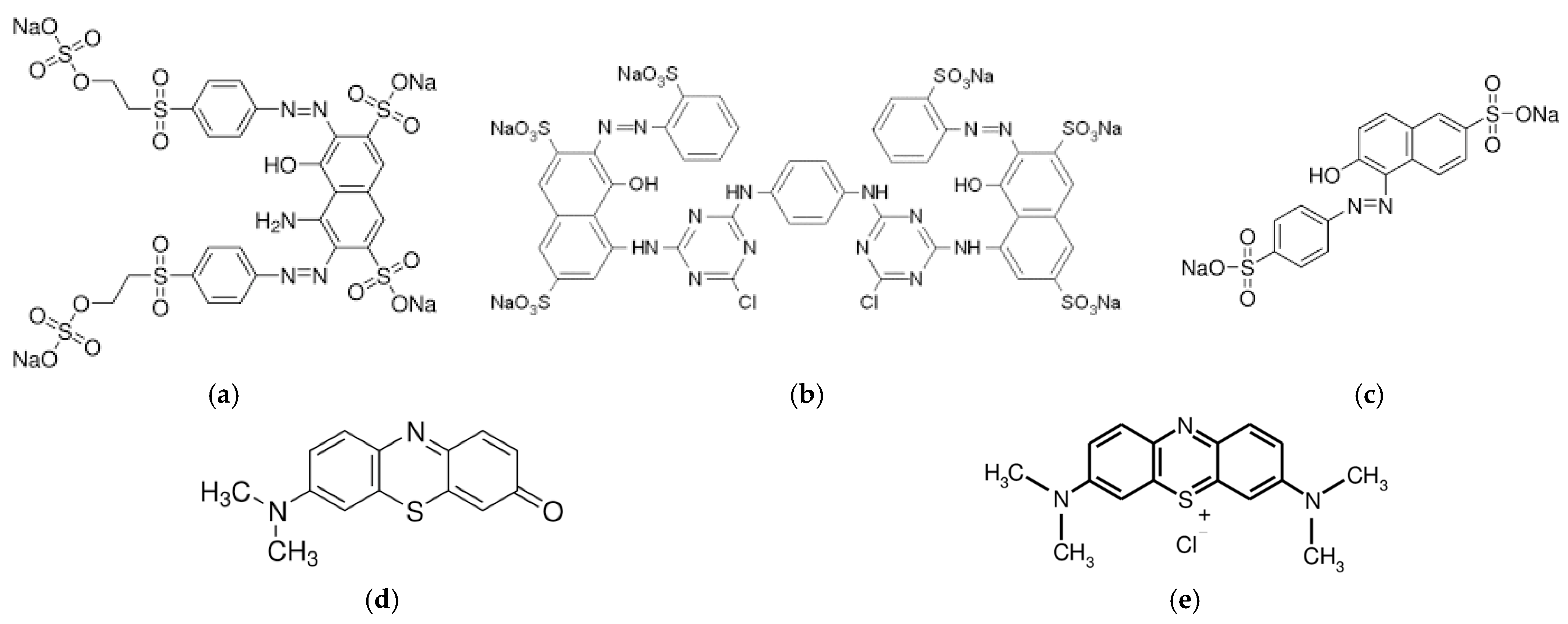

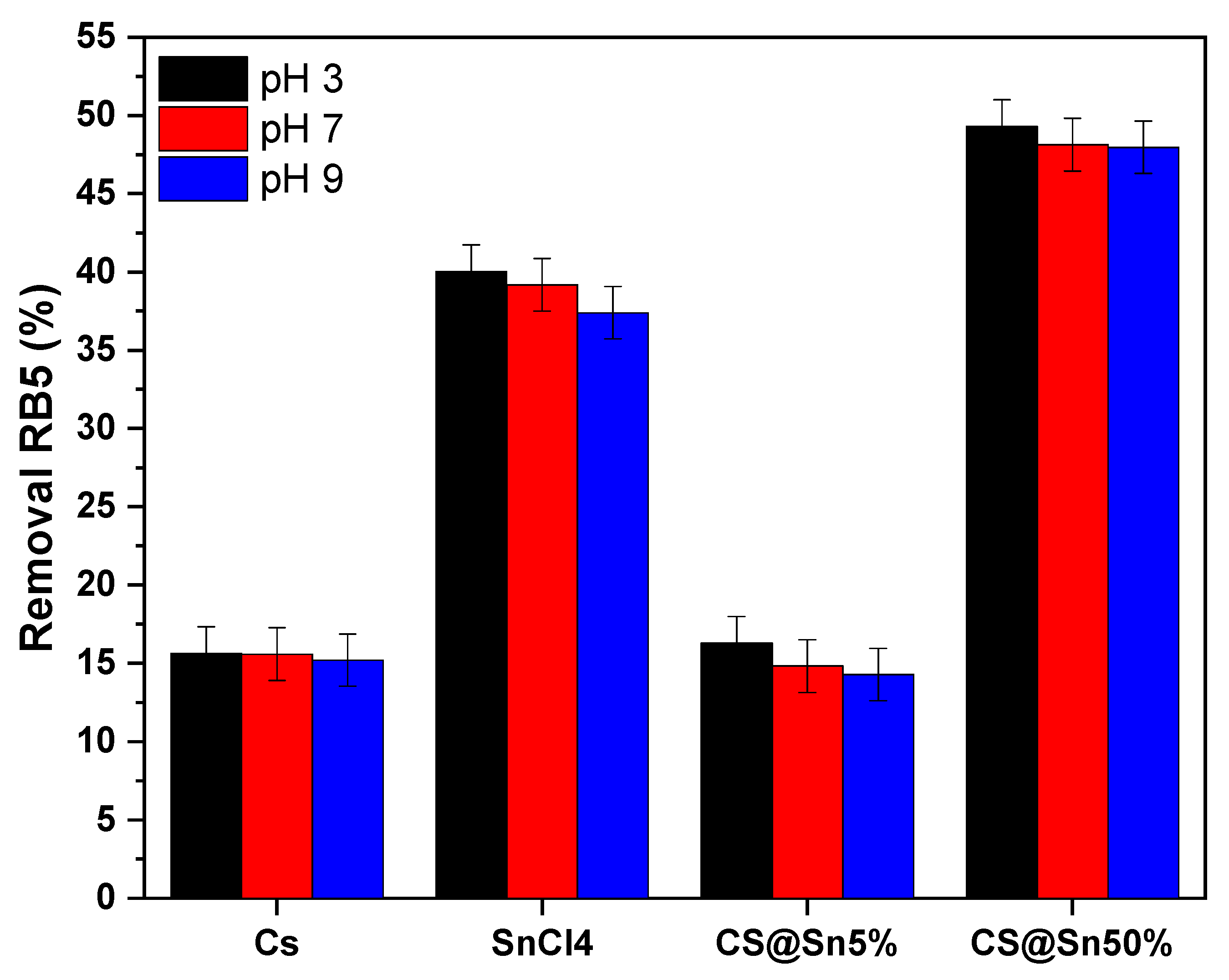

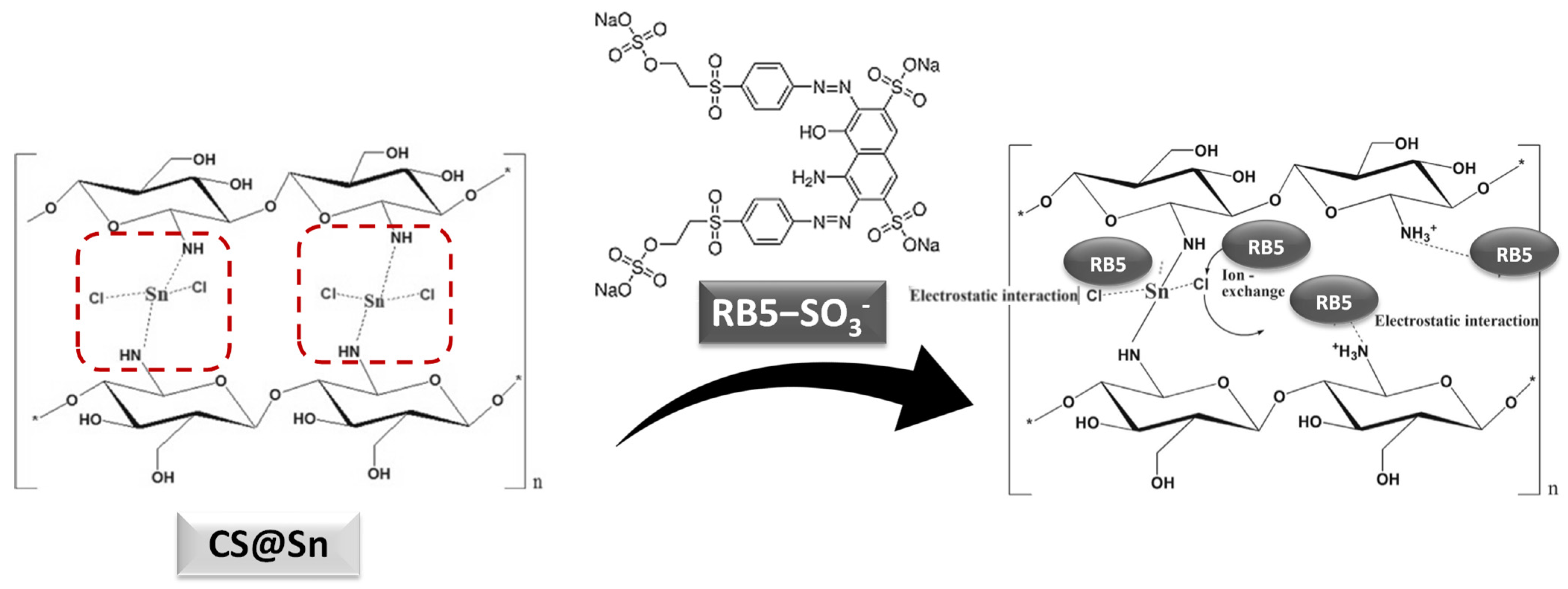
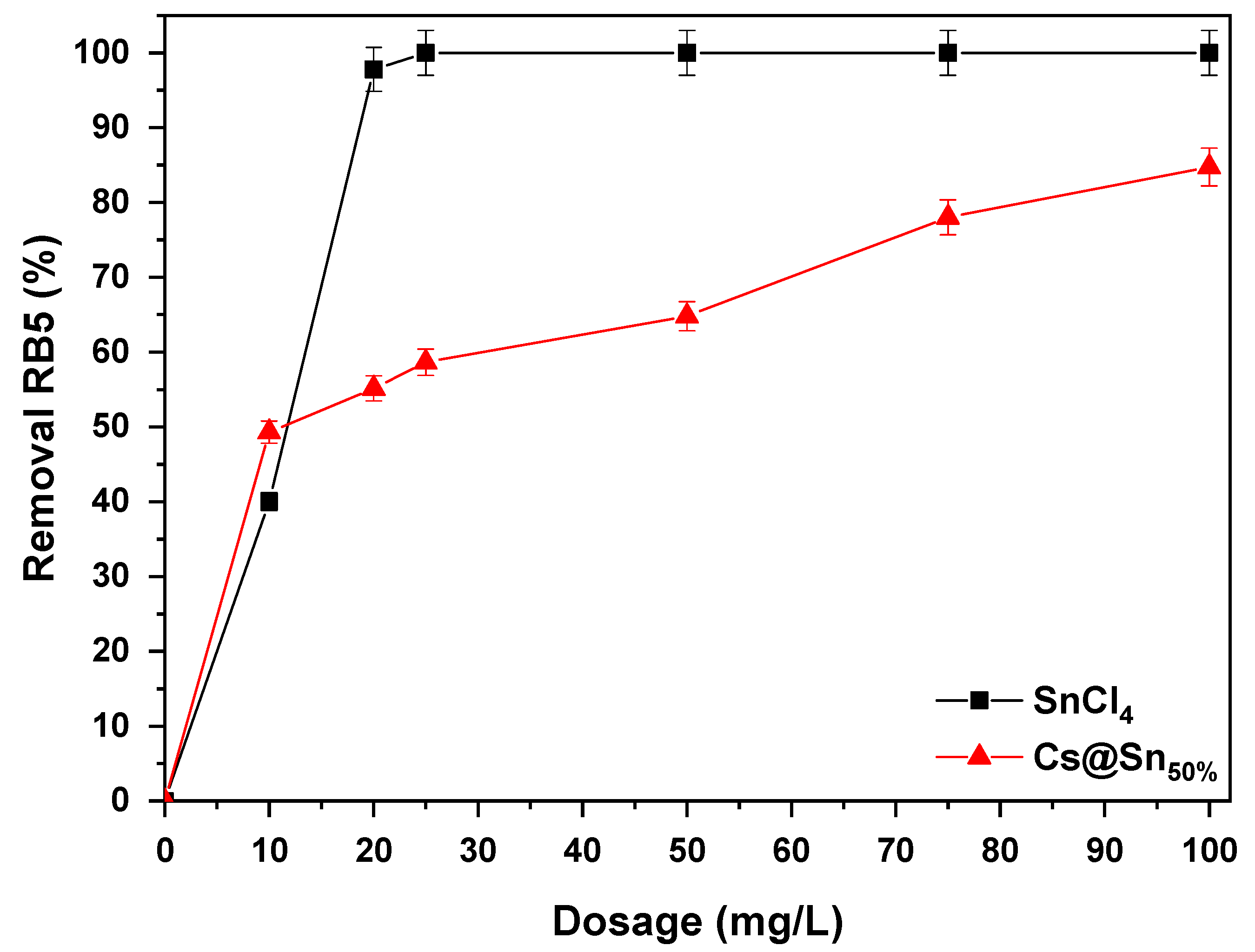
| Coagulant Type | Comments | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SnCl4 | 0.1 M with respect to Sn | 1.00 | |
| CS | CS in 2% v/v acetic acid | 4.09 | |
| CS@Sn5% | 3.60 | ||
| CS@Sn50% | 2.37 | ||
| Rapid Mixing Period (Charge Destabilization) | Slow Mixing Period (Floc Formation) | Sedimentation (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration (min) | Mixing Rate (rpm) | Duration (min) | Mixing Rate (rpm) | |
| 1 | 200 | 15 | 50 | 45 |
| Coagulant | C0 (mg/L) | pH | Dosage (mg/L) | Mixing Rates | Dye | Removal % | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | rpm | |||||||
| Chitosan | 100 | 5.0 | 55 | 3 | 200 | RB5 | 99.5 | [56] |
| 15 | 40 | |||||||
| 120 | 0 | |||||||
| Al2SO4•5H2O | 50 | 8.0 | 200 | 2 | 200 | RB5 | 98.0 | [57] |
| 30 | 50 | |||||||
| 30 | 0 | |||||||
| Fe2(SO4)3 | 75 | 4.0 | 200 | 2 | 200 | RB5 | 97.7 | [57] |
| 30 | 50 | |||||||
| 30 | 0 | |||||||
| FeCl3•6H2O | 50 | 8.0 | 100 | 1.5 | 120 | RR196 | 84.8 | [58] |
| 20 | 30 | |||||||
| 30 | 0 | |||||||
| FeCl3•6H2O | 100 | 2.2 | 170 | n/a * | n/a | Eosin Yellow | 98.0 | [59] |
| n/a | n/a | |||||||
| n/a | ||||||||
| FeCl3•6H2O | n/a | 6.0 | 500 | 2 | 250 | RY24 | 71.3 | [60] |
| 15 | 40 | |||||||
| 30 | 0 | |||||||
| MgCl2 | 50 | 11.5 | 95 | 1 | 300 | DO26 | 99.0 | [28] |
| 15 | 50 | DY11 | 95.0 | |||||
| 30 | 0 | DB19 | 95.0 | |||||
| AlCl3 | 50 | 7.0 | 27 | 1 | 300 | DO26 | 93.0 | [28] |
| 15 | 50 | DY11 | 87.4 | |||||
| 30 | 0 | DB19 | 99.8 | |||||
| Chitosan | 200 | 4.0 | 25.0 | n/a | 200 | CR | 94.5 | [61] |
| n/a | n/a | |||||||
| 60 | 0 | |||||||
| Al2SO4•5H2O | 30 | 2.0 | 60 | 3 | 150 | MV | 32.5 | [62] |
| 17 | 45 | |||||||
| 30 | 0 | |||||||
| Al2SO4•5H2O | 3 | 12.0 | 87.0 | 3 | 160 | MB | 98.4 | [63] |
| 20 | 30 | |||||||
| 30 | 0 | |||||||
| SnCl4 | 20 | 3.0 | 20 | 1 | 200 | RB5 | 97.8 | This study |
| RR120 | 100.0 | |||||||
| 15 | 50 | Y5 | 100.0 | |||||
| MB | 18.2 | |||||||
| 45 | 0 | MV | 14.1 | |||||
| CS@Sn50% | 20 | 3.0 | 20 | 1 | 200 | RB5 | 64.8 | This study |
| RR120 | 26.1 | |||||||
| 15 | 50 | Y5 | 81.3 | |||||
| MB | 0.1 | |||||||
| 45 | 0 | MV | 27.5 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolkou, A.K.; Giannoulaki, A.; Chalkidi, P.; Arvaniti, E.; Fykari, S.; Kritaki, S.; Kyzas, G.Z. Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Wastewater by Tetravalent Tin-Based Novel Coagulants. Processes 2025, 13, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072103
Tolkou AK, Giannoulaki A, Chalkidi P, Arvaniti E, Fykari S, Kritaki S, Kyzas GZ. Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Wastewater by Tetravalent Tin-Based Novel Coagulants. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072103
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolkou, Athanasia K., Argyro Giannoulaki, Paraskevi Chalkidi, Eleftheria Arvaniti, Sofia Fykari, Smaragda Kritaki, and George Z. Kyzas. 2025. "Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Wastewater by Tetravalent Tin-Based Novel Coagulants" Processes 13, no. 7: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072103
APA StyleTolkou, A. K., Giannoulaki, A., Chalkidi, P., Arvaniti, E., Fykari, S., Kritaki, S., & Kyzas, G. Z. (2025). Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Wastewater by Tetravalent Tin-Based Novel Coagulants. Processes, 13(7), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072103











