Evaluation of Particle and Nanoparticle Emissions in Fiber and CO2 Laser Cutting Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
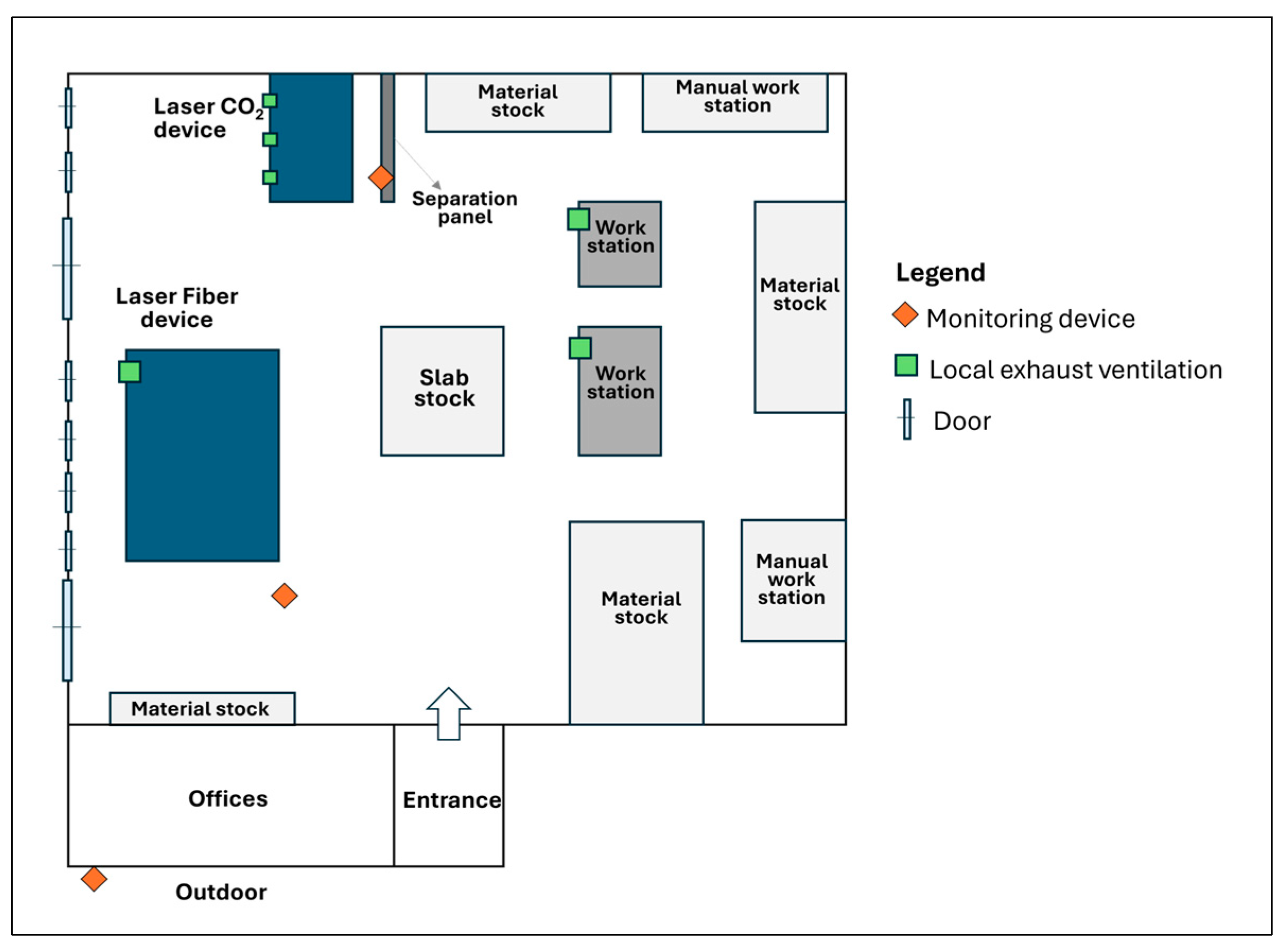
2.1. Workspace and Features of Laser Cutting Devices
2.2. IMNP Measurement
2.3. Measurements Implementation
- -
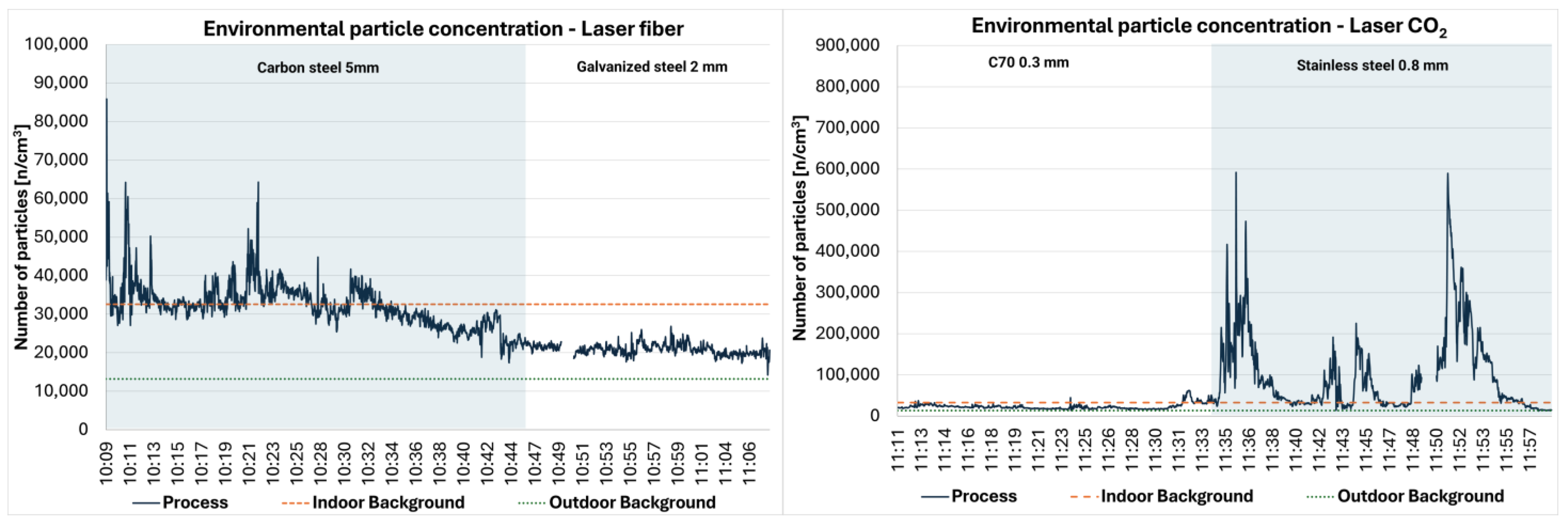
- Aluminum 1.5 mm; laser power 7000–9000 Watt; speed: 50,000–60,000 mm/min; frequency 1000 Hz; nitrogen pressure 10–12 bar; 43 min.
- -
- Satin-finished stainless steel with a plastic polymer film; 1 mm for the steel cut; power 6500–9000 Watt; speed: 60,000–68,000 mm/min; frequency 5000 Hz; nitrogen pressure 10 bar; 24 min.
- -
- SAF (austenitic-ferritic) stainless steel 0.9 mm; laser power 500 Watt; frequency 250 Hz; speed 1000 mm/min; nitrogen pressure 1 bar; 30 min.
- -
- Stainless steel 2 mm; power 2500 Watt; frequency 500 Hz; speed 5000 mm/min; nitrogen pressure 8 bar; 20 min.
3. Results
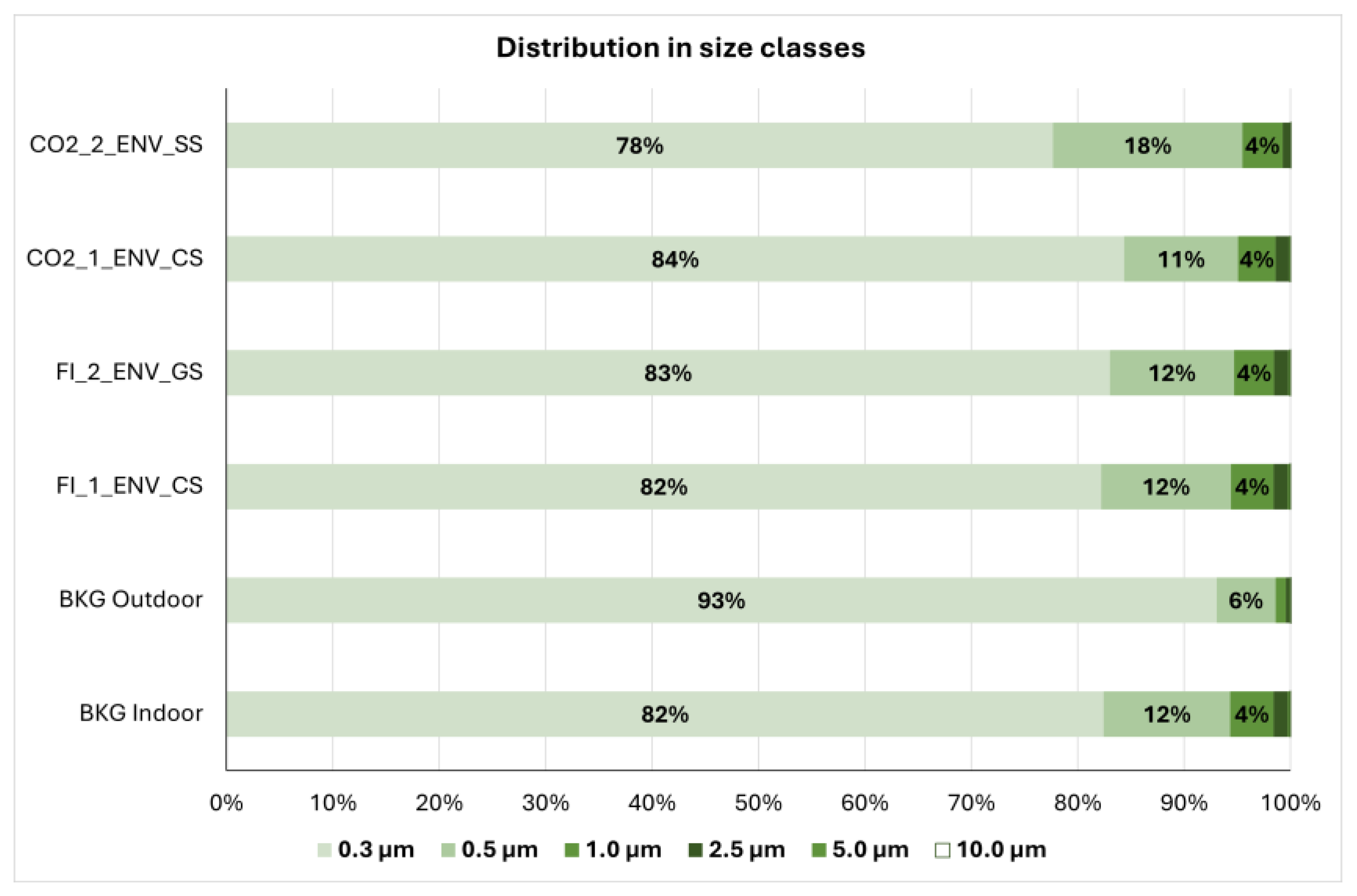
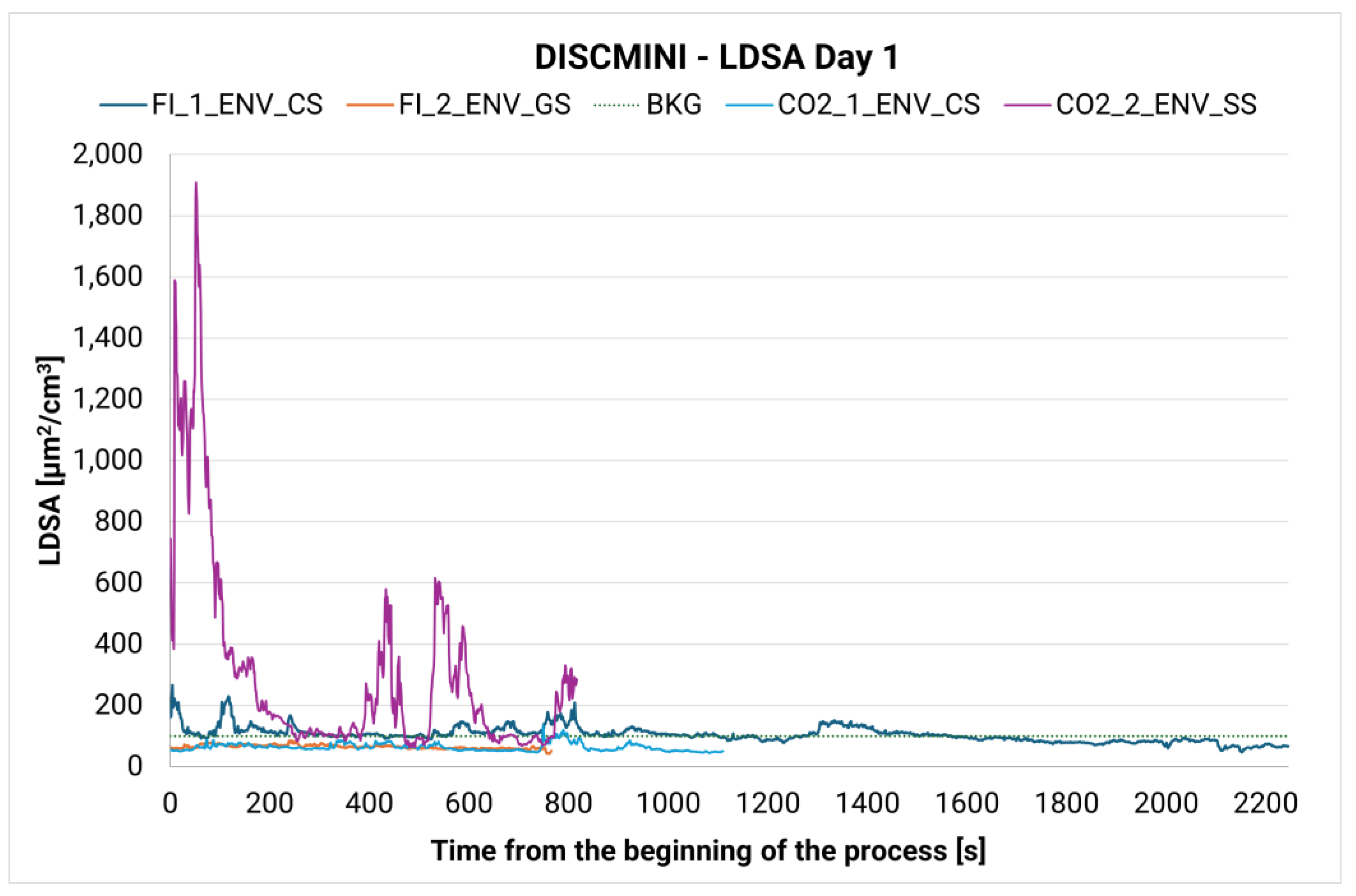
3.1. Environmental Monitoring
3.2. Personal Monitoring
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study and Further Developments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NP | Nanoparticles |
| UFP | Ultrafine particles |
| IMNP | Incidental metal nanoparticles |
| LDSA | Lung deposited surface area |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| FI | Fiber |
| C70—CS | Carbon steel |
| Al | Aluminum |
| SS | Stainless Steel |
| SAF | Sandvik Austenite Ferrite |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| Min | Minimum |
| Max | Maximum |
| BKG | Background |
| PPE | Personal protective equipment |
References
- Sharma, A.; Yadava, V. Experimental Analysis of Nd-YAG Laser Cutting of Sheet Materials—A Review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 98, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaadawy, M.; Dewidar, M.; Said, A.; Maher, I.; Shehabeldeen, T.A. A Comprehensive Review of Studying the Influence of Laser Cutting Parameters on Surface and Kerf Quality of Metals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 1039–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, J.R.; Anirudh, R.P.; Sundar, S.S. Applications of Lasers in Industries and Laser Welding: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, S221478532300620X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xie, H.; Ge, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Wang, B.; Jin, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y. Laser Cutting Technologies and Corresponding Pollution Control Strategy. Processes 2022, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.; Kaplan, A. Laser Cutting: From First Principles to the State of the Art. In Proceedings of the Pacific International Conference on Applications of Lasers and Optics, Melbourne, Australia, 19–21 April 2004; Laser Institute of America: Melbourne, Australia, 2004; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Cena, L.G.; Chen, B.T.; Keane, M.J. Evolution of Welding-Fume Aerosols with Time and Distance from the Source: A Study Was Conducted on the Spatiotemporal Variability in Welding-Fume Concentrations for the Characterization of First- and Second-Hand Exposure to Welding Fumes. Weld. J. 2016, 95, 280s–285s. [Google Scholar]
- Dugheri, S.; Cappelli, G.; Trevisani, L.; Kemble, S.; Paone, F.; Rigacci, M.; Bucaletti, E.; Squillaci, D.; Mucci, N.; Arcangeli, G. A Qualitative and Quantitative Occupational Exposure Risk Assessment to Hazardous Substances during Powder-Bed Fusion Processes in Metal-Additive Manufacturing. Safety 2022, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulin, N.; Pernetti, R.; Bergamaschi, E.; Oddone, E. Nanoparticles Released during Metal-Processing Operations: A Systematic Review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2025, 24, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernetti, R.; Maffia, S.; Previtali, B.; Oddone, E. Assessment of Nanoparticle Emission in Additive Manufacturing: Comparing Wire and Powder Laser Metal Deposition Processes. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2023, 20, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.; Arezes, P.; Silva, F. Occupational Exposure to Ultrafine Particles in Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Qualitative and Quantitative Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jian, L.; Bin, P.; Xing, M.; Lou, J.; Cong, L.; Zou, H. Workplace Exposure to Nanoparticles from Gas Metal Arc Welding Process. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Yang, W.; Chae, N.; Choi, S. Aerodynamic Diameter Distribution of Aerosols from Plasma Arc Cutting for Steels at Different Cutting Power Levels. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 323, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hoang, T.; Floyd, E.L.; Regens, J.L. Characterization of Particulate Fume and Oxides Emission from Stainless Steel Plasma Cutting. Ann. Work. Expo. Health 2017, 61, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen Hammer, S.; Halvorsen, J.Ø.; Graff, P.; Ervik, T.K. Characterisation of Particles Emitted during Laser Cutting of Various Metal Sheets and an Exposure Assessment for the Laser Operators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO. Nanotechnologies—Plain Language Explanation of Selected Terms from the ISO/IEC 80004 Series, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:tr:18401:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Bengalli, R.; Gualtieri, M.; Capasso, L.; Urani, C.; Camatini, M. Impact of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on an in Vitro Model of the Human Air-Blood Barrier. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 279, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreyling, W.G.; Hirn, S.; Möller, W.; Schleh, C.; Wenk, A.; Celik, G.; Lipka, J.; Schäffler, M.; Haberl, N.; Johnston, B.D.; et al. Air–Blood Barrier Translocation of Tracheally Instilled Gold Nanoparticles Inversely Depends on Particle Size. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G. Pulmonary Effects of Inhaled Ultrafine Particles. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2000, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, J.I.; Lecca, L.I.; Meloni, F.; Campagna, M. Metals and Metal-Nanoparticles in Human Pathologies: From Exposure to Therapy. Molecules 2021, 26, 6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, R.P.; Brown, J.M. Engineered Nanomaterials and Oxidative Stress: Current Understanding and Future Challenges. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 13, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Song, B.; Liang, H.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Shao, L. Toxicity of Graphene-Family Nanoparticles: A General Review of the Origins and Mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M. Metals, Toxicity and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedova, A.A.; Pietroiusti, A.; Fadeel, B.; Kagan, V.E. Mechanisms of Carbon Nanotube-Induced Toxicity: Focus on Oxidative Stress. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 261, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevallet, M.; Veronesi, G.; Fuchs, A.; Mintz, E.; Michaud-Soret, I.; Deniaud, A. Impact of Labile Metal Nanoparticles on Cellular Homeostasis. Current Developments in Imaging, Synthesis and Applications. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subjects 2017, 1861, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Mo, C.; Li, S.; Huang, M.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, P.; Liu, Z.; Jia, B.; Xu, S. Immunotoxicity of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: From Toxic Mechanisms to Metabolism and Outcomes. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 4151–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocca, B.; Leso, V.; Battistini, B.; Caimi, S.; Senofonte, M.; Fedele, M.; Cavallo, D.M.; Cattaneo, A.; Lovreglio, P.; Iavicoli, I. Human Biomonitoring and Personal Air Monitoring. An Integrated Approach to Assess Exposure of Stainless-Steel Welders to Metal-Oxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammapdour, R.; Ghandehari, H. Mechanisms of Immune Response to Inorganic Nanoparticles and Their Degradation Products. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 180, 114022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chou, C.-L.; Chang, Y.-S.; Liu, W.-C.; Chiu, H.-W. Oxidative Stress and Potential Effects of Metal Nanoparticles: A Review of Biocompatibility and Toxicity Concerns. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Li, F. Machine Learning Models for Quantitatively Prediction of Toxicity in Macrophages Induced by Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Alijagic, A.; Persson, A.; Odnevall, I.; Särndahl, E.; Karlsson, H.L. Toxicity Evaluation of Particles Formed during 3D-Printing: Cytotoxic, Genotoxic, and Inflammatory Response in Lung and Macrophage Models. Toxicology 2022, 467, 153100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljunggren, S.A.; Karlsson, H.; Ståhlbom, B.; Krapi, B.; Fornander, L.; Karlsson, L.E.; Bergström, B.; Nordenberg, E.; Ervik, T.K.; Graff, P. Biomonitoring of Metal Exposure During Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing). Saf. Health Work 2019, 10, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFA. Criteria for Assessment of the Effectiveness of Protective Measures. Available online: https://www.dguv.de/ifa/fachinfos/nanopartikel-am-arbeitsplatz/beurteilung-von-schutzmassnahmen/index-2.jsp (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- VAN Broekhuizen, P.; VAN Veelen, W.; Streekstra, W.-H.; Schulte, P.; Reijnders, L. Exposure Limits for Nanoparticles: Report of an International Workshop on Nano Reference Values. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2012, 56, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, A.C.; Soler, J.G.; Caicedo, G.R. The Characterization of Aerosols Generated During the Cutting of Metallic Materials with Lasers. Environ. Technol. 1998, 19, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viitanen, A.-K.; Uuksulainen, S.; Koivisto, A.J.; Hämeri, K.; Kauppinen, T. Workplace Measurements of Ultrafine Particles—A Literature Review. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2017, 61, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leso, V.; Ercolano, M.L.; Mazzotta, I.; Romano, M.; Cannavacciuolo, F.; Iavicoli, I. Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing: Implications for Risk Assessment and Management in Occupational Settings. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2021, 65, 617–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cena, L.G.; Chisholm, W.P.; Keane, M.J.; Chen, B.T. A Field Study on the Respiratory Deposition of the Nano-Sized Fraction of Mild and Stainless Steel Welding Fume Metals. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2015, 12, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Torvela, T.; Leskinen, J.T.T. Physicochemical Characterization of Aerosol Generated in the Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of Stainless Steel. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2016, 60, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajedifar, J.; Kokabi, A.H.; Dehghan, S.F.; Mehri, A.; Azam, K.; Golbabaei, F. Evaluation of Operational Parameters Role on the Emission of Fumes. Ind. Health 2018, 56, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.; Arezes, P.; Silva, F. Occupational Exposure to Incidental Nanomaterials in Metal Additive Manufacturing: An Innovative Approach for Risk Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.F.; Miranda, R.M.; Carvalho, P.A.; Quintino, M.L. The Effect of Metal Transfer Modes and Shielding Gas Composition on the Emission of Ultrafine Particles in MAG Steel Welding. Soldag. insp. 2014, 19, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.F.; Miranda, R.M.; Oliveira, J.P.; Esteves, H.M.; Albuquerque, P.C. Evaluation of the Amount of Nanoparticles Emitted in LASER Additive Manufacture/Welding. Inhal. Toxicol. 2019, 31, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Employment, Social Affairs and Inclusion. Non-Binding Guide to Good Practice for Implementing Directive 2006/25/EC “Artificial Optical Radiation”; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rubbonello, G. Sicurezza Laser. 2024. INAIL Guideline. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www.inail.it/content/dam/inail-hub-site/documenti/catalogo-generale/2024/11/SicurezzaLaser.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwjwwLXVhvuNAxUOgf0HHZh6EesQFnoECBoQAQ&usg=AOvVaw3DwYY5Ptxjj6HgOEOTNcIk (accessed on 2 April 2025).

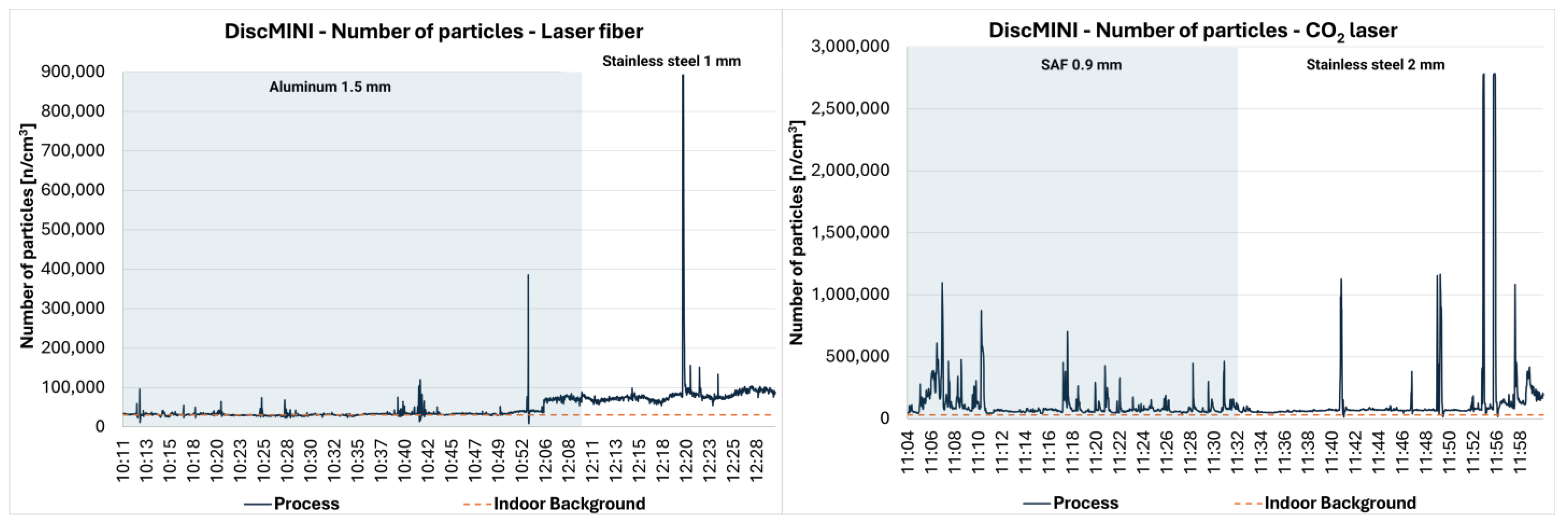
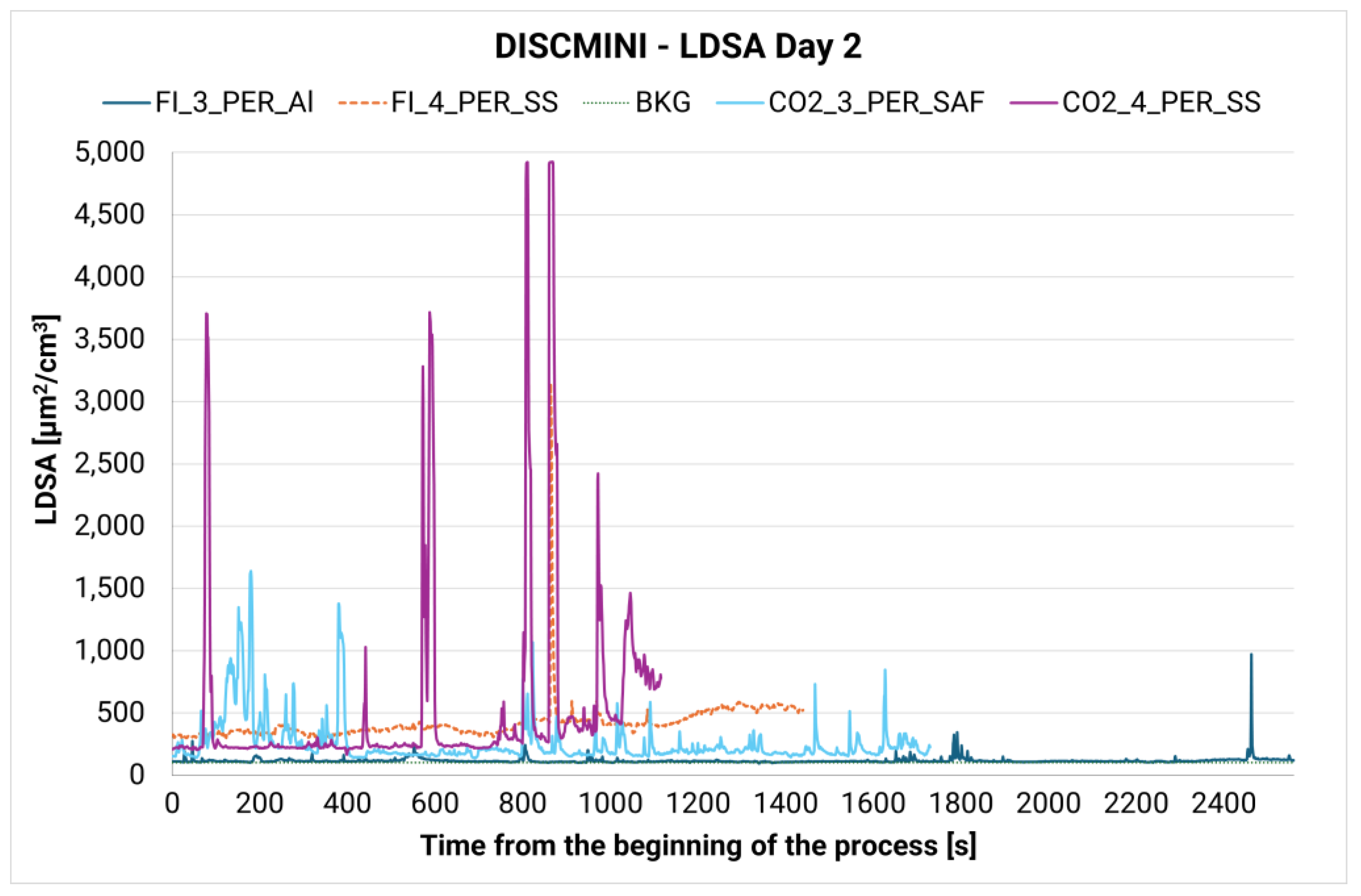
| Process | Laser Cut Device | Feedstock | Thickness | Date | Duration | Type of Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI_1_ENV_CS | Fiber (FI) | Carbon steel (C70) | 5 mm | 19/9 | 37′ 46″ | Environmental |
| FI_2_ENV_GS | Fiber (FI) | Galvanized steel (GS) | 2 mm | 19/9 | 12′ 45″ | Environmental |
| CO2_1_ENV_C70 | CO2 | Carbon Steel (C70) | 0.3 mm | 19/9 | 18′ 31″ | Environmental |
| CO2_2_ENV_SS | CO2 | Stainless Steel (SS) | 0.8 mm | 19/9 | 23′ 8″ | Environmental |
| FI_3_PER_Al | Fiber (FI) | Aluminium | 1.5 mm | 5/12 | 42′ 40″ | Personal |
| FI_4_PER_SS | Fiber (FI) | Stainless Steel (SS) | 1 mm | 5/12 | 24′ 1″ | Personal |
| CO2_3_PER_SAF | CO2 | SAF Steel | 0.9 mm | 5/12 | 28′ 50″ | Personal |
| CO2_4_PER_SS | CO2 | Stainless Steel (SS) | 2 mm | 5/12 | 18′ 36″ | Personal |
| Environmental Monitoring | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI_1_ENV_CS | FI_2_ENV_GS | ||||||
| Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | ||
| Mean | 32,204 | 56 | 104 | Mean | 20,774 | 54 | 64 |
| Median | 31,944 | 55 | 102 | Median | 20,562 | 54 | 64 |
| 75 percent | 35,157 | 58 | 112 | 75 percent | 21,668 | 56 | 69 |
| 25 percent | 28,815 | 53 | 88 | 25 percent | 19,769 | 53 | 60 |
| SD | 5948 | 4.6 | 25 | SD | 1550 | 2.6 | 6 |
| min | 17,364 | 42 | 47 | Min | 14,202 | 42 | 42 |
| max | 85,873 | 78 | 266 | Max | 26,861 | 64 | 84 |
| CO2_1_ENV_CS | CO2_2_ENV_SS | ||||||
| Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | ||
| Mean | 21,242 | 52 | 63 | Mean | 95,670 | 58 | 316 |
| Median | 20,606 | 51 | 60 | Median | 51,195 | 57 | 183 |
| 75 percent | 23,329 | 54 | 70 | 75 percent | 132,841 | 62 | 402 |
| 25 percent | 18,412 | 48 | 53 | 25 percent | 30,657 | 51 | 101 |
| SD | 3525 | 6.5 | 13 | SD | 96,944 | 13 | 315 |
| min | 13,605 | 41 | 44 | Min | 11,955 | 36 | 36 |
| max | 44,451 | 10 | 133 | Max | 592,018 | 300 | 1907 |
| Personal Monitoring | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI_3_PER_Al | FI_4_PER_SS | ||||||
| Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | ||
| Mean | 32,971 | 62 | 117 | Mean | 84,300 | 86 | 415 |
| Median | 31,798 | 61 | 112 | Median | 75,387 | 87 | 391 |
| 75 percent | 33,659 | 64 | 117 | 75 percent | 83,801 | 92 | 444 |
| 25 percent | 30,143 | 58 | 109 | 25 percent | 70,534 | 82 | 346 |
| SD | 9854 | 8.9 | 26 | SD | 99,148 | 8.3 | 142 |
| min | 8768 | 40 | 94 | min | 54,106 | 23 | 290 |
| max | 385,269 | 300 | 972 | max | 2,661,747 | 110 | 3148 |
| CO2_3_PER_SAF | CO2_4_PER_SS | ||||||
| Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | Number [n/cm3] | Size [nm] | LDSA [μm2/cm3] | ||
| Mean | 103,111 | 48 | 257 | Mean | 161,960 | 65 | 530 |
| Median | 69,846 | 49 | 196 | Median | 72,407 | 58 | 241 |
| 75 percent | 97,002 | 5 | 248 | 75 percent | 117,054 | 61 | 412 |
| 25 percent | 57,985 | 46 | 171 | 25 percent | 67,963 | 55 | 224 |
| SD | 102,496 | 5.9 | 186 | SD | 351,864 | 36.8 | 795 |
| min | 42,274 | 26 | 139 | min | 14,493 | 33 | 167 |
| max | 1,096,557 | 63 | 1640 | max | 2,781,962 | 300 | 4924 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paulin, N.; Pernetti, R.; Scafa, F.; Candura, S.M.; Oddone, E. Evaluation of Particle and Nanoparticle Emissions in Fiber and CO2 Laser Cutting Processes. Processes 2025, 13, 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061942
Paulin N, Pernetti R, Scafa F, Candura SM, Oddone E. Evaluation of Particle and Nanoparticle Emissions in Fiber and CO2 Laser Cutting Processes. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061942
Chicago/Turabian StylePaulin, Noemi, Roberta Pernetti, Fabrizio Scafa, Stefano M. Candura, and Enrico Oddone. 2025. "Evaluation of Particle and Nanoparticle Emissions in Fiber and CO2 Laser Cutting Processes" Processes 13, no. 6: 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061942
APA StylePaulin, N., Pernetti, R., Scafa, F., Candura, S. M., & Oddone, E. (2025). Evaluation of Particle and Nanoparticle Emissions in Fiber and CO2 Laser Cutting Processes. Processes, 13(6), 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061942







