Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Quantifies Stress-Dependent Permeability in Shale: Heterogeneous Compressibility of Seepage and Adsorption Pores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Sampling Locations and Mineral Composition
2.2. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
2.3. Experimental Equipment and Procedure
2.3.1. Experimental Equipment
2.3.2. Experimental Schemes
3. Experimental Results
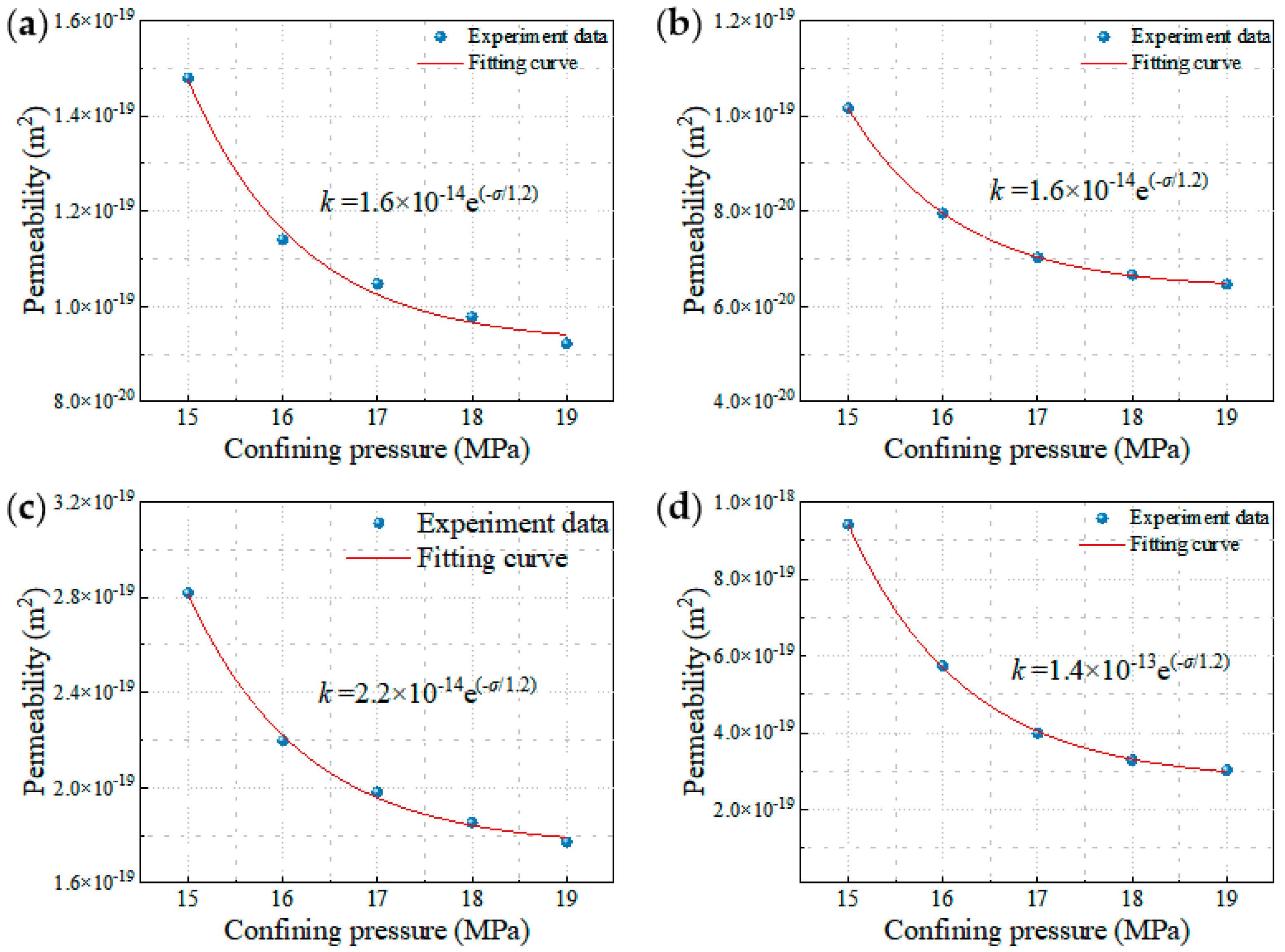
3.1. Effect of Confining Pressure on Permeability
3.2. Pore Size Distribution at Different Confining Pressures
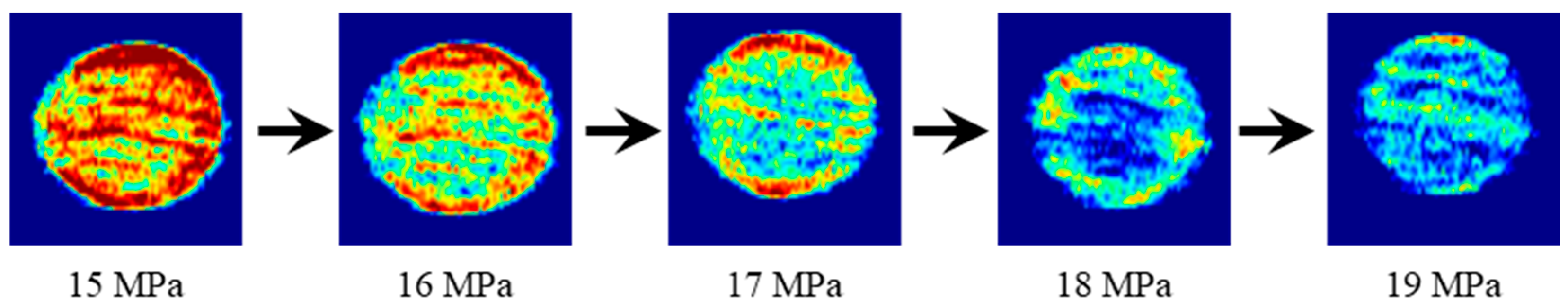
3.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging at Increasing Confining Pressure
4. Discussions
4.1. Determination of T2 Cutoff Based on NMR-Displacement Tests
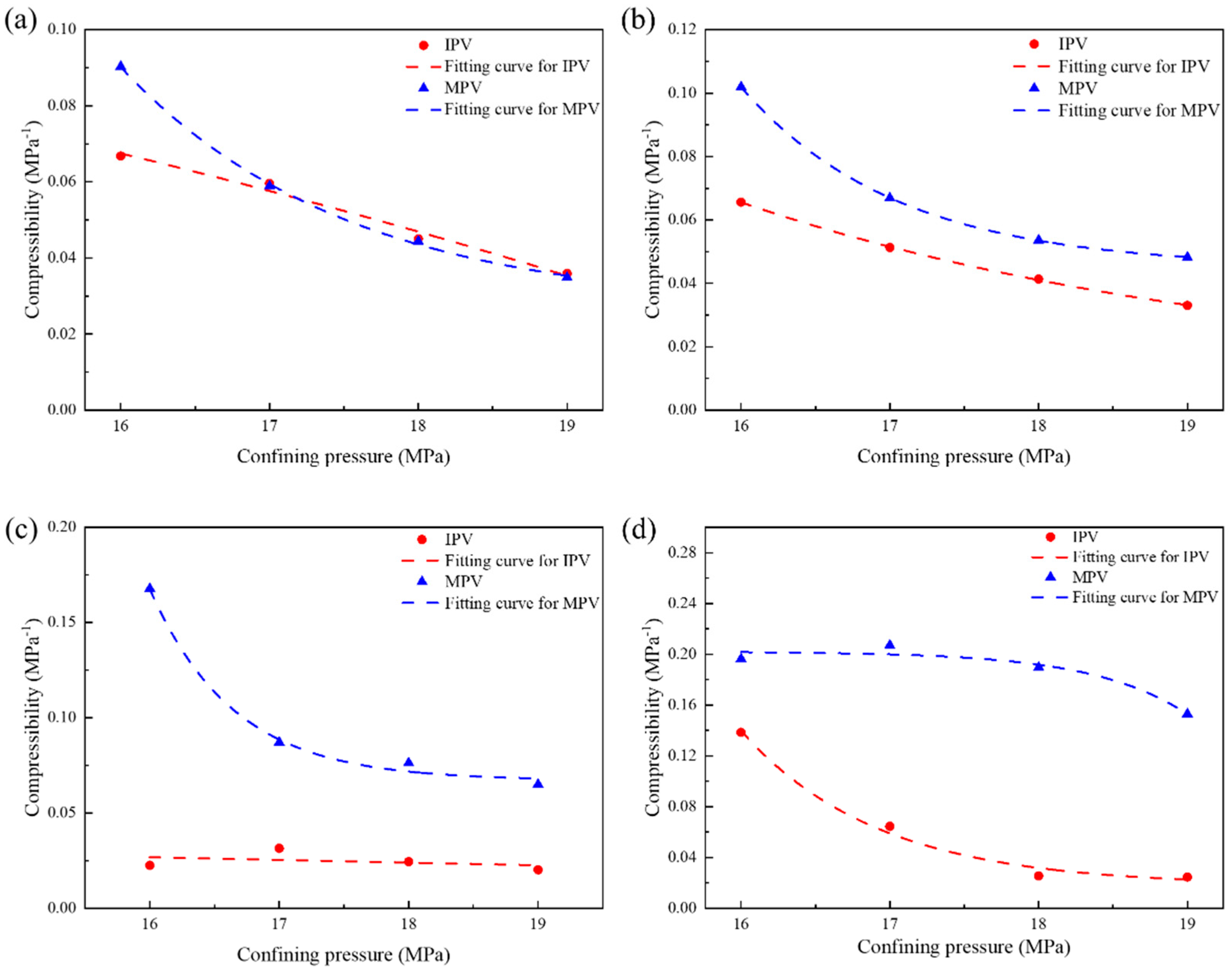
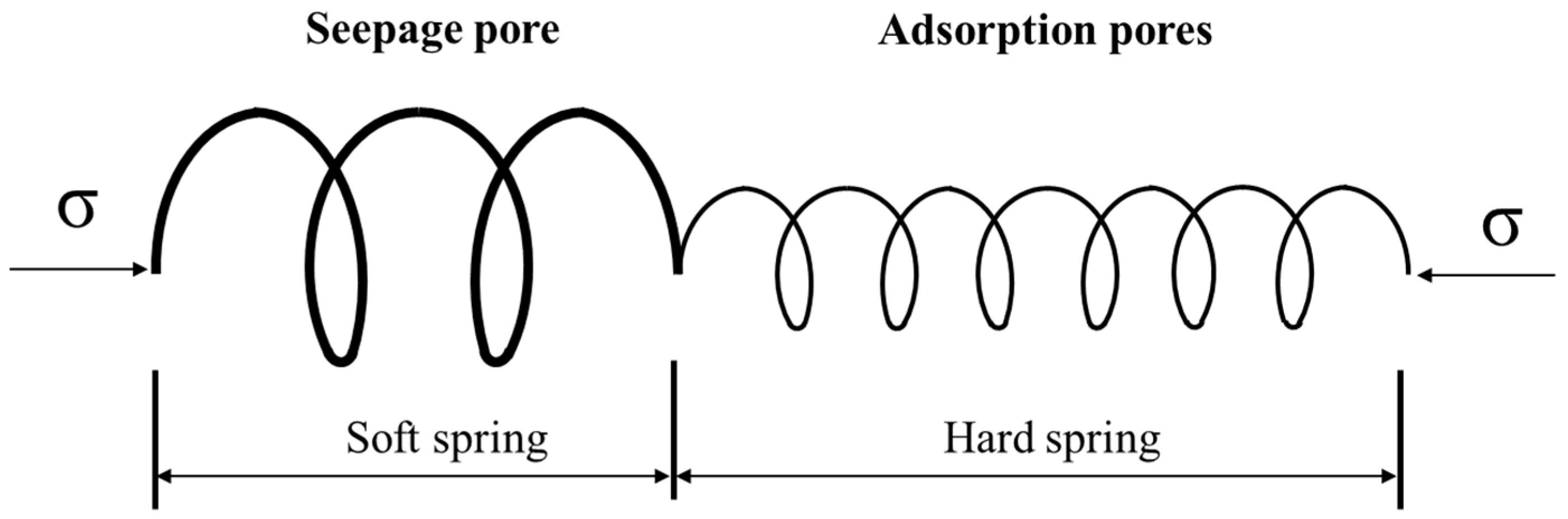
4.2. Compression Coefficients for Adsorption and Seepage Pores
4.3. Mechanism of Stress Sensitivity to Permeability Evolution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGlade, C.; Ekins, P. The geographical distribution of fossil fuels unused when limiting global warming to 2 °C. Nature 2015, 517, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Wu, H.; Leung, C.; Tian, J. A multiphysical-geochemical coupling model for caprock sealing efficiency in CO2 geosequestration. Deep Undergr. Sci. Eng. 2023, 2, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Liu, J.; Wei, M.; Elsworth, D. Evolution of permeability during the process of shale gas extraction. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 49, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Sheng, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, L. Competing impacts of internal pores dissolution and external compression on the permeability evolution during the infiltration of weakly acidic fluids. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yu, Z.; Luo, X.; Wu, S. Self-sealing of caprocks during CO2 geological sequestration. Energy 2022, 252, 124064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Assessment of CO2 Sequestration Capacity in a Low-Permeability Oil Reservoir Using Machine Learning Methods. Energies 2024, 17, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.; Haljasmaa, I.; Soong, Y. On Caprock Seal Integrity of Tuscaloosa Mudstone at Cranfield, MS (USA), CO2 Injection Site. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, B.; You, J.; Pu, W.; Tang, J.; Lu, J. Performance of a tight reservoir horizontal well induced by gas huff–n–puff integrating fracture geometry, rock stress-sensitivity and molecular diffusion: A case study using CO2, N2 and produced gas. Energy 2023, 263, 125696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.A.; Goshtasbi, K.; Kazemzadeh, E.; Bakhtiari, H.A.; Esfahani, M.R.; Vali, J. Relationship between porosity and permeability with stress using pore volume compressibility characteristic of reservoir rocks. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Maharjan, N.; Sheng, J. NMR investigation on pore-scale stress sensitivity during pore fluid pumping cycles: Implication for geological fluid storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 120, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xie, R.; Li, C.; Gao, L. A new method for determining tight sandstone permeability based on the characteristic parameters of the NMR T2 distribution. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2017, 48, 1009–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Zuo, X.B.; Sun, Q.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Hou, Z.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Tian, J.L. Preparation superhydrophobic surfaces of concrete via evaporation-induced self-assembly of TiO2 and MA-TiO2 suspension. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 475, 140984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenutsi, C.D.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Sun, L. Influence of net confining stress on NMR T2 distribution and two-phase relative permeability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 178, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tang, D.; Pan, Z.; Xu, H.; Huang, W. Characterization of the stress sensitivity of pores for different rank coals by nuclear magnetic resonance. Fuel 2013, 111, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. A novel NMR-capillary pressure method for quantifying pore connectivity and its impact on permeability evolution. J. Hydrol. 2025, 660, 133330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Tong, Q.; Cao, C.; Zhang, Y. Effect of pore-throat structure on movable fluid and gas–water seepage in tight sandstone from the southeastern Ordos Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Guo, C.; Chen, P.; Shi, H.; Tan, C.; Cheng, M.; Xing, Y.; Luo, X. Stress sensitivity of carbonate gas reservoirs and its microscopic mechanism. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Cheng, L.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W. A new approach to calculate permeability stress sensitivity in tight sandstone oil reservoirs considering micro-pore-throat structure. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 133, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, L.; Yang, J. Relationships between permeability, porosity and effective stress for low-permeability sedimentary rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2015, 78, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimienta, L.; Fortin, J.; Guéguen, Y. New method for measuring compressibility and poroelasticity coefficients in porous and permeable rocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 2670–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Experimental study of the interplay between pore system and permeability using pore compressibility for high rank coal reservoirs. Fuel 2019, 254, 115712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, L.; Sima, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H. Understanding stress-sensitive behavior of pore structure in tight sandstone reservoirs under cyclic compression using mineral, morphology, and stress analyses. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 218, 110987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, C.; Cao, J.; He, M.; Dou, L. Quantitative study on the stress sensitivity of pores in tight sandstone reservoirs of Ordos basin using NMR technique. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 172, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Xiao, C.; Qin, Z. Investigation of pore structure and petrophysical property in tight sandstones. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 91, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Combined effects of CO2 adsorption-induced swelling and dehydration-induced shrinkage on caprock sealing efficiency. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Dong, H.; Kong, F.; Jiang, Z. Investigation of pore characteristics and irreducible water saturation of tight reservoir using experimental and theoretical methods. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 3368–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, D.; Yao, C.; Tang, D.; Tang, S.; Huang, W. Petrophysical characterization of coals by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Fuel 2010, 89, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.J.; Tang, H.M.; Zhu, X.M.; Li, G.; Lin, D. Study on stress sensitivity in ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoir of Chang 8 oil formation in Xifeng Oilfield based on microscopic methods. J. China Univ. Pet. 2012, 36, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Yang, S.L.; Liao, W.W.; Gao, W.L.; Nie, X.R. Stress sensitivity of extra-low permeability volcanic gas reservoir Jilin oilfield and its origin. J. Xi’Shiyou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, J. Experimental investigation of water sensitivity effects on microscale mechanical behavior of shale. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 145, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, J.G. Estimates and rigorous bounds on pore-fluid enhanced shear modulus in poroelastic media with hard and soft anisotropy. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2006, 15, 133–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Rutqvist, J.; Berryman, J.G. On the relationship between stress and elastic strain for porous and fractured rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2009, 46, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gu, Z.; Guo, P.; Zhao, W. Comparative laboratory wettability study of sandstone, tuff, and shale using 12-MHz NMR T1-T2 fluid typing: Insight of shale. SPE J. 2024, 29, 4781–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Shang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, H.; Mews, K.S. Characterization of brittleness index of gas shale and its influence on favorable block exploitation in southwest China. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1389378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Luo, L.; Tian, Y.; Zeng, S. Seepage characteristics of broken carbonaceous shale under cyclic loading and unloading conditions. Energy Fuels 2023, 38, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Q.; Durucan, S. Drawdown induced changes in permeability of coalbeds: A new interpretation of the reservoir response to primary recovery. Transp. Porous Media 2004, 56, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Effects of pore structure on stress-dependent fluid flow in synthetic porous rocks using microfocus x-ray computed tomography. Transp. Porous Media 2019, 128, 653–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
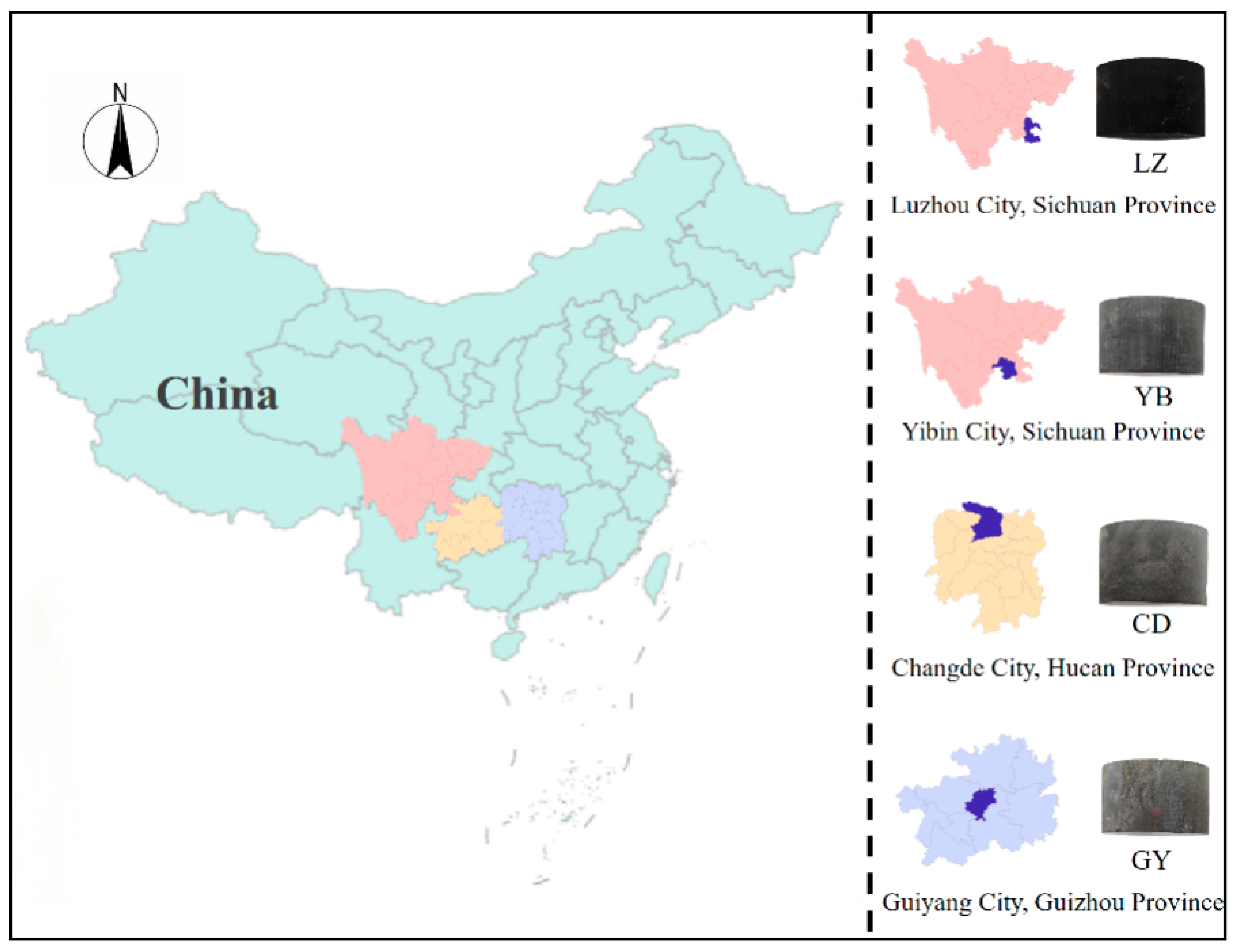





| Shale | Mineral Weight (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | Quartz | Dolomite | Illite | Calcite | Pyrite | Siderite |
| CD | 1.6 | 83.7 | 0 | 14.7 | 0 | 0 |
| GY | 4.4 | 34.8 | 0 | 57.7 | 0 | 3.1 |
| YB | 62.1 | 11.5 | 16.2 | 9 | 1.2 | 0 |
| LZ | 49.2 | 15.7 | 18.6 | 14.9 | 1.6 | 0 |
| Sample | Shi and Durucan Model | Dual-Spring Model |
|---|---|---|
| CD | 0.0777 | 0.0069 |
| GY | 0.1908 | 0.0136 |
| YB | 0.1619 | 0.0085 |
| LZ | 0.2947 | 0.0118 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Yue, J.; Liu, X.; Sheng, J.; Wang, H. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Quantifies Stress-Dependent Permeability in Shale: Heterogeneous Compressibility of Seepage and Adsorption Pores. Processes 2025, 13, 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061858
Tian J, Yue J, Liu X, Sheng J, Wang H. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Quantifies Stress-Dependent Permeability in Shale: Heterogeneous Compressibility of Seepage and Adsorption Pores. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061858
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jiali, Juan Yue, Xingxing Liu, Jinchang Sheng, and Huimin Wang. 2025. "Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Quantifies Stress-Dependent Permeability in Shale: Heterogeneous Compressibility of Seepage and Adsorption Pores" Processes 13, no. 6: 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061858
APA StyleTian, J., Yue, J., Liu, X., Sheng, J., & Wang, H. (2025). Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Quantifies Stress-Dependent Permeability in Shale: Heterogeneous Compressibility of Seepage and Adsorption Pores. Processes, 13(6), 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061858






