Abstract
The shale oil reservoirs in the Liang Gaoshan area of the Sichuan Basin exhibit extremely low porosity and permeability, as well as significant heterogeneity. Consequently, hydraulic fracturing of horizontal wells is critical for achieving effective production enhancement. Early diagnostic monitoring revealed substantial variations in fracture propagation. Some hydraulic fractures extended beyond the target layer into adjacent river sandstone, leading to increased fracturing costs and reduced reserve utilization rates. To address these challenges, temporary plugging fracturing (TPF) was implemented to optimize fluid distribution among fracture clusters. However, previous TPF operations in this basin relied heavily on empirical methods, resulting in a relatively low sealing success rate of approximately 70%. This study proposes a fracture propagation model that incorporates stress interference dynamics induced by temporary plugging fracturing agents. Additionally, through laboratory experiments, a high-pressure (30.2 MPa) degradable temporary-plugging agent was selected for use in horizontal well fracturing. Key process parameters, including the insertion timing, dosage, and distribution strategy of the temporary-plugging agent, were optimized using a numerical simulation system. The results indicate that injecting 50% of the fracturing fluid followed by the simultaneous deployment of 12 temporary blocking nodes ensures uniform fracture cluster extension while maximizing the reconstruction volume. Furthermore, deploying all temporary blocking nodes at once reduces the fracturing operation time by approximately 20%. These findings were validated via field applications at Well NC1. Microseismic monitoring during fracturing confirmed the accuracy of the research outcomes presented in this paper. After temporary plugging, the extension uniformity of each fracture cluster significantly improved, with the stimulated reservoir volume (SRV) of a single section reaching 530,000 cubic meters. These results provide a foundation for optimizing horizontal well fracturing in Liang Gaoshan shale oil reservoirs within the Sichuan Basin, facilitating efficient and economical fracturing operations.
1. Introduction
The escalating global energy demand has positioned shale oil and other unconventional resources as critical focal points in energy research [1,2]. In China, economically viable shale oil accumulations have been confirmed in multiple petroliferous basins, notably the Songliao, Bohai Bay, Junggar, and Sichuan Basins [3,4]. Petrophysical analyses reveal that these reservoirs are characterized by a sub-10% porosity, microdarcy-range permeability (typically < 0.1 mD), and pronounced heterogeneity—features that collectively define them as tight hydrocarbon systems [5]. To enhance the recovery efficiency in such challenging formations, multistage hydraulic fracturing has been established as an essential stimulation technique for creating conductive fracture networks [6,7,8]. Nevertheless, reservoir heterogeneity induces significant variability in fracture propagation patterns among different clusters within horizontal wellbores. This geomechanical complexity not only diminishes the effective stimulated reservoir volume (ESRV) that is critical for production enhancement, but also necessitates costly remedial operations to optimize fracture geometry, thereby escalating overall development expenditures [9,10].
The global investigation of hydraulic fracturing for shale oil has advanced into a comprehensive multidisciplinary study encompassing fundamental fracture propagation mechanisms, advancements in stimulation techniques, and the optimization of field applications. These studies systematically integrate fracture network modeling, multiphysics numerical simulations (including coupled fluid mechanics processes), and laboratory-scale characterization techniques (such as triaxial stress testing and core flooding experiments) to address the engineering challenges associated with low porosity, low permeability, and heterogeneous shale oil reservoirs [11,12,13]. Hou et al. [9] developed a three-dimensional discrete element numerical model that accounts for randomly distributed natural bedding planes and complex fracture networks. By simulating complex fracture propagation modes under varying cluster numbers and cluster spacings, increasing the cluster density and reducing the cluster spacing significantly enhance competition among multiple hydraulic fractures. Zhu et al. [14] proposed optimizing cluster spacing and well spacing to maximize the estimated ultimate recovery (EUR). Compact cluster spacing was found to enhance well productivity, improve economic efficiency, and potentially increase ultimate recovery. Zou et al. [15] utilized a complex fracture model based on the three-dimensional discrete element method (DEM) to simulate high-frequency propagation processes in naturally fractured strata during hydraulic fracturing (THF). Zhang et al. [16] introduced a novel experimental approach to simulate multiple-fracture propagation using rock splitting and 3D reconstruction techniques for characterizing fracture geometry. The presence of pre-existing fractures led to a reduced fracture aperture. Wang et al. [17] systematically evaluated the plugging performance of temporary-plugging fibers and particles on fractures of various scales, proposing a combination of fibers and particles as an effective temporary-plugging agent for ultra-deep well fracturing. Zhang et al. [18] conducted large-scale true triaxial temporary-plugging fracturing simulation experiments using five shale outcrops, discussing the effects of horizontal stress differences and the amount of temporary-plugging agent on plugging effectiveness and fracture propagation behavior. The results indicated that the amount of temporary-plugging agent determines the location of plugging and the diversion mode of fractures. Crack steering within existing fractures occurs due to partial sealing at the crack tip. Yuan et al. [19] proposed a novel method for characterizing the location of crack sealing by utilizing the normal width of the crack and further investigated the sealing behavior of fibers and particles within 2 mm cracks. Wang et al. [20] examined the effects of various factors on the activation characteristics of natural fractures. Specifically, when the approach angle is less than 60°, hydraulic fracturing (HF) initially activates the acute branch of the natural fracture (NF) before propagating through the NF. Liu et al. [21] introduced a three-dimensional fluid-mechanics coupling-element partitioning method (3D-epm). This approach is capable of simulating the propagation process of three-dimensional hydraulic fractures, their interaction with natural fractures, and the impact of in situ stress. It offers an alternative solution for simulating three-dimensional hydraulic fractures in complex reservoirs while considering the hydrodynamic coupling effect within fractures. Liu et al. [22] employed the element division method to model natural fractures, taking into account the fracture zones surrounding cavities, and investigated local high-frequency cavity interactions as well as those near the wellbore. The results indicate that higher in situ stress levels enhance the repulsive force exerted by cavities on high-frequency (HF) fracturing. Pore pressure and the fracture area around the cavities can mitigate stress concentration, thereby promoting the connectivity of high-frequency cavities. When the differential ground stress is relatively low, distributed natural fractures play a predominant role in determining the direction of HF propagation.
Extensive research has yielded significant progress in evaluating temporary-plugging agents and modeling fracture propagation for horizontal well fracturing. However, in the complex lithology of Sichuan Basin shale oil reservoirs—characterized by pronounced heterogeneity and significant horizontal stress differences—conventional fiber and particle temporary-plugging agents demonstrate suboptimal sealing effectiveness. Furthermore, existing fracture propagation models fail to account for the influence of temporary-plugging pressure on stress interference.
The hydraulic fracturing of shale oil reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin faces two primary challenges: the irregular fracture propagation pattern and the inadequate sealing performance of conventional temporary-plugging agents. These factors significantly impair the effectiveness of production enhancement. To address these issues, this study proposes an integrated approach comprising the following: (1) a stress interference fracture propagation model for horizontal wells, (2) the laboratory-based screening of advanced composite sealing materials, and (3) a systematic optimization of design parameters for temporary-plugging fracturing, including the dosage, timing, and frequency of temporary plugging agent application. This methodological framework offers both theoretical insights and technical guidance for optimizing hydraulic fracturing in heterogeneous shale oil reservoirs.
2. Mechanism of Temporary Plugging Fracturing
The shale oil reservoirs in the Liang Gaoshan Formation of the Sichuan Basin exhibit distinct fluvial channelized depositional patterns, where economically viable hydrocarbon resources are preferentially concentrated within narrow, discontinuous channel sand bodies [23]. Horizontal well fracturing has become an indispensable technique for the commercial development of these unconventional resources [24,25]. However, as is illustrated in Figure 1, the extreme reservoir heterogeneity within these channelized sandstone formations creates significant challenges for fracture propagation control. Field observations reveal substantial variability in fracture geometry among multiple clusters, with some fractures breaching channel boundaries into non-productive intervals, while others demonstrate insufficient lateral extension. The heterogeneous propagation of clustered hydraulic fractures, exacerbated by stress interference and reservoir heterogeneity in complex geological settings, significantly impedes the effective stimulation of fluvial sandstone reservoirs within the Liang Gaoshan Formation, presenting a critical technical challenge for shale oil development through horizontal well fracturing in the Sichuan Basin [26].
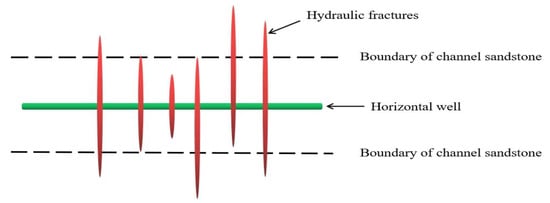
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of hydraulic fracture propagation during horizontal well fracturing in shale reservoirs within the Sichuan Basin.
2.1. Temporary-Plugging-Material Optimization
In order to identify efficient temporary sealing materials suitable for the horizontal well fracturing of shale oil in the Sichuan Basin, a series of evaluation tests were conducted on various temporary sealing materials using a high-temperature and high-pressure three-dimensional fracture temporary sealing evaluation instrument. The experimental temperature was set at 60 °C, corresponding to the reservoir temperature, and nine sets of sealing experiments were performed utilizing temporary sealing balls, combinations of temporary sealing balls and particles, as well as temporary sealing joints. As is shown in Table 1 and Table 2, compared with other combinations of temporary-plugging agents, the combination of temporary-plugging agents demonstrated the highest sealing efficiency, ranging from 96.2% to 98.8%. The sealing pressure for temporarily blocking paired perforations could reach over 30.2 MPa. As is illustrated in Figure 2, this is primarily attributed to the three-dimensional interwoven structure of highly elastic polymer fibers, which allows the segments to gradually deform under downhole conditions and effectively fill irregular perforations. Moreover, the cross-woven structure of the temporary sealing joint ensures the reliable sealing of the perforations even under continuous proppant wear [25,27]. Based on these findings, the combination of temporary-plugging agents is recommended as the optimal choice for temporary-plugging material in the horizontal well fracturing of shale oil in the Sichuan Basin.

Table 1.
Comparison of sealing efficiency of different temporary-plugging materials.

Table 2.
Comparison of plugging pressure of different temporary-plugging materials.

Figure 2.
Temporary-plugging knot.
One of the fundamental technical criteria for successful temporary-plugging fracturing operations requires that the diverting materials must fulfill two critical functions: (1) achieving the effective sealing of perforation channels during hydraulic fracturing to ensure precise fluid diversion and controlled fracture propagation, and (2) undergoing complete chemical degradation within the reservoir environment post-stimulation to maintain the optimal conductivity of production pathways, thereby eliminating any detrimental impact on subsequent hydrocarbon recovery efficiency [28,29,30,31].
Considering that the shale oil horizontal well needs to be braised after fracturing in the Sichuan Basin, it is required that the temporary-plugging knot can be completely degraded after 120 h of fracturing. Based on the salinity characteristics of shale oil reservoir fluids in the Sichuan Basin, simulated formation water was prepared. The dissolution experiment was conducted at a reference reservoir temperature of 60 °C, as illustrated in Figure 3. After immersion in the simulated formation water for 120 h at 60 °C, the temporary-plugging rope nodes were fully dissolved, thereby satisfying the requirements for efficient sealing during the fracturing process and ensuring complete dissolution post-fracturing without impacting fluid production.

Figure 3.
Image of temporary-plugging-knot dissolution. (a) Image of a temporary-plugging knot soaked in water at 60 °C (0 h). (b) Image of a temporary-plugging knot soaked in water at 60 °C (120 h).
2.2. Numerical Simulation Model of Temporary-Plugging Fracturing
In this paper, we establish a temporary-plugging fracture propagation model for horizontal shale oil wells in the Sichuan Basin. This model takes into account the local stress interference induced by temporary plugging, as illustrated below.
- (1)
- Fluid-flow governing equation [32]:
- w: fracture width (m), t: time (s), : fluid viscosity (Pas), : fluid pressure (Pa),
- : injection rate (m3/s), : leak-off rate (Carter model, m3/(sm)),
- : Carter leak-off coefficient, : time when fluid reaches position x(s)
- (2)
- Fracture width–stress coupling [33]:
- : Poisson’s ratio, E: Young’s modulus (Pa), : minimum horizontal stress (Pa),
- : Green’s function for fracture deformation(m−1),
- : fracture length at time t(m).
- (3)
- Pressure jump across the plugged zone:
- : pressure jump across plugged zone (Pa),
- : dimensionless resistance factor,
- flow rate through plugged zone (m3/s),
- permeability of plugged zone (m2),
- cross-sectional area of plugged zone (m2).
- (4)
- Stress interference induced by temporary plugging:
- stress interference increment due to temporary plugging (MPa),
- temporary-plugging efficiency coefficient,
- net pressure (MPa),
- area of the fracture sealed by the temporary-plugging agent (m2),
- fracture volume (m3).
- (5)
- Fracture propagation model equation:
- dL/dt: fracture propagation velocity (m/s). This represents the rate of change in fracture length with respect to time.
- C: fracture propagation coefficient. L: fracture length at time t (m).
- : net pressure within the fracture (MPa). This represents the fluid pressure exceeding the minimum confining stress (P_net = p − σ_min).
- : stress interference increment due to temporary plugging (MPa), defined in the fourth equation.
- : mode I fracture toughness of the rock (MPa·m1/2): a material property representing resistance to tensile fracture propagation.
- : fracture propagation exponent (dimensionless): an empirical constant typically ranging between 1 and 2.
The developed numerical model for fracture propagation in Sichuan Basin shale oil horizontal wells integrates heterogeneous layer characterization and stress shadow effects induced by temporary-plugging balls, enabling the high-fidelity simulation of temporary-plugging fracturing (TPF) processes under complex geological conditions.
Based on the geomechanical parameters of the Liang Gaoshan shale oil reservoir in the Sichuan Basin, including porosity, permeability, oil saturation, Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio, maximum horizontal principal stress, and minimum horizontal principal stress, a numerical model for staged hydraulic fracturing of horizontal wells was established using the finite-element numerical simulation method. This model incorporates the interference effects of temporary-plugging pressure on the fracturing stress of horizontal wells, enabling the more accurate simulation of fracture propagation characteristics for each cluster following temporary plugging. Additionally, the influence of different temporary-plugging durations and the number of temporary-plugging knots on fracture propagation was quantitatively analyzed using the fracture non-uniformity coefficient and stimulated reservoir volume (SRV). The model domain measures 500 m in both length and width, with a minimum mesh size of 1 m. To enhance the computational efficiency, a representative fracturing section was selected, dividing a 60 m horizontal wellbore section into five clusters. Key operational parameters include an injection rate of 18 m3/min, a total fluid volume of 2400 m3, and a fracturing fluid viscosity of 15 mPa·s. The critical input parameters for the temporary plugging fracturing numerical model are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Input parameters of the numerical simulation model.
Factors affecting temporary-plugging fracturing primarily include the dosage of temporary-plugging knots, the timing of their injection, and the frequency of their application [32]. In this study, we developed a temporary plugging fracturing model for shale oil horizontal wells in the Sichuan Basin, with a focused investigation on the optimization of these three critical parameters.
2.3. Optimization of the Dosage of Temporary-Plugging Knots
The geological and engineering parameters utilized in the simulation were primarily derived from Table 3. A 60 m horizontal wellbore was designed with five perforation clusters spaced at 12 m intervals, comprising a total of 36 perforations. The fracture propagation patterns under different dosages of temporary-plugging agents were simulated, as shown in Figure 4. Compared to scenarios without temporary-plugging agents, the application of these agents substantially enhanced the uniformity of fracture propagation across clusters. In the absence of such agents, the inability to artificially control fluid distribution among clusters resulted in excessive fluid intake in perforations located within high-permeability reservoir zones, while limited fluid entered the low-permeability zones [34]. Consequently, significant disparities in fracture lengths emerged among clusters.
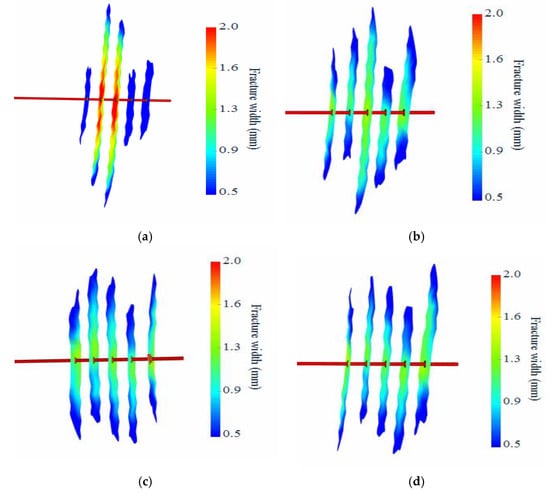
Figure 4.
Simulation of fracture propagation with varying dosages of temporary-plugging knots. (a) Fracture propagation simulation with three temporary-plugging knots. (b) Fracture propagation simulation with six temporary-plugging knots. (c) Fracture propagation simulation with twelve temporary-plugging knots. (d) Fracture propagation simulation with eighteen temporary-plugging knots.
The primary objective of temporary-plugging fracturing is to achieve uniform fracture propagation across multiple clusters. To systematically evaluate the impact of temporary-plugging agent dosage on fracture behavior, numerical simulations were conducted for perforation configurations with 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, and 24 temporary-plugging knots. The fracture uniformity coefficient () was jointly adopted to assess plugging effectiveness. The fracture uniformity coefficient was defined as the weighted average of the ratios of two-wing-fracture half-lengths among clusters, where a value closer to 1 indicates higher uniformity in fracture geometry.
As is illustrated in Figure 5, the fracture uniformity coefficient exhibited a non-monotonic trend, initially decreasing and subsequently increasing with elevated plugging agent dosage. At 12 temporary-plugging knots, the coefficient approached 1 (.18), suggesting optimal uniformity. However, excessive plugging (21 temporary-plugging knots) resulted in a significant deviation ( 1.55), demonstrating that over-plugging induces preferential fluid flow through unblocked perforations, thereby exacerbating fracture length disparities. Notably, configurations with 12 and 15 agents yielded statistically equivalent uniformity coefficients. Considering cost efficiency, we recommend deploying 12 temporary-plugging agents per stage for shale oil horizontal well fracturing in the Sichuan Basin.
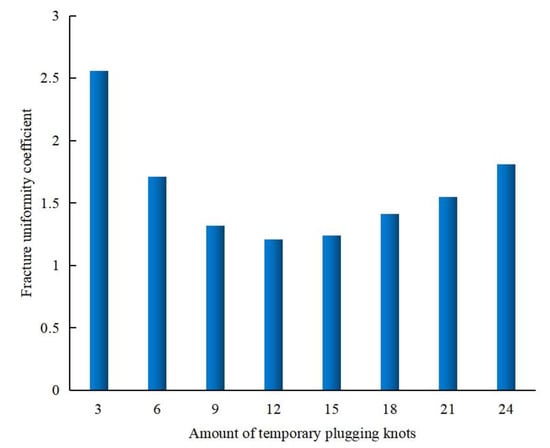
Figure 5.
Comparison of fracture uniformity coefficients under different amounts of temporary-plugging knots.
2.4. Optimization of Filling Time for Temporary-Plugging Knots
It is well known that, apart from the amount of temporary-plugging rope knots used, the timing of their addition also affects the extension and expansion of fractures [35,36]. In the past, in the horizontal wells of shale oil in the Sichuan Basin, temporary-plugging rope knots were added only after 30% of the fracturing fluid was used. The microseismic monitoring results showed that the fracture expansion remained non-uniform after the addition of temporary-plugging rope knots. In this paper, a numerical simulation model was established to clarify the fracture expansion characteristics under different timings of adding temporary-plugging rope knots, and the optimal timing was selected based on the uniformity coefficient of fractures and the fracture area.
As is shown in Figure 6, delayed temporary-plugging initiation timing resulted in progressively more uniform fracture propagation patterns across clusters. Notably, the deployment of knotted fiber diverters following 20% fracturing fluid injection exhibited no significant improvement in cluster uniformity. Although partial uniformity enhancement was observed when implementing temporary-plugging knots at 30% fluid injection, the three central clusters demonstrated 18–22% shorter fracture lengths compared to peripheral clusters. In contrast, synchronized knotted fiber placement at 40% and 50% fluid injection stages achieved both optimized cluster uniformity and a balanced fracture length distribution among all clusters.
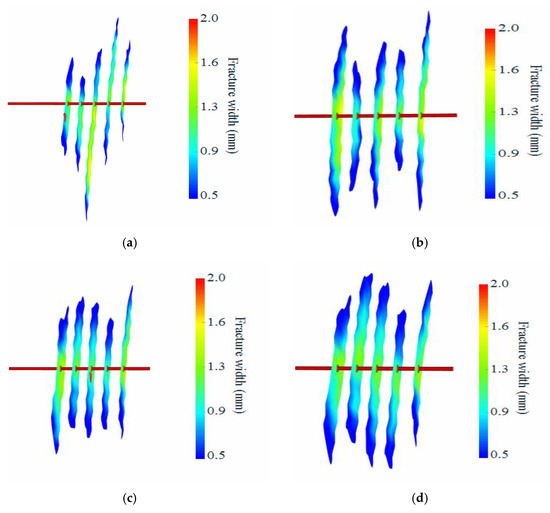
Figure 6.
Fracture propagation under varying temporary-plugging initiation timings. (a) Simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation incorporating temporary-plugging knots following 20% fracturing fluid injection. (b) Simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation incorporating temporary-plugging knots following 30% fracturing fluid injection. (c) Simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation incorporating temporary-plugging knots following 40% fracturing fluid injection. (d) Simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation incorporating temporary-plugging knots following 50% fracturing fluid injection.
To optimize temporary-plugging initiation timing, a systematic investigation was conducted through hydraulic fracture propagation simulations triggered at 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, and 70% fracturing fluid injection stages. The fracture uniformity coefficient (FUC) and stimulated reservoir volume (SRV) were jointly analyzed to quantitatively determine the optimal plugging timing, driven by the dual objectives of achieving balanced fracture network geometry and maximizing shale oil reservoir drainage efficiency.
As is illustrated in Figure 7, the temporal deployment of temporary-plugging agents significantly influences both the fracture uniformity coefficient (FUC) and stimulated reservoir volume (SRV). For shale oil horizontal well fracturing in the Sichuan Basin, the operational objective requires the simultaneous optimization of fracture network uniformity and SRV maximization. Systematic simulations demonstrate that knotted fiber diverter implementation at 20–70% fluid injection stages induces a characteristic FUC reduction–increase pattern, while the SRV follows an inverse increase–decrease trend. This bimodal behavior stems from the existence of an optimal plugging window—premature deployment fails to adequately redistribute fluid flow among clusters, whereas delayed intervention cannot counteract stress shadowing effects. Notably, while 40% and 50% fluid injection stages yield comparable FUC values (1.18 vs. 1.22), their SRV diverge substantially, with the 50% timing achieving a 3.1% greater SRV (0.64 × 106 m3 vs. 0.66 × 106 m3). Field implementation data confirm that mid-stage plugging at 50% fluid injection optimally balances fracture uniformity and reservoir contact enhancement (SRV maximization), establishing this timing as the recommended operational threshold for Sichuan Basin shale oil developments.
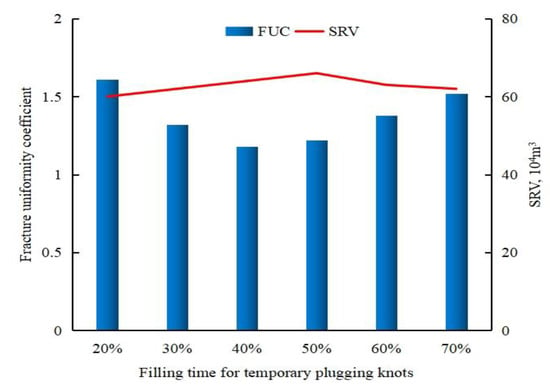
Figure 7.
Comparison of FUC and SRV at different temporary-plugging times.
2.5. Optimization of Temporary-Plugging Frequency in Hydraulic Fracturing
As was mentioned earlier, 12 temporary-plugging rope knots are used per stage in the fracturing of horizontal wells in the Sichuan Basin. This study compared and analyzed the impact of injecting all of the temporary-plugging rope knots at once versus in two separate batches on the uniformity of fracture propagation. Given the limited number of temporary-plugging rope knots, injecting them in multiple batches might increase the operational complexity of the fracturing process. As is shown in Figure 8, the uniformity of the fractures formed by injecting all of the temporary-plugging rope knots at once is comparable to that achieved by injecting them in two batches. Therefore, in the fracturing of horizontal wells in the Sichuan Basin’s shale oil reservoirs, it is recommended to prioritize the option of injecting all of the temporary-plugging rope knots at once.
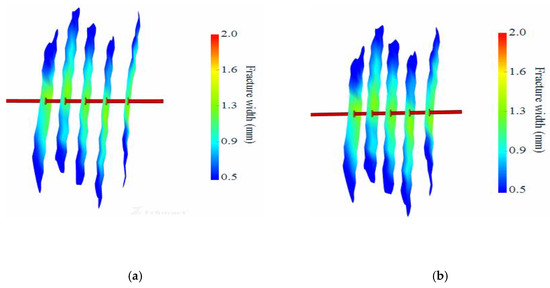
Figure 8.
Numerical Investigation of Fracture Propagation Under Varied Temporary-Plugging Frequencies. (a) Numerical simulation of fracture propagation with single-batch temporary-plugging knots. (b) Numerical simulation of fracture propagation with dual-batch temporary-plugging knots.
In this study, the fracture propagation uniformity of single- and double-batch (12 temporary-plugging knots per stage) temporary-plugging agents was systematically evaluated during horizontal fracturing of the shale oil reservoir in the Sichuan Basin. The operational analysis showed that dividing a limited number of blocked tubes into multiple batches would introduce unnecessary procedural complexity and would not improve fracture geometry control. Quantitative evaluation of the fracture uniformity coefficient (FUC) showed that the results of single (FUC = 1.15) and dual (FUC = 1.18) fracturing were statistically identical, with no significant difference (Figure 8). Field implementation data further show that a single batch of fracturing can reduce the staging time by 15–20% compared to staged fracturing. These results ultimately support the technical advantages of a single batch of temporary plugging to achieve optimal fracture network uniformity while minimizing operational efficiency. Therefore, we recommend that a single batch be used as a standard practice for shale oil fracturing operations in the Sichuan Basin.
3. Field Application
Well NC1, a horizontal well in the Gongshanmiao Oilfield of the Sichuan Basin, China, is situated within the northern sector of the low-angle tectonic belt in the Central Sichuan Paleo-Uplift. The 1400 m horizontal section targets a clastic reservoir dominated by medium- to coarse-grained sandstones. Petrographic analysis identifies the lithology as lithic arkose sandstone (quartz: 30–50%; feldspar: 20–60%). Reservoir characterization reveals a pore network that is primarily governed by an intergranular mixed pore system. Petrophysical evaluation demonstrates marginal reservoir quality, with an average porosity of 8.5%, permeability of 0.22 mD, and oil saturation of 40%. Geomechanical measurements indicate a horizontal stress differential of 8 MPa.
The NC1 reservoir exhibits low porosity, low permeability, and pronounced heterogeneity, with significant variability in fracture propagation between individual clusters. This strong heterogeneity poses a critical challenge for hydraulic fracturing operations. Ensuring uniform fracture propagation across all clusters represents a key engineering objective for optimizing stimulation efficiency in this reservoir.
In order to improve the extension form of each cluster of fractures in well NC1 and ensure that each cluster of fractures extends evenly and does not extend to the outside of the channel, the entirety of well NC1 adopts the temporary-plugging-fracturing technology. Variable viscous slip water with real-time adjustable viscosity is used as the fracturing fluid, and the viscosity adjustment range is 10–60 mPa·s. Degradable and high-pressure temporary-plugging knots are used as temporary-plugging agents. According to the research results outlined in this paper, 12 temporary-plugging knots should be added to each fracturing stage, and the temporary-plugging knots should be added after 50% of the fracturing fluid is injected in a one-time manner. In order to verify the temporary-plugging effect, the fracturing site was equipped with two technical means, microseismic and high-frequency pressure monitoring. The results of microseismic monitoring (Figure 9) show that the uniform degree of fracture extension and the reconstruction volume of well NC1 are improved after the temporary-plugging knot is added. The high-frequency pressure monitoring data show that the fluid intake of each cluster is greatly improved after temporary plugging; in particular, the fluid intake of the perforating cluster with low fluid intake in the early stage is greatly increased after temporary plugging, which further ensures the uniform fracture extension of each cluster.
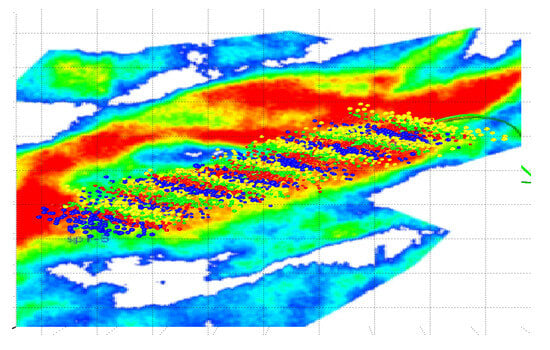
Figure 9.
Map of Microseismic Monitoring Results for Hydraulic Fracturing Operations in Well NC1.
NC1 implemented slickwater fracturing technology. The selected proppants included 40/70 mesh quartz sand and 30/50 mesh quartz sand. The fracturing fluid intensity was 41.84 m3/m, the sand addition intensity was 5.3 t/m, the average compressive fracture length monitored by microseismic techniques was 409 m, and the single-stage SRV (stimulated reservoir volume) reached 573,000 cubic meters. The distribution of microseismic event points exhibited characteristics of double-wing fractures. The low coincidence rate between clusters and the uniform morphology of the two fracture wings indicate that temporary-plugging fracturing effectively promotes the uniform extension of fractures.
The integrated diagnosis of microseismic monitoring and high-frequency pressure monitoring confirmed that the fracture propagation uniformity of well NC1 was enhanced following the implementation of temporary plug fracturing (TPF). These findings have established a robust engineering foundation for the economically efficient development of shale oil in the Liangshan Formation of the Sichuan Basin, particularly in addressing the technical challenges associated with the stimulation of heterogeneous reservoirs in horizontal wells.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Field practice has proved that temporary-plugging fracturing technology can improve the problem of non-uniform fracture extension of various clusters of shale oil horizontal wells in the Sichuan Basin. The optimal solution for the temporary-plugging fracturing of shale oil horizontal wells in the Sichuan Basin is to inject 12 temporary-plugging knots at one time after 50% of the pumping fracturing has occurred.
- (2)
- Compared with the temporary plugging of fibers and particles, the temporary-plugging knot has a better plugging ability for perforating holes. Due to the good flexibility of the temporary-plugging knot, it has a stronger adaptability for plugging irregular perforating holes formed by proppant erosion.
- (3)
- To optimize the fracture network complexity and stimulated reservoir volume (SRV) in shale oil horizontal wells within the Sichuan Basin, this study recommends a systematic investigation of intra-fracture temporary plugging and diversion (TPD) technology. Particular emphasis should be placed on determining the optimal timing for diversion operations and characterizing the performance of temporary-plugging agents with respect to their composition, particle size distribution, and degradation behavior under downhole conditions.
Author Contributions
Software, Y.W. and Q.Y.; Formal analysis, Y.W.; Investigation, Q.Y. and W.C.; Writing—original draft, Y.W., Q.Y., W.C., J.Y., X.Z. and S.L.; Writing—review & editing, Y.W., Q.Y. and X.Z.; Visualization, Y.W. and Q.Y.; Project administration, Y.W.; Funding acquisition, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the China National Petroleum Corporation project (2023ZZ17YJ03).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Yang Wang, Qingyun Yuan, Weihua Chen, Jie Yan, Xiangfei Zhang, Song Li were employed by the company PetroChina. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The PetroChina had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Li, S.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.; He, R. A new fracturing method to improve stimulation effect of Marl tight oil reservoir in Sichuan basin. Processes 2023, 11, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, Z. Composite stimulation technology for improving fracture length and conductivity of unconventional reservoirs. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 1181302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Deng, S.; Sun, Y. Recent advances on shale oil and gas exploration and development technologies. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2024, 11, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, D. A review of phase behavior simulation of hydrocarbons in confined space: Implications for shale oil and shale gas. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 68, 102901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.M.; Han, X.X.; Cui, Z.G. Progress and recent utilization trends in combustion of Chinese oil shale. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 552–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; He, X.; Li, C.; Geng, S.; Zhu, R. A new permeability model for smooth fractures filled with spherical proppants. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, C. Basic characteristics and evaluation of shale oil reservoirs. Pet. Res. 2016, 1, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, J.; Ren, L.; Chen, X.; Lin, R.; Hu, Y.; Du, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, D.; et al. Ten years of gas shale fracturing in China: Review and prospect. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2022, 9, 158–175. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, B.; Chang, Z.; Wu, A.; Derek, E. Simulation of competitive propagation of multi-fractures on shale oil reservoir multi-clustered fracturing in Jimsar sag. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, X.; Shu, C.; Yang, Y.; Cao, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhong, A. Imbibition mechanisms of fracturing fluid in shale oil formation: A review from the multiscale perspective. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 9822–9840. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Liu, G.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Xian, C.; Liu, H. Optimization method of favorable lithofacies and fracturing parameter for continental shale oil. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 1405. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-B.; Qu, Z.-Q.; Guo, T.-K.; Xue, X.-J.; Xu, R.-L.; Chen, M.; Hu, Z.-P. Numerical simulation of fracturing and imbibition in shale oil horizontal wells. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 2981–3001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M. Field experiments and main understanding of shale oil hydraulic fracturing. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1410524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Forrest, J.; Hong, X.; Kianinejad, A. Cluster spacing and well spacing optimization using multi-well simulation for the lower Spraberry shale in Midland basin. In Proceedings of the SPE Liquids-Rich Basins Conference-North America, Midland, TX, USA, 13–14 September 2017; SPE: Richardson, TX, USA, 2017; p. D011S001R003. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S. Numerical modeling of fracture propagation during temporary-plugging fracturing. SPE J. 2020, 25, 1503–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zou, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, N.; Liu, L. Experimental investigation into simultaneous and sequential propagation of multiple closely spaced fractures in a horizontal well. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 202, 108531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, C.; Luo, Z.; Chen, W.; He, T.; Fang, H.; Fu, Y. Research and application of segmented acid fracturing by temporary plugging in ultradeep carbonate reservoirs. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 28620–28629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hou, B.; Tan, P.; Muhadasi, Y.; Fu, W.; Dong, X.; Chen, M. Hydraulic fracture propagation behavior and diversion characteristic in shale formation by temporary plugging fracturing. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 190, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhou, F.; Li, B.; Gao, J.; Yang, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J. Experimental study on the effect of fracture surface morphology on plugging efficiency during temporary plugging and diverting fracturing. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 81, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Gu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, F. Insights into the activation characteristics of natural fracture during in-fracture temporary plugging and diverting fracturing. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 162, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z. Three-Dimensional hydraulic fracture simulation with hydromechanical coupled-element partition method. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Numerical study on hydraulic fracture-cavity interaction in fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoir. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 213, 110426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, M.; Deng, H.; Zhao, S.; Gluyas, J.G.; Ye, T.; Ruan, Y. River channel pattern controls on the quality of sandstone reservoirs: A case study from the Jurassic Shaximiao formation of western Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, L.; Morales, O.; Sierra, F.; Teran, N.; Monge, A.; Alvarez, J. Abrasive Perforation Technique Optimize Production and Avoid Reservoir Damage in COCA Field Ecuador. In Proceedings of the SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, Quito, Ecuador, 18–20 November 2015; SPE: Richardson, TX, USA, 2015; p. D031S028R004. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Shi, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Study on field test and plugging simulation of the knot temporary plugging agent. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2022, 58, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, R.; Yang, H.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, T.; Han, Z. Research of a Self-Adaptive High-Performance Re-Fracturing Technology with Knot Temporary Plugging in a Thin Reservoir with High Stress. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2023, 58, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, P.; Du, J.; Liang, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, D.; Liu, F. A critical review of key points in temporary plugging fracturing: Materials, injection, temporary plugging, and design. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 240, 212981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Peng, S.; Zhao, J.; Lin, R.; Wu, J.; Wu, J. Optimization design of plugging agent dosage and application of deep shale gas inner-diversion fracturing. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 239, 212908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xu, H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T. Study on the velocity of the temporary plugging agent along wellbore in a fracturing operation. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2022, 58, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Peng, J.; Han, H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z. Temporary Plugging Agent Evaluation Technology and Its Applications in Shale Reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin. Processes 2023, 11, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Bian, X.; Zhong, G.; Wei, R.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, B.; Kao, J. Case Study: Dual Temporary Plugging & High Proppant Intensity Fracturing Stimulation Technique in Deep Shale Gas Play in Sichuan Basin, China. In Proceedings of the ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 26–29 June 2022; ARMA: West Perth, WA, USA, 2022; p. ARMA-2022-0659. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Kresse, O.; Weng, X.; Cohen, C.; Gu, H. Modeling of interaction of hydraulic fractures in complex fracture networks. In Proceedings of the SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 6–8 February 2012; SPE: Richardson, TX, USA, 2012; p. SPE-152052-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, D.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Jin, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. Fracturing and production analysis of the efficacy of hydraulic fracture stage reduction in the improvement of cost-effectiveness in shale oil development: A case study of Jimsar shale oil, China. Energy Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersma, T.; Hoekstra, R.; Dekinga, A.; Koolhaas, A.; Wolf, P.; Battley, P.; Wiersma, P. Scale and intensity of intertidal habitat use by knots Calidris canutus in the western Wadden Sea in relation to food, friends and foes. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1993, 31, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Experimental validation and numerical analysis of temporary plugging ball transport dynamics in horizontal wellbore. Particuology 2025, 98, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zening, S.; Zhanglong, T.; Junwen, L.; Qi, A.; Yushi, Z.; Shikang, L.; Ziwen, Z. Investigation into hydraulic fracture propagation behavior during temporary plugging and diverting fracturing in deep coal seam. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1369428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).