Experimental Assessment of the Effects of Gas Composition on Volatile Flames of Coal and Biomass Particles in Oxyfuel Combustion Using Multi-Parameter Optical Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
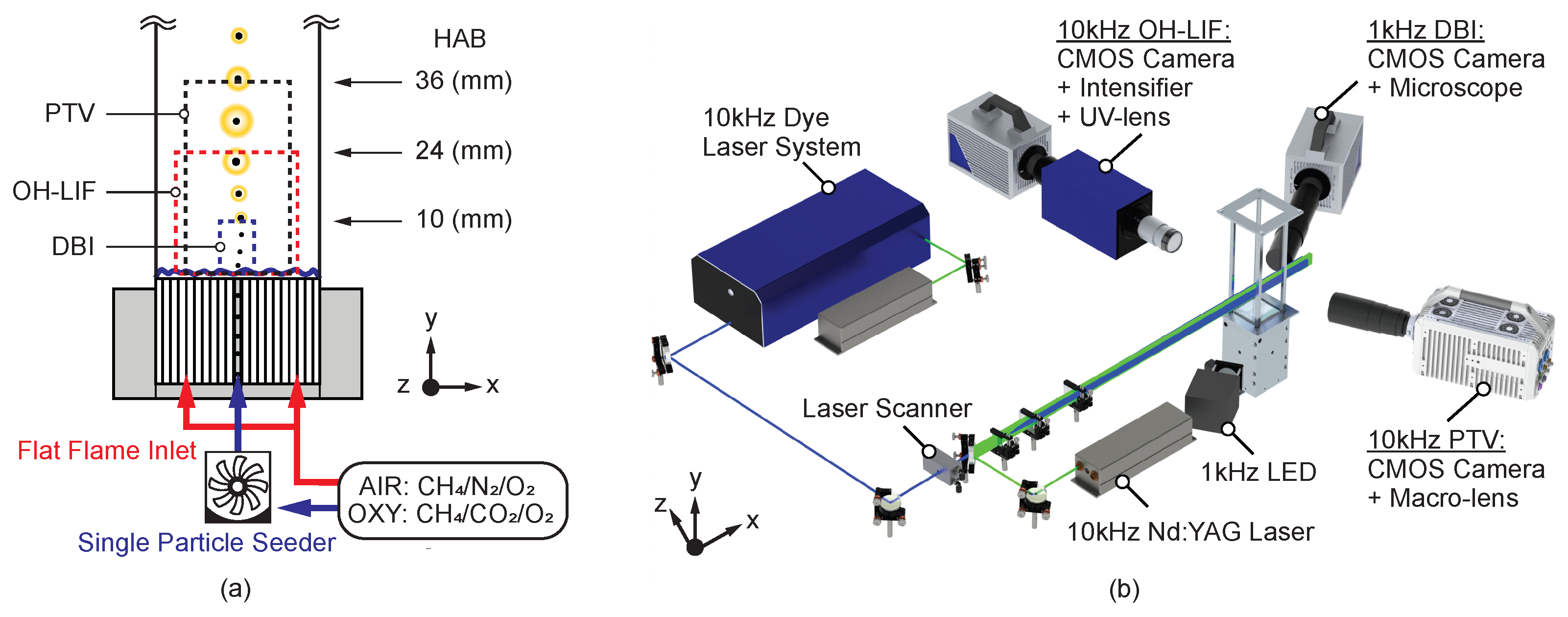
2. The Experimental Methodology
2.1. Combustion Atmospheres and Fuel Particles
2.2. Optical Diagnostics
2.3. Evaluation of Particle Size, Velocity, and Ignition
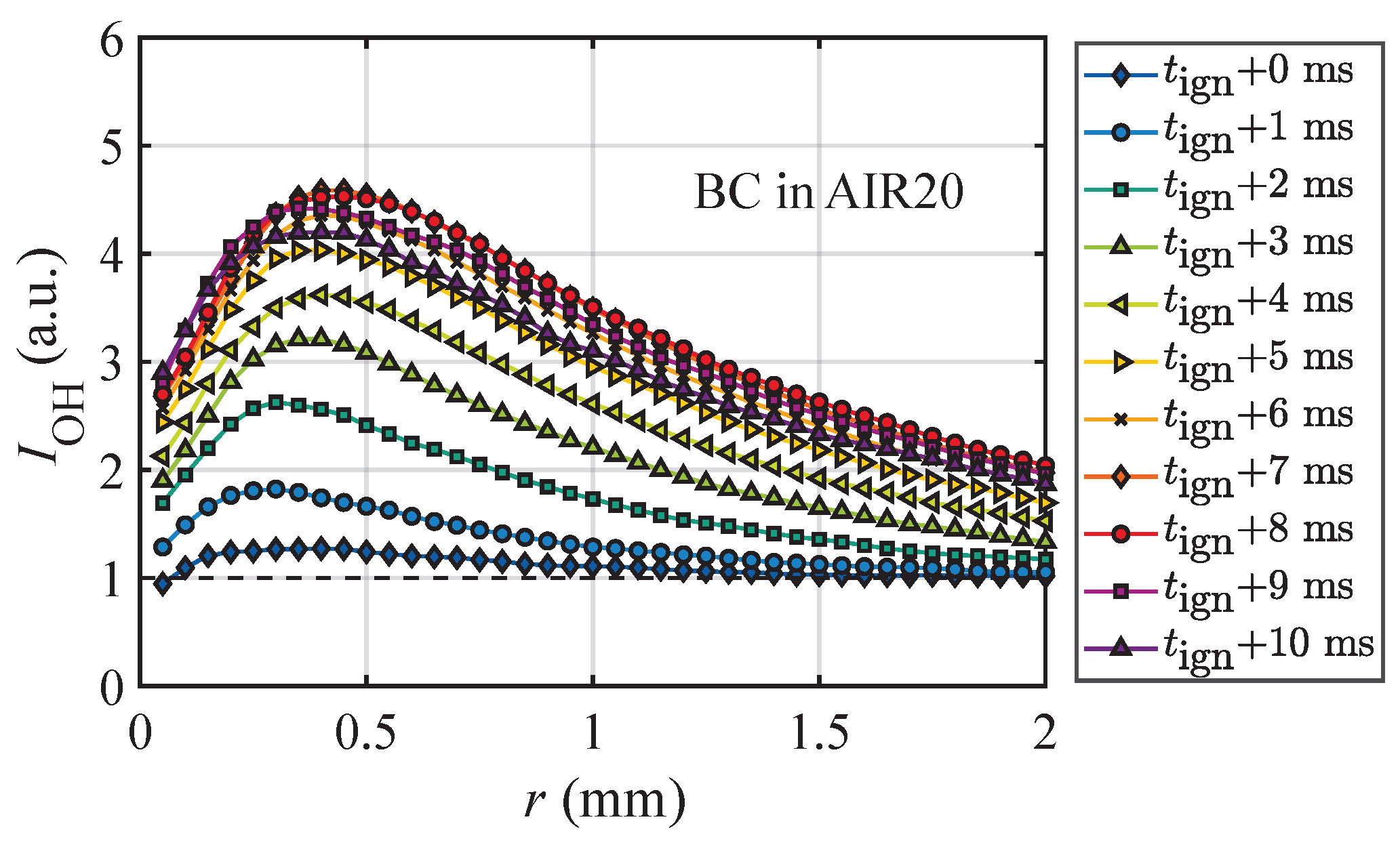
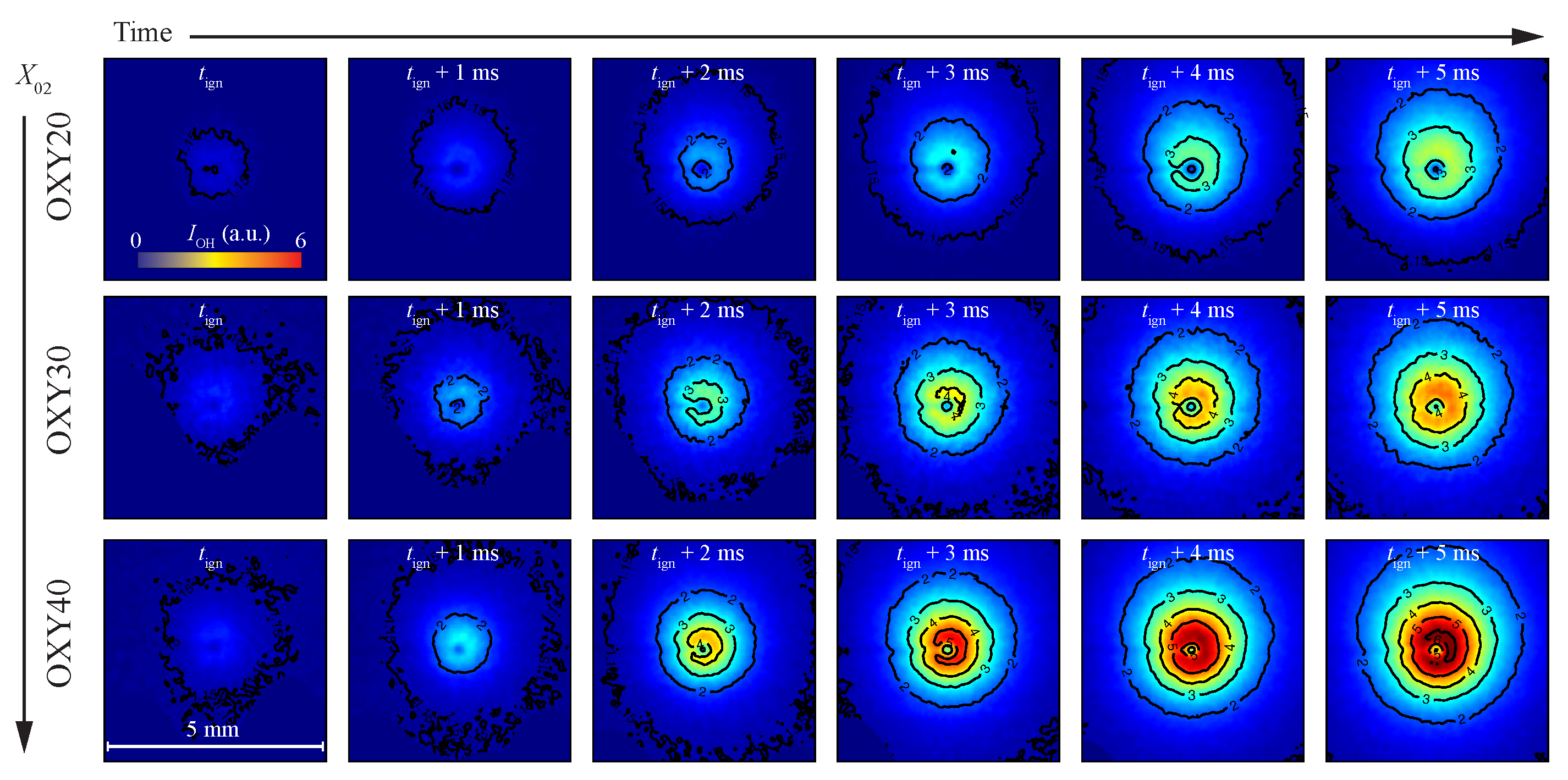
- The first approach identifies ignition based on radial profiles of the OH-LIF intensity (). Figure 2 shows an example for a BC particle at various time steps post-ignition. When a particle intersects with the laser sheet, it appears as a dark stripe, which is excluded from the orientation-averaged intensity calculations. As shown in prior 3D studies [41], increases toward the reaction zone and decreases in the post-flame region. Ignition is defined as the moment when surpasses the normalized background level (unity), attributed to the formation of OH via the dissociation of water in hot gas environments. A rapid rise in is observed within a few milliseconds, followed by a plateau and an eventual decline after 7–8 ms. This behavior reflects the continuous release and consumption of volatiles in a diffusion-controlled, non-premixed flame, where the oxidizer and the fuel meet from opposite directions. The temporal evolution of the radial intensity profile further enables quantification of the flame stand-off distance and the location of the reaction zone, as discussed in Section 3.4.
- The second method employs the structure and signal (SAS) analysis algorithm, which detects the onset of gas-phase reactions by identifying contiguous OH-LIF signal regions. As reported in [19], this technique has proven effective for identifying ignition in particles with diameters near 100 µm.
- The third ignition detection method employs a deep learning approach based on a residual neural network (ResNet) architecture for feature recognition. The implementation details, including the network depth, training data volume, and learning process, are provided in [20]. In this study, a pre-trained ResNet18 model—fine-tuned using planar OH-LIF data from [19]—is used to detect ignition events in the current multi-plane dataset. The advantage of this model is its proven capability to generalize to a new dataset without parameter adjustments, as demonstrated in [20]. The model and training datasets are available on request.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Particle Size Distribution and Velocity Profiles
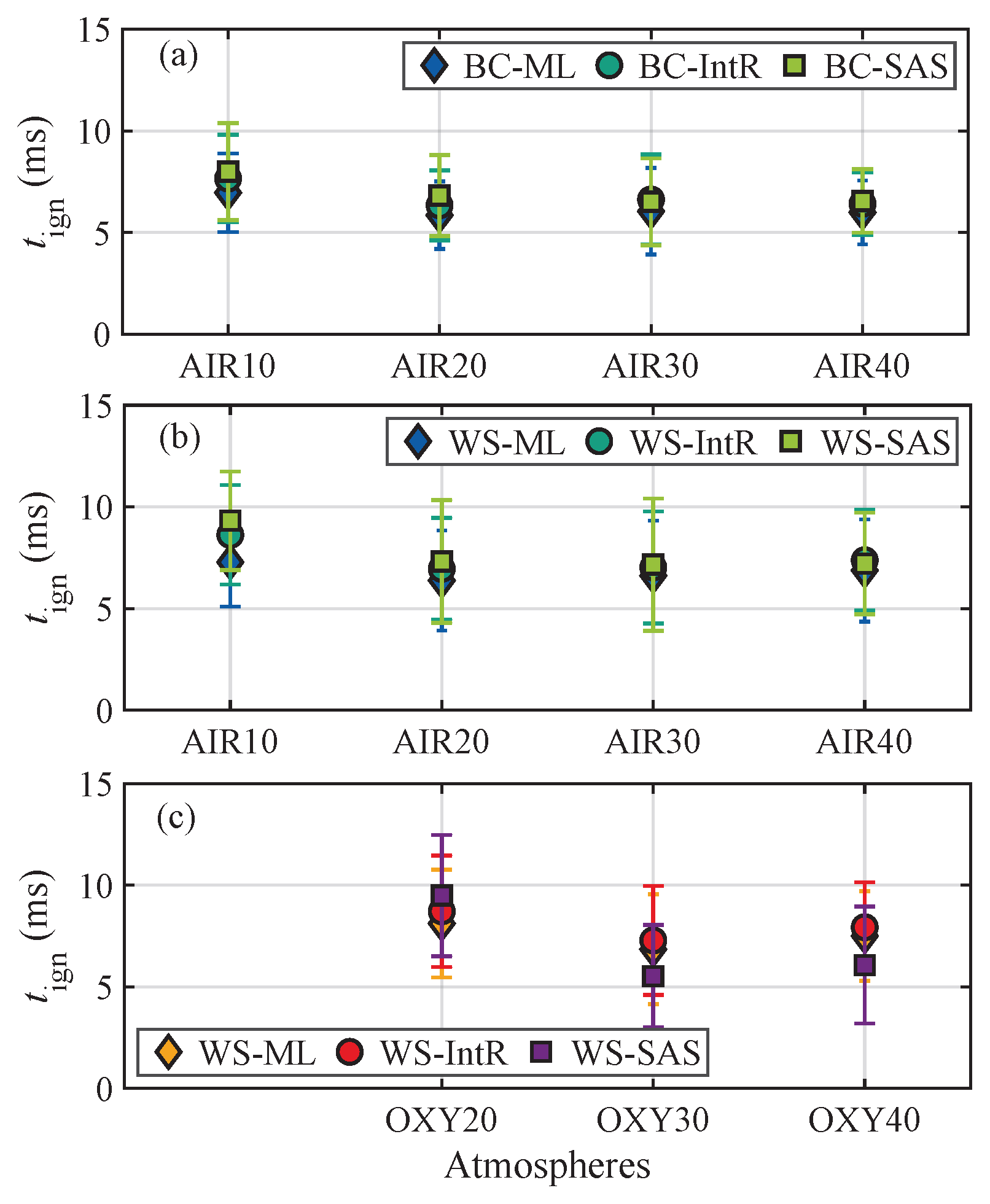
3.2. Homogeneous Ignition Delay Times
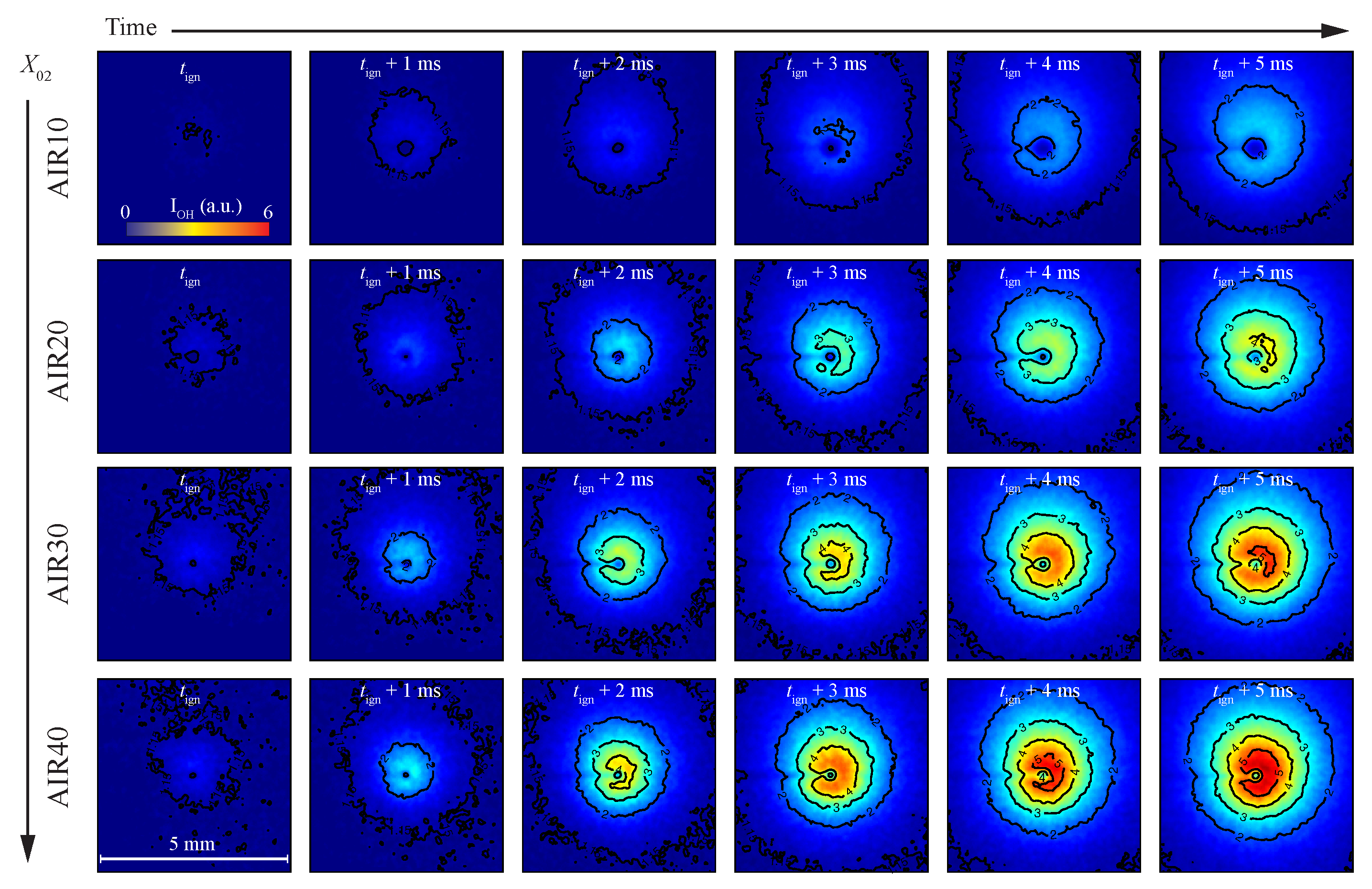
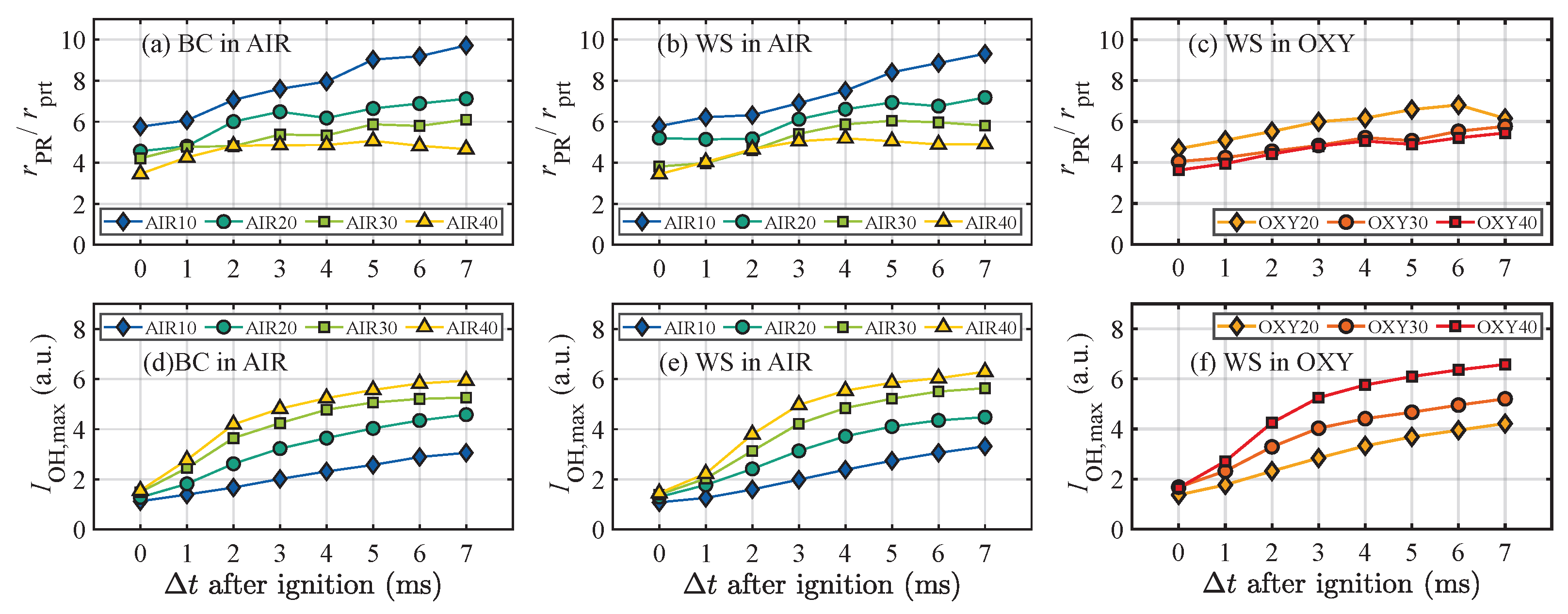
3.3. The Temporal and Spatial Evolution of the Volatile Flame Structure
3.4. The Stand-Off Distances of the Volatile Flames
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toftegaard, M.B.; Brix, J.; Jensen, P.A.; Glarborg, P.; Jensen, A.D. Oxy-fuel combustion of solid fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 581–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Pourkashanian, M.; Jones, J.M. Combustion of pulverised coal and biomass. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2001, 27, 587–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupa, M.; Karlström, O.; Vainio, E. Biomass combustion technology development—It is all about chemical details. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Q. Measurements and modelling of oxy-fuel coal combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 2643–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, C.; Debiagi, P.; Wen, X.; Hildebrandt, K.; Vascellari, M.; Faravelli, T. Advanced modeling approaches for CFD simulations of coal combustion and gasification. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 86, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Geschwindner, C.; Dreizler, A.; Böhm, B. Particle-resolved optical diagnostics of solid fuel combustion for clean power generation: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhre, B.; Elliott, L.K.; Sheng, C.D.; Gupta, R.P.; Wall, T.F. Oxy-fuel combustion technology for coal-fired power generation. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2005, 31, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, T.; Liu, Y.; Spero, C.; Elliott, L.; Khare, S.; Rathnam, R.; Zeenathal, F.; Moghtaderi, B.; Buhre, B.; Sheng, C.; et al. An overview on oxyfuel coal combustion—State of the art research and technology development. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffknecht, G.; Al-Makhadmeh, L.; Schnell, U.; Maier, J. Oxy-fuel coal combustion—A review of the current state-of-the-art. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2011, 5, S16–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yong, S.Z.; Ghoniem, A.F. Oxy-fuel combustion of pulverized coal: Characterization, fundamentals, stabilization and CFD modeling. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 156–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, D. Biomass cofiring: The technology, the experience, the combustion consequences. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 19, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Combustion characteristics of different biomass fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2004, 30, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Jones, J.M.; Ma, L.; Pourkashanian, M. Pollutants from the combustion of solid biomass fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köser, J.C. Untersuchung der frühen Abbrandphase von Feststoffpartikeln mit optischer Diagnostik. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoliMolina, A.; Shaddix, C.R. Ignition and devolatilization of pulverized bituminous coal particles during oxygen/carbon dioxide coal combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Q. Experimental and theoretical analyses on ignition and surface temperature of dispersed coal particles in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 ambients. Fuel 2017, 201, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddix, C.R.; Molina, A. Particle imaging of ignition and devolatilization of pulverized coal during oxy-fuel combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Duan, L.; Zeng, D.; Lu, D.Y.; Bu, C.; Zhao, C. Ignition and volatile combustion behaviors of a single lignite particle in a fluidized bed under O2/H2O condition. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 4451–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Farmand, P.; Geschwindner, C.; Greifenstein, M.; Köser, J.; Schumann, C.; Attili, A.; Pitsch, H.; Dreizler, A.; Böhm, B. Homogeneous ignition and volatile combustion of single solid fuel particles in air and oxy-fuel conditions. Fuel 2021, 291, 120101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liang, Z.; Dreizler, A.; Böhm, B. Accurate determination of homogeneous ignition of single solid fuel particles enabled by machine learning. Fuel 2023, 338, 127171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Huang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Lyu, J.; Li, S. Optical diagnostics on coal ignition and gas-phase combustion in co-firing ammonia with pulverized coal on a two-stage flat flame burner. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2023, 39, 3457–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, P.A.; Levendis, Y.A. Single-coal-particle combustion in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 environments. Combust. Flame 2008, 153, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, C.; Lee, H.; Choi, S.; Manovic, V. Combustion Behavior of Relatively Large Pulverized Biomass Particles at Rapid Heating Rates. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 10809–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Abdallah, M.; Dreizler, A.; Böhm, B.; Li, T. Simultaneous LII, PAH-LIF, OH-LIF, and Mie scattering measurements in solid fuel particle combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2024, 40, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, S. An observation of combustion behavior of a single coal particle entrained into hot gas flow. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wall, T. Ignition of coal particles: The influence of experimental technique. Fuel 1994, 73, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levendis, Y.A.; Joshi, K.; Khatami, R.; Sarofim, A.F. Combustion behavior in air of single particles from three different coal ranks and from sugarcane bagasse. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Stivers, C.; Joshi, K.; Levendis, Y.A.; Sarofim, A.F. Combustion behavior of single particles from three different coal ranks and from sugar cane bagasse in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 atmospheres). Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, C.; Lee, H.; Choi, S.; Manovic, V. Flame structures and ignition characteristics of torrefied and raw sewage sludge particles at rapid heating rates. Fuel 2017, 200, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, G.; Magalhães, D.; Rabaçal, M.; Costa, M. Effect of gas temperature and oxygen concentration on single particle ignition behavior of biomass fuels. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, A.; Vorobiev, N.; Schiemann, M.; Tarakcioglu, M.; Delichatsios, M.; Levendis, Y.A. Combustion details of raw and torrefied biomass fuel particles with individually-observed size, shape and mass. Combust. Flame 2019, 207, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Ye, B.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, D. Combustion Characteristics of Single Particles from Bituminous Coal and Pine Sawdust in O2/N2, O2/CO2, and O2/H2O Atmospheres. Energies 2017, 10, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaza, J.; Khatami, R.; Levendis, Y.A.; Álvarez, L.; Gil, M.V.; Pevida, C.; Rubiera, F.; Pis, J.J. Combustion of single biomass particles in air and in oxy-fuel conditions. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 64, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Farmand, P.; Chen, H.; Boehme, C.; Nicolai, H.; Hasse, C.; Pitsch, H.; Böhm, B. Homogeneous ignition and volatile flame structure of single bituminous coal and walnut shell particles: Effects of particle size and gas atmosphere. Fuel 2024, 371, 131955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farazi, S.; Hinrichs, J.; Davidovic, M.; Falkenstein, T.; Bode, M.; Kang, S.; Attili, A.; Pitsch, H. Numerical investigation of coal particle stream ignition in oxy-atmosphere. Fuel 2019, 241, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufano, G.L.; Stein, O.T.; Kronenburg, A.; Frassoldati, A.; Faravelli, T.; Deng, L.; Kempf, A.M.; Vascellari, M.; Hasse, C. Resolved flow simulation of pulverized coal particle devolatilization and ignition in air- and O2/CO2 -atmospheres. Fuel 2016, 186, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshayeshi, B.; Sutherland, J.C. A comparison of various models in predicting ignition delay in single-particle coal combustion. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, B.; Farmand, P.; Dreizler, A.; Pitsch, H.; Böhm, B. Motion and swelling of single coal particles during volatile combustion in a laminar flow reactor. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2023, 39, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Geschwindner, C.; Dreizler, A.; Böhm, B. An experimental study of coal particle group combustion in conventional and oxy-fuel atmospheres using multi-parameter optical diagnostics. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2023, 39, 3259–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Pareja, J.; Becker, L.; Heddrich, W.; Dreizler, A.; Böhm, B. Quasi-4D laser diagnostics using an acousto-optic deflector scanning system. Appl. Phys. B 2017, 123, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Schiemann, M.; Köser, J.; Dreizler, A.; Böhm, B. Experimental investigations of single particle and particle group combustion in a laminar flow reactor using simultaneous volumetric OH-LIF imaging and diffuse backlight-illumination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 136, 110377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaza, J.; Khatami, R.; Levendis, Y.A.; Álvarez, L.; Gil, M.V.; Pevida, C.; Rubiera, F.; Pis, J.J. Single particle ignition and combustion of anthracite, semi-anthracite and bituminous coals in air and simulated oxy-fuel conditions. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, M.; Scherer, V.; Wirtz, S. Optical Coal Particle Temperature Measurement under Oxy-Fuel Conditions: Measurement Methodology and Initial Results. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2009, 32, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, T.; Khatami, R.; Pierucci, S.; Faravelli, T.; Ranzi, E.; Levendis, Y.A. Experimental and modeling study of single coal particle combustion in O2/N2 and Oxy-fuel O2/CO2 atmospheres. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Levendis, Y.A.; Delichatsios, M.A. Soot loading, temperature and size of single coal particle envelope flames in conventional- and oxy-combustion conditions (O2/N2 and O2 /CO2). Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 2508–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Atmospheres | (K) | (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIR10 | 0.1 | 1874 | 1766 |
| AIR20 | 0.2 | 1839 | 1753 |
| AIR30 | 0.3 | 1829 | 1739 |
| AIR40 | 0.4 | 1829 | 1737 |
| OXY20 | 0.2 | 1835 | 1731 |
| OXY30 | 0.3 | 1831 | 1729 |
| OXY40 | 0.4 | 1825 | 1722 |
| Fuel | Hvb Coal | Walnut Shell | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate analysis (dry by weight) | C | 0.7860 | 0.5132 |
| H | 0.0530 | 0.0621 | |
| O | 0.1370 | 0.4236 | |
| N | 0.0140 | 0.0011 | |
| Proximate analysis (wet) | Fixed carbon | 0.5090 | 0.1693 |
| Volatiles | 0.3690 | 0.7293 | |
| Moisture | 0.0350 | 0.0948 | |
| Ash | 0.0870 | 0.0066 |
| Particles | (µm) | Conditions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hvb coal (BC) | 126 | 1.5 | AIR |
| Walnut shell (WS) | 126 | 1.5 | AIR, OXY |
| Diagnostics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| DBI | OH-LIF | Mie Scattering | |
| Parameters | and | , , and | |
| Light Source | LED (ILA LPS3) | Nd:YVO4 laser (Edgewave IS8II) + Dye laser (Sirah Credo) | Nd:YAG laser (Edgewave Innoslab) |
| Detection System | HSS6 (LaVision) | HS IRO + HSS6 (LaVision) | SA-X2 (Photron) |
| Frequency | 1 kHz | 10 kHz (real) 1 kHz (effective) | 10 kHz |
| HAB (mm) | 0–10 | 0–24 | 0–36 |
| Pixel Size (µm) | 9.2 | 32.4 | 36.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Chen, H.; Böhm, B. Experimental Assessment of the Effects of Gas Composition on Volatile Flames of Coal and Biomass Particles in Oxyfuel Combustion Using Multi-Parameter Optical Diagnostics. Processes 2025, 13, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061817
Li T, Chen H, Böhm B. Experimental Assessment of the Effects of Gas Composition on Volatile Flames of Coal and Biomass Particles in Oxyfuel Combustion Using Multi-Parameter Optical Diagnostics. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061817
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tao, Haowen Chen, and Benjamin Böhm. 2025. "Experimental Assessment of the Effects of Gas Composition on Volatile Flames of Coal and Biomass Particles in Oxyfuel Combustion Using Multi-Parameter Optical Diagnostics" Processes 13, no. 6: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061817
APA StyleLi, T., Chen, H., & Böhm, B. (2025). Experimental Assessment of the Effects of Gas Composition on Volatile Flames of Coal and Biomass Particles in Oxyfuel Combustion Using Multi-Parameter Optical Diagnostics. Processes, 13(6), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061817







