Examining the Key Denitrifying Bacterial Community Structure and Individual Proliferation of Activated Sludge in Wastewater Treatment Plants Operating at Low Temperatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Treatment Plant Description and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Technology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Operation Conditions of the Wastewater Treatment Plant
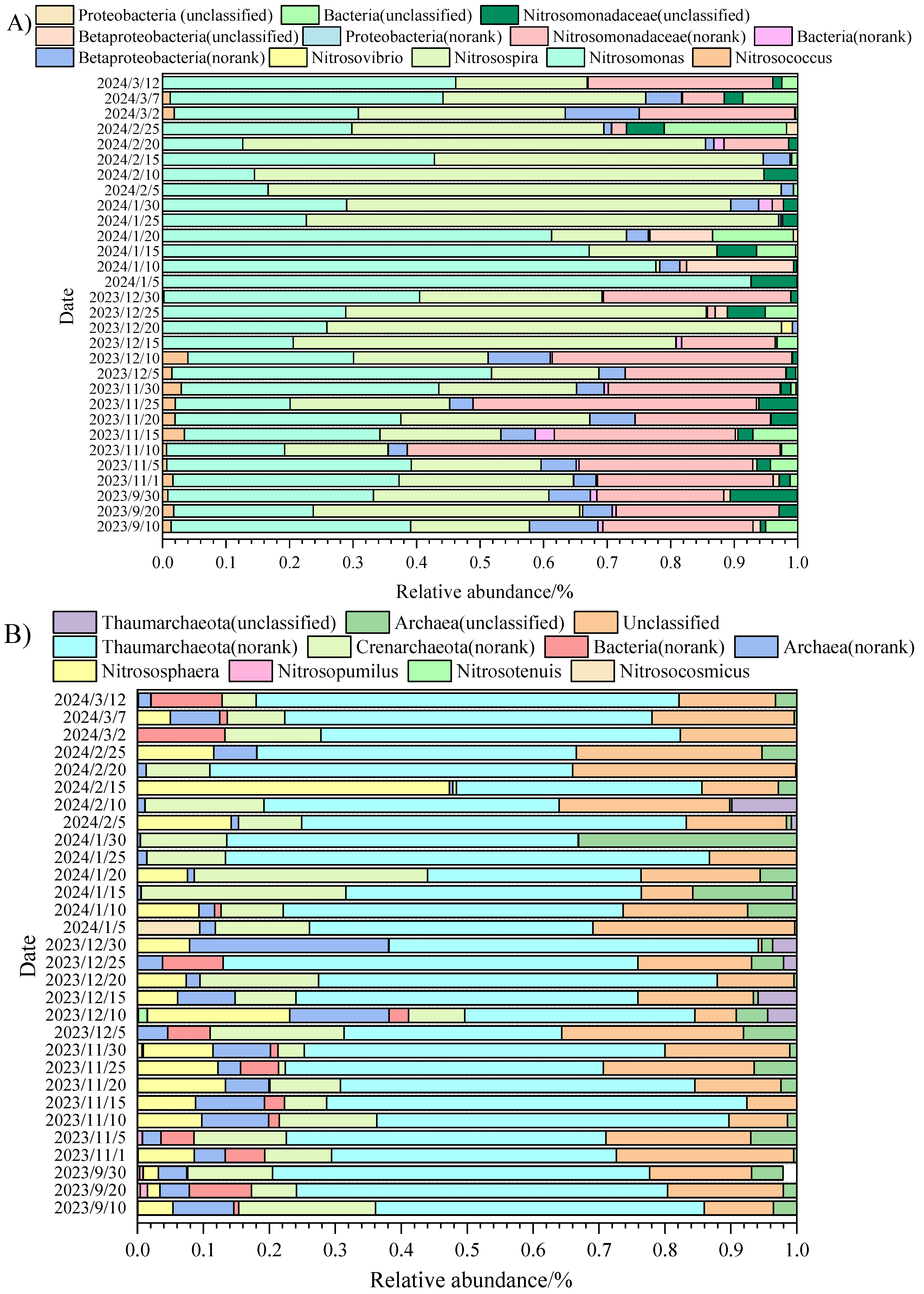
3.2. The Structure of AOA, AOB, and Denitrifying Bacteria During the Low Temperature Period
3.3. Effects of Influent Denitrification Microorganisms on the Structure of Key Denitrification Bacteria in Activated Sludge
- nAS—activated sludge AOB, AOA, denitrifying bacteria, absolute abundance of genes measured by real-time quantitative PCR;
- Ginw—absolute abundance of AOB, AOA, and denitrifying bacteria genes in the influent, ×106 copies/g SS;
- GAS—absolute abundance of AOB, AOA, and denitrifying bacteria genes in activated sludge, ×106 copies/g dry sludge;
- Px,AS—relative abundance of various denitrifying microorganisms in activated sludge (%);
- ninw—the amount of AOB, AOA, and denitrifying bacteria entering the system with wastewater every day, calculated based on the absolute abundance of genes determined by real-time quantitative PCR;
- Px,inw—relative abundance of various denitrifying microbial genera in the influent (%);
- new—AOB, AOA, and denitrifying bacteria in excess sludge, calculated based on the absolute abundance of genes determined by real-time quantitative PCR;
- Q—water inflow, m3/d;
- SS—SS concentration in the influent, mg/L;
- ΔX—residual sludge discharge, ×103 kg/d;
- X—mixed liquor suspended solids, mg/L;
- V—effective volume of an improved A2O process biochemical pool, 35,250 m3.
| Date (Influent) | Date (AS) | Q (m3/d) | SS (mg/L) | MLSS (mg/L) | Excess Sludge (×103 kg/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 November 2023 | 20 December 2023 | 144192 | 183 | 4699 | 23.22 |
| 30 November 2023 | 30 December 2023 | 145440 | 214 | 5535 | 23.53 |
| 10 December 2023 | 10 January 2024 | 144256 | 185 | 5092 | 22.26 |
| 20 December 2023 | 20 January 2024 | 143712 | 204 | 4448 | 22.20 |
| 30 December 2023 | 30 January 2024 | 143328 | 221 | 4578 | 22.42 |
| 10 January 2024 | 10 February 2024 | 144192 | 283 | 5055 | 21.81 |
| 20 January 2024 | 20 February 2024 | 156512 | 274 | 4654 | 21.26 |
| 30 January 2024 | 30 February 2024 | 156832 | 264 | 4832 | 22.49 |
3.3.1. Relative Abundance of Denitrifying Bacteria in Influent
3.3.2. Absolute Abundance of Key Functional Genes in the Denitrification Process
3.3.3. Net Proliferation Rate of Key Denitrifying Bacteria
- μ—specific proliferation rate of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (including archaea ammoxidation);
- μmax—maximum specific proliferation rate at 15 °C;
- Na—ammonia nitrogen concentration;
- Kn—semi-saturation rate constant;
- T—temperature.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saunders, A.; Albertsen, M.; Vollertsen, J.; Nielsen, P. The activated sludge ecosystem contains a core community of abundant organisms. ISME J. 2016, 10, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wen, D. Advances in Space–Temporal Distribution and Assembly Mechanisms of Microbial Community in Wastewater Treatment Systems. Environ. Eng. 2022, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fanaei, F.; Shahryari, T.; Mortazavis, M.; Nasseh, N.; Pourakbar, M.; Barikbin, B. Hazard identification and integrated risk assessment of drinkingwater supply system from catchment to consumer based on the World Health Organization’s Water Safety Plan. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 286, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Zhou, J.; Qu, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L. Biodecolorization of Azo Dye Acid Red B under High Salinity Condition. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, S. Machine–learning insights into nitrate–reducing communities in a full–scale municipal wastewater treatment plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz–Haddad, L.; Shaw, D.; Ali, M.; Pronk, M.; Loosdrecht, M.; Saikaly, P. Characterization of the core microbial community across different aggregate sizes in full–scale aerobic granular sludge plants and their relevance to wastewater treatment performance. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Xie, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y. Effect of Temperature on Pollutant Removal and Nitrous Oxide Emission of Wastewater Nitrogen Removal System. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Huo, M.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L. Effect ofs carbon sources on sludge settling and filamentous bacteria growth. CIESC J. 2011, 62, 3471–3477. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, W.S.; Huang, L.N. Microbial diversity in extreme environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Huang, P.; Ma, C.; Peng, X.; Fu, M.; Ren, T.; Kan, J. Treatment of cold pressed Zanthoxylum schinifolium oil wastewater: Process, sludge characteristics, and microbial diversity analysis using biochemical methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, G.; Yu, D.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Miao, Y. Effects of Low Temperature on Mainstream SNAD Process and Restoration of Nitrogen Removal Performance. Technol. Water Treat. 2024, 50, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, G.; Zhi, J. A novel simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox, denitrification and fermentation process: Enhancing nitrogen removal and sludge reduction in a single reactor. Bioresource Technol. 2023, 369, 128484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, J.; Peng, Y. An effective strategy for in situ start–up of mainstream anammox process treating domestic sewage. Bioresource Technol. 2021, 339, 125525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Peng, Y. Enhancing sewage nitrogen removal via anammox and endogenous denitrification: Significance of anaerobic/oxic/anoxic operation mode. Bioresource Technol. 2019, 289, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, J. The nitrification recovery capacity is the key to enhancing nitrogen removal in the AOA system at low temperatures. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, J. Effect of low temperature shock on nitrogen removal performance of Anammox in CRl systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Bi, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Pan, K.; Fan, X.; Zhou, X. Nitrogen Removal Performance of a Pilot–scale Pure Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor System at Low Temperature. China Water Supply Drain. 2023, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, J.; Zhu, T.; Xiao, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. A novel sulfur–based fiber carrier fixed–bed reactor for nitrate–contaminated wastewater treatment: Performance, operational characteristics and cold–tolerant mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeynali, R.; Asadi, M.; Ankley, P.; Esser, M.; Brinkmann, M.; Soltan, J.; McPhedran, K. Sustainable enhancement of biogas production from a cold–region municipal wastewater anaerobic digestion process using optimized sludge–derived and commercial biochar additives. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Fang, Z.; Yang, W.; Song, X. Application of cold–adapted microbial agents in soil contaminate remediation: Biodegradation mechanisms, case studies, and safety assessments. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 12720–12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Xie, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, D. Iron–based multi–carbon composite and Pseudomonas furukawaii ZS1 co–affect nitrogen removal, microbial community dynamics and metabolism pathways in low–temperature aquaculture wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Ding, X.; Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Lv, H.; Zhao, M.; Yu, R. Nitrogen removal by a novel heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacterium Acinetobacter calcoaceticus TY1 under low temperatures. Bioresource Technol. 2022, 353, 127148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB18918–2002; Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Guo, Y.; Qi, R.; Xiao, S.; Dou, D.; Su, G.; Gao, J. Microbial Community Structure Analysis of Activated Sludge in Chinese Biological Sewage Wastewater Treatment Process. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 934–943. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Liu, W.; Nie, Z.; Li, Q.; Liang, X.; Zhao, W.; Qu, H.; Bian, D. Seasonal effects on pilot–scale high–concentration activated sludge systems in cold regions. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 52, 103575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, Q. Potential application of bioelectrochemical systems in cold environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qin, Z.; Liang, M. Meta–analysis of Microbial Communities in the Activated Sludge of Wastewater Treatment Plants Under Different Climate Types. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4844–4852. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, P.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Jin, D. Microbial community diversity and its response to environmental factors during sewage treatment. Microbiol. China 2020, 47, 3004–3020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, B.; Ning, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, T.; Wu, L.; Li, T.; Liu, W.; Zhou, J.; Wen, X. Seasonal dynamics of the microbial community in two full–scale wastewater treatment plants: Diversity, composition, phylogenetic group based assembly and co–occurrence pattern. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, P.; Zheng, Z. Enhanced nitrogen removal from low–temperature wastewater by an iterative screening of cold–tolerant denitrifying bacteria. Bioproc. Bloyst. Eng. 2021, 45, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Microorganisms | Key Genes | Primer Name and Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplification Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria | amoA gene | amoA–1F(GGGGTTTCTACTGGTGGT) amoA–2R(CCCCTCKGSAAAGCCTTCTTC) | 95 °C 5 min; (94 °C 45 s, 55 °C 30 s, 72 °C 1 min) × 35; 72 °C 5 min |
| Ammonia-oxidizing archaea | amoA gene | archea–amoAF (STAATGGTCTGGCTTAGACG) archea–amoAR (GCGGCCATCCATCTGTATGT) | 95 °C 5 min; (94 °C 45 s, 53 °C 60 s, 72 °C 1 min) × 35, 72 °C 5 min |
| Denitrifying bacteria | nirK gene | nirK1aCuF(ATCATGGTSCTGCCGCG) nirKR3CuR(GCCTCGATCAGRTTGTGGTT) | 95 °C 5 min; (95 °C 30 s, 53 °C 30 s, 72 °C 45 s) × 35; 72 °C 10 min |
| Microorganisms | Key Genes | Primer Name and Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplification Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria | amoA gene | bamoA1F(GGGGTTTCTACTGGTGGT) bamoA2R(CCCCTCKGSAAAGCCTTCTTC) | 95 °C 5 min; (94 °C 30 s, 55 °C 30 s, 72 °C 1 min) × 35 |
| Ammonia-oxidizing archaea | amoA gene | archea–amoAF (STAATGGTCTGGCTTAGACG) archea–amoAR (GCGGCCATCCATCTGTATGT) | 95 °C 5 min; (94 °C 45 s, 53 °C 60 s, 72 °C 1 min) × 35 |
| Denitrifying bacteria | nirK gene | nirK1aCuF(ATCATGGTSCTGCCGCG) nirKR3CuR(GCCTCGATCAGRTTGTGGTT) | 95 °C 5 min; (95 °C 30 s, 55 °C 30 s, 72 °C 30 s) × 35 |
| AOB | 2023/12/20 | 2023/12/30 | 2024/1/10 | 2024/1/20 | 2024/1/30 | 2024/2/10 | 2025/2/20 | 2025/3/2 | N/Nr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrosococcus | −1.039 | 0.114 | 1/8 | ||||||
| Nitrosomonas | 0.005 | −0.010 | 0.093 | 0.111 | −0.002 | −0.306 | −0.297 | −0.016 | 3/8 |
| Nitrosospira | 0.100 | 0.014 | −1.638 | −0.092 | 0.064 | 0.078 | 0.088 | −0.115 | 5/8 |
| Nitrosovibrio | 0.137 | 1/8 | |||||||
| Betaproteobacteria (norank) | −0.447 | −3.113 | 0.021 | 0.140 | −0.065 | −0.476 | 0.113 | 3/8 | |
| Bacteria (norank) | 0.140 | 0.142 | 0.108 | 3/8 | |||||
| Nitrosomonadaceae (norank) | 0.056 | −3.056 | 0.142 | 0.108 | 0.086 | 4/8 | |||
| Proteobacteria (norank) | 0/8 | ||||||||
| Betaproteobacteria (unclassified) | 0.138 | 0.126 | 0.140 | 0.142 | 4/8 | ||||
| Nitrosomonadaceae (unclassified) | 0.031 | −0.403 | −0.020 | 0.102 | −0.093 | −5.480 | 2/8 | ||
| Bacteria (unclassified) | −30.113 | 0.074 | 0.140 | −2.550 | 2/8 | ||||
| Proteobacteria (unclassified) | 0.140 | 1/8 |
| AOA | 2023/12/20 | 2023/12/30 | 2024/1/10 | 2024/1/20 | 2024/1/30 | 2024/2/10 | 2025/2/20 | 2025/3/2 | N/Nr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrosocosmicus | −0.640 | 0/8 | |||||||
| Nitrosotenuis | 0/8 | ||||||||
| Nitrosopumilus | 0/8 | ||||||||
| Nitrososphaera | 0.045 | 0.138 | 0.045 | 0.140 | 4/8 | ||||
| Archaea (norank) | −0.021 | −0.014 | 0.052 | −0.073 | −0.479 | −0.099 | −1.526 | 1/8 | |
| Bacteria (norank) | 0.073 | −68.307 | −0.166 | −157.136 | 0.085 | 2/8 | |||
| Crenarchaeota (norank) | 0.046 | −46.746 | −0.032 | 0.104 | 0.043 | −0.004 | 0.011 | −0.090 | 4/8 |
| Thaumarchaeota (norank) | −0.061 | −0.137 | 0.079 | −0.079 | −0.040 | −0.171 | −0.047 | 0.022 | 2/8 |
| Unclassified | 0.038 | −12.367 | 0.087 | 0.099 | −25.690 | 0.032 | 0.106 | 0.114 | 6/8 |
| Archaea (unclassified) | −1.088 | 0.077 | 0.074 | 0.096 | 0.141 | −0.068 | −1.983 | −18.470 | 4/8 |
| Thaumarchaeota (unclassified) | 0.126 | 1/8 |
| Denitriing Bacteria | 2023/12/20 | 2023/12/30 | 2024/1/10 | 2024/1/20 | 2024/1/30 | 2024/2/10 | 2025/2/20 | 2025/3/2 | N/Nr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Achromobacter | 0.098 | 0.140 | 0.111 | 0.114 | 4/8 | ||||
| Bosea | 0.014 | −0.029 | 0.047 | −0.188 | 0.033 | −0.341 | −0.117 | 0.016 | 4/8 |
| Bradyrhizobium | 0.136 | 0.138 | 0.131 | 0.025 | 0.106 | −0.005 | −0.061 | 0.013 | 6/8 |
| Luteovulum | 0.108 | 1/8 | |||||||
| Mesorhizobium | 0.137 | 0.030 | 0.101 | −0.273 | 0.100 | 0.111 | −0.477 | 5/8 | |
| Nitrosospira | 0/8 | ||||||||
| Ochrobactrum | −0.114 | −0.214 | −0.066 | −0.043 | −0.153 | −0.085 | 0.060 | 1/8 | |
| Paracoccus | −0.428 | −1.422 | −1.681 | −0.035 | −0.010 | −0.291 | −0.081 | −0.001 | 0/8 |
| Pseudomonas | 0/8 | ||||||||
| Rhizobium | −0.030 | −0.077 | −0.007 | −0.136 | 0.070 | −0.200 | −0.255 | −0.241 | 1/8 |
| Sinorhizobium | 0.132 | 0.138 | 0.131 | −0.347 | 0.024 | −0.131 | −0.209 | −0.190 | 4/8 |
| Bacteria (norank) | 0.070 | 0.040 | 0.081 | 0.092 | 0.070 | −0.148 | −0.153 | 0.098 | 6/8 |
| Alphaproteobacteria (unclassified) | 0.052 | 0.035 | −0.087 | 0.019 | −0.064 | −0.168 | 0.039 | 4/8 | |
| Unclassified | 0.120 | −0.040 | 0.111 | 2/8 | |||||
| Bradyrhizobiaceae (unclassified) | 0.137 | 0.138 | 0.131 | −0.016 | 0.103 | −0.018 | −0.032 | 4/8 | |
| Rhizobiaceae (unclassified) | 0.000 | −0.080 | 0.034 | −0.229 | 0.017 | −0.143 | −0.288 | −0.217 | 2/8 |
| Rhodobacteraceae (unclassified) | 0.083 | −0.024 | −0.029 | 0.037 | 0.111 | 0.033 | −0.055 | 4/8 | |
| Bacteria (unclassified) | 0.040 | 0.009 | 0.054 | 0.051 | −0.026 | 0.027 | −0.338 | 0.059 | 6/8 |
| Rhizobiales (unclassified) | −0.020 | −0.086 | −0.020 | −0.293 | −0.004 | −0.286 | −0.238 | −0.047 | 0/8 |
| Proteobacteria (unclassified) | −0.103 | −0.125 | −0.471 | −0.004 | 0.090 | −0.036 | −0.339 | 0.052 | 2/8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Jia, B.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Examining the Key Denitrifying Bacterial Community Structure and Individual Proliferation of Activated Sludge in Wastewater Treatment Plants Operating at Low Temperatures. Processes 2025, 13, 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061814
Zhang X, Jia B, Lu H, Wang X, Li S. Examining the Key Denitrifying Bacterial Community Structure and Individual Proliferation of Activated Sludge in Wastewater Treatment Plants Operating at Low Temperatures. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061814
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoyu, Bowen Jia, Hai Lu, Xiaoling Wang, and Shengnan Li. 2025. "Examining the Key Denitrifying Bacterial Community Structure and Individual Proliferation of Activated Sludge in Wastewater Treatment Plants Operating at Low Temperatures" Processes 13, no. 6: 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061814
APA StyleZhang, X., Jia, B., Lu, H., Wang, X., & Li, S. (2025). Examining the Key Denitrifying Bacterial Community Structure and Individual Proliferation of Activated Sludge in Wastewater Treatment Plants Operating at Low Temperatures. Processes, 13(6), 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061814







