Efficient Ionic Liquid-Based Leaching and Extraction of Metals from NMC Cathodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
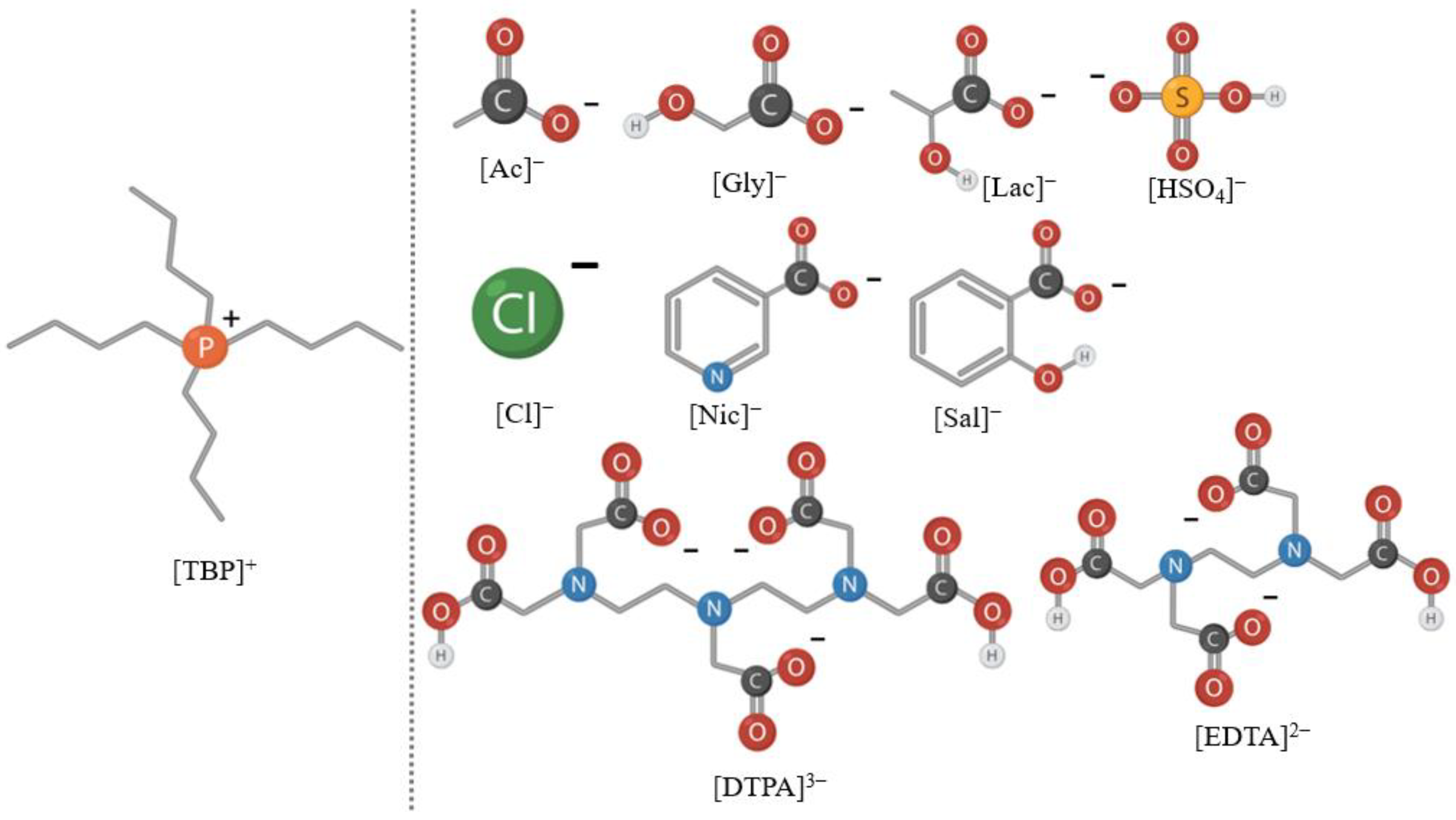
2.2. Synthesis of Tetrabutylphosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids
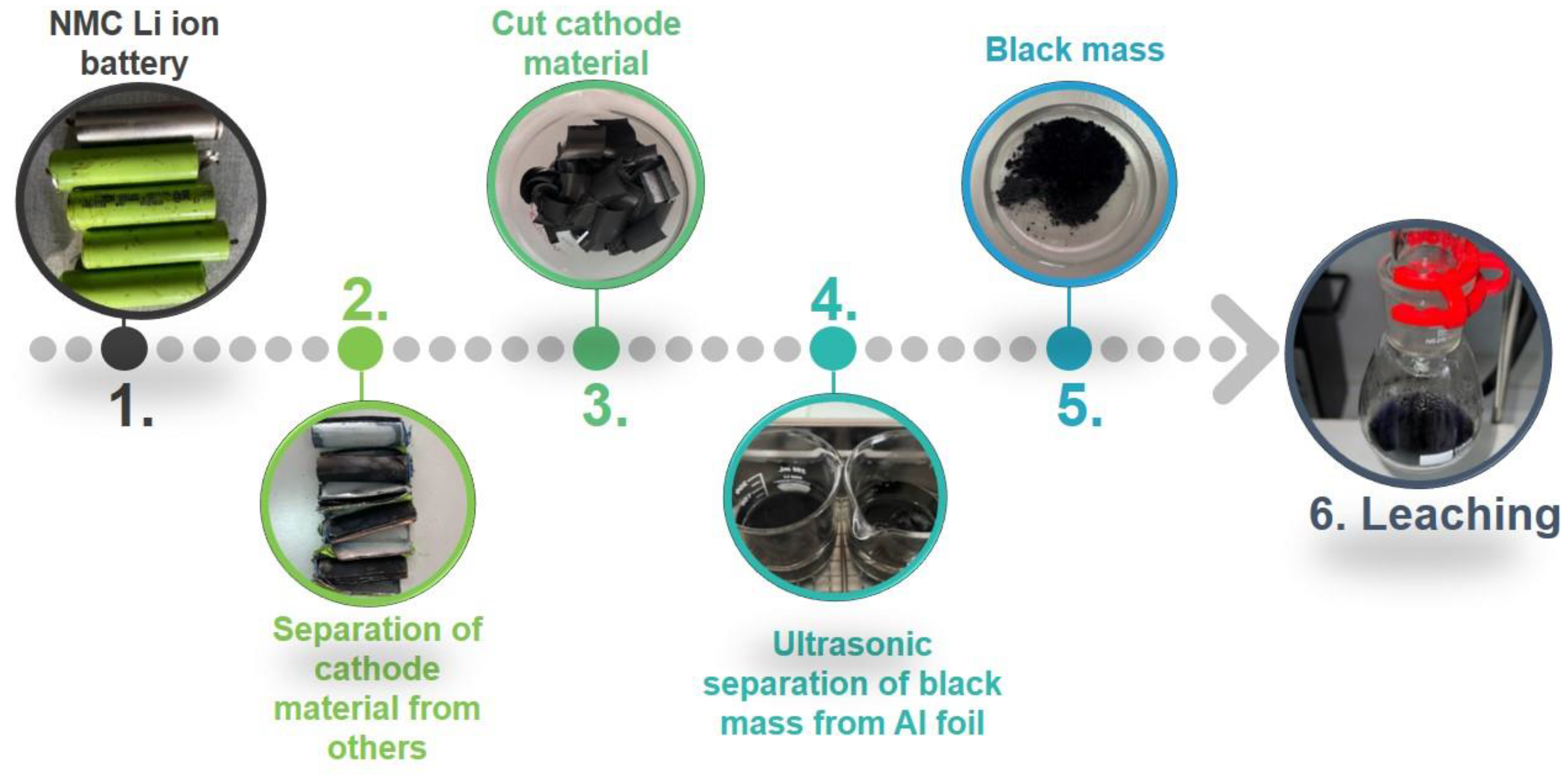
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Leaching Procedures
2.5. Extraction of Metals Using an IL-Based Aqueous Biphasic System
3. Results and Discussion
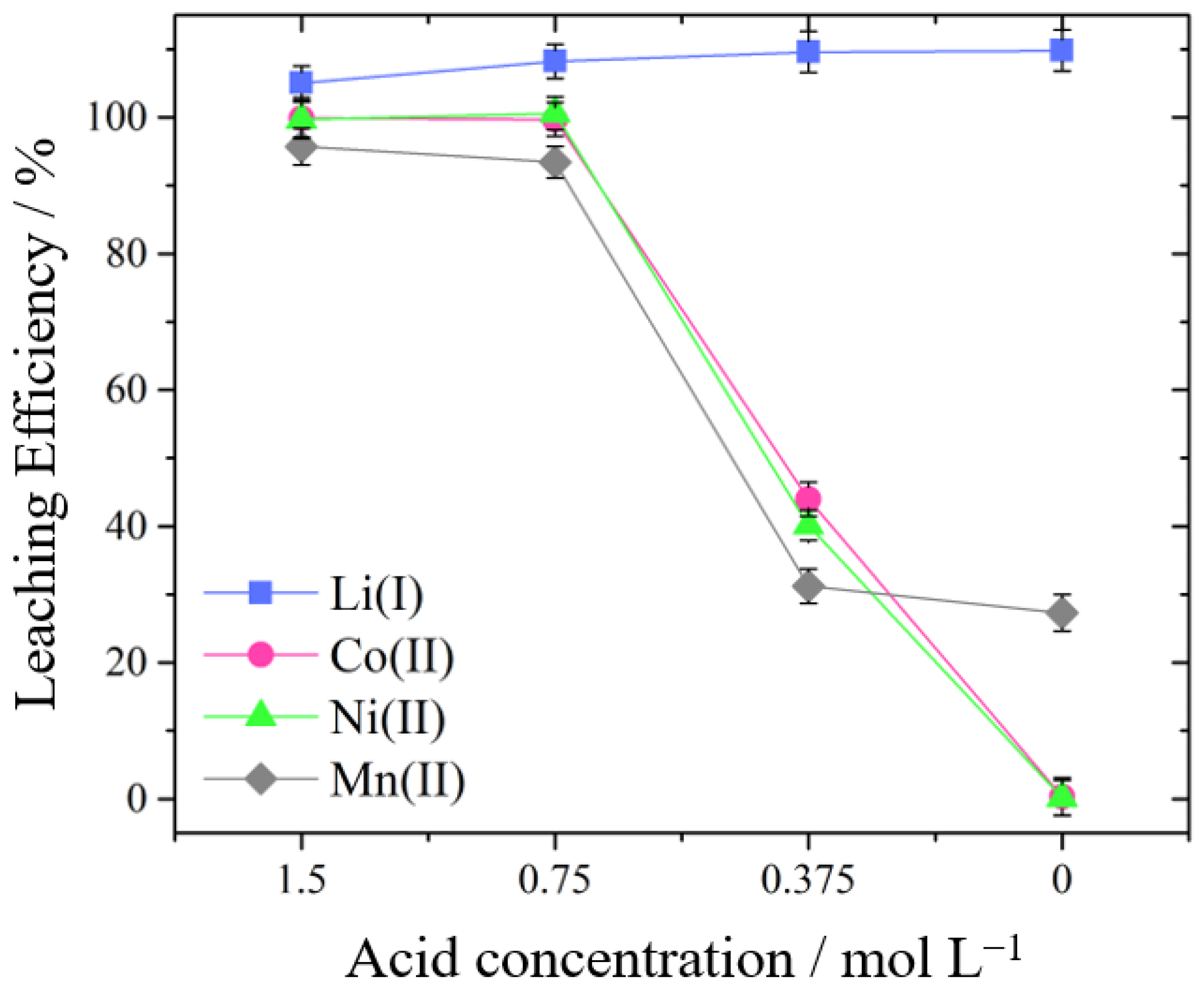
3.1. Leaching of Metals from NMC Cathode Material Using Mineral Acids
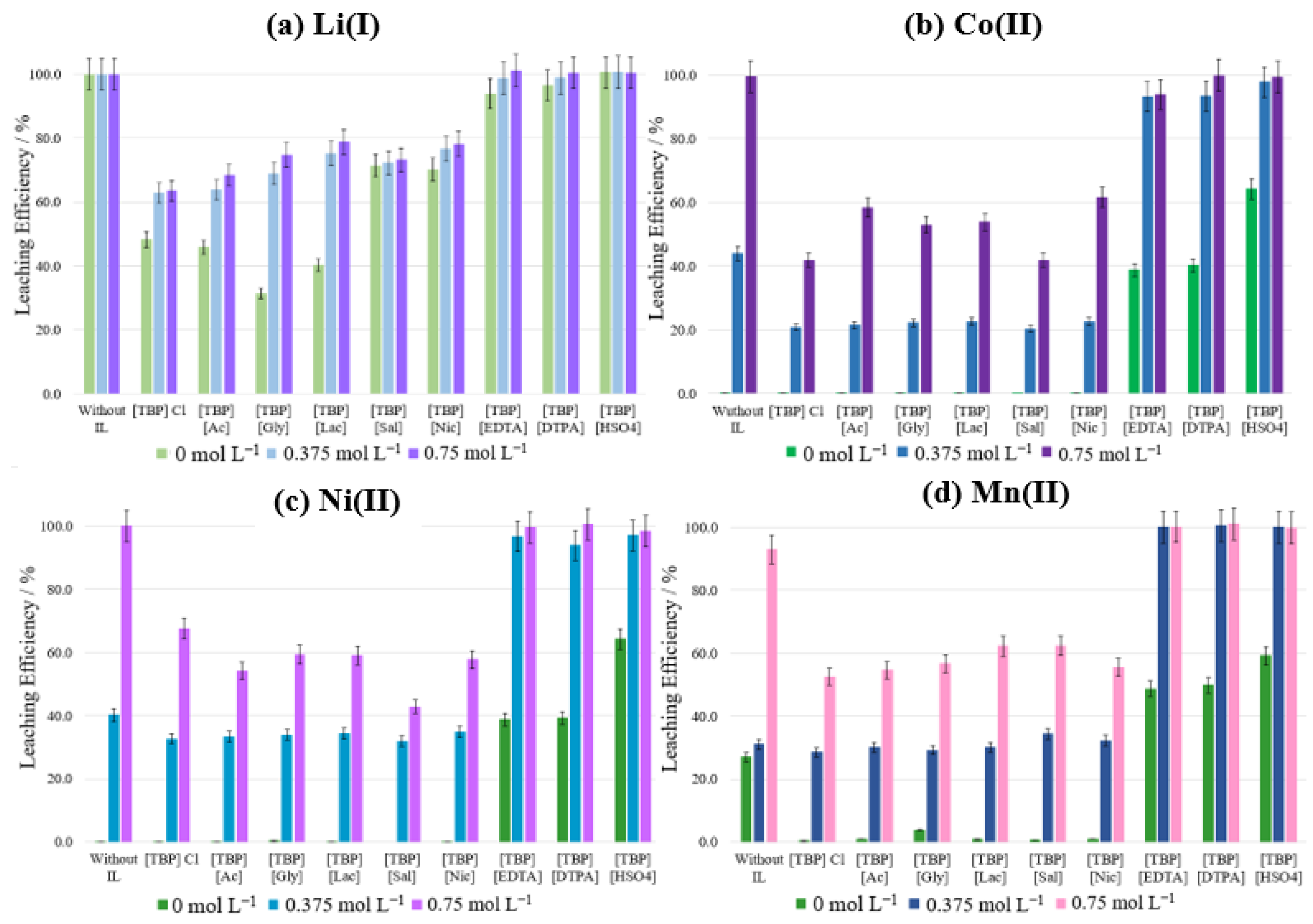
3.2. Leaching Studies of Metals from NMC Cathode Material Using Ionic Liquids
3.3. Optimization Study of Metal Leaching
3.3.1. Effect of Ionic Liquid Concentration
3.3.2. Effect of Temperature and Time
3.3.3. Effect of Solid-to-Liquid (S/L) Ratio
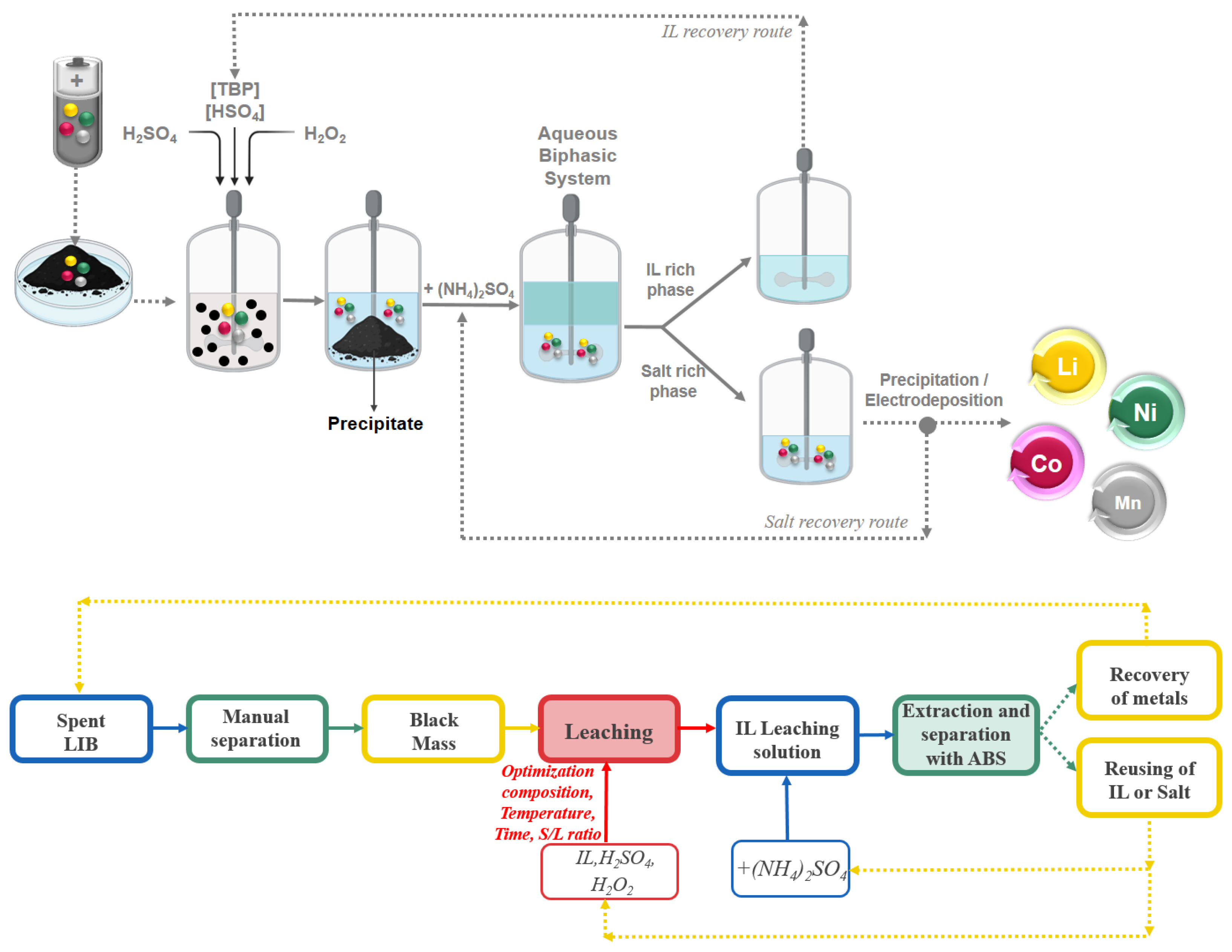
3.4. Proposed Ionic Liquid-Based Leaching and Extraction Process for NMC Cathode Material
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Singh, N. Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 1129–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Jha, R.; Meshram, A.; Singh, K.K. A Review on Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries to Recover Critical Metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. A Critical Review and Analysis on the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, W.; Chandra Mouli, G.R.; Bauer, P. A Comprehensive Review on the Characteristics and Modeling of Lithium-Ion Battery Aging. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 2205–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, F. Sustainable Recycling Technology for Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond: Challenges and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7020–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, E.; Sa, Q.; Apelian, D.; Wang, Y. A Closed Loop Process for Recycling Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, G.; Nlebedim, I.C.; Prodius, D. Application of Ionic Liquids for the Recycling and Recovery of Technologically Critical and Valuable Metals. Energies 2022, 15, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Jaiswal, R.V.; Abhilash; Baiju, C.; Gardas, R.L. An Emerging Trend of Ionic Liquids in the Separation of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium and Nickel Based Batteries. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 400, 124594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, A.M.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Tenório, J.A.S. Recycling of Batteries: A Review of Current Processes and Technologies. J. Power Sources 2004, 130, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Kim, N.H.; Sohn, J.S.; Yang, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Development of a Metal Recovery Process from Li-Ion Battery Wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 79, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, J.F.; Busnardo, N.G.; Afonso, J.C. Recovery of Valuable Elements from Spent Li-Batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lecce, D.; Verrelli, R.; Hassoun, J. Lithium-Ion Batteries for Sustainable Energy Storage: Recent Advances towards New Cell Configurations. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3442–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.P.; Prabaharan, G.; Kumar, L. Leaching and Separation of Co and Mn from Electrode Materials of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Hydrochloric Acid: Laboratory and Pilot Scale Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulié, M.; Laucournet, R.; Billy, E. Hydrometallurgical Process for the Recovery of High Value Metals from Spent Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide Based Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacova, Z.; Havlik, T.; Kukurugya, F.; Orac, D. Cobalt and Lithium Recovery from Active Mass of Spent Li-Ion Batteries: Theoretical and Experimental Approach. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Su, R.; Gao, G.; Song, H.; Yuan, H.; Liang, B.; Guo, Z. Mechanochemical Process Enhanced Cobalt and Lithium Recycling from Wasted Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Yoo, B.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Son, S. Study on Roasting for Selective Lithium Leaching of Cathode Active Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Metals 2021, 11, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tan, Q.; Li, J. Exploring a Green Route for Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Revealing and Solving Deep Screening Problem. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R. Extraction of Lithium from Primary and Secondary Sources by Pre-Treatment, Leaching and Separation: A Comprehensive Review. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musariri, B.; Akdogan, G.; Dorfling, C.; Bradshaw, S. Evaluating Organic Acids as Alternative Leaching Reagents for Metal Recovery from Lithium Ion Batteries. Miner. Eng. 2019, 137, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dunn, J.B.; Zhang, X.X.; Gaines, L.; Chen, R.J.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Recovery of Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries with Organic Acids as Leaching Reagents and Environmental Assessment. J. Power Sources 2013, 233, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. The Twelve Principles of Circular Hydrometallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrueto, Y.; Hernández, P.; Jiménez, Y.; Morales, J. Leaching of Metals from Printed Circuit Boards Using Ionic Liquids. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-J.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.-T.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.-X.; Yang, B. Copper Leaching from Waste Printed Circuit Boards Using Typical Acidic Ionic Liquids Recovery of E-Wastes’ Surplus Value. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Sun, Q. Leaching Behavior of Copper from Waste Printed Circuit Boards with Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, H. Lead during the Leaching Process of Copper from Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Five Typical Ionic Liquid Acids. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Huang, J.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Zhu, N.; Wang, Y. min Comparative Study on Copper Leaching from Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Typical Ionic Liquid Acids. Waste Manag. 2015, 41, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, M.; Dong, Q.; Zou, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, S.; Yan, F. Green and Sustainable Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries via an Ionic Liquid-Driven Cathode Reduction Method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 4238–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrueto, Y.; Hernández, P.; Jiménez, Y.P.; Morales, J. Properties and Application of Ionic Liquids in Leaching Base/Precious Metals from e-Waste. A Review. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 212, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada-Maldonado, E.; Olea, F.; Sepúlveda, R.; Castillo, J.; Cabezas, R.; Merlet, G.; Romero, J. Possibilities and Challenges for Ionic Liquids in Hydrometallurgy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Ionic Liquids: A Brief History. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Savoy, A.W. Ionic Liquids Synthesis and Applications: An Overview. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.N.; Boxall, J.A.; Lichtenthaler, R. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids and Their Mixtures—A Review. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2004, 219, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Passos, H.; Billard, I.; Papaiconomou, N.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Recovery of Metals from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Using Unconventional Solvents Based on Ionic Liquids. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 859–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R. Ionic Liquids-Mediated Recovery of Metals from Spent Batteries. J. Ion. Liq. 2023, 3, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušović, J.; Tekić, D.; Marić, S.; Jocić, A.; Stanković, D.; Dimitrijević, A. Sustainable Recovery of Cobalt and Lithium from Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Material by Combining Sulfate Leachates and Aqueous Biphasic Systems Based on Tetrabutylphosphonium-Ionic Liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 348, 127707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušović, J.; Vraneš, M.; Papović, S.; Gadžurić, S.; Ražić, S.; Trtić-Petrović, T. Greener Sample Preparation Method for Direct Determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) in River Sediment Based on an Aqueous Biphasic System with Functionalized Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 369, 120974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, E.A.; Ijardar, S.P. Insights into the Separation of Metals, Dyes and Pesticides Using Ionic Liquid Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulego, P.; Blanco, D.; Ramos, D.; Viesca, J.L.; Díaz, M.; Hernández Battez, A. Environmental Properties of Phosphonium, Imidazolium and Ammonium Cation-Based Ionic Liquids as Potential Lubricant Additives. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, F.; Zeng, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Tan, Z. Assessment of the Toxicity and Biodegradation of Amino Acid-Based Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10100–10108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, J.; Abd Ghani, N.; Yunus, M.N.B.; Bt Hasanudin, N. Evaluating Acute Toxicity of Amino Acid Ionic Liquids towards Poecilia Reticulata Fish for Designing Sustainable Chemical Processes. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 12, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, C.; Trapp, S.; Polesel, F.; Kuehr, S.; Schlechtriem, C. Biomagnification of Ionizable Organic Compounds in Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus Mykiss. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morina, R.; Merli, D.; Mustarelli, P.; Ferrara, C. Lithium and Cobalt Recovery from Lithium-Ion Battery Waste via Functional Ionic Liquid Extraction for Effective Battery Recycling. ChemElectroChem 2023, 10, e202201059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea, F.; Allendes, C.; del Valle, T.; Jofré-Ulloa, P.P.; Tapia, R.; Isaacs, M.; Diaz, G.; Pizarro, J.; Quijada-Maldonado, E. Impact of Hydrophobic Ionic Liquid Mixtures on Cobalt (II) Extraction from Sulfate Media at Low PH: Stoichiometry and Operating Variables Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 8880–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Huang, J.; Dong, T.; Sha, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S. A Novel Strategy of Lithium Recycling from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Imidazolium Ionic Liquid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 41, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Li, J. Separation of Metals from Acetic Acid Leaching Solution of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Ionic Liquid System. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 145006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, C.; Fu, M.L. Separation of Cobalt and Lithium from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Leach Liquors by Ionic Liquid Extraction Using Cyphos IL-101. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, S.; Gupta, B. Partition Studies on Cobalt and Recycling of Valuable Metals from Waste Li-Ion Batteries via Solvent Extraction and Chemical Precipitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Ranjan Srivastava, R.; Singh, V.K.; Chi, R.; Kim, H. Recovery of Critical Metals from Spent Li-Ion Batteries: Sequential Leaching, Precipitation, and Cobalt–Nickel Separation Using Cyphos IL104. Waste Manag. 2022, 154, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Srivastava, R.R.; Kim, H. Cradle-to-Cradle Recycling of Spent NMC Batteries with Emphasis on Novel Co2+/Ni2+ Separation from HCl Leached Solution and Synthesis of New Ternary Precursor. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Devi, N. Separation of Critical Metals Using Trihexyl(Tetradecyl) Phosphonium Thiocyanate from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2023, 77, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, D.; Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Metz, S.J.; Binnemans, K.; Kroon, M.C. Selective Extraction of Metals from Chloride Solutions with the Tetraoctylphosphonium Oleate Ionic Liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 5149–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Benstead, M.; Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K. Recycling of Metals from LiFePO4 Battery Cathode Material by Using Ionic Liquid Based-Aqueous Biphasic Systems. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 9262–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, N.J.; Gutowski, K.E.; Rogers, R.D. Investigation of Aqueous Biphasic Systems Formed from Solutions of Chaotropic Salts with Kosmotropic Salts (Salt–Salt ABS). Green Chem. 2007, 9, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aqueous Biphasic Systems: A Boost Brought about by Using Ionic Liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4966–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, J.; Tsunashima, K.; Ue, M.; Iwasaki, K.; Tsuda, T.; Kuwabata, S.; Kanematsu, H.; Hirai, N.; Kogo, T.; Ogawa, A. Physical and Electrochemical Properties of Ionic Liquids Based on Quaternary Phosphonium Cations and Carboxylate Anions as Electrolytes. ECS Trans. 2017, 75, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojanen, S.; Lundström, M.; Santasalo-Aarnio, A.; Serna-Guerrero, R. Challenging the Concept of Electrochemical Discharge Using Salt Solutions for Lithium-Ion Batteries Recycling. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Aldous, I.; Hartley, J.M.; Thompson, D.L.; Scott, S.; Hanson, R.; Anderson, P.A.; Kendrick, E.; Sommerville, R.; Ryder, K.S.; et al. Lithium Ion Battery Recycling Using High-Intensity Ultrasonication. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4710–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, K.E.; Broker, G.A.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the Aqueous Miscibility of Ionic Liquids: Aqueous Biphasic Systems of Water-Miscible Ionic Liquids and Water-Structuring Salts For Recycle, Metathesis, and Separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6632–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchuk, J.C.; Andrews, B.A.; Arsenjo, J.A. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems for Protein Separation. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 711, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocky, M.M.H.; Rahman, I.M.M.; Endo, M.; Hasegawa, H. Comprehensive Insights into Aqua Regia-Based Hybrid Methods for Efficient Recovery of Precious Metals from Secondary Raw Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.P.; Sun, S.Y.; Song, X.F.; Yu, J.G. Leaching Process for Recovering Valuable Metals from the LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Cathode of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Xie, Y.; Ning, P.; An, H.; You, H.; Nawaz, F. A Closed-Loop Process for Recycling LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 from the Cathode Scraps of Lithium-Ion Batteries: Process Optimization and Kinetics Analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Kang, M. Recovery of Cobalt from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries Using Sulphuric Acid Leaching Followed by Solid-Liquid Separation and Solvent Extraction. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85303–85311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.J.; Chien, S.K.; Jhang, S.R.; Lin, Y.C. Chemical Leaching, Precipitation and Solvent Extraction for Sequential Separation of Valuable Metals in Cathode Material of Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 100, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Kumari, A.; Panda, R.; Jha, S.; Gupta, D.; Goel, S.; Jha, M.K. Close Loop Separation Process for the Recovery of Co, Cu, Mn, Fe and Li from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Environmental Friendly Leaching Reagent for Cobalt and Lithium Recovery from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Tanaka, I.; Adachi, H.; Makimura, Y.; Ohzuku, T. Crystal and Electronic Structures of Superstructural Li1-x[Co1/3Ni1/3Mn1/3]O2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1). J. Power Sources 2003, 119–121, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellens, S.; Thijs, B.; Binnemans, K. An Environmentally Friendlier Approach to Hydrometallurgy: Highly Selective Separation of Cobalt from Nickel by Solvent Extraction with Undiluted Phosphonium Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, M.; Papaiconomou, N.; Schaeffer, N.; Chainet, E.; Tedjar, F.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Billard, I. Ionic-Liquid-Based Acidic Aqueous Biphasic Systems for Simultaneous Leaching and Extraction of Metallic Ions. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Gras, M.; Passos, H.; Mogilireddy, V.; Mendonça, C.M.N.; Pereira, E.; Chainet, E.; Billard, I.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Papaiconomou, N. Synergistic Aqueous Biphasic Systems: A New Paradigm for the “One-Pot” Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Critical Metals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.S.S.; Ascenso, O.S.; Barros, M.T.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Pre-Treatment of the Paper Pulp in the Bleaching Process Using Biodegradable Chelating Agents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal-Varela, R.; Pérez-Fernández, F.; Valencia, L.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Platas-Iglesias, C.; Caravan, P.; Esteban-Gómez, D. Thermodynamic Stability of Mn(II) Complexes with Aminocarboxylate Ligands Analyzed Using Structural Descriptors. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 14173–14186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repo, E.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Warchol, J.K.; Sillanpää, M.E.T. Removal of Co(II) and Ni(II) Ions from Contaminated Water Using Silica Gel Functionalized with EDTA and/or DTPA as Chelating Agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byegård, J.; Skarnemark, G.; Skålberg, M. The Stability of Some Metal EDTA, DTPA and DOTA Complexes: Application as Tracers in Groundwater Studies. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1999, 241, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaq, M.; Uroos, M. Applications of Tetrabutylphosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 406, 125075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, X.; He, M.; Lin, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling—Reductive Ammonia Leaching of Metals from Cathode Scrap by Sodium Sulphite. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F.; Wu, Y. Optimization, Kinetic Studies of Tin Leaching from Waste Printed Circuit Boards and Selective Tin Recovery from Its Pregnant Solution. Metals 2022, 12, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, C.; Cao, H.; Zheng, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Comprehensive Evaluation on Effective Leaching of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.N.H.; Song, S.J.; Lee, M.S. Recovery of Pure Pd(II) from Spent Electroplating Solutions by Solvent Extraction with Ionic Liquids from Sulfuric Acid Leaching Solution of Cemented Pd. Metals 2021, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, B.; Fan, Y.; Hua, Z. Hydrometallurgical Processes for Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Critical Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13611–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvial-Hein, G.; Mahandra, H.; Ghahreman, A. Separation and Recovery of Cobalt and Nickel from End of Life Products via Solvent Extraction Technique: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Chemical Industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmentier, D.; Paradis, S.; Metz, S.J.; Wiedmer, S.K.; Kroon, M.C. Continuous Process for Selective Metal Extraction with an Ionic Liquid. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Ionic Liquids and Deep-Eutectic Solvents in Extractive Metallurgy: Mismatch Between Academic Research and Industrial Applicability. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
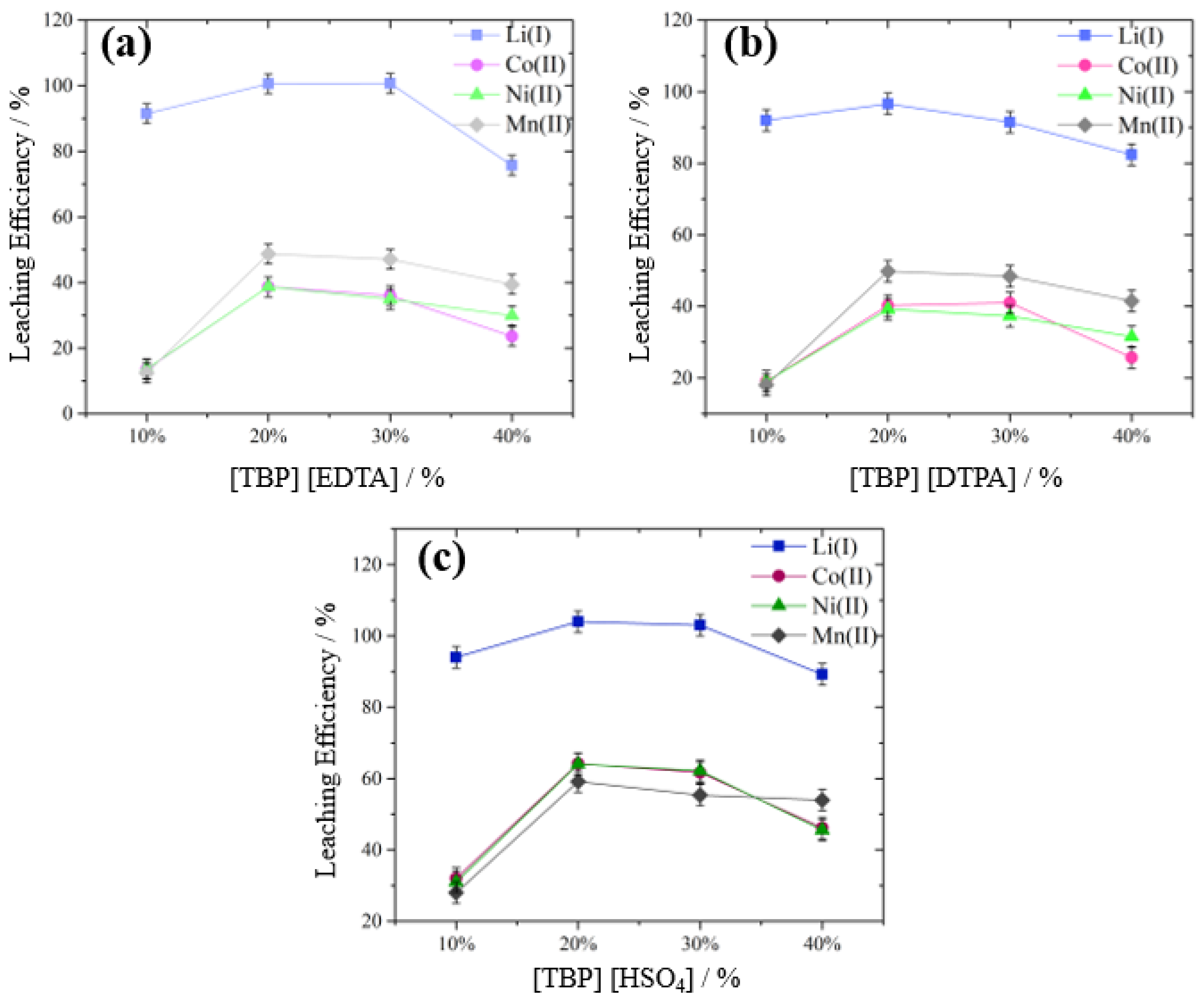
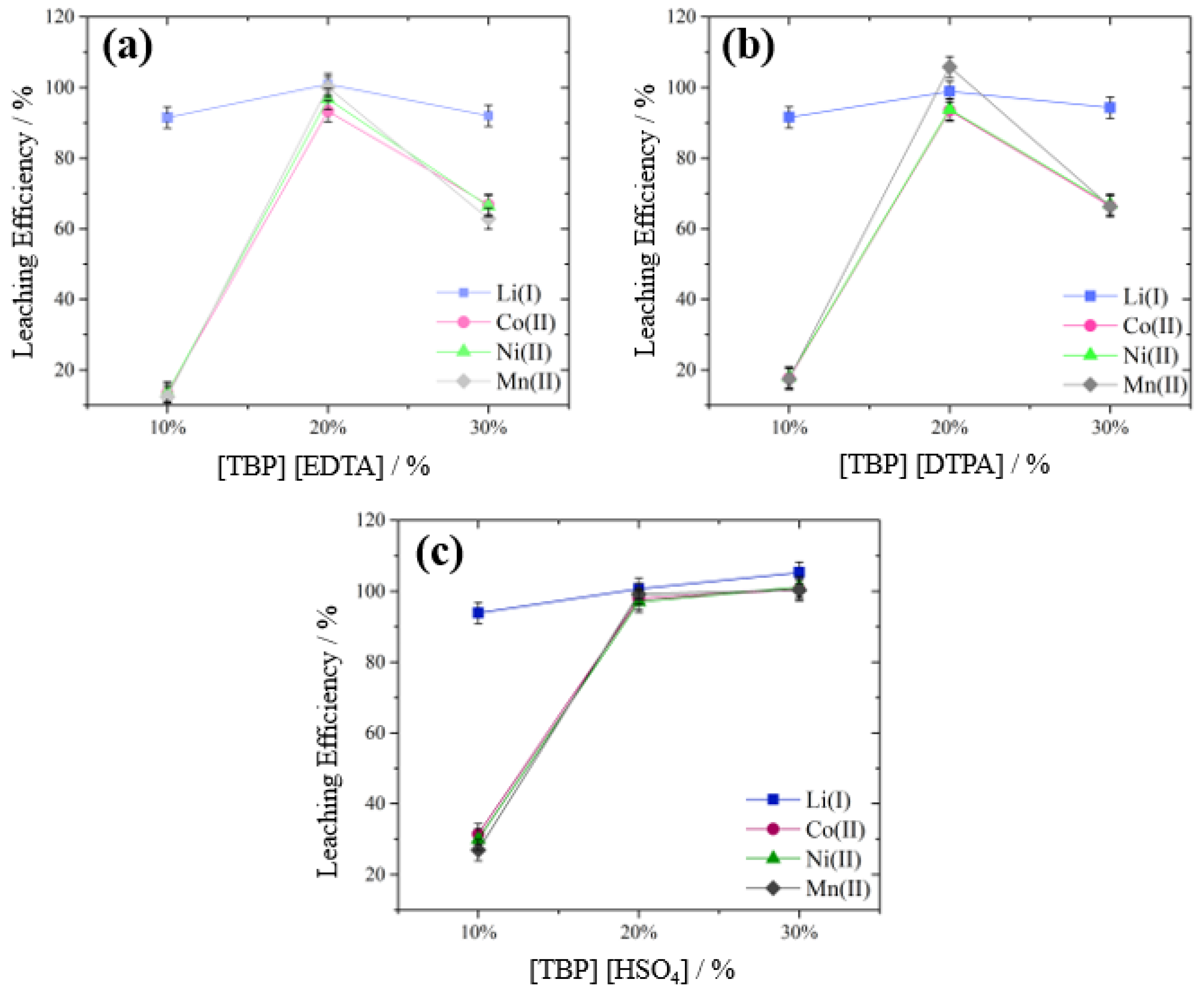
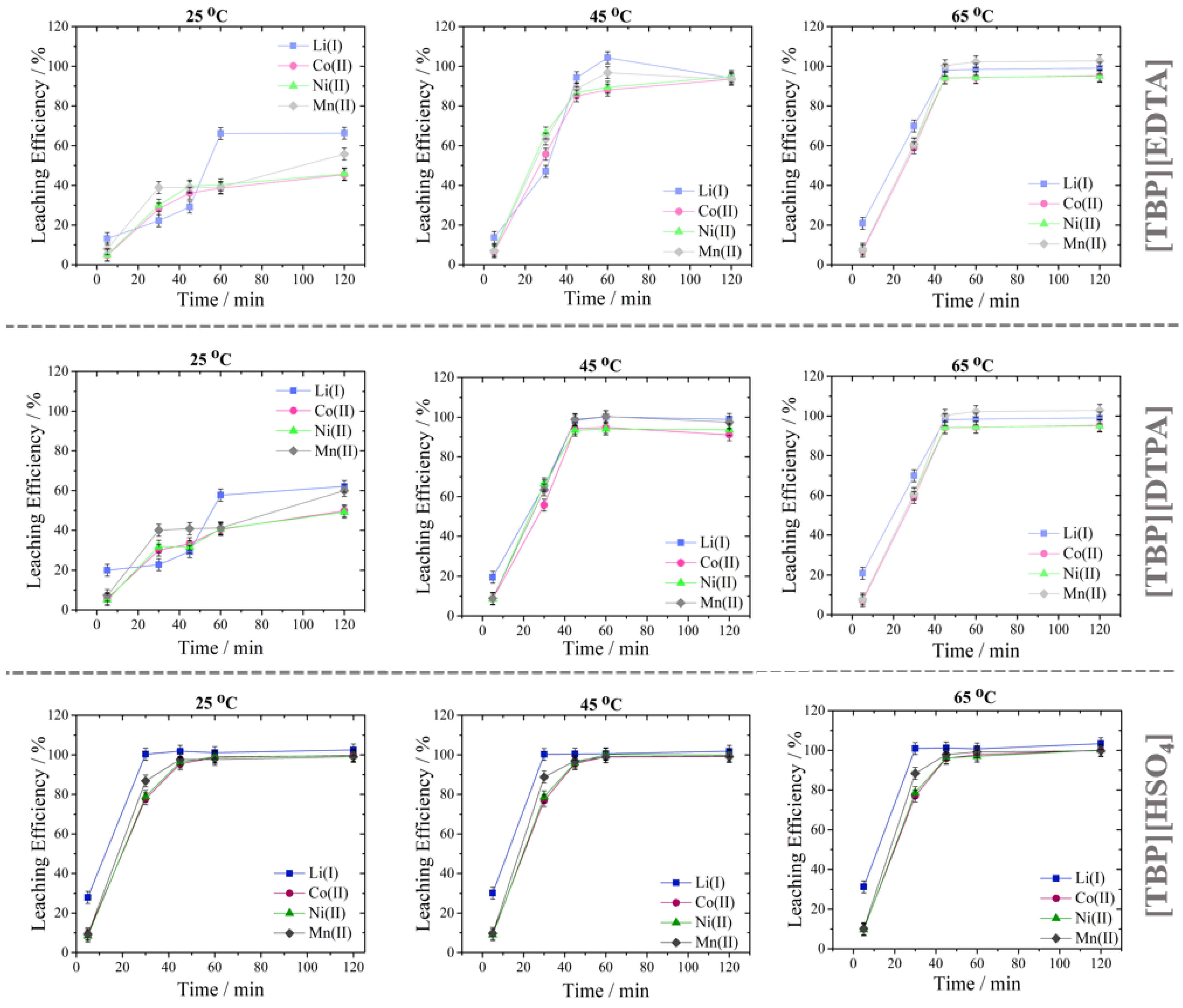
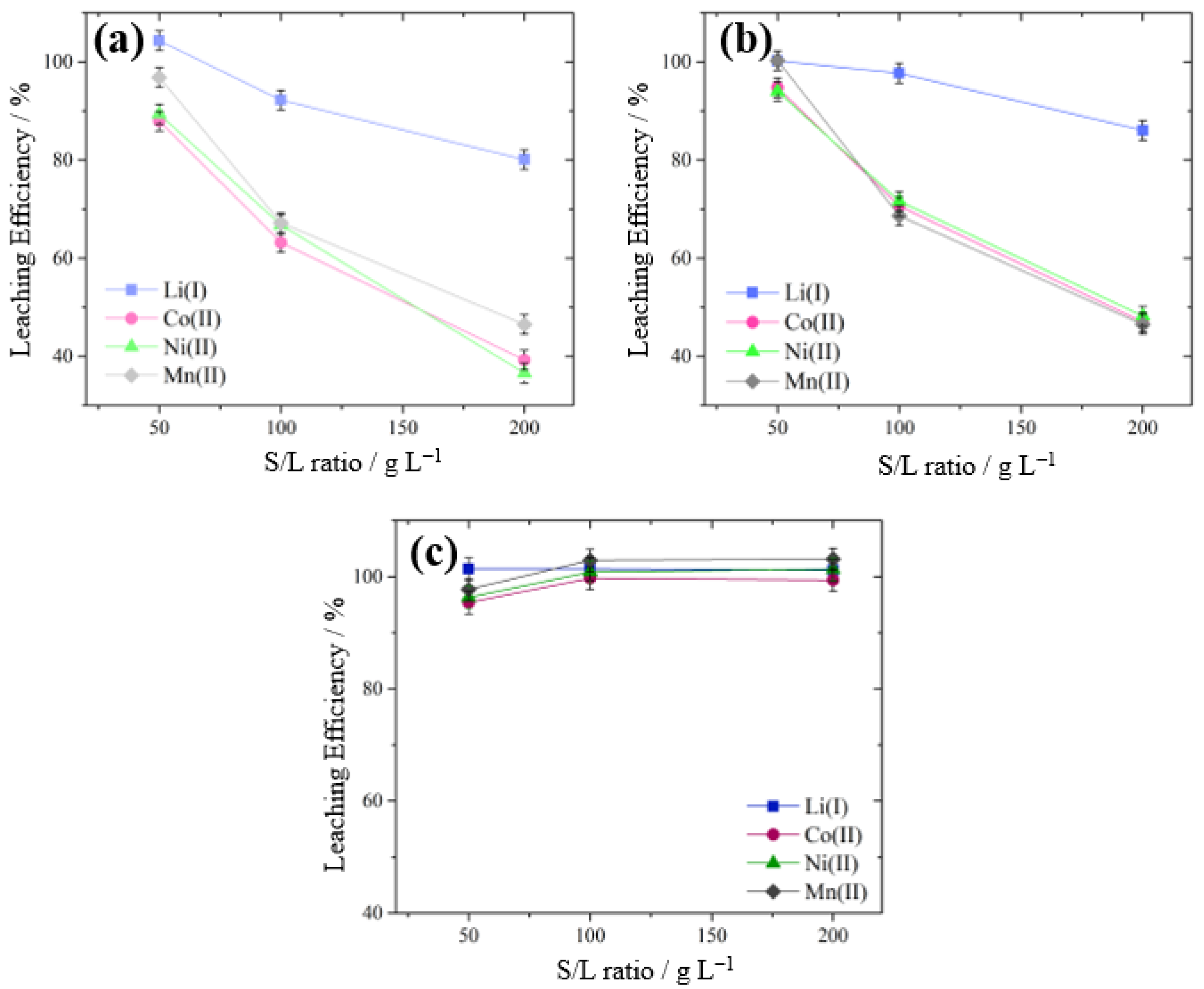
| Investigated Parameter | Investigated Levels | Constant Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid concentration (mol L−1) | 0.000, 0.375, 0.750, 1.500 | temperature = 65 °C, reaction time = 60 min, S/L ratio = 50 g L−1, stirring speed = 400 rpm |
| Amount of IL (wt.%) | 10, 20, 30, 40 | Concentration H2SO4 = 0.000 mol L−1, temperature = 65 °C, reaction time = 60 min, S/L ratio = 50 g L−1, stirring speed = 400 rpm |
| Amount of IL (wt.%) | 10, 20, 30 | Concentration H2SO4 = 0.375 mol L−1, temperature = 65 °C, reaction time = 60 min, S/L ratio = 50 g L−1, stirring speed = 400 rpm |
| Temperature (°C) | 25, 45, 65 | Concentration H2SO4 = 0.375 mol L−1, % of IL = 20%, S/L ratio = 50 g L−1, stirring speed = 400 rpm |
| Reaction time (min) | 5, 30, 45, 60, 120 | Concentration H2SO4 = 0.375 mol L−1, % of IL = 20%, S/L ratio = 50 g L−1, stirring speed = 400 rpm |
| Solid-to-liquid ratio (g L−1) | 50, 100, 200 | Concentration H2SO4 = 0.375 mol L−1, % of IL = 20%, temperature = 45 °C for [TBP][EDTA] and [TBP][DTPA], or 25 °C for [TBP][HSO4], stirring speed = 400 rpm |
| [TBP][EDTA] | [TBP][DTPA] | [TBP][HSO4] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li(I) | 29.66 | 35.75 | −0.15 |
| Co(II) | 37.20 | 33.31 | 6.26 |
| Ni(II) | 36.62 | 33.35 | 4.58 |
| Mn(II) | 50.09 | 46.82 | 6.89 |
| [TBP][EDTA] | [TBP][DTPA] | [TBP][HSO4] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL composition (wt.%) | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Acid concentration (mol L−1) | 0.375 | 0.375 | 0.375 |
| Temperature (°C) | 45 | 45 | 25 |
| Reaction time (min) | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| Solid-to-liquid ratio (g L−1) | 50 | 50 | 200 |
| Leaching efficiency (%) | >85% for Co(II), Ni(II), Mn(II) ≈100% for Li(I) | >94% for Co(II), Ni(II), Mn(II) ≈100% for Li(I) | >97% for Co(II), Ni(II), Mn(II) ≈100% for Li(I) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mušović, J.; Tekić, D.; Jocić, A.; Marić, S.; Dimitrijević, A. Efficient Ionic Liquid-Based Leaching and Extraction of Metals from NMC Cathodes. Processes 2025, 13, 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061755
Mušović J, Tekić D, Jocić A, Marić S, Dimitrijević A. Efficient Ionic Liquid-Based Leaching and Extraction of Metals from NMC Cathodes. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061755
Chicago/Turabian StyleMušović, Jasmina, Danijela Tekić, Ana Jocić, Slađana Marić, and Aleksandra Dimitrijević. 2025. "Efficient Ionic Liquid-Based Leaching and Extraction of Metals from NMC Cathodes" Processes 13, no. 6: 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061755
APA StyleMušović, J., Tekić, D., Jocić, A., Marić, S., & Dimitrijević, A. (2025). Efficient Ionic Liquid-Based Leaching and Extraction of Metals from NMC Cathodes. Processes, 13(6), 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061755







