Enhanced Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Water by Nitrogen-Doped Wheat Straw Biochar Loaded with Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Materials
2.2.1. Material Preparation
2.2.2. Activation and Doping Process
2.2.3. nZVI Loading
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Analytical Determination Method
3. Results and Discussion
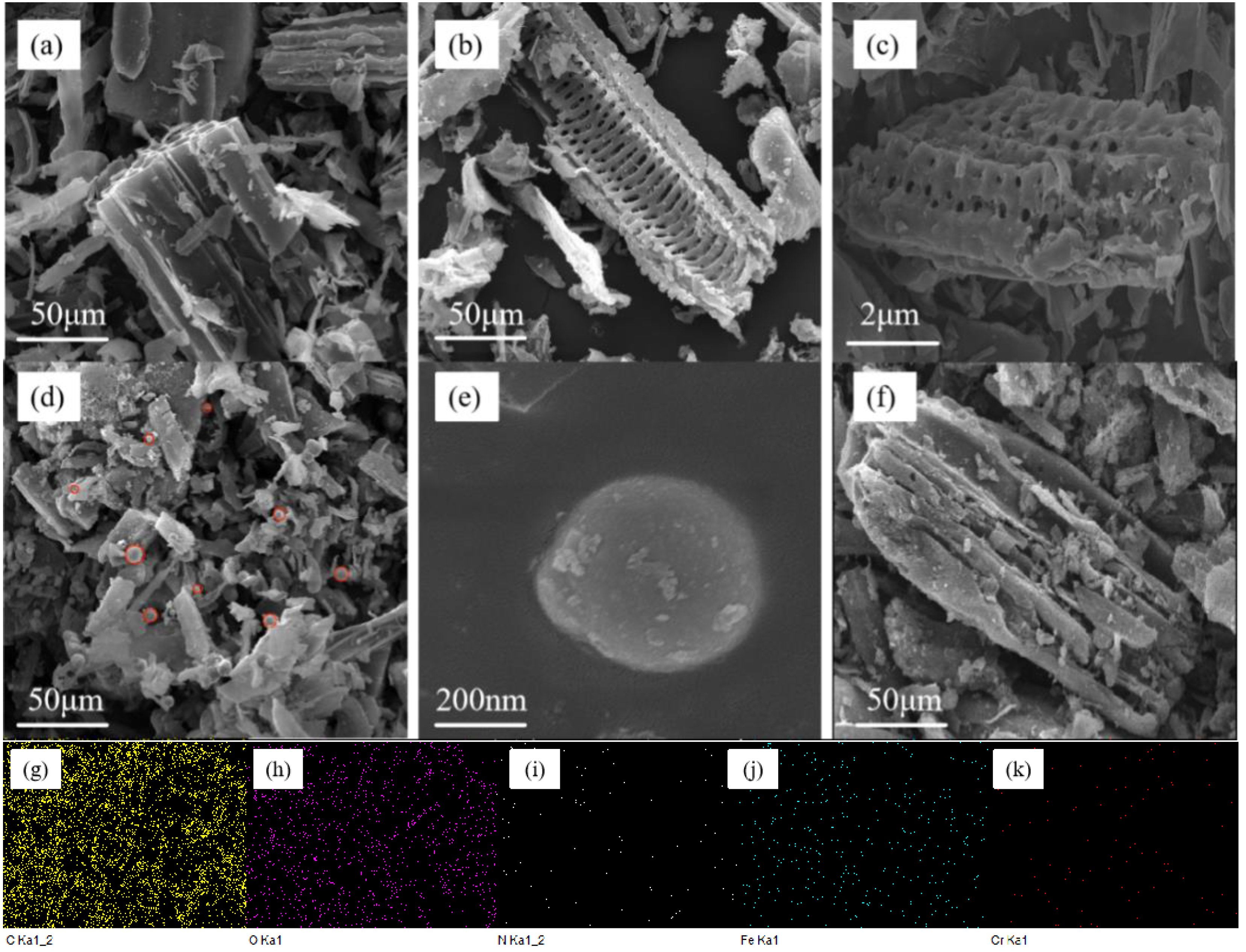
3.1. Characterization Analysis
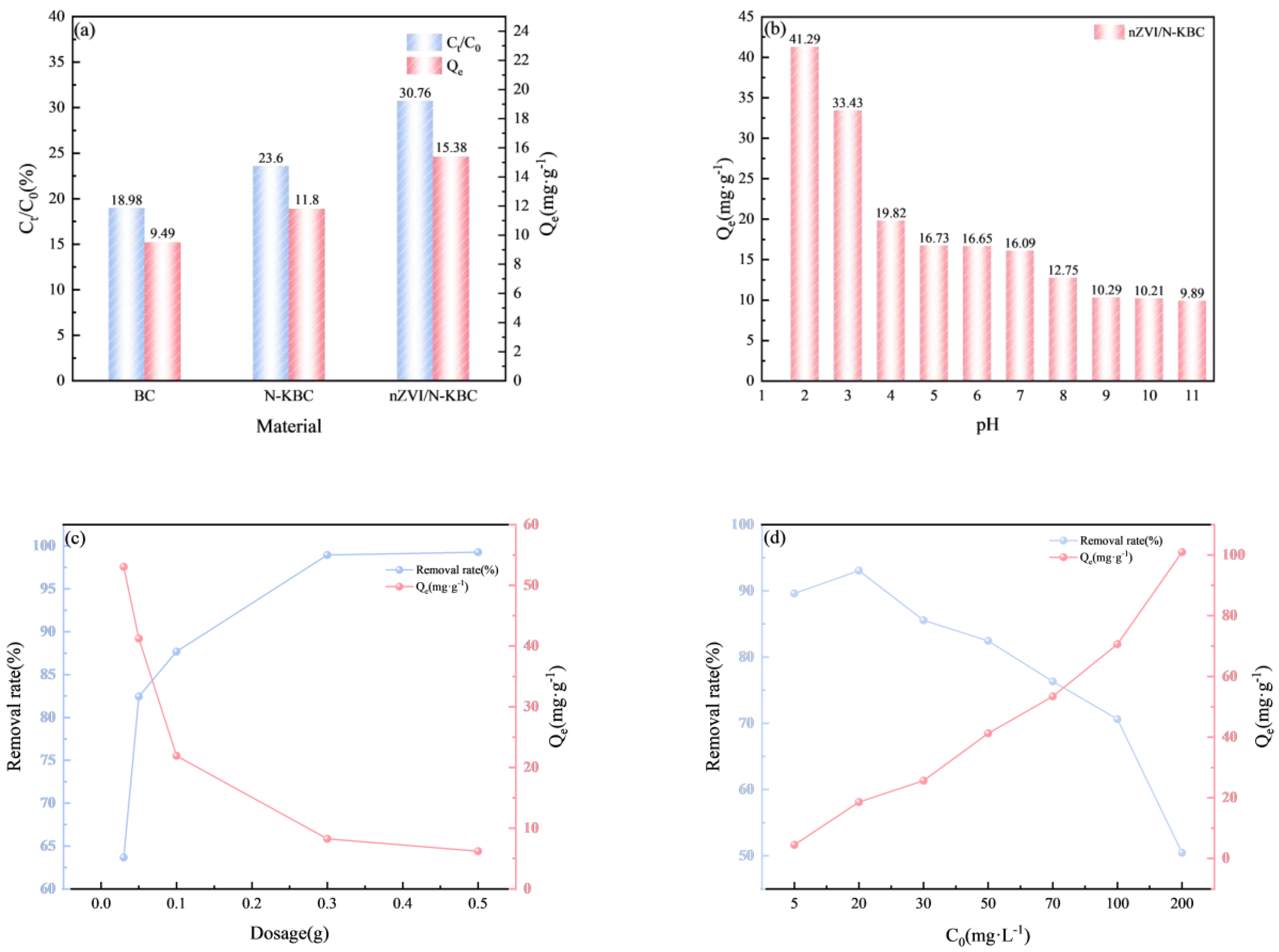
3.2. Selection of Adsorbent
3.3. Study on the Adsorption Characteristics of Cr(VI)
3.3.1. Different pH
3.3.2. Different Dosages
3.3.3. Different Initial Concentrations of Cr(VI)
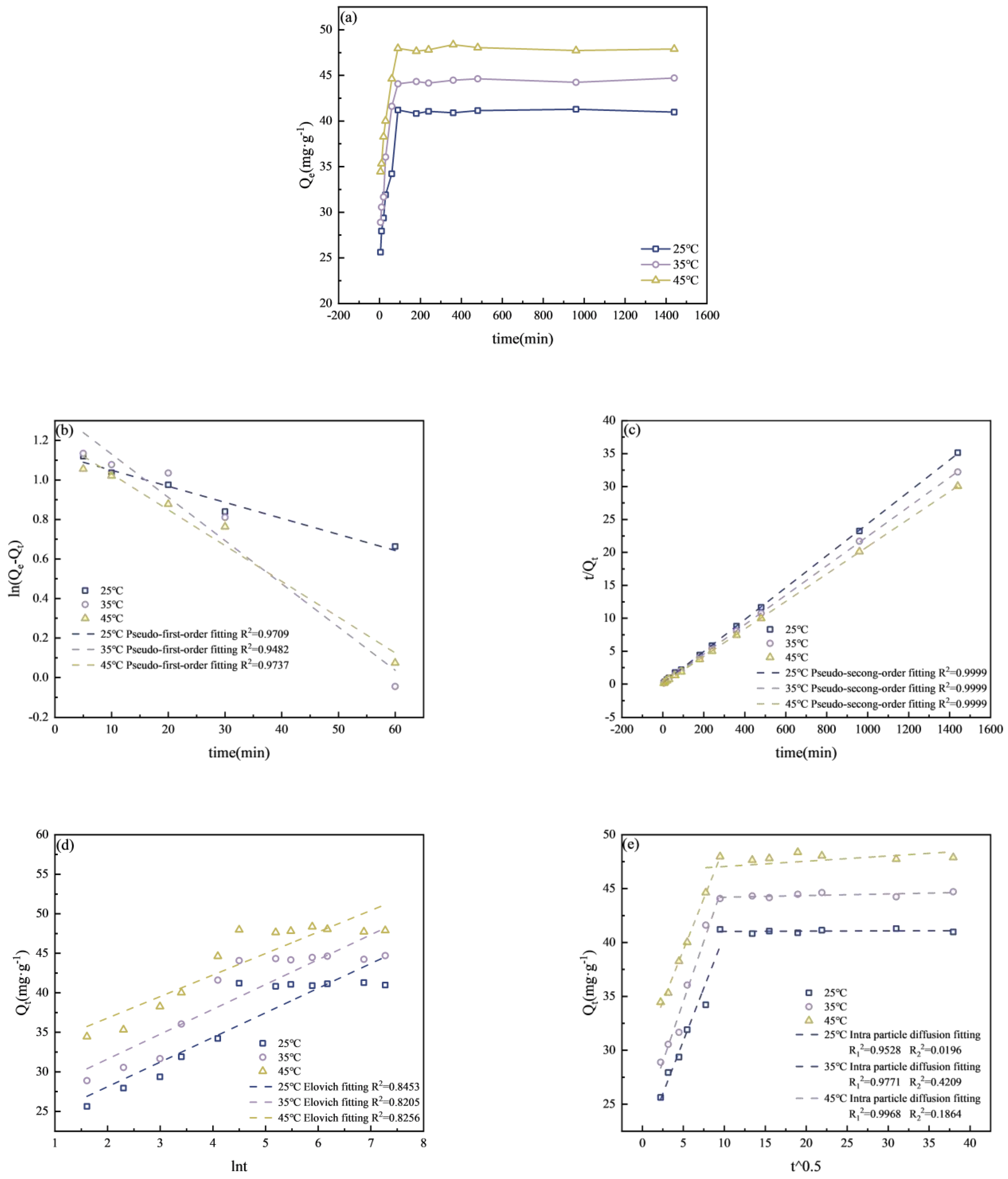
3.3.4. Adsorption Kinetics Experiment
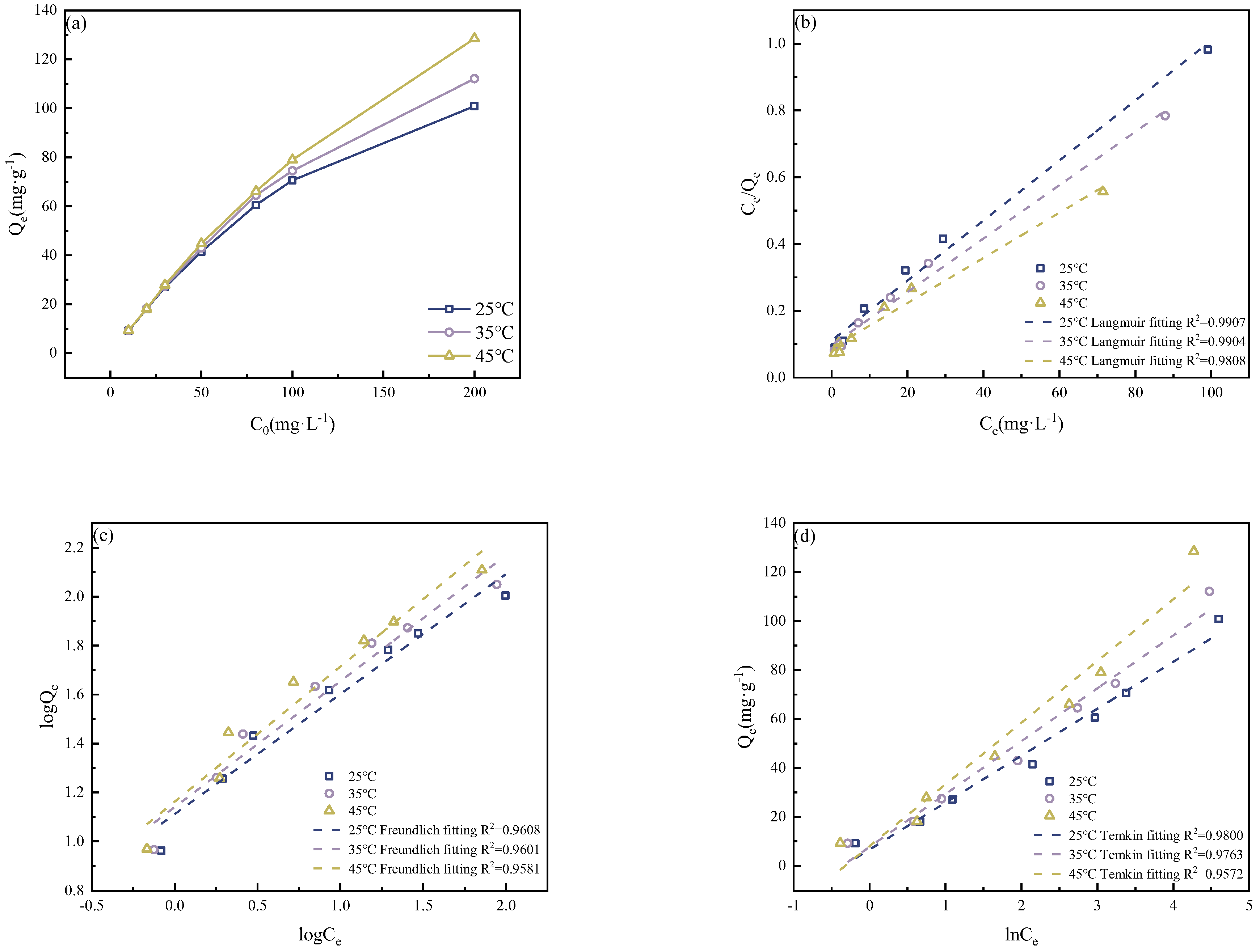
3.3.5. Isotherm
3.3.6. Thermodynamic Analysis
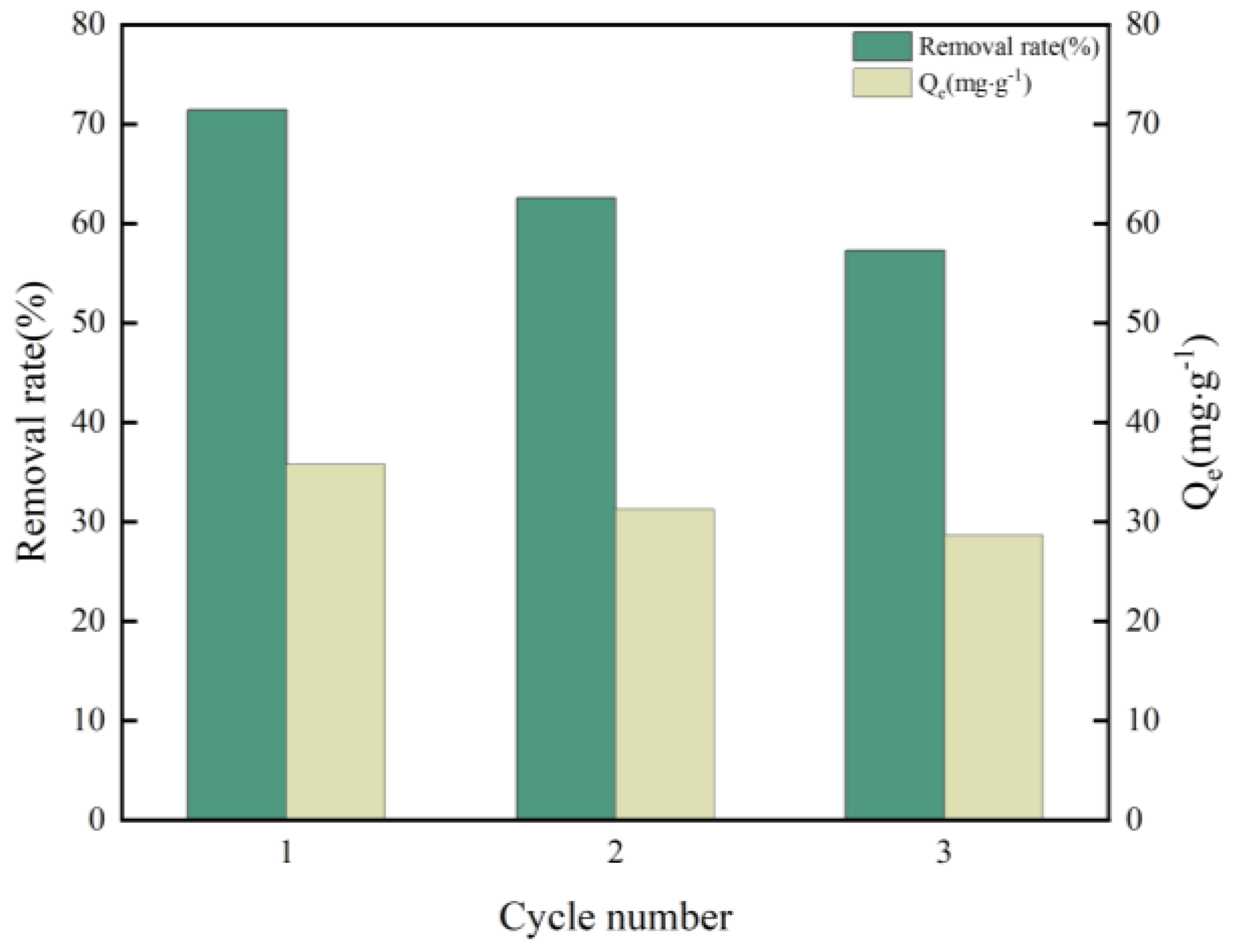
3.3.7. Recycling of nZVI/N-KBC
3.4. Mechanism Analysis
3.4.1. FTIR Analysis
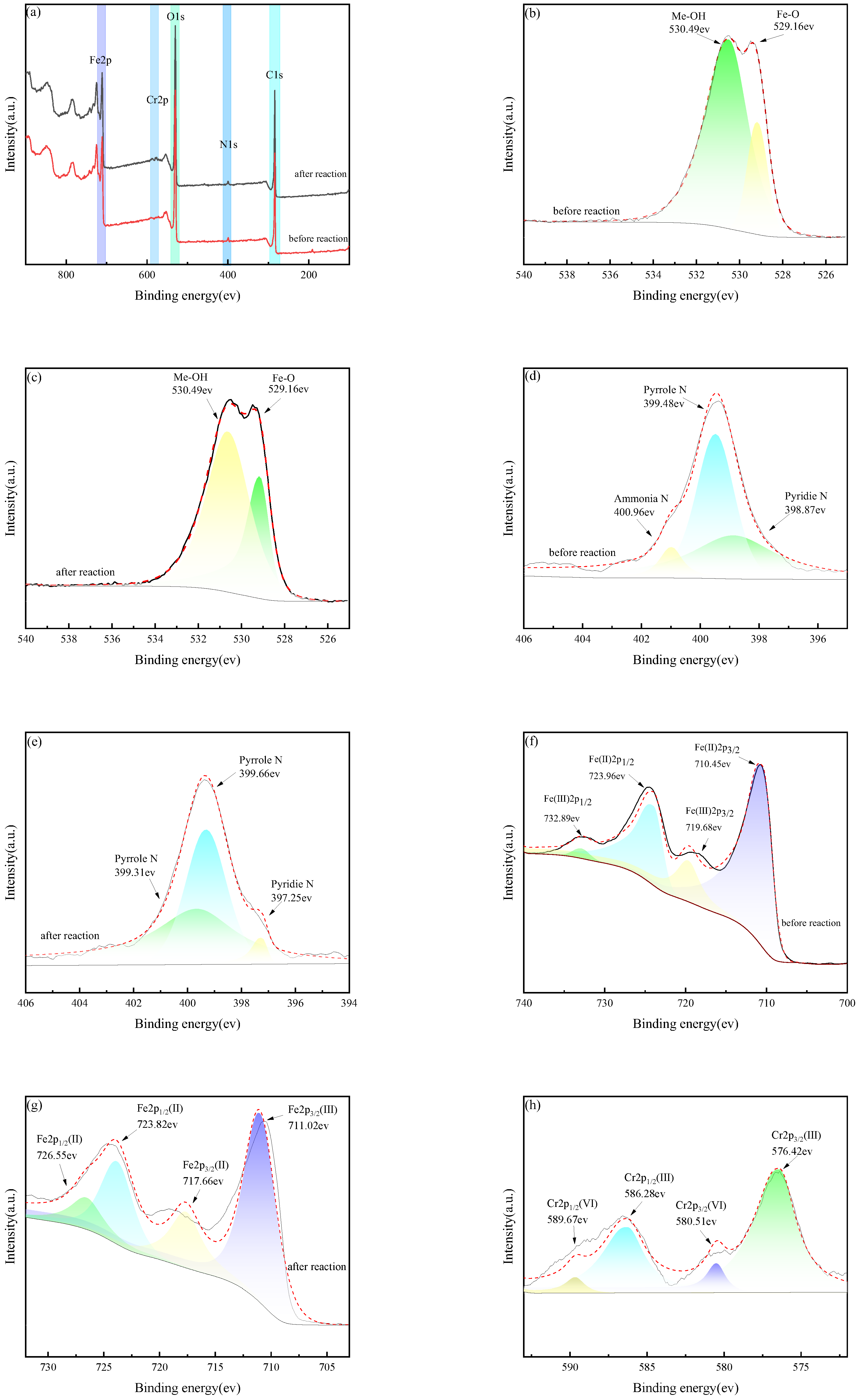
3.4.2. XPS Analysis
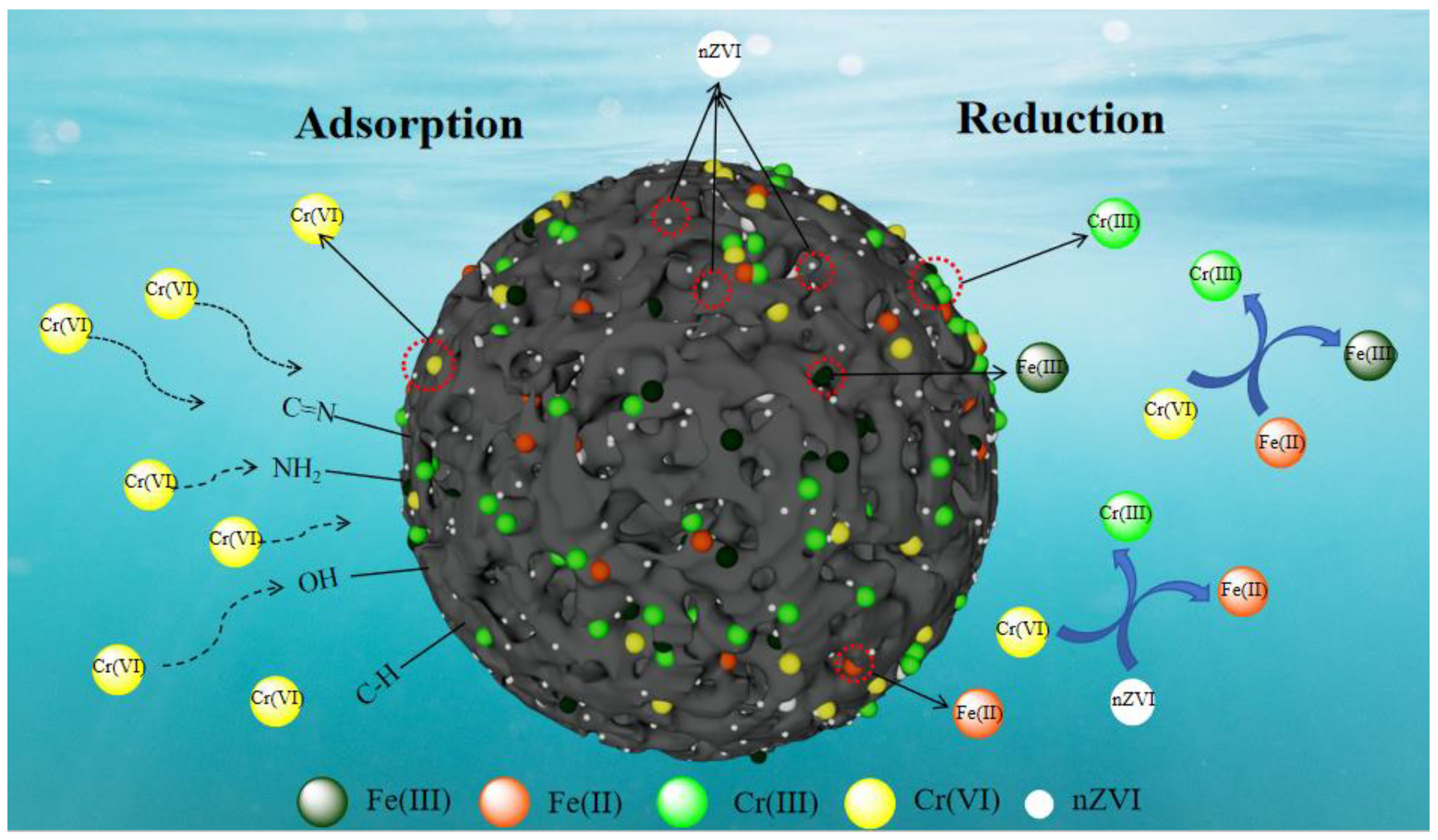
3.4.3. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| nZVI/N-KBC | Nitrogen-doped wheat straw biochar loaded with nanoscale zero-valent iron |
| Cr(VI) | Hexavalent chromium |
| nZVI | Nanoscale zero-valent iron |
| Cr(III) | Trivalent chromium |
| N-KBC | Nitrogen-doped biochar |
| KBC | Biochar modified by KOH |
| BC | Original biochar |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Sun, Y.; Lyu, H.; Gai, L.; Sun, P.; Shen, B.; Tang, J. Biochar-Anchored Low-Cost Natural Iron-Based Composites for Durable Hexavalent Chromium Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Mei, M.; Liu, J.; Du, P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Li, J. Deep Eutectic Solvent Assisted Facile and Efficient Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Magnetic Biochar for Hexavalent Chromium Elimination: Mechanism and Performance Insights. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 132012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Lin, N.; Li, X.; Pang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lei, M.; Yang, Q. Efficient Hexavalent Chromium Removal by Nano-Cerium Oxide Functionalized Biochar: Insight into the Role of Reduction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z. Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Water and Soil Using Magnetic Ceramsite Coated by Functionalized Nano Carbon Spheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Troyer, L.D.; Catalano, J.G.; Giammar, D.E. Dynamics of Chromium(VI) Removal from Drinking Water by Iron Electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13502–13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Chen, G.; Chen, C.; Sanghvi, R.; Iddya, A.; Walker, S.; Liu, H.; Ronen, A.; Jassby, D. Electrochemical Removal of Hexavalent Chromium Using Electrically Conducting Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Composite Ultrafiltration Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 531, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altundogan, H.S. Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution by Iron (III) Hydroxide-Loaded Sugar Beet Pulp. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I.; Poch, J. New Approach in Modeling Cr(VI) Sorption onto Biomass from Metal Binary Mixtures Solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Ma, F. Enhanced Hexavalent Chromium Removal Performance and Stabilization by Magnetic Iron Nanoparticles Assisted Biochar in Aqueous Solution: Mechanisms and Application Potential. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, L.; Guan, Y. Novel Co-Polymerization of Polypyrrole/Polyaniline on Ferrate Modified Biochar Composites for the Efficient Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium in Water. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, Z.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H. Characteristics and Applications of Biochar for Remediating Cr(VI)-Contaminated Soils and Wastewater. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1543–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W. Enhanced Adsorption of Aromatic Chemicals on Boron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Lian, F.; Cui, G.; Liu, Z. N-Doping Effectively Enhances the Adsorption Capacity of Biochar for Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, B. Preparation of Amino-Functionalized Magnetic Biochar with Excellent Adsorption Performance for Cr(VI) by a Mild One-Step Hydrothermal Method from Peanut Hull. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 563, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambika, S.; Kumar, M.; Pisharody, L.; Malhotra, M.; Kumar, G.; Sreedharan, V.; Singh, L.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Bhatnagar, A. Modified Biochar as a Green Adsorbent for Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Various Environmental Matrices: Mechanisms, Methods, and Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Hu, D.; Song, C.; Chen, K.; Du, X.; Chen, D.; Jin, X.; He, F.; Huang, Q. Pyrolysis of Different Biomass Feedstocks Impregnated with Mohr’s Salt to Prepare Ferrous Sulfide-Loaded Nitrogen-Doped Biochar Composites for Sequestration of Aqueous Cr(VI) Ions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 164, 105545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hua, S.; Ding, D.; Cai, T.; Zhang, R. Pyrrolic N-Rich Biochar without Exogenous Nitrogen Doping as a Functional Material for Bisphenol A Removal: Performance and Mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 291, 120093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Lv, J.; Tang, R. Novel Carbothermal Synthesis of Fe, N Co-Doped Oak Wood Biochar (Fe/N-OB) for Fast and Effective Cr(VI) Removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 600, 124926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-C.; Ji, X.-Y.; Pan, X.-Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.-J. Ionothermal Carbonization of Biomass to Construct Fe, N-Doped Biochar with Prominent Activity and Recyclability as Cathodic Catalysts in Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Fu, B.; Sun, Y.; Jin, P.; Bai, X.; Jin, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Nie, S. Degradation of Organic Pollutants by Fe/N Co-Doped Biochar via Peroxymonosulfate Activation: Synthesis, Performance, Mechanism and Its Potential for Practical Application. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lyu, H.; Tang, J.; Song, B.; Zhen, M.; Liu, X. A Novel Biochar Supported CMC Stabilized Nano Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Water. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X. Removal of Atrazine by Nanoscale Zero Valent Iron Supported on Organobentonite. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, M.; Fan, Z.; Sang, W.; Hao, H.; Wei, X. Removal Mechanisms of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by Biochar Supported Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron: Synergy of Adsorption, Reduction and Transformation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhu, F.; Li, L.; Ren, W. Box–Behnken Design for the Optimization of the Removal of Cr(VI) in Soil Leachate Using NZVI/Ni Bimetallic Particles. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2018, 27, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Huang, X.; Xie, S.; Du, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, K.; Zhuang, Q.; Huang, X. Removal of Chromium (VI) by a Magnetic Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron–Assisted Chicken Manure-Derived Biochar: Adsorption Behavior and Synergetic Mechanism. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 935525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, H.; Tang, Y.; Hu, H.; Ma, Z.; Wang, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Nitrogen-Doped Biochar Catalysts for Organic Pollutant Removal and Hexavalent Chromium Reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Liao, R.; Liu, F.; Luo, Z. Adsorption of Tetracycline Hydrochloride by KOH Modified Peanut Shell Biochar and Its Mechanism. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 2038–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, A.; Layne, C.A.; Perez, F.; Hassan, E.B.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T.E. KOH-Activated High Surface Area Douglas Fir Biochar for Adsorbing Aqueous Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Cd(II). Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Ma, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, B.; He, M.; Li, G.; Fu, H.; Zhao, P. Soybean Straw Biochar Activating Peroxydisulfate to Simultaneously Eliminate Tetracycline and Tetracycline Resistance Bacteria: Insights on the Mechanism. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Gao, F.; Lyu, H.; Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Xu, S.; Ri, C.; Tang, J. Temperature-Dependent Carbothermally Reduced Iron and Nitrogen Doped Biochar Composites for Removal of Hexavalent Chromium and Nitrobenzene. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Lin, X.; Zheng, Z. Insight into the KOH/KMnO4 Activation Mechanism of Oxygen-Enriched Hierarchical Porous Biochar Derived from Biomass Waste by in-Situ Pyrolysis for Methylene Blue Enhanced Adsorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhai, X.; Shao, W.; Bo, H.; Xu, L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, W. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Biochar-Supported Fe3O4 Derived from Oily Sludge to Enhance the Oxidative Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Fang, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Creamer, A.E.; Sun, Y.; Yang, L. Characterization and Environmental Applications of Clay-Biochar Composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xie, D.; Ai, S.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Xie, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, F. Facile Fabrication of Core-Shell α-Fe2O3@PPy Imbedded into Porous Biomass-Derived Carbon for Enhanced Lithium Storage. J. Energy Storage 2023, 67, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Gao, X.; Wu, C.; Xie, R.; Feng, S.; Chen, C. Facile Preparation of Amino Functionalized Graphene Oxide Decorated with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for the Adsorption of Cr(VI). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 384, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Xin, J.; Sun, P.; Wu, D. Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Cr(VI) by Modified Biochar Derived from Enteromorpha Prolifera. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, M. Effective Removal of Cr(VI) by Attapulgite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron from Aqueous Solution: Enhanced Adsorption and Crystallization. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Duan, Y.; Xu, X. Facile Preparation of Amine-Rich Polyamidoamine (PAMAM) Gel for Highly Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) Ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Sun, H.; Jiao, C.; Lin, A.-J. Performance and Mechanism of Cr(VI) Removal by Zero-Valent Iron Loaded onto Expanded Graphite. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. Fabrication of Chitin Microspheres Supported Sulfidated Nano Zerovalent Iron and Their Performance in Cr (VI) Removal. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, J.; Wen, S.; Shi, X.; He, Q.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, R.; Xue, W. Amino-Modified Biochar-Supported S-NZVI for Cr(VI) and Total Cr Removal from Water: Parameter Regulation, Kinetic and Mechanistic Analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 105936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; An, W.; Lyu, T.; Zhang, P. Processes and Mechanisms in Remediation of Aqueous Chromium Contamination by Sulfidated Nano-Scale Zerovalent Iron (S-NZVI): Experimental and Computational Investigations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidokht, L.; Khataee, A.R.; Reyhanitabar, A.; Oustan, S. Reductive Removal of Cr(VI) by Starch-Stabilized Fe0 Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solution. Desalination 2011, 270, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Zhao, L. Adsorption Characteristics and the Removal Mechanism of Two Novel Fe-Zn Composite Modified Biochar for Cd(II) in Water. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X. Enhanced Arsenate Removal by Novel Fe-La Composite (Hydr)Oxides Synthesized via Coprecipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangwandi, C.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Albadarin, A.B. Comparative Biosorption of Chromium (VI) Using Chemically Modified Date Pits (CM-DP) and Olive Stone (CM-OS): Kinetics, Isotherms and Influence of Co-Existing Ions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 156, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Anastopoulos, I. A Critical Review of the Estimation of the Thermodynamic Parameters on Adsorption Equilibria. Wrong Use of Equilibrium Constant in the Van’t Hoof Equation for Calculation of Thermodynamic Parameters of Adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, G.S.; Grigore Cazacliu, B.; Rodriguez Correa, C.; Ovsyannikova, E.; Kruse, A.; Hoffmann Sampaio, C.; Lima, E.C.; Dotto, G.L. Adsorption and Recovery of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by the Construction and Demolition Wastes Sludge and Its Potential Use as Phosphate-Based Fertiliser. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Yao, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Kim, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, X.; Mihucz, V.G.; Minkina, T.; Knudsen, T.Š. Superior Elimination of Cr(VI) Using Polydopamine Functionalized Attapulgite Supported NZVI Composite: Behavior and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Rajput, S.; Singh, V.K.; Steele, P.H.; Pittman, C.U. Modeling and Evaluation of Chromium Remediation from Water Using Low Cost Bio-Char, a Green Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, P. Chemical Processes of Cr(VI) Removal by Fe-Modified Biochar under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions and Mechanism Characterization under Aerobic Conditions Using Synchrotron-Related Techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Ran, Z. Synthesis of Magnetic Kaolin and Adsorption of Lead(II). Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Amira, M.F.; Seleim, S.M.; Mohamed, A.K. Amino-Decorated Magnetic Metal-Organic Framework as a Potential Novel Platform for Selective Removal of Chromium (Vl), Cadmium (II) and Lead (II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Bi, F.; Li, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Polyethylenimine-Grafted Nanocellulose with Ultra-High Adsorption Capacity for Lead and Phosphate Scavenging from Water. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhang, X.; Bi, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylenimine-Grafted Nitrogen-Doping Magnetic Biochar for Efficient Cr(VI) Decontamination: Insights into Synthesis and Adsorption Mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, W.; Gao, L.; Liang, X.; Yang, Q. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium in Water by Chitosan-Modified Enteromorpha Prolifera Biochar Loaded with Iron-Manganese Oxides: Application Performances and Reaction Mechanisms. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 317, 129189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Du, K.; Yin, Q.; Yin, Q. Polypyrrole/Graphene/Polyaniline Ternary Nanocomposite with High Thermoelectric Power Factor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20124–20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Ke, J.; Xu, J.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, R. One-Step Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of Flowerlike Ce/Fe Bimetallic Oxides for Efficient As(V) and Cr(VI) Remediation: Performance and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Jiang, X.; Luo, H.; Geng, J. Synthesis of Graphene/SiO2@polypyrrole Nanocomposites and Their Application for Cr(VI) Removal in Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Bi, D. The Removal of Chromium (VI) and Lead (II) from Groundwater Using Sepiolite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere 2015, 138, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, J.; Huang, N.; Baig, S.A.; Hu, D. Facile Improvement of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Activity with Exceptional Stability for Reduction of Cr(VI). J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.-L.; Liu, W.-J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H. Magnesium Oxide Embedded Nitrogen Self-Doped Biochar Composites: Fast and High-Efficiency Adsorption of Heavy Metals in an Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10081–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, M.; Zhang, X.; Ling, C.; Li, A. Nitrogen-Doped Chitosan-Fe(III) Composite as a Dual-Functional Material for Synergistically Enhanced Co-Removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Based on Adsorption and Redox. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, Y.; Tang, J.; He, J.; Sun, H. Aqueous Cr(VI) Removal by a Novel Ball Milled Fe0-Biochar Composite: Role of Biochar Electron Transfer Capacity under High Pyrolysis Temperature. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zheng, X.; Chen, B.; Ma, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M.; Zhou, S. Enhanced Adsorption of Sulfamethoxazole from Aqueous Solution by Fe-Impregnated Graphited Biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fan, G.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X. Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Particles Supported on Sludge-Based Biochar for the Removal of Chromium (VI) from Aqueous System. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3853–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Guo, J.; Muhammad, Y.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Yun, J.; Liang, Y. Mechanisms of Enhanced Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Groundwater by Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Stabilized Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Liang, X.; Wei, L.; Yang, Q.; Qian, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, P. The Ce-Fe Loaded Biochar for Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium: Broad PH Adaptation and Mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Long, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Liang, C.; Liu, R.; Chen, M. Unveiling the Role of Biochar in Simultaneous Removal of Hexavalent Chromium and Trichloroethylene by Biochar Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 889, 164243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, J. Study on the Remediation Effect and Influencing Factors of Stabilized Biochar Supported with Nano Zero-Valent Iron on Cr(VI) in Groundwater. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2024, 51, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, X.; Jing, G. Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal from Simulated Electroplating Rinse Wastewater by Amino-Functionalized Vermiculite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Ishak, A.R.; Mohd Aris, M.S.; Mohamad Shaifuddin, S.N.; Ding, S.; Deng, T. Enhanced Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Water by Nitrogen-Doped Wheat Straw Biochar Loaded with Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanisms. Processes 2025, 13, 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061714
Li H, Ishak AR, Mohd Aris MS, Mohamad Shaifuddin SN, Ding S, Deng T. Enhanced Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Water by Nitrogen-Doped Wheat Straw Biochar Loaded with Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanisms. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061714
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hansheng, Ahmad Razali Ishak, Mohd Shukri Mohd Aris, Siti Norashikin Mohamad Shaifuddin, Su Ding, and Tiantian Deng. 2025. "Enhanced Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Water by Nitrogen-Doped Wheat Straw Biochar Loaded with Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanisms" Processes 13, no. 6: 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061714
APA StyleLi, H., Ishak, A. R., Mohd Aris, M. S., Mohamad Shaifuddin, S. N., Ding, S., & Deng, T. (2025). Enhanced Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Water by Nitrogen-Doped Wheat Straw Biochar Loaded with Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanisms. Processes, 13(6), 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061714






