Design Optimization of an Inclined Inlet Channel, an Archimedean Spiral Basin, and a Discharge Cone in a Gravitational Vortex Turbine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Principles of Turbine Operation
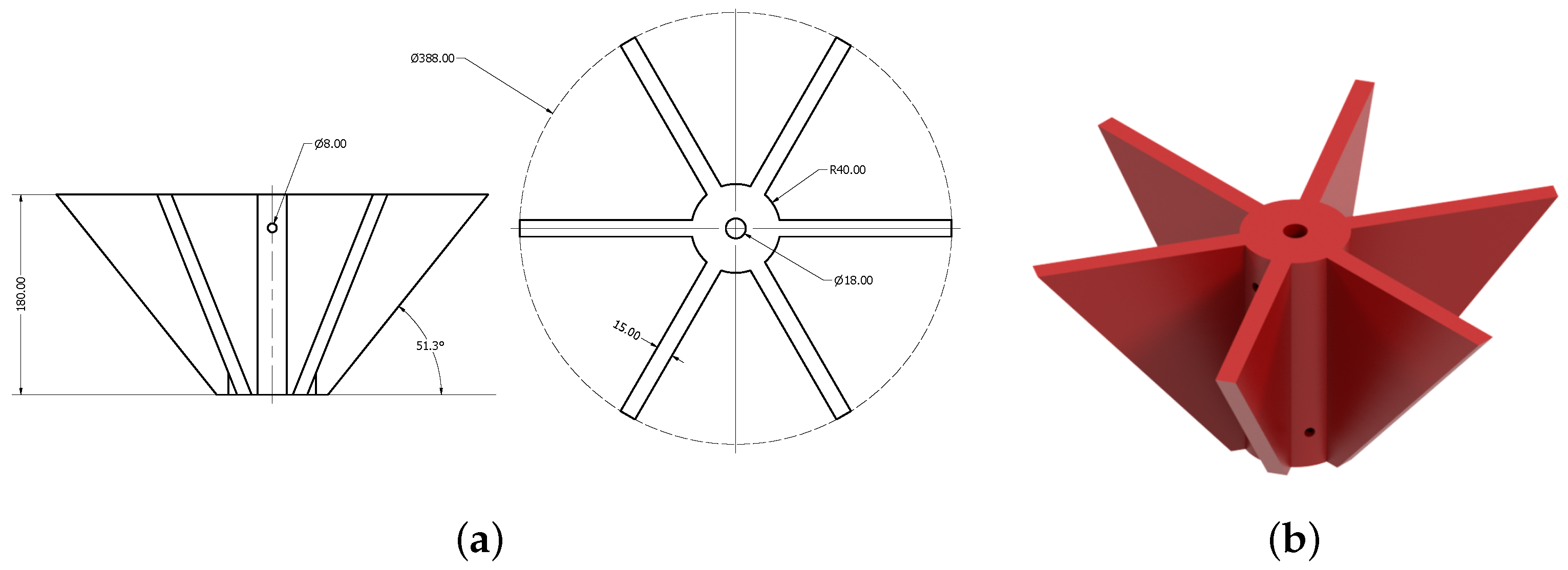
2.2. Turbine Design
2.3. Application of RSM in Design Optimization
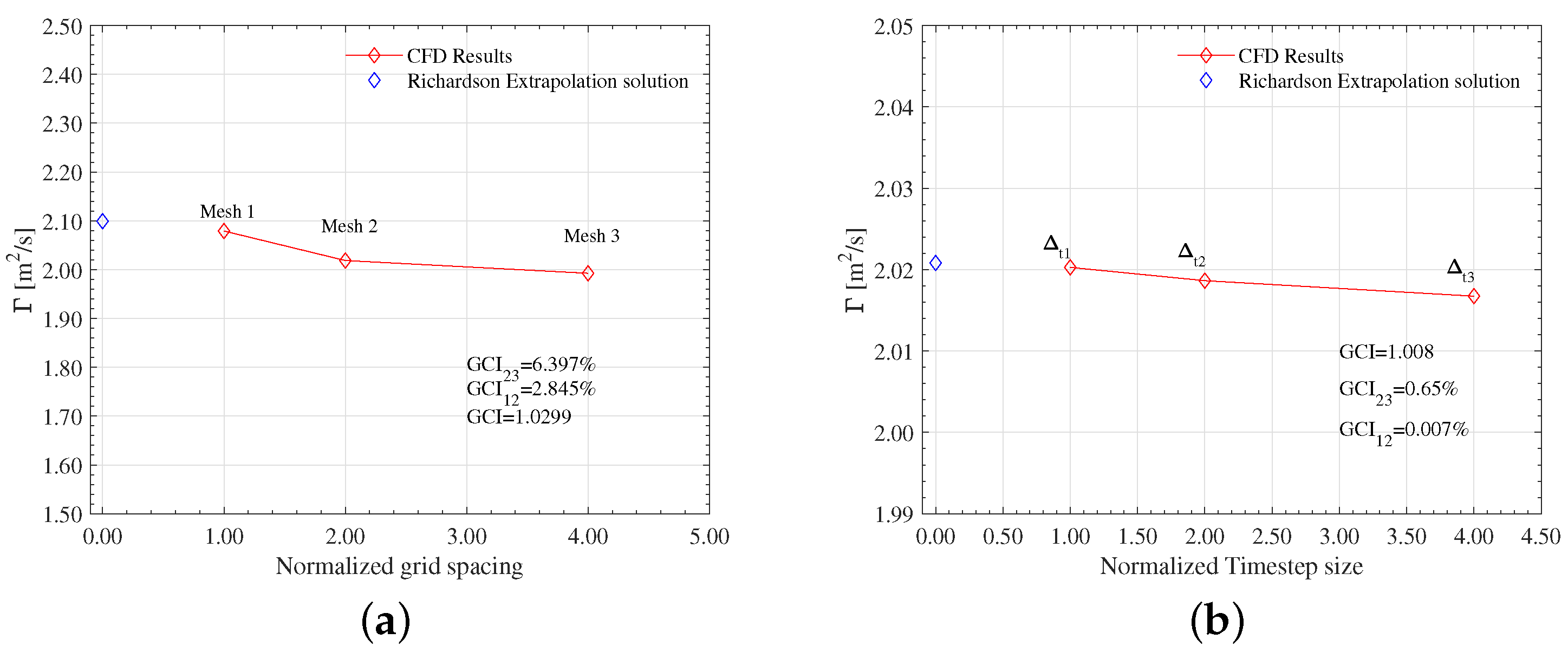
2.4. Numerical Simulation
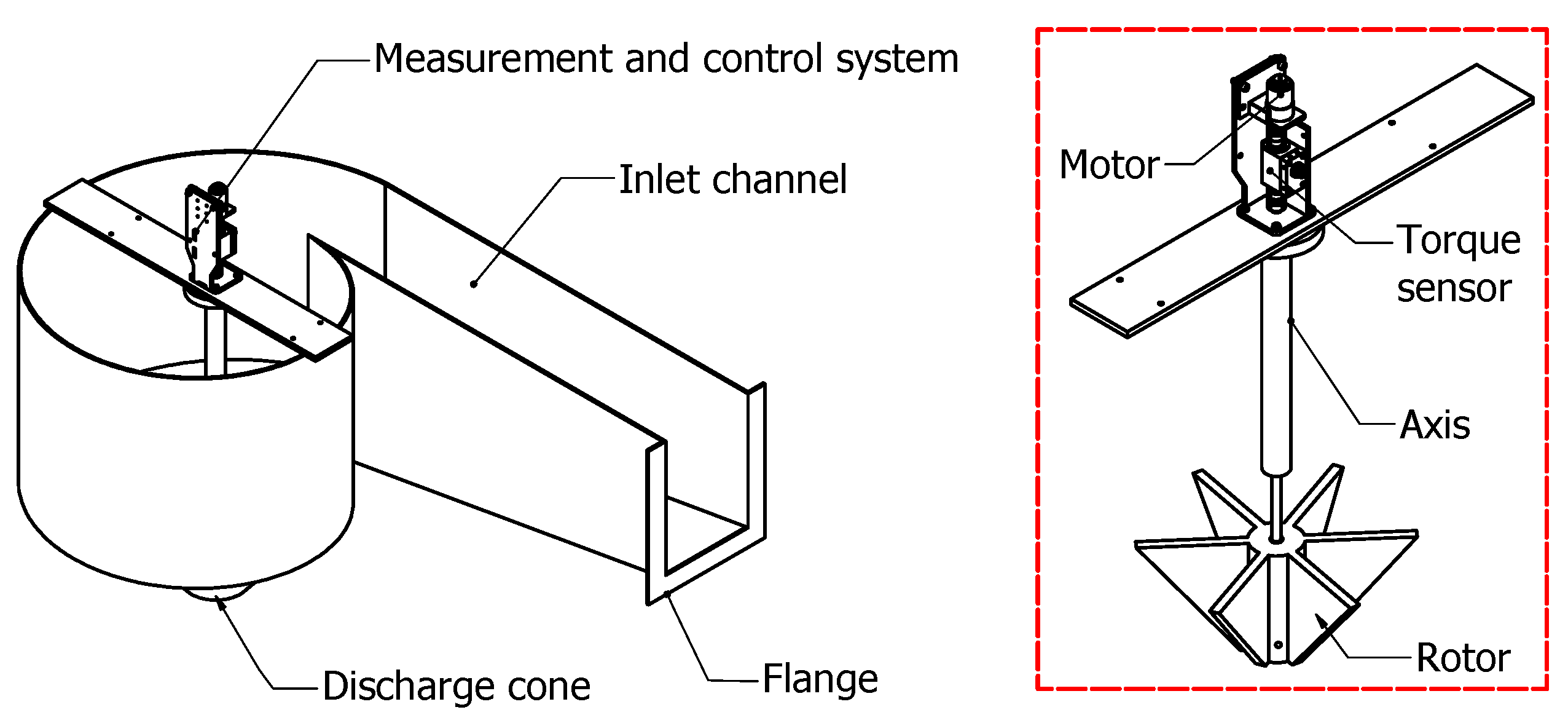
2.5. Experimental Validation
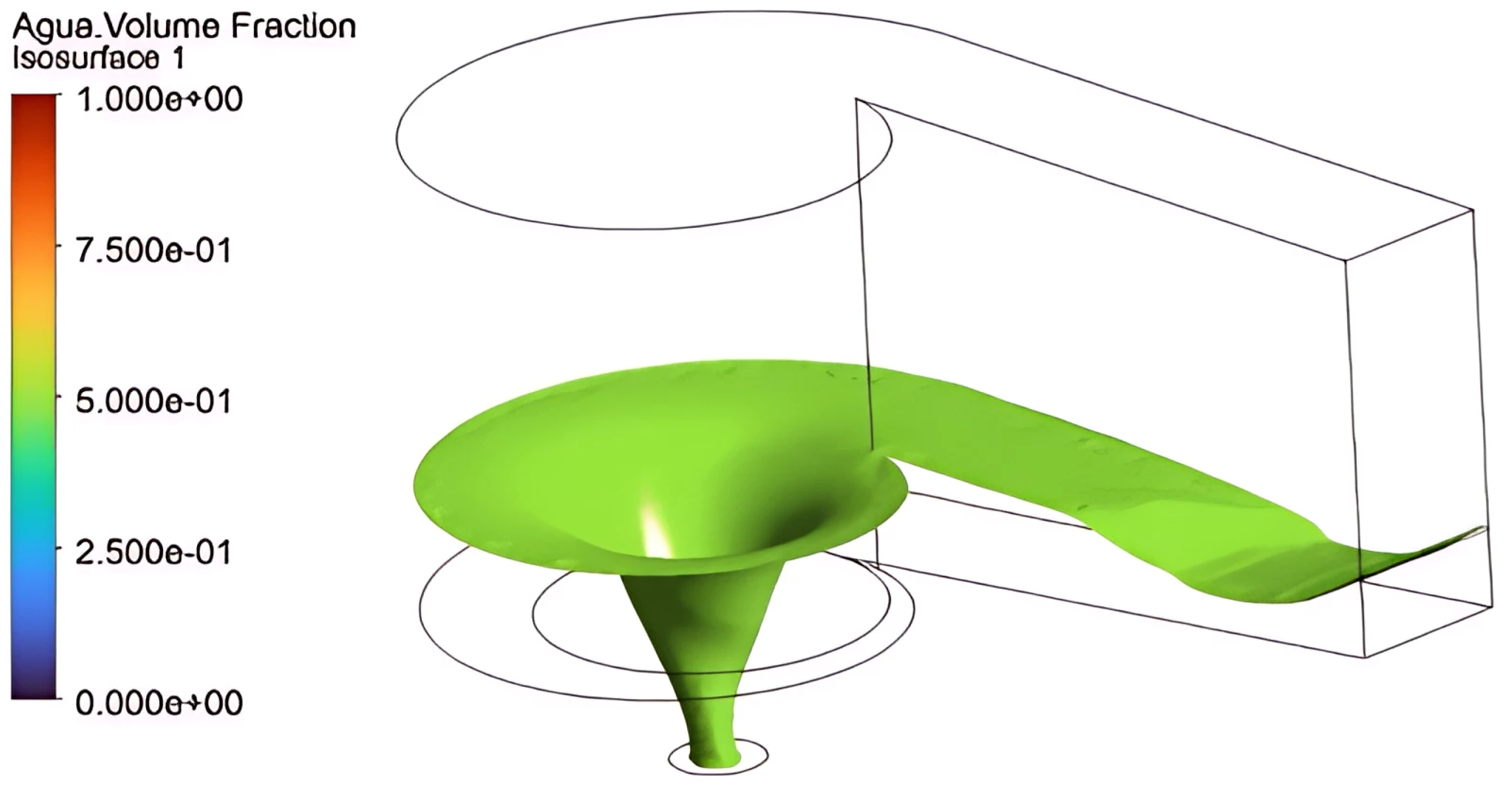
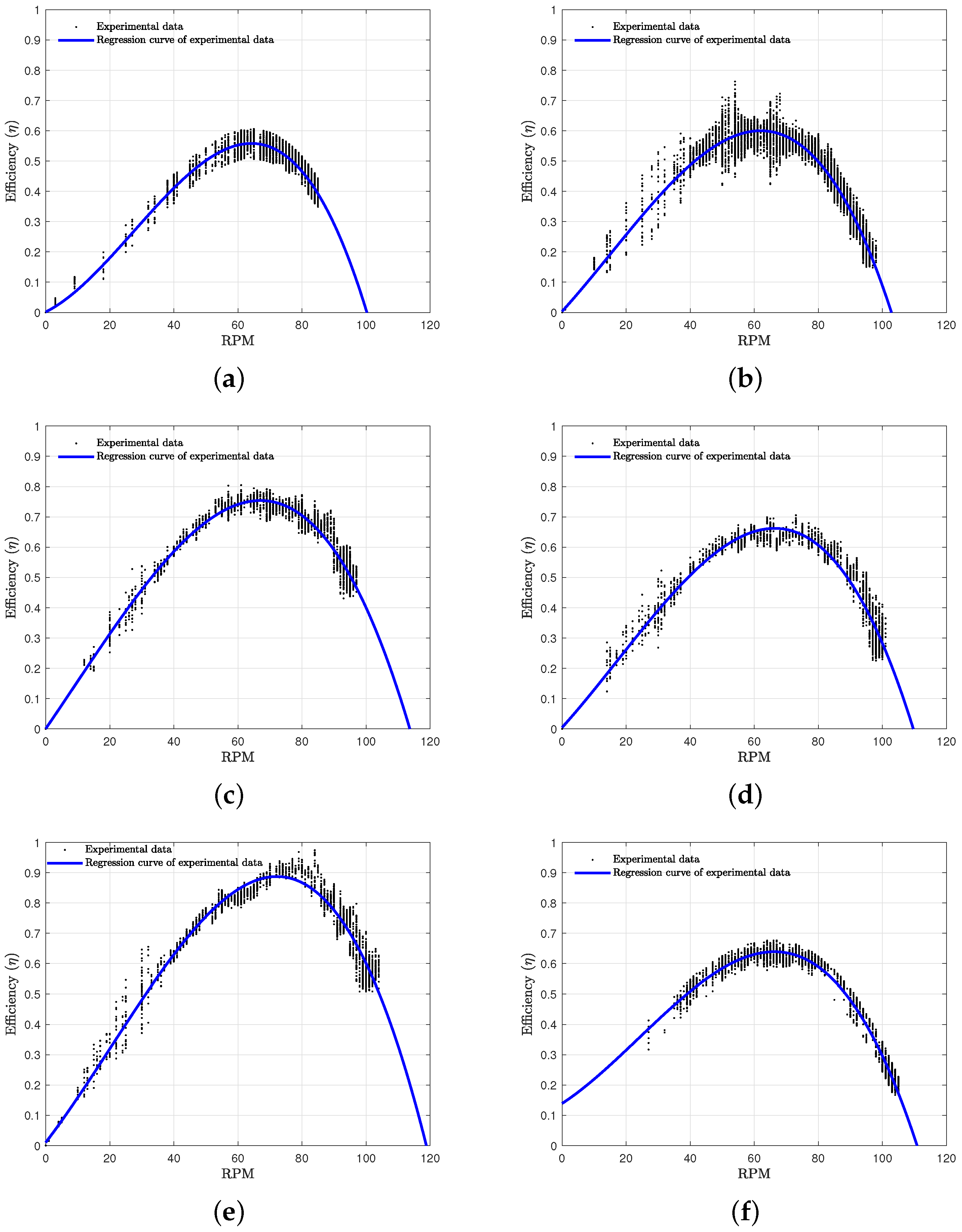
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jie, H.; Khan, I.; Alharthi, M.; Zafar, M.W.; Saeed, A. Sustainable energy policy, socio-economic development, and ecological footprint: The economic significance of natural resources, population growth, and industrial development. Util. Policy 2023, 81, 101490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, S. Economic growth and human well-being. In Human Ecology, Human Economy; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020; pp. 98–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemian, S.; Faridzad, A.; Abbaszadeh, P.; Taklif, A.; Ghasemi, A.; Hafezi, R. An overview of global energy scenarios by 2040: Identifying the driving forces using cross-impact analysis method. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 21, 7749–7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molotoks, A.; Smith, P.; Dawson, T.P. Impacts of land use, population, and climate change on global food security. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Rahman, A.R.; Zhang, J. Trends in rice research: 2030 and beyond. Food Energy Secur. 2023, 12, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosan, S.; Karmaker, S.C.; Rahman, M.M.; Chapman, A.J.; Saha, B.B. Dynamic links among the demographic dividend, digitalization, energy intensity and sustainable economic growth: Empirical evidence from emerging economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D. A critical review of comparative global historical energy consumption and future demand: The story told so far. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1973–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R. How China Is Reshaping the Global Economy: Development Impacts in Africa and Latin America; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs; Hertog, S.; Gerland, P.; Wilmoth, J. India overtakes China as the world’s most populous country. In UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) Policy Briefs; UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Echendu, A.J.; Okafor, P.C.C. Smart city technology: A potential solution to Africa’s growing population and rapid urbanization? Dev. Stud. Res. 2021, 8, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinin, L.; Korotayev, A. Africa: The continent of the future. Challenges and opportunities. In Reconsidering the Limits to Growth: A Report to the Russian Association of the Club of Rome; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Kabeyi, M.J.B.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Sustainable energy transition for renewable and low carbon grid electricity generation and supply. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 743114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Gusain, D. Energy: Present and Future Demands. In Advanced Nanocatalysts for Biodiesel Production; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Breyer, C.; Khalili, S.; Bogdanov, D.; Ram, M.; Oyewo, A.S.; Aghahosseini, A.; Gulagi, A.; Solomon, A.; Keiner, D.; Lopez, G.; et al. On the history and future of 100% renewable energy systems research. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 78176–78218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strielkowski, W.; Civín, L.; Tarkhanova, E.; Tvaronavičienė, M.; Petrenko, Y. Renewable energy in the sustainable development of electrical power sector: A review. Energies 2021, 14, 8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Farrok, O.; Haque, M.M. Environmental impact of renewable energy source based electrical power plants: Solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal, tidal, ocean, and osmotic. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, M.; Weigt, H.; Hirsch, P.E. Environmental flows or economic woes—Hydropower under global energy market changes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maika, N.; Lin, W.; Khatamifar, M. A review of gravitational water vortex hydro turbine systems for hydropower generation. Energies 2023, 16, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, L.; Posada, A.; Chica, E. Optimization of the basin and inlet channel of a gravitational water vortex hydraulic turbine using the response surface methodology. Renew. Energy 2022, 187, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, L.; Rubio-Clemente, A.; Chica, E. Numerical and Experimental Analysis of Vortex Profiles in Gravitational Water Vortex Hydraulic Turbines. Energies 2024, 17, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.Q.A.; Idris, J.; Abdullah, M.F. Experimental study on enclosed gravitational water vortex turbine (GWVT) producing optimum power output for energy production. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2022, 95, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Velásquez, L.; Chica, E.; Posada, J. Advances in the Development of Gravitational Water Vortex Hydraulic Turbines. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2021, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisinghe, D.S.; Yang, H.S.; Gunawardane, S.; Lee, Y.H. Enhancing the performance of gravitational water vortex turbine by flow simulation analysis. Renew. Energy 2022, 194, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Raji, A.P.; Raja, V.; Wang, F.; AL-bonsrulah, H.A.; Murugesan, R.; Ranganathan, S. Multi–disciplinary optimizations of small-scale gravitational vortex hydropower (SGVHP) system through computational hydrodynamic and hydro–structural analyses. Sustainability 2022, 14, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancour, J.; Romero-Menco, F.; Velásquez, L.; Rubio-Clemente, A.; Chica, E. Design and optimization of a runner for a gravitational vortex turbine using the response surface methodology and experimental tests. Renew. Energy 2023, 210, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobeen, M.; Jaweed, S.; Abdullah, A.; Rasheed, S.; Masud, M. Parametric Optimization of Gravitational Water Vortex Turbines for Enhanced Torque Generation. Eng. Proc. 2023, 45, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, L.; Posada, A.; Chica, E. Surrogate modeling method for multi-objective optimization of the inlet channel and the basin of a gravitational water vortex hydraulic turbine. Appl. Energy 2023, 330, 120357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septyaningrum, E.; Hantoro, R.; Mouti, N.K.; Rahayu, W.R.; Banta Cut, S. Gravitational Vortex Water Turbine (GVWT) conical basin design: The effects of cone angle and outlet diameter on vortex characteristics. J. Mech. Eng. (JMechE) 2024, 21, 177–198. [Google Scholar]
- Spichal, L. Gielis transformation of the Archimedean spiral. Kragujev. J. Math. 2025, 49, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamidi, S.; Olaleye, N.; Bankole, Y.; Obalola, A.; Aribike, E.; Adigun, I. Applications of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) in Product Design, Development, and Process Optimization; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hadiyat, M.A.; Sopha, B.M.; Wibowo, B.S. Response surface methodology using observational data: A systematic literature review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpisják-Gulyás, N.; Al-Tayawi, A.N.; Horváth, Z.H.; László, Z.; Kertész, S.; Hodúr, C. Methods for experimental design, central composite design and the Box–Behnken design, to optimise operational parameters: A review. Acta Aliment. 2023, 52, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamandani, M.; Hashemi, S.H. Central composite design (CCD) and Box-Behnken design (BBD) for the optimization of a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based pipette tip micro-solid phase extraction (SPE) for the spectrophotometric determination of chlorpyrifos in food and juice. Anal. Lett. 2022, 55, 2394–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigdon, S.E.; Englert, B.R.; Lawson, I.A.; Borror, C.M.; Montgomery, D.C.; Pan, R. Experiments for reliability achievement. Qual. Eng. 2012, 25, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Runger, G.C. Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S. Central composite design for response surface methodology and its application in pharmacy. In Response Surface Methodology in Engineering Science; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Peck, E.A.; Vining, G.G. Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- bin Ismail, H.; Nguyen, M.Q. A Comparative Analysis of Efficiency in Fluid Dynamic Devices: Experimental and Computational Approaches. Q. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. 2023, 8, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.; Yeoh, G.H.; Liu, C.; Tao, Y. Computational Fluid Dynamics: A Practical Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Urrego-Pabón, J.; Mercado, J.; Obando-Vega, F.; Rubio-Clemente, A.; Chica, E. Numerical and experimental study of several passive wave absorber behavior in a wave channel. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekaraiah, T.; Panigrahi, S.P.; Sanjai, G.S.; Dulabhai, H.P.; Vijaykumar, V. Investigating Various Meshing Techniques in Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) for their Impact on Heat Transfer Parameters of Fins. J. Mines Met. Fuels 2025, 73, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Liu, L.B.; Huang, Z. Richardson extrapolation method on an adaptive grid for singularly perturbed Volterra integro-differential equations. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 2021, 42, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soori, Z.; Aminataei, A. Numerical solution of space fractional diffusion equation by spline method combined with Richardson extrapolation. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 39, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS, Inc. ANSYS Fluent 14.5 User’s Guide; ANSYS, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dabbagh, M.A.; Yuce, M.I. Simulation and comparison of helical and straight-bladed hydrokinetic turbines. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2018, 8, 504–513. [Google Scholar]
- Antar, E.; Elkhoury, M. Parametric sizing optimization process of a casing for a Savonius Vertical Axis Wind Turbine. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhna, D.B.; Benavides, O.; Grajeda, J.S.; Ramirez, S.F.; de la Cruz May, L. A parametric study of the effect of leading edge spherical tubercle amplitudes on the aerodynamic performance of a 2D wind turbine airfoil at low Reynolds numbers using computational fluid dynamics. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4184–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereu, R.; Passoni, S.; Inzoli, F. Scale-resolving CFD modeling of a thick wind turbine airfoil with application of vortex generators: Validation and sensitivity analyses. Energy 2019, 187, 115969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-quraishi, B.A.J.; Aboaltabooq, M.H.K.; AL-Fatlwe, F.M.K. A simulation investigation the performance of a small scale Elliptical Savonius wind turbine with twisting blades and sloping ends plates. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN) 2022, 10, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmousalami, H.H. Artificial intelligence and parametric construction cost estimate modeling: State-of-the-art review. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 03119008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, B. Time Series Models for Revenue Forecasting in the Semiconductor Industry: A Case Study of ASML. Master’s Thesis, Tilburg School of Economics and Management, Tilburg, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Roustaei, N. Application and interpretation of linear-regression analysis. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2024, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoe, I. Applied Regression Modeling; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, H. Testing for normality: What is the best method. ForsChem Res. Rep. 2021, 6, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mignon, V. Heteroskedasticity and Autocorrelation of Errors. In Principles of Econometrics: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 171–221. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.A.A.; Ozel, G.; Chesneau, C.; Mohsin, M.; Jamal, F.; Bhatti, M.F. A statistical study of the determinants of rice crop production in Pakistan. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 33, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đalić, I.; Terzić, S. Violation of the assumption of homoscedasticity and detection of heteroscedasticity. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2021, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyanto, S.S. Monte Carlo power comparison of seven most commonly used heteroscedasticity tests. Commun.-Stat. Comput. 2022, 51, 2065–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
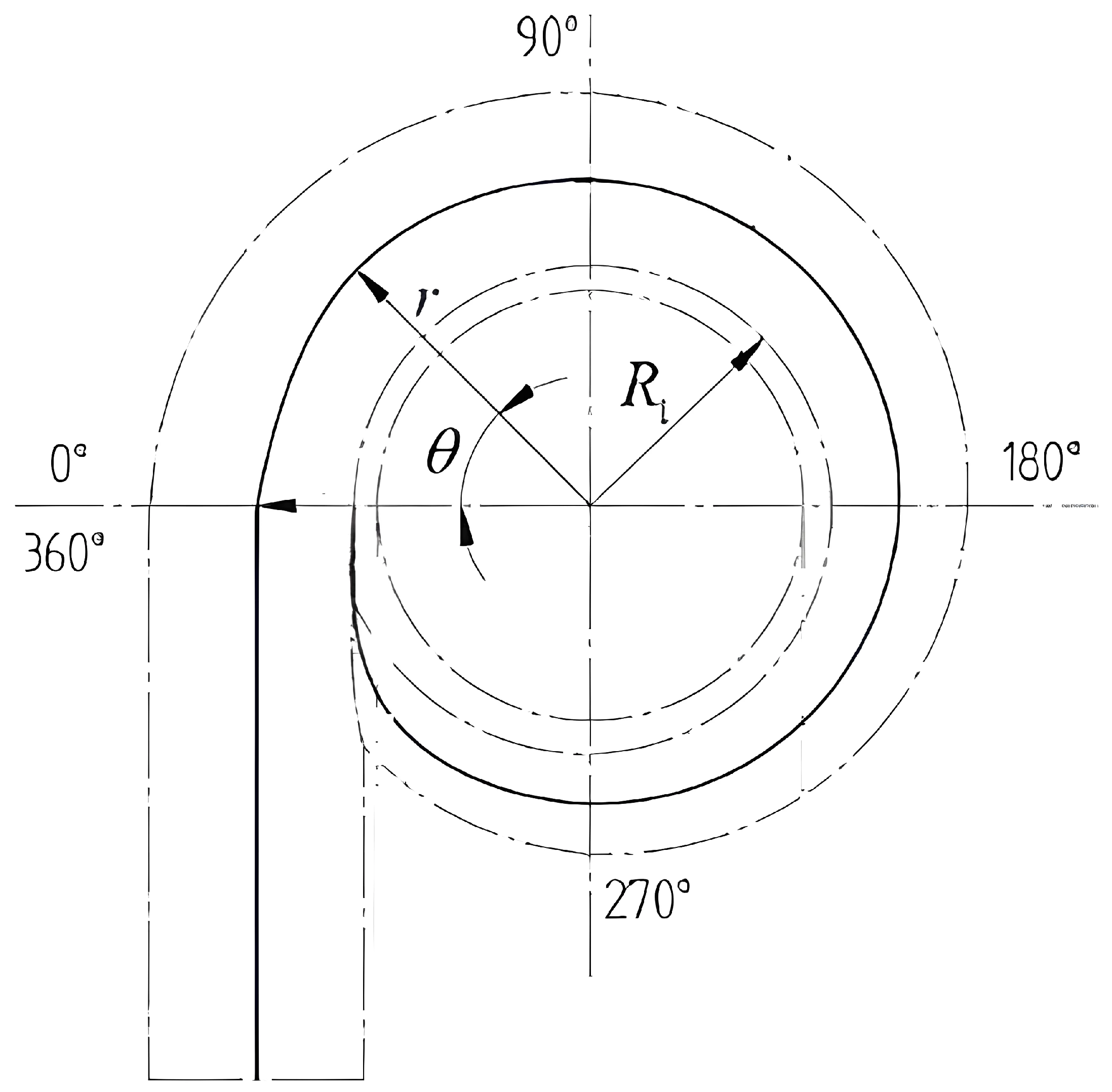
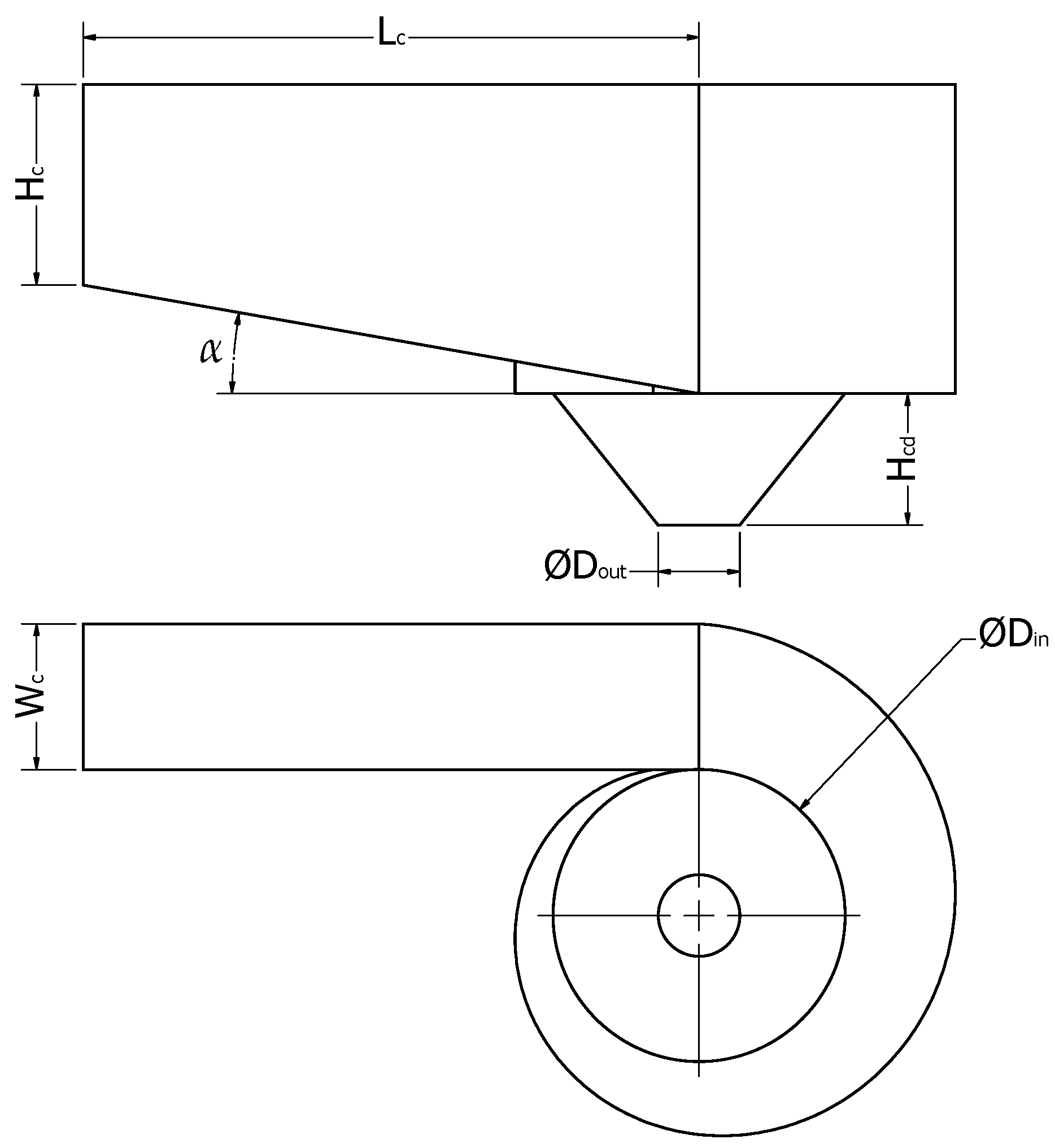
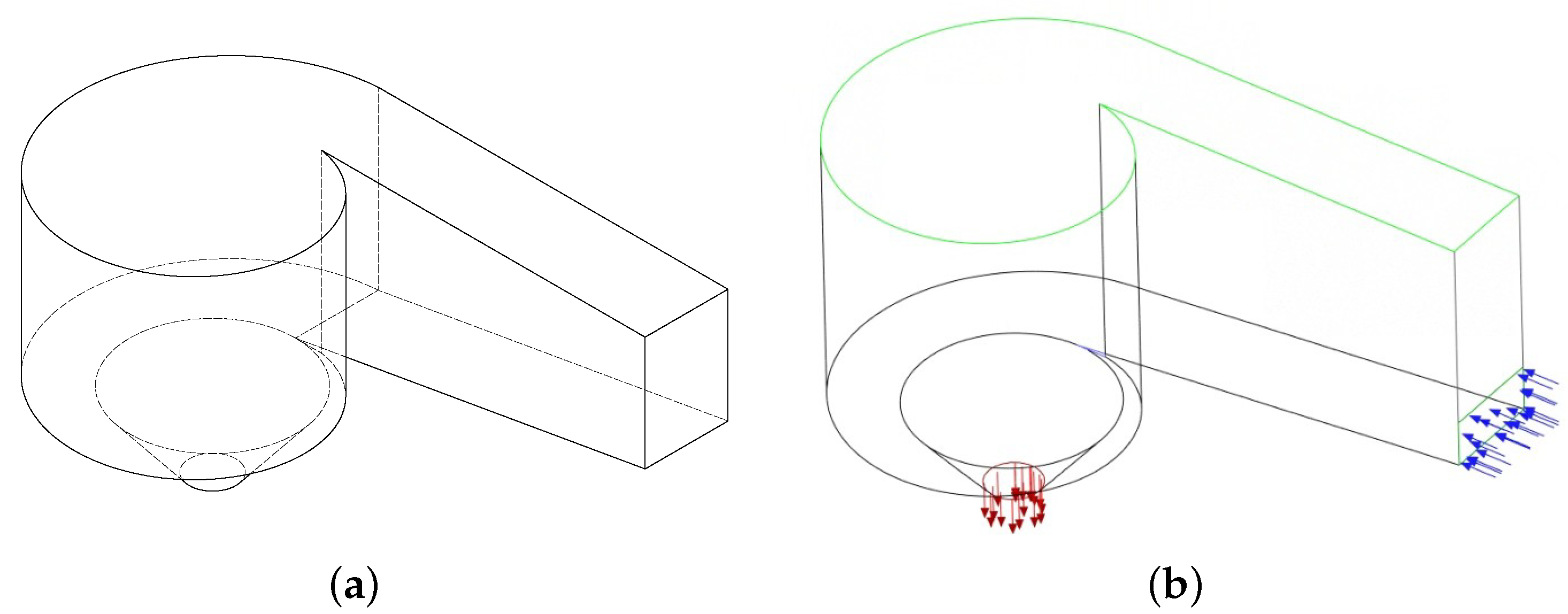
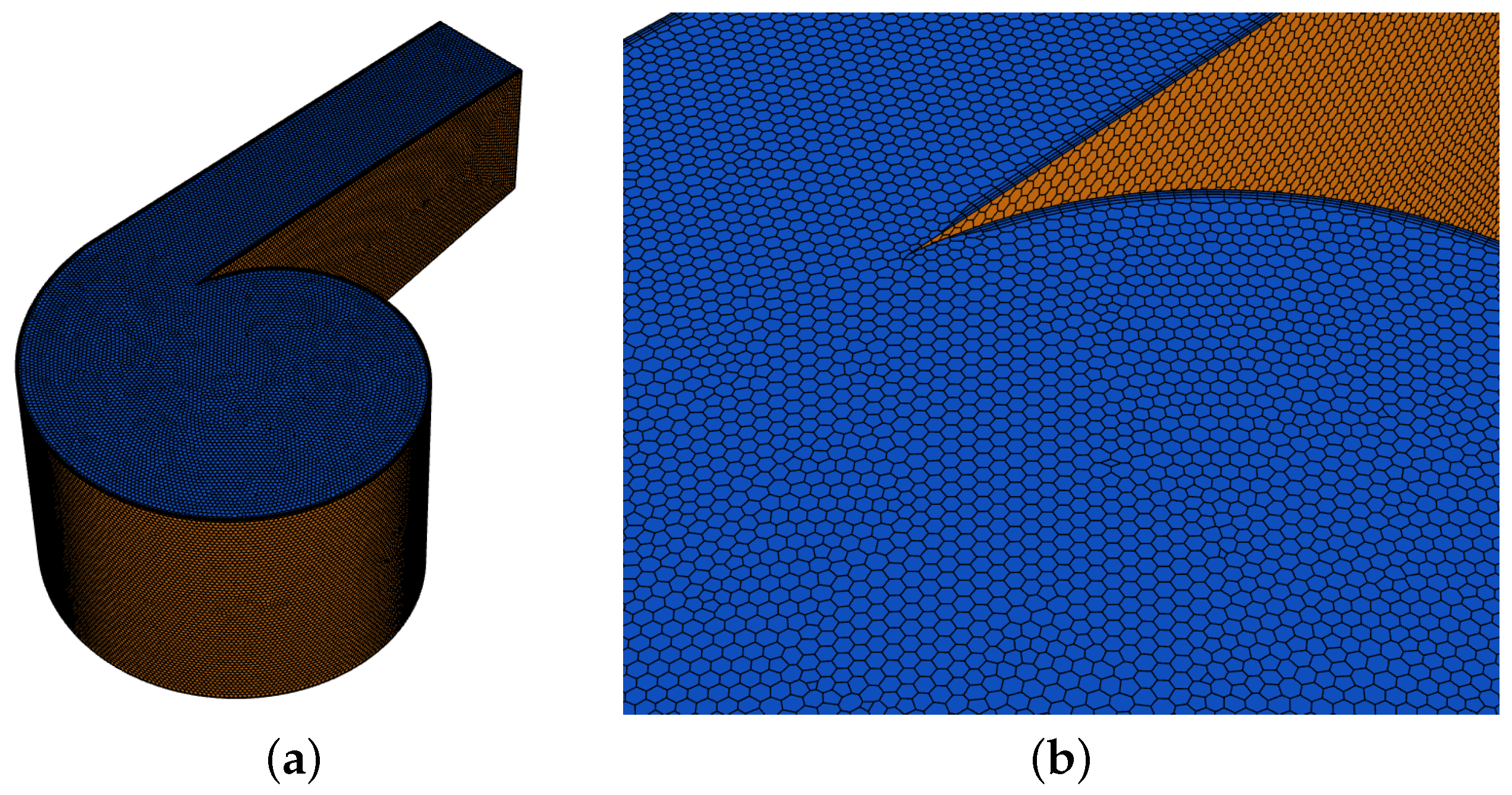


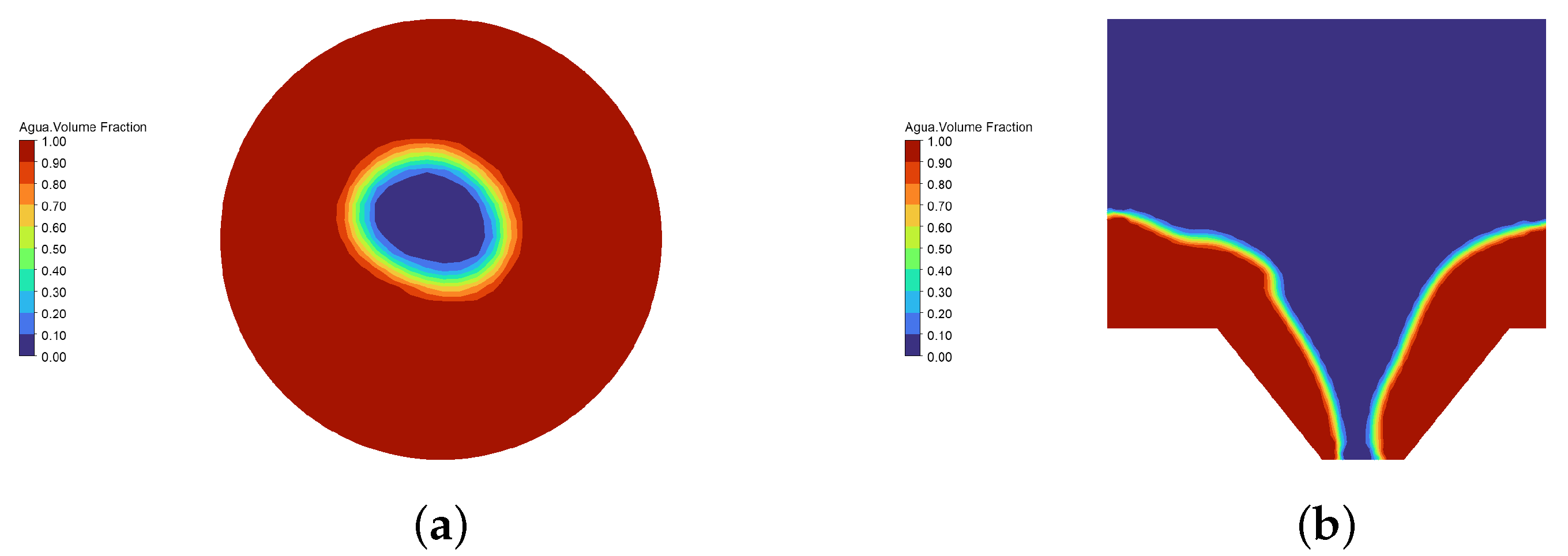
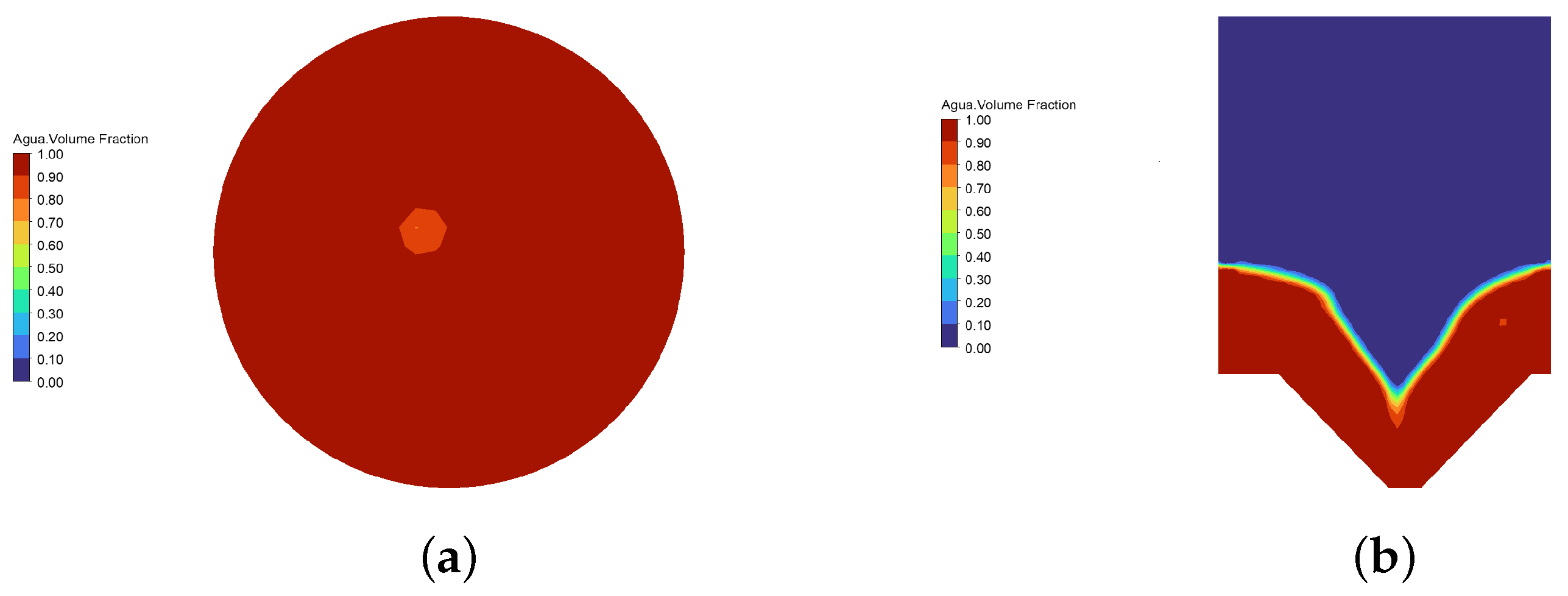
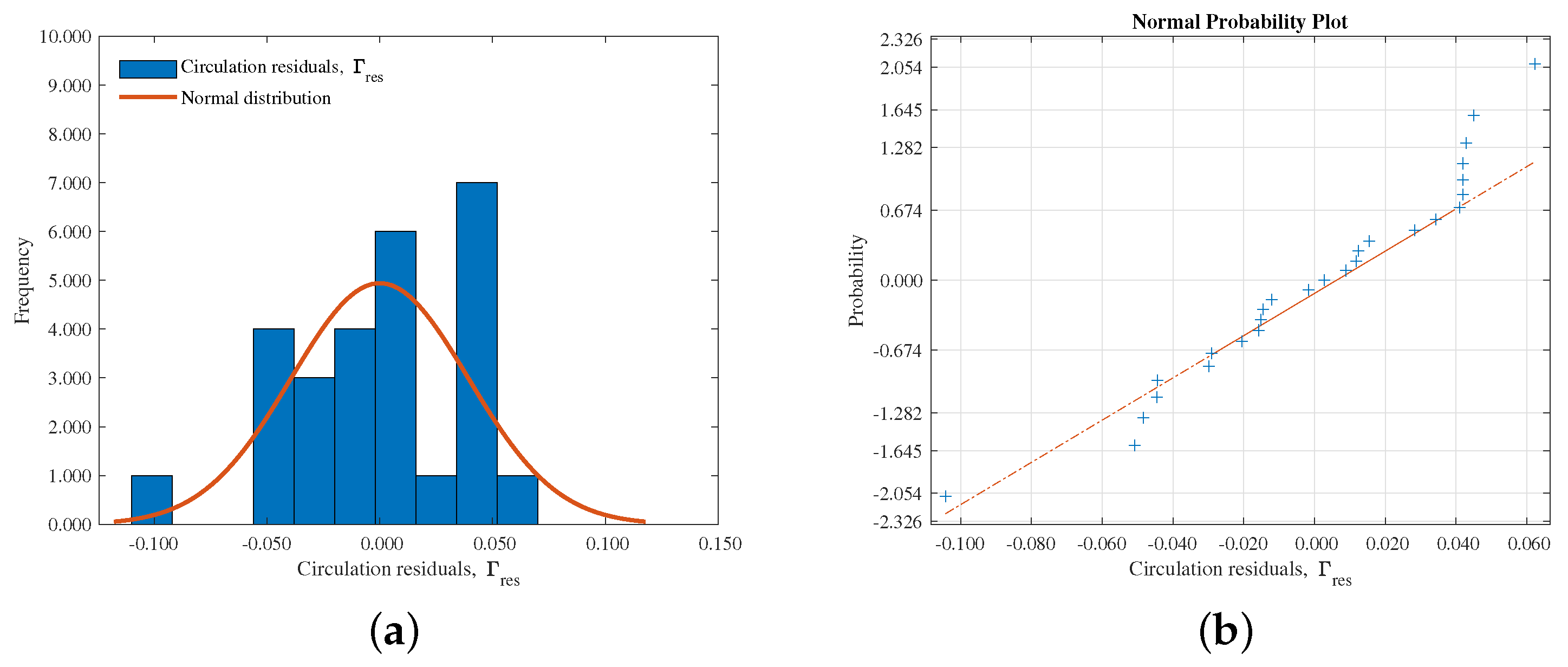
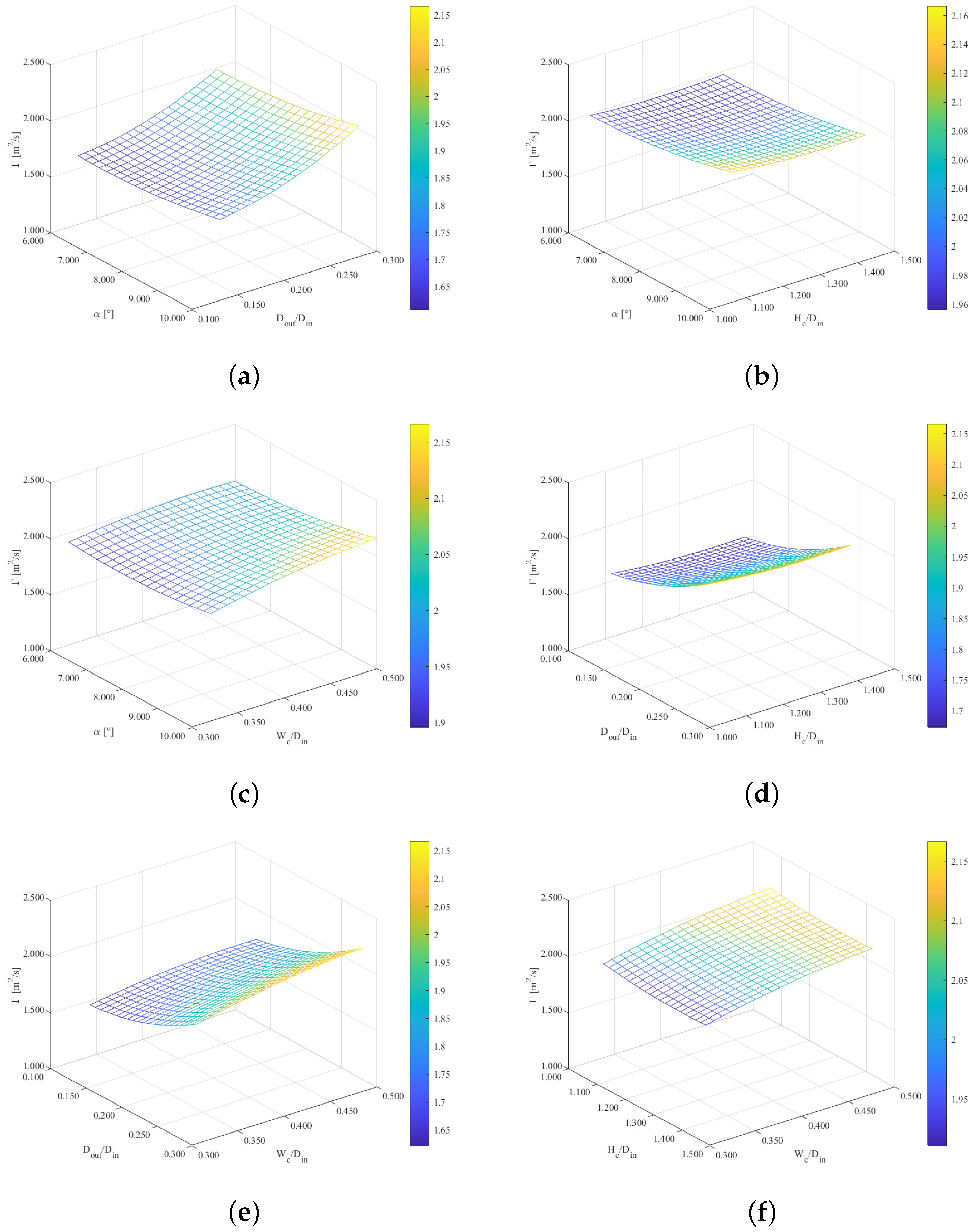

| Factor | Variable | −1 | 0 | +1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inclined angle of the channel [°] | 6 | 8 | 10 | |
| Outlet diameter ratio | 0.130 | 0.205 | 0.280 | |
| Inlet channel height ratio | 1.06 | 1.24 | 1.42 | |
| Inlet channel width ratio | 0.32 | 0.41 | 0.50 |
| Run | [°] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 0.280 | 1.42 | 0.50 |
| 2 | 6 | 0.130 | 1.42 | 0.50 |
| 3 | 8 | 0.205 | 1.24 | 0.32 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.280 | 1.06 | 0.32 |
| 5 | 6 | 0.205 | 1.42 | 0.41 |
| 6 | 8 | 0.130 | 1.06 | 0.50 |
| 7 | 10 | 0.205 | 1.06 | 0.41 |
| 8 | 10 | 0.130 | 1.42 | 0.32 |
| 9 | 10 | 0.130 | 1.06 | 0.50 |
| 10 | 10 | 0.130 | 1.06 | 0.32 |
| 11 | 8 | 0.280 | 1.24 | 0.41 |
| 12 | 6 | 0.205 | 1.24 | 0.41 |
| 13 | 6 | 0.280 | 1.06 | 0.50 |
| 14 | 6 | 0.130 | 1.06 | 0.32 |
| 15 | 10 | 0.130 | 1.42 | 0.50 |
| 16 | 6 | 0.280 | 1.42 | 0.32 |
| 17 | 10 | 0.280 | 1.06 | 0.50 |
| 18 | 10 | 0.205 | 1.24 | 0.41 |
| 19 | 10 | 0.280 | 1.06 | 0.32 |
| 20 | 6 | 0.130 | 1.42 | 0.32 |
| 21 | 10 | 0.280 | 1.42 | 0.50 |
| 22 | 8 | 0.205 | 1.24 | 0.50 |
| 23 | 10 | 0.280 | 1.42 | 0.32 |
| 24 | 8 | 0.130 | 1.24 | 0.41 |
| 25 | 8 | 0.205 | 1.24 | 0.41 |
| 26 | 8 | 0.205 | 1.24 | 0.41 |
| 27 | 8 | 0.205 | 1.24 | 0.41 |
| Run | Γ [m2/s] | % Water Phase | Γwater [m2/s] | Mass Flow [kg/s] | % Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.2268 | 0.9065 | 2.0186 | 14.7205 | 2.18% |
| 2 | 1.5919 | 0.9904 | 1.5909 | 14.7205 | 9.72% |
| 3 | 1.6963 | 0.9707 | 1.6913 | 9.4211 | 4.93% |
| 4 | 2.2411 | 0.8363 | 1.8742 | 9.4211 | 3.13% |
| 5 | 1.6760 | 0.9956 | 1.6686 | 12.0708 | 5.78% |
| 6 | 1.5975 | 0.9993 | 1.5964 | 14.7205 | 9.15% |
| 7 | 1.7535 | 0.9980 | 1.7500 | 12.0708 | 5.37% |
| 8 | 1.5569 | 0.9971 | 1.5524 | 9.4211 | 11.44% |
| 9 | 1.7779 | 0.9972 | 1.7730 | 14.7205 | 9.88% |
| 10 | 1.5777 | 0.9974 | 1.5736 | 9.4211 | 9.82% |
| 11 | 2.2774 | 0.8645 | 1.9687 | 12.0708 | 5.43% |
| 12 | 1.6919 | 0.9910 | 1.6887 | 12.0708 | 5.96% |
| 13 | 2.2274 | 0.9048 | 1.9513 | 14.7205 | 5.05% |
| 14 | 1.6752 | 0.9971 | 1.6706 | 9.4211 | 10.08% |
| 15 | 1.7239 | 0.9967 | 1.7183 | 14.7205 | 9.83% |
| 16 | 2.2419 | 0.8360 | 1.8742 | 9.4211 | 6.69% |
| 17 | 2.3762 | 0.9051 | 2.1508 | 14.7205 | 4.52% |
| 18 | 1.7750 | 0.9974 | 1.7704 | 12.0708 | 5.70% |
| 19 | 2.3626 | 0.8384 | 1.9807 | 9.4211 | 6.22% |
| 20 | 1.6316 | 0.9976 | 1.6277 | 9.4211 | 10.00% |
| 21 | 2.2934 | 0.9152 | 2.0990 | 14.7205 | 4.87% |
| 22 | 1.6154 | 0.9991 | 1.6140 | 14.7205 | −0.83% |
| 23 | 2.3357 | 0.8254 | 1.9280 | 9.4211 | 1.17% |
| 24 | 1.5506 | 0.9975 | 1.5467 | 12.0708 | 0.14% |
| 25 | 1.7532 | 0.9972 | 1.7484 | 12.0708 | 5.88% |
| 26 | 1.7532 | 0.9972 | 1.7484 | 12.0708 | 5.88% |
| 27 | 1.7532 | 0.9972 | 1.7484 | 12.0708 | 5.88% |
| Term | Effect | Df | SS | MS | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0194 | 0.0194 | 5.831 | 0.03263 | ||
| 1 | 0.5903 | 0.5903 | 176.976 | |||
| 1 | 0.0052 | 0.0052 | 1.569 | 0.2342 | ||
| 1 | 0.0359 | 0.0359 | 10.760 | 0.00658 | ||
| 1 | 0.0435 | 0.0435 | 13.027 | 0.00358 | ||
| 1 | 0.0157 | 0.0157 | 4.693 | 0.05112 | ||
| 1 | 0.0006 | 0.0006 | 0.173 | 0.68485 | ||
| 1 | 0.0028 | 0.0028 | 0.833 | 0.37945 | ||
| 1 | 0.0037 | 0.0037 | 1.121 | 0.31055 | ||
| 1 | 0.0011 | 0.0011 | 0.345 | 0.56802 | ||
| 1 | 0.0177 | 0.0177 | 5.298 | 0.04008 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0.92169 | ||
| 1 | 0.0087 | 0.0087 | 2.597 | 0.13306 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.97191 | ||
| Residuals | - | 12 | 0.04 | 0.0033 | - | - |
| 0.9871 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Adjusted | 0.9777 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Test Name | p-Value | Test Statistic |
|---|---|---|
| Shapiro–Francia Test | 0.1715 | 0.9484 |
| Anderson–Darling Test | 0.2890 | 0.4417 |
| Shapiro–Wilk Test | 0.2039 | 0.9491 |
| Cramer–Von Mises Test | 0.4486 | 0.0544 |
| Jarque–Bera Test | 0.5027 | 1.3757 |
| KS Lilliefors Modification | 0.2000 | 0.1114 |
| KS Limiting Form | 0.8907 | 0.5791 |
| KS Marsaglia Method | 0.8543 | 0.5791 |
| Flow Rate [L/s] | Flow Rate [m3/s] | Power [W] |
|---|---|---|
| 3.3 | 0.0033 | 11.4114 |
| 5.6 | 0.0056 | 19.3649 |
| 7.6 | 0.0076 | 26.2809 |
| 8.3 | 0.0083 | 28.7016 |
| 8.9 | 0.0089 | 30.7764 |
| 9.4 | 0.0094 | 32.5054 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez, R.; Velásquez, L.; Rubio-Clemente, A.; Chica, E. Design Optimization of an Inclined Inlet Channel, an Archimedean Spiral Basin, and a Discharge Cone in a Gravitational Vortex Turbine. Processes 2025, 13, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051533
Gómez R, Velásquez L, Rubio-Clemente A, Chica E. Design Optimization of an Inclined Inlet Channel, an Archimedean Spiral Basin, and a Discharge Cone in a Gravitational Vortex Turbine. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051533
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez, Rubén, Laura Velásquez, Ainhoa Rubio-Clemente, and Edwin Chica. 2025. "Design Optimization of an Inclined Inlet Channel, an Archimedean Spiral Basin, and a Discharge Cone in a Gravitational Vortex Turbine" Processes 13, no. 5: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051533
APA StyleGómez, R., Velásquez, L., Rubio-Clemente, A., & Chica, E. (2025). Design Optimization of an Inclined Inlet Channel, an Archimedean Spiral Basin, and a Discharge Cone in a Gravitational Vortex Turbine. Processes, 13(5), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051533








