Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Air Quality Prediction: A Case Study in Macau
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of Macau AQI
1.2. Health Effects of Air Pollution
1.3. Novelty and Objective of This Work
2. Materials and Methods
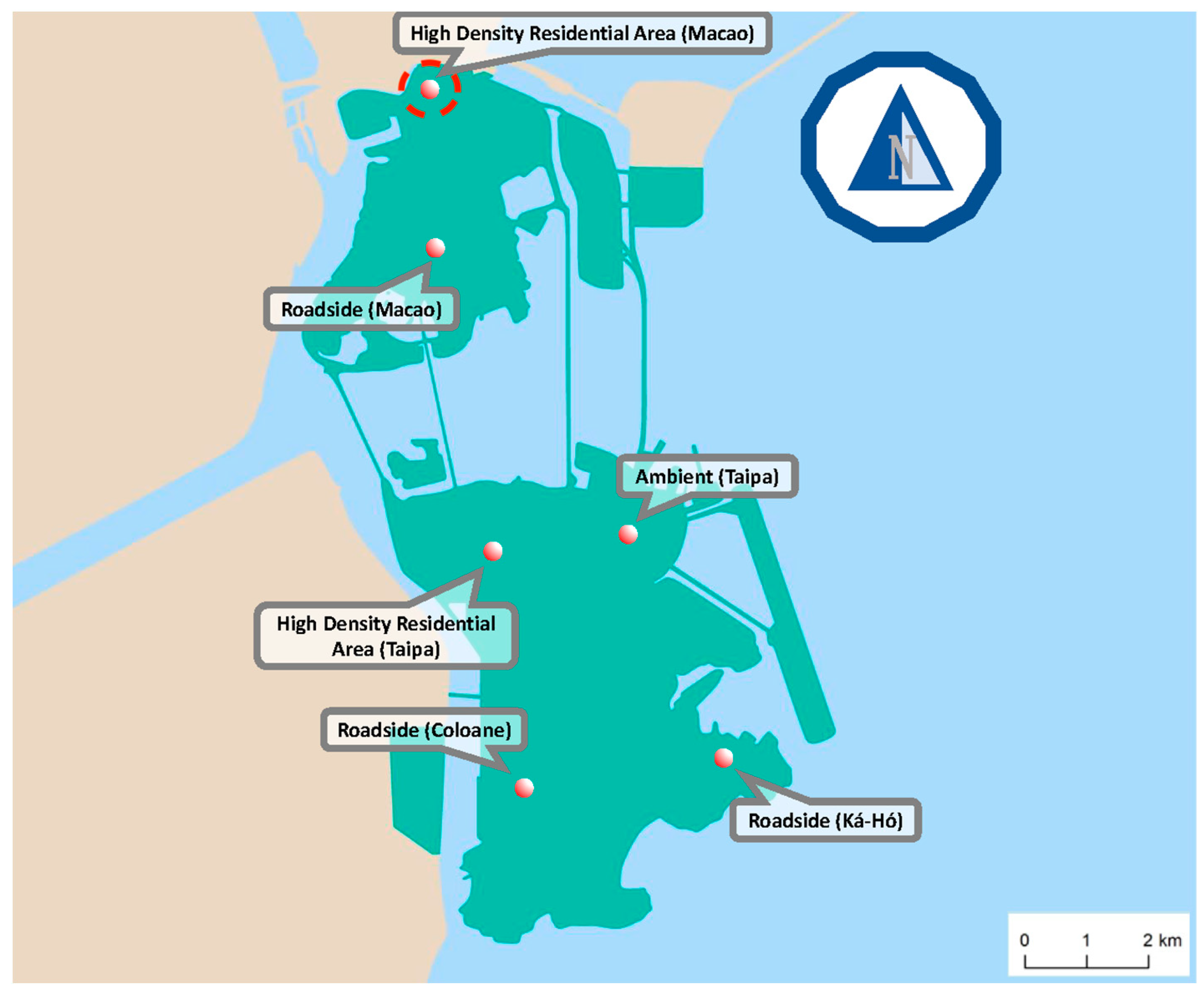
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Study Workflow
2.3. Variable Predictors, Model Parameters, and Hyperparameters
2.4. Learning Algorithm
2.5. Model Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussions
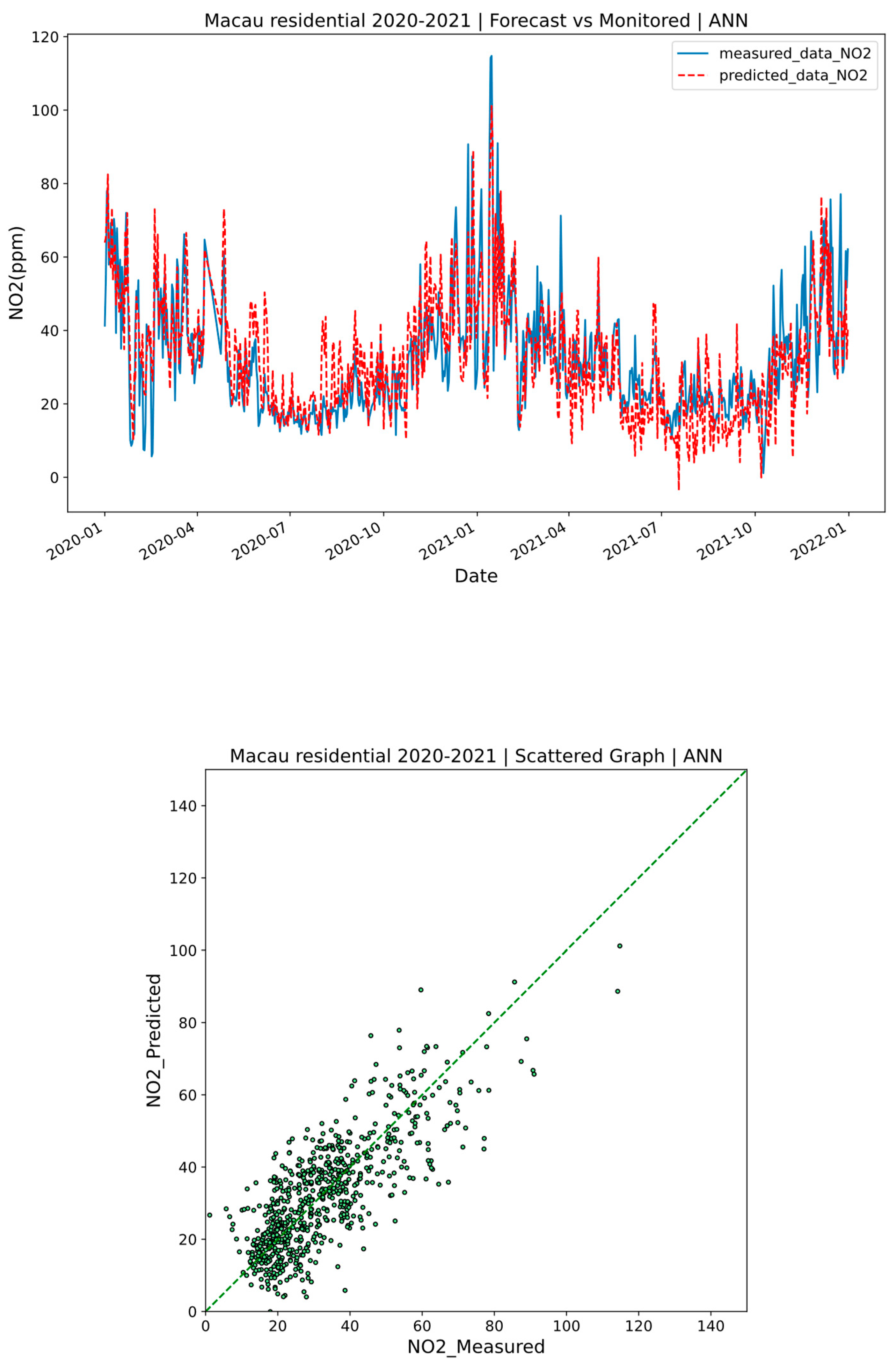
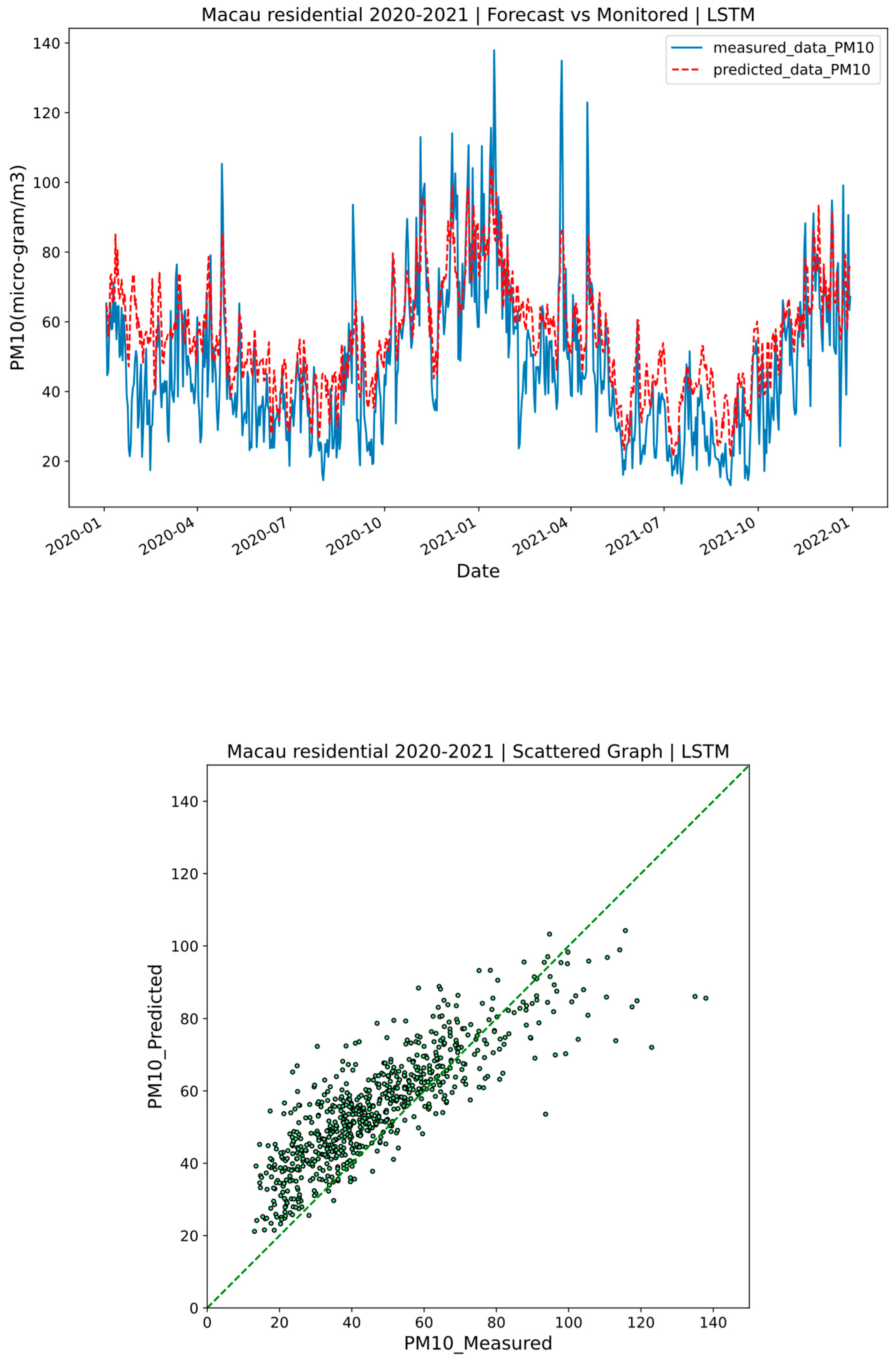
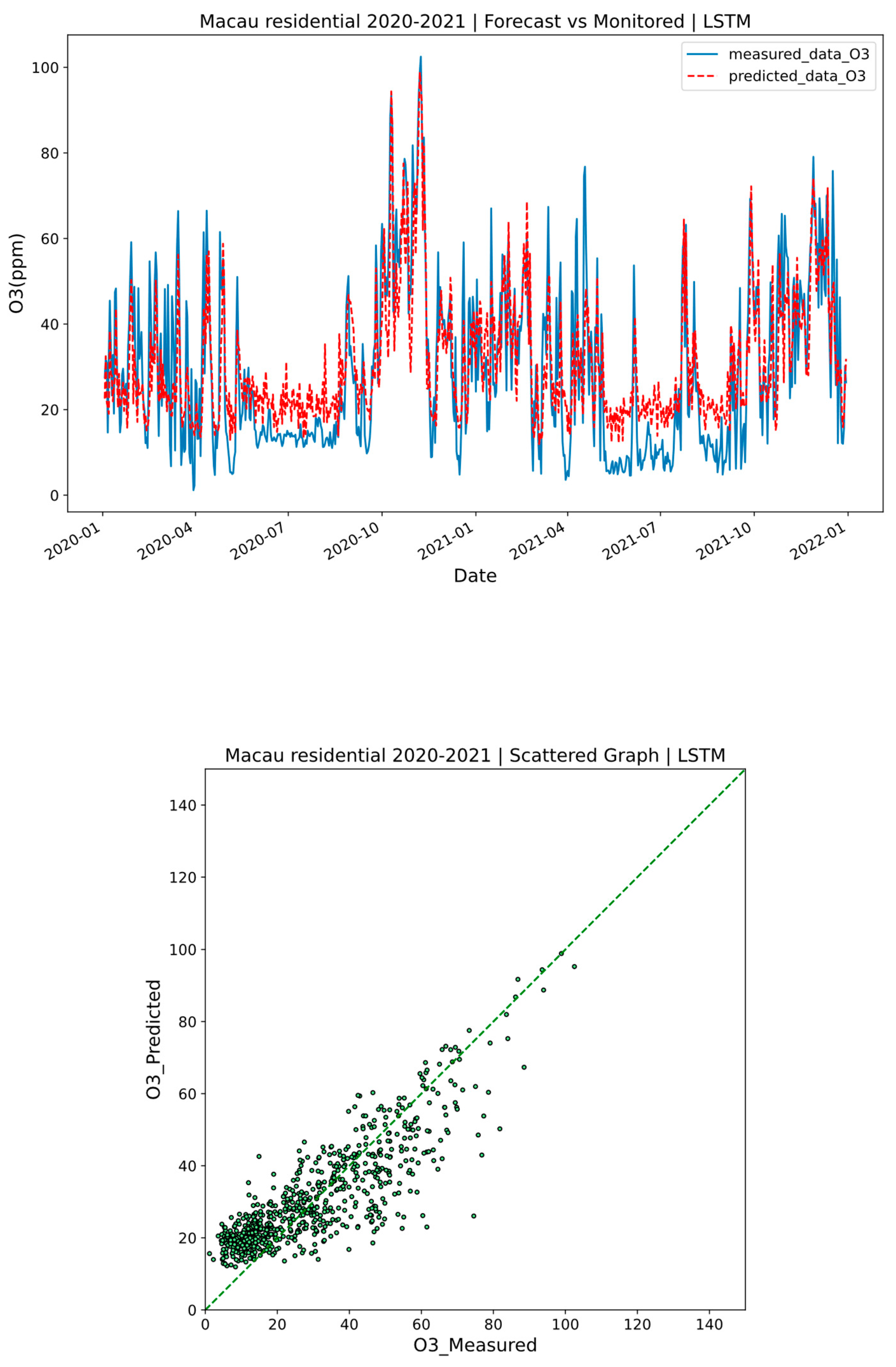
3.1. Performance of the Models
3.2. Standard Deviation of the Models
3.3. Comparison to Previous Works
3.4. Limitations and Mitigation Strategies
3.5. Implications for Air Quality Management and Public Health Protection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SMG. Definition of Air Quality Index; SMG: Macao, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics and Census Service (DSEC). Tourism Statistics: Whole Year and 4th Quarter of 2024. 2024. Available online: https://www.dsec.gov.mo/getAttachment/6dc2a848-1201-4d87-99ea-3ee4a18c90ba/E_TUR_FR_2024_Q4.aspx (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Statistics and Census Service (DSEC). Transport and Communication Statistics. Number of Licensed Motor Vehicles. 2024. Available online: https://www.dsec.gov.mo/getAttachment/1553b21c-97cb-4ea1-985c-83a972a85d9f/E_ETC_FR_2024_M12.aspx (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Statistics and Census Service (DSEC). Gross Domestic Product: 4th Quarter of 2024. 2024. Available online: https://www.dsec.gov.mo/getAttachment/1dbae334-44e8-4699-b672-4ec7667282b2/E_PIB_FR_2024_Q4.aspx (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines. 2021. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/345329/9789240034228-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Macau Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau (SMG). Macau Air Quality Monitoring Statistics Annual Report 2024. 2024. Available online: https://cms.smg.gov.mo/uploads/sync/pdf/AIR_report/c_IQA_annual_report/IQA_2024.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Anggraini, T.S.; Irie, H.; Sakti, A.D.; Wikantika, K. Machine learning-based global air quality index development using remote sensing and ground-based stations. Environ. Adv. 2024, 15, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glencross, D.A.; Ho, T.R.; Camiña, N.; Hawrylowicz, C.M.; Pfeffer, P.E. Air pollution and its effects on the immune system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conibear, L.; Reddington, C.L.; Silver, B.J.; Arnold, S.R.; Turnock, S.T.; Klimont, Z.; Spracklen, D.V. The contribution of emission sources to the future air pollution disease burden in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 064027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusworth, D.H.; Mickley, L.J.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Liu, T.; Marlier, M.E.; Defries, R.S.; Guttikunda, S.K.; Gupta, P. Quantifying the influence of agricultural fires in northwest India on urban air pollution in Delhi, India. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 044018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Gulia, S.; Goyal, S.K. Review of land use specific source contributions in PM 2.5 concentration in urban areas in India. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Feng, C.; Jia, X. Effects of dust emissions from wind erosion of soil on ambient air quality. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, B.S.; Latha, R.; Tiwari, A.; Rathod, A.; Singh, S.; Beig, G. Impact of mixing layer height on air quality in winter. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 197, 105157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Giagloglou, E.; Steinle, S.; Davis, A.; Sleeuwenhoek, A.; Galea, K.S.; Dixon, K.; Crawford, J.O. Indoor exposure to selected air pollutants in the home environment: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.A. Local integrated air quality predictions from meteorology (2015 to 2020) with machine and deep learning assisted by data mining. Sustain. Anal. Model. 2022, 2, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, C.A.; Mazei, Y.; Saldaev, D.; Efstathiou, M.; Voronova, T.; Xue, Y. Nowcasting of air pollution episodes in megacities: A case study for Athens, Greece. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almetwally, A.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Allam, A.A. Ambient air pollution and its influence on human health and welfare: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24815–24830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.M.T.; Siu, S.W.I.; Monjardino, J.; Mendes, L.; Ferreira, F. Using Machine Learning Methods to Forecast Air Quality: A Case Study in Macao. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrabadi, S.; Adão, T.; Peres, E.; Morais, R.; Magalhães, L.G.; Alves, V. Automatic Optimization of Deep Learning Training through Feature-Aware-Based Dataset Splitting. Algorithms 2024, 17, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumailov, I.; Shumaylov, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Papernot, N.; Anderson, R.; Gal, Y. AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data. Nature 2024, 631, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Yang, B.; Brauer, M.; Zhang, K.M. Enhancing the evaluation and interpretability of data-driven air quality models. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.M.T.; Cai, J.; Molla, A.H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Kong, S.S.-K. Evaluation of Machine Learning Models in Air Pollution Prediction for a Case Study of Macau as an Effort to Comply with UN Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, G. A hybrid deep learning model to forecast particulate matter concentration levels in Seoul, South Korea. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.R.; Jahani, A.; Kalantary, S.; Moeinaddini, M.; Khorasani, N. The evaluation on artificial neural networks (ANN) and multiple linear regressions (MLR) models for predicting SO2 concentration. Urban Clim. 2021, 37, 100837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Ding, Y.; Lin, C.; Xu, Z. Air quality prediction at new stations using spatially transferred bi-directional long short-term memory network. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, V.; Geetha, P.; Vinayakumar, R.; Soman, K.P. DeepAirNet: Applying Recurrent Networks for Air Quality Prediction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, G. A Deep Spatial-Temporal Ensemble Model for Air Quality Prediction. Neurocomputing 2018, 314, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheja, S.; Malik, S. Prediction of Air Quality Using LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. Int. J. Softw. Innov. 2022, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Shores, K.; Xu, Y. A Comparison of Machine Learning-Based Approaches in Estimating Surface PM2.5 Concentrations Focusing on Artificial Neural Networks and High Pollution Events. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamsing, P.; Cao, C.; Boonpook, W.; Boonprong, S.; Xu, M.; Boonsrimuang, P. Artificial Neural Network for Air Pollutant Concentration Predictions Based on Aircraft Trajectories over Suvarnabhumi International Airport. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratković, K.; Kovač, N.; Simeunović, M. Hybrid LSTM Model to Predict the Level of Air Pollution in Montenegro. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esager, M.W.M.; Ünlü, K.D. Forecasting Air Quality in Tripoli: An Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Hourly PM2.5 Surface Mass Concentrations. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navares, R.; Aznarte, J.L. Predicting air quality with deep learning LSTM: Towards comprehensive models. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xayasouk, T.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, G. Air pollution prediction using long short-term memory (LSTM) and deep autoencoder (DAE) models. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Bingchun, L.; Jiali, C.; Xiaogang, Y. Air Quality Index Prediction Based on a Long Short-Term Memory Artificial Neural Network Model. J. Comput. 2023, 34, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zhan, Y.; Yang, F. A review of machine learning for modeling air quality: Overlooked but important issues. Atmos. Res. 2024, 300, 107261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Garuda, S.; Vogt, U.; Yang, B. Air pollution prediction using machine learning techniques—An approach to replace existing monitoring stations with virtual monitoring stations. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 310, 119987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, A.; Karakuş, O. Predicting air quality via multimodal AI and satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 293, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Cheng, W.; Xu, Z.; Kalam, A. Outlier Detection of Air Quality for Two Indian Urban Cities Using Functional Data Analysis. Open J. Air Pollut. 2023, 12, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.M.T.; Ng, S.C.W.; Siu, S.W.I. Application of ANN, XGBoost, and Other ML Methods to Forecast Air Quality in Macau. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdou, A.; El Badisy, I.; Khomsi, K.; Abdala, S.A.; Abdulla, F.; Najmi, H.; Obtel, M.; Belyamani, L.; Ibrahimi, A.; Khalis, M. Interpretable Machine Learning Approaches for Forecasting and Predicting Air Pollution: A Systematic Review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2024, 24, 230151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Khan, S.; Mohyuddin, A.; Haider, A.; Lei, T.M.T.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Zhang, D.; Anouzla, A.; Aziz, F.; et al. Technological solutions for air pollution control to mitigate climate change: An approach to facilitate global transition toward blue sky and net-zero emission. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 6843–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, M.; Fowler, D.; Monks, P.S.; Reis, S.; Rudich, Y.; Williams, M.L.; Fuzzi, S. Air quality and climate change: Designing new win-win policies for Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 65, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadipoor, M.; Keivanimehr, F.; Baghban, A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Habibzadeh, S. Carbon dioxide as a main source of air pollution: Prospective and current trends to control. In Sorbents Materials for Controlling Environmental Pollution; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 623–688. [Google Scholar]
- Afifa Arshad, K.; Hussain, N.; Ashraf, M.H.; Saleem, M.Z. Air pollution and climate change as grand challenges to sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofremu, G.O.; Raimi, B.Y.; Yusuf, S.O.; Dziwornu, B.A.; Nnabuife, S.G.; Eze, A.M.; Nnajiofor, C.A. Exploring the Relationship between Climate Change, Air Pollutants and Human Health: Impacts, Adaptation, and Mitigation Strategies. Green Energy Resour. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kinnon, M.M. Editorial: Air pollution and climate change: Interactions and co-mitigation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Chandra, I.; Lei, T.M.T. Modeling PM10 Emissions in Quarry and Mining Operations: Insights from AERMOD Applications in Malaysia. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailenko, V.; Nitsenko, V.S.; Gerasymchuk, N.; Sambulov, A.; Demchuk, V. Air pollution by persistent organic pollutants from organic fuel combustion by stationary sources: The case of the Odesa agglomeration. Environ. Syst. Res. 2024, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar Attiq, A.; Nawaz, R.; Atif Irshad, M.; Nasim, I.; Nasim, M.; Latif, M.; Hussain Shah, S.I.; Fatima, A. Urban Air Quality Nexus: PM2.5 Bound-Heavy Metals and their Alarming Implication for Incremental Lifetime Cancer Risk. Pollution 2024, 10, 580–594. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor-Fernández, A.; Lama-Ruiz, J.-R.; Otero-Mateo, M.; Narváez, A.C.; Ramírez-Peña, M.; Alzola, A.S. Air Quality Assessment During the Initial Implementation Phase of a Traffic-Restricted Zone in an Urban Area: A Case Study Based on NO2 Levels in Seville, Spain. Processes 2025, 13, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banciu, C.; Florea, A.; Bogdan, R. Monitoring and Predicting Air Quality with IoT Devices. Processes 2024, 12, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodić, M.; Rajs, V.; Vasiljević Toskić, M.; Bajić, J.; Batinić, B.; Arbanas, M. Methods of Measuring Air Pollution in Cities and Correlation of Air Pollutant Concentrations. Processes 2023, 11, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Air Pollutants | WHO AQG 2021 (in µg/m3) | MAQI 2024 (in µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 15.0 | 42.4 |
| PM2.5 | 5.0 | 20.2 |
| SO2 | 40.0 | 4.8 |
| NO2 | 10.0 | 43.2 |
| O3 | 60.0 | 66.5 |
| CO | 4.0 | 0.9 |
| Pollutant | Number of Instances of the Training Set (Entries of Daily Concentrations) | Number of Instances of the Test Set (Entries of Daily Concentrations) | Total (Entries of Daily Concentrations) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 1500 | 726 | 2226 |
| PM2.5 | 1486 | 726 | 2212 |
| NO2 | 1502 | 726 | 2228 |
| O3 | 1546 | 726 | 2272 |
| SO2 | 1489 | 726 | 2215 |
| CO | 1563 | 726 | 2289 |
| Categories of Data | Parameters | Description of Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Air Variables | PM10, PM2.5, NO2, O3, SO2, CO | Hourly mean concentration readings (micrograms per cubic meter) |
| 16D1, 23D0, 23D1, 23D2, 23D3 | 16D1: The average 24 h concentration period from 4:00 pm of D1 to 3:00 pm of D0 23D0: The average 24 h concentration period between 12:00 am and 11:59 pm of D0 23D1: The average 24 h concentration period between 12:00 am and 11:59 pm of D1 23D2: The average 24 h concentration period between 12:00 am and 11:59 pm of D2 23D3: The average 24 h concentration period between 12:00 am and 11:59 pm of D3 | |
| D0, D1, D2, D3 | D0: Day of Prediction; D1: One Day Before Day of Prediction; D2: Two Days Before Day of Prediction; D3: Three Days Before Day of Prediction | |
| Weather Variables | H1000, H850, H700, H500 | Geopotential height at 1000, 850, 700, and 500 hectopascals (in meters) |
| TAR925, TAR850, TAR700 | Temperature of Air at 925, 850, and 700 Hectopascals (in Celsius) | |
| HR925, HR850, HR700 | Relative humidity at 925, 850, and 700 hectopascal (in percentage) | |
| TD925, TD850, TD700 | Temperature of Dew point at 925, 850, and 700 (in Celsius) | |
| THI850, THI700, THI500 | Thickness of Air at 850, 700, and 500 Hectopascals (in meters) | |
| STB925, STB850, STB700 | Stability of Air at 925, 850, and 700 hectopascal (in Celsius) | |
| T_AIR_MX, T_AIR_MD, T_AIR_MN | Temperature of Air (max, average, and min) (in Celsius) | |
| HRMX, HRMD, HRMN | Relative Humidity (max, average, and min) (in percentage) | |
| TD_MD | Average Temperature of Dew Point (in Celsius) | |
| RRTT | Wet Deposition (in mm) | |
| VMED | Average Speed of Wind (in m/s) | |
| PREV_WDIR | Prevailing direction of wind (in degree) | |
| Other Variables | DD | Hours of Sunshine in a day (in hour) |
| FF | Weekday or Weekend: weekday = 0 and weekend = 1 |
| Models | Model Parameters and Hyperparameters | |
|---|---|---|
| ANN | learning rate | 0.0005 |
| epochs | 100 | |
| batch_size | 32 | |
| validation split | 0.3 | |
| LSTM | optimizer | adam |
| epochs | 20 | |
| batch size | 64 | |
| Model | Pollutant | Model Performance Indicator | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB (µg/m3) | MFB (µg/m3) | RMSE (µg/m3) | MAE (µg/m3) | PCC (r) | KTC | ||
| ANN | PM10 | 4.59 | 0.11 | 15.42 | 11.83 | 0.84 | 0.66 |
| PM2.5 | 3.91 | 0.26 | 11.05 | 8.78 | 0.76 | 0.56 | |
| NO2 | 6.05 | 0.13 | 10.34 | 7.71 | 0.83 | 0.61 | |
| O3 | −8.02 | 0.43 | 16.70 | 13.05 | 0.76 | 0.56 | |
| SO2 | 0.04 | −0.05 | 2.36 | 1.89 | 0.70 | 0.50 | |
| CO | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.77 | 0.58 | |
| LSTM | PM10 | 6.62 | 0.18 | 13.44 | 10.89 | 0.87 | 0.70 |
| PM2.5 | 8.25 | 0.54 | 10.02 | 8.72 | 0.84 | 0.65 | |
| NO2 | 7.04 | 0.26 | 11.52 | 9.62 | 0.83 | 0.59 | |
| O3 | 4.90 | 0.29 | 11.60 | 9.71 | 0.85 | 0.63 | |
| SO2 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 1.44 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.66 | |
| CO | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.82 | 0.62 | |
| Model | Pollutant | Model Performance Indicator | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB (µg/m3) | MFB (µg/m3) | RMSE (µg/m3) | MAE (µg/m3) | PCC (r) | KTC | ||
| ANN | PM10 | 4.38 | 0.10 | 4.35 | 3.49 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| PM2.5 | 0.94 | 0.05 | 4.64 | 3.90 | 0.07 | 0.07 | |
| NO2 | 3.07 | 0.06 | 2.81 | 2.15 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| O3 | 3.76 | 1.71 | 5.96 | 4.56 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| SO2 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.07 | 0.07 | |
| CO | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.03 | |
| LSTM | PM10 | 1.16 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 1.09 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| PM2.5 | 0.85 | 0.03 | 1.75 | 1.68 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| NO2 | 2.30 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.03 | 0.09 | |
| O3 | 1.07 | 0.04 | 1.29 | 1.17 | 0.02 | 0.04 | |
| SO2 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.08 | 0.07 | |
| CO | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, T.M.T.; Cai, J.; Cheng, W.-H.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Molla, A.H.; Mohd Nadzir, M.S.; Kong, S.S.-K.; Chen, L.-W.A. Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Air Quality Prediction: A Case Study in Macau. Processes 2025, 13, 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051507
Lei TMT, Cai J, Cheng W-H, Kurniawan TA, Molla AH, Mohd Nadzir MS, Kong SS-K, Chen L-WA. Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Air Quality Prediction: A Case Study in Macau. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051507
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Thomas M. T., Jianxiu Cai, Wan-Hee Cheng, Tonni Agustiono Kurniawan, Altaf Hossain Molla, Mohd Shahrul Mohd Nadzir, Steven Soon-Kai Kong, and L.-W. Antony Chen. 2025. "Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Air Quality Prediction: A Case Study in Macau" Processes 13, no. 5: 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051507
APA StyleLei, T. M. T., Cai, J., Cheng, W.-H., Kurniawan, T. A., Molla, A. H., Mohd Nadzir, M. S., Kong, S. S.-K., & Chen, L.-W. A. (2025). Application of Deep Learning Techniques for Air Quality Prediction: A Case Study in Macau. Processes, 13(5), 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051507









