Combined Removal of NOx and SO2 in Circulating Fluidized Beds with Post-Combustion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Fuel Characteristics
2.2. Test Platform
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Experimental Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. NOx and SO2 Emissions with Sorbent Addition: Conventional vs. Post-Combustion
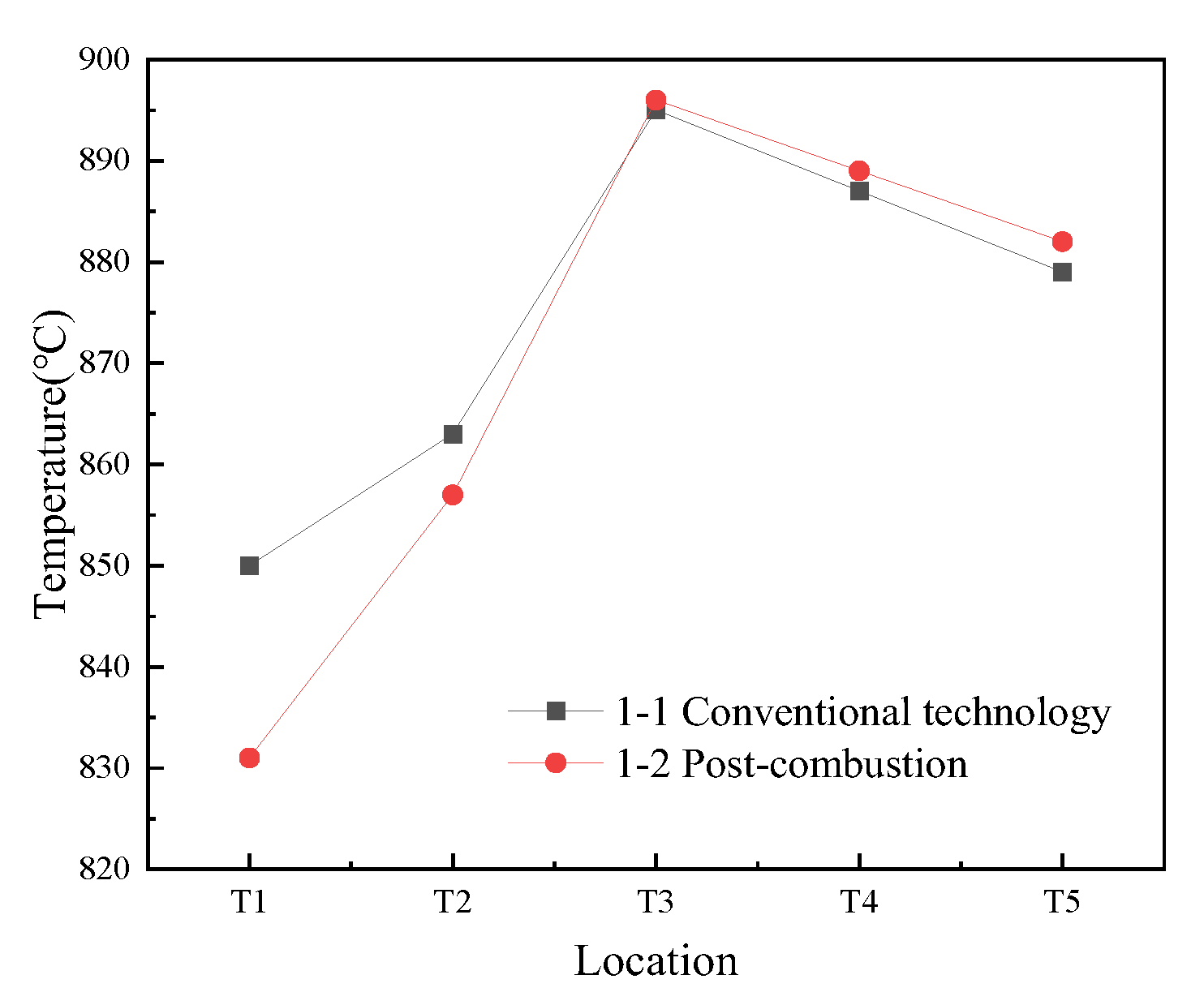
3.1.1. Temperature Profile in the CFB Furnace
3.1.2. NOx and SO2 Emissions with Sorbent Addition Under Both Combustion Methods
3.2. NOx and SO2 Emissions with Sorbent Addition: Conventional vs. Post-Combustion
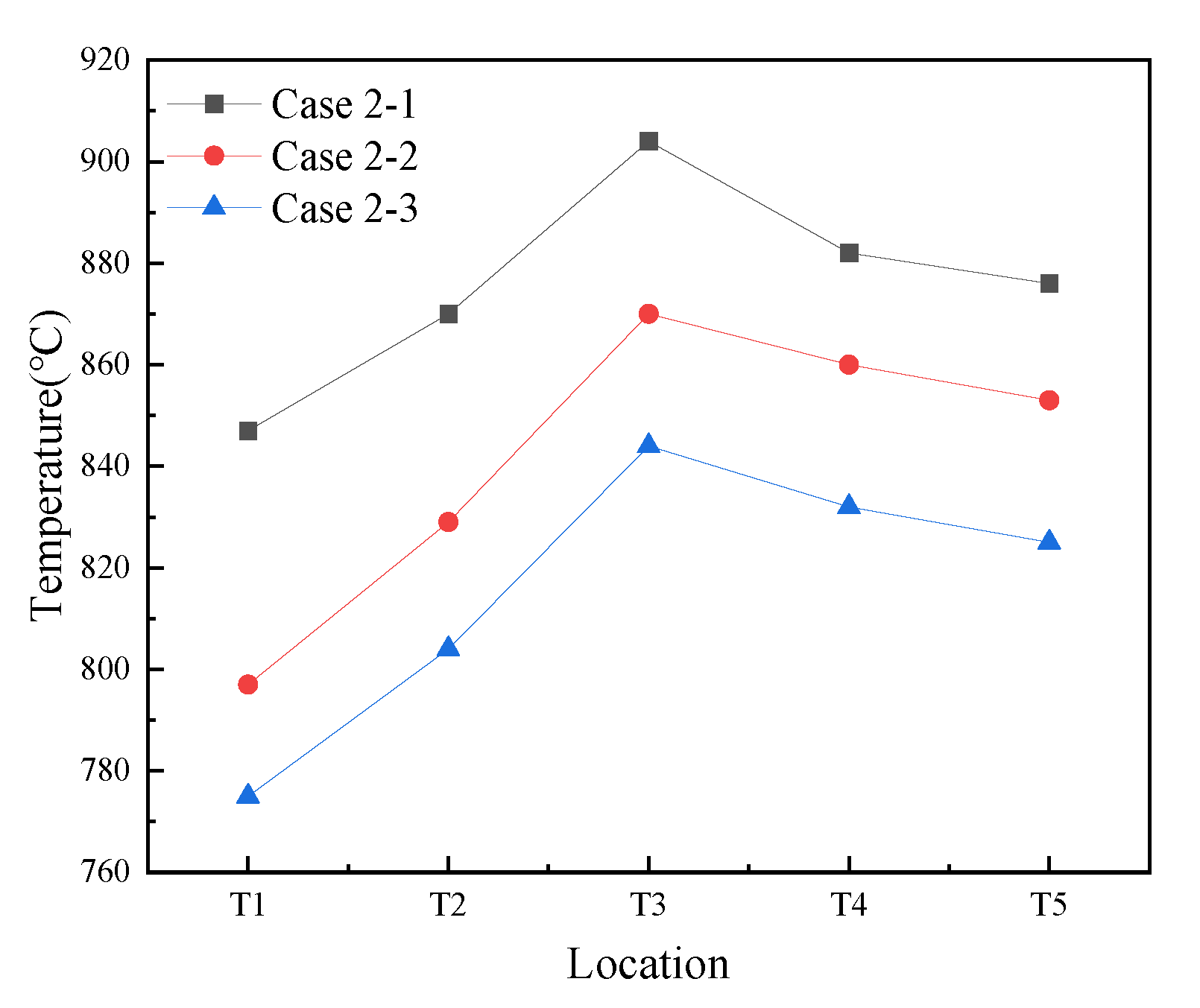
3.2.1. Temperature Profile in the CFB Furnace
3.2.2. Effects of Temperature on NOx and SO2 Emissions with Sorbent Addition Under Post-Combustion
3.2.3. Characteristics of Fly Ash at Cyclone Outlet and at Tail Flue
Particle Size Distribution of Fly Ash at Cyclone Outlet and at Tail Flue
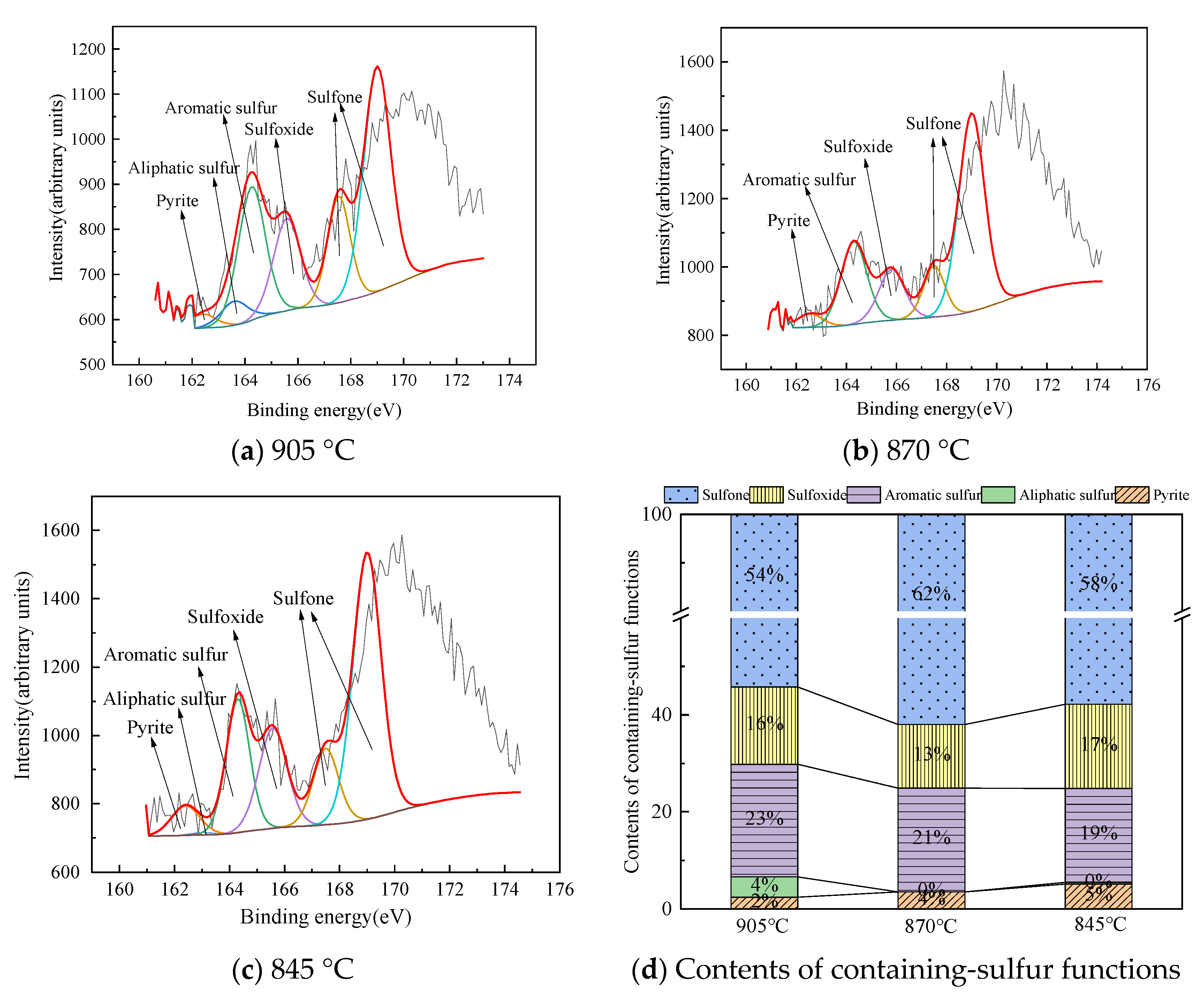
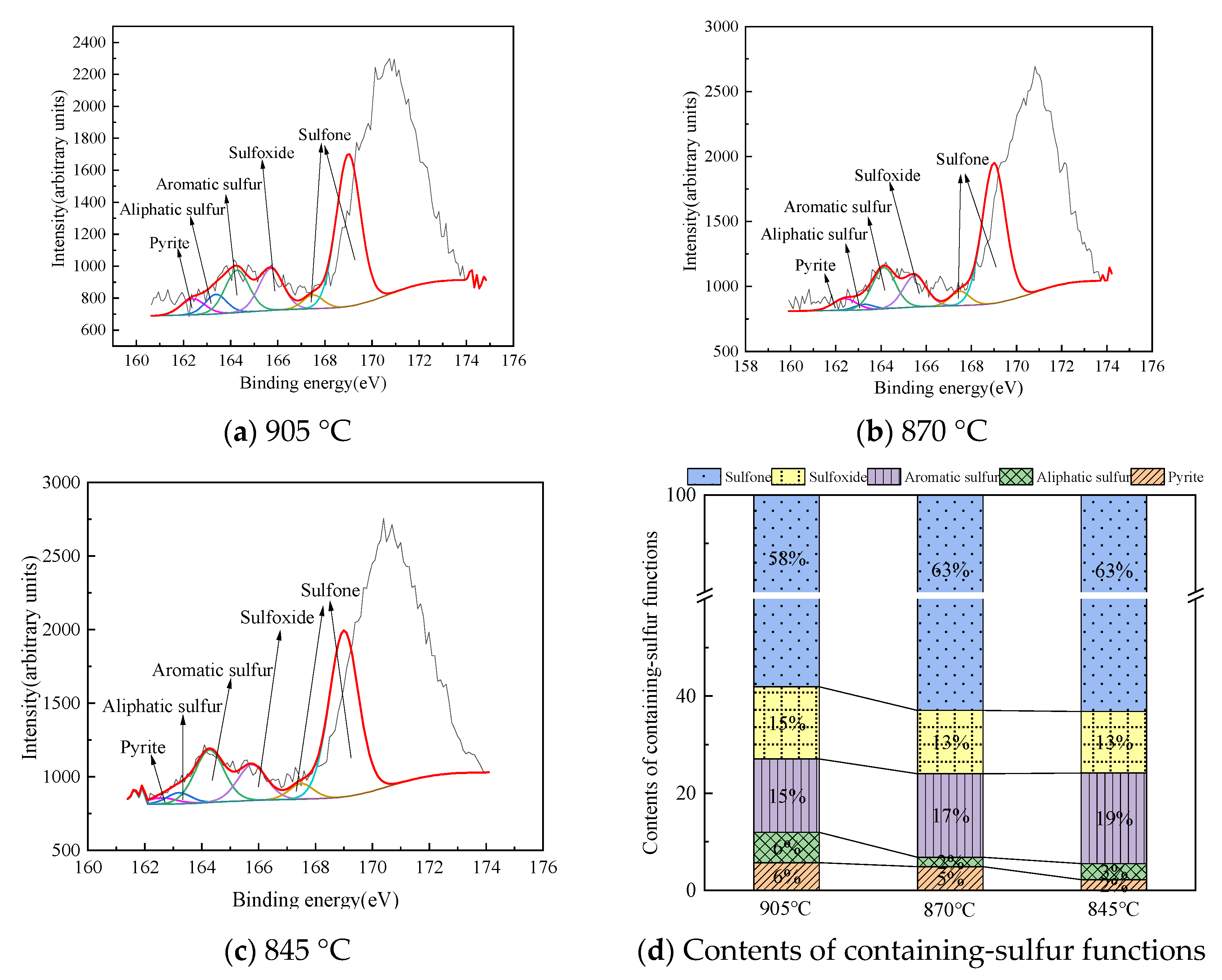
Structural Characteristics of Organic Sulfur in Fly Ash
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CSY. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Yang, H.; Guangxi, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. An update of circulating fluidised bed combustion (CFB) technology in China. VGB Power Tech. 2012, 92, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, G.; Cai, R.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. From a CFB reactor to a CFB boiler—The review of R&D progress of CFB coal combustion technology in China. Powder Technol. 2017, 316, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Koornneef, J.; Junginger, M.; Faaij, A. Development of fluidized bed combustion—An overview of trends, performance, and cost. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 19–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangchen, M.; Jin, C.; Kunling, J.; Lan, M.; Sijie, Z.; Kai, W. Environmental influence and countermeasures for high humidity flue gas discharging from power plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngfelt, A.; Amand, L.E.; Bo, L. Low N2O, NO and SO2 emissions from circulating fluidized bed boilers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fluidized Bed Combustion, Orlando, FL, USA, 7–10 May 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lyngfelt, A.; Aamand, L.E.; Leckner, B. Obtaining low N2O, NO, and SO2 emissions from circulating fluidized bed boilers by reversing the air staging conditions. Energy Fuels 1995, 9, 386–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Emis. Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction. 2018. Available online: https://emis.vito.be/en/techniekfiche/selective-non-catalytic-reduction (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Emis. Selective Catalytic Reduction. 2018. Available online: https://emis.vito.be/en/techniekfiche/selective-catalytic-reduction (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.M.; Yang, D.H.; Qin, W.J. Research of the SNCR Process and its Application. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 953, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, A.L.; Nielsen, R.B. Gas Purification, 5th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 1997; pp. 466–669. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) for SO2 Control. 2006. Available online: http://www.iea-coal.org.uk/ (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Warych, J.; Szymanowski, M. Optimum values of process parameters of the “wet limestone flue gas desulfurization system”. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2015, 25, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, T.-A. Summary of research progress on industrial flue gas desulfurization technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Recent advances in simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx from exhaust gases: Removal process, mechanism and kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Lei, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, H.; Ding, E.; Ning, P. Novel method for high-performance simultaneous removal of NOx and SO2 by coupling yellow phosphorus emulsion with red mud. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Shin, J.; Tae, U.Y.; Hwang, J. Simultaneous removal of gaseous NOx and SO2 by gas-phase oxidation with ozone and wet scrubbing with sodium hydroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, G.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Lyu, Q. Influence of operating parameters on NOx and SO2 emissions in circulating fluidized bed with post-combustion. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 32, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, S. Study on the combustion and NOx emission characteristics of low rank coal in a circulating fluidized bed with post-combustion. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 95, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Y. Experimental study on ultra-low initial NOx emission characteristics of Shenmu coal and char in a high temperature CFB with post-combustion. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 94, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Lyu, Q. A comparative experimental study on characteristics of ultra-low NOx emission and fly ash between Fugu bituminous and its semi-coke with post-combustion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 211, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Lyu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Q. Operating characteristics and ultra-low NOx emission of 75 t/h coal slime circulating fluidized bed boiler with post-combustion technology. Fuel 2021, 292, 120276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereb, J.B.; Wendt, J.O.L. Air staging and reburning mechanisms for NOx abatement in a laboratory coal combustor. Fuel 1994, 73, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åmand, L.E.; Leckner, B.; Dam-Johansen, K. Influence of SO2 on the NO/N2O chemistry in fluidized bed combustion: 1. Full-scale experiments. Fuel 1993, 72, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.; Fraser, S.A. Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, A.; Johnsson, J.E.; Dam-Johansen, K. Nitrogen chemistry in FBC with limestone addition. Symp. Combust. 1997, 26, 3335–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, G.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, X.; Ji, Z.; Lyu, Q. Influence of limestone addition on combustion and emission characteristics of coal slime in the 75 t/h CFB boiler with post-combustion chamber. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 32, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.C.; Liu, H.-P.; Bai, J.-R.; Ye, J.-B. Characterization of organic nitrogen and sulfur in the oil shale kerogens. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 160, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, S.R.; Afeworki, M.; Gorbaty, M.L.; Sansone, M.; Kwiatek, P.J.; Walters, C.C.; Freund, H.; Siskin, M.; Bence, A.E.; Curry, D.J.; et al. Direct characterization of kerogen by X-ray and solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance methods. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 1548–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbaty, M.L.; Kelemen, S.R.; George, G.N.; Kwiatek, P.J. Characterization and thermal reactivity of oxidized organic sulphur forms in coals. Fuel 1992, 71, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Item | Proximate Analysis (wt %, ad) | Ultimate Analysis (wt %, ad) | Low Heating Value (MJ/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Ash | Volatile Matter | Fixed Carbon | Carbon | Hydrogen | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Sulfur | ||
| Shenmu coal | 11.80 | 9.82 | 39.01 | 47.80 | 62.94 | 3.88 | 0.98 | 10.18 | 0.40 | 24.52 |
| Composition | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | SO3 | K2O | MnO | Cl | P2O5 | ZnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt, %) | 74.10 | 0.96 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Case | T (°C) | Ca/S | λ | λCFB | Primary Air (m3/h) | Post-Combustion Air (m3/h) | Other Air (m3/h) | Feeding Coal (kg/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | 900 | 2.5 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 27 | 0 | 6 | 5.94 |
| 1-2 | 900 | 2.5 | 1.15 | 0.9 | 27 | 9.12 | 6 | 5.94 |
| 2-1 | 905 | 2.5 | 1.15 | 0.9 | 27 | 9.12 | 6 | 5.94 |
| 2-2 | 870 | 2.5 | 1.15 | 0.9 | 27 | 9.12 | 6 | 5.94 |
| 2-3 | 845 | 2.5 | 1.15 | 0.9 | 27 | 9.12 | 6 | 5.94 |
| T (°C) | Fly Ash | D10 (μm) | D50 (μm) | D90 (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 905 | a | 4.10 | 33.12 | 139.97 |
| b | 7.42 | 55.15 | 269.14 | |
| 870 | a | 5.30 | 27.57 | 149.62 |
| b | 8.23 | 52.52 | 452.55 | |
| 845 | a | 4.53 | 28.05 | 119.98 |
| b | 6.61 | 34.78 | 239.18 |
| T (°C) | Fly Ash | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 905 | a | Ca (%) | O (%) | Si (%) | Fe (%) | Al (%) | S (%) | Na (%) | Others (%) |
| 41.25 | 36.47 | 8.87 | 4.38 | 3.70 | 2.50 | 0.63 | 2.19 | ||
| b | Ca | O | Si | Fe | Al | S | Na | others | |
| 36.21 | 38.76 | 11.11 | 4.28 | 3.51 | 3.91 | 0.50 | 1.72 | ||
| 870 | a | Ca | O | Si | Fe | Al | S | Na | others |
| 39.40 | 36.93 | 9.08 | 5.36 | 3.93 | 2.70 | 0.74 | 1.87 | ||
| b | Ca | O | Si | Fe | Al | S | Na | others | |
| 36.30 | 38.66 | 10.41 | 4.49 | 3.75 | 4.17 | 0.61 | 1.63 | ||
| 845 | a | Ca | O | Si | Fe | Al | S | Na | others |
| 38.48 | 37.58 | 8.93 | 4.74 | 4.32 | 3.46 | 0.77 | 1.71 | ||
| b | Ca | O | Si | Fe | Al | S | Na | others | |
| 36.33 | 38.80 | 10.00 | 4.49 | 3.83 | 4.52 | 0.56 | 1.48 |
| Sulfur Functionality | Binding Energy/eV | Functional Form |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrite | 162.5 ± 0.1 | FeS2 |
| Aliphatic sulfur | 163.3 ± 0.3 | 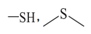 |
| Aromatic sulfur | 164.1 ± 0.2 | 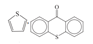 |
| Sulfoxide | 165.7 ± 0.3 |  |
| Sulfone | 168.0 ± 0.5 168.5 ± 0.5 | 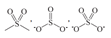 |
| T (°C) | Fly Ash | Pyrite (%) | Aliphatic Sulfur (%) | Aromatic Sulfur (%) | Sulfoxide (%) | Sulfone (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 905 | a | 2.43 | 4.18 | 23.18 | 15.99 | 54.22 |
| b | 5.7 | 6.22 | 15.12 | 14.87 | 58.09 | |
| 870 | a | 3.5 | 0 | 21.38 | 13.16 | 61.96 |
| b | 4.87 | 1.94 | 17.19 | 13.03 | 62.97 | |
| 845 | a | 5.14 | 0.33 | 19.32 | 17.4 | 57.8 |
| b | 2.22 | 3.28 | 18.65 | 12.66 | 63.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Lyu, Q. Combined Removal of NOx and SO2 in Circulating Fluidized Beds with Post-Combustion. Processes 2025, 13, 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051496
Wang C, Lyu Q. Combined Removal of NOx and SO2 in Circulating Fluidized Beds with Post-Combustion. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051496
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chao, and Qinggang Lyu. 2025. "Combined Removal of NOx and SO2 in Circulating Fluidized Beds with Post-Combustion" Processes 13, no. 5: 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051496
APA StyleWang, C., & Lyu, Q. (2025). Combined Removal of NOx and SO2 in Circulating Fluidized Beds with Post-Combustion. Processes, 13(5), 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051496





