Adaptive Speed Tuning of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Intelligent Fuzzy Based Controllers for Pumping Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
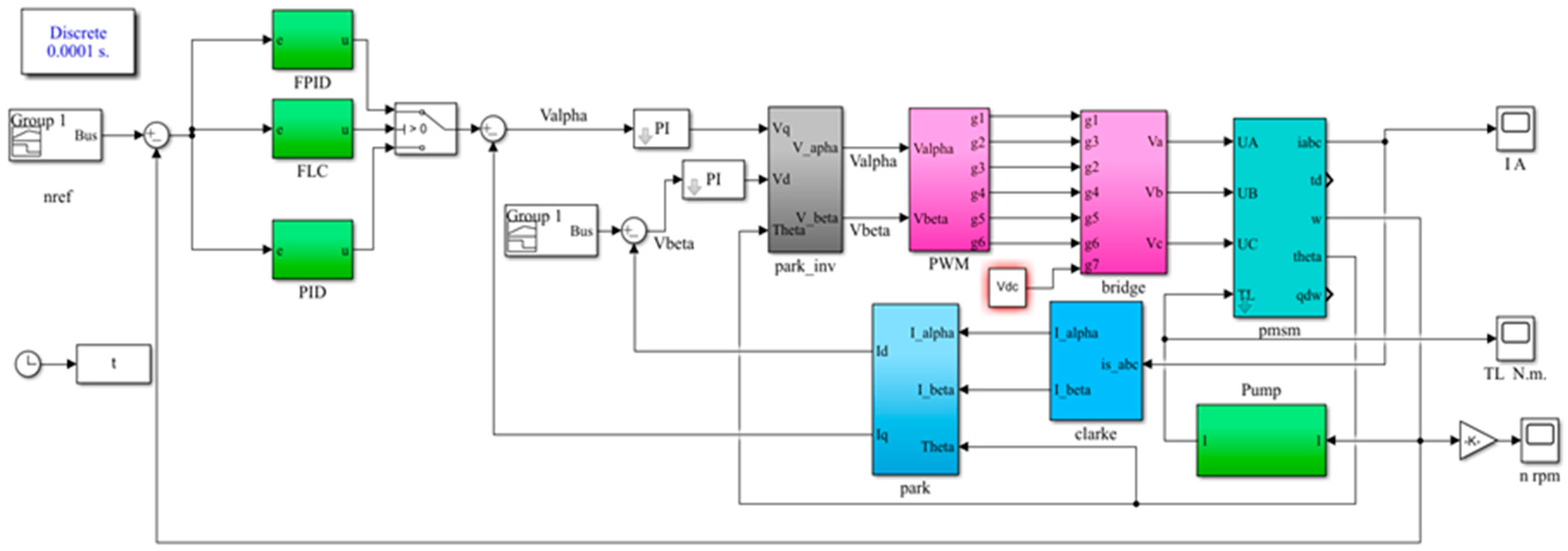
2. PMSM-Pumping Structure
2.1. System Description
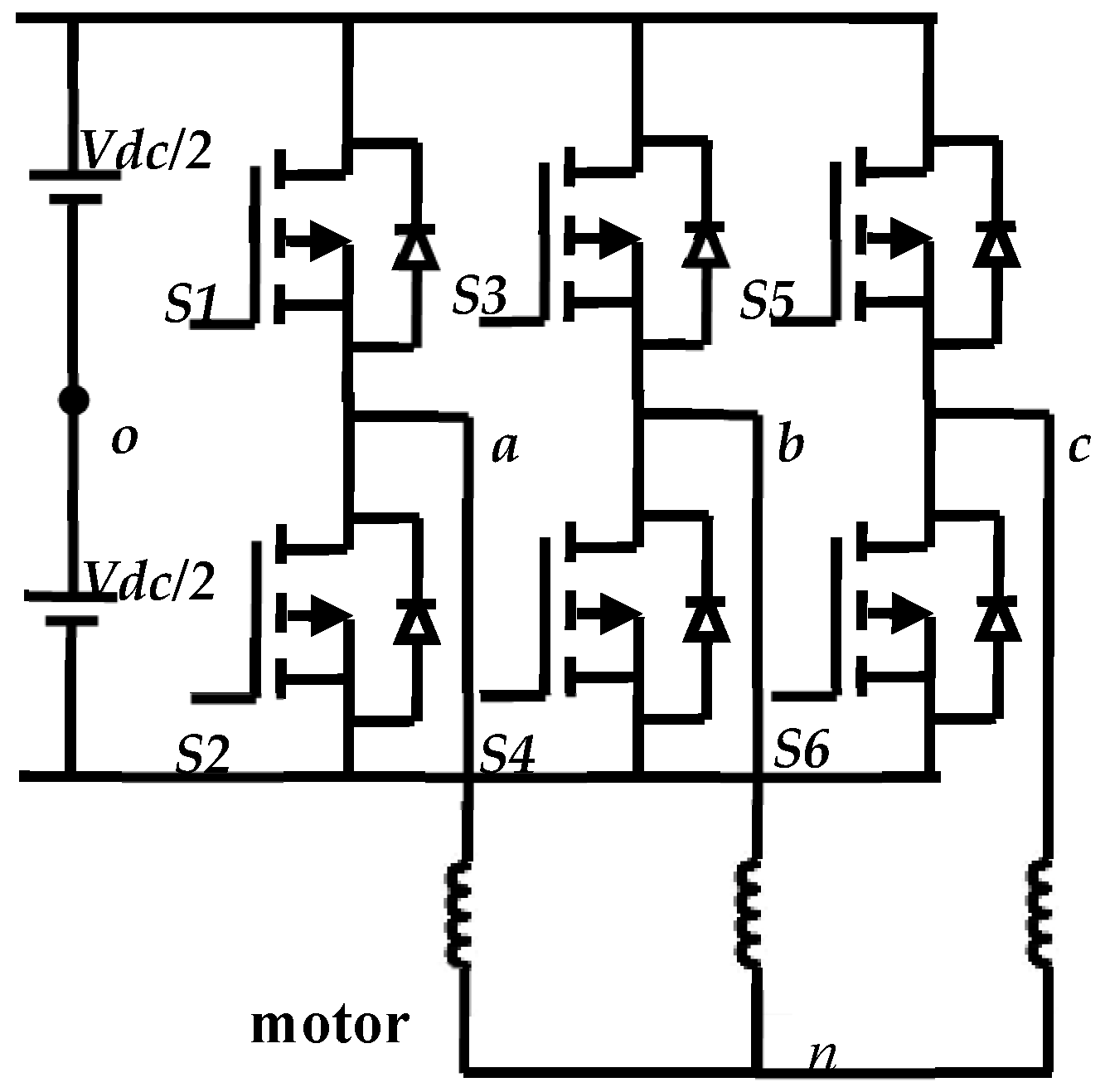
2.2. Three-Phase Vector Control Inverter
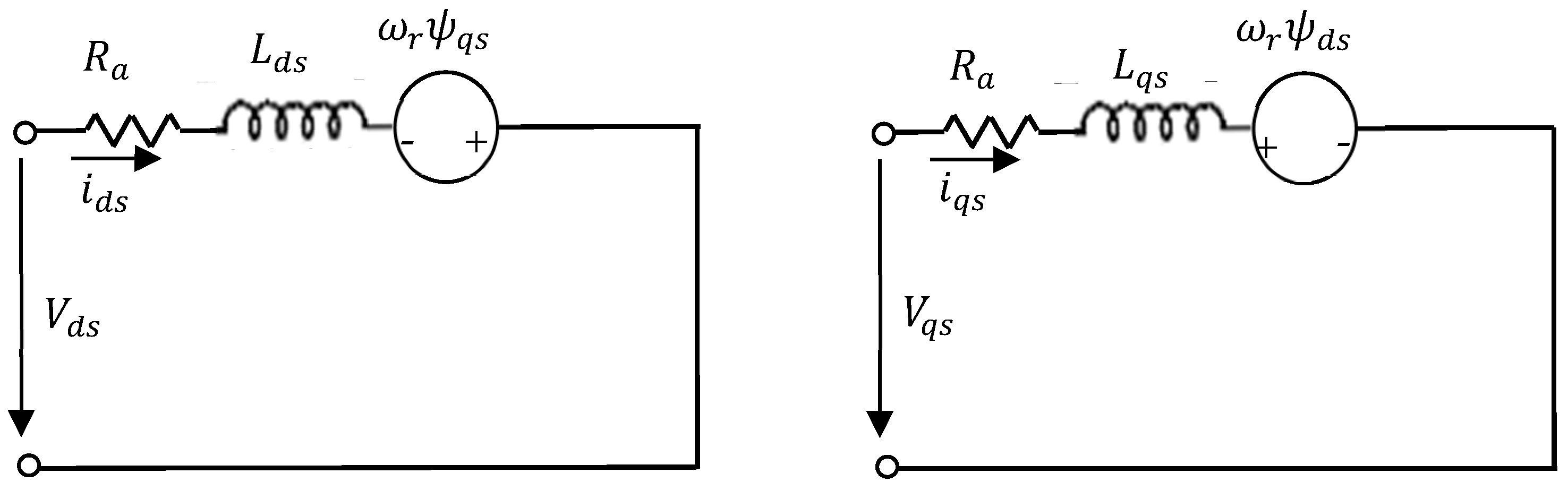
2.3. Dynamic Model of Salient Pole PMSMs
2.4. Centrifugal Pump Model
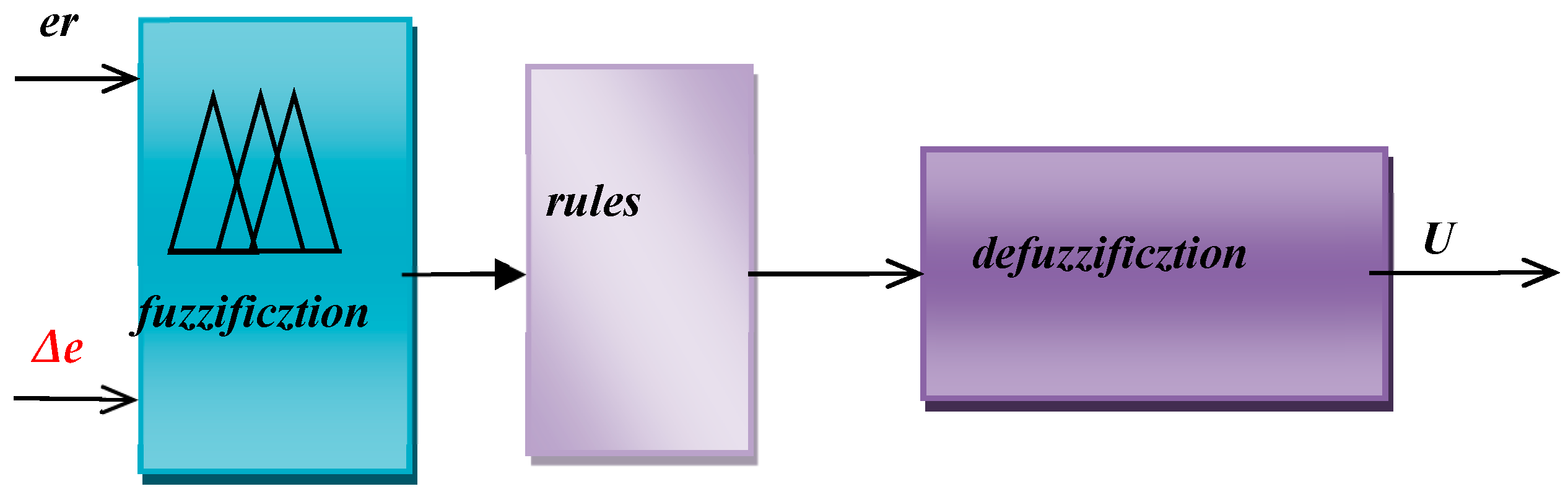
3. The Suggested Fuzzy Logic of PMSMs
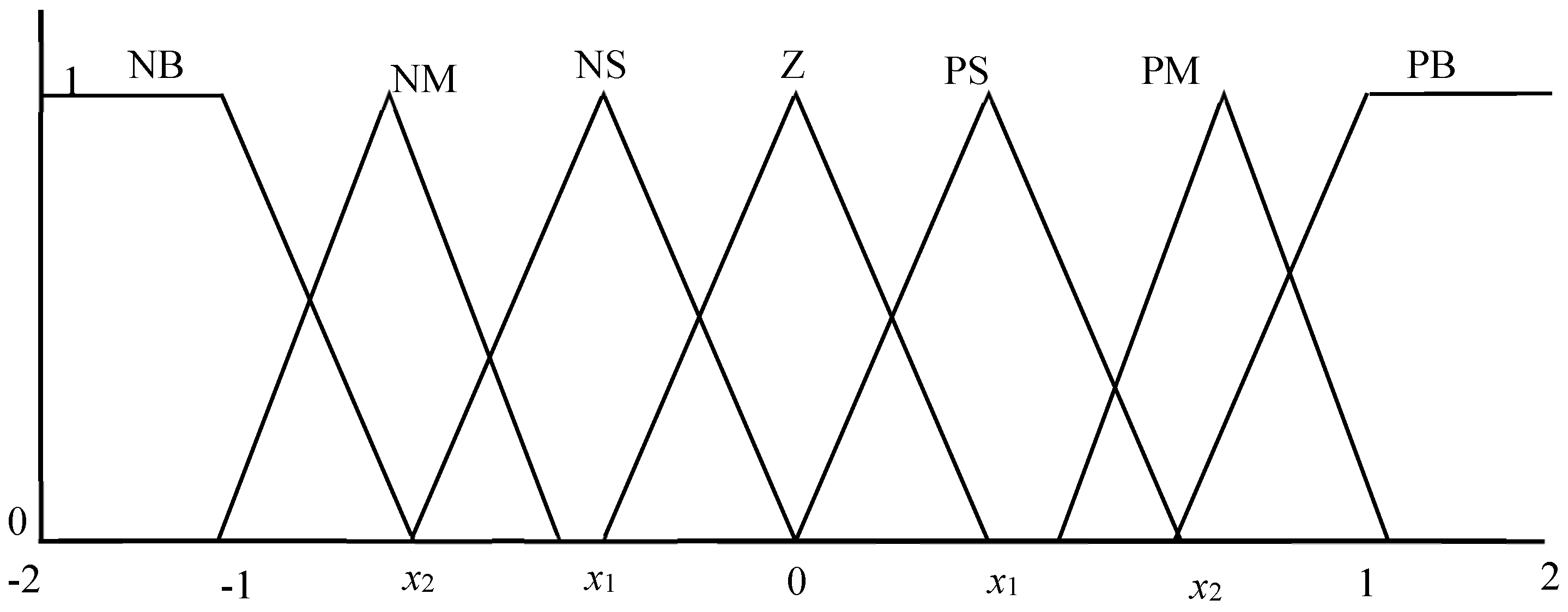
3.1. Auto-Tuned Fuzzy Logic Controller
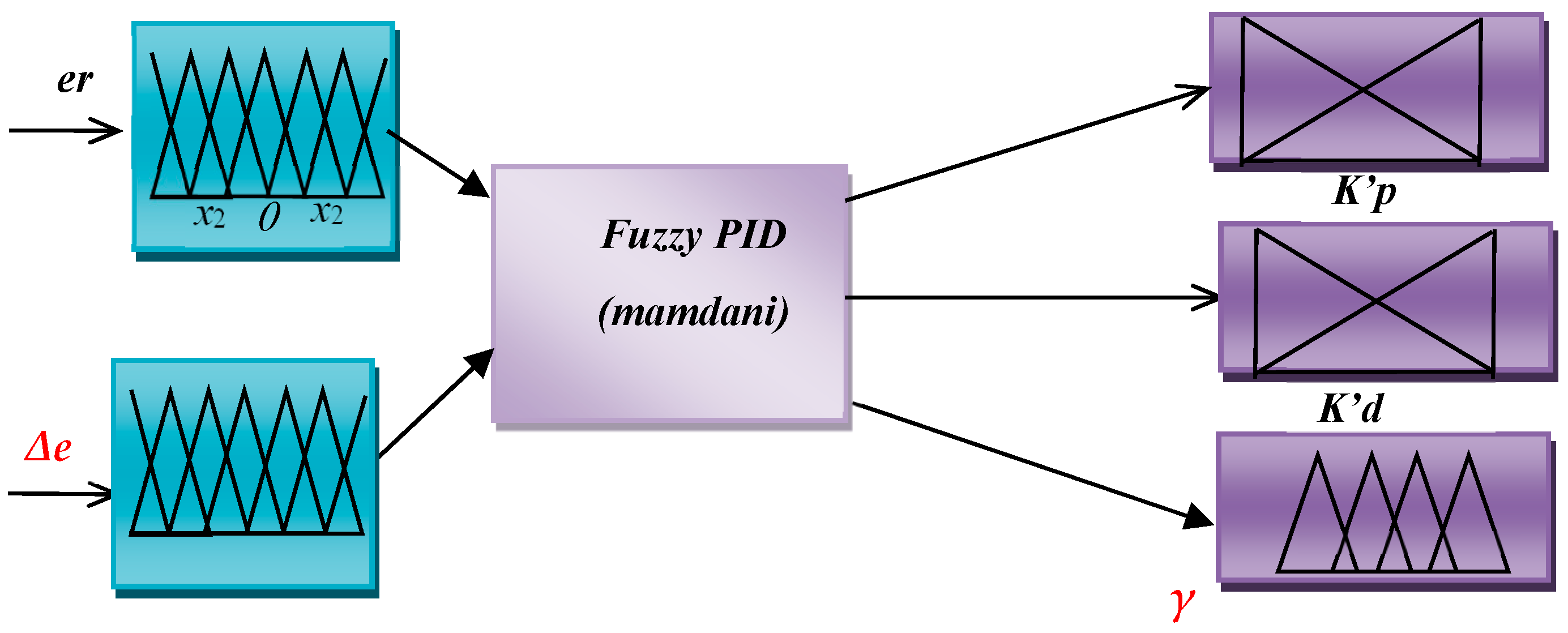
3.2. Fuzzy PID Controller
4. Applications
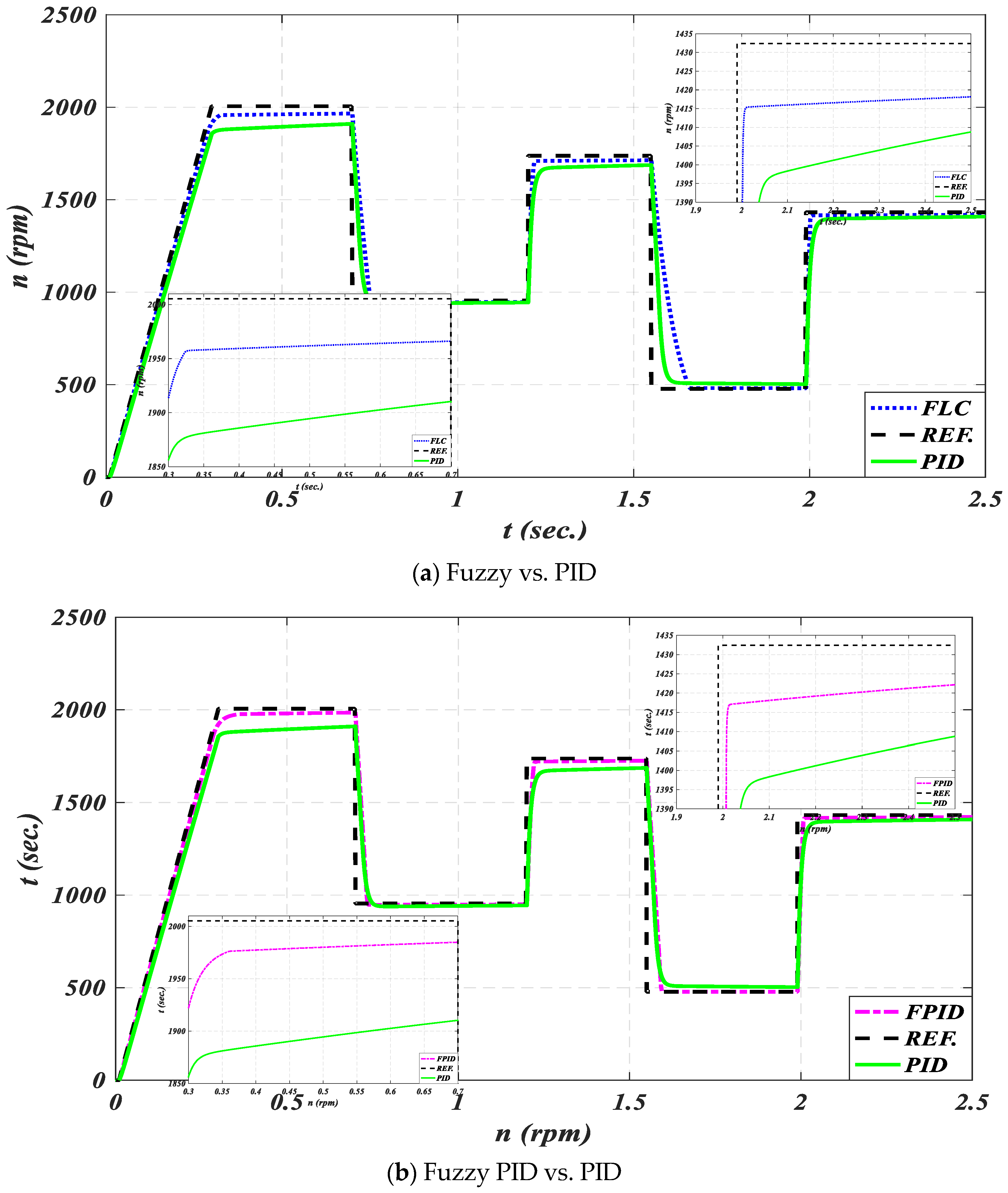
- When the FLC and FPID controllers are used, the steady-state error (SSE), speed overshoot (OS), and undershoot of periods 1–6 are reduced.
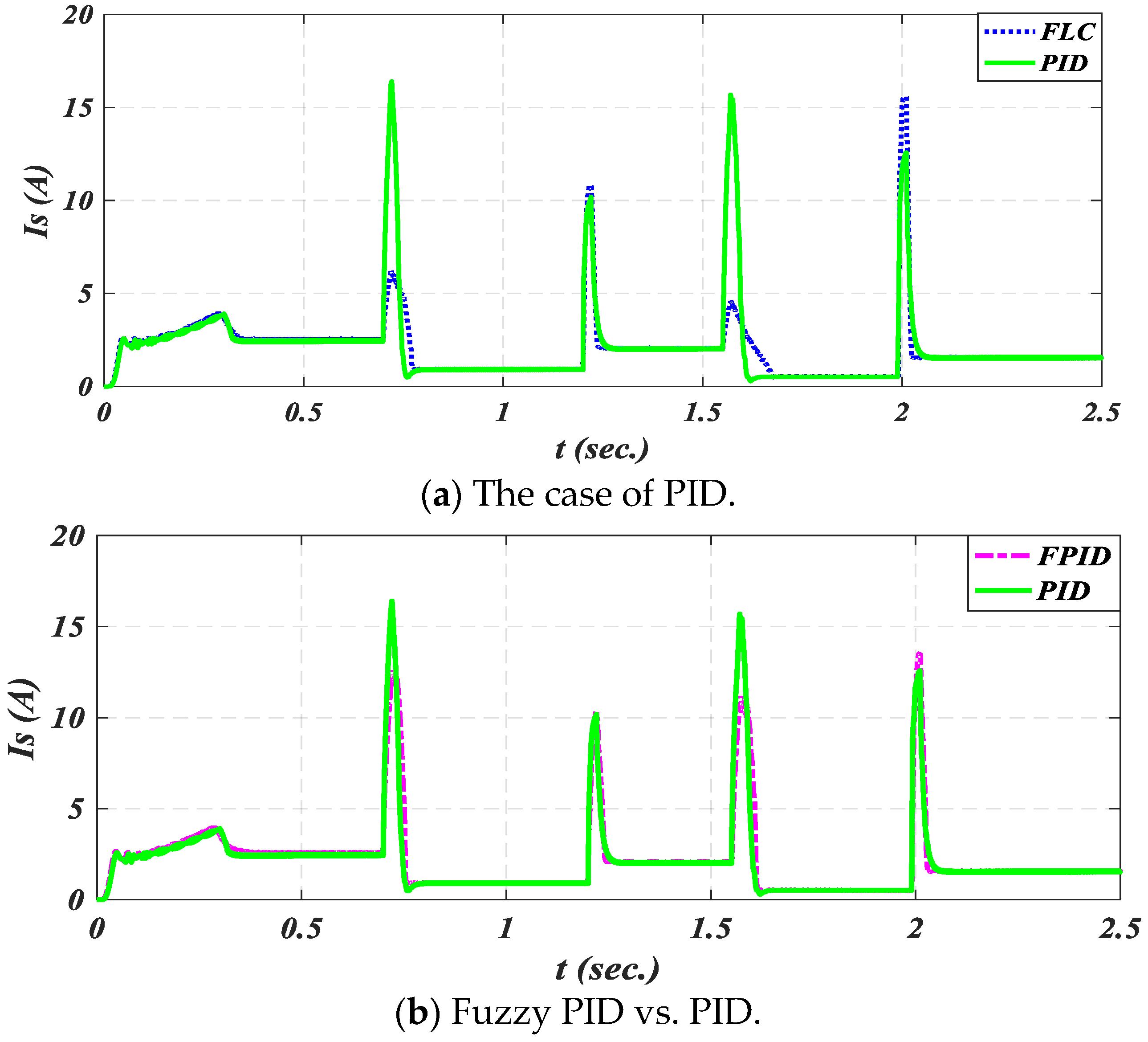
- In period 2, at a pump torque of 5.9 N.m., the speed error caused by the load using PID is 105.4 rpm, and the speed oscillation is 16 rpm; the speed error when using FLC is 46.4 rpm and speed oscillation is 3 rpm; and the speed error when using FPID is 25.4 rpm and the speed oscillation is 8 rpm. Figure 9a depicts the second zooming inner graph controlled by FLC and PID, which takes around 2 to 2.5 s to complete. With a loading torque of 3.5 N.m., this figure indicates that the speed error caused by the load using PID is 27 rpm, and the speed oscillation is 14 rpm; the speed error when using FLC is 16 rpm and speed oscillation 4 rpm; and the speed error when using FPID is 13 rpm, and the speed oscillation is 5 rpm.
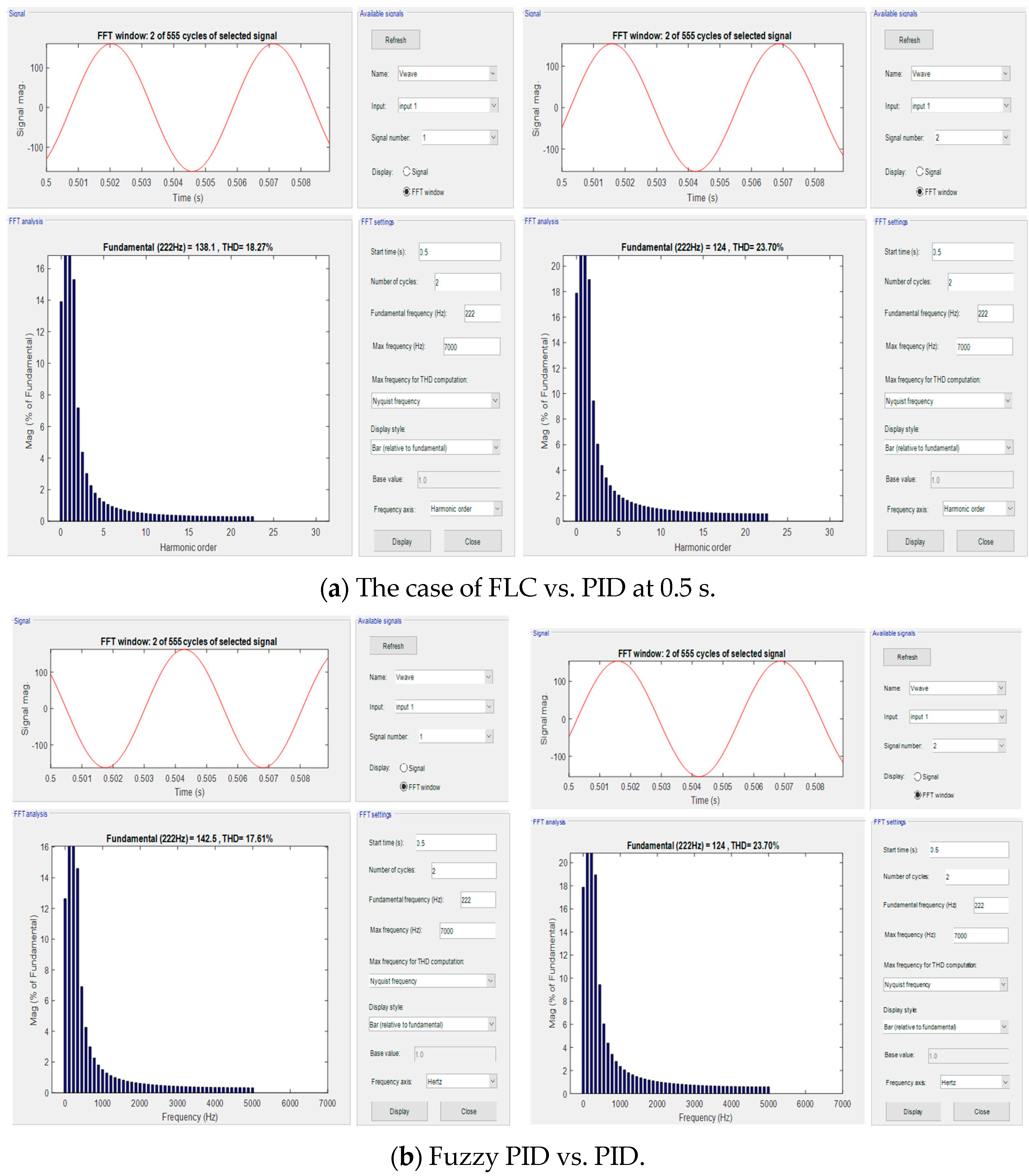
- In comparison, the THD in voltage values in period 4, between the PID controller, FLC, and FPID, are 21.19%, 6.59%, and 3.6%, respectively.
- In comparison, the starting current values in period 5, between the PID controller, FLC, and FPID, are 15.8 A, 5 A, and 12 A, respectively.
5. Conclusions and Future Trends
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalyan, H.; Syal, P. Design of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Efficient Solar Pumping System. In International Conference on Emerging Electronics and Automation; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, L.; Lang, T.; Jiang, Y. Low-Voltage Water Pump System Based on Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Electronics 2024, 13, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelo-Zuluaga, C.; Riba, J.-R.; Espinosa, A.G.; Tubert, P. Customized PMSM Design and Optimization Methodology for Water Pumping Applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T. Energy-Saving Trajectory Tracking Control of a Multi-Pump Multi-Actuator Hydraulic System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179156–179166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L. Fuzzy-PID Strategy Based on PSO Optimization for pH Control in Water and Fertilizer Integration. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 4471–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadi, A.I.M.; Al Mamlook, R.E.; Almarhabi, Y.; Ullah, I.; Jamal, A.; Bandara, N. A Fuzzy-Logic Approach Based on Driver Decision-Making Behavior Modeling and Simulation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, M.; Akdeniz, C.; Demir, V.; Yurdem, H. Fuzzy logic control for watering system. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussama, M.; Abdelghani, C.; Lakhdar, C. Efficiency and robustness of type-2 fractional fuzzy PID design using salps swarm algorithm for a wind turbine control under uncertainty. ISA Trans. 2022, 125, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkuhayli, A.; Noman, A.M.; Al-Shamma’a, A.A.; Abdurraqeeb, A.M.; Alharbi, M.; Hussein Farh, H.M.; Qamar, A. Enhancing Photovoltaic-Powered DC Shunt Motor Performance for Water Pumping through Fuzzy Logic Optimization. Machines 2024, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahami, H.; Saberi, S.; Ali, B.M.; AbdulAmeer, S.; Hussein, A.H.A.; Chaoui, H. A Robust Hꝏ-Based State Feedback Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Using Adaptive Fuzzy Sliding Mode Observers. Actuators 2024, 13, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Wan, H.; Huang, Z.; Gu, M. PMSM Vector Control Based on Fuzzy PID Controller. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1617, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazbayev, B.; Tanirbergenova, A.; Orazbayeva, K.; Berikbaeva, M.; Kaliyeva, S.; Kurmangaziyeva, L.; Makhatova, V. Decision Making for Control of the Gasoline Fraction Hydrotreating Process in a Fuzzy Environment. Processes 2024, 12, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, Y.A.; Longsheng, C.; Shah, S.A.; Alsanad, A.; Ahmad, M.; Akbar, M.A.; Gumaei, A.; Ali, S. Analyzing Renewable Energy Sources of a Developing Country for Sustainable Development: An Integrated Fuzzy Based-Decision Methodology. Processes 2020, 8, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sehiemy, R.A.; Aleem, S.H.E.A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Balci, M.E. A new fuzzy framework for the optimal placement of phasor measurement units under normal and abnormal conditions. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudinov, Y.I.; Kolesnikov, V.A.; Pashchenko, F.F.; Pashchenko, A.F.; Papic, L. Optimization of Fuzzy PID Controller’s Parameters. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 103, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Baz, A.; Alhakami, H.; Alhakami, W.; Agrawal, A.; Khan, R.A. A hybrid fuzzy rule-based multi-criteria framework for sustainable-security assessment of web application. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 2227–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, F.V.A.; Kannan, V.K. Particle Swarm Optimized Deep Convolutional Neural Sugeno-Takagi Fuzzy PID Controller in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahhan, A.; Temurtaş, F. Enhanced Fuzzy Logic Control Model and Sliding Mode Based on Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor. World J. Eng. Technol. 2024, 12, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh, P.Q.; Anh, H.P.H. Advanced PMSM speed control using fuzzy PI method for hybrid power control technique. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguenna, I.F.; Tahour, A.; Kennel, R.; Abdelrahem, M. Multiple-Vector Model Predictive Control with Fuzzy Logic for PMSM Electric Drive Systems. Energies 2021, 14, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, H. A novel PID controller for BLDCM speed control using dual fuzzy logic systems with HSA optimization. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Das, D.K. A novel PID controller for pressure control of artificial ventilator using optimal rule based fuzzy inference system with RCTO algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolano, K. New Method of Vector Control in PMSM Motors. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 43882–43890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraja, T.; Ramya, K. Vector control of PMSM take over by photovoltaic source. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. (ACES) 2018, 33, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, M.; Wang, H.; Jin, L. Simulation Study on Dynamic Characteristics of the Chain Drive System for Mining Scraper Conveyor Driven by the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Processes 2024, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shi, Z.; Yu, B.; Qi, H. Research on a Sensorless ADRC Vector Control Method for a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on the Luenberger Observer. Processes 2024, 12, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, M.A.; Abdelwanis, M.I.; El-Sehiemy, R. Parameter Estimation of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Using Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Rev. Roum. Sci. Tech.—Série Électrotechnique Énergétique 2022, 67, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Betka, A.; Moussi, A. Performance optimization of a photovoltaic induction motor pumping system. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, M.; Messai, F.; Benalla, H. Vectorial Command of Induction Motor Pumping System Supplied by a Photovoltaic Generator. J. Electr. Eng. 2011, 62, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwanis, M.I.; El-Sehiemy, R.A. A Fuzzy-Based Controller of a Modified Six-Phase Induction Motor Driving a Pumping System. Iran. J. Sci. Technol.-Trans. Electr. Eng. 2019, 43, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošević, M.; Radić, M.; Rašić-Amon, M.; Litričin, D.; Stajić, Z. Diagnostics and Control of Pumping Stations in Water Supply Systems: Hybrid Model for Fault Operating Modes. Processes 2022, 10, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, Z.Q. Fuzzy Logic Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine and Feedback Voltage Ripple Reduction in Flux-Weakening Operation Region. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, R.; Kalyani, S.; Devie, P.M. Design and performance analysis of adaptive neuro-fuzzy controller for speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Niu, P.; Guo, X.; He, J. Fuzzy PID control of permanent magnet synchronous motor electric steering engine by improved beetle antennae search algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin H, Yi W, Wu J, Wang K, Guan JAdaptive Fuzzy Neural Network PID Algorithm for BLDCM Speed Control System. Mathematics 2022, 10, 118. [CrossRef]
- Abdelwanis, M.I.; El-Sehiemy, R.A. Performance enhancement of split-phase induction motor by using fuzzy-based PID controller. J. Electr. Eng. 2019, 70, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwanis, M.I.; El-Sousy, F.F.M.; Ali, M.M. A Fuzzy-Based Proportional–Integral–Derivative with Space-Vector Control and Direct Thrust Control for a Linear Induction Motor. Electronics 2023, 12, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwanis, M.I. Optimizing the performance of six-phase induction motor-powered electric vehicles with fuzzy-PID and DTC. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, M.; Krim, S.; Kraiem, Y.; Hajjaji, M.A.; Alshammari, B.M.; Alsaif, H.; Alshammari, A.S.; Guesmi, T. Design of Vector Control Strategies Based on Fuzzy Gain Scheduling PID Controllers for a Grid-Connected Wind Energy Conversion System: Hardware FPGA-in-the-Loop Verification. Electronics 2023, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamanpira, M.; Ghahremani, M.; Dadfar, S.; Khaksar, M.; Rezvani, A.; Wakil, K. A novel MPPT technique to increase accuracy in photovoltaic systems under variable atmospheric conditions using Fuzzy Gain scheduling. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 43, 2960–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Controller Type | Description | Advantages | Limitations | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scalar Control Volts/Hertz (V/f) | This control method adjusts voltage and frequency proportionally to motor speed. | Cost-effective, simple design, reliable for applications. | Limited for dynamic loads, lacks precise speed and torque control. | Centrifugal pumps, fans, conveyors. |
| Sensorless Vector | Estimates motor speed and torque without needing a physical sensor. | Better torque control and efficiency compared to V/f, moderate cost. | Accuracy depends on motor characteristics; not suitable for applications needing precise control. | Electric vehicles, HVAC systems, wind turbines. |
| Field-Oriented Control (FOC) | Advanced method maintaining precise control over motor magnetic fields for optimal performance. | High efficiency, excellent torque control at low speeds, and precise motor operation. | Higher cost, complexity requires careful setup and tuning. | Elevators, robotics, CNC machines, electric vehicles. |
| Direct Torque Control (DTC) | Provides direct control of motor torque and flux without requiring modulation. | Fast dynamic response, precise control, reduced energy losses. | Complex algorithm, may require specialized hardware. | Traction systems, industrial drives, high-performance drives. |
| PID Controller | Uses proportional, integral, and derivative gains to maintain desired motor speed based on feedback. | Ideal for maintaining steady flow or pressure, easy integration with control systems. | Requires tuning for optimal performance; slower response in dynamic systems. | Pressure pumps, HVAC systems. |
| Adaptive Control | Adjusts control parameters in real-time to optimize performance. | High efficiency under varying loads, reduced energy consumption. | High cost, complexity requires advanced software and hardware. | High-performance drives, renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, aerospace variable-load pumping systems. |
| ECE | NB | NM | NS | Z | PS | PM | PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NB | NB | NB | NB | NM | NS | Z |
| NM | NM | NM | NS | Z | PS | ||
| NS | NM | NS | NS | Z | PS | PM | |
| Z | Z | PS | PM | PB | |||
| PS | NM | NS | Z | PS | |||
| PM | NS | Z | PS | PM | PM | PB | |
| PB | Z | PS | PM | PB | PB |
| er | Δe | kp | kd | γ | er | Δe | Kp | kd | γ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG, NB | NB | BG | SM | PS | PS, NM | NB | SM | BG | BG |
| NM | NM | SM | |||||||
| NS | NS | BG | |||||||
| Z | Z | SM | PS | ||||||
| PS | PS | BG | SM | ||||||
| PM | PM | SM | |||||||
| PB | PB | BG | |||||||
| PM, NM | NB | SM | BG | SM | Z | NB | PB | ||
| NM | BG | NM | BG | ||||||
| NS | SM | PS | NS | SM | |||||
| Z | Z | BG | |||||||
| PS | PS | SM | |||||||
| PM | BG | SM | PM | BG | |||||
| PB | PB | PB |
| No. | Periods | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| From | To | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0.3 sec. | Starting state |
| 2 | 0.3 sec. | 0.7 sec. | Normal speed (1200 rpm) at 5.9N.m |
| 3 | 0.7 sec. | 1.2 sec. | Reduced speed (1000 rpm) at 2 N.m. |
| 4 | 1.2 sec. | 1.55 sec. | Increase speed (2100 rpm), 4.6 N.m. |
| 5 | 1.55 sec. | 1.99 sec. | More speed amendment (500 rpm), 1 N.m. |
| 6 | 1.99 sec. | 2.5 sec. | Increase speed to (1400 rpm), 3.5 N.m. |
| Parameters | Magnitude | Parameters | Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator voltage, Vph | 220 (V) | Moment of inertia, J | 0.00609 (kg.m2) |
| Motor stator current | 2.5 (A) | Motor-rated torque | 5.8 (N.m) |
| stator q-axis inductance, Lqs | 0.0038 (H) | Permanent magnet flux, ψm | 0.14 (Wb.turns) |
| Stator d-axis inductance, Lds | 0.0038 (H) | Saliency ratio | 2 |
| Stator resistance, Rs | 0.45 (Ω) | No. of poles, p (poles) | 6 |
| Frequency Hz | Time sec. | % THD of Current | % THD of Voltage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | PID | FC | FPID | PID | FC | FPID | ||
| 0.3–0.7 | 222 | 0.5 | 22.11 | 25.37 | 18.07 | 23.7 | 18.27 | 17.61 |
| 0.7–1.2 | 93 | 1 | 2.95 | 5.71 | 3.085 | 3.07 | 5.75 | 3.91 |
| 1.2–1.55 | 172 | 1.4 | 7.05 | 2.36 | 0.05 | 7.96 | 2.32 | 0.02 |
| 1.55–1.99 | 47 | 1.7 | 18.04 | 5.09 | 3.33 | 21.19 | 6.59 | 3.6 |
| 1.99–2.5 | 143 | 2.3 | 3.75 | 2.09 | 1.18 | 3.26 | 2.34 | 1.07 |
| Controller | Period | Speed (rpm) | Current (A) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| PID | Steady state | 1900 | 940 | 1680 | 504.5 | 1405.4 | 2.5 | 0.9 | 2.04 | 0.53 | 1.55 |
| FLC | 1962 | 945.5 | 1711 | 480.5 | 1416.4 | 2.51 | 0.9 | 2.06 | 0.53 | 1.56 | |
| FPID | 1980 | 949 | 1725 | 477.75 | 1419.4 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 2.07 | 0.52 | 1.54 | |
| PID | Oscillating range | 16 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 14 | 0.06 | 15.8 | 9 | 15 | 11.25 |
| FLC | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0.1 | 5 | 8.2 | 4 | 15.24 | |
| FPID | 8 | 2.5 | 4 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.06 | 12 | 9.1 | 8 | 13 | |
| PID | Rise time (sec.) | 0.31 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 2.05 | 0.35 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.66 | 2.08 |
| FLC | 0.325 | 0.75 | 1.23 | 1.66 | 2.01 | 0.35 | 0.775 | 1.25 | 1.68 | 2.04 | |
| FPID | 0.36 | 0.68 | 1.22 | 1.65 | 2.01 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 1.25 | 1.615 | 2.03 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelwanis, M.I.; Hegab, A.; Albatati, F.; El-Sehiemy, R.A. Adaptive Speed Tuning of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Intelligent Fuzzy Based Controllers for Pumping Applications. Processes 2025, 13, 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051393
Abdelwanis MI, Hegab A, Albatati F, El-Sehiemy RA. Adaptive Speed Tuning of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Intelligent Fuzzy Based Controllers for Pumping Applications. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051393
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelwanis, Mohamed I., Abdelkarim Hegab, Faisal Albatati, and Ragab A. El-Sehiemy. 2025. "Adaptive Speed Tuning of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Intelligent Fuzzy Based Controllers for Pumping Applications" Processes 13, no. 5: 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051393
APA StyleAbdelwanis, M. I., Hegab, A., Albatati, F., & El-Sehiemy, R. A. (2025). Adaptive Speed Tuning of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Intelligent Fuzzy Based Controllers for Pumping Applications. Processes, 13(5), 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051393










