Effect of Mixed-Charge Surfactants on Enhanced Oil Recovery in High-Temperature Shale Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Interfacial Tension Measurement
2.3. Anti-Adsorption Performance Measurement
2.4. High-Temperature Resistance Evaluation Experiment
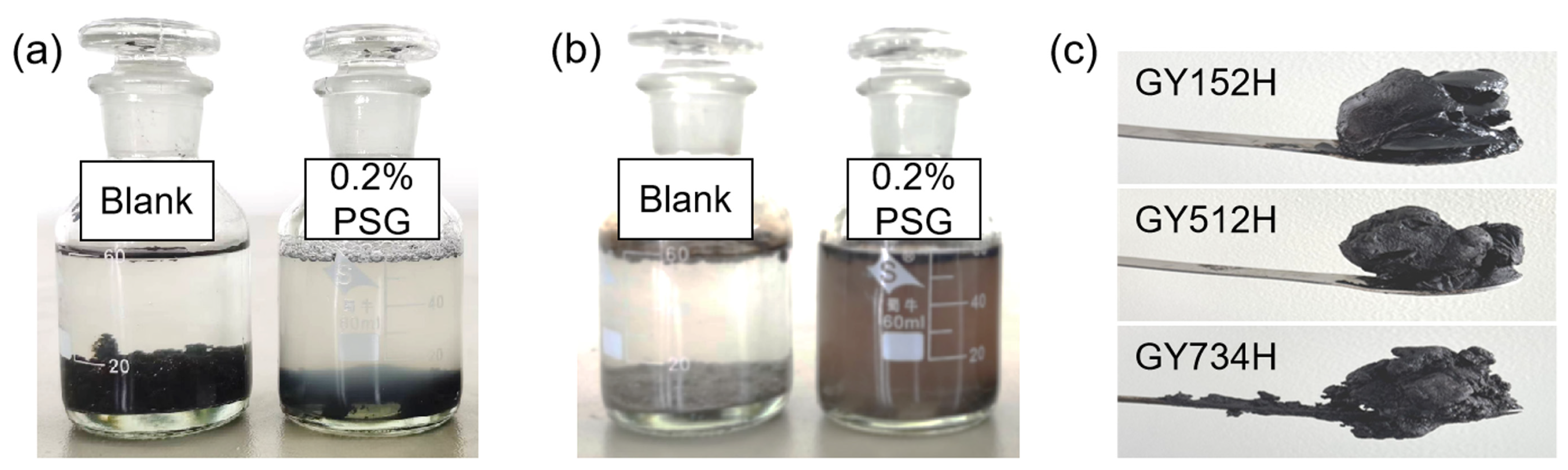
2.5. Static Oil-Washing Experiment
2.6. Dynamic Imbibition Experiment
2.7. Wettability Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
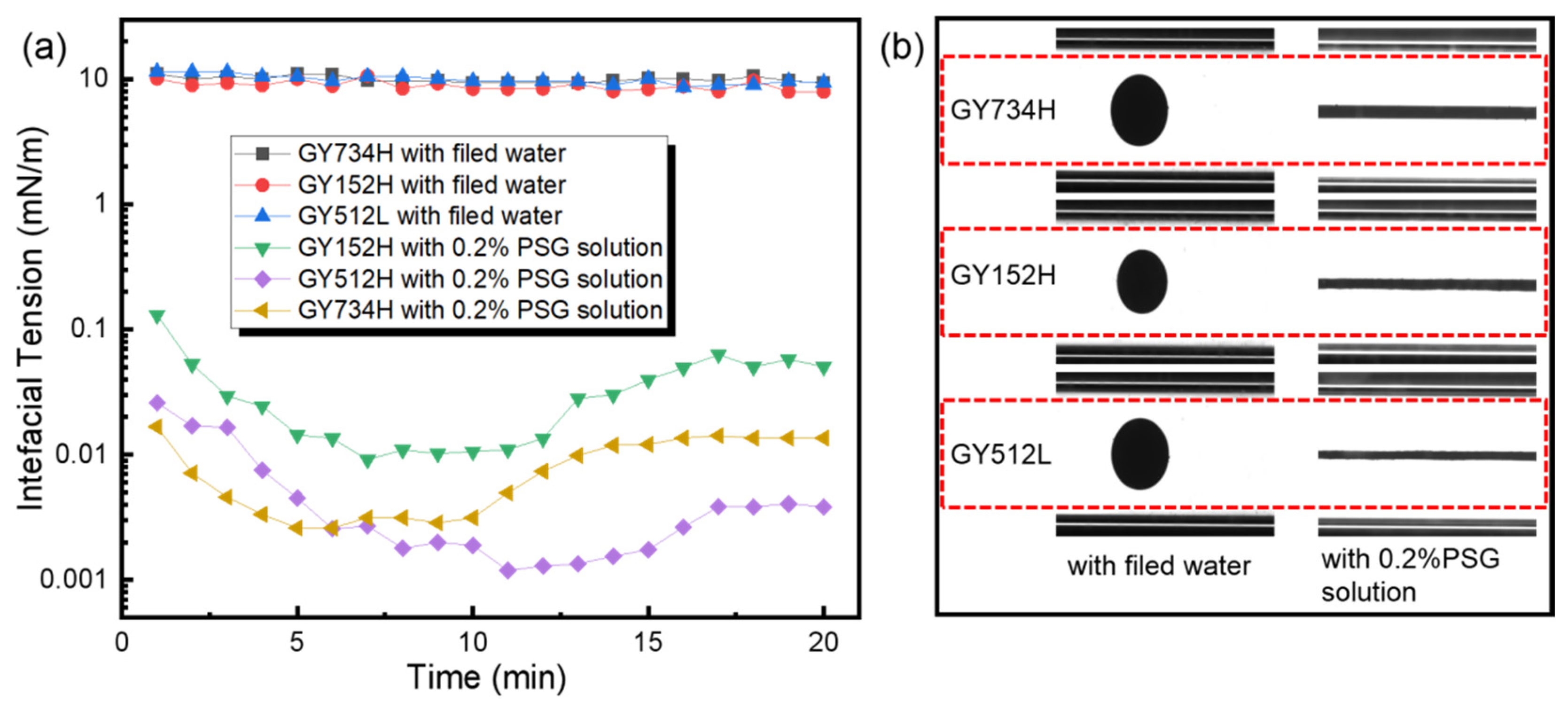
3.1. Interfacial Tension Evaluation
3.2. Anti-Adsorption Performance
3.3. Static Oil-Washing Efficiency
3.4. High-Temperature Resistance
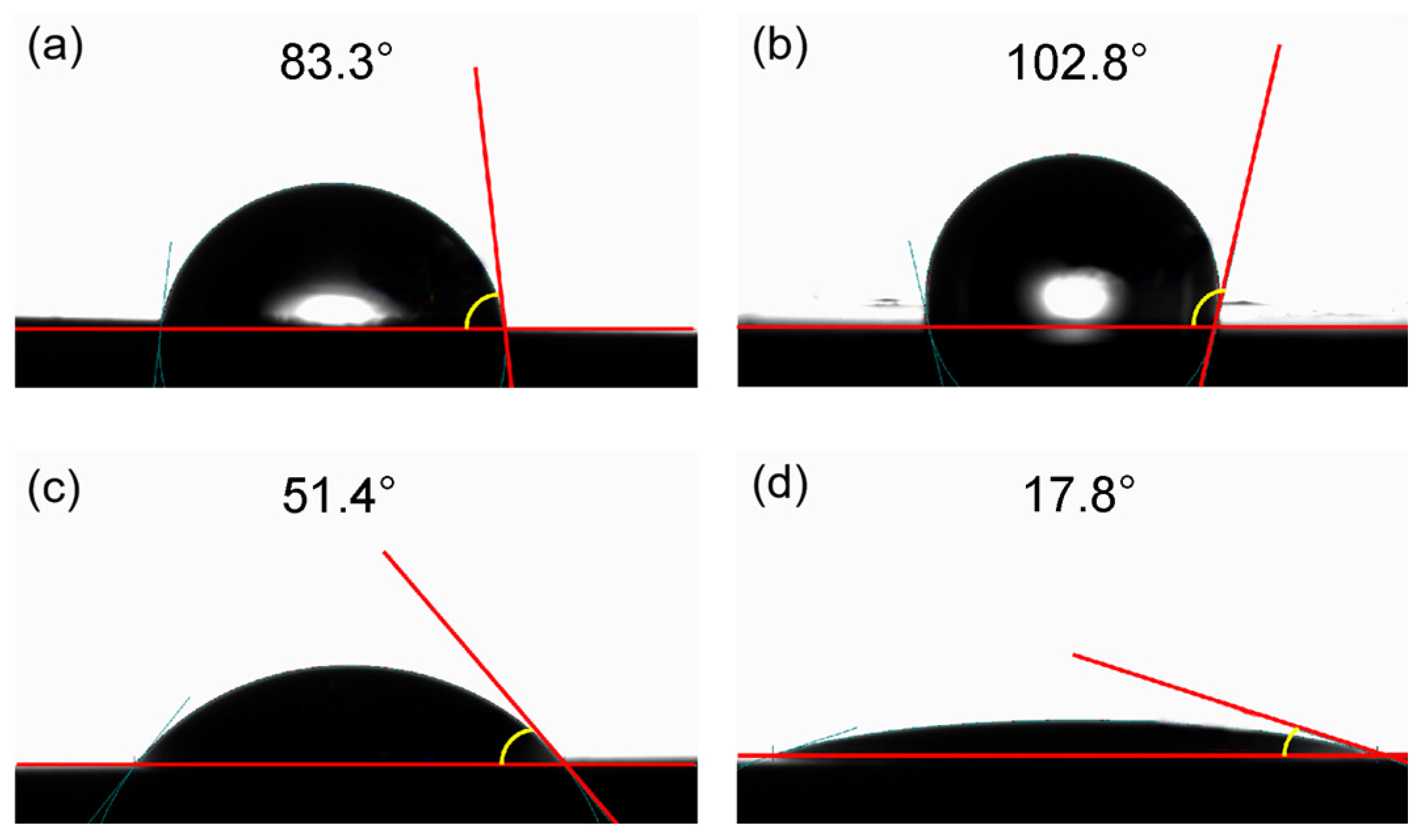
3.5. Wettability Analysis
3.6. Imbibition Efficiency
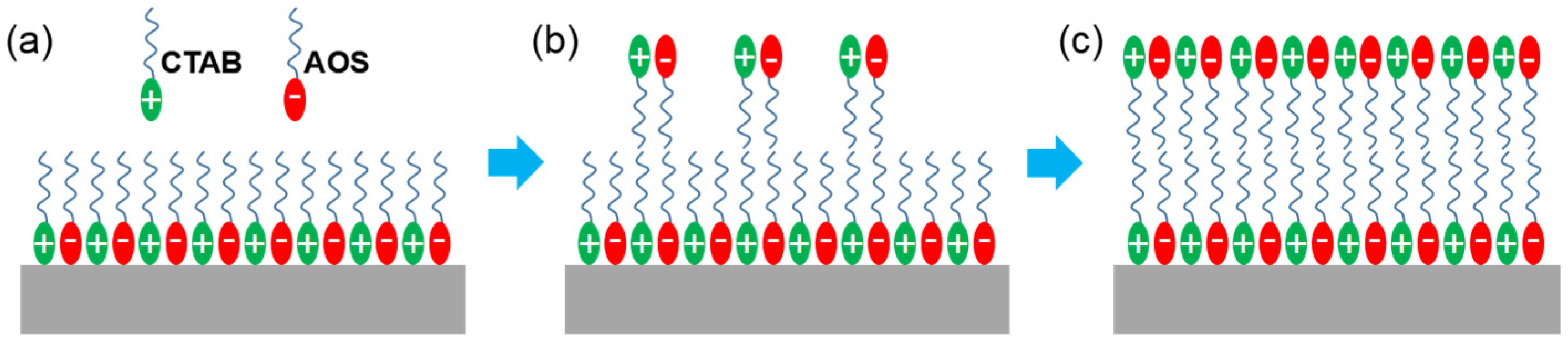
3.7. Mechanism Analysis of Enhanced Oil Recovery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSG | Mixed-charge surfactants, i.e., a pseudogemini surfactant |
| IFT | Interfacial tension |
| EOR | Enhancing oil recovery |
| CAB | Cocoamidopropyl betaine |
| EK2 | The second member of Kongdian Formation of Cangdong Sag |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide |
| AOS | α-olefin sulfonate |
| CNPC | China National Petroleum Corporation |
References
- Wang, M.; Guo, Z.; Jiao, C.; Lu, S.; Li, J.; Xue, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Chen, G. Exploration progress and geochemical features of lacustrine shale oils in China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 178, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Pan, S.; Jing, Z.; Gao, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Q. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact. Acta Pet. Sin. 2020, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Blackbourn, G.; Ma, F.; He, Z.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Luan, T.; Wu, Z. Heavy oils and oil sands: Global distribution and resource assessment. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2019, 93, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bai, M.; Xu, L.; Du, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, E.; Shan, J. Study on oil extraction characteristics in micropores of a typical terrestrial shale reservoir in China by CO2 injection and surfactant imbibition. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 6927–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Gao, M.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J. A review on shale oil and gas characteristics and molecular dynamics simulation for the fluid behavior in shale pore. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376, 121507–121541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Yin, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, G. Surfactant slug assisting CO2 huff and puff in enhancing shale oil reservoir recovery. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 16601–16610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Weng, D.; Guan, B.; Shi, J.; Cai, B.; He, C.; Sun, Q.; Huang, R. Shale oil and gas exploitation in China: Technical comparison with US anddevelopment suggestions. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y. Current status, advances, and prospects of CNPC’s exploration of onshoremoderately to highly mature shale oil reservoirs. Oil Gas Geol. 2024, 45, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, W. Progress and key scientific and technological problems of shale oil exploration and development in China. World Pet. Ind. 2024, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Ma, F.; Pan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Fu, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z. Formation and distribution potential of global shale oil and the developments of continental shale oil theory and technology in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2023, 30, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, I.W.R.; Park, K.H.; Zhang, F.; Adel, I.A.; Schechter, D.S. Surfactant-assisted spontaneous imbibition to improve oil recovery on the Eagle Ford and Wolfcamp shale oil reservoir: Laboratory to field analysis. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 6904–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Cao, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. The Crack Propagation Behaviour of CO2 Fracturing Fluid in Unconventional Low Permeability Reservoirs: Factor Analysis and Mechanism Revelation. Processes 2025, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tian, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; Yao, B.; Wang, S.; Winterfeld, P.H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Advances in improved/enhanced oil recovery technologies for tight and shale reservoirs. Fuel 2017, 210, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lei, X.; Feng, D.; Ahmadi, M.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L. Nanoconfinement effect on the miscible behaviors of CO2/shale oil/surfactant systems in nanopores: Implications for CO2 sequestration and enhanced oil recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129826–129838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, R.; Guo, F. The characteristics and effects of Huff-n-Puff in shale with brine, aqueous surfactant solutions and CO2. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 79, 102655–102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhao, J.; Ji, Z.; Cao, M.; Xu, L.; Ma, Y. Effect of CO2 Huff-n-Puff mode with a horizontal well on shale oil recovery: A three-dimensional experimental study. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 9318–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosultchi, A.; Rossbach, P.; Hernandez-Calderon, I. XPS analysis of petroleum well tubing adherence. Surf. Interface Anal. 2003, 35, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, J.J. Experimental investigation of surfactant enhanced spontaneous imbibition in Chinese shale oil reservoirs using NMR tests. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 72, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadehmojarad, A.A.; Fazelabdolabadi, B.; Vuković, L. Surfactant-controlled mobility of oil droplets in mineral nanopores. Langmuir 2020, 36, 12061–12067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, J.J.; Wang, X.; Ge, H.; Yao, E. Experimental study of wettability alteration and spontaneous imbibition in Chinese shale oil reservoirs using anionic and nonionic surfactants. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 175, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Sheng, J.J. Experimental and numerical study of surfactant solution spontaneous imbibition in shale oil reservoirs. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 106, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bai, B.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Ding, W. Effect of surfactants on the interface characteristics and imbibition processes in shale oil reservoirs. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 706, 135818–135828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospisil, G.; Griffin, L.; Souther, T.; Strickland, S.; McChesney, J.; Pearson, C.M.; Dalkhaa, C.; Sorensen, J.; Hamling, J.; Kurz, B.; et al. East Nesson Bakken enhanced oil recovery pilot: Coinjection of produced gas and a water-surfactant mixture. In Proceedings of the 10th Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, URTEC-3722974-MS, Houston, TX, USA, 20–22 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Bian, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Qin, B.; Pu, X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, S.; Guan, M.; Dong, J.; et al. “Component flow” conditions and its effects on enhancing production of continental medium-to-high maturity shale oil. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Ge, H.; Han, X.; Xue, E. Catanionic surfactant systems for emulsifying and viscosity reduction of shale oil. Energies 2024, 17, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q/SY 17583-2018; Specifications of Surfactants Used in SP Binary Combination Flooding. China National Petroleum Group Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Jia, S. Alkali-free three-component emulsification flooding system. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, O.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, B. Mixed cationic and anionic surfactant systems achieve ultra-low interfacial tension in the Karamay oil field. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2014, 30, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q/SH 1020 2191-2021; Technical Requirements of Surfactants for Oil Displacement. Sinopec Shengli Petroleum Administration Bureau: Dongying, China, 2021.
- Sheng, J.J. What type of surfactants should be used to enhance spontaneous imbibition in shale and tight reservoirs? J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 159, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Kunjappu, J.T. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Mu, M.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y. Sodium fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether carboxylate/cationic surfactant binary system for high-salt oil reservoir. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2023, 26, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Ai, C.; Wu, J. Preparation and performance evaluation of a novel temperature-resistant anionic/nonionic surfactant. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5710–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, D.; Hua, J.; Jiang, K.; Xu, Z.; Tong, K. Enhancing low-temperature thermal remediation of petroleum sludge by solvent deasphalting. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135278–135287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, F.; Cui, Y.; Song, S.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, F. Research and breakthrough of benefit shale oil development in Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2023, 28, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Jia, R.; Fu, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Jiang, C.; Yang, B. A novel high temperature tolerant and high salinity resistant gemini surfactant for enhanced oil recovery. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 112114–112122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, I.W.R.; Adebisi, O.; Ladan, E.B.; Bagareddy, A.; Sarmah, A.; Schechter, D.S. The influence of oil composition, rock mineralogy, aging time, and brine pre-soak on shale wettability. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, F.; Gandomkar, A. Experimental evaluation of CO2-soluble nonionic surfactants for wettability alteration to intermediate CO2-oil wet during immiscible gas injection. SPE J. 2024, 29, 5071–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, R.; Shi, J.; Zhao, K.; Chu, Y.; Du, D. Interfacial properties and efficient imbibition mechanism of anionic–nonionic surfactants in shale porous media. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 11955–11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, J.J.; Tu, J. Effect of spontaneous emulsification on oil recovery in tight oil-wet reservoirs. Fuel 2020, 279, 118456–118466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pu, X.; Jin, F.; Chen, C.; Shi, Z.; Chai, G.; Han, W.; Jiang, W.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, W.; et al. Enrichment law and favorable exploration area of shale-type shale oil in Huanghua depression. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. The Effect of Surfactant System on Imbibition Bahavior. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Petroleum (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Li, J.; Zhou, G. Analysis of parameters influencing oil displacement efficiency of oil displacement agent. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2008, 32, 99–102. Available online: http://zgsydxxb.ijournals.cn/zgsydxxben/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080321&flag=1 (accessed on 15 January 2024).



| GY152H | GY734H | GY512L | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (50 °C, mPa·s) | 143 | 2220 | 726 |
| Density (20 °C, g/cm3) | 0.9016 | 0.9048 | 0.8997 |
| pour point (°C) | 37 | 42 | 49 |
| Wax content (%) | 30.49 | 23.54 | 20.24 |
| Ion Composition | Na+ + K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | SO42− | CO32− | HCO3− | Cl− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ion content (mg/L) | 10,183 | 73 | 260 | 264 | 31 | 411 | 15,897 |
| Field Water (%) | 0.2% PSG Solution (%) | Increase Amplitude (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil sand (GY152H) | 31.15 | 66.24 | 35.09 |
| Oil sand (GY512L) | 26.34 | 55.67 | 29.33 |
| Oil sand (GY734H) | 21.63 | 47.48 | 25.85 |
| Performance Index | Before Aging | After Aging |
|---|---|---|
| Interfacial tension (mN/m) | 0.0027 ± 0.0008 | 0.0316 ± 0.0035 |
| Viscosity reduction rate (%) | 98.60 ± 0.52 | 95.41 ± 0.78 |
| Demulsification rate (%) | 88.75 ± 1.50 | 92.25 ± 1.75 |
| Static oil-washing efficiency (%) | 47.48 ± 1.38 | 48.54 ± 1.23 |
| Field Water | 0.2% PSG Solution | |
|---|---|---|
| Interfacial tension (mN/m) | 10.2 | 2.7 × 10−3 |
| Contact angle (°) | 51.4 | 17.8 |
| Adhesion work (mJ) | 3.84 | 1.29 × 10−4 |
| Adhesion work factor, E | 1 | 3.44 × 10−5 |
| Imbibition recovery factor (%) | 9.84 | 29.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Ge, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Effect of Mixed-Charge Surfactants on Enhanced Oil Recovery in High-Temperature Shale Reservoirs. Processes 2025, 13, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041187
Li Q, Wang X, Tang Y, Ge H, Zhou X, Li D, Wang H, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Wang W. Effect of Mixed-Charge Surfactants on Enhanced Oil Recovery in High-Temperature Shale Reservoirs. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041187
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qi, Xiaoyan Wang, Yiyang Tang, Hongjiang Ge, Xiaoyu Zhou, Dongping Li, Haifeng Wang, Nan Zhang, Yang Zhang, and Wei Wang. 2025. "Effect of Mixed-Charge Surfactants on Enhanced Oil Recovery in High-Temperature Shale Reservoirs" Processes 13, no. 4: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041187
APA StyleLi, Q., Wang, X., Tang, Y., Ge, H., Zhou, X., Li, D., Wang, H., Zhang, N., Zhang, Y., & Wang, W. (2025). Effect of Mixed-Charge Surfactants on Enhanced Oil Recovery in High-Temperature Shale Reservoirs. Processes, 13(4), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041187







