Abstract
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) are emerging as efficient materials for environmental remediation due to their dual functionality in selective pollutant adsorption and catalytic degradation. This review examines recent advances in MIP-based technologies, focusing on their role in photocatalysis and advanced oxidation processes. Experimental findings highlight impressive degradation efficiencies, such as 95.8% methylene blue degradation using ZnO/CuFe2O4 MIPs and a 60% improvement in refractory organic degradation with TiO2-MIPs. Adsorption studies show high uptake capacities, including 273.65 mg/g for ciprofloxacin with MOF-supported MIPs and 2350.52 µg/g for rhodamine B using magnetic MIPs. Despite these advancements, several challenges remain, including issues with long-term stability, scalability, and economic feasibility. Future research should prioritize optimizing polymer synthesis, integrating MIPs with high-surface-area matrices like MOFs and COFs and enhancing recyclability to ensure sustained performance. MIPs hold significant potential for large-scale water treatment and pollution control, provided their stability and efficiency are further improved.
1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been growing concern about water scarcity and pollution, both on a local and global scale. As our planet’s population continues to increase and industrialization expands, the demand for clean and accessible water has reached an alarming level. Even though more than 70% of the Earth is covered in water, access to clean water remains a critical challenge, with approximately 30% of the people worldwide lacking safely managed drinking water and almost 60% of people facing risks due to improper sanitation practices [1,2,3]. Environmental pollution, particularly water contamination, has become a significant global concern, posing threats to ecosystems, human health, and economic stability. Key sources of pollution include industrial [4], agricultural [5], and domestic discharges [6], introducing substances such as dyes [7], heavy metals [8], pesticides [9], and endocrine disruptors [10] into aquatic systems. Addressing this issue requires innovative and selective remediation technologies. Among these, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) and functional materials, such as molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), stand out for their ability to target persistent pollutants effectively [7].
Poor water quality affects every aspect of life, including the spread of diseases, disruptions in food production, depletion of natural resources, and increased mortality rates [11]. Human activities such as industrial manufacturing, agriculture, and improper waste disposal practices significantly contribute to the contamination of rivers, lakes, and groundwater [12]. Pollutants including chemicals, heavy metals, and bacteria not only degrade water quality but also pose direct risks to human and environmental health [13]. The pollution of water bodies disrupts aquatic ecosystems, reduces biodiversity, and affects the livelihoods of communities that rely on clean water [6]. Therefore, addressing water pollution requires a comprehensive approach. Efforts must be made to improve water management practices, invest in sustainable infrastructure, promote water conservation and efficiency, and implement stricter regulations on pollution control. Moreover, raising awareness about the importance of clean water and empowering individuals to act in their daily lives can contribute to mitigating these challenges [14].
In recent years, the presence of emerging pollutants (EPs), also known as Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs), has gained increasing attention. EPs refer to a wide range of chemical substances that are not commonly regulated or routinely monitored in water systems [15]. These pollutants originate from various sources, including pharmaceuticals, personal care products, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. They enter water bodies through improper disposal, wastewater discharges, and runoff from agricultural fields. One of the major concerns about EPs is their potential adverse effects on human health and the environment [16].
Studies have shown that EPs, even at low concentrations, can negatively impact aquatic life, such as fish and amphibians [17]. Some of these substances may also infiltrate drinking water sources, posing a threat to human health [18]. Although the long-term effects of EP exposure are still under investigation, concerns include endocrine disruption, antibiotic resistance, and other serious health risks [16]. To combat this issue, authorities worldwide have intensified their efforts to monitor and regulate EPs. The World Health Organization (WHO), within the framework of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), has emphasized the need for action in this matter. Two SDGs are particularly relevant: Goal 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and Goal 14 (Life Below Water) [19].
Goal 6 targets the provision of access to clean water and sanitation for all, as well as the improvement of water quality and the efficiency of water use. It emphasizes the importance of integrated water resources management, including the protection of ecosystems and the reduction of pollution. However, issues such as water scarcity, pollution, and EPs hinder progress toward achieving this goal. By tackling these challenges, we can contribute to ensuring universal access to clean water and sanitation, safeguarding human health, and restoring and conserving water-related ecosystems [20]. Goal 14 focuses on the conservation and sustainable use of marine resources and ecosystems. It highlights the need to prevent and reduce marine pollution, including pollution from land-based sources. Because many water pollutants ultimately reach coastal and marine environments, addressing EPs is essential for the preservation of marine life and biodiversity. By implementing effective pollution control measures and promoting sustainable practices, we can protect marine life, preserve biodiversity, and maintain the health and vitality of our oceans and coastal areas [21].
In light of the SDGs, it is imperative that governments, organizations, and individuals work together to develop innovative solutions and take concerted action to ensure clean and accessible water resources, protect ecosystems, and prevent the spread of EPs. By aligning our efforts with the SDGs, we can pave the way toward a sustainable and resilient future for both present and future generations. A key component of this strategy is improving detection and monitoring methods to track the presence and concentration of these contaminants in water systems. Furthermore, the development of advanced treatment technologies is crucial for their removal from wastewater and drinking water supplies. Conventional treatment methods (such as AOPs and biological degradation) often fall short of effectively degrading these pollutants, necessitating the exploration of novel approaches.
AOPs involve the use of powerful oxidizing agents, such as ozone (O3), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), or photogenerated hydroxyl radicals (OH), to break down pollutants. These processes generate highly reactive species that can effectively degrade a wide range of emerging water pollutants. However, AOPs face several challenges, including high energy consumption, the formation of toxic byproducts, and the requirement for specialized equipment, which hinder widespread implementation [22]. Biological degradation methods, on the other hand, utilize microorganisms or enzyme systems to process and metabolize organic pollutants. Biological treatment processes are commonly used in wastewater treatment plants; however, they exhibit limited effectiveness against EPs due to the pollutants’ recalcitrant nature, low concentrations, and potential toxicity. Furthermore, biological degradation is slow, often requiring long contact times, and can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, pH, and nutrient availability [23].
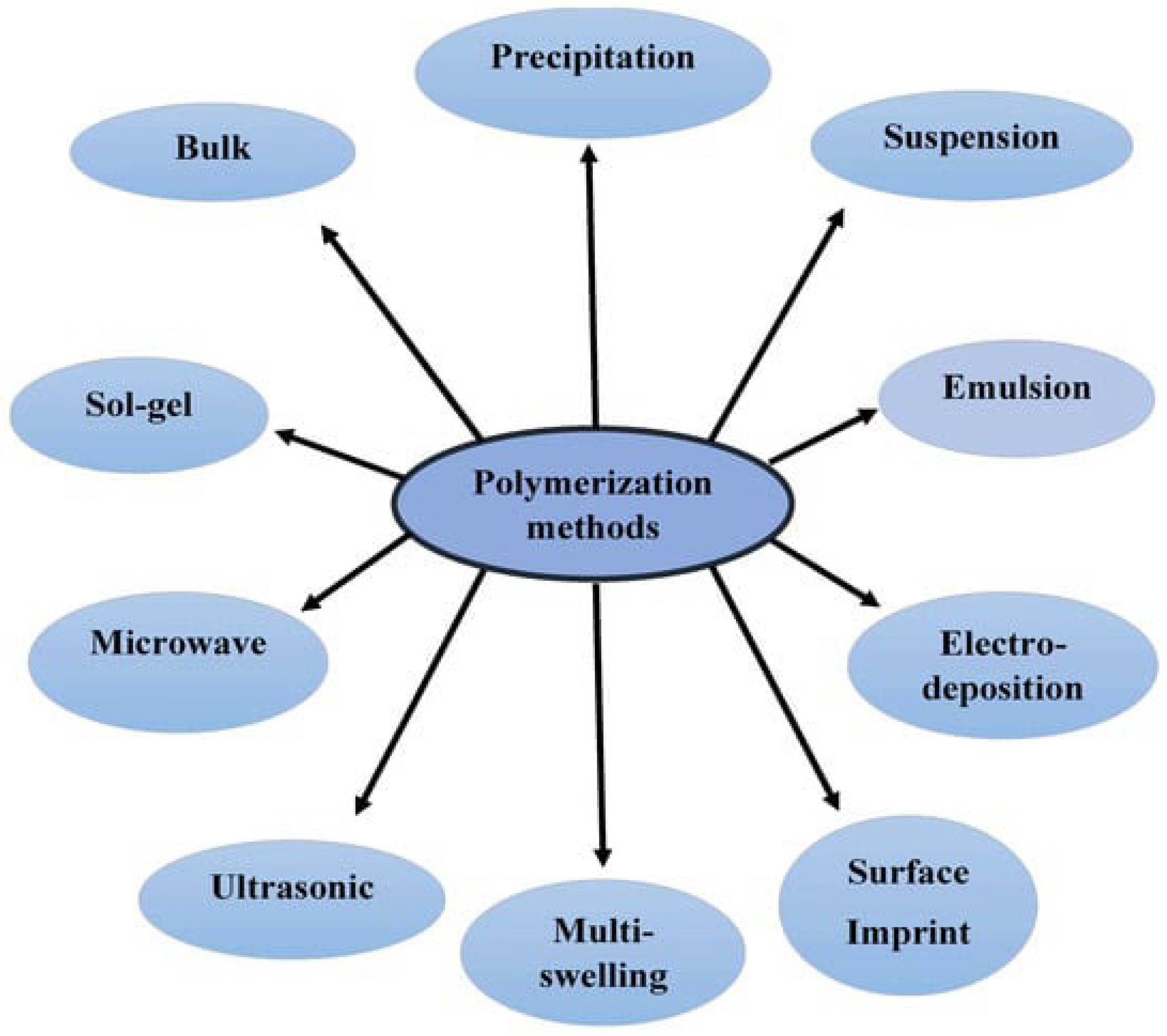
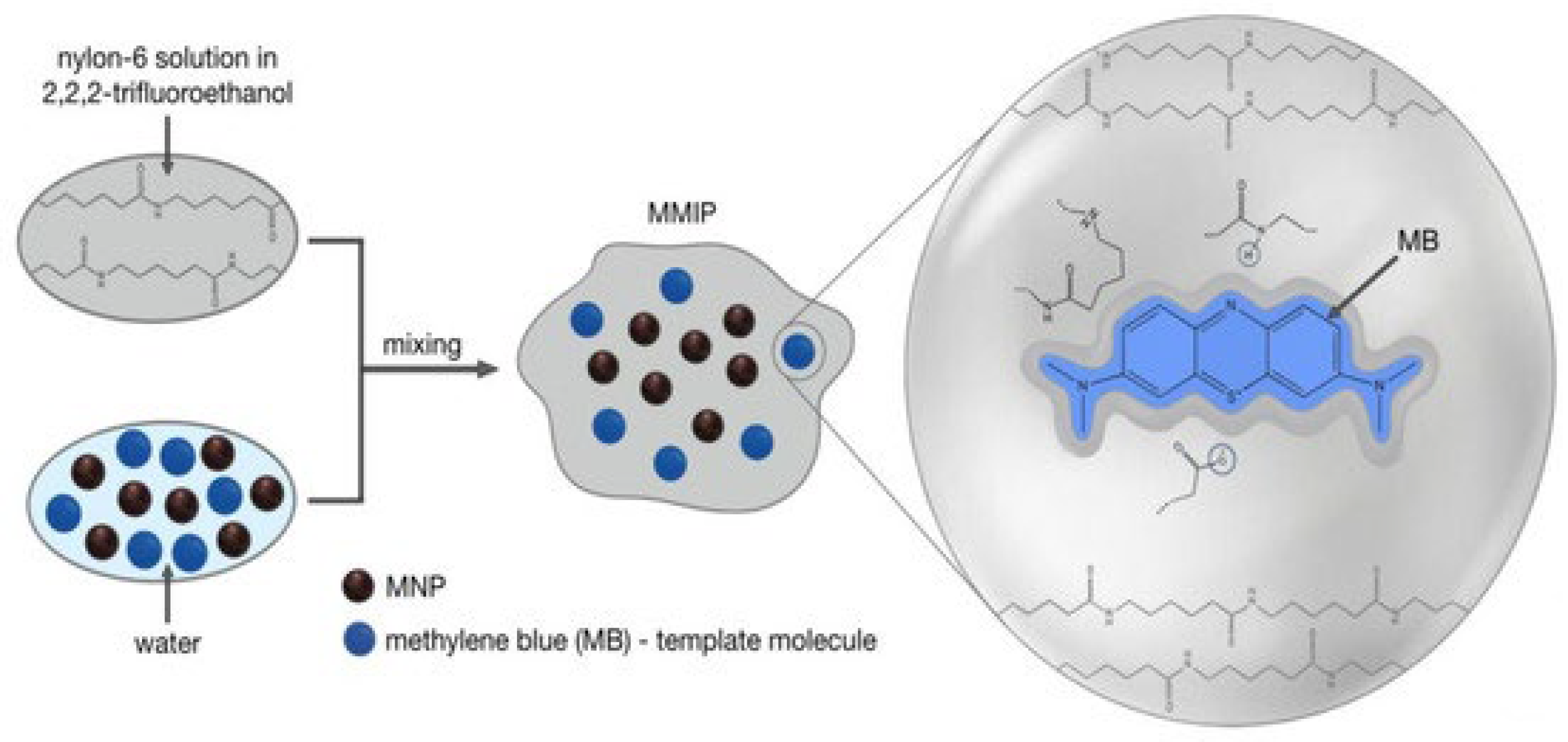
MIPs, a class of advanced functional materials, have recently gained attention as a promising alternative for the removal of EPs. MIPs are synthetic polymers engineered with molecular recognition sites designed to selectively mimic the shape, size, and functional groups of the target pollutant molecule [24,25]. MIPs can be specifically designed to selectively recognize and bind the target pollutant, enhancing the adsorption and degradation process while minimizing interference from other coexisting compounds via diverse polymerization techniques (Figure 1). This selective binding ability results in high removal efficiency and reduced potential for the generation of harmful byproducts.
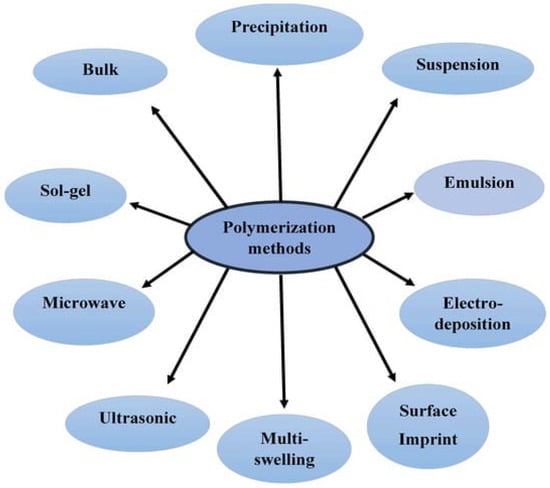
Figure 1.
Common polymerization methods for MIP synthesis. Reproduced from Metwally et al., 2021 [26] under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
MIPs have evolved from mere separation tools into multifunctional systems with catalytic capabilities, particularly in photocatalysis. These materials excel in coupling recognition with reaction, particularly in applications where they are integrated with metal oxides like TiO2 [23] or ZnO [27]. By concentrating specific pollutants on their surface, MIPs enhance catalytic degradation performance while overcoming limitations of traditional photocatalysts, such as poor selectivity and rapid recombination of charge carriers [28].
The goal of this manuscript is to provide a comprehensive overview of the dual role of MIPs in both selective pollutant adsorption and catalytic degradation. By analyzing recent advancements, this review highlights key trends, challenges, and opportunities in the field. Special emphasis is placed on the mechanisms that enhance MIP performance, such as their integration with photocatalytic materials, high-surface-area matrices, and advanced polymerization techniques. Ultimately, this work aims to guide future research toward optimizing MIP design for large-scale environmental applications, with a focus on improving stability, efficiency, and sustainability in water treatment and pollution remediation. The novelty of this review lies in its focused analysis of MIPs’ combined role as both selective adsorbents and catalysts, emphasizing recent innovations, performance metrics, and emerging strategies for enhanced efficiency and scalability in real-world applications.
2. Methodology
2.1. Bibliometric Analysis
Bibliometric analysis is a systematic methodology used to evaluate and synthesize large volumes of scientific literature by applying quantitative techniques to measure research output and map academic trends [29]. In this study, the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection® from Clarivate Analytics™ was selected as the database for analysis, focusing on its comprehensive and widely recognized coverage of high-quality scientific publications. However, the use of a single source may limit the scope of the analysis, as it does not account for literature from other databases such as Scopus or Google Scholar, which could potentially include relevant studies not indexed in WoS. To address this limitation, we emphasize the WoS database’s robustness in capturing peer-reviewed journal articles, which were the primary focus of the search. The inclusion criteria were strictly defined to consider only peer-reviewed journal articles, excluding preprints, conference papers, and other literature, to ensure the reliability and academic rigor of the selected studies.
The search was conducted using the string “imprinted polymer*” and “degradation” to identify relevant publications related to the use of MIPs in degradation processes. Bias in the data extraction and review processes was minimized through several steps: clear inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied, and rigorous validation and cross-referencing procedures were conducted throughout the analysis. Furthermore, citation analysis, co-authorship analysis, co-citation, and bibliographic coupling were utilized to identify research relationships and cluster-related topics, ensuring an objective and comprehensive overview of the field [30]. This methodological rigor allowed for reliable conclusions about the state of research, identification of knowledge gaps, and proposals for future directions in the field of MIP-based degradation.
2.2. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
This review presents a comprehensive exploration of the relationship between MIPs and their effectiveness in degradation processes, guided by a rigorous methodology based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines (PRISMA). By adhering to PRISMA standards, this review ensures a systematic, transparent, and replicable approach, which aligns with the best practices in synthesizing scientific evidence [31]. The initial phase involved conducting an extensive literature search across WoS Core Collection®. The search strategy systematically combined relevant keywords, such as “molecularly imprinted polymers”, “MIPs”, “degradation”, “selective adsorption”, “photodegradation”, etc., to retrieve all pertinent research articles. Studies were included if they specifically examined the use of MIPs for the targeted degradation or removal of pollutants from different environments. Exclusion criteria were carefully applied, eliminating non-English language studies, conference abstracts, and research not directly related to MIPs’ efficiency in degradation.
The screening and selection process was rigorous, with two or more reviewers independently assessing titles and abstracts to determine their relevance and adherence to the inclusion criteria. Full-text articles that passed initial screening were further evaluated for eligibility, with any discrepancies between reviewers resolved through discussion. Data extraction focused on critical details such as the design of the MIPs, the experimental conditions used, degradation efficiency, and reported limitations or challenges. The extraction was conducted by one reviewer and subsequently verified for accuracy by another to maintain data integrity. The quality assessment of the included studies was performed using established criteria, considering factors such as the robustness of the experimental setup, reproducibility, and clarity in data presentation. Any disagreements in quality evaluation were resolved through consensus among the reviewers.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Bibliometric Trends
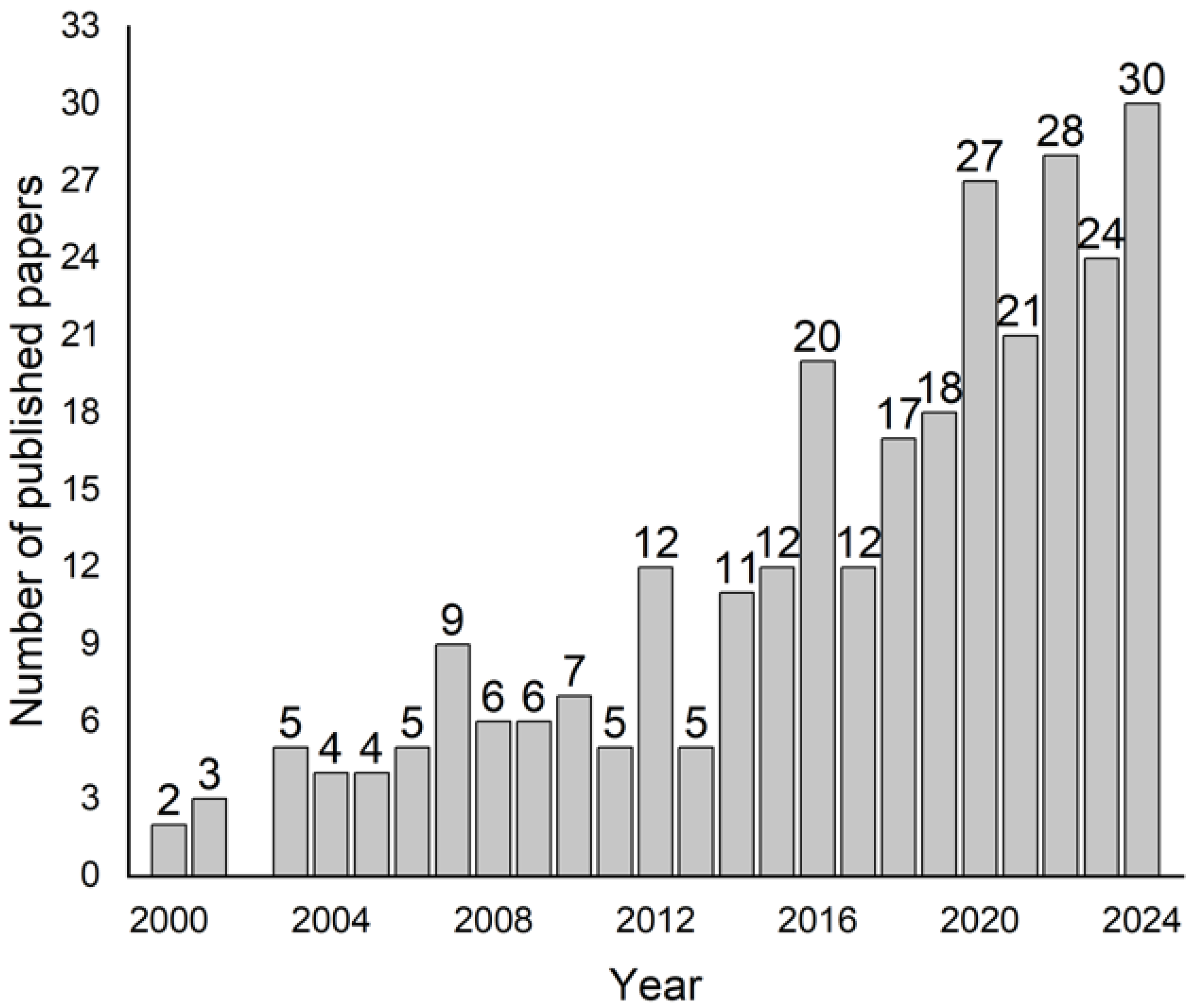
Applying the search criteria described in the Section 2, 315 published research papers were found and registered in the database reviewed. Figure 2 shows a significant increase over time in the scientific literature related to the use of MIPs for degradation purposes from 2000 onwards. The information demonstrates a steady upward trend, with notable growth over the years. In the early 2000s, publication numbers were relatively low, starting from two papers in 2000 and gradually increasing to nine papers by 2008. From 2010 onward, the rate of publication accelerated, peaking significantly in recent years. The most substantial growth occurs from 2016 onwards, with publications consistently rising each year. In 2020, there was a marked increase to 27 papers, and this growth continues, reaching 30 papers in 2024. It is necessary to note that of the 315 published works, 293 were published after 2000, and of those, 45% were published in the past five years (2020–2024). Over the past five years, 130 publications have addressed this issue, with the largest number appearing this year, as depicted in Figure 1. This significant increase in publications since 2020 is likely due to several factors, including advancements in materials science, particularly in the synthesis of more efficient MIPs, and the growing global emphasis on sustainability. The surge in research activity can also be attributed to increased funding, international collaborations, and a heightened awareness of the need for sustainable solutions to environmental and health-related challenges. This trend reflects the expanding interest in the field and emphasizes the increasing significance of MIPs in addressing pressing global issues, such as water pollution and health crises, further driving their growing impact on the scientific community.
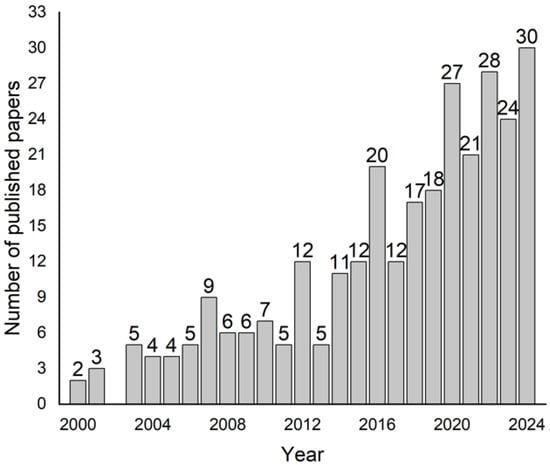
Figure 2.
Distribution of publications on MIPs for degradation from 2000 to 2024.
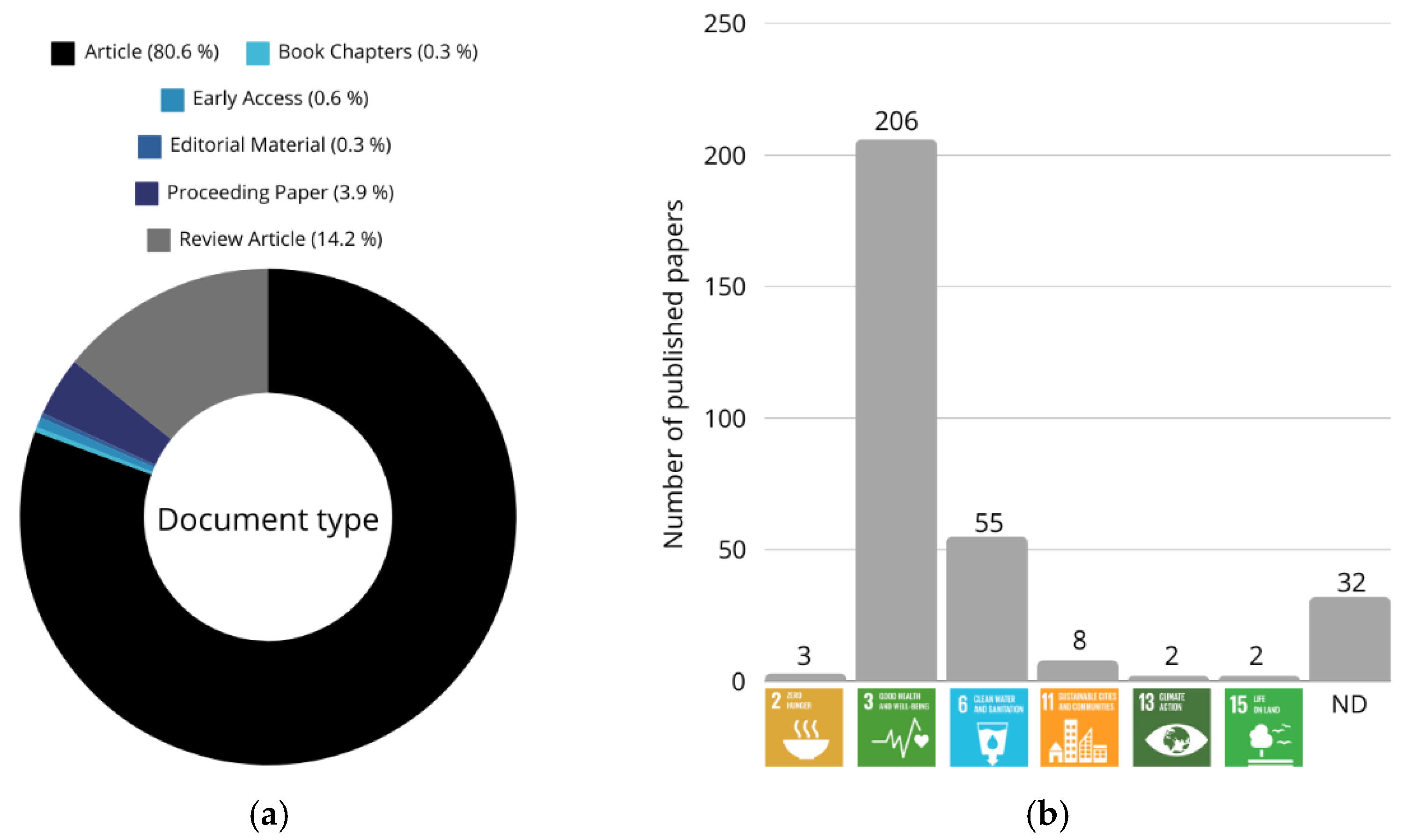
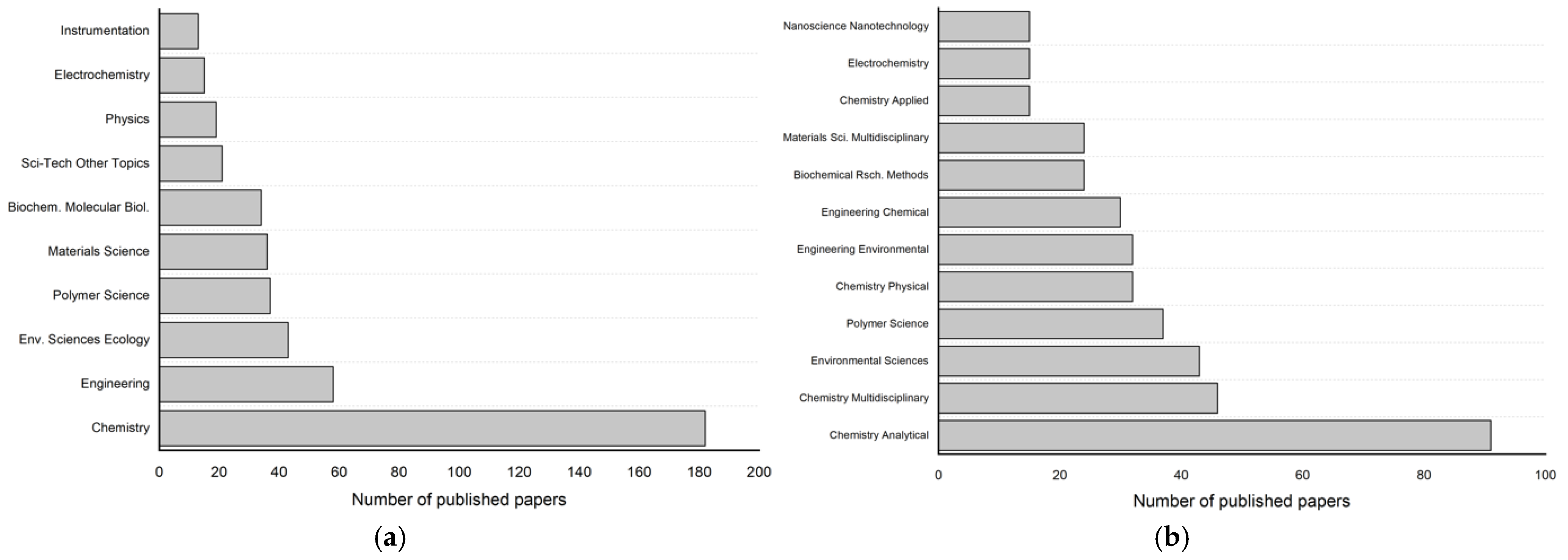
As depicted in Figure 3a, approximately 81% of the published works are research articles, while 14% consist of review articles, and 3.9% are peer-reviewed proceeding papers. Only 0.6% are early access publications, and about 0.3% are book chapters and editorial materials, respectively. Figure 3b illustrates the distribution of published papers corresponding to various Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). A significant finding is the overwhelming dominance of SDG 3, “Good Health and Well-Being”, which accounts for 206 papers. This suggests that a considerable amount of research has been dedicated to health-related challenges, reflecting the global prioritization of advancements in medical applications such as biosensing, diagnostics, and drug delivery.

Figure 3.
Distribution of publications by (a) document type and (b) SDGs.
The second-highest concentration is for SDG 6, “Clean Water and Sanitation”, with 55 publications. This focus underscores the importance of developing innovative solutions for water quality monitoring and treatment, further indicating a critical area where advanced materials play a pivotal role. In contrast, SDG 7 (“Affordable and Clean Energy”), SDG 11 (“Sustainable Cities and Communities”), SDG 13 (“Climate Action”), and SDG 15 (“Life on Land”) have significantly fewer publications, with only eight, two, two, and two papers, respectively. These findings suggest that, while these areas are essential for global sustainability, they may not yet have received as much attention from the research community, particularly concerning emerging technologies like MIPs. This may be due to the focus of MIP research on areas like health and water treatment, which are more immediately relevant to researchers. SDG 13, dealing with climate change, may not yet have fully embraced MIPs as a solution, potentially because other technologies such as carbon capture or renewable energy solutions have taken precedence. We believe this represents an opportunity for future research to explore the potential of MIPs in climate-related applications, which could further broaden their impact on global sustainability goals.
Nevertheless, the ongoing global focus on sustainability presents an opportunity for future expansion in these areas. Figure 3b also includes 32 papers categorized as ND (Non-Defined), representing research that either does not directly align with any specific SDG or comprises foundational and interdisciplinary work that supports multiple sustainability objectives. This category highlights the complexity and interconnectedness of modern research, where some studies may not be easily classified under a single goal. Overall, the data reveal a strong emphasis on health and water sanitation research, indicating well-established areas of application. However, the limited focus on energy, urban sustainability, and climate action suggests potential growth opportunities. As sustainability and environmental impact become increasingly critical, there is a pressing need to explore innovative materials and technologies that address these challenges. Moreover, the presence of ND papers emphasizes the interdisciplinary nature of scientific research, which may benefit from clearer frameworks to align more comprehensively with global sustainability priorities.
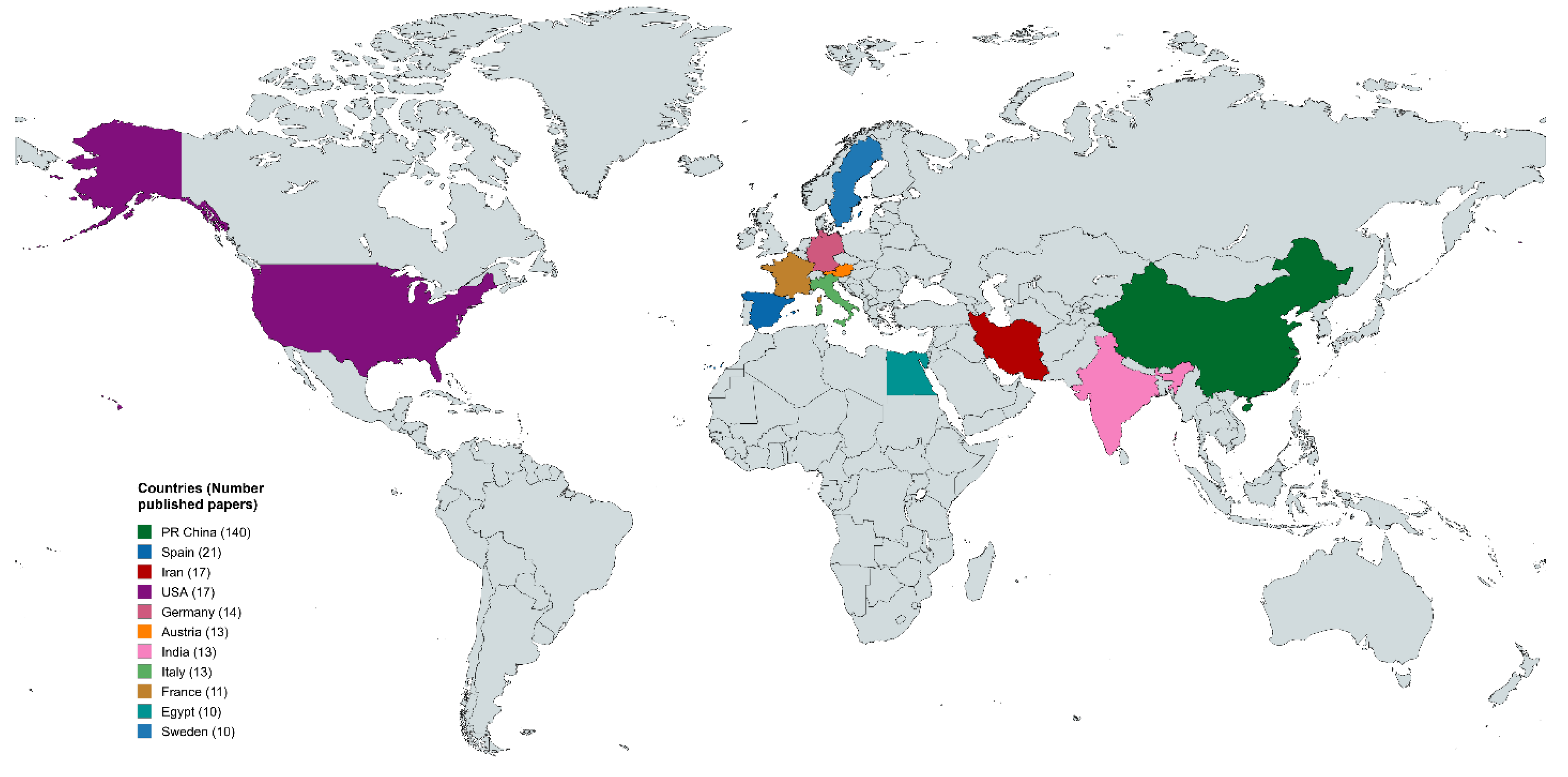
Figure 4 depicts the geographical distribution of published research papers related to the topic, highlighting contributions from various countries. China leads with 149 papers, reflecting its prominent role in this research area, likely driven by significant investments in science and technology. Iran follows with 71 papers, indicating a substantial research output, possibly in fields like material science and environmental monitoring. The United States ranks third with 37 publications, emphasizing its focus on innovative technologies and applications. European countries, including Germany (n = 18), Austria (n = 14), and Italy (n = 11), show moderate contributions, which may be attributed to collaborative projects and advancements in applied research. Other notable contributors are India (n = 14) and Egypt (n = 10), showcasing growing research efforts in developing regions. The map highlights global research trends and underscores the need for international collaboration to advance this field further.
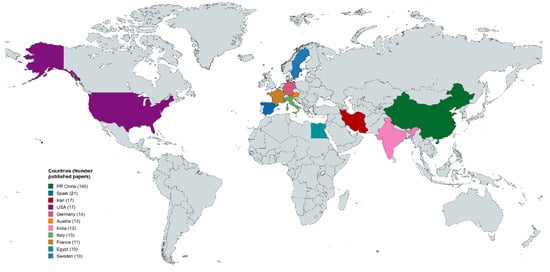
Figure 4.
Top countries by number of publications.
The journals with the largest number of publications on this issue (Table 1) are Analytica Chimica Acta and the Journal of Chromatography A (n = 9 published works each), followed by the Journal of Chromatography A, Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, and Environmental Science and Pollution Research (n = 8 each), the Journal of Separation Science (n = 7), the Chemical Engineering Journal, the Journal of Hazardous Materials, and Talanta (n = 6 each).

Table 1.
Top five journals by number of publications.
By research areas (Figure 5a), the largest number of items were in Chemistry (n = 182), followed by Engineering (n = 58), Environmental Sciences Ecology (n = 43), Polymer Science (n = 37), and Materials Science (n = 36). By WoS category (Figure 5b), studies were most frequently grouped in Analytical Chemistry (n = 91), followed by Multidisciplinary Chemistry (n = 46), Environmental Sciences (n = 43), Polymer Science (n = 37), and Physical Chemistry (n = 32). Other categories included Environmental Engineering, Chemical Engineering, and Biochemical Research Methods.

Figure 5.
Top research areas (a) and WoS Categories (b) by number of publications.
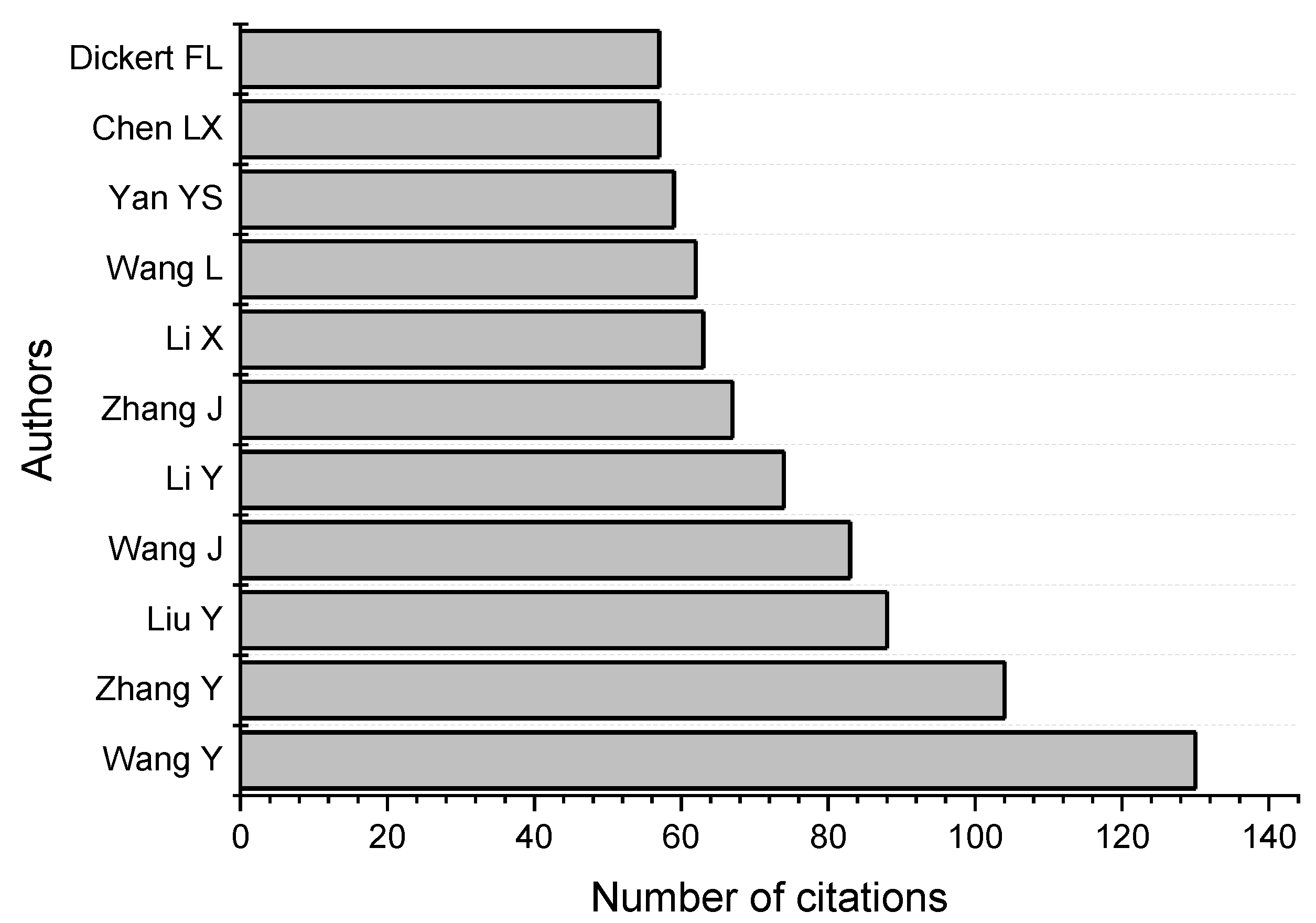
Table 2 presents the top five leading authors, ranked by the number of publications they have contributed on this topic, while Figure 6 illustrates the top 10 most cited authors in this field. Wang Y. is the most cited author with 130 citations, followed by Zhang Y. with 104 citations, and Liu Y. with 88 citations.

Table 2.
Top five authors according to the number of publications.
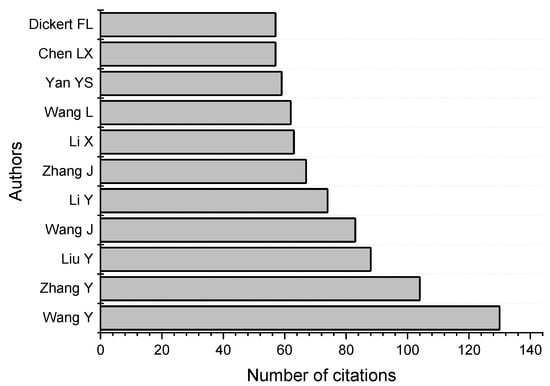
Figure 6.
Top 10 most cited authors.
3.2. MIPs for Pollutant Uptake and Degradation
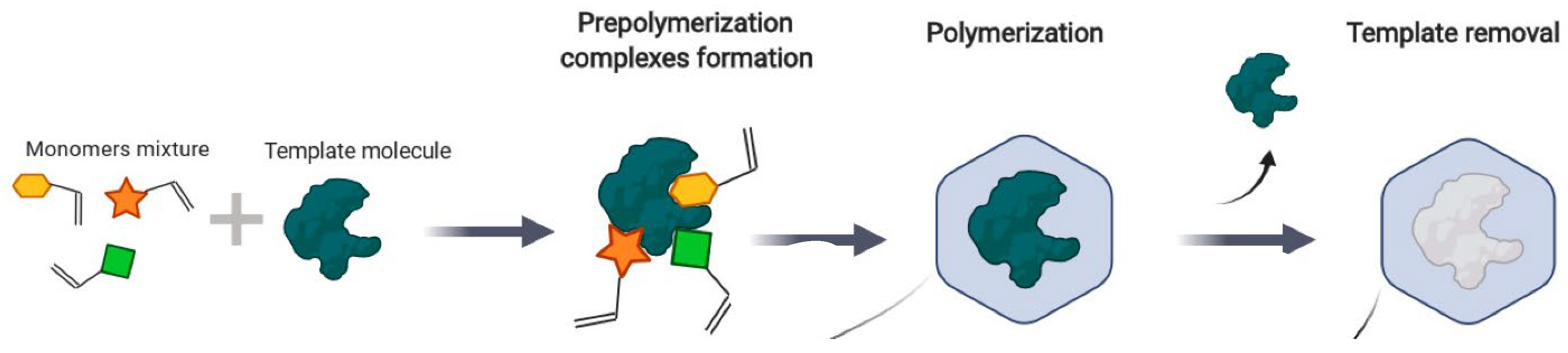
MIPs have emerged as a powerful tool in biomimetic catalysis, demonstrating significant advancements over the past two decades. These synthetic materials are designed to mimic the selectivity and specificity of natural enzymes while overcoming their limitations, such as instability under extreme conditions. MIPs are robust and stable materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for long-term use. Furthermore, MIPs can be easily regenerated and reused, enhancing their cost-effectiveness and overall sustainability [32]. These imprinted polymers can be tailored to target a wide range of EPs by modifying the choice of monomers, functional groups, and polymerization conditions [33]. This versatility allows for customization based on the specific characteristics of the target pollutants, improving the overall effectiveness of the degradation process (Figure 7).
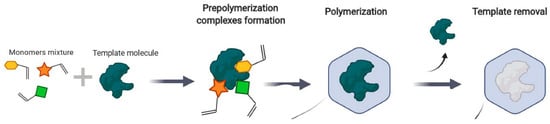
Figure 7.
MIP synthesis principle. Adapted from Garnier et al., 2021 [34] under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
In recent decades, MIPs have transitioned from being primarily separation tools to multifunctional systems integrated into catalytic processes [7]. These materials excel in coupling recognition with reaction, particularly in photocatalytic applications. For instance, MIPs combined with metal oxides, such as TiO2 [35] or ZnO, have addressed the limitations of traditional photocatalysts, including low selectivity and the recombination of charge carriers, which diminish efficiency. By concentrating specific pollutants on their surface, MIPs enhance the performance of catalytic degradation. AOPs rely on the generation of highly reactive species, such as hydroxyl radicals (·OH), to degrade organic pollutants into harmless products like CO2 and water. Techniques such as heterogeneous photocatalysis have shown promise in eliminating recalcitrant contaminants. However, conventional AOPs often lack specificity, potentially leading to the formation of toxic by-products. Integrating MIPs as selective layers in photocatalysts has significantly improved these processes, allowing targeted degradation of specific pollutants [36].
MIPs’ dual functionality as both adsorbents and catalysts makes them pivotal in environmental remediation. When combined with photocatalytic materials, these composites leverage the selective adsorption of MIPs and the catalytic activity of oxides to concentrate and degrade pollutants efficiently [37]. Studies highlight that MIP composites not only reduce degradation time but also enhance catalytic performance under milder conditions, such as using visible light instead of UV, increasing their applicability in real-world scenarios [24]. For instance, Zhan et al., 2020 [38] reported that a TiO2-based MIP composite achieved a removal efficiency of 89.82% under visible light (λ = 400–700 nm) for ethyl parahydroxybenzoate, emphasizing the material’s effectiveness in photocatalysis under milder conditions. Similarly, Sun et al., 2022 [35] demonstrated that an amino-functionalized TiO2 MIP composite successfully degraded methylene blue (93.9%) under visible light (λ = 663 nm), with hydroxyl (·OH) and superoxide (O2−) radicals playing a dominant role in the degradation process. Moreover, Guo et al., 2021 [28] highlighted the efficiency of a ZnO/CuFe2O4 (ZCF) MIP composite, achieving 95.8% removal efficiency under visible light, further reinforcing the potential of MIP-based materials in sustainable photocatalysis. Additionally, Lu et al., 2018 [39] investigated PPy@CdS@MFA and ZnFe2O4/Ag/PEDOT MIP composites, reporting removal efficiencies of 75.78% and 71.77% for tetracycline under visible light, respectively. Despite their potential, MIPs face challenges such as complex synthesis processes, associated costs, and mass-transfer limitations [40]. Innovative strategies, such as alternative templating methods and nanocomposite fabrication [41], offer promising solutions. Additionally, designing MIPs with application-specific properties remains an active research area, with efforts focused on optimizing performance and scalability for practical environmental applications.
Recent innovations have focused on expanding their application to catalyze challenging reactions, including hydrolytic processes, oxidation reactions, and unique transformations, like Diels–Alder and Kemp elimination reactions, which are not naturally enzyme-mediated. Notably, dual-template MIPs and stimuli-responsive systems, such as temperature- and pH-sensitive designs, have further enhanced their functionality, making them valuable in both industrial and environmental applications. One of the primary strengths of MIPs lies in their ability to achieve high specificity and stability, enabling selective catalytic activity in diverse conditions. Their robustness under extreme pH, temperature, and organic solvent environments positions them as a superior alternative to natural enzymes for certain applications. The integration of novel materials, including metals and ionic liquids, has not only improved their catalytic efficiency but also their recyclability, making them a sustainable choice for green chemistry initiatives. Furthermore, the versatility of MIPs allows them to be tailored for a wide range of applications, from detoxifying environmental pollutants, such as organophosphates and chlorophenols, to facilitating complex synthetic processes.
Despite their potential, MIPs face notable limitations. While their specificity is comparable to natural enzymes, their catalytic efficiency often lags behind due to restricted reaction kinetics and challenges such as product inhibition or substrate diffusion constraints within the polymer matrix. Moreover, scaling up the synthesis of MIPs while maintaining precision in active site design presents practical challenges. These issues highlight the need for further research into optimizing polymer architectures and reaction mechanisms to bridge the gap between performance and scalability. Future directions in MIP research are promising. Advances in polymer design, such as nanogels, hybrid, and stimuli-responsive materials, and co-polymers, hold the potential to enhance their catalytic activity and substrate binding capabilities. Additionally, the incorporation of environmentally friendly materials could align MIP development with the principles of green chemistry. A particularly exciting avenue is the development of MIPs for multifunctional catalysis, enabling them to facilitate multi-step or cascade reactions, which are critical in complex synthetic and environmental processes. Such innovations could elevate MIPs as indispensable tools in both academic research and industrial applications.
Compared to natural enzymes, MIPs excel in their operational stability and resistance to harsh conditions but still fall short in reaction kinetics. Against traditional heterogeneous catalysts, MIPs provide unparalleled molecular-level specificity and selectivity. These features make MIPs particularly suitable for applications requiring precise substrate recognition, such as pollutant degradation and regioselective synthesis. However, achieving scalability without compromising functionality will be crucial for their widespread adoption. Overall, MIPs represent a transformative approach to synthetic catalysis and offer significant potential to address pressing environmental and industrial challenges. Their ability to combine enzyme-like specificity with the robustness of synthetic materials positions them at the forefront of next-generation catalytic technologies. Continued innovations in material science and computational modeling will undoubtedly drive MIPs toward broader applications, making them a cornerstone of future advancements in chemistry and environmental science. MIPs are consistently being investigated for their potential in environmental remediation. For example, a review article by Mumtaz et al., 2024 [42] highlights the versatility of hybrid MIPs in addressing antibiotic contamination. These materials show remarkable selectivity and adsorption capacities, but the research lacks real-world validation, such as testing with industrial wastewater samples. Additionally, the synthesis complexity of hybrid systems may pose barriers to practical implementation.
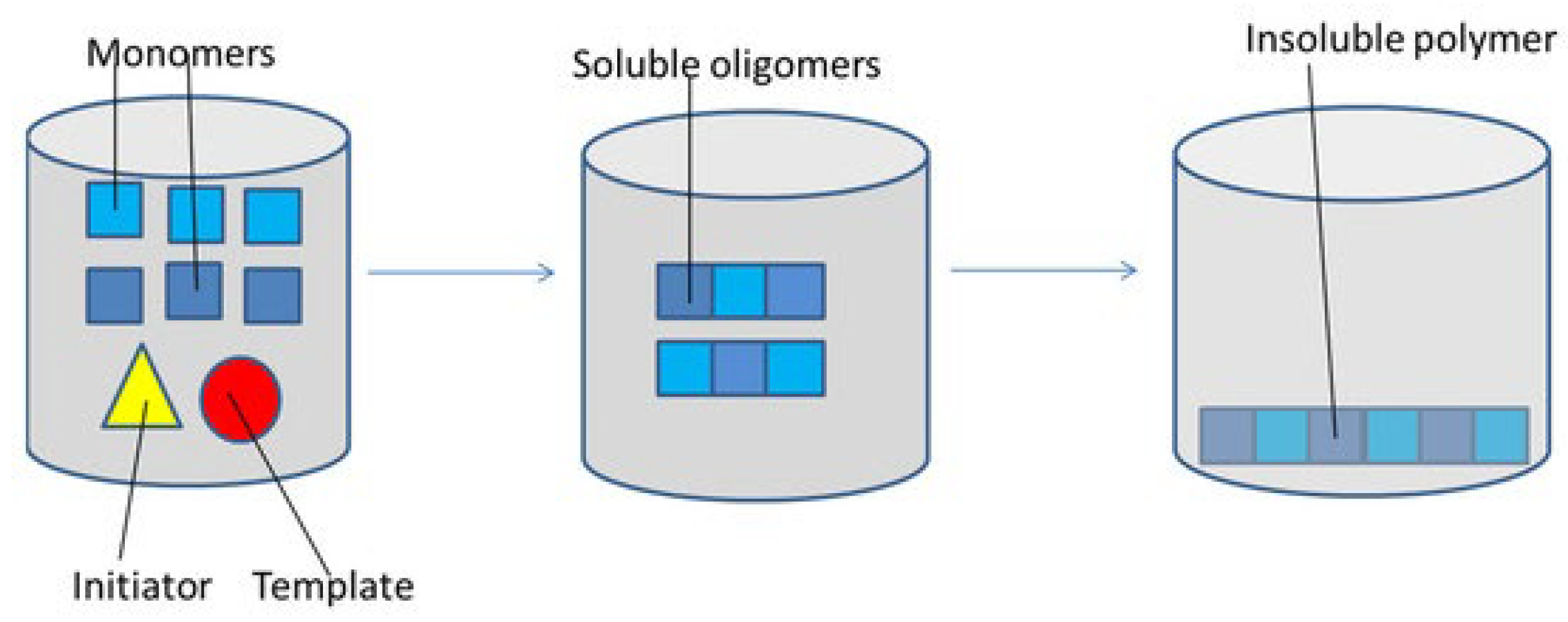
In a related study, a core–shell magnetic MIP was fabricated via precipitation polymerization (Figure 8) to enhance adsorption and selectivity for dichlorophen. Adsorption studies comparing magnetic non-imprinted polymers (MNIPs) and MIPs revealed the highest adsorption rates for dichlorophen. Isotherm modeling using Langmuir and Freundlich equations indicated a maximum binding capacity of 63.291 mg/g for MIPs, compared to 54.640 mg/g for MNIPs. Regeneration experiments demonstrated that MIPs retained an equivalent adsorption capacity even after seven reuse cycles [43]. Additionally, Liu et al., 2014 [44] developed a magnetic imprinted polymer for selective adsorption of rhodamine B, achieving a maximum adsorption capacity of 2350.52 μg/g, with superior selectivity over structural analogs. The adsorbed dye could be effectively desorbed (81.49% ± 1.33%) within 10 min using solvents such as acetone, water, and ethanol.
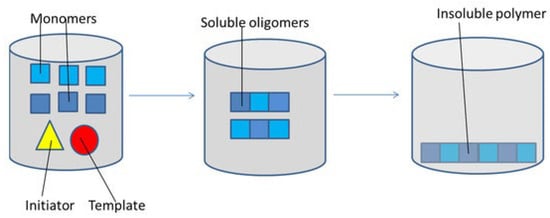
Figure 8.
Precipitation polymerization schematic mechanism. Reprinted from Parisi et al., 2022 [45] under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
In a study performed by Haller et al., 2021 [46], Fe(III)-complex-imprinted polymers were developed as Fenton-like heterogeneous catalysts for the degradation of methyl orange dye in aqueous systems. This work emphasizes the sustainable nature of the process, utilizing low-cost ligands and green oxidative mechanisms. Another study by Franco et al., 2017 [47] focuses on magnetic MIPs (MMIPs) designed for the selective preconcentration and subsequent photoelectrocatalytic degradation of dispersed red 73 dye. The magnetic properties of the MMIPs enable easy recovery and reuse, an advantage over traditional adsorption techniques. Meanwhile, the third study explores hybrid MIPs that combine traditional polymers with advanced materials, like magnetic nanoparticles, carbon nanomaterials, and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), to enhance both selectivity and efficiency in the removal of antibiotics from wastewater. These hybrid systems demonstrate synergistic benefits, such as increased adsorption capacities and improved mechanical stability.
Methodologically, both studies employ sophisticated synthesis strategies tailored to specific contaminants. For example, Fe(III)-complex MIPs are synthesized using radical polymerization with crosslinking agents like N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAA). Similarly, MMIPs incorporate magnetic cores during the polymerization process (Figure 9), enabling separation through magnetic fields. In the case of hybrid MIPs, the inclusion of nanomaterials is achieved through sol–gel processes or in situ growth techniques, offering enhanced surface area and functional properties. The study on Fe(III)-complex-imprinted polymers presents a robust and cost-effective approach for dye degradation using Fenton-like catalysis. A key strength lies in its focus on green chemistry principles, utilizing inexpensive ligands, and minimizing waste production. However, the work primarily investigates methyl orange, which may limit the applicability of its findings to other structurally different dyes. The study on MMIPs for dispersed red 73 dye combines magnetic separation with advanced oxidation processes, presenting a significant improvement in operational convenience. However, its reliance on photoelectrocatalytic treatment raises questions about energy efficiency and applicability under non-laboratory conditions.
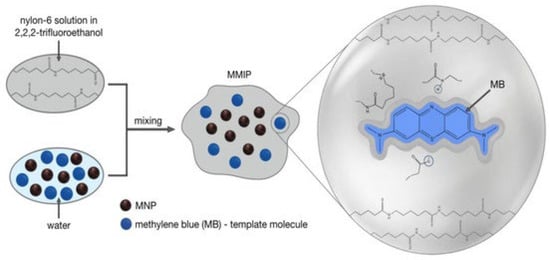
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of MMIP synthesis. Reprinted from Sedelnikova et al., 2023 [48] under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
A clear trend across these studies is the increasing use of hybrid materials to overcome the limitations of conventional MIPs. By integrating nanoparticles, carbon-based materials, or MOFs, researchers aim to enhance the selectivity, stability, and multifunctionality of MIPs. This is particularly evident in the third study, where hybrid systems demonstrate simultaneous adsorption and catalytic degradation capabilities. Another commonality is the reliance on AOPs as a complementary strategy to adsorption. Both the Fe(III)-complex-imprinted polymers and MMIPs incorporate oxidative mechanisms to degrade contaminants beyond simple removal.
These reviewed studies collectively underscore the potential of MIPs as a powerful tool for environmental remediation. The ability to tailor these materials for specific contaminants makes them a versatile option for addressing diverse pollution challenges. However, to transition from laboratory research to practical applications, future work must address several key issues. First, broader contaminant testing and the evaluation of MIP performance in mixed-matrix environments are essential. Second, strategies to simplify the synthesis of hybrid MIPs without compromising functionality could enhance their scalability. Lastly, economic analyses and lifecycle assessments are needed to establish the feasibility of these technologies for widespread use.
While the field has made significant strides, bridging the gap between experimental innovations and real-world implementation remains a critical challenge. Cantarella et al. 2018 [49], for instance, investigated the photocatalytic degradation of acetaminophen (paracetamol) using molecularly imprinted zinc oxide nanospheres. The molecularly imprinted nanonuts were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller adsorption–desorption of N2, X-ray diffraction analyses, high-resolution transmission scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Through precise characterization, the interaction between ZnO and paracetamol was clarified. The photodegradation of acetaminophen in an aqueous solution was demonstrated under UV light exposure. Additionally, the selectivity of the photodegradation process was evaluated by comparing it with the degradation of methyl orange and phenol, which are also common water pollutants. The imprinted ZnO nanonuts exhibited a strong affinity and selectivity for paracetamol, successfully degrading all the paracetamol in the solution within 3 h. This study presents a new, cost-effective, and straightforward method for preparing molecularly imprinted ZnO nanonuts with high selectivity, making it valuable for environmental protection applications. Comparative studies on the degradation efficiency of various pollutants, including acetaminophen and phenol, confirmed that molecularly imprinted catalysts exhibit strong selectivity and effectiveness in photodegradation, particularly for acetaminophen. Similarly, Amiri et al., 2020 [50] designed a Bi2WO6/CuO/Ag2O-based molecularly imprinted photocatalyst with a high surface area, specifically targeting the degradation of methyl green MG and auramine O dyes. The imprinted sites significantly enhanced pollutant binding by increasing local concentration through multiple hydrogen and electrostatic interactions. Additionally, the catalyst improved charge separation efficiency, promoting the generation of hydroxyl radicals and enhancing overall photocatalytic performance.
Another study by Li et al., 2022 [51] presents a novel approach to addressing the challenge of pharmaceutical pollution in water environments, specifically targeting ciprofloxacin (CIP). The researchers designed and synthesized a MOF-based mesoporous carrier-supported surface MIP with a magnetic core (Fe3O4). This innovative material combines the advantages of molecular imprinting technology with the high surface area and abundant mesoporous channels of MOFs. The methodology employed in this study is comprehensive and multi-faceted. The researchers used a microwave irradiation method to synthesize the core–shell magnetic Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) structure, followed by a sol–gel method to create the molecularly imprinted polymer layer. This approach allowed for the creation of a material with both high selectivity and uptake capacity for CIP. One of the key strengths of this study is the thorough characterization of the synthesized material. The researchers employed a wide range of analytical techniques, including X-ray powder diffraction, Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy, surface area and pore size distribution analysis, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and zeta potential measurements. This comprehensive characterization provides a detailed understanding of the material’s structure and properties.
The study’s results are particularly noteworthy. The MIL-100-based imprinted polymer demonstrated both high specificity (α(QMIP/QNIP) = 3.54) and the highest uptake capacity (Q = 273.65 mg/g) for CIP reported to date. This exceptional performance can be attributed to the synergistic effect of the MOF structure and the molecularly imprinted polymer layer. A significant strength of this research is its consideration of real-world applications. The researchers evaluated the material’s performance in the presence of environmental competitors, including inorganic ions and natural organic matter. Furthermore, they tested the material’s effectiveness in removing CIP from real secondary effluents from Beijing, demonstrating its potential for practical application in wastewater treatment. The study also explores the degradation of CIP under visible light irradiation with a small amount of hydrogen peroxide added, showcasing the material’s potential for both adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of the target pollutant. This dual functionality represents a significant advancement in water treatment technology. However, the study has some limitations. While it focuses extensively on CIP, it does not provide a comprehensive comparison with other pharmaceuticals or pollutants. Additionally, the long-term stability and reusability of the material in real-world conditions could be further explored. Lastly, this study makes a significant contribution to the field of water treatment, particularly in addressing pharmaceutical pollution. It demonstrates a novel approach to material design that combines molecular imprinting technology with MOF structures, resulting in a highly effective adsorbent for CIP. The comprehensive characterization and evaluation of the material’s performance in realistic conditions provide a strong foundation for future research and potential practical applications in wastewater treatment.
Research findings highlight the crucial role of MIP catalysts in enhancing the efficiency of targeted antibiotic degradation. For example, Huo et al., 2012 [52] developed a surface molecularly imprinted catalyst aimed at degrading ciprofloxacin. Their study demonstrated that photocatalysts imprinted with ciprofloxacin molecular templates showed superior adsorption and photodegradation specificity compared to non-imprinted versions. Specifically, under visible light, the degradation rate of the molecular template reached 70% within 60 min. Lai et al., 2016 [53] utilized bisphenol A as a template molecule and o-phenylenediamine (OPDA) as the functional monomer to create a molecularly imprinted TiO2/graphene photocatalyst (MIP-TiO2/GR). Their results showed a noticeable shift in the absorption edges of NIP-TiO2/GR and MIP-TiO2/GR towards longer wavelengths, with MIP-TiO2/GR exhibiting enhanced light absorption in the visible region. This redshift indicated a reduced band gap, leading to better excitability, more electron-hole pair generation, and, consequently, enhanced photocatalytic activity.
Another study synthesized four molecularly imprinted TiO2 photocatalysts targeting sulfonamide antibiotics: MIP-TiO2/sulfadiazine (SD), MIP-TiO2/sulfamethoxazole (SMX), MIP-TiO2/sulfamide (SN), and MIP-TiO2/aniline (AN) [54]. The catalysts showed varying selectivity toward SD and SMX, with degradation rate constants of SD being highest in MIP-TiO2/AN (0.1051 min−1) and for SMX in MIP-TiO2/AN (0.5848 1/min). In particular, MIP-TiO2/SN and MIP-TiO2/AN generated a higher concentration of low-molecular-weight products, with intermediates undergoing further oxidation and hydroxylation.
The modification of catalysts by introducing metals or forming heterojunctions has also proven effective in boosting photocatalytic performance. Sun et al., 2019 [55] synthesized a series of Z-type Ag/Ag3VO4/CN composites using precipitation and UV reduction methods. The Z-scheme Ag3VO4/g-C3N4 heterostructure, combined with the surface plasmon resonance of photo-reduced Ag(0), enhanced photogenerated electron–hole separation efficiency. Molecular imprinting enabled the composites to specifically recognize and adsorb target contaminants, improving selectivity in photocatalysis. The study also proposed a reaction mechanism where ·O2− and h+ are the primary active species responsible for photocatalysis.
Further strategies for enhancing photocatalytic activity and selectivity involve doping TiO2 with metals like Zr. Molecular imprinting also increased the surface area (94.01 m2/g) and pore volume (0.10 cm3/g) of MIP-ZrO2-TiO2, leading to more active sites and higher photocatalytic efficiency, particularly in treating recalcitrant hydroquinone [56]. Similarly, Zhu et al., 2020 [57] examined factors such as metal content, imprinting molecules, calcination temperature, and active substance capture to assess the selectivity of Ag/Zn-MIP-TiO2 through UV–vis spectra, group absorbance variations, and reaction kinetics parameters. Additionally, Liu et al., 2024 [58] developed Fe3O4/g-C3N4/TiO2 molecularly imprinted catalysts (MI-FCT) using hydrothermal and molecular imprinting methods. Their study explored the synergistic mechanism of selective adsorption and targeted catalysis with tetracycline (TC) as the template. The MI-FCT catalyst demonstrated exceptional recognition abilities and efficient catalytic activity toward TC, achieving an equilibrium adsorption capacity of 24.54 mg/g and a removal rate of 91.87%. These results highlight the catalyst’s specific effectiveness in eliminating TC and its capacity to promote free radical generation.
Continuing with the exploration of selective photocatalytic degradation, Zhang et al., 2022 [59] introduced a method for the selective catalytic degradation of antibiotics using molecularly imprinted Cr3+-doped ZnGa2O4 (ZnGa2O4: Cr3+, ZGO). This semiconductor, known for its exceptional afterglow properties, can degrade pollutants even in the absence of light, with its photoluminescence acting as a self-reporting mechanism for pollutant degradation. Additionally, ZGO demonstrates impressive selectivity and strong resistance to interference during post-photocatalytic degradation. The study presents a novel and efficient approach for selectively degrading antibiotics or other low-concentration, highly toxic emerging contaminants under both light and dark conditions.
As can be noticed from these studies, while MIP catalysts improve selectivity, there is a lack of studies examining their long-term stability and performance in complex environmental conditions. Most studies focus on efficiency but overlook the catalyst’s behavior over time or in the presence of multiple pollutants. The studies show strong advancements in catalyst selectivity and efficiency. However, few address long-term stability, a critical factor for real-world applications. The methodologies used, including molecular imprinting and semiconductor doping, are effective but need further exploration in practical settings. Some discrepancies arise regarding the best materials and conditions for maximum performance, with varying results in catalyst choice and experimental results. While the trend toward improving photocatalytic efficiency with MIPs is clear, there is no consensus on the ideal materials or methods. For instance, Liu et al., 2024 [58] focus on Fe3O4, while Zhang et al., 2022 [59] suggest Cr3+ doping. Additionally, long-term durability remains underexplored, highlighting an area for future research. All these studies contribute significantly to the field, but more work is needed to address stability and real-world application. Future research should focus on improving catalyst durability and performance in complex environmental conditions.
On the other hand, several methodologies have been employed in recent studies, with surface molecular imprinting (S-MIP) being the most widely adopted due to its superior accessibility of catalytic sites compared to bulk molecular imprinting. MOFs and metal oxide catalysts, including TiO2, ZnO, and CuFe2O4, are frequently used as substrates for MIP synthesis due to their large surface areas and catalytic potential. The molecular imprinting process enhances the selectivity of these catalysts by creating specific binding sites for target pollutants, thereby improving degradation efficiency and reducing non-selective oxidation [28].
Building on the importance of synthesis methods, recent studies have highlighted how various approaches to MIP synthesis, including surface molecular imprinting, significantly influence the structural characteristics and catalytic efficiency of these materials. The method of synthesis and morphology play critical roles in determining the efficiency of MIP-based catalysts in pollutant degradation. The synthesis method influences the porosity, surface area, and binding sites of the MIPs, which are crucial factors for their ability to interact with and degrade pollutants. For example, techniques like bulk polymerization or precipitation can lead to different pore structures, affecting the accessibility of pollutants to active sites within the MIP structure. Similarly, the morphology of the MIPs—whether they are synthesized as nanoparticles, microspheres, or films—directly impacts their surface area and reactivity. Nanoparticles, for instance, have a higher surface area-to-volume ratio, which can enhance their catalytic activity by providing more active sites for pollutant adsorption and degradation. On the other hand, larger particles or films may have limited accessibility for the target pollutants. In pollutant degradation studies, the effectiveness of the catalyst is closely related to how well these structural and morphological factors promote efficient mass transfer, adsorption, and the subsequent degradation or transformation of the pollutants. Therefore, understanding the relationship between synthesis method, morphology, and catalytic performance is essential for optimizing MIP-based catalysts for water treatment applications.
Understanding the relationship between synthesis methods, morphology, and catalytic performance is further supported by photocatalytic degradation studies, which demonstrate that MIP-modified catalysts significantly outperform their non-imprinted counterparts in pollutant removal. Photocatalytic degradation studies demonstrate significant improvements in pollutant removal when using MIP-modified catalysts (Table 3). A ZnO/CuFe2O4-based MIP achieved a degradation efficiency of 95.8% under simulated sunlight for methylene blue (MB), significantly higher than the 70% observed for non-imprinted counterparts [28]. Similarly, MIP-modified TiO2 exhibited a 60% higher degradation rate for refractory organic compounds under UV light compared to unmodified TiO2 [60]. For pharmaceuticals like sulfamethoxazole (SMX), a MOF-based MIP (NH2-MIL-53(Fe)) exhibited an adsorption capacity of 38.04 mg/g and facilitated a total organic carbon (TOC) removal of 67%, indicating its potential for targeted pharmaceutical degradation [61].

Table 3.
MIP-based catalysts for pollutant degradation.
In the field of electrocatalysis, MIP-based electrodes have demonstrated enhanced pollutant degradation performance. A boron-doped diamond electrode modified with MIP exhibited a 2.5-fold higher current response for bisphenol A oxidation compared to non-imprinted electrodes. Additionally, MIP-coated graphene electrodes improved the selective degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol, increasing the BOD5/CODCr ratio from 0.186 to 0.412, thus enhancing biodegradability and making wastewater treatment more effective. These results indicate that MIP integration with electrocatalysis can significantly enhance specificity and degradation efficiency [60]. Fenton-like catalysis has also benefited from molecular imprinting. Fe-MOF/MIP hybrids achieved 1.8-fold higher catalytic efficiency in dimethyl phthalate degradation compared to traditional Fe-based catalysts. Additionally, Fe-zeolite-based MIPs enhanced selectivity, reducing byproduct formation by 30% while maintaining high degradation efficiency. These findings suggest that molecular imprinting can fine-tune the catalytic activity of transition-metal-based materials, leading to more efficient pollutant breakdown with reduced secondary pollution [62].
MIP-based catalysts play a crucial role in pollutant degradation by leveraging photocatalysis, Fenton-like reactions, enzymatic mimicry, and redox-mediated mechanisms. These catalytic pathways facilitate the efficient breakdown of organic contaminants into non-toxic byproducts. Photocatalysis in MIP-based catalysts, incorporating materials, such as TiO2, ZnO, or g-C3N4, utilizes light energy to generate reactive species for pollutant degradation. When exposed to UV or visible light, the semiconductor catalyst generates electron–hole pairs [70]:
TiO2 + hv → e− + h+
e− + O2 → O2•−
h+ + H2O → •OH + H+
h+ + OH− → •OH
These reactive oxygen species (ROS) interact with organic pollutants, leading to oxidative degradation:
R + •OH → CO2 + H2O
MIPs doped with Fe-based nanoparticles facilitate Fenton and Fenton-like reactions, leading to hydroxyl radical (•OH) formation from hydrogen peroxide. The reaction follows these steps [71]:
Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + •OH + OH−
Fe3+ + H2O2 → Fe2+ + O2•− + H+
The hydroxyl radicals generated oxidize organic pollutants, breaking them down into carbon dioxide and water:
R + •OH → CO2 + H2O
MIP-based nanozymes mimic natural peroxidases and oxidases, offering stable and reusable catalytic activity. The mechanism follows the following pathways [72] and enables efficient oxidative breakdown of contaminants without the need for biological enzymes:
H2O2 + Mn2+ → Mn3+ + OH− + •OH
Mn3+ + R → Mn2+ + RO•
RO• + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Redox-active elements, such as Mn, Ce, or Cu, incorporated into MIP-based catalysts drive pollutant degradation via electron transfer mechanisms [73]. By facilitating oxidation–reduction reactions, these catalysts enhance pollutant removal efficiency.
MnO2 + R → Mn2+ + RO•
Ce4+ + R → Ce3+ + RO•
Cu+ + O2 → Cu2+ + O2•−
O2•− + H+ → HO2•
HO2• + R → CO2 + H2O
Despite the listed advancements, several limitations persist. While molecular imprinting significantly enhances selectivity, it is limited to specific pollutants, requiring careful template selection. The imprinted layer may also block active catalytic sites, potentially reducing overall efficiency. Material stability remains a concern, with potential issues such as template leakage and structural degradation over time. Furthermore, although some studies simulate real wastewater conditions, comprehensive evaluations in complex wastewater matrices are still lacking. Trends in the field indicate a shift from bulk to surface molecular imprinting, improving target pollutant accessibility and reaction kinetics. Computational simulations are increasingly employed to predict binding site configurations and optimize catalyst design, but experimental validation is needed to confirm theoretical predictions. Additionally, while degradation pathways have been explored, limited studies assess the toxicity and environmental impact of intermediate degradation products, highlighting an urgent research gap. To contextualize their performance, it is essential to compare them with other emerging technologies such as nanomaterials and bio-adsorbents. Table 4 below summarizes the key characteristics of these technologies. While MIPs demonstrate excellent selectivity and competitive adsorption/degradation performance, nanomaterials often provide higher degradation efficiency, particularly in photocatalytic processes. However, concerns regarding their environmental toxicity remain. Bio-adsorbents, on the other hand, are cost effective and eco-friendly but may lack the specificity and efficiency of MIPs. Activated carbon is widely used for adsorption due to its high surface area but has limited degradation capability. MOFs show high adsorption and degradation performance but may pose environmental risks. Enzyme-based systems provide high selectivity and biodegradability but can be expensive. Photocatalysts, while highly efficient in degradation, may have toxicity concerns due to the use of metal-based materials.

Table 4.
Overview of CEC removal techniques.
The widespread use of pesticides, combined with their complex chemical structures and the discharge of untreated wastewater, also poses a significant environmental hazard. Even after conventional treatment, trace levels of hazardous pollutants (ranging from ng/L to μg/L) often persist in water systems [74]. MIPs, in this case, also offer a promising approach for the targeted degradation of such contaminants. For example, one extensively used herbicide, diuron, has a prolonged half-life, allowing it to remain in the environment for extended periods. To address this issue, an MIP was synthesized with magnetic TiO2 through oxidative polymerization, acting as a photosensitizer. Analysis via the Kubelka–Munk plot revealed that the bandgap of magnetic TiO2 (3.18 eV) falls within the ultraviolet range, limiting its applicability. However, when combined with a conductive polymer, the absorption spectrum of the MIP was extended into the visible region (432.1 nm), effectively reducing the bandgap to 2.87 eV. The MIP demonstrated a maximum adsorption capacity of 29.8 mg/g within the first 30 min of experimentation, ultimately achieving a 98% degradation efficiency for diuron under 40 min of visible light irradiation. Vibrating sample magnetometry analysis confirmed that the magnetic saturation value for the TiO2-MIP composite was 4.4 emu/g, significantly lower than that of bare magnetic TiO2 (16.6 emu/g), indicating the influence of the non-magnetic polymer coating. Despite a gradual decline in degradation efficiency from 98% to 83% after five reuse cycles, the photocatalyst exhibited excellent magnetic recoverability [75].
Beyond organic pollutant degradation, imprinted photocatalysts have also been utilized for the selective adsorption and reduction of toxic metal ions in wastewater. A novel Ag(I)-imprinted photocatalyst was developed using Fe3O4 nanoparticles, TiO2, and methanol as sacrificial agents, effectively reducing Ag(I) to Ag(0). The presence of -SH ligand groups within the MIP facilitated selective adsorption, achieving a maximum capacity of 30.55 mg/g, significantly outperforming NIPs, which reached only 17.21 mg/g. Following photocatalytic reduction, the adsorbed silver ions were efficiently separated via a magnetic field, with the imprinted cavities maintaining 77.85% regeneration capacity for subsequent use [76]. Recent advancements in dark catalytic oxidation techniques have enabled pollutant degradation without the need for light activation or external energy sources. Traditional semiconductor-based photocatalysis is often hindered by a wide bandgap, which limits the absorption of solar energy. To address this issue, adsorption-mediated catalytic oxidation methods such as ozonation and Fenton reactions have been explored. Magnetic particles enhance catalytic performance by generating electrons from the Fe3O4 core, which interact with the semiconductor matrix to degrade adsorbed pollutants [77].
A conductive molecularly imprinted polypyrrole (PPy)-coated TiO2 composite (Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@MIP) was synthesized using methyl orange as a template. At pH levels above 4, protonation of PPy increased the adsorption of Congo red via electrostatic and hydrogen-bonding interactions. Both Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 and Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@MIP exhibited significant catalytic efficiency. Unlike traditional light-activated systems, the dark catalytic process involved electron transfer from the Fe3O4 core to the conduction band of TiO2, generating superoxide radicals while holes reacted with hydroxyl anions to produce hydroxyl radicals. The MIP composite successfully degraded 93% of Congo red within 25 min under dark conditions, significantly outperforming the NIP, which achieved only 52% degradation. The catalyst retained reusability, although degradation efficiency decreased from 91 to 70% over five cycles. Minor losses in adsorption capacity were attributed to damage to imprinted cavities due to analyte accumulation, mass loss, and surface fissures formed during repeated use. Despite these challenges, the imprinted layer effectively prevented catalyst leaching, preserving overall catalytic activity [78].
MIPs have also demonstrated significant advantages in sensing applications over traditional chemical and biosensors, which often suffer from poor signal expression, lengthy response times, low selectivity, and susceptibility to denaturation. The integration of MIP layers with nanocomposite sensors, combined with fluorescent materials, enhances signal transduction at active binding sites [79]. A fluorescence-based MIP sensor developed by Zhu et al., 2021 [80] was designed for the detection of 4-nitrophenol in food samples, offering dual-recognition capabilities. The sensor exhibited a detection limit of 23.45 nmol/L, with a high imprinting factor (12.2). Rapid response times (2 min) and high recovery rates (93.20 to 102.15%) confirmed the sensor’s efficiency and reusability, with minimal fluorescence variation observed over multiple cycles.
Further advancements have been made in electrochemical sensing, such as MIP-coated Fe3O4@GO (graphene oxide) electrodes for detecting capecitabine, an anticancer drug. Square wave voltammetry studies revealed that Fe3O4@GO-modified glassy carbon electrodes exhibited the highest signal at a scan rate of 50 mV/s. The polymeric matrix of GO facilitated capecitabine transport, enhancing detection sensitivity. The MIP-based sensor retained long-term stability (98.5%) and demonstrated strong magnetic recovery [81]. In another study, Han et al., 2021 [82] synthesized an MIP using deep eutectic solvents (DES) for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin protein. The polymer exhibited high adsorption capacity (175.44 mg/g) and an imprinting factor of 4.77, while NIPs showed significantly lower binding efficiency (24.38 mg/g). Over three adsorption–elution cycles, the DES-MIP maintained 92.07% of its original capacity, showcasing enhanced stability. These advancements highlight the extensive applications of MMIPs in pollutant degradation, selective adsorption, and sensing, as summarized in Table 3.
4. Main Challenges and Future Perspectives
Despite the promising performance of MIP-based catalysts, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize their potential in large-scale applications for pollutant degradation. One of the primary concerns is material stability, particularly in real-world wastewater conditions. While MIPs show high efficiency in controlled laboratory settings, their long-term stability and performance in mixed contaminant systems remain underexplored. Real-world conditions often introduce a variety of pollutants, environmental factors, and complex interactions that can impact the efficiency of MIP-based systems. Future research should focus on testing MIPs under more complex and diverse environmental conditions to better understand their behavior and ensure their reliability in practical applications.
Another significant challenge is the safety of degradation byproducts, especially the potential toxicity of intermediate products formed during partial degradation. In many cases, photocatalytic and other degradation processes can break down pollutants into intermediate products, which might be more toxic or harmful than the original pollutants [83,84]. The current research tends to focus on the overall degradation efficiency but often overlooks the potential environmental risks associated with these byproducts. There is a need for a deeper investigation into the toxicity of these intermediates, ensuring that they do not pose additional threats to the ecosystem. Additionally, strategies to mitigate or control the formation of toxic intermediates should be developed to enhance the safety of these technologies.
For example, in the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants like methylene blue using TiO2-based MIPs, ROS can lead to the formation of benzothiazole derivatives [85]. These intermediates have been found to be more toxic than the parent compound. Similarly, the degradation of pharmaceuticals such as ciprofloxacin using MIPs could produce intermediates like quinolone derivatives, which have been shown to exhibit higher toxicity to aquatic organisms compared to the original antibiotic [86]. The environmental impact of these degradation intermediates needs to be thoroughly assessed in future studies. For instance, in the degradation of dyes like rhodamine B using magnetic MIPs, incomplete breakdown can result in the formation of partially degraded products that may persist in the environment [87]. Studies have shown that these intermediate compounds can exhibit toxicity towards microorganisms and aquatic species [88]. Furthermore, the byproducts may be more resistant to further degradation or more harmful to ecosystems. A key example is the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater treatment, where intermediate products such as aldehydes and ketones can accumulate, leading to bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms. This emphasizes the importance of evaluating not only the final degradation products but also the toxicological effects of these intermediates on the environment and human health.
To address the potential toxicity of degradation byproducts, strategies must be developed to minimize the formation of harmful intermediates. For example, research on photocatalytic degradation of pollutants like methyl orange using ZnO/CuFe2O4 MIPs has shown that optimizing the process to ensure complete mineralization can help reduce the formation of toxic byproducts. In addition, combining MIPs with other materials, such as MOFs may enhance the photocatalytic degradation efficiency and facilitate the full breakdown of pollutants into non-toxic substances like CO2 and water [89]. Another potential solution is to design MIPs with selective catalytic properties, which could not only degrade pollutants efficiently but also limit the formation of hazardous intermediates. For example, studies on the degradation of bisphenol A using TiO2-based MIPs have shown that controlling reaction conditions can reduce the formation of toxic phenolic intermediates [90].
The narrow scope of target pollutants is another limitation of current research. While MIPs have shown great promise in targeting azo dyes and a limited range of antibiotics, many emerging pollutants remain largely unexplored. The growing concern about pollutants like pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and microplastics calls for an expansion in the range of contaminants studied. By diversifying the range of target pollutants, MIPs can become a more versatile tool for environmental remediation. Further research should focus on understanding how MIPs interact with a broader spectrum of contaminants, particularly those that pose significant environmental and health risks.
Regeneration and reuse of MIPs are crucial for their economic and environmental feasibility. Although MIPs can be recycled, the degradation of their performance over multiple cycles remains insufficiently analyzed. More studies are needed to quantify the loss of binding capacity and efficiency during repeated use, as well as to explore methods for improving their durability. Economic feasibility also remains a concern, as the synthesis of hybrid MIPs often involves expensive nanomaterials. Exploring more cost-effective production methods and alternative materials could make MIP-based technologies more accessible, particularly in resource-limited settings. Additionally, the current synthesis processes for MIPs often rely on toxic reagents and organic solvents, which need to be replaced with more sustainable, eco-friendly alternatives, such as ionic liquids or deep eutectic solvents, to align with green chemistry principles.
Lastly, to overcome the limitation of the relatively low adsorption capacity of MMIPs, especially those with thicker imprinted layers, innovative design strategies are necessary. Integrating MMIPs with high-surface-area matrices such as MOFs and COFs could significantly enhance their adsorption capacity. Computational molecular modeling can also aid in optimizing polymer matrices and improving their stimuli responsiveness, making them more adaptable to various pollutant types. Furthermore, improving the morphology of imprinted polymers through novel polymerization techniques could aid in more efficient template removal, particularly for rigid or deeply embedded templates. Future research should also focus on the mass transfer dynamics between components during pollutant degradation, ensuring that the process is both efficient and environmentally safe. This will require more attention to secondary pollution control, specifically targeting the degradation of toxic intermediates and enhancing the efficiency of AOPs.
Future research should also focus on the integration of green chemistry principles in the synthesis of MIPs, aiming to reduce the environmental impact of the production process. This includes exploring eco-friendly solvents, such as ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents, which can replace toxic reagents and organic solvents commonly used in MIP synthesis. These alternatives align with the principles of green chemistry by offering lower toxicity, recyclability, and biodegradability, ensuring that MIP production is more sustainable without compromising material performance [91]. In addition, computational modeling approaches, such as molecular dynamics simulations and quantum chemistry calculations, offer significant potential for optimizing the design of MIP binding sites. These tools can provide detailed insights into the interactions between pollutants and the imprinted sites, enabling more precise tailoring of the polymer matrices to enhance selectivity and efficiency. By utilizing computational models, researchers can predict the most effective binding site configurations, reduce trial-and-error experimentation, and expedite the development of MIPs with improved catalytic activity [92]. Finally, combining green chemistry methods with advanced computational strategies will not only improve the sustainability and performance of MIPs but also make them more cost-effective and scalable for large-scale environmental remediation applications.
The successful implementation of MIP-based technologies in real-world wastewater treatment facilities requires addressing several policy and regulatory considerations. First, there must be clear guidelines for the safe production, use, and disposal of MIPs, particularly with regard to potential environmental and health risks. Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or the European Environment Agency (EEA), will need to establish standards to ensure that MIP-based materials do not introduce new pollutants or pose risks to ecosystems. For example, the disposal of used MIPs, particularly those loaded with adsorbed contaminants or degradation byproducts, must be carefully regulated to prevent secondary pollution [93].
Additionally, integrating MIPs into existing wastewater treatment infrastructure may face challenges in terms of compliance with water quality regulations. Many wastewater treatment plants are subject to stringent effluent discharge standards, and any new materials or technologies introduced must not only meet these standards but also provide cost-effective solutions. Therefore, policy frameworks should prioritize the development of MIP-based systems that can be easily integrated with current technologies, such as activated carbon filtration or AOPs, to ensure scalability and compliance with treatment standards. Lastly, incentives and funding programs may be needed to support the large-scale commercialization of MIP-based technologies. Given that MIP production can involve high synthesis costs and specialized materials, government support in the form of subsidies, grants, or tax incentives could help mitigate these challenges. Public-private partnerships may also play a role in facilitating the transition from laboratory-scale research to full-scale implementation in wastewater treatment facilities. Overall, a coordinated effort between regulatory agencies, industry stakeholders, and researchers is necessary to ensure the successful and sustainable deployment of MIPs for environmental remediation.
5. Conclusions
The efficiency of MIP-based catalysts in pollutant removal and degradation has significantly improved through strategic modifications in their synthesis and structural design, bringing them closer to potential commercialization for large-scale water treatment applications. The integration of MIPs with photocatalytic materials like TiO2 and ZnO has notably enhanced pollutant degradation by generating reactive oxygen species under light irradiation. For example, TiO2-MIP composites have demonstrated up to 60% higher degradation efficiency compared to non-imprinted photocatalysts due to their ability to selectively concentrate target pollutants at the catalytic surface. Additionally, incorporating MIPs into high-surface-area matrices such as MOFs and COFs has proven effective in increasing adsorption capacity and pollutant interaction, with MOF-based MIPs achieving pollutant uptake capacities exceeding 270 mg/g. These innovations have not only improved mass transfer, adsorption, and degradation processes but also positioned MIPs as a promising solution for environmental remediation. Advances in polymerization techniques, such as surface imprinting and nanoimprint lithography, have further enhanced MIP performance by reducing diffusion limitations and increasing binding efficiency. Moreover, green polymerization strategies that use ionic liquids or deep eutectic solvents contribute to the sustainability of MIP production while maintaining selectivity and stability. While these improvements position next-generation MIPs as a durable, scalable, and effective technology for pollutant removal, further studies on long-term stability, economic feasibility, and real-world applicability are needed to fully realize their commercialization for large-scale water treatment. With ongoing advancements, MIPs could potentially be integrated into water treatment systems within the next few years, but their large-scale deployment will depend on overcoming challenges related to cost, scalability, and regulatory approval.
Author Contributions
L.A.G.-F.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, and Visualization. B.M.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Resources, and Supervision. N.A.M.-C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Resources, and Supervision. J.E.V.-C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, and Writing—Original Draft. I.A.R.-D.: Conceptualization, Methodology, and Writing—Original Draft. L.D.d.L.-M.: Conceptualization, Methodology, and Writing—Original Draft. A.H.: Conceptualization, Methodology, and Writing—Original Draft. M.S.-P.: Visualization, Resources, and Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors thank CONAHCyT (CVU 1014829) and the Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD—Research-Grants-One-Year-Grants for Doctoral Candidates) for funding this research. This work forms part of a doctoral thesis in Chemistry at the University of Granada (Spain) and in Environmental Sciences at the Autonomous University of San Luis Potosi (Mexico).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Singh, N.; Poonia, T.; Siwal, S.S.; Srivastav, A.L.; Sharma, H.K.; Mittal, S.K. Challenges of water contamination in urban areas. Curr. Dir. Water Scarcity Res. 2022, 6, 173–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, M.; Graham, J. Toward Universal Access to Basic and Safely Managed Drinking Water: Remaining Challenges and New Opportunities in the Era of Sustainable Development Goals. In Water and Sanitation-Related Diseases and the Changing Environment: Challenges, Interventions, and Preventive Measures, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, J.; Otoo, M.; Danso, G. Progress in delivering SDG6: Safe water and sanitation. Camb. Prism. Water 2023, 1, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaroth, M.P.; Boczkaj, G.; Aubry, O.; Aravind, U.K.; Aravindakumar, C.T. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Degradation of Water Pollutants—Ambivalent Impact of Carbonate Species: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.A.; Aziz, H.A.; Pueh, L.L.L.; Othman, I.B.; Zawawi, M.H.; Hung, Y.-T. Management of Various Sources of Hazardous Waste. In Waste Treatment in the Biotechnology, Agricultural and Food Industries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 2, pp. 19–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Liu, G.; Balaram, V.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Lu, Z.; Stock, F.; Carmona, E.; Teixeira, M.R.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; et al. Worldwide cases of water pollution by emerging contaminants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2311–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Aramesh, N.; Khan, A.A.; Gul, I.; Ghotekar, S.; Bilal, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based adsorption and photocatalytic approaches for mitigation of environmentally-hazardous pollutants─A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Liu, W.; Zada, A.; Raziq, F.; Ali, S.; Shah, M.I.A.; Ateeq, M.; Khan, M.; Alei, D.; Fazil, P.; et al. Recent progress in emerging materials and hybrid nanocomposites for peroxymonosulfate and peroxydisulfate activation towards solar light-driven photocatalytic degradation of emerging pollutants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 499, 215466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Gupta, S. Agrochemicals as a potential cause of ground water pollution: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 985–990. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350874038 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Kasonga, T.K.; Coetzee, M.A.A.; Kamika, I.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Momba, M.N.B. Endocrine-disruptive chemicals as contaminants of emerging concern in wastewater and surface water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Ishak, M.I.S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.E.; Meybeck, M. Water Quality Degradation Effects on Freshwater Availability: Impacts of Human Activities. Water Int. 2000, 25, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang-Erlandsson, L.; Tobian, A.; van der Ent, R.J.; Fetzer, I.; Wierik, S.T.; Porkka, M.; Staal, A.; Jaramillo, F.; Dahlmann, H.; Singh, C.; et al. A planetary boundary for green water. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 380–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.; Quinete, N.; Maldonado, S.; Lugo, K.; Purrinos, J.; Briceño, H.; Gardinali, P. Understanding the occurrence and distribution of emerging pollutants and endocrine disruptors in sensitive coastal South Florida Ecosystems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 757, 143720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Khan, Z.A.; Shahane, S.; Rai, D.; Chauhan, D.; Kant, C.; Chaudhary, V.K. Chaudhary, Emerging pollutants in aquatic environment: Source, effect, and challenges in biomonitoring and bioremediation—A review. Pollution 2020, 6, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Govarthanan, M.; Iqbal, J.; Alfadul, S.M. Emerging contaminants of high concern for the environment: Current trends and future research. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silodia, K.; Bhardwaj, L.; Kumar, A.; Nigam, S.; Yadav, P.; Singh, R.P.; Anza; Singh, R.K.; Hasem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; et al. Strategies for bioremediation of emerging pollutants: A green and sustainable environment. Adv. Chem. Pollut. Environ. Manag. Prot. 2025, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; UNICEF. Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2020: Five Years into the SDGs; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzwerland, 2021; Available online: http://apps.who.int/bookorders (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Arora, N.K.; Mishra, I. Sustainable development goal 6: Global Water Security. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 5, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamahefazafy, M.; Touron-Gardic, G.; March, A.; Hosch, G.; Palomares, M.; Failler, P. Sustainable development goal 14: To what degree have we achieved the 2020 targets for our oceans? Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 227, 106273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yi, H.; Lai, C.; Liu, X.; Huo, X.; An, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; et al. Critical review of advanced oxidation processes in organic wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Fourmentin, M.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Mapelli, F.; Fenyvesi, É.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; et al. Removal of emerging contaminants from wastewater using advanced treatments. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1333–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Recent advances in the removal of emerging contaminants from water by novel molecularly imprinted materials in advanced oxidation processes—A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 883, 163702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, M.; Imam, M.S.; Albugami, A.S.; Hunjur, S.A.; Aldhalmi, A.K.; AbdElrahman, M.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Ali, H.M.; Abdelwahab, N.S.; Eissa, M.S. Current advances in the implementation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers tailored for enrichment of target analytes in different environmental samples: An overview from a comprehensive perspective. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 43, e00236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, M.G.; Benhawy, A.H.; Khalifa, R.M.; El Nashar, R.M.; Trojanowicz, M. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Waters and Wastewaters. Molecules 2021, 26, 6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Wei, C. Molecularly imprinted polyaniline immobilized on Fe3O4/ZnO composite for selective degradation of amoxycillin under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 609, 155324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Sun, L. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based photocatalyst for highly selective degradation of methylene blue. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passas, I. Bibliometric Analysis: The Main Steps. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Kaji, A.H.; Boermeester, M.A. PRISMA Reporting Guidelines for Meta-analyses and Systematic Reviews. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapiano, M.; Akyol, Ç.; Foglia, A.; Pisani, M.; Astolfi, P.; Eusebi, A.L.; Fatone, F. Selective removal of contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) from urban water cycle via Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs): Potential of upscaling and enabling reclaimed water reuse. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Shi, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Men, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers by the surface imprinting technique. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 145, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, M.; Sabbah, M.; Ménager, C.; Griffete, N. Hybrid Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: The Future of Nanomedicine? Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Bai, L.; Han, C.; Lv, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, T. Hybrid amino-functionalized TiO2/sodium lignosulfonate surface molecularly imprinted polymer for effective scavenging of methylene blue from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandis, P.K.; Kalogirou, C.; Kanellou, E.; Vaitsis, C.; Savvidou, M.G.; Sourkouni, G.; Zorpas, A.A.; Argirusis, C. Key Points of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Wastewater, Organic Pollutants and Pharmaceutical Waste Treatment: A Mini Review. Chemengineering 2022, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yue, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, K.; Wang, P.; Zhan, S. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in the water environmental field: A review on the detection and efficient removal of emerging contaminants. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 27, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Cao, X.; Xu, B.; Yan, P.; Yang, T.; Ye, Z.; Chen, X. Visible light induced molecularly imprinted Dawson-type heteropoly acid cobalt (II) salt modified TiO2 composites: Enhanced photocatalytic activity for the removal of ethylparaben. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Dong, J.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, Z.; Su, H.; Yan, Y.; Huo, P. Facile microwave synthesis of a Z-scheme imprinted ZnFe2O4/Ag/PEDOT with the specific recognition ability towards improving photocatalytic activity and selectivity for tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Bottaro, C.S. A critical review of molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis of organic pollutants in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 460603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, N.; Mohammadi, R.; Ghassemzadeh, H.R.; Heris, S.S.S. Design and synthesis of a new magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite for specific adsorption and separation of diazinon insecticides from aqueous media. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Atif, M.; Naz, F.; Li, B.; Wang, K.; AlShehhi, M.R. Advanced Hybrid Molecular Imprinted Polymers for Antibiotics Remediation from Wastewater. ChemBioEng Rev. 2024, 11, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yu, M.; Wei, X.; Huang, L. Preparation of Core–Shell Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with Uniform Thin Polymer Layer for Adsorption of Dichlorophen. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 3068–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Yu, Y.; Ji, S. Preparation of a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective recognition of rhodamine B. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, O.I.; Francomano, F.; Dattilo, M.; Patitucci, F.; Prete, S.; Amone, F.; Puoci, F. The Evolution of Molecular Recognition: From Antibodies to Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) as Artificial Counterpart. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, P.; Machado, I.; Torres, J.; Vila, A.; Veiga, N. Fe(III)-Complex-Imprinted Polymers for the Green Oxidative Degradation of the Methyl Orange Dye Pollutant. Polymers 2021, 13, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, J.H.; Ben Aissa, A.; Bessegato, G.G.; Fajardo, L.M.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Pividori, M.I.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Assessment of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) in the preconcentration of disperse red 73 dye prior to photoelectrocatalytic treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4134–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedelnikova, A.; Poletaeva, Y.; Golyshev, V.; Chubarov, A.; Dmitrienko, E. Preparation of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Methylene Blue Capture. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarella, M.; Di Mauro, A.; Gulino, A.; Spitaleri, L.; Nicotra, G.; Privitera, V.; Impellizzeri, G. Selective photodegradation of paracetamol by molecularly imprinted ZnO nanonuts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 238, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Dashtian, K.; Ghaedi, M.; Mosleh, S. A dual surface inorganic molecularly imprinted Bi2WO6-CuO/Ag2O heterostructure with enhanced activity-selectivity towards the photocatalytic degradation of target contaminantst. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Lv, Z.; Wang, B. Ultrahigh ciprofloxacin accumulation and visible-light photocatalytic degradation: Contribution of metal organic frameworks carrier in magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 616, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, P.; Lu, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Pan, J.; Gao, X.; Guo, W.; Li, H.; Yan, Y. Preparation photocatalyst of selected pho-todegradation antibiotics by molecular imprinting technology onto TiO2/fly-ash cenospheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Wang, M.-M.; Zeng, G.-M.; Liu, Y.-G.; Huang, D.-L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, R.-Z.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; Huang, C.; et al. Synthesis of surface molecular imprinted TiO2/graphene photocatalyst and its highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of target pollutant under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yuan, R.; Zhou, B.; Chen, H. Selective photocatalytic removal of sulfonamide antibiotics: The performance differences in molecularly imprinted TiO2 synthesized using four template molecules. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Huo, P.; Yan, Y.S. Molecularly imprinted Ag/Ag3VO4/g-C3N4 Z-scheme photocatalysts for enhanced preferential removal of tetracycline. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Yu, H.; He, J.; Chen, K.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X. Study on the preparation of molecularly imprinted ZrO2-TiO2 photocatalyst and the degradation performance of hydroquinone. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 83575–83586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Meng, X. Evaluation of photocatalytic selectivity of Ag/Zn modified molecularly imprinted TiO2 by multiwavelength measurement. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 703, 134732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Han, X.; Liu, R.; Qi, Z.; Ren, B.; Sun, Y. Molecularly imprinted Fe3O4/g-C3N4/TiO2 catalyst for selective photodegradation of chlorotetracycline. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 680, 132691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.-W.; Yang, X.-T.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Wang, H.-F. Afterglow-catalysis and molecular imprinting: A promising union for elevating selectivity in degradation of antibiotics. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 305, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, B.; Xiao, K.; Duan, H.; Wan, J.; Zhao, H. Targeted degradation of refractory organic compounds in wastewaters based on molecular imprinting catalysts. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wan, J.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, T.; Hou, J.; Chen, H. Targeted degradation of sulfamethoxazole in wastewater by molecularly imprinted MOFs in advanced oxidation processes: Degradation pathways and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Pu, M. Targeted degradation of dimethyl phthalate by activating persulfate using molecularly imprinted Fe-MOF-74. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.; Nong, F.; Li, M.; Li, D. Selective Photoelectrocatalytic Degradation of Recalcitrant Contaminant Driven by an n-P Heterojunction Nanoelectrode with Molecular Recognition Ability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10182–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, J.; Qu, L. A highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on polydopamine functionalized graphene and molecularly imprinted polymer for the 2,4-dichlorophenol recognition and detection. Talanta 2019, 195, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroughirad, S.; Arabzadeh, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Khosravi, A. Synthesis and characterization of novel water-compatible magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for tartrazine. J. Chin. Adv. Mater. Soc. 2018, 6, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Tang, K.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of norfloxacin by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: Influencing factors and mechanisms. Environ. Technol. 2021, 44, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Miao, Y.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Efficient removal of norfloxacin in water using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Mao, J.H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Cao, M.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, K.Y.; Xiong, X.H. A novel strategy for selective removal and rapid collection of triclosan from aquatic environment using magnetic molecularly imprinted nano−polymers. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hou, J. Facile fabrication of snowman-like magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres for bisphenol A via one-step Pickering emulsion polymerization. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 164, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Minhas, M.A.; Shaikh, H.; Xiao, H.-M.; Malik, M.I. Enhancement in photocatalytic selectivity of TiO2-based nano-catalyst through molecular imprinting technology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 121929–121947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, Z. Fe-based catalysts for heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of emerging contaminants in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Kim, M.-J.; Jang, H.-G.; Mugunthan, A.; Kim, C.-S.; Yoon, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Chung, K.W.; Chang, S.-C. Fabrication of bio-mimic nanozyme based on Mxene@AuNPs and molecular imprinted poly(thionine) films for creatinine detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 271, 117075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanoglu, S.; Yarman, A.; Zhang, X.; Scheller, F.W. Electrochemical MIP Sensors for Environmental Analysis. In Biosensors for the Marine Environment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Muthwa, S.F.; Chimuka, L. Determination of triclosan and ketoprofen in river water and wastewater by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2014, 67, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Long, J.; Xi, Y.; Luo, X. Recovery of Silver from Wastewater Using a New Magnetic Photocatalytic Ion-Imprinted Polymer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Minh Tri, N.; Kim, J.; Giang, B.L.; Al Tahtamouni, T.; Huong, P.T.; Lee, C.; Viet, N.M.; Trung, D.Q. Ag-doped graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst with remarkably enhanced photocatalytic activity towards antibiotic in hospital wastewater under solar light. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 80, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Mo, Z.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z. Magnetic recyclable TiO2/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite: Synthesis, characterization and enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 402, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wong, A.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Electrochemical sensors based on biomimetic magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective quantification of methyl green in environmental samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, M.; Du, J.; Fan, J.; Xiong, H.; Peng, H. A novel magnetic fluorescent molecularly imprinted sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of 4-nitrophenol in food samples through a dual-recognition mechanism. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, M.; Mostafavi, A.; Shamspur, T. A novel electrochemical sensor based on magnetic core@shell molecularly imprinted nanocomposite (Fe3O4@graphene oxide@MIP) for sensitive and selective determination of anticancer drug capecitabine. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6626–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yao, A.; Ding, Y.; Leng, Q.; Teng, F. A molecularly imprinted polymer based on MOF and deep eutectic solvent for selective recognition and adsorption of bovine hemoglobin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5409–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, M.; Mensah, K.; Alalm, M.G. A review on photodegradation mechanism of bio-resistant pollutants: Analytical methods, transformation products, and toxicity assessment. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 103151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klementová, Š.; Poncarová, M.; Langhansová, H.; Lieskovská, J.; Kahoun, D.; Fojtíková, P. Photodegradation of fluoroquinolones in aqueous solution under light conditions relevant to surface waters, toxicity assessment of photoproduct mixtures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 13941–13962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, H.; Song, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, X. A review of the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water by modified TiO2. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.R.; Prasasti, A.; Islamiah, S.; Firdaus, A.N.; Marita, A.W.; Fajriyah, S.; Noviyanti, A.R.; Eddy, D.R. Degradation of Ciprofloxacin by Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles: Optimization of Conditions, Toxicity, and Degradation Pathway. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2021, 16, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikerchalen, S.; Akhsassi, B.; Bakiz, B.; Villain, S.; Taoufyq, A.; Guinneton, F.; Gavarri, J.-R.; Benlhachemi, A. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B dye over oxygen-rich bismuth oxychloride Bi24O31Cl10 photocatalyst under UV and Visible light irradiation: Pathways and mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2024, 196, 112342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Ullah, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Shah, A.; Farooq, M.; Saeed, T.; Ullah, I.; Li, H. In-Depth Photocatalytic Degradation Mechanism of the Extensively Used Dyes Malachite Green, Methylene Blue, Congo Red, and Rhodamine B via Covalent Organic Framework-Based Photocatalysts. Water 2024, 16, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Li, C.; Huang, M.; Wan, J.; Zhou, X.; Yan, B. Targeted accumulation and spatial confinement effect of Fe(II)-MOFs@MIP for efficiently removing low concentration dibutyl phthalate. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoulad El Hadj Ali, Y.; Azzouz, A.; Ahrouch, M.; Lamaoui, A.; Raza, N.; Lahcen, A.A. Molecular imprinting technology for next-generation water treatment via photocatalysis and selective pollutant adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Sole, R.; Mele, G.; Bloise, E.; Mergola, L. Green Aspects in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers by Biomass Waste Utilization. Polymers 2021, 13, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZLiu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Ma, L.; Lin, T.; Liu, H. A Review on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Preparation by Computational Simulation-Aided Methods. Polymers 2021, 13, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayivi, R.D.; Obare, S.O.; Wei, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers as chemosensors for organophosphate pesticide detection and environmental applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).