Abstract
This study presents data on the water quality of the Guarani Aquifer based on samples collected from distinct groundwater wells in the western region of Santa Catarina State, Brazil. Among the analyses performed, the results indicated the need for treatment to ensure suitability for human consumption, particularly concerning Fe3+ and Mn2+ ions. Accordingly, natural (NCLIN) and activated clinoptilolite (ACLIN) zeolites were evaluated for ion removal from synthetic aqueous solutions through adsorption. NCLIN demonstrated excellent performance in adsorbing Fe3+ and Mn2+ ions, achieving removal efficiencies of over 98% and 95%, respectively, at a controlled pH of 6.0 (NCLIN) or 4.0 (ACLIN). A non-linear approach to modeling adsorption kinetics indicated that the pseudo-second-order model best represented the experimental data. This finding suggests that the interaction between the adsorbent and Fe3+ and Mn2+ ions occur through electron sharing and chemisorption. Equilibrium modeling analysis revealed that adsorption on NCLIN occurred in a monolayer, whereas adsorption on ACLIN followed a multilayer pattern. This behavior is attributed to the activation process with H2SO4, which led to dealumination and the formation of HSO3− groups on the adsorbent surface.
1. Introduction
In a report released by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, alarming data describe a substantial increase in the consumption of freshwater in the last hundred years, where since 1980, there has been a growth of 1 vol.% per year in total consumption, reaching a value exceeding 2 trillion m3 at the beginning of 2022 [1]. In this scenario, a global water deficit is estimated to exceed 25% by 2030 [2]. Associated with this worrying situation, there is also a decrease in the quality of available freshwater, a result of the increasing pollution of the main hydric sources in different countries. It is estimated that, globally, around 80% of industrial and municipal wastewater is released into the environment without any prior treatment, causing drastic effects on human health and ecosystems [1]. Considering this scenario, water pollution has motivated various research efforts focused on proposing alternative treatment and purification methods.
Comprising about 99% of the Earth’s liquid freshwater, groundwater has the capacity to provide societies with social, economic, and environmental benefits [3]. Currently, groundwater supplies approximately half of the total water extracted globally for domestic purposes, catering to the drinking water needs of a substantial portion of the rural population without access to public or private water supply systems [4,5]. Additionally, it contributes to around 25% of the total water used for irrigation [3]. Contextually, the Guarani Aquifer is one of the largest underground freshwater reserves in the world and represents a significant water resource for South America, especially Brazil. Its reserves are located in different sedimentary basins in Brazil, covering parts of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, São Paulo, Paraná, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do Sul, as well as parts of Paraguay, Uruguay, and Argentina. Accordingly, its total extent is estimated at a colossal volume of approximately 1.0 million square kilometers, playing a vital role in the public water supply for various communities and in the maintenance of local ecosystems as well as economic activities in these regions [6]. Although there is a recommendation for human consumption of water from underground wells, the Guarani Aquifer, as well as other underground water sources, faces challenges related to uncontrolled exploitation and, mainly, contamination by human activities [7]. Among the main biological and chemical contaminants usually detected in these water sources, the contamination by metals and high loads of other compounds stands out due to its harmful potential for the population, where although some substances (in low concentrations) are essential for human metabolism, larger concentrations can induce harmful effects on health, causing neurological, kidney, and liver issues [8]. In particular, excessive consumption of Fe3+ and Mn2+ can cause gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort [9,10]. Furthermore, hydric wells with excessive concentrations of Fe3+ and Mn2+ can have a yellowish or brown color and a metallic or earthy taste, making the water unpalatable to drink [11].
Among the conventional methods for the removal of metals present in water bodies (coagulation, micro- and ultrafiltration membranes, and ion exchange resins), the adsorption method has well-known advantages regarding simple operation, versatility regarding available diverse adsorbent materials, and milder process conditions [12,13,14]. However, the efficiency of the technique is closely dependent on the selection of a suitable adsorbent material, where activated carbons, modified clays, nanoparticulate oxides, and zeolites are the main materials evaluated for removing water contaminants [15]. Among natural zeolites, clinoptilolite is the most abundant and widely used adsorbent for the removal of different ions from water bodies [16,17]. Clinoptilolites are hydrated aluminosilicate minerals that typically have a high surface area and porosity, providing ample active sites for adsorptive systems in addition to a significant cation exchange capacity and pH stability [18]. Interestingly, Vaezi et al. [19] applied a combination of experimental techniques and molecular dynamics simulations to enhance the understanding of how Cu2+ ions substitute Na+ ions in clinoptilolite and mordenite zeolites. The authors reported that the ion exchange capacity of the zeolites was evaluated through EDS analysis. The results indicated that the mordenite zeolite incorporated more copper ions than clinoptilolite, aligning with the computational findings. Similarly, Munir et al. [20] developed a modified clinoptilolite to simultaneously remove Cd2+, Ni2+, Mn2+, Sr2+, and Fe3+ from aqueous solutions. The authors investigated the effects of zeolite dosage, initial metal ion concentrations, temperature, contact time, and pH on the adsorption performance of these metal ions. The findings demonstrated remarkably high adsorption capacities, reaching 2000, 1720, 1875, 1510, and 22 mg g−1 for Ni2+, Fe3+, Cd2+, Mn2+, and Sr2+, respectively.
Even though the adsorption process presents established advantages for metal capturing, it is crucial to address challenges associated with the adsorbent effectiveness and system design to understand the viability and efficiency of the water treatment. Contextually, modeling the system to acquire kinetic and thermodynamic parameters is crucial in overcoming the described points. Therefore, this work reports unpublished data for non-linear modeling of the adsorption of Fe3+ and Mn2+ from groundwater samples by a natural (or an activated) clinoptilolite. The research proposes a comprehensive analysis of the kinetic and equilibrium adsorption process supported by a robust statistical and computational approach, presenting, in addition to the estimated parameters, their respective confidence intervals to ensure the reliability of the reported data, which allows the determination of the mechanisms involved. Such points are commonly ignored in similar research that merely focuses on evaluating the adsorptive capacity of the material or even using a simplified linearization of the models to perform the modeling without proving the reliability and reproducibility of the data. Finally, the text also presents updated data concerning the Guarani Aquifer groundwater quality of well samples collected in different locations of the Santa Catarina state (Brazil), relating the potential of the tested adsorbents to treat the compounds detected in the aquifer trials.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The adsorbent used in the adsorption processes was an aluminum silicate zeolite of the clinoptilolite type, with the commercial name of WaterCell® ZZ, obtained from Celta Brazil Ltd. (São Paulo, Brazil). According to the specifications provided by the manufacturer, the material is composed of SiO4 (68.00 wt.%), Al2O4 (12.00 wt.%), Na2O (2.67 wt.%), CaO (1.98 wt.%), K2O (1.40 wt.%), FeO2 (1.11 wt.%), MgO (0.80 wt.%), TiO4 (0.37 wt.%), and P2O5 (0.03 wt.%), with a nominal ion exchange capacity of 1.57 meq g−1, particle size varying between 0.4 and 1.0 mm, density of 0.98 g cm−3, and pH of 7.6. Sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride (analytical grade, Synth, São Paulo, Brazil) as well as standard iron and manganese solutions (Spex CertiPrep®, São Paulo, Brazil) were the chemicals used in the tests.
2.2. Zeolite Activation
The evaluation of ion removal from solutions containing heavy metals was verified using two materials: clinoptilolite zeolite in its natural form (NCLIN) and activated by sulfonation method (ACLIN). For the activation process, NCLIN zeolite was initially screened using a 28-mesh sieve (Tyler Series, 0.589 mm of free aperture). Subsequently, the material was washed with water and dried at 100 °C for 24 h. The ACLIN zeolites were prepared by placing 5 g of natural zeolite in contact with H2SO4 (4 mol L−1) in a mass-to-volume ratio of 0.1 g (mL of H2SO4)−1 under constant stirring (130 rpm) for 24 h at 25 °C, according to methodology suggested by Chuesutham et al. [21]. After this process, the material was filtered under vacuum and washed with 5 L of water to remove free SO3− ions and finally dried at 100 °C and stored for 24 h.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) was employed to identify the chemical groups of the zeolites. The spectra of the materials were obtained using a Prestige-21 spectrometer (Shimadzu, Japan—from 400 to 4000 cm−1). The NCLIN and ACLIN materials were pulverized and diluted in a KBr solution for later analysis through diffuse reflectance. Data related to the textural properties and physical structure of the adsorbent surface can be consulted in a work published by our research group [18].
2.3. Groundwater Wells: Collect and Characterization
Different groundwater well samples were collected from the Guarani Aquifer that surrounds different cities in Santa Catarina state, Brazil: São João do Oeste (SJO), Alto Bela Bista (ABV), and Chapecó (CCO), with average depths and flowrates of 930, 720, and 550 m; and 30, 40, and 33 m3 h−1, respectively. The samples, collected in confined regions and which hardly present variations in their characteristics, were analyzed concerning the content of Fe3+ and Mn2+ as well as aluminum, chlorides, total fluorides, sulfates (mg L−1), total alkalinity (mg L−1), apparent color (uH), total hardness (mg L−1), and pH, following methods described by the American Public Health Association (APHA) [22]. Apart from the pH analyses (performed by potentiometry), the contents of total iron, manganese, and aluminum were accomplished by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (Perkin-Elmer, model 800 AAnalyst AAS, Shelton, USA). The water hardness, chlorides, sulfate, and fluoride were determined by UV–Vis spectrophotometry (Merk, model Spectroquant Pharo 300, Germany).
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
Firstly, aiming to understand how the evaluated materials behave in different pH conditions during the adsorption process, tests to determine the point of zero charge (PZC) of the compounds were accomplished. Following an adaptation of the operational protocol proposed by Aziz et al. [23], 1.5 g of NCLIN and ACLIN were immersed in pH solutions of 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, and 10.0, with the pH adjusted using a solution of 0.1 mol mL−1 of HCl or NaOH. The suspension was homogenized in an orbital shaker at 130 rpm and room temperature (24 ± 1 °C) for 24 h. Afterward, the samples were filtered in order to remove the compounds. The PZC was determined by direct subtraction of the pH (initial pH—final pH) of the solutions.
Batch adsorption kinetic assays were performed, individually, for synthetic solutions containing Fe3+ and Mn2+. For that, samples with 1.5 g of adsorbent were mixed with 30 mL of each synthetic ion solution containing 15 mg L−1 of each metal and shaken at 130 rpm. Samples were collected periodically (5, 10, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 240, 300, 360, 420, and 480 min), filtered, and subjected to metal analysis using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Merck, model Spectroquant Pharo 300) to determine the remaining ion in the solutions. All assays were performed in duplicate at room temperature (24 ± 1 °C), at pH 6.0 for NCLIN and at pH 4.0 for ACLIN.
The adsorption isotherms were obtained for each ion separately, using different adsorbent quantities (from 0.2 to 2.0 g). The flasks containing the adequate amount of NCLIN and ACLIN with 30 mL of each ion solution (15 mg L−1) were shaken at 130 rpm and room temperature (24 ± 1 °C). The aliquots collected after the assays containing the ions of Fe3+ and Mn2+ were analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometry (Perkin-Elmer, model 800 AAnalyst AAS, Shelton, USA). Calibration curves were prepared by serial dilutions of stock solution 1000 mg L−1 standard (Assurance Grade Interference Check Standard/SPEX CertiPrep®).
2.5. Kinetic and Isotherm Studies
Fe3+ and Mn2+ uptakes () expressed as ion removal per mass of clinoptilolite (mg g−1) were calculated according to Equation (1), where and are the initial and final (at equilibrium) ion concentration (mg mL−1), respectively. is the batch volume (mL) and, is the mass of adsorbent (g).
2.5.1. Adsorption Kinetic Modeling
Pseudo-first-order (PFO) and pseudo-second-order (PSO) models are the two most commonly used empirical kinetic models in liquid adsorption studies [24,25,26]. The characteristic constant for the pseudo-first-order equation of Lagergren [27], based on solid capacity, was determined using Equation (2), where is the constant rate of pseudo-first-order adsorption (min−1), is the amount of solute adsorbed at equilibrium (mg g−1), and is the amount of solute sorbed on the surface of the sorbent at any time (mg g−1).
The PSO kinetic model is based on the solid phase [28], considering the assumption that the rate-limiting step may be chemical sorption involving valence forces through the sharing or exchange of electrons between sorbent and sorbate. It is assumed that the sorption capacity is proportional to the number of active sites occupied by the sorbent. Accordingly, the kinetic rate law can be written as Equation (3), where is the rate constant of PSO adsorption (g (mg min)−1).
2.5.2. Adsorption Isotherm Modeling
Adsorption isotherms are experimental curves depicting changes in the mass or volume of adsorbed substrate per weight of adsorbent. Langmuir’s theory is based on the following assumptions: (i) adsorption occurs on sites of equal energy; (ii) adsorption occurs in monolayers; (iii) there is no lateral interaction between molecules adsorbed on the surface; and (iv) the reaction is reversible. The Langmuir model [28] is the most widely used isotherm—represented by Equation (4)—where is the equilibrium concentration of solute in the liquid phase (mg L−1), is the Langmuir constant, and is the maximum adsorption capacity of solute adsorbed per weight of adsorbent (maximum monolayer) (mg g−1) [29,30,31]. The Freundlich model [32], which is based on heterogeneous surfaces and multilayer adsorption, is the second most used isotherm model, and it is characterized by an exponential distribution of adsorption site energies on the surface of the support characterized by adsorption at localized sites. It should also be mentioned that this fact applies to dilute solutions. It can be described by Equation (5), where and are Freundlich constants. A favorable adsorption of the adsorbate on the adsorbent is generally indicated by . The value of increases as the adsorption strength increases [29,30,31].
2.5.3. Statistical and Computational Details
The non-linear regression methodology was applied to kinetic and equilibrium analysis. MATLAB® (v2018) was used to simulate the ODE system with the ode15s routine, and the rate parameters were determined using the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. The confidence intervals (95%) were calculated using the MATLAB® built-in routine nlparci, and the correlation coefficient (R2) was considered to measure the agreement between the experimental data and the proposed models [33]. Spearman’s correlation (Equation (6)) was used to measure, in a non-parametric form, the dependence of the ranks of the considered variables, where is the Spearman’s coefficient, is the rank parameters covariance, and and are the standard deviations of the ranked parameters i and j.
Akaike’s information criterion () was used to rank kinetic and equilibrium models and was applied for the Fe3+ and Mn2+ adsorption mechanism prediction on NCLIN and ACLIN adsorbents. The Akaike approach [34] is a methodology for model selection in a situation where more than one model has been fitted to experimental data. Since the model errors are normally and independently distributed, is the number of data points, and is the sum of squares for the residual. The becomes Equation (7), where is the number of parameters in the model [35].
This work used AICc—Equation (8)—a bias adjustment or correction proposed by Burnham and Anderson [36] when having a small number of observations (n).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Clinoptilolites’ Functional Groups
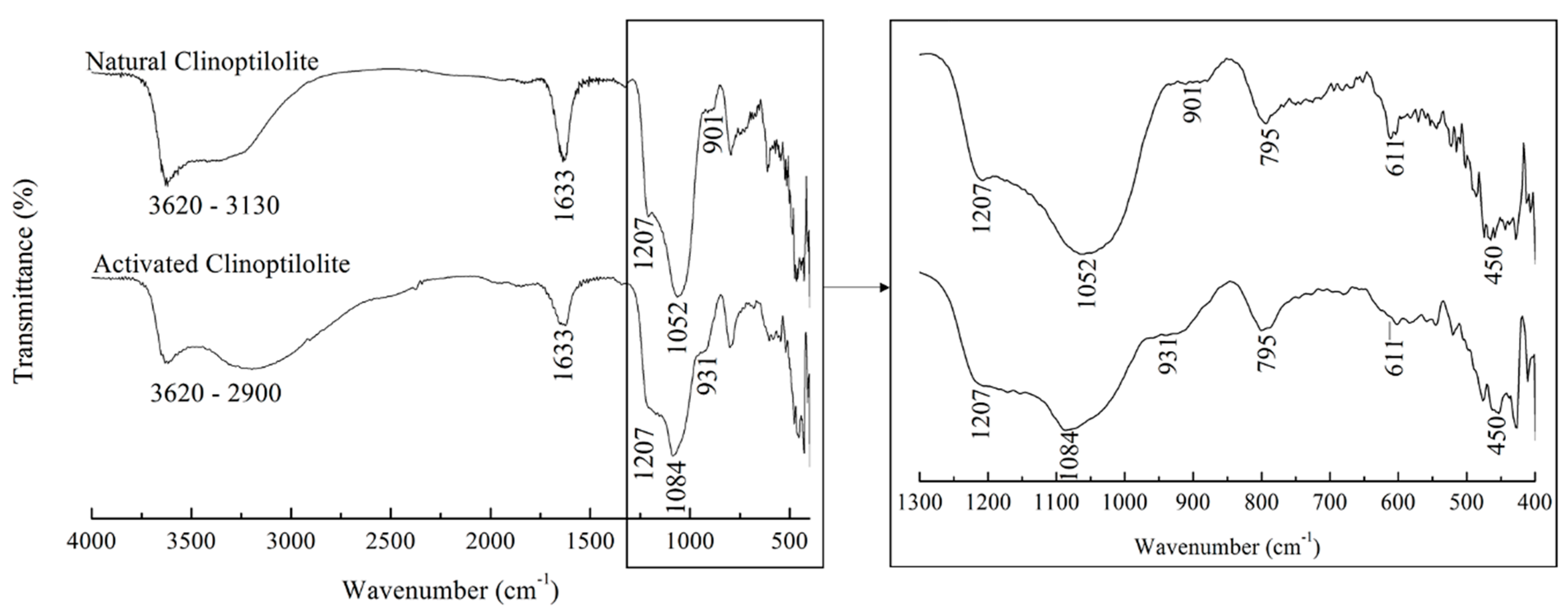
FTIR spectra for the NCLIN and ACLIN are presented in Figure 1. The bands detected at 3550–3680 cm−1 correspond to the bridging OH− groups in Al–OH–Si≡ bonds, presenting primarily in the zeolite’s active sites even as groups ≡Al–OH and ≡Si–OH [37]. The broader bands at 3200–3500 cm−1 are related to the stretching vibrations of O-H from the adsorbed water, while the band at 1633 cm−1 characterizes the signal stretching and angular deformation of the hydroxyl molecules of water, indicating the hydration of both zeolites [38]. Interestingly, the ACLIN spectra have a broader band in the region of 3200 cm−1 in comparison to the NCLIN, which can be associated with the increase of HSO3− groups in its adsorbent surface [39].
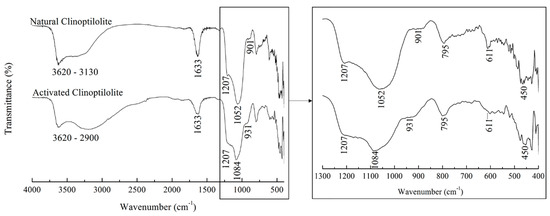
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of NCLIN and ACLIN from 400 to 4000 cm−1 and magnified in the region between 400 and 1300 cm−1.
The main characteristic bands of the NCLIN are observed at wavelengths of 611 cm−1, 795 cm−1, and 1052 cm−1. Bands at 795 cm−1 and 1052 cm−1 are attributed to Si–O–Si bonds, while the wide absorption band in the range of 900–1200 cm−1 is assigned to Si(Al)–O stretching vibrations of zeolite framework structures [39]. Aluminum silicate zeolite often exhibits bands around 600 cm−1 due to tension vibrations in the aluminum (AlO4) and silicon (SiO4) tetrahedra of its structure, related to the bonds between oxygen, aluminum, and silicon atoms [40]. After the chemical modification, the ACLIN zeolite spectrum shows that the peak at 611 cm−1 practically disappeared and the amorphous silica of the characteristic peak at 450 cm−1 increased its intensity, suggesting an acid-induced structural alteration of the compound treated with H2SO4. On the other hand, the zeolite band shift from 1052 to 1084 cm−1 denotes a partial structural breakdown, accompanied by a dealumination process [41].
3.2. Adsorptive Process
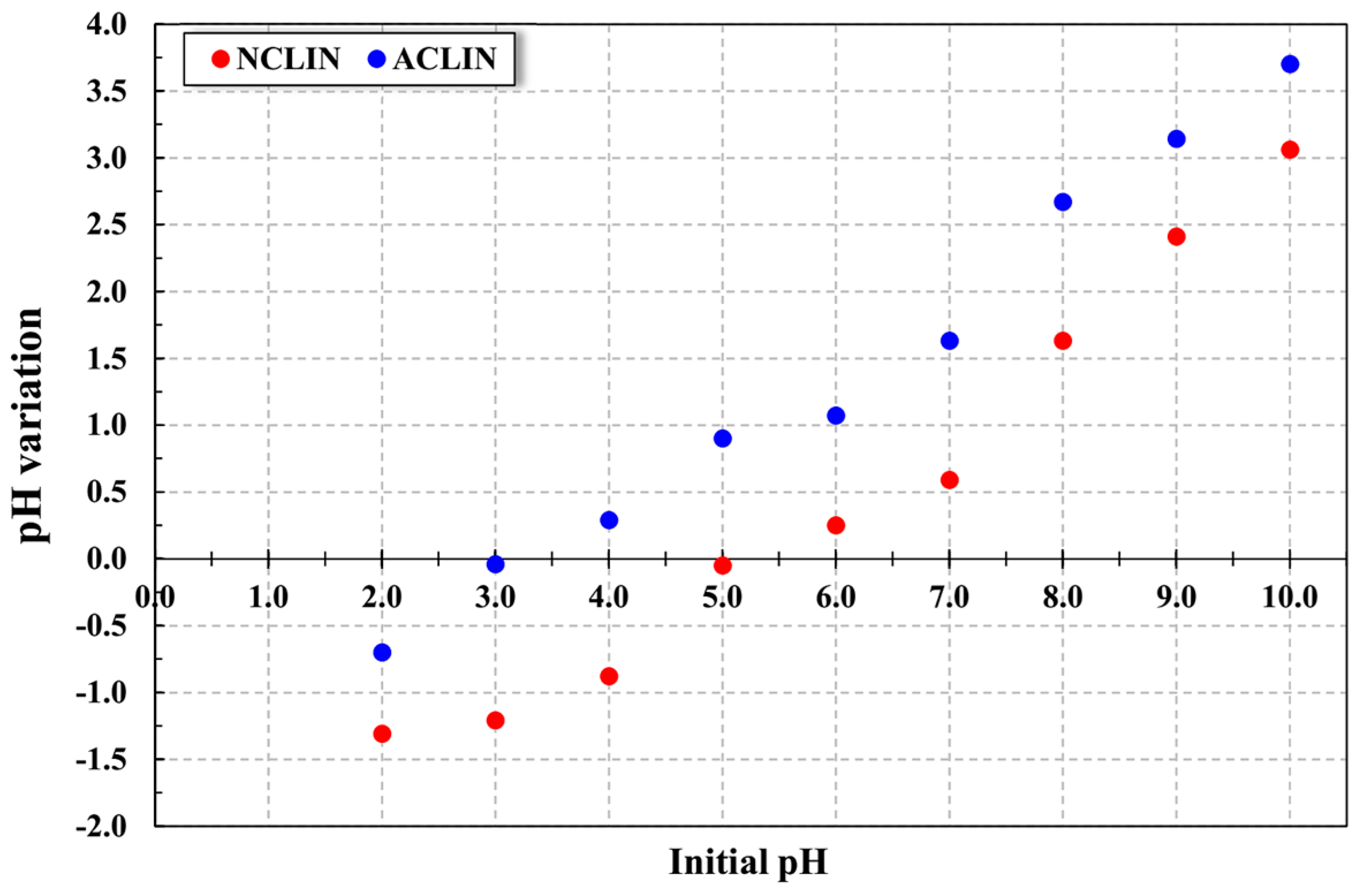
Preliminary tests to investigate the surface electric charge of the adsorbent were accomplished, where the PZC of the NCLIN and ACLIN were determined, as presented in Figure 2. The PZC directly influences the interaction between the adsorbent and the ions present in the solution, where knowing this parameter is important to understand how the material will act in different pH conditions during adsorption processes. In other words, Bellaj et al. [38] described that the PZC plays a chief role in the adsorption process since it can affect the electrostatic attraction or repulsion between the adsorbent and adsorbate. The data obtained revealed that the NCLIN presented the PZC in pH 5.13, indicating that the adsorbent surface has a positive charge in pH below 5.13 and, consequently, a negative charge in pH above this value. After the chemical treatment, the zeolite PZC was reduced to pH 3.38 due to the increase of negative charges in the adsorbent surface, indicating that in a pH above this value, the adsorbent surface has a negative liquid charge, tending to have affinity with positively charged ions.
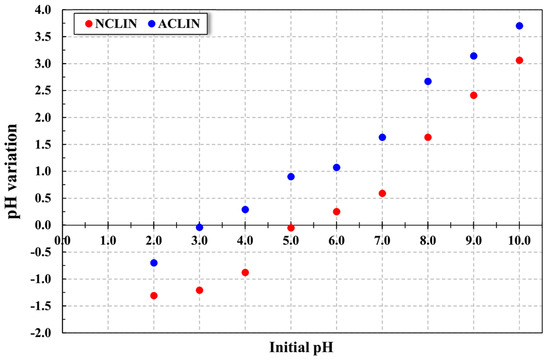
Figure 2.
The pH variation of the natural and activated zeolite clinoptilolite for PZC determination. Operational conditions: 1.5 g of NCLIN and ACLIN emerged in pH solutions of 2.0 to 10.0, with the pH adjusted using a solution of 0.1 mol mL−1 of HCl or NaOH, 130 rpm, 24 ± 1 °C, and 24 h.
The evaluation of the influence of the PZC and ion concentration is commonly used in the literature involving adsorption. Giraldo-Bareño [42] used a biosorbent based on natural Macaúba (Acrocomia aculeata) endocarp and the material chemically treated to remove Al3+, Mn2+, and Fe3+ from aqueous solutions. The PZC values obtained for the natural and treated material were 6.3 and 8.1, respectively. According to the authors, these values demonstrated that the treatment considered was able to remove some carboxylic compounds; even so, the adsorption of the metals was not impaired. Gomma et al. [43] used hierarchical TiO2 and TiOF2 adsorbents to remove ion pollutants from water solutions. According to the zeta-potential profile, the PZC of the adsorbent was obtained at pH 3.4. When the outer adsorbent surface was negatively charged (at pH > pH PZC), a strong interaction with Pb2+, Fe3+, and Al3+ cations was observed.
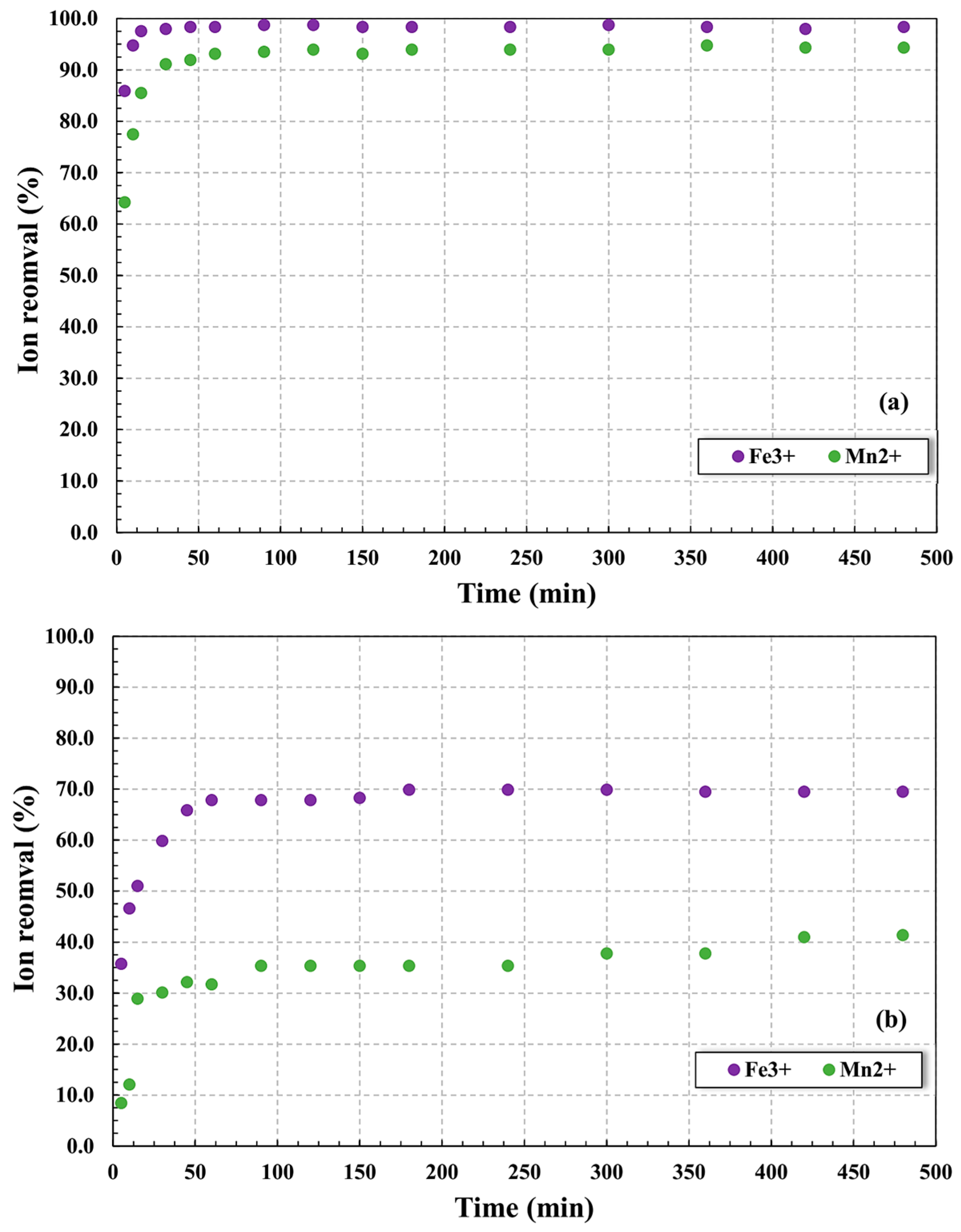
The ion adsorption profiles for the zeolites considered in this study were evaluated to determine the equilibrium data of the process, where the results obtained allowed for verification of the ion removal efficiency and the ideal contact time between adsorbent and solution to ensure the maximum adsorption. Figure 3 presents the results obtained for the removal of Mn2+ and Fe3+ ions using NCLIN (Figure 3a) and ACLIN (Figure 3b) as adsorbents. From these data, it is possible to verify that the NCLIN presented as highly efficient in the removal of Fe3+ and Mn2+, returning values above 90% of adsorption for both cations in 25 min of the process for a final ion removal >98% for Fe3+ > 94% for Mn2+. These results can be associated with the pH of the system that was maintained at 6.0 to ensure the negative charges in the adsorbent surface; at pH values lower than 6.0, the precipitation of metals is substantially limited, as can be perceived in the results obtained for ACLIN zeolite, where the Fe3+ and Mn2+ removal decreased to approximately 70% and 42%, respectively. This behavior is attributed to the higher concentration of H3O+ at low pH values and the consequent increase in competition for negative sites on the zeolite surface, reducing the material’s adsorption capacity [44]. Accordingly, at high pH, the cations (Mn2+ and Fe3+) may form complexes with OH− ions, favoring the Mn/Fe–hydroxyl species to participate in the adsorption and precipitation processes onto the zeolite structure [12,26]. Furthermore, the mesoporous characteristic of the NCLIN particles verified in a work published by our research group should also be considered, where the material presented an average surface area and pore diameter of 59.6 m2 g−1 and 38.7 Å, respectively [18]. This feature demonstrates that its pores are large enough to allow easy diffusion of Mn2+ and Fe3+ ions into the adsorbent structure, ensuring that metal ions can reach the adsorption sites located inside the pores of the adsorbent material.
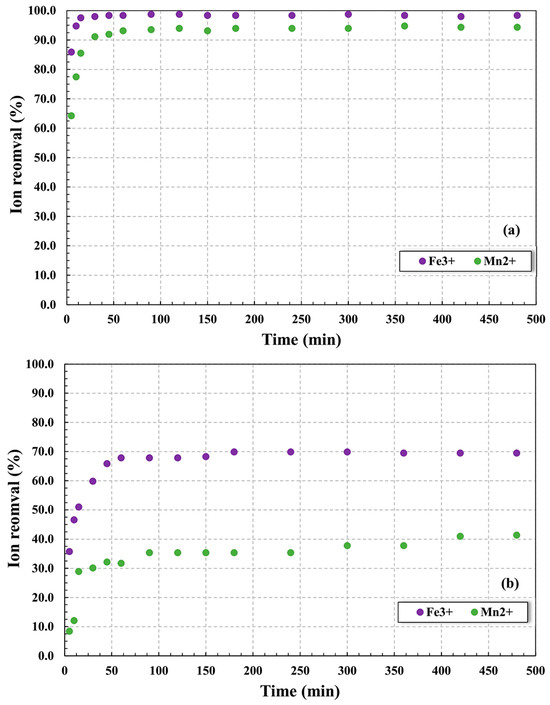
Figure 3.
Removal of Fe3+ and Mn2+ using NCLIN (a) and ACLIN (b) clinoptilolite at pH 6.0 (NCLIN) or 4.0 (ACLIN). Operational conditions: 0.05 g mL−1 of adsorbent in the ion solution containing 15 mg L−1 of each metal, 130 rpm, 24 ± 1 °C, 6 h, pH 6.0 to the NCLIN, and pH 4.0 to the ACLIN.
3.3. Process Modeling
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
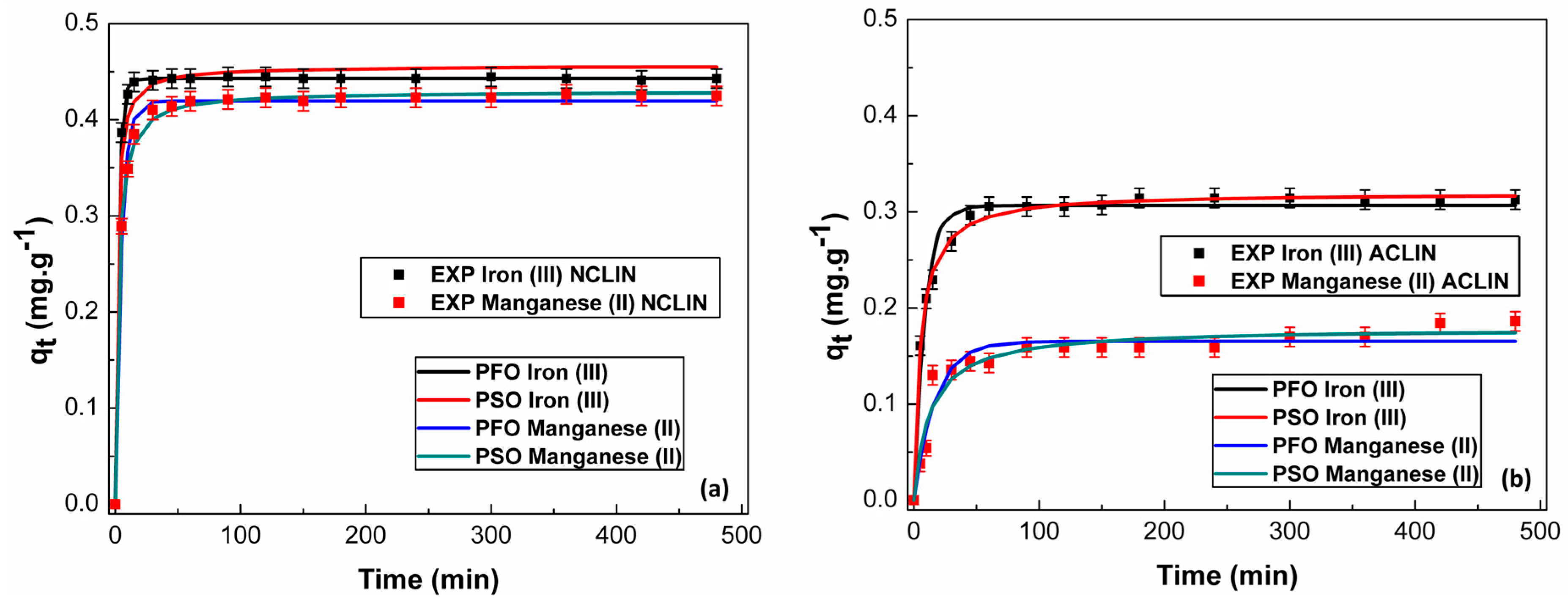
The adsorption kinetics of Fe3+ and Mn2+ on NCLIN and ACLIN zeolites were evaluated using PFO and PSO models. The parameters and fitting curves are presented in Table 1 and Figure 4, respectively. The correlation coefficient (R2) was excellent in all fittings, but high R2 values as the only adjustment criterion are insufficient to guarantee model adequacy [26]. Therefore, to broaden the approach, Table 1 shows that the PFO and PSO adsorption kinetic models have no parametric correlation coefficient above |0.9|, i.e., as the correlation coefficients obtained were less than |0.9|, there was no overparameterization of the PFO and PSO models, which suggests independence between estimated parameters and a reliable estimation procedure [45]. However, the PSO model has the minimum AICc value for the adsorption of Fe3+ and Mn2+ onto both ACLIN and NCLIN. This point implies that the theoretical data obtained from the PSO model fit the experimental data better than the PFO approach [35]. The PSO model was also the most appropriate to represent the adsorption kinetics of Al3+, Mn2+, and Fe3+ ions on a biosorbent based on natural and chemically modified Macaúba endocarp reported by Giraldo-Bareño [42]. The PSO approach can satisfactorily model the kinetic adsorption of the other ions as Cu(II) and Pb(II) on persimmon powder-formaldehyde resin [46], Ni(II) and Zn(II) on biochar from wine press residues [47], and U(VI) on boron nitride/polyindole composite [48], as well as Zn(II), Pb(II), and Cr(VI) on MgFe2O4 nanoparticles [49]. According to Robati [50], the PSO kinetic model is suitable to describe the adsorption phenomenon at low concentrations, as used in this work. This result suggests that there is the possibility of interaction between the adsorbate and the adsorbent, happening through the sharing of electrons as well as a chemisorption (or chemical) adsorption between the Fe3+ and Mn2+ and the adsorbents [51]. This mechanism can be represented in a simplified way by Equation (9), where Mn+ indicates the metal ion (Fe3+ or Mn2+), δ indicates the active site of the adsorbent, and M∙δ(ads) indicates the electrostatic attraction pair formed between both on the surface of the adsorbent [52].

Table 1.
Kinetic and statistic parameters of Fe3+ and Mn2+ adsorption on NCLIN and ACLIN adsorbents. Operational conditions: 6.67 × 10−2 to 6.67 × 10−1 g mL−1 of adsorbent in the ion solution containing 15 mg L−1 of each metal, 130 rpm, 24 ± 1 °C, 6 h, pH 6.0 to the NCLIN, and pH 4.0 to the ACLIN.
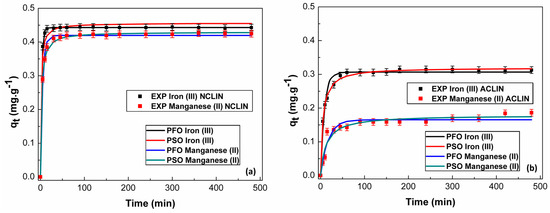
Figure 4.
Kinetic fitting of Fe3+ and Mn2+ by pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models on NCLIN (a) and ACLIN (b). Operational conditions: 6.67 × 10−2 to 6.67 × 10−1 g mL−1 of adsorbent in the ion solution containing 15 mg L−1 of each metal, 130 rpm, 24 ± 1 °C, 6 h, pH 6.0 to the NCLIN, and pH 4.0 to the ACLIN.
3.3.2. Adsorption Isotherms
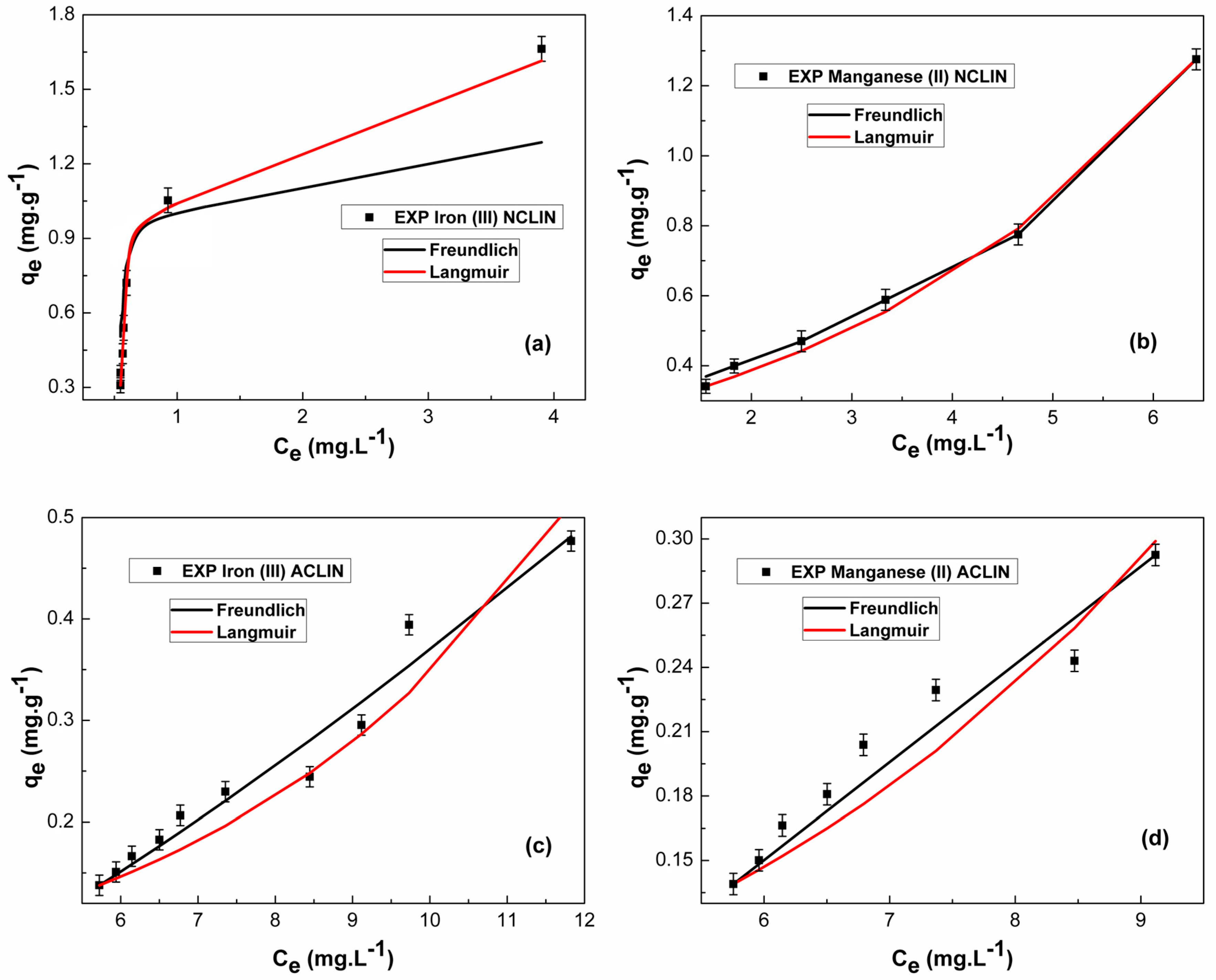
The adsorption equilibrium was evaluated using the Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms. The parameters and fitting curves are presented in Table 2 and Figure 5, respectively. Except for the Freundlich model adjusted for the adsorption of Fe3+ on the NCLIN adsorbent, the coefficients of determination (R2) and parametric correlation coefficient () indicate an excellent fit of the data to the models. For the Langmuir model, the maximum adsorption capacity () of solute adsorbed per weight of adsorbent was higher in the ACLIN than in the NCLIN. For the Freundlich model, values of indicate favorable adsorption for Fe3+ on the ACLIN and NCLIN adsorbents, while for Mn2+, this conduct was observed for the NCLIN.

Table 2.
The Langmuir and Freundlich parameters for the Fe3+ and Mn2+ adsorption on ACLIN and NCLIN adsorbents. Operational conditions: 6.67 × 10−2 to 6.67 × 10−1 g mL−1 of adsorbent in the ion solution containing 15 mg L−1 of each metal, 130 rpm, 24 ± 1 °C, 6 h, pH 6.0 to the NCLIN, and pH 4.0 to the ACLIN.
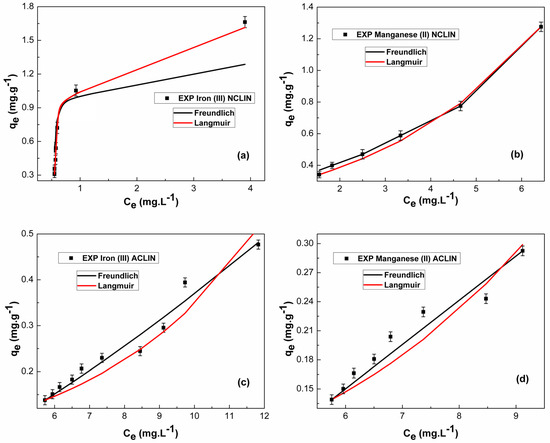
Figure 5.
Equilibrium fitting of Fe3+ and Mn2+ by the Langmuir and Freundlich models of Fe3+ on NCLIN (a), Mn2+ on NCLIN (b), Fe3+ on ACLIN (c), and Mn2+ on ACLIN (d). Operational conditions: 6.67 × 10−2 to 6.67 × 10−1 g mL−1 of adsorbent in the ion solution containing 15 mg L−1 of each metal, 130 rpm, 24 ± 1 °C, 6 h, pH 6.0 to the NCLIN, and pH 4.0 to the ACLIN.
The AICc evaluation indicates different behaviors between the NCLIN and ACLIN adsorbents. For NCLIN, the Langmuir model fits the experimental data better than the Freundlich model. The Langmuir model assumes a monolayer covering adsorption technique with an equal and energetically similar adsorption site [29,30,31,53,54]. As for ACLIN, the Freundlich model fits the experimental data better than the Langmuir model. The Freundlich model describes non-ideal and reversible adsorption processes, and it may be used for multilayer adsorption over a heterogeneous surface [29,30,31,53,54]. The multilayer adsorption mechanism associated with ACLIN zeolite may be related to the structural modification promoted by H2SO4. It is suggested that HSO3− groups on the adsorbent surface and dealumination (presented in the FTIR analysis) favored this behavior. According to Shukla [54], the occurrence of basic species as HSO3− or SO42− can increase delocalized π electron density on the adsorbent layers, which in turn can facilitate π-π stacking interaction. Abboud et al. [55] report that sulfur groups are substantially effective for removing heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions since these components show a high affinity toward sulfur groups. This situation is associated with Pearson’s rule, which suggests that strong Lewis acids prefer bonding with strong Lewis bases and weak Lewis acids to weak Lewis bases.
3.4. The Guarani Aquifer: A Preliminary Analysis of Its Groundwater Wells
The Guarani Aquifer is one of the largest underground freshwater reserves in the world and represents a significant water resource for South America, especially in Brazil. Its reserves are located in different sedimentary basins in Brazil, covering parts of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, São Paulo, Paraná, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do Sul, as well as parts of Paraguay, Uruguay, and Argentina. Accordingly, its total extent is estimated at a colossal volume of approximately 1.0 million square kilometers [6].
Contextually, to identify the physicochemical characteristics of the groundwater wells from the Guarani Aquifer in western Santa Catarina (Brazil), analyses of the main physicochemical characteristics were accomplished for different collection points. The results obtained are presented in Table 3. From these data, it is possible to verify that the wells presented high levels of Fe3+ and Mn2+ as well as F− and alkalinity. Although some samples presented parameters at acceptable levels according to the World Health Organization [56], these water sources may confer undesirable characteristics for human consumption, especially affecting the water taste, causing problems for public supply [57]. On the other hand, loads of Fe3+ (in the ABV samples), Mn2+ (in the CCO samples), alkalinity (in the ABV samples), and F− in the well samples collected were above the limit recommended for human consumption [56]. These results indicate a warning sign for the society that uses this water source, indicating the need to evaluate alternatives capable of overcoming this issue. Appropriately, the results presented in this research suggest the possibility of applying the clinoptilolite zeolites as a potential adsorbent for the removal of metals—especially Fe3+ and Mn2+—detected in the groundwater wells of the Guarani Aquifer located in the western part of the state of Santa Catarina, Brazil.

Table 3.
Physicochemical characteristics of the groundwater wells from Guarani Aquifer in different locations in the western part of Santa Catarina state, Brazil.
4. Conclusions
The analyses of the water samples from different Guarani Aquifer groundwater wells indicated that the concentration of Fe3+ and Mn2+ was at the limit (or above) according to the indication of the Brazilian legislation for human consumption. Contextually, this research presents data concerning the removal of these metals from synthetic aqueous solutions using clinoptilolite zeolite as a potential system for the treatment of groundwater. The PZC determination for adsorbents made it possible to optimize the adsorption capacity of the materials, while NCLIN was efficient in the removal of Fe3+ and Mn2+ due to its negative surface charge. Regarding the modeling data, the PSO model was the most suitable, suggesting the possibility of interaction between the adsorbent and the Fe3+ and Mn2+ through the sharing of electrons and chemisorption. Finally, the equilibrium analysis modeling indicated that the activation with H2SO4 contributes to the dealumination and formation of HSO3− groups on the adsorbent surface (ACLIN), which promoted multilayer adsorption and expanded the adsorption capacity.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. The paper conceptualization as well as punctual resources were accomplished by J.V.O. The original draft as well as review and editing were performed by W.D.A., F.K., and J.H.C.W., and G.Z. and J.D.M. also worked on manuscript revision. W.D.A., J.F.F.C., J.S., F.L.C., and A.C.d.M. worked on experimental investigation as well as formal analysis. F.K. and G.Z. worked on the methodologies approach. C.A.R., J.S., and F.L.C. were responsible for data curation. J.D.M. and J.V.O. were responsible for the supervision and project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that they received financial support and grants from the Foundation to Support the Research and Innovation of State of Santa Catarina (FAPESC)—Research Project “Rede Guarani Serra Geral” (CTHidro/ANA/CNPq).
Data Availability Statement
All data used in the research are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support and scholarships of the FAPESC (Foundation to Support the Research and Innovation of State of Santa Catarina—Research Project “Rede Guarani Serra Geral” (CTHidro/ANA/CNPq)), CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel, 001), the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), as well as of the Human Resources Program of the Brazilian Agency for Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels—PRH/ANP through the Human Resources Training Program for Petroleum and Biofuels Processing (PRH 52.1).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- UNESCO. The United Nations World Water Development Report: Valuing Water; UNESCO: Perugia, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.K.; Tortajada, C. Water Crisis and Water Wars: Myths and Realities. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2019, 35, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO Groundwater: Making the Invisible Visible. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/articles/groundwater-making-invisible-visible (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Che Nordin, N.F.; Mohd, N.S.; Koting, S.; Ismail, Z.; Sherif, M.; El-Shafie, A. Groundwater Quality Forecasting Modelling Using Artificial Intelligence: A Review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padikkal, S.; Sumam, K.S.; Sajikumar, N. Sustainability Indicators of Water Sharing Compacts. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 2027–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, E.H.; Gonçalves, R.D.; Chang, H.K. Hydrochemistry of the Guarani Aquifer System Modulated by Mixing with Underlying and Overlying Hydrostratigraphic Units. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 30, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, R.; Kirchheim, R.E.; Manganelli, A. Diplomatic Advances and Setbacks of the Guarani Aquifer System in South America. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 114, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, A.E.; Fatima, R.; Aslam, S.; Hussain, A.; un Nisa, Z.; Khan, M.; Mohammed, A.A.A.; Sillanpaa, M. Health Risks Assessment and Source Admeasurement of Potentially Dangerous Heavy Metals (Cu, Fe, and Ni) in Rapidly Growing Urban Settlement. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessling-Resnick, M. Excess Iron: Considerations Related to Development and Early Growth. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1600S–1605S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.C.; Khan, M.J.H.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Zaman, S.; Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Tanaka, H. Human Health Risk Assessment of Elevated and Variable Iron and Manganese Intake with Arsenic-Safe Groundwater in Jashore, Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuce, G.; Alptekin, C. In Situ and Laboratory Treatment Tests for Lowering of Excess Manganese and Iron in Drinking Water Sourced from River–Groundwater Interaction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.-L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Natural Zeolites: A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmani, Y.; Ba Mohammed, B.; Oukhrib, R.; Dehbi, A.; Lamhasni, T.; Brahmi, Y.; El-Kordy, A.; Franco, D.S.P.; Georgin, J.; Lima, E.C.; et al. Adsorption of Various Inorganic and Organic Pollutants by Natural and Synthetic Zeolites: A Critical Review. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Singh, C.K.; Sodhi, K.K.; Singh, V.K. Circular Economy Approaches for Water Reuse and Emerging Contaminant Mitigation: Innovations in Water Treatment. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 27, 5753–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-habacha, M.; Miyah, Y.; Lagdali, S.; Mahmoudy, G.; Dabagh, A.; Chiban, M.; Sinan, F.; Iaich, S.; Zerbet, M. General Overview to Understand the Adsorption Mechanism of Textile Dyes and Heavy Metals on the Surface of Different Clay Materials. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural Zeolites as Effective Adsorbents in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Cammarano, A.; Carotenuto, G.; Longo, A.; Palomba, M.; Nicolais, L. An Overview of the Advanced Nanomaterials Science. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2024, 559, 121802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, E.; Scapinello, J.; de Oliveira, M.; Rambo, C.L.; Franscescon, F.; Freitas, L.; de Mello, J.M.M.; Fiori, M.A.; Oliveira, J.V.; Dal Magro, J. Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Wastewater Graphic Industry Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite as Adsorbent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 105, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.; Noormohammadbeigi, M.; Cruciani, G.; Zendehdel, M. Ion-Exchange of Copper into Mordenite and Clinoptilolite Zeolites by Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Experimental Investigations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2025, 382, 113397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, T.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Bai, S.; Sun, J. Interfacial Adsorption for Efficient Removal of Fe3+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, and Sr2+ from Wastewater Using Synthetic Clinoptilolite via Single-Treatment Approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 305, 121098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuesutham, T.; Sirivat, A.; Paradee, N.; Changkhamchom, S.; Wattanakul, K.; Anumart, S.; Krathumkhet, N.; Khampim, J. Improvement of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Y Zeolite -SO3H via Organo-Functionalization Method for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; SIDALC: Washington DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, K.; Aziz, F.; Mamouni, R.; Aziz, L.; Anfar, Z.; Azrrar, A.; Kjidaa, B.; Saffaj, N.; Laknifli, A. High Thiabendazole Fungicide Uptake Using Cellana Tramoserica Shells Modified by Copper: Characterization, Adsorption Mechanism, and Optimization Using CCD-RSM Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 86020–86035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the Adsorption Kinetics Models for the Removal of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodaifa, G.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Driss Alami, S.B.; Rodriguez-Vives, S.; Martinez-Ferez, A. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Parameters of Iron Adsorption onto Olive Stones. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption Kinetic Modeling Using Pseudo-First Order and Pseudo-Second Order Rate Laws: A Review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie Der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoff. K. Sven. Vetenskapasakademiens Handl. 1989, 4, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemici, B.T.; Ozel, H.U.; Ozel, H.B. Removal of Methylene Blue onto Forest Wastes: Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalah, J. Removal of the Textile Dyes by a Resin Adsorbent Polymeric: Insight into Optimization, Kinetics and Isotherms Adsorption Phenomenally. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, Z.N.; Imam, M.; Adamu, H.; Agbaji, E.B. Optimization of Adsorption Conditions for Acid Chrome Blue K Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Sugar-Based Activated Carbon: Equilibrium Isotherms and Kinetics Modeling. Sustain. Chem. One World 2024, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Colloid & Capillary Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Methuen & Company Limited: Malton, UK, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Ketzer, F.; Wancura, J.H.C.; Tres, M.V.; de Oliveira, J.V. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study of Enzymatic Hydroesterification Mechanism to Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Synthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 356, 127335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpa, O.M.; Unuabonah, E.I. Small-Sample Corrected Akaike Information Criterion: An Appropriate Statistical Tool for Ranking of Adsorption Isotherm Models. Desalination 2011, 272, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Multimodel Inference. Sociol. Methods Res. 2004, 33, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hubadillah, S.K.; Abd Aziz, M.H.; Jamalludin, M.R. Application of Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for the Removal of Ammonia in Wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaj, M.; Aziz, K.; El Achaby, M.; El Haddad, M.; Gebrati, L.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Chen, Z.; Yap, P.-S.; Aziz, F. Cationic and Anionic Dyes Adsorption from Wastewater by Clay-Chitosan Composite: An Integrated Experimental and Modeling Study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 285, 119615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghadavoud, A.; Rezaee Ebrahim Saraee, K.; Shakur, H.R.; Sayyari, R. Removal of Uranium Ions from Synthetic Wastewater Using ZnO/Na-Clinoptilolite Nanocomposites. Radiochim. Acta 2016, 104, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, X.; Meng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Qiao, Q.; Yan, C. Clinoptilolite Based Zeolite-Geopolymer Hybrid Foams: Potential Application as Low-Cost Sorbents for Heavy Metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, S.; Sagliano, P.; Iovino, P.; Capasso, S.; Colella, C. Atrazine Adsorption by Acid-Activated Zeolite-Rich Tuffs. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo-Bareño, Y.Y.; Pinzón-García, A.D.; Sousa, D.V.M.; Bomfim Filho, L.F.O.; Lopes, D.H.A.; Cortés, N.S.; Morávia, M.C.S.A.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Orlando, R.M. Efficient and Easily Scaled-up Biosorbent Based on Natural and Chemically Modified Macauba (Acrocomia Aculeata) to Remove Al3+, Mn2+ and Fe3+ from Surface Water Contaminated with Iron Mining Tailings. Talanta 2023, 256, 124273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H.; Shenashen, M.A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Alamoudi, A.S.; Abdelmottaleb, M.; Cheira, M.F.; Seaf El-Naser, T.A.; El-Safty, S.A. Highly-Efficient Removal of AsV, Pb2+, Fe3+, and Al3+ Pollutants from Water Using Hierarchical, Microscopic TiO2 and TiOF2 Adsorbents through Batch and Fixed-Bed Columnar Techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biblioteca, I.; Sambucci, M.; Valente, M. Zeolite-Clinoptilolite Conditioning for Improved Heavy Metals Ions Removal: A Preliminary Assessment. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 39649–39656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketzer, F.; de Castilhos, F. An Assessment on Kinetic Modeling of Esterification Reaction from Oleic Acid and Methyl Acetate over USY Zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 314, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Fan, R.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Z. NaOH Modification of Persimmon Powder-Formaldehyde Resin to Enhance Cu2+ and Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solution. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.L.; Pinto, D.; Schio, R.R.; dos Santos, J.P.; Ketzer, F.; Silva, L.F.O.; Dotto, G.L. Polishing of Painting Process Effluents through Adsorption with Biochar from Winemaking Residues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 66348–66358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, D.; Zorer, Ö.S.; Bilici, A.; Budak, E.; Yilmaz, S.; Kilic, N.C.; Sogut, E.G. Adsorption of Uranium (VI) from Aqueous Solutions Using Boron Nitride/Polyindole Composite Adsorbent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, 54856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, T.; Krishnan, K.A.; Joseph, A.; Krishnan, R.R. Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Modelling of Liquid Phase Adsorption of the Heavy Metal Ions Zn(II), Pb(II) and Cr(VI) onto MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D. Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Equations for Modeling Adsorption Systems for Removal of Lead Ions Using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2013, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Iftekhar, S.; Wang, Z.; Babu, I.; Sillanpää, M. Synthesis and Application of Biocompatible Nontoxic Nanoparticles for Reclamation of Ce3+ from Synthetic Wastewater: Toxicity Assessment, Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Study. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, B.; Wu, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Cao, X.; Feng, Q. Revealing the Role of Calcium Alginate-Biochar Composite for Simultaneous Removing SO42− and Fe3+ in AMD: Adsorption Mechanisms and Application Effects. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouzayed, F.I.; El-nassr, N.T.A.; Abouel-Enein, S.A. Synthesis, Characterization of Functionalized Grafted Cellulose and Its Environmental Application in Uptake of Copper (II), Manganese (II) and Iron (III) Ions. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1270, 133907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Panchal, D.; Prakash, O.; Mondal, P.; Hiwrale, I.; Dhodapkar, R.S.; Pal, S. Magnetically Engineered Sulfurized Peat-Based Activated Carbon for Remediation of Emerging Pharmaceutical Contaminants. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami Abboud, A.; Ghaffarinejad, A.; Mollahosseini, A. Removal of Lead and Cadmium Ions from Wastewater Using Magnetic Alginate Impregnated Sulfur. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2023, 20, 100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nawa, N.; Miyazaki, K. The Analysis of Saltwater Intrusion through Komesu Underground Dam and Water Quality Management for Salinity. Paddy Water Environ. 2009, 7, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Ministry of Health. Ordinance n. 888 of 4th May 2021; Brazilian Ministry of Health: Brasilia, Brazil, 2021; p. 21.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).