Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Modified Ultrafine ABC Powder on CH4/Coal Dust Coexistence Explosions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Modified Samples
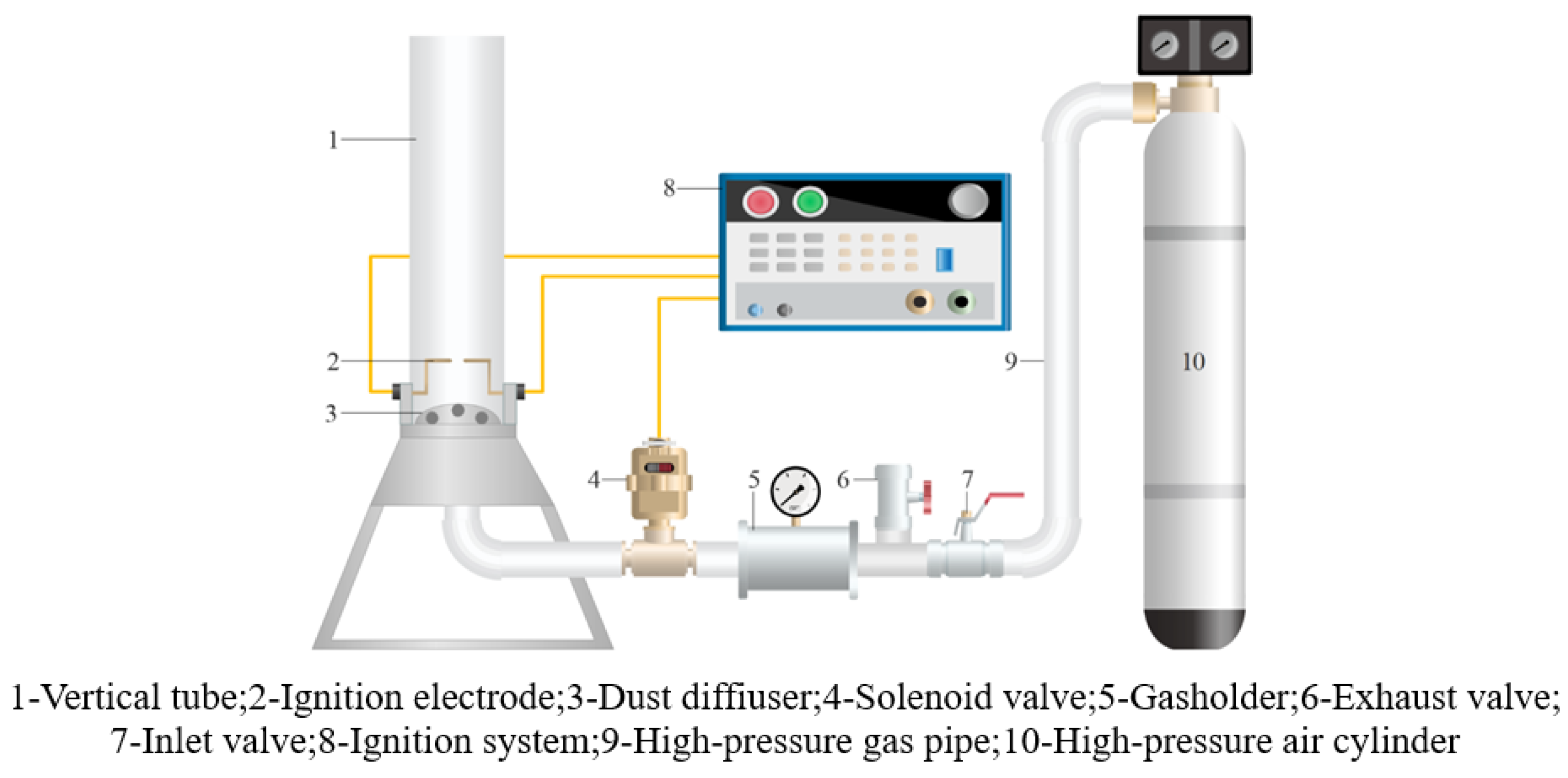
2.2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Parameters of Modified ABC Powder
3.1.1. Hydrophobicity and Fluidity
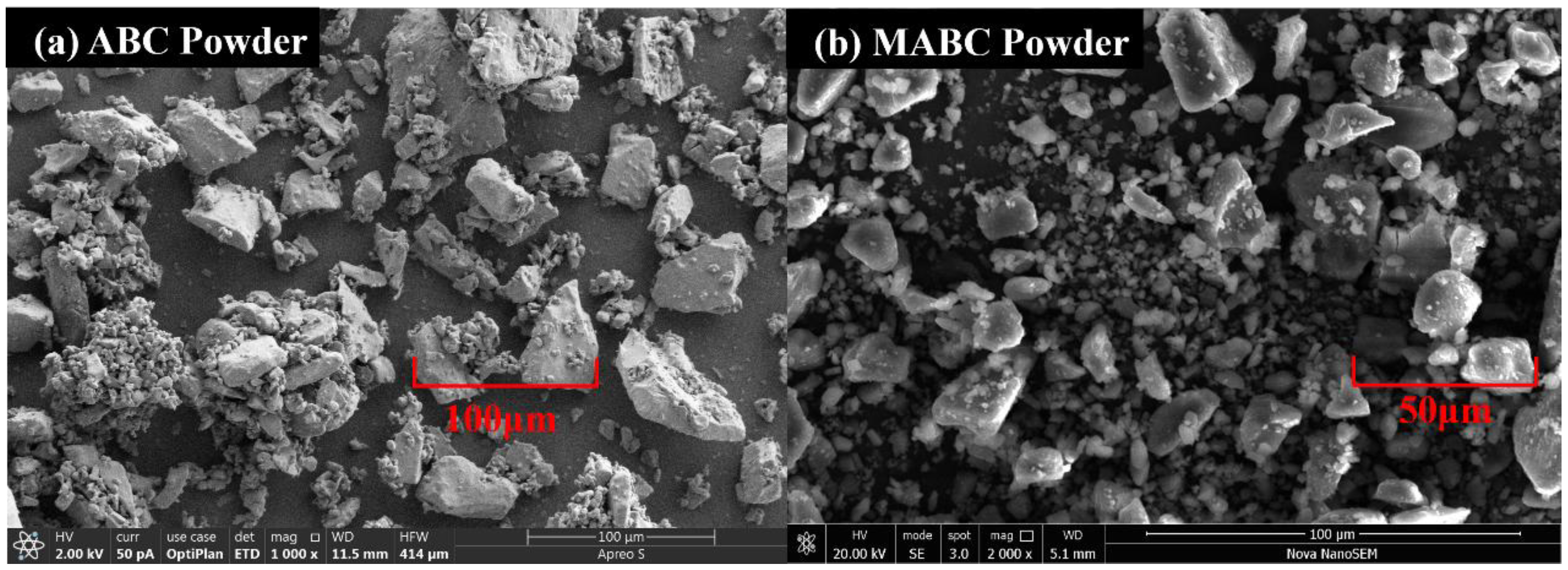
3.1.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Image Analysis
3.2. Explosion Overpressure Characteristics of CH4/Coal Powder Mixture System
3.2.1. Explosion Overpressure Characteristics of CH4/Coal Powder Mixed System
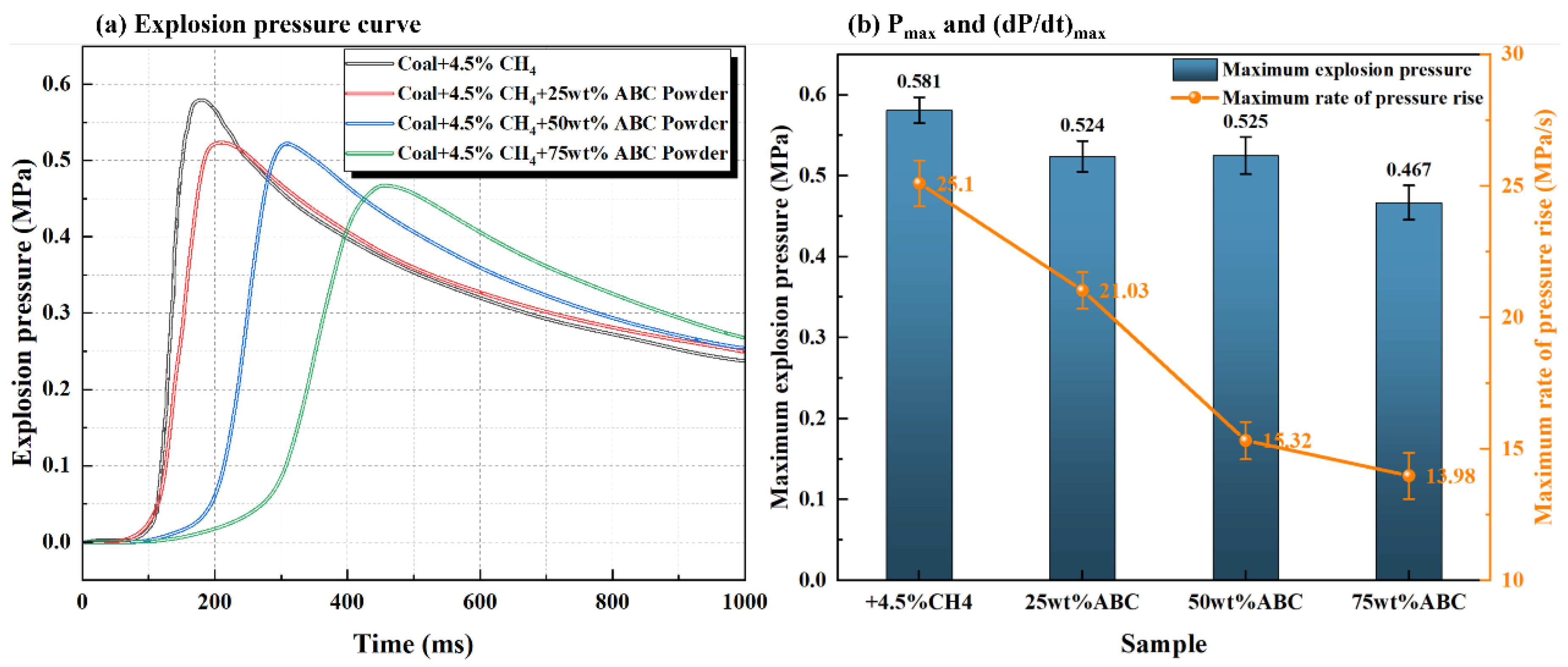
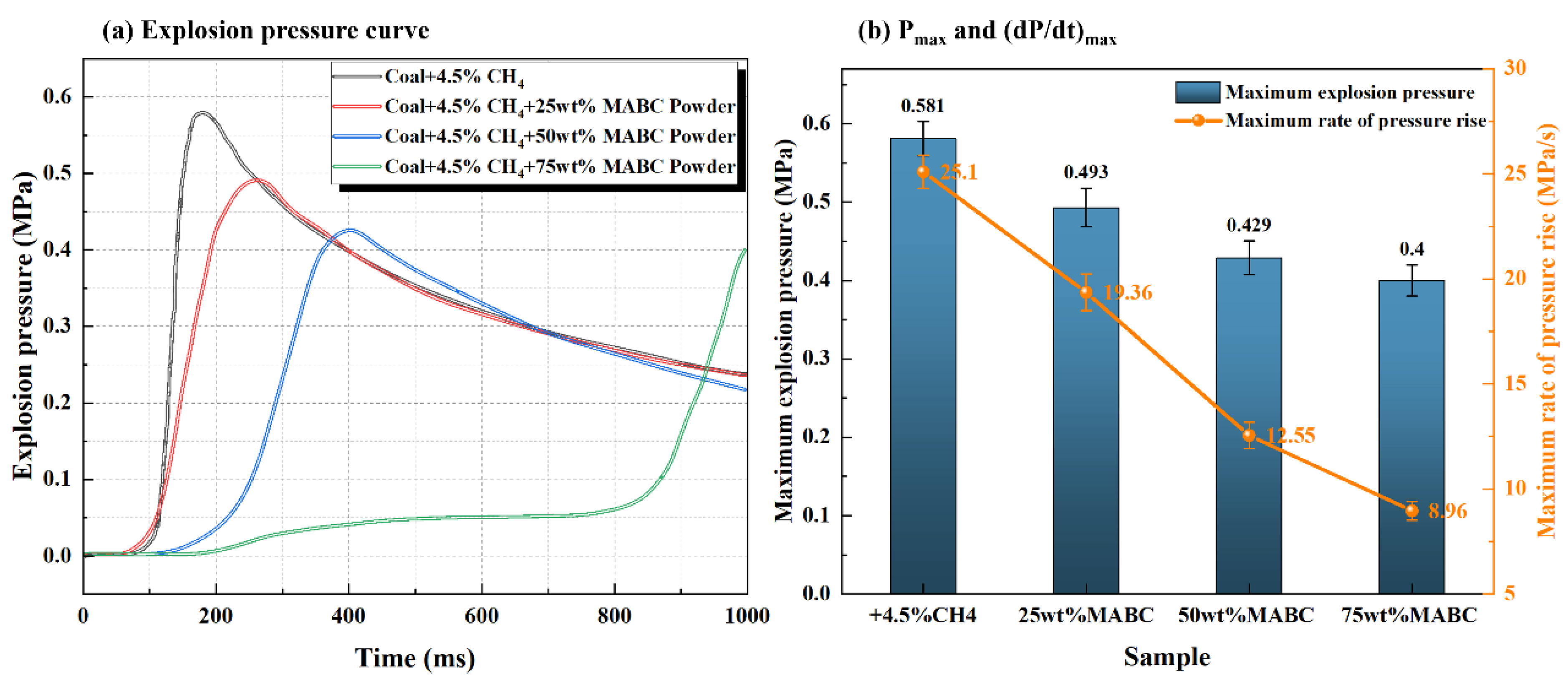
3.2.2. The Inhibition Law of ABC or MABC on Explosion Overpressure Characteristics of Mixed Systems
3.3. The Propagation Law of Explosive Flames
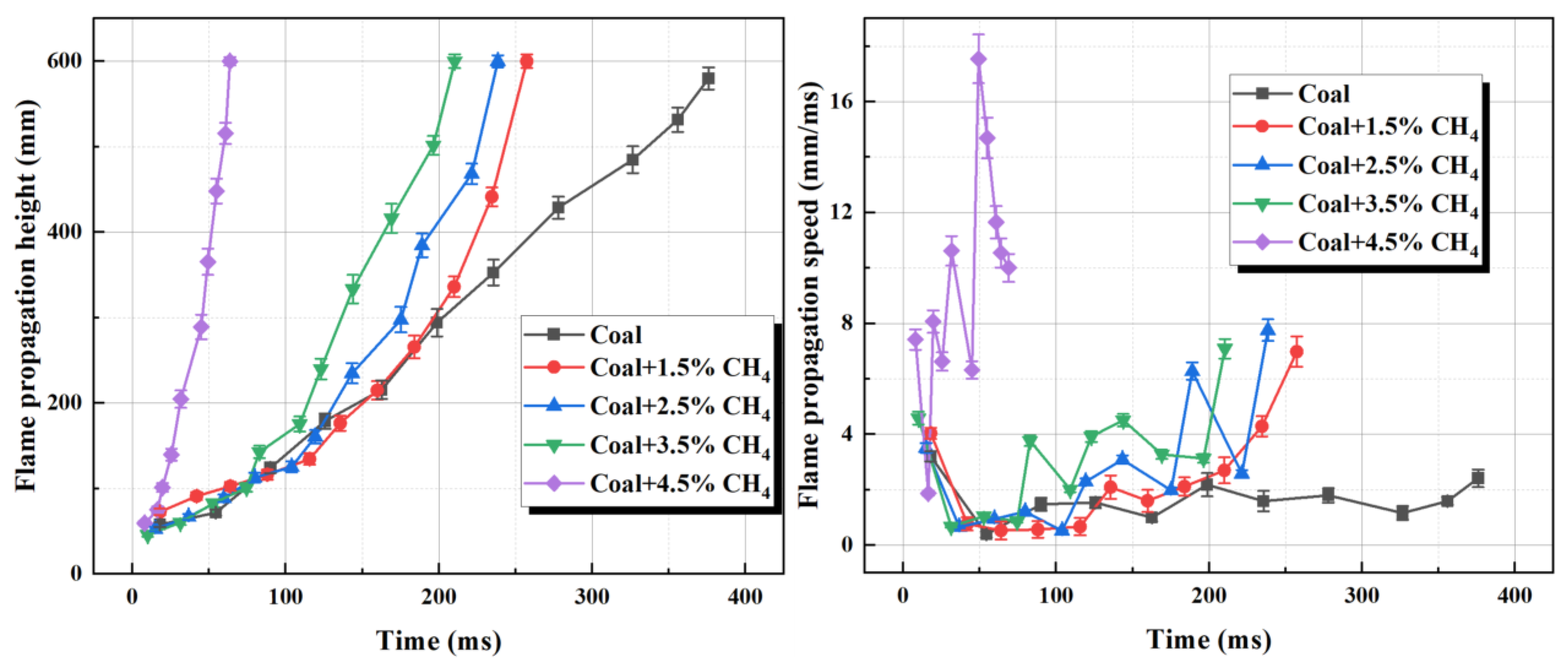
3.3.1. The Influence of CH4 Concentration on the Propagation Mode of Detonation Flames
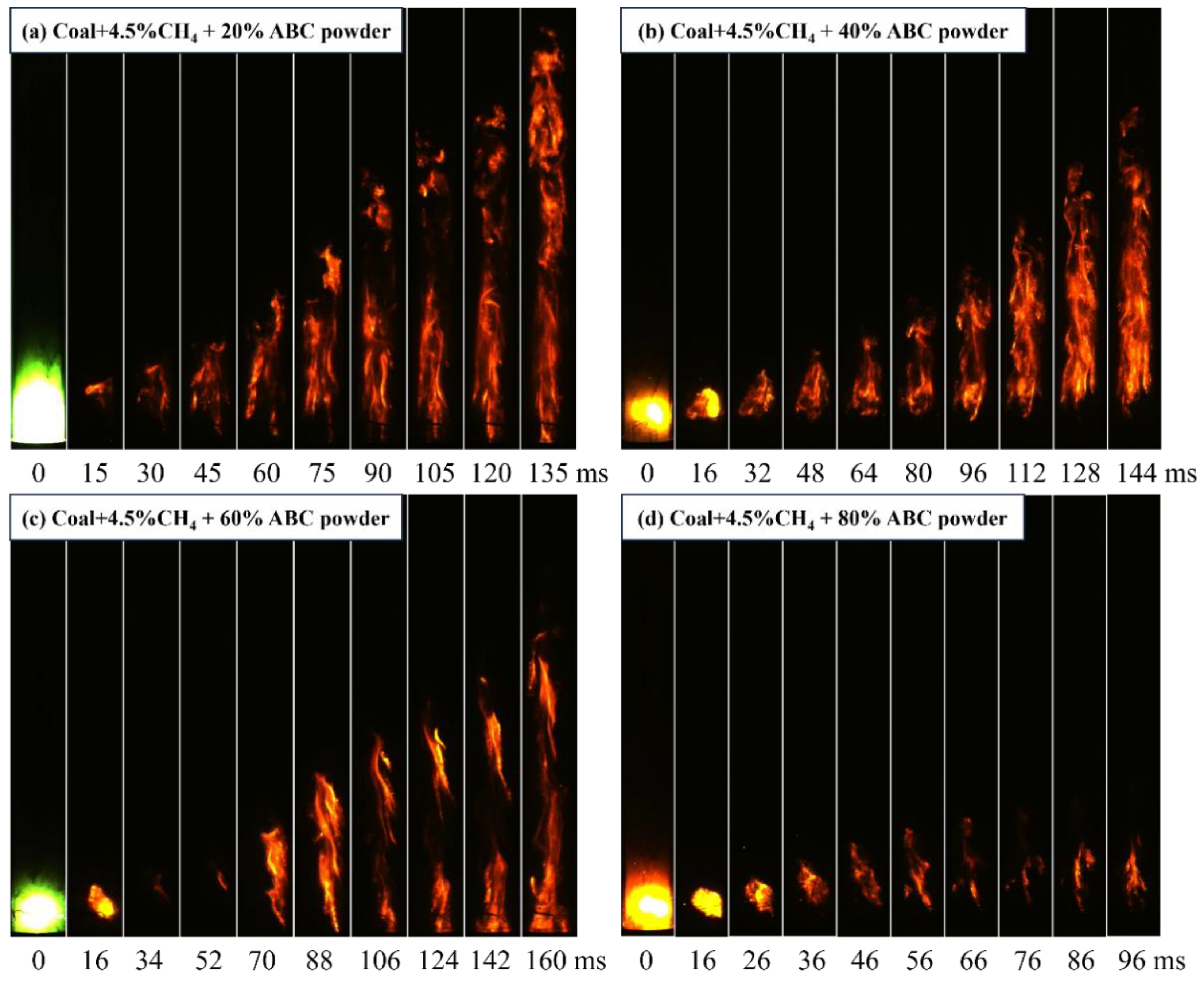
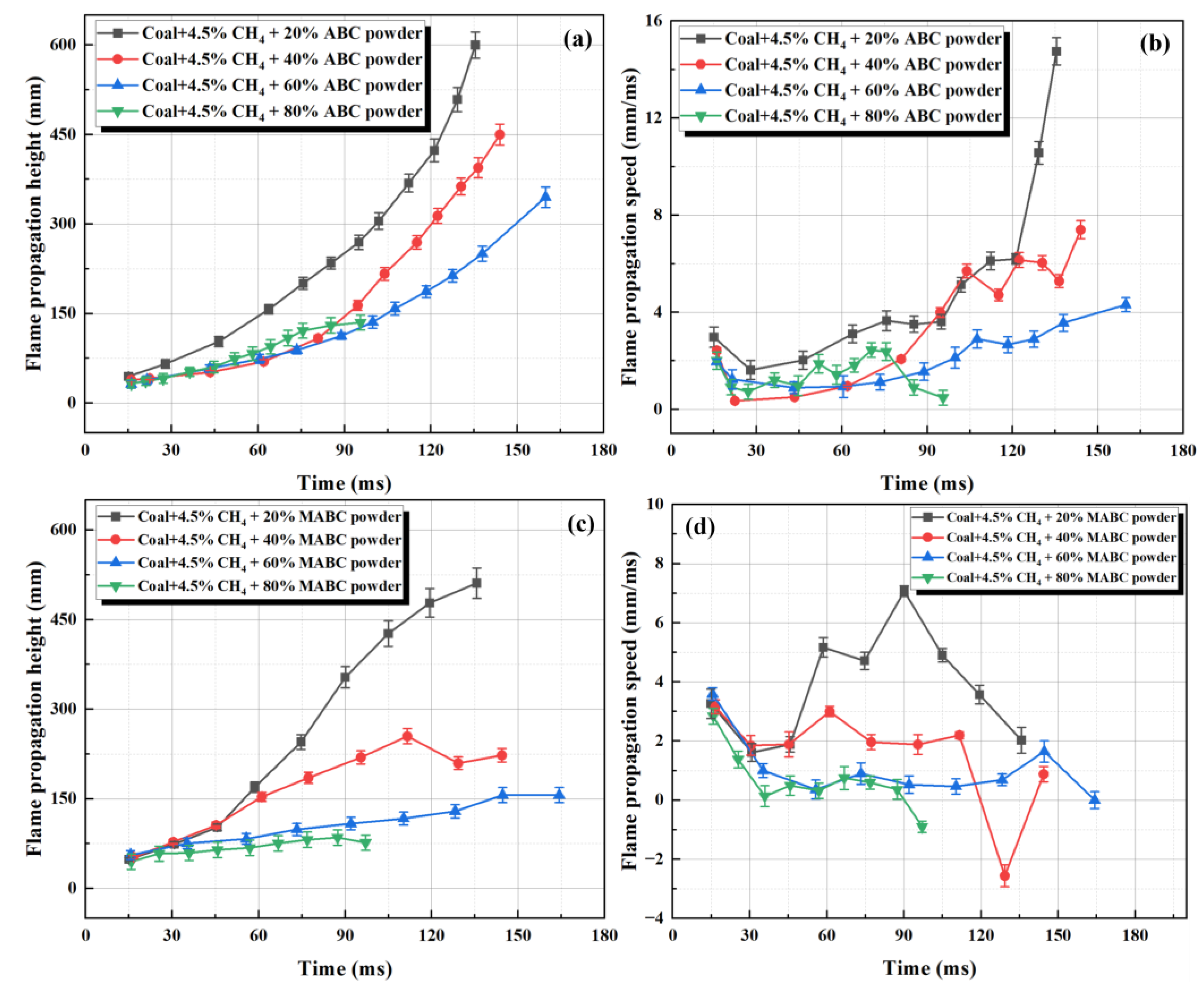
3.3.2. The Inhibitory Effect of ABC Powder on Flame Propagation Before and After Modification
3.4. Thermal Decomposition Analysis of ABC Powder Before and After Modification
3.5. Inhibition Mechanism of ABC Powder on Explosion of Mixed System
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Methane significantly exacerbates the intensity of coal dust explosions, and its concentration is positively correlated with the Pmax and (dP/dt) of the mixed system. The heat released by methane combustion accelerates the pyrolysis of coal powder, forming a self-sustaining chain reaction that leads to a significant increase in explosion intensity.
- (2)
- Modified ABC powder was treated with a hydrophobic agent (KH550) and a flow aid (talc powder) to improve particle dispersion and flowability, making it more evenly distributed in the explosion space. Compared to unmodified powder, its explosion suppression efficiency is significantly improved: adding 60–80% modified ABC can completely suppress flame propagation, and the amount of explosion suppression agent used is reduced by about 20%.
- (3)
- ABC powder undergoes endothermic decomposition to produce P2O5, which covers the surface of coal powder to form an insulation layer and reduce the system temperature. The decomposition products HPO3 and PO2 consume key free radicals in the explosive chain reaction, interrupting the transmission of the combustion chain. Modified powders maintain higher activity at high temperatures due to enhanced thermal stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CH4 | methane |
| APP | ammonium polyphosphate |
| (dP/dt)max | maximum rate of increase in explosion pressure |
| Pmax | maximum explosion pressure |
| MABC | modified ABC powder |
| MIE | minimum ignition energy |
| tPmax | pressure peak arrival time |
| Vmax | maximum flame propagation speed |
References
- Chen, C.; Wei, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of abrasive volume fraction on energy utilization in suspension abrasive water jets based on VOF-DEM method. Powder Technol. 2025, 449, 120427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Lai, X.; Cui, F.; Liu, Y.; Pan, R.; Karlovšek, J. The failure of edge-cracked hard roof in underground mining: An analytical study. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. Sci. 2024, 183, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Study on explosion suppression of coal powder with different particle size by shell powder and NaHCO3. Fuel 2021, 306, 121709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Si, R.; Wang, L.; Jia, Q.; Xin, C. Explosion and explosion suppression of gas/deposited coal powder in a realistic environment. Fuel 2024, 357, 129710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W. Interaction between gas explosion flame and deposited dust. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Tian, X. Propagation and attenuation characteristics of shock waves in a gas–coal powder explosion in a diagonal pipeline network. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yan, K.; Wang, T. Experimental study on the suppression of coal powder explosion by silica aerogel. Energy 2023, 267, 126372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Cao, M.; Wei, X.; Shi, L.; Wang, X. Experimental numerical study on suppressing coal powder deflagration flame with, NaHCO3. and MPP. Fuel 2024, 358, 130152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajrash, M.J.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. Methane-coal powder hybrid fuel explosion properties in a large scale cylindrical explosion chamber. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 40, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.K.; Zanganeh, J.; Eschebach, D.; Moghtaderi, B. Explosion severity of methane–coal powder hybrid mixtures in a ducted spherical vessel. Powder Technol. 2018, 323, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Cheng, Y.; Meng, X.; Ma, H.; Dai, H.; Kan, J.; Shen, Z. Hybrid CH4/coal powder explosions in a 20-L spherical vessel. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 122, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Bai, C.; Chen, M. Methane/coal powder/air explosions and their suppression by solid particle suppressing agents in a large-scale experimental tube. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2013, 26, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, F.; He, T.; Li, H.; Han, S.; Lou, R.; Zheng, K.; Yu, Y. Experimental exploration and mechanism analysis of the deflagration pressure of methane/pulverized coal blenders inhibited by modified kaoline-containing compound inhibitors. Fuel 2023, 333, 126353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Dai, H. Suppression mechanisms of ammonium polyphosphate on methane/coal powder explosion: Based on flame characteristics, thermal pyrolysis and explosion residues. Fuel 2022, 326, 125014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Dai, H. Suppression of methane/coal powder deflagration by Al(OH)3 based on flame propagation characteristics and thermal decomposition. Fuel 2022, 311, 122530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Dai, H. Characteristics of coal powder deflagration under the atmosphere of methane and their inhibition by coal ash. Fuel 2021, 291, 120121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Fire extinguishing and explosion suppression characteristics of explosion suppression system with N2/APP after methane/coal powder explosion. Energy 2022, 257, 124767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.; Dai, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J. Suppression of methane/coal powder deflagration flame propagation by CO2/fly ash as a flue gas layer. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 2770–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Bi, M.; Huang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, W. Suppression mechanism of ultrafine water mist containing phosphorus compounds in methane/coal powder explosions. Energy 2022, 239, 121987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Shao, Z.; Xu, B.; Wei, H.; Wang, T. Analysis of explosion pressure and residual gas characteristics of micro-nano coal dust in confined space. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 64, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, M.; Jia, B. Inhibition of Gas Explosion by Nano-SiO2 Powder under the Condition of Obstacles. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2021, 216, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cui, Y.; Mebarki, A.; Cai, Y. Effect of a Tilted Obstacle on the Flame Propagation of Gas Explosion in Case of Low Initial Pressure. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2021, 193, 2405–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Dai, H.; Liang, G. Inhibition evaluation of magnesium hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide, and hydrotalcite on the flame propagation of coal dust. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Liang, P.; Zhang, Y. Effectiveness and mechanism of carbamide/fly ash cenosphere with bilayer spherical shell structure as explosion suppressant of coal dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ji, S.; Li, Q.; Yao, Y.; Xie, Q. Study on suppression of ABC powder and potassium bicarbonate-zeolite composite powder on explosion of hydrogen enriched compressed natural gas. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 81, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zheng, L.; Gao, J. The suppression characteristics of NH4H2PO4/Red Mud composite powders on methane explosion. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Dongye, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Research on the influence of phosphorus regulation on the explosion suppression performance and mechanism of NiB/Hβ-Al2O3 suppressant. Powder Technol. 2025, 454, 120742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, A. Investigation on slag resource utilization: KHCO3/modified slag composite powder applied to methane/air explosion suppression. Powder Technol. 2024, 441, 119814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Song, S.; Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, Z. Piperazine pyrophosphate-functionalized Ni-MOF metal framework: Fabrication and synergistic explosion suppression mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, P.; Wei, X. Influencing mechanism study on heptafluoropropane of different concentrations to the explosive characteristics of ethylene. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy. 2025, 109, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Ding, J.; Song, S. Macroscopic behavior and kinetic mechanism of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate for suppressing polyethylene dust deflagration. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Meng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yan, K.; Song, S. Polyethylene deflagration characterization and kinetic mechanism analysis. Energy 2024, 303, 131990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Cai, L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, X. Study on suppression of coal powder explosion by superfine NaHCO3/shell powder composite suppressant. Powder Technol. 2021, 394, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, X.; Wei, X.; Shi, J.; He, J. Explosion characteristics and mechanism research of the EG-APP composite powder to inhibit APC powder. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO6184-1:1985; Explosion Protection Systems—Part 1: Determination of Explosion Indices of Combustible Dusts in Air. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1985.
- GB/T 16428-1996; Determination of the Minimum Ignition Energy of Dust Cloud. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 1996.
- GB/T 3836.12-2019; Explosive Atmospheres—Part 12: Material Characteristics for Combustible Dusts—Test Methods. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2019.
- ISO/IEC 80079-20-2:2016; Explosive Atmospheres Part 20-2: Material characteristics—Combustible Dusts Test Methods. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.






| Sample | Industrial Analysis (wt%, ad) | Elemental Analysis (wt%, ad) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Ash Content | Volatile Matter | Fixed Carbon | C | H | N | O | S | |
| Lignite | 12.28 | 7.93 | 39.55 | 42.24 | 56.24 | 4.47 | 1.22 | 37.47 | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Deng, P.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X. Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Modified Ultrafine ABC Powder on CH4/Coal Dust Coexistence Explosions. Processes 2025, 13, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030858
Guo Y, Deng P, Zhang B, Liu X, Zhang Y, Wei X. Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Modified Ultrafine ABC Powder on CH4/Coal Dust Coexistence Explosions. Processes. 2025; 13(3):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030858
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Youwei, Pengjiang Deng, Bingbing Zhang, Xiancong Liu, Yansong Zhang, and Xiangrui Wei. 2025. "Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Modified Ultrafine ABC Powder on CH4/Coal Dust Coexistence Explosions" Processes 13, no. 3: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030858
APA StyleGuo, Y., Deng, P., Zhang, B., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., & Wei, X. (2025). Study on the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Modified Ultrafine ABC Powder on CH4/Coal Dust Coexistence Explosions. Processes, 13(3), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030858






