Carotenoid Degradation in Annatto Dye Wastewater Using an O3/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Carotenoids and Their Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
1.2. Application of O3 and H2O2 to Remediation Processes
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Wastewater
2.2. Experimental Setup and O3/H2O2 Process
2.3. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
2.4. Carotenoid Quantification
2.5. Performance Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Carotenoid Degradation
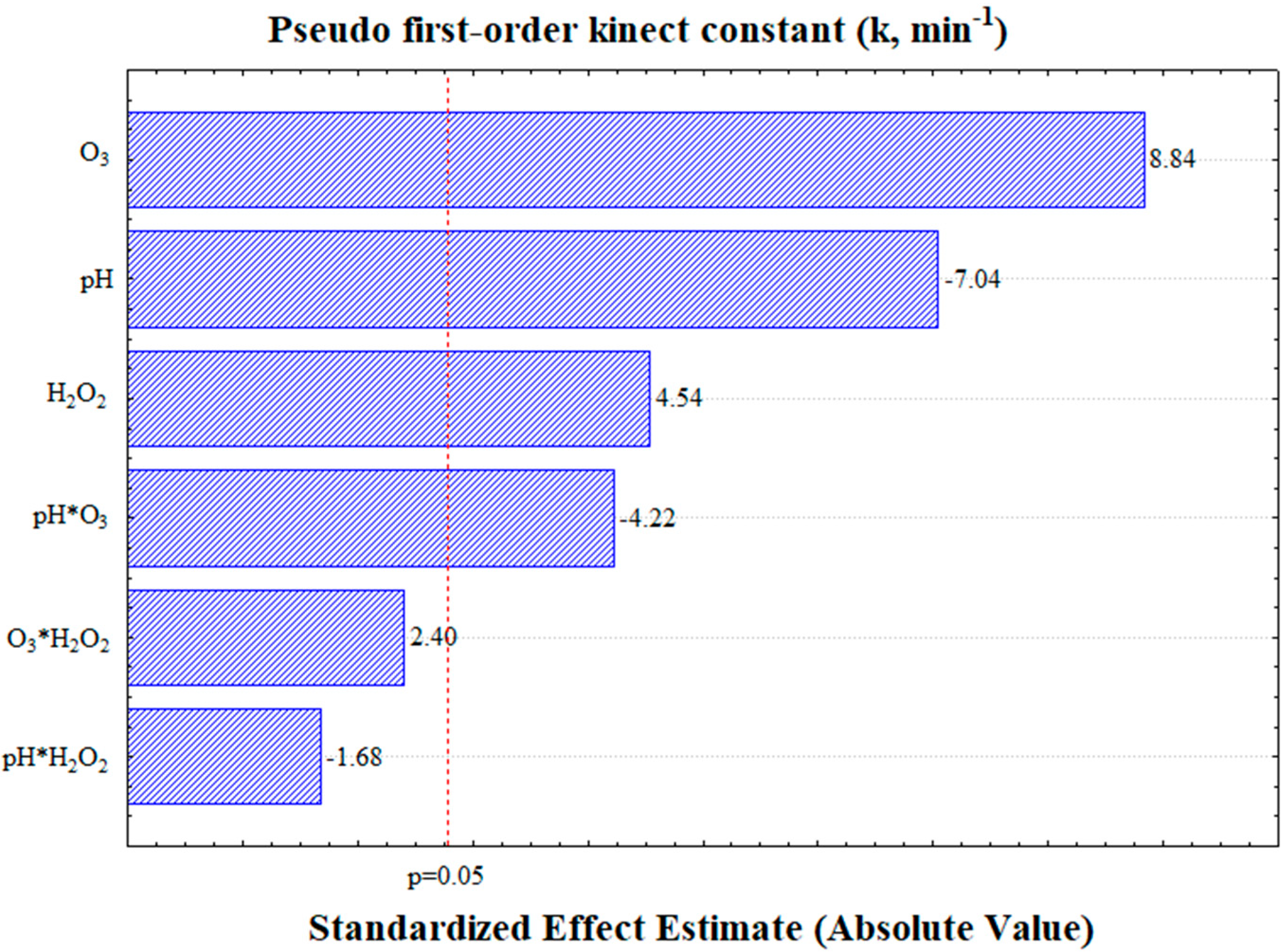
3.2. Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Constant (k)


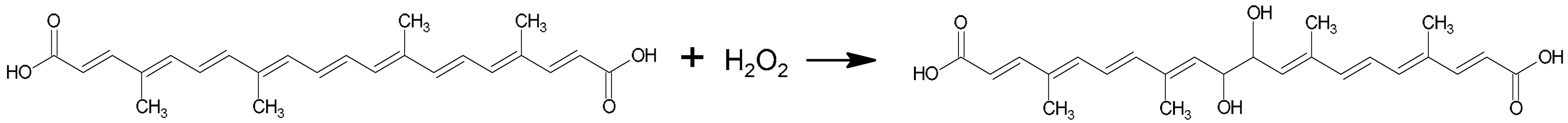
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Car | Carotenoids |
| Neutral carotenoid radical | |
| Acyl carotenoid radical | |
| Carotenoid radical cation | |
| E0 | Oxidation potential |
| pKa | Antilogarithm of the acid dissociation constant |
| k | Pseudo-first-order kinetic constant |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| C/C0 | Carotenoid normalized concentration |
| SHE | Standard hydrogen electrode |
| UV | Ultraviolet electromagnetic radiation (wavelengths shorter than 400 nm) |
| Vis | Visible electromagnetic radiation (~400 nm to ~700 nm) |
| ITO | Tin oxide electrode |
References
- Polyakov, N.E.; Leshina, T.V. Certain aspects of the reactivity of carotenoids. Redox processes and complexation. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2006, 75, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Hassan, A.; Kumar, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. The role of cobalt-based catalysts in activating peracetic acid for environmental pollutants degradation: A mini review. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shinopoulos, K.E.; Tracewell, C.A.; Focsan, A.L.; Brudvig, G.W.; Kispert, L.D. Formation of Carotenoid Neutral Radicals in Photosystem II. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 9901–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kispert, L.D.; Konovalova, T.; Gao, Y. Carotenoid radical cations and dications: EPR, optical, and electrochemical studies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 430, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konovalova, T. EPR spin trapping detection of carbon-centered carotenoid and Î2-ionone radicals. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pituco, M.M.; Marrocos, P.H.; Méndez, S.; Montes, R.; Rodil, R.; Moreira, F.C.; Vilar, V.J.P. Ozone injection system based on NETmix technology for quaternary treatment of urban wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R. A review on the catalytic ozonation of pollutants in wastewater by heteroelements-doped biochar: Internal and external doping strategies. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 119, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, U.; Spahr, S.; Lutze, H.; Wieland, A.; Rüting, S.; Gernjak, W.; Wenk, J. Advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—Guidance for systematic future research. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. Hydrogen Peroxide. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Hydrogen-Peroxide (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.S.; De Castro Peixoto, A.L. Amoxicillin Degradation by Reactive Oxygen Species on H2O2-Alone Process. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 41, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Kang, S.; Pan, Z.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Sheng, X.; Li, B.; Lu, W.; Wang, L.; Nie, M. Mo-based MXenes as highly selective two-electron oxygen reduction catalysts for H2O2 production. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 491, 144356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaccia, P.; Lipocelli, L.; Moschetti, G.; Francesca, N.; De Martino, S.; Arrigo, V.; Gaglio, R.; Settanni, L. Application of Hydrogen Peroxide to Improve the Microbiological Stability of Food Ice Produced in Industrial Facilities. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomičić, R.; Tomičić, Z.; Nićetin, M.; Knežević, V.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Raspor, P. Food grade disinfectants based on hydrogen peroxide/peracetic acid and sodium hypochlorite interfere with the adhesion of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel of differing surface roughness. Biofouling 2023, 39, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.A.D.O.; Peruchi, V.; Fernandes, L.D.O.; Anselmi, C.; Soares, I.P.M.; Hebling, J.; Costa, C.A.D.S. the influence of violet LED application time on the esthetic efficacy and cytotoxicity of a 35% H2O2 bleaching gel. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 40, 103069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.C.; Cherian, P.A.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Safety Assessment of Hydrogen Peroxide as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2024, 43, 5S–63S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.N. A Vertical Empire: The History of the UK Rocket and Space Programme, 1950–1971; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, W.; Lee, M.; Son, H.; Lee, C.; Cho, M.; Lee, Y. Efficiency of ozonation and O3/H2O2 as enhanced wastewater treatment processes for micropollutant abatement and disinfection with minimized byproduct formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Bai, C.-W.; Huang, X.-T.; Sun, Y.-J.; Chen, X.-J. Ozone meets peroxides: A symphony of hybrid techniques in wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, B.F.; Salazar, R.F.S.; Esperança, M.N.; De Castro Peixoto, A.L. Adsorption of Carotenoids, Chloride, and Sulfate from Annatto Dye Agro-Industrial Effluent. Glob. NEST J. 2024, 26, 06047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, J.F.; Gielen, J.W. Properties of Bixin and Norbixinand the Composition of Annatto Extracts. J. Food Sci. 1971, 36, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunjević, V.; Musa, M.M.; Zurak, D.; Svečnjak, Z.; Duvnjak, M.; Grbeša, D.; Kljak, K. Carotenoid degradation rate in milled grain of dent maize hybrids and its relationship with the grain physicochemical properties. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Skibsted, L.H.; Sampson, J.; Rice-Evans, C.; Everett, S.A. Comparative mechanisms and rates of free radical scavenging by carotenoid antioxidants. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semitsoglou-Tsiapou, S.; Meador, T.B.; Peng, B.; Aluwihare, L. Photochemical (UV–vis/H2O2) degradation of carotenoids: Kinetics and molecular end products. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, D.; Song, J.; Liu, C.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Q. Thermal degradation kinetics of all-trans and cis-carotenoids in a light-induced model system. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay-Agbozo, S.; Street, S.; Kispert, L. The carotenoid Bixin found to exhibit the highest measured carotenoid oxidation potential to date consistent with its practical protective use in cosmetics, drugs and food. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 186, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.; Edge, R.; Land, E.J.; McGarvey, D.J.; Truscott, T.G. One-electron reduction potentials of dietary carotenoid radical cations in aqueous micellar environments. FEBS Lett. 2001, 500, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čižmek, L.; Komorsky-Lovrić, Š. Study of Electrochemical Behaviour of Carotenoids in Aqueous Media. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontinele, L.P.; De Sousa, R.C.; Viana, V.G.F.; Farias, E.A.D.O.; Queiroz, E.L.; Eiras, C. Norbixin extracted from urucum (Bixa orellana L.) for the formation of conductive composites with potential applications in electrochemical sensors. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 13, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdeano, M.C.; Wilhelm, A.E.; Goulart, I.B.; Tonon, R.V.; Freitas-Silva, O.; Germani, R.; Chávez, D.W.H. Effect of water temperature and pH on the concentration and time of ozone saturation. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2018, 21, e2017156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardoni, D.; Vailati, A.; Canziani, R. Decay of Ozone in Water: A Review. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2012, 34, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, T.; Plagens, A. Named Organic Reactions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Benevides, C.M.D.J.; Veloso, M.C.D.C.; De Paula Pereira, P.A.; Andrade, J.B.D. A chemical study of β-carotene oxidation by ozone in an organic model system and the identification of the resulting products. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, K.L.; Puspitasari-Nienaber, N.L.; Jarén-Galán, M.; Van Breemen, R.B.; Catignani, G.L.; Schwartz, S.J. Effects of Ozone and Oxygen on the Degradation of Carotenoids in an Aqueous Model System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5008–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Variable | Code | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| pH | x1 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 5.5 |
| O3 (mg min−1) | x2 | 8.0 | 12.0 | 18.0 |
| H2O2 (g L−1) | x3 | 1.572 | 3.144 | 4.716 |
| Assay | pH | O3 | H2O2 | Carotenoid Degradation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 87.4 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 84.0 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 96.6 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 90.4 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 92.2 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 86.0 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 97.4 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 94.5 |
| 9 (C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 94.8 |
| 10 (C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 95.6 |
| 11 (C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 95.8 |
| Assay | pH | O3 | H2O2 | k (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 0.0354 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 0.0310 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 0.0586 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 0.0379 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0.0426 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 0.0338 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0805 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0485 |
| 9 (C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0492 |
| 10 (C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0513 |
| 11 (C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0497 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, P.C.; Esperança, M.N.; Turquetti, J.R.; de Castro Peixoto, A.L. Carotenoid Degradation in Annatto Dye Wastewater Using an O3/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Process. Processes 2025, 13, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030824
Garcia PC, Esperança MN, Turquetti JR, de Castro Peixoto AL. Carotenoid Degradation in Annatto Dye Wastewater Using an O3/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Process. Processes. 2025; 13(3):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030824
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Priscila Carriel, Mateus Nordi Esperança, José Ricardo Turquetti, and André Luís de Castro Peixoto. 2025. "Carotenoid Degradation in Annatto Dye Wastewater Using an O3/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Process" Processes 13, no. 3: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030824
APA StyleGarcia, P. C., Esperança, M. N., Turquetti, J. R., & de Castro Peixoto, A. L. (2025). Carotenoid Degradation in Annatto Dye Wastewater Using an O3/H2O2 Advanced Oxidation Process. Processes, 13(3), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030824







