Abstract
Urucum, also known as annatto, is a plant native to Brazil. However, there is a notable scarcity of scientific studies focusing on the wastewater generated by the annatto natural dye industry. This study seeks to address the existing knowledge gaps by presenting original and substantive data pertaining to this economic sector. This study investigates the degradation of carotenoids in real annatto dye wastewater through the application of an O3/H2O2 oxidation process. A 23 factorial experimental design was utilized to determine the influence of three key variables—pH (2.5–5.5), O3 mass flow rate (8.0–18.0 mg min−1), and initial H2O2 concentration (between 1.572 and 4.716 g L−1)—on both the degradation efficiency and the associated reaction kinetics. The process demonstrated impressive carotenoid removal, achieving degradation efficiencies between 84% and 97% with pseudo-first-order kinetic constants ranging from 0.0310 to 0.0805 min−1. A statistical analysis revealed that the O3 mass flow rate was the most influential factor on the degradation efficiency, while all the operational parameters played significant roles in determining the degradation kinetics. Notably, the process achieved optimal performance without the need for pH adjustment, presenting a cost-efficient solution for industrial applications. These findings offer critical insights into the treatment of high-strength agro-industrial wastewater, thereby advancing the development and implementation of oxidation processes for wastewater management.
1. Introduction
1.1. Carotenoids and Their Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
Carotenoids encompass a diverse group of terpenes known for their vibrant colors. These molecules typically consist of elongated polyene chains made up of isoprene units, which may conclude in either a cyclohexene (ionone) ring or isoprene residues at one or both ends. Most naturally occurring carotenoid pigments are classified as tetraterpenes, characterized by their 40 carbon atoms (C40) structure. In plants, C40 carotenoids are generally divided into two main groups: carotenes, which are purely hydrocarbons, such as β-carotene, its isomers, and lycopene; and xanthophylls, which contain oxygen and feature notable compounds like lutein, zeaxanthin, canthaxanthin, and violaxanthin. Furthermore, carotenoids can have less than 40 carbon atoms (e.g., or- and apocarotenoids) or more (e.g., homocarotenoids) [1].
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as peroxide, superoxide, and hydroxyl radicals, play a crucial role in the degradation of organic matter in both natural and industrial wastewater [2]. Carotenoid degradation occurs through three principal mechanisms when interacting with peroxide radicals [1,3]: (1) the addition of a free radical to a double bond within a carotenoid molecule, (2) the removal of a hydrogen atom from the allylic fragment of a carotenoid, and (3) the transfer of an electron from a carotenoid to a peroxide radical, resulting in the generation of a carotenoid radical cation.
These reactions emphasize the dynamic interactions between carotenoids and reactive oxygen species (ROS) across diverse environmental conditions [4].
The pro-oxidant activity of carotenoids is predominantly attributed to neutral radicals (), acyl radicals (), and radical cations (). These species are generated through the processes described in reactions (1)–(3) [1,4]. The mechanism underlying this pro-oxidant effect involves the interactions between these neutral carotenoid radicals and oxygen molecules [5], leading to the formation of the corresponding peroxide radicals, as detailed in reactions (4) and (5).
Neutral carotenoid radicals may also form through the protonation or deprotonation [3] of the corresponding radical ions. Typically, the generation of neutral radicals occurs during the chemical or electrochemical oxidation of carotenoids into radical cations, followed by the deprotonation of these cations [reaction (6)]. Alternatively, neutral radicals can arise via the protonation of radical anions [reaction (7)] [1,4]. These processes underscore the dynamic transformations that carotenoids undergo through their interactions with diverse chemical agents.
1.2. Application of O3 and H2O2 to Remediation Processes
Ozone (O3), known for its potent oxidative properties and environmental compatibility, possesses an oxidation potential of 2.07 V [6], rendering it a valuable agent in water purification and various industrial treatments. However, its broader application is hindered by challenges, such as its limited chemical selectivity towards pollutants, insufficient removal of total organic carbon (TOC), and the generation of by-products [7]. The combination of O3 with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) has been demonstrated as an effective approach to overcome these limitations [8].
Ozone interacts with pollutants through two principal mechanisms [7]: direct oxidation by O3 molecules and indirect oxidation mediated by hydroxyl radicals (•OH). In the direct oxidation process, O3 exhibits high reactivity with electron-rich pollutants, such as carotenoids, but is less effective against electron-deficient compounds. In contrast, indirect oxidation encompasses a broader range of pollutant reactivity due to the strong oxidative potential of •OH (2.8 V).
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its expanding range of applications. This versatile molecule H2O2 appears colorless at low concentrations and exhibits a pale blue hue at high concentrations. While it possesses a higher density and lower vapor pressure at room temperature, H2O2 is fully miscible with water and shares many of water’s physical properties [9]. Additionally, H2O2 is classified as a weak acid (Equation (8)) and is characterized by its high oxidation potential (E0 = 1.77 V). Its standard electrode potential (E0) increases with decreasing pH, ranging from 0.87 V at pH 14 to 1.80 V at pH 0 [10]. Although H2O2 alone does not independently generate hydroxyl radicals (•OH) (Equations (1)–(4)), it can initiate chain reactions that produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). The detailed mechanisms of these reactions and their pathways are elaborated elsewhere [11]. Hydrogen peroxide has diverse applications, including its widespread use in medicinal treatments [12], food processing [13], disinfection [14], bleaching [15], and cosmetics [16]. Additionally, it serves as a propellant in gas generators and has applications in the textile and energy industries. In recent years, H2O2 has gained increasing significance in environmental remediation, particularly in advanced oxidation processes and fuel cell technologies [17].
An O3/H2O2 (peroxone) advanced oxidation process entails the addition of an appropriate amount of H2O2 to the conventional O3 oxidation process. This combination facilitates the generation of hydroxyl radicals (•OH) [18], which effectively degrade organic compounds. The peroxone process exhibits significant contaminant degradation under neutral and slightly alkaline conditions [19]. In the present study, as the process was developed in an acidic medium, no synergistic interaction between the oxidants, O3 and H2O2, was anticipated. Instead, their actions were expected to occur independently. An acidic medium was selected due to the inherent acidic nature of the wastewater produced by the industry.
This study examined the degradation of the total carotenoids present in real and complex industrial wastewater, utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and ozone (O3) as the oxidizing agents. To the best of our knowledge, no scientific studies have specifically addressed the application of O3 and H2O2 to aqueous wastewater treatment in the annatto industry. There is a notable lack of data regarding wastewaters derived from the annatto industry (urucum or annatto, a plant native to Brazil). The originality of this study lies in addressing this gap by employing oxidants that are both easy to control and operate. The key operational parameters, such as the pH, ozone (O3) dosage, and the initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), were optimized using a structured Design of Experiments (DoE) approach. In this study, we conducted a systematic analysis of the degradation efficiency and kinetics of the O3/H2O2 process. This work represents a groundbreaking investigation into the feasibility of using H2O2 and O3 for the treatment of real annatto dye wastewater, characterized by its high pollution potential.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Wastewater
The wastewater used in this study was provided by an annatto dye company in Americana, São Paulo, Brazil. During the industrial process, potassium hydroxide (KOH 3% m/v) is utilized to extract pigments, while sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is employed to precipitate them. The wastewater sample was collected at the conclusion of the natural dye production process and refrigerated at 3 °C. To more effectively preserve its physicochemical properties, the sample was stored in a dark environment and maintained under refrigeration.
The raw wastewater comprised a saline aqueous phase containing carotenoids, such as norbixinate, along with a solid phase in suspension, composed of liposoluble carotenoids known as bixin. The initial concentration of carotenoids was determined to be 0.0838 ± 0.0053 mol L−1, and the original pH of the raw wastewater was measured at 1.9. Furthermore, the untreated wastewater contained various compounds formed by metal ions, including cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), barium (Ba), chromium (Cr), and copper (Cu), in association with anions, such as chloride and sulfate. The detailed composition of these compounds was previously described by Rosa et al. [20].
For the ozonation assays, the raw wastewater was prepared by adding four drops of an antifoaming agent. This antifoam solution was created by performing a tenfold dilution of a 30% simethicone emulsion (Dow Corning, São Paulo, SP, Brazil).
2.2. Experimental Setup and O3/H2O2 Process
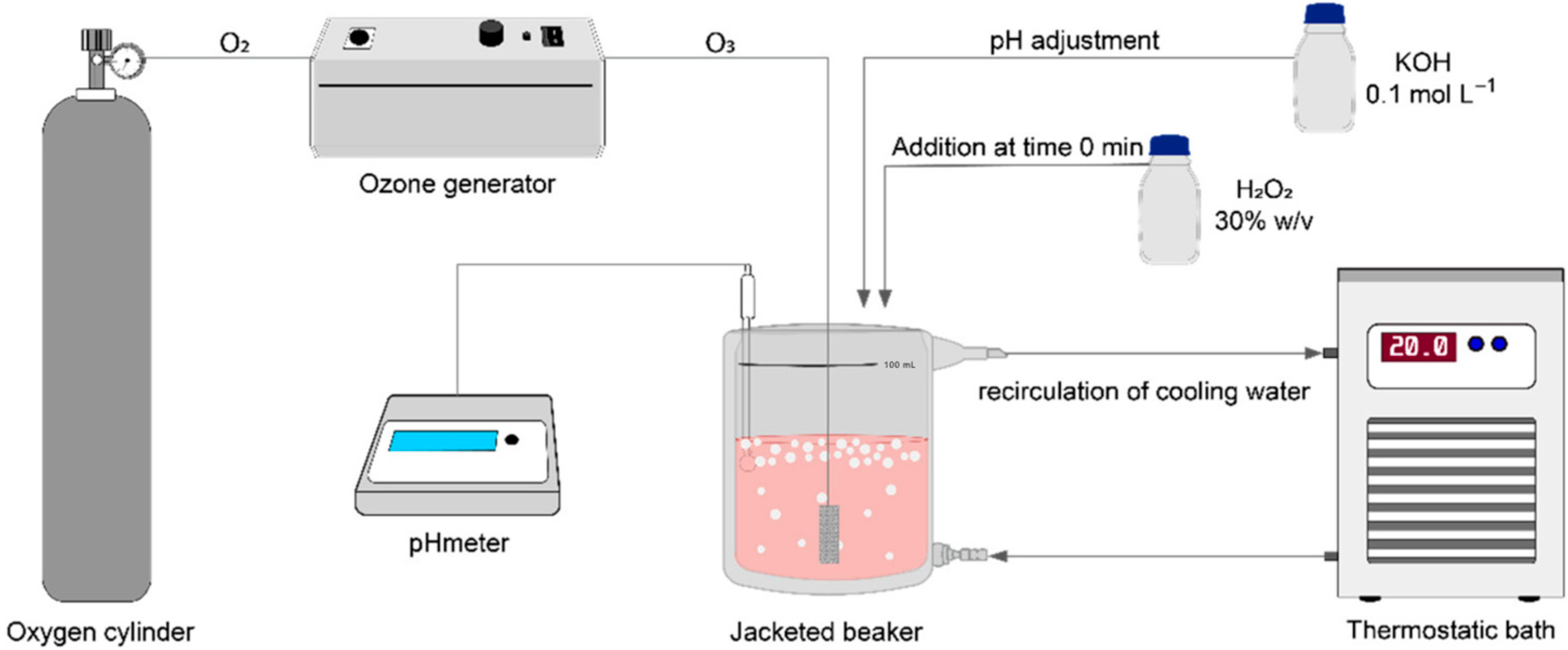
Carotenoid degradation was conducted using a semi-batch process. In all experiments, 50 mL of raw wastewater was transferred into a 100 mL jacketed beaker, with a predefined initial concentration of H2O2 as outlined in Table 1. Ozone bubbles were then continuously sparged at a flow rate of 1.0 L min−1 through a sintered glass diffuser (15 mm × 20 mm) for a duration of 60 min (Figure 1). The ozone (O3) was generated ex situ via the corona effect, using equipment provided by Ozone & Life (model O&L 3.0 RM, São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil). Oxygen (O2) with a purity of >99% (supplied by White Martins, Jundiaí, SP, Brazil) was used to feed the ozone generator.

Table 1.
Coded and real values of independent variables.
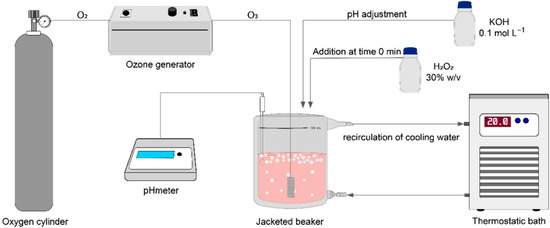
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the apparatus for carotenoid degradation.
The pH and temperature were monitored using Tecnal equipment (R-TEC-7/2-MP, Piracicaba, SP, Brazil). Temperature control was achieved through the use of a Solab thermostatic bath (SL-152/18, Piracicaba, SP, Brazil). The pH of the experiments (Table 1) was adjusted using a 1 mol L−1 KOH solution, and the temperature was consistently maintained at 20 °C.
Samples were periodically collected to evaluate the total carotenoid concentrations and to analyze the kinetics of their degradation.
2.3. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
A 23 factorial design was employed to evaluate the effects of pH, ozone mass flow rate, and initial hydrogen peroxide concentration on carotenoid degradation and pseudo-first-order kinetic constant (k). The factorial design consisted of eleven assays, which included eight factorial points and three central points, conducted as randomized experiments. The coded and real values of the independent variables are summarized in Table 1.
In the annatto industry, natural dyes are precipitated by reducing the pH through the addition of sulfuric or hydrochloric acid. Consequently, the resulting wastewater displays a markedly low pH (pH < 2). In this study, ozone-based experiments were consistently conducted within this acidic pH range, as detailed in Table 1.
The experimental results were modeled using a first-order polynomial equation, as described in Equation (9). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted with a 95% confidence interval to identify significant and non-significant factors and to generate response surface plots. All statistical analyses were performed using Statsoft v. 7.0 software (Tulsa, OK, USA).
In Equation (9), y represents the response variable; β0 denotes the mean value of the predicted variable; β1, β2, and β3 correspond to the linear coefficients; and β12, β13, and β23 represent the coefficients of the interaction terms. The coded independent variables x1, x2, and x3 refer to pH, ozone mass flow rate, and initial hydrogen peroxide concentration, respectively. For each experimental condition, the mean value from three replicates was used.
2.4. Carotenoid Quantification
Carotenoid concentration was determined through spectrophotometric analysis, following the methodology outlined by Reith and Gielen [21]. This method involves diluting a sample in 0.5% KOH and obtaining readings using a double-beam UV–visible spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at a wavelength of 453 nm with an absorption coefficient of ε = 2850. Care was taken to ensure that the absorbance readings fell within the expected range of 0.3 to 0.7 units.
2.5. Performance Parameters
The treatment of annatto dye wastewater was assessed by evaluating two dependent variables: carotenoid degradation (%) and the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant (k).
Carotenoid degradation is defined as the percentage variation in the total carotenoid concentration, as represented in Equation (10).
where C0 and Ct represent the initial and final carotenoid concentrations, respectively.
The kinetics of carotenoid degradation were analyzed according to a pseudo-first-order model for carotenoid concentration, as described in Equation (11). A plot of ln(Ct/C0) versus time (t) was generated, and Equation (11) was fitted to the experimental data using nonlinear least-squares (LSQ) optimization with Origin 2020 software (OriginLab Co., Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
Carotenoids demonstrate considerable reactivity in food matrices [22], water, and model systems, primarily due to their unsaturated structures. This makes them susceptible to oxidation, isomerization, and degradation induced by various factors, including heat, light, oxygen, ozone, and catalytic agents.
The degradation rates of carotenoids vary significantly depending on the environmental factors, including the solvent, light exposure, presence of catalysts, temperature, pH, concentration of radical scavengers [23], dissolved oxygen levels, and the presence of other oxidants.
Our study aimed to quantify the efficiency parameters associated with carotenoid degradation in wastewater generated by the annatto dye industry, which is notably rich in carotenoids and their by-products. To this end, the reaction temperature and initial carotenoid concentration were kept constant through this study. For calculation purposes, the carotenoids were expressed as norbixin equivalents, following the standard methodology. However, a gap in the existing literature on carotenoid degradation in water underscores the significance of this study. Where applicable, our findings were compared with data available in the literature.
To the best of our knowledge, no prior study has investigated the treatment of annatto dye wastewater using a peroxone process. The efficiency of the carotenoid degradation was evaluated based on two key parameters: (i) the percentage reduction in the carotenoid concentration and (ii) the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant, which characterizes the degradation rate.
The dependent variable results, derived from the data in Table 2 and Table 3, were analyzed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) in the StatSoft (v. 7.0) statistical software package. This analysis was performed to identify the most significant independent variables affecting the O3/H2O2 process. Pareto charts were generated to highlight the independent variables influencing carotenoid degradation and the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant, with a confidence level of 95%.

Table 2.
Full 23 factorial experimental design. Independent variables include pH, ozone mass flow rate (mg min−1), and initial hydrogen peroxide concentration (mg L−1); each are represented by coded values. The response variable analyzed is carotenoid degradation (%). The central-point (C) experiment was conducted in triplicate for increased reliability.

Table 3.
Full 23 factorial experimental design. Independent variables are pH, ozone mass flow rate (mg min−1), and initial hydrogen peroxide concentration (mg L−1), each represented by coded values. Response variable is pseudo-first-order kinetic constant (k, min−1). The central-point (C) experiment was conducted in triplicate for accuracy and reliability.
3.1. Carotenoid Degradation
The interaction of ozone bubbles with H2O2 in the raw wastewater led to highly efficient carotenoid degradation, achieving rates between 84 and 97% (Table 2).
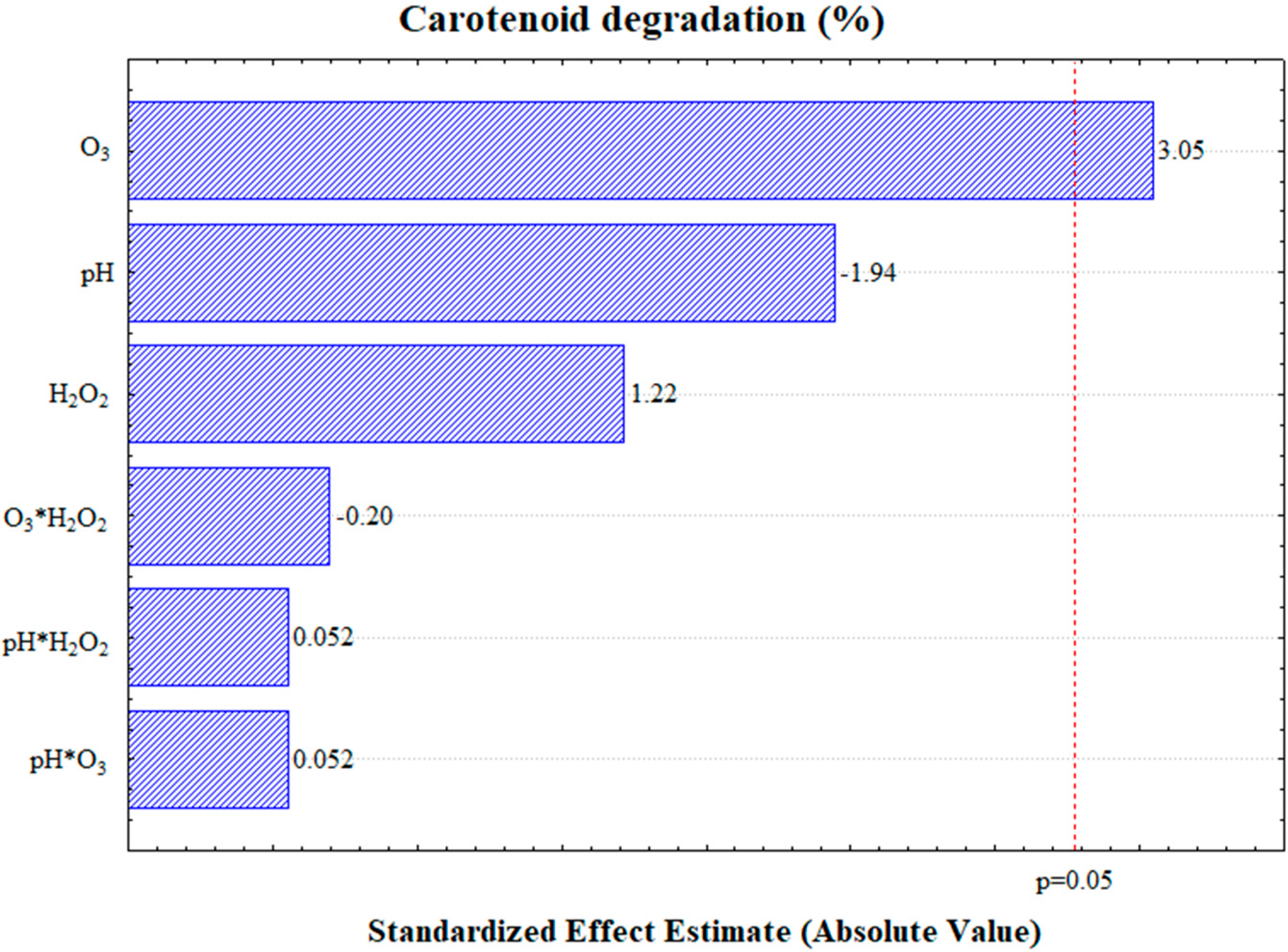
The degradation exhibited an error of 0.55%, as determined from the central point, which was conducted in triplicate (Table 2). The analysis of variance (Supplementary Materials) and the Pareto chart (Figure 2) revealed that only the ozone mass flow rate was statistically significant at a 95% confidence level, demonstrating a positive effect on carotenoid degradation. This indicates that an increase in the ozone supply enhances carotenoid degradation.
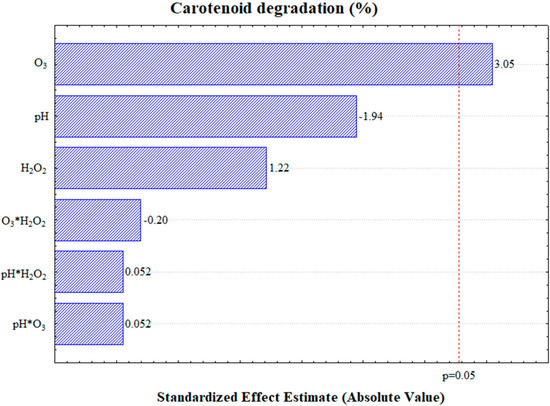
Figure 2.
Pareto chart depicting carotenoid degradation at a 95% confidence level.
The other independent variables, pH and hydrogen peroxide concentration, showed no significant influence on carotenoid degradation. Practically, this implies that neither pH adjustment nor the addition of H2O2 is required to achieve high levels of carotenoid degradation.
The independent variables, pH and H2O2, though relevant to carotenoid degradation (as discussed in Section 3.2), do not show a statistically significant difference between their low and high levels in relation to the response variable. The difference in E0 values between the H2O2 and carotenoids is expected to favor the oxidation of the organic molecule, resulting in the initial formation of more reactive chemical species derived from the carotenoids present in the studied matrix (Equations (1)–(7)).
The high solubility of H2O2 in water likely facilitates the interaction between the oxidant and the carotenoid molecules dispersed in the solvent. Conversely, the lower solubility of gaseous O3 in water may restrict its direct contact with the carotenoids, potentially reducing its oxidative efficiency.
The degradation products of carotenoids formed through H2O2 oxidation exhibit a higher number of groups within the hydrophobic region (central chain) compared to an undegraded carotenoid molecule. As a result, this modification reduces the hydrophobic nature of the chain while encouraging the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the solvent and the degradation products. Additionally, the constant motion of the solvent molecules, combined with the ongoing formation and disruption of hydrogen bonds, enhances the interaction between the oxidants and target molecules, thereby promoting subsequent chemical reactions.
To the best of our knowledge, no studies in the existing literature have provided a direct comparison to our results. However, a prior study examined the removal of the total carotenoids, sulfate, and chloride from the same effluent sample through adsorption. Additionally, most research on carotenoids has predominantly addressed applications within the food industry rather than water and wastewater treatment, making direct comparisons with our experimental data particularly challenging. In our previous study, Rosa et al. [20], we utilized adsorption to remove carotenoids from the same annatto dye wastewater. The study employed commercial activated carbon to evaluate carotenoid removal under varying conditions, including temperatures (20–40 °C), adsorbent masses (2–4 g), and pH levels (2.50–5.50). The results from 6 h assays demonstrated carotenoid removal efficiencies ranging from 60 to 90%. Thus, the O3/H2O2 process has been proven to be faster and more efficient than adsorption for carotenoid removal, requiring only one-sixth of the time to achieve a one-order-of-magnitude reduction in organic matter.
Semitsoglou-Tsiapou et al. [24] investigated the degradation of β-carotene, astaxanthin, fucoxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin in a solvent mixture of tetrahydrofuran (THF) and water (THF:H2O) under solar irradiation utilizing hydrogen peroxide (UV-Vis/H2O2). At a hydrogen peroxide concentration of 20 mg L−1, the authors reported carotenoid degradation efficiencies ranging from approximately 85% to 95%.
Xiao et al. [25] examined the thermal degradation kinetics of carotenoids (C0 up to 30 mg L−1) in a model system at temperatures of 25, 35, and 45 °C. The study investigated the degradation of lutein, zeaxanthin, β-cryptoxanthin, and β-carotene facilitated by iodine-catalyzed photoisomerization (1800 lx) under varying temperature conditions. The researchers identified 29 geometrical isomers and four oxidation products across the tested carotenoids. The degradation data conformed to a first-order kinetic model, demonstrating that higher temperatures and extended heating times significantly reduced the content of all-trans carotenoids. Specifically, after eight hours of heating, the degradation of all-trans lutein was observed to be 82.1% at 25 °C, 96.9% at 35 °C, and 97.3% at 45 °C. Additionally, the degradation levels were recorded as 48.1%, 77.5%, and 90.7%, respectively. In comparison, β-carotene exhibited more rapid degradation, with losses of 93.1%, 95.7%, and 97.6% occurring after just 2.5 h of heating at the same respective temperatures.
3.2. Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Constant (k)
The kinetics of carotenoid degradation were assessed using the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant, which varied between 0.0310 and 0.0805 min−1 (Table 3).
Significant variability in the kinetic constant (k) values was observed (Table 3), whereas the variability in the carotenoid degradation was relatively minor (Table 2). A comparison between the lowest and highest values of the dependent variables revealed that a 1.16-fold increase in carotenoid degradation was associated with a 2.6-fold increase in the kinetic constant. This finding underscores the greater sensitivity of the kinetic constant to variations in the independent variables.
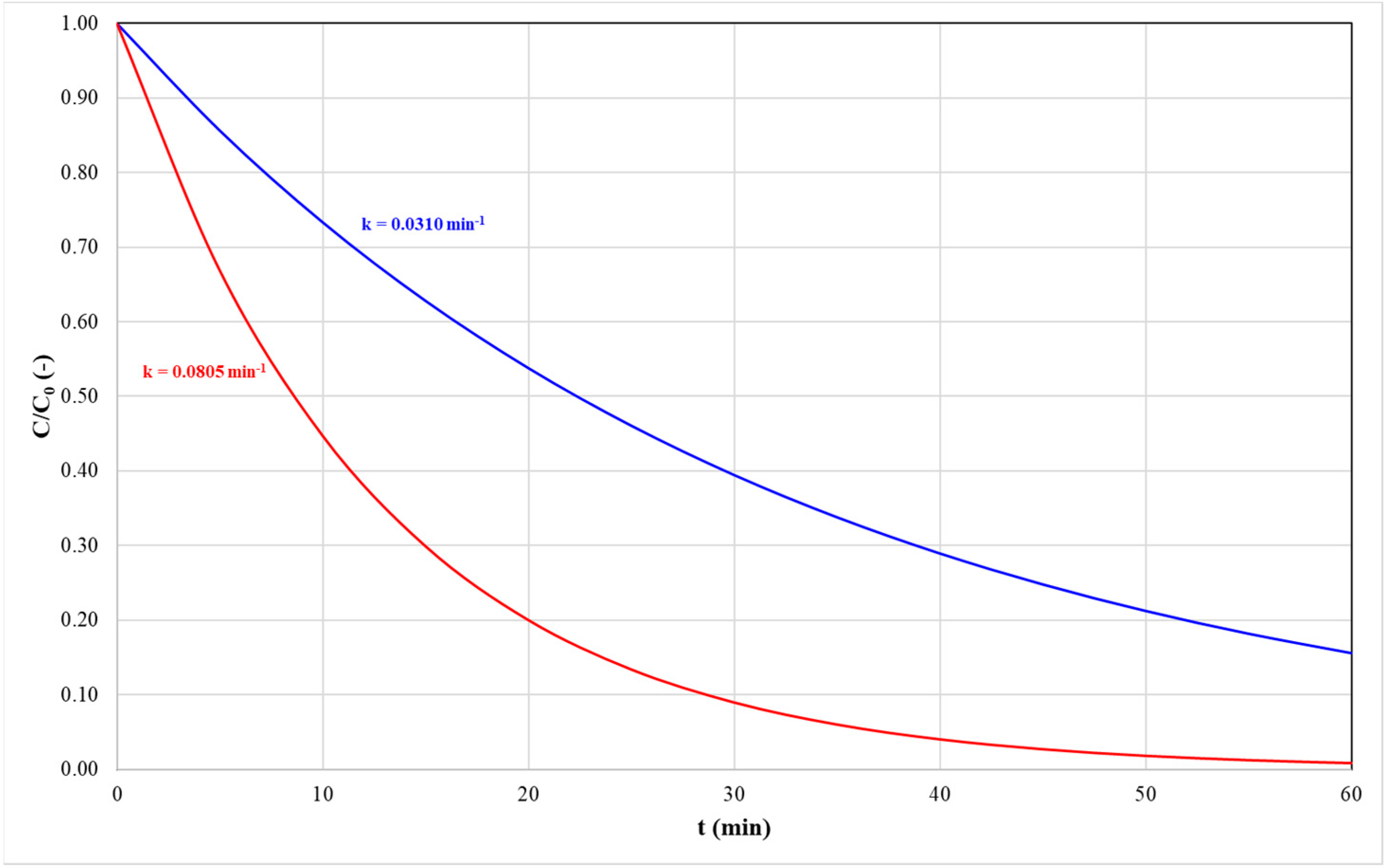
The lowest and highest values of the dependent variables were recorded under identical operating conditions. Specifically, assay 2 exhibited the minimum values for both the kinetic constant (k) and carotenoid degradation, measured at 0.0310 min−1 and 84.0%, respectively. In contrast, assay 7 presented the maximum values, with the k reaching 0.0805 min−1 and carotenoid degradation of 97.4%. This result suggests that the quantity of degradable carotenoids exhibited minimal variation, while the time required to achieve this condition differed markedly (Figure 3). For instance, the time required for a one-order-of-magnitude reduction in the total carotenoid concentration (C/C0) was 78.3 min for assay 2 compared to 28.6 min for assay 7.
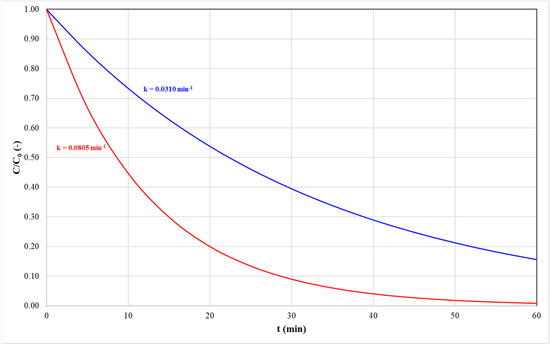
Figure 3.
Profiles of normalized carotenoid concentration over time illustrating two scenarios: slow degradation, represented by the red line, and fast degradation, represented by the blue line.
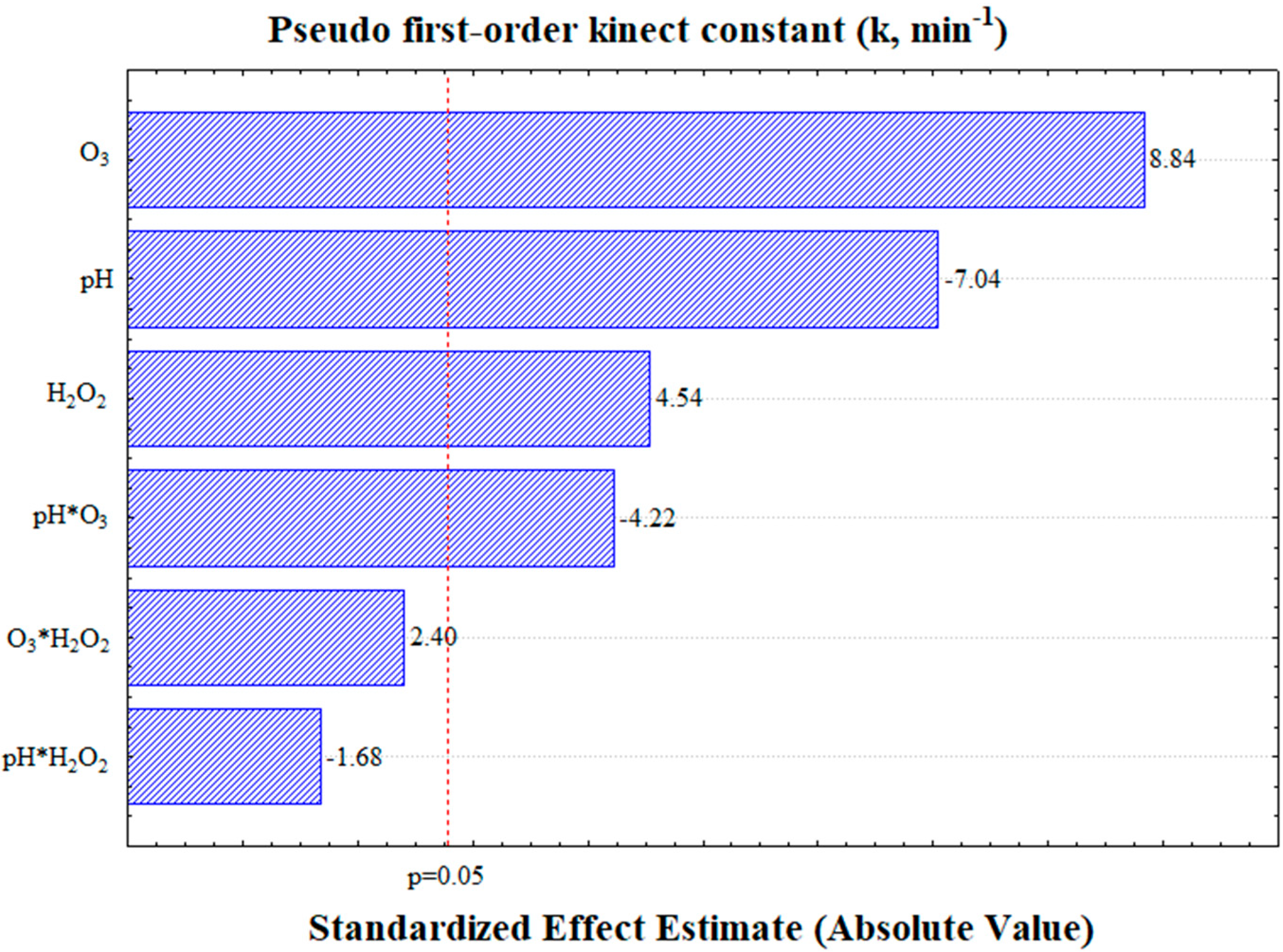
Based on the central point measured in triplicate, the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant exhibited an error margin of 2.2% (Table 3). The analysis of variance (Supplementary Materials) and Pareto chart (Figure 4) demonstrated that all the linear independent variables (pH, O3, and H2O2) were statistically significant at the 95% confidence level. In addition, among the interaction terms, only the interaction between the pH and ozone was found to influence the kinetic constant (k).
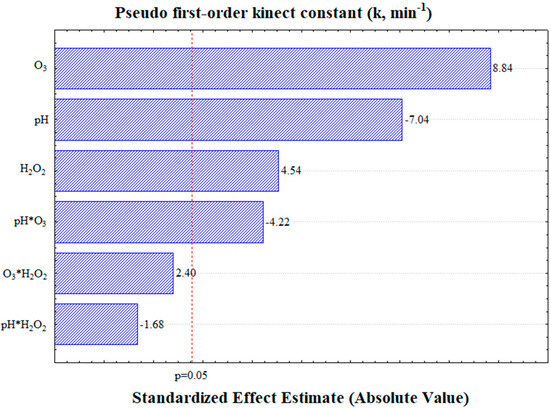
Figure 4.
Pareto chart illustrating the effects of the variables on the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant, evaluated at a 95% confidence level.
An analysis of the effects of the independent variables revealed a positive correlation for both ozone (O3) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). This indicates that an increase in the ozone supply and hydrogen peroxide content accelerates carotenoid degradation. However, the pH exhibited a negative impact on the k values, suggesting that faster carotenoid degradation occurs at lower pH levels. This implies that, under industrial conditions, adjusting the pH is not required to achieve accelerated carotenoid degradation.
According to the ANOVA results for the complete model (Supplementary Materials), the linear terms for the pH, O3, and H2O2, as well as the interaction between the pH and O3, were found to be statistically significant at the 95% confidence level. Subsequently, the non-significant terms were excluded from the model, and a revised ANOVA was conducted. These findings indicate that the proposed pseudo-first-order kinetic constant model (Equation (12)) effectively captures the relationship between the process parameters and the response variable.
where x1, x2, and x3 represent the coded factors of the pH, O3, and H2O2, respectively.
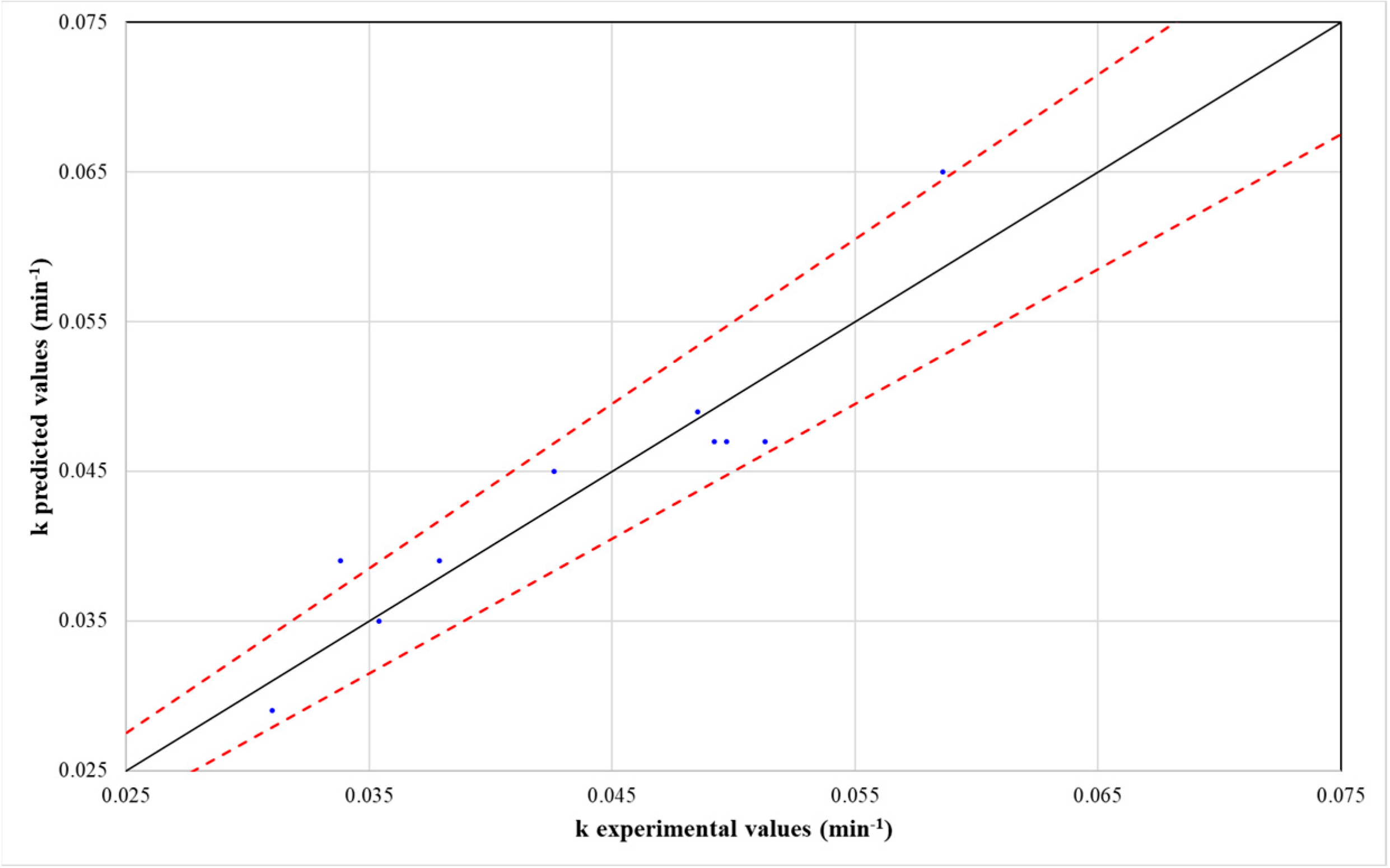
To assess the predictive accuracy of the model, a plot comparing the predicted and experimental k values was constructed (Figure 5). The analysis demonstrated that k, as estimated by Equation (12), exhibited an error of less than 10%. These findings, along with the corresponding R2 values, confirm the model’s suitability for predicting the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant with a high degree of reliability.
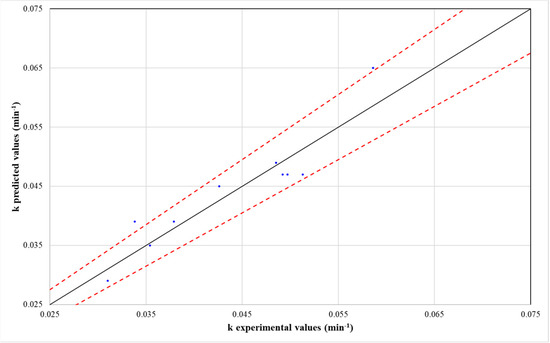
Figure 5.
Predicted versus experimental values of pseudo-first-order kinetic constant (k).
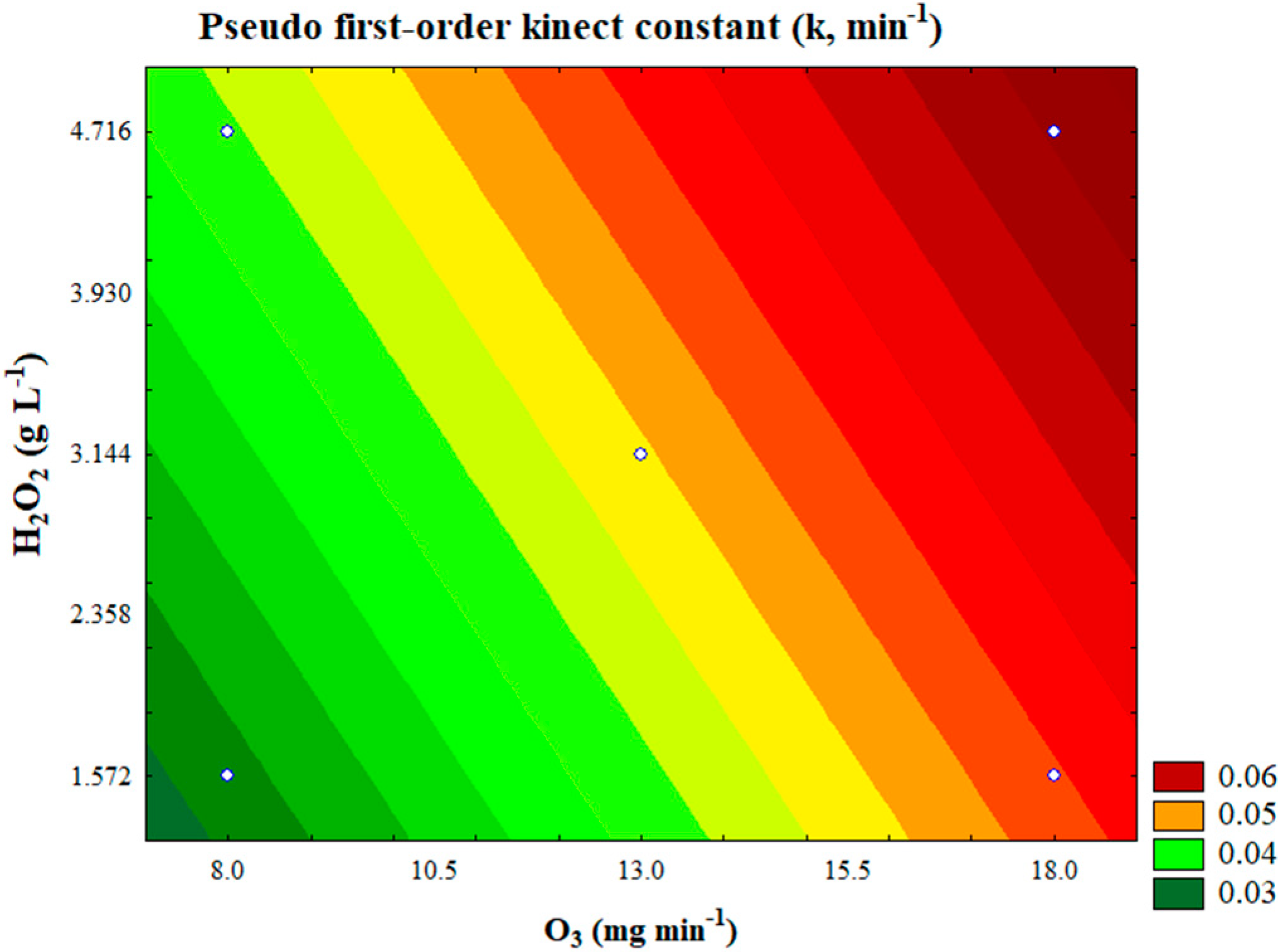
To illustrate the impact of the independent variables on the k, a contour plot was developed (Figure 6). Since the regression model for the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant incorporated all the parameters, the central value of the pH (coded value of 0) was chosen as the fixed point for generating the plot.
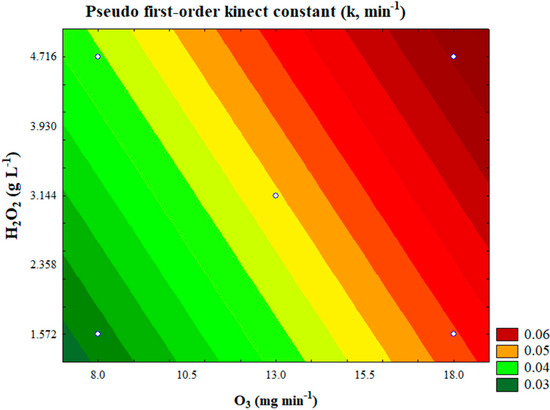
Figure 6.
Contour plot of pseudo-first-order kinetic constant (k) as a function of ozone mass flow rate (O3) and initial hydrogen peroxide concentration (H2O2) (pH = 4.0; x1 = 0).
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) plays a crucial role in environmental remediation, particularly within advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Its powerful oxidizing properties enable the degradation and mineralization of various contaminants. Under acidic conditions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) serves as an effective oxidant (as shown in Equation (13)). Moreover, acidic environments enhance the stability of H2O2 molecules and increase their oxidation potential to 1.78 V. These properties—combined with its full solubility in water, high stability in acidic media, and significant oxidative power—create optimal conditions for H2O2 to degrade carotenoids present in complex wastewater.
Tay-Agbozo et al. [26] reported that bixin, the primary carotenoid found in annatto, exhibited the highest measured oxidative potential among carotenoids. Remarkably, bixin accounts for approximately 80% of the carotenoid content in annatto seeds. Therefore, bixin and norbixin, along with their salts and by-products, constitute the primary carotenoid-based coloring components in wastewater. Their oxidation follows a two-electron process, with observed potentials of approximately 0.94 V and 1.14 V versus the saturated calomel electrode (SCE) in tetrahydrofuran (THF). The introduction of water into the system altered the electrochemical behavior of the carotenoids under investigation. This modification affected the coupled chemical reactions from higher to lower positive values. However, carotenoids exhibit distinctive behaviors in both organic and aqueous acidic media. Investigations into natural or controlled aqueous systems have been conducted in the following contexts: (a) aqueous micellar systems [27]; (b) solvent mixtures containing water [26]; and (c) water-based electrolytic media, utilizing immobilized carotenoid microparticles on graphite electrodes or films deposited on ITO electrodes [28,29]. Burke et al. [27] specifically examined the one-electron reduction potentials (E0) of dietary carotenoids within aqueous micellar environments. The investigation encompassed β-carotene, zeaxanthin, astaxanthin, canthaxanthin, and lycopene. Under equilibrium conditions, all five Car+/Car pairs exhibited similar E0 values, approximately 1.02 ± 0.04 V relative to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). These systems demonstrated lower E0 values compared to H2O2, rendering them susceptible to oxidation by it. Carotenoids, including β-carotene, lutein, and astaxanthin, have been investigated as films deposited on paraffin-impregnated graphite electrodes. In contrast, norbixin has been studied on ITO electrodes. Both studies employed Cyclic Voltammetry techniques [28,29]. The oxidation of these carotenoids is an irreversible process involving two electrons, protons, and solvent molecules in an aqueous acidic media. This process encompasses both electrochemical and coupled chemical reactions. Čižmek and Komorsky-Lovrić [28] proposed mechanisms for the oxidation, suggesting that it occurs through the formation of radicals, radical cations, or cations in the center of the chain by the oxidation of the central π bond. Following the initial oxidation step, chemically coupled reactions involving the oxidized species and water molecules were also proposed according to the electrochemical results. The observed similarities—namely, acidic aqueous media, molecular structure, and solid-state carotenoids—between these prior studies and our work support the proposal of oxidation half-reactions for norbixin and bixin, as outlined in Equations (14) and (15):


The intermediate species formed during the initial step is doubly allylic, a characteristic that thermodynamically stabilizes the radicals, radical cations, or cations. In the second oxidation step, the reaction between the radical or radical cation and the solvent results in the formation of a geminal diol. This process involves the transfer of an electron and a proton within the half-reaction.
The reduction half-reaction of H2O2 involves the transfer of two protons and two electrons. Simultaneously, the carotenoid norbixin undergoes oxidation through its reaction with H2O2:
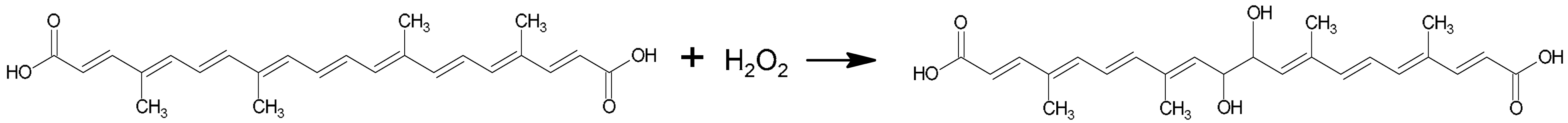
However, bixin and norbixin molecules are extensive unsaturated conjugated systems, within which oxidation can occur concurrently at multiple reactive sites throughout their structure.
Ozone (O3) is widely utilized as an oxidizing agent in the treatment process for both drinking water and wastewater. Its applications includes disinfection, color removal, and the oxidative degradation of trace organic pollutants and natural organic matter. The stability of ozone (O3) in water is primarily affected by factors, such as its concentration, pH, temperature, the presence of hydroxyl radicals (•OH), and various compounds—both inorganic and organic carbon—that may act as scavengers or promoters under specific conditions. In the context of reducing carotenoid levels, the statistical analysis revealed that only the O3 dosage parameter had a significant impact, as illustrated in Table 2 and Figure 2. Based on the degradation rate of the carotenoids (as presented in Table 3 and Figure 5), ozone (O3) was identified as the predominant influencing factor, followed by the pH and the initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The observed lack of synergy between the O3 and H2O2 indicates that the formation of hydroxyl radicals (•OH) was not favored under the operational conditions, likely due to (1) the low pH and (2) the high salinity levels present. Salts, such as chlorides, compete with radical species, influencing the formation of hydroxyl radicals (•OH). The generation of •OH requires the presence of the anion , which plays a crucial role as an initiator in the formation of radical species. As indicated by Equation (17), the formation of the anion is favored at higher pH levels, with an optimal range of pH 8–10.
In the acidic medium employed in the present study, the stability of the ozone (O3) molecules in an aqueous environment was enhanced. This enhanced stability favored the electrophilic addition mechanism of ozone to the unsaturated bonds of the carotenoid molecules, leading to the degradation of these unsaturated bonds. Furthermore, a reduction in the pH increases the saturation concentration of ozone (O3) in water. This phenomenon helps to elucidate the observed synergy between the pH levels and O3, as demonstrated in Figure 5 and described by Equation (12) [30]. It is noteworthy that anions, such as sulfate, chloride, and nitrate, exert minimal influence on the decay of ozone. Consequently, the presence of various dissolved salts in the wastewater had a negligible effect on the degradation of the carotenoids via ozonation, as highlighted in [31].
The observed degradation kinetics indicate that ozone (O3), due to its high reactivity, was more effective at oxidizing the carotenoids, resulting in a statistically significant percentage of carotenoid degradation. In contrast to ozone (O3), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) exhibited lower efficiency as an oxidizing agent, likely attributed to its relatively lower reactivity. This observation is consistent with thermodynamic principles, which suggest that reactions with greater differences in oxidation potential are generally more spontaneous and proceed at faster rates. The oxidative mechanism of O3 involves the cleavage of the double bonds () in the carotenoid structures through the Criegee mechanism [32]. This reaction generates smaller molecular fragments containing functional groups, such as aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. Aldehydes exhibit instability in aqueous acidic media and are likely converted into carboxylic acids. The observed reduction in the degradation rate can be attributed to the shorter molecular chains, which possess greater chemical stability (Figure 4).
Xiao et al. [25] conducted a study to analyze the kinetic and thermodynamic parameters associated with carotenoid degradation. Their analysis involved comparing the catalytic degradation data against zero-order, first-order, and second-order kinetic models. Overall, the findings indicated that the data aligned most closely with the first-order model. For example, at 25 °C, the degradation rates of carotenoids were observed in the following order: kβ-carotene (0.0187 min−1) > kβ-cryptoxanthin (0.0092 min−1) > klutein (0.0029 min−1) > kcis-zeaxanthin (0.0010 min−1). The activation energy required for carotenoid degradation was determined to be inversely proportional to their respective kinetic degradation constants. Notably, the activation energy values varied from 8.6324 kJ mol−1 for β-carotene to 65.5539 kJ mol−1 for zeaxanthin.
Semitsoglou-Tsiapou et al. [24] identified a connection between the accumulation of dissolved organic matter in the ocean and linear terpenoid structures. The authors propose that carotenoid degradation products could potentially act as precursors. Experiments were conducted on the degradation of β-carotene, astaxanthin, fucoxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin in a solvent mixture of tetrahydrofuran (THF) and water (THF:H2O) under solar light irradiation, facilitated by hydrogen peroxide (UV-Vis/H2O2). The degradation of all the carotenoids was influenced by both photolysis and •OH scavenging. Fucoxanthin showed the fastest degradation kinetics, with a rate constant of 0.2214 min−1, whereas meso-zeaxanthin showed the slowest degradation, with a rate constant of 0.0262 min−1. The carotenoid solution was subjected to irradiation under simulated sunlight, at an intensity of 100 mW cm−2. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was added to the solution at a concentration of 20 mg L−1, which was twice the concentration of the carotenoids. This adjustment was made to accelerate the degradation process while preventing the excessive scavenging of •OH by H2O2.
Benevides et al. [33] examined the degradation of β-carotene solutions using ozone (O3). The reaction was monitored over a period of seven hours, and the data were modeled using a zero-order kinetic approach. Despite the limited number of studies addressing carotenoid degradation in industrial effluents, most of the existing research emphasizes the degradation of carotenoids dissolved in organic solvents. Conversely, our study employed an aqueous effluent, wherein carotenoids were present both in suspension and dissolved forms. Benevides et al. [33] conducted experiments using an analytical standard of β-carotene dissolved in acetonitrile. In their study, a 25 mL β-carotene solution was placed within a glass impinger, shielded from light, and subjected to zone bubbling at a flow rate of 1 L min−1 for a duration of seven hours. Experiments were conducted at four different ozone concentrations (0.8, 1.1, 1.5, and 2.5 ppm). The reaction rate constants ranged from 0.8 to 6.3 ppm h−1, corresponding to initial ozone concentrations of 0.80 and 2.54 ppm, respectively. The degradation percentage of β-carotene degradation varied between 17.2% and 99.8%, contingent upon the ozone concentration, which spanned from 0.80 to 2.54 ppm.
Henry et al. [34] examined the effects of O3 and O2 on the degradation of carotenoids within an aqueous model system. O3 was produced by exposing a continuous flow of pure O2 at 200 mL/min to ultraviolet (UV) radiation at 185 nm. N2 was utilized as the control, representing a non-oxidative condition. Prior to each experiment, ultrafiltered water was saturated with O3, O2, or N2 at 30 °C for a duration of 12 h. The calculated concentrations of O3, O2, and N2 in the water at this temperature were 2.3 × 10−4 mol/L, 1.6 × 10−4 mol/L, and 7.3 × 10−4 mol/L, respectively. All the carotenoids degraded according to a zero-order kinetic model, with the degradation rates observed to be three times higher in the presence of O3 compared to O2. Specifically, for 9-cis-β-carotene, the reaction rate was determined to be 0.0025 ± 0.0003 h−1 in the presence of O3 and 0.0002 ± 0.0003 h−1 in the presence of O2.
4. Conclusions
This study evaluated the efficacy of the O3/H2O2 process for degrading carotenoids present in annatto dye wastewater. The findings demonstrated high degradation rates, ranging from 84% to 97%, with pseudo-first-order kinetic constants varying between 0.0310 and 0.0805 min−1. The statistical analysis identified the ozone mass flow rate as the principal factor influencing the degradation efficiency, whereas the pH and H2O2 concentration were found to significantly affect the reaction kinetics. Notably, the process demonstrated optimal performance without requiring a pH adjustment, as the natural acidic conditions of the wastewater (pH 1.9) enhanced ozone stability and facilitated direct oxidation. The lack of synergy between the O3 and H2O2 indicates that the degradation predominantly occurred through direct ozonation and direct H2O2 oxidation, rather than •OH formation. The lower pH improved the stability of the O3 and H2O2 molecules in the aqueous solution, thereby facilitating their direct interaction with the carotenoid molecules. These findings offer valuable insights into the industrial application of the O3/H2O2 process, highlighting its technical feasibility for treating complex wastewater streams with high organic loads. Future research should investigate hybrid processes that combine adsorption, biological degradation, and oxidation with O3 and H2O2 to enhance the removal efficiency while achieving shorter reaction times. Additionally, the integration of economic analyses should be prioritized in future studies addressing carotenoid degradation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information is available for download at www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13030824/s1, Section S1: Statistical analysis of O3/H2O2 process; Section S2: Before and after annatto dye wastewater treatment; Video S1: O3/H2O2 process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L.d.C.P.; methodology, P.C.G.; software, M.N.E.; validation, P.C.G., M.N.E. and A.L.d.C.P.; formal analysis, M.N.E., J.R.T. and A.L.d.C.P.; investigation, P.C.G.; resources, A.L.d.C.P.; data curation, P.C.G. and A.L.d.C.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N.E. and A.L.d.C.P.; writing—review and editing, M.N.E., J.R.T. and A.L.d.C.P.; visualization, P.C.G., M.N.E., J.R.T. and A.L.d.C.P.; supervision, A.L.d.C.P.; project administration, A.L.d.C.P.; funding acquisition, M.N.E. and A.L.d.C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received financial support from the Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of São Paulo (IFSP).
Data Availability Statement
The experimental data used in this study are provided in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to Paulo Roberto Nogueira Carvalho and the New Max industry for generously supplying the wastewater utilized in this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors affirm that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are utilized throughout this manuscript:
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Car | Carotenoids |
| Neutral carotenoid radical | |
| Acyl carotenoid radical | |
| Carotenoid radical cation | |
| E0 | Oxidation potential |
| pKa | Antilogarithm of the acid dissociation constant |
| k | Pseudo-first-order kinetic constant |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| C/C0 | Carotenoid normalized concentration |
| SHE | Standard hydrogen electrode |
| UV | Ultraviolet electromagnetic radiation (wavelengths shorter than 400 nm) |
| Vis | Visible electromagnetic radiation (~400 nm to ~700 nm) |
| ITO | Tin oxide electrode |
References
- Polyakov, N.E.; Leshina, T.V. Certain aspects of the reactivity of carotenoids. Redox processes and complexation. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2006, 75, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Hassan, A.; Kumar, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. The role of cobalt-based catalysts in activating peracetic acid for environmental pollutants degradation: A mini review. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shinopoulos, K.E.; Tracewell, C.A.; Focsan, A.L.; Brudvig, G.W.; Kispert, L.D. Formation of Carotenoid Neutral Radicals in Photosystem II. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 9901–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kispert, L.D.; Konovalova, T.; Gao, Y. Carotenoid radical cations and dications: EPR, optical, and electrochemical studies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 430, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konovalova, T. EPR spin trapping detection of carbon-centered carotenoid and Î2-ionone radicals. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pituco, M.M.; Marrocos, P.H.; Méndez, S.; Montes, R.; Rodil, R.; Moreira, F.C.; Vilar, V.J.P. Ozone injection system based on NETmix technology for quaternary treatment of urban wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R. A review on the catalytic ozonation of pollutants in wastewater by heteroelements-doped biochar: Internal and external doping strategies. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 119, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, U.; Spahr, S.; Lutze, H.; Wieland, A.; Rüting, S.; Gernjak, W.; Wenk, J. Advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—Guidance for systematic future research. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. Hydrogen Peroxide. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Hydrogen-Peroxide (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.S.; De Castro Peixoto, A.L. Amoxicillin Degradation by Reactive Oxygen Species on H2O2-Alone Process. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 41, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Kang, S.; Pan, Z.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Sheng, X.; Li, B.; Lu, W.; Wang, L.; Nie, M. Mo-based MXenes as highly selective two-electron oxygen reduction catalysts for H2O2 production. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 491, 144356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaccia, P.; Lipocelli, L.; Moschetti, G.; Francesca, N.; De Martino, S.; Arrigo, V.; Gaglio, R.; Settanni, L. Application of Hydrogen Peroxide to Improve the Microbiological Stability of Food Ice Produced in Industrial Facilities. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomičić, R.; Tomičić, Z.; Nićetin, M.; Knežević, V.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Raspor, P. Food grade disinfectants based on hydrogen peroxide/peracetic acid and sodium hypochlorite interfere with the adhesion of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel of differing surface roughness. Biofouling 2023, 39, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.A.D.O.; Peruchi, V.; Fernandes, L.D.O.; Anselmi, C.; Soares, I.P.M.; Hebling, J.; Costa, C.A.D.S. the influence of violet LED application time on the esthetic efficacy and cytotoxicity of a 35% H2O2 bleaching gel. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 40, 103069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.C.; Cherian, P.A.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Safety Assessment of Hydrogen Peroxide as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2024, 43, 5S–63S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.N. A Vertical Empire: The History of the UK Rocket and Space Programme, 1950–1971; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, W.; Lee, M.; Son, H.; Lee, C.; Cho, M.; Lee, Y. Efficiency of ozonation and O3/H2O2 as enhanced wastewater treatment processes for micropollutant abatement and disinfection with minimized byproduct formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Bai, C.-W.; Huang, X.-T.; Sun, Y.-J.; Chen, X.-J. Ozone meets peroxides: A symphony of hybrid techniques in wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, B.F.; Salazar, R.F.S.; Esperança, M.N.; De Castro Peixoto, A.L. Adsorption of Carotenoids, Chloride, and Sulfate from Annatto Dye Agro-Industrial Effluent. Glob. NEST J. 2024, 26, 06047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, J.F.; Gielen, J.W. Properties of Bixin and Norbixinand the Composition of Annatto Extracts. J. Food Sci. 1971, 36, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunjević, V.; Musa, M.M.; Zurak, D.; Svečnjak, Z.; Duvnjak, M.; Grbeša, D.; Kljak, K. Carotenoid degradation rate in milled grain of dent maize hybrids and its relationship with the grain physicochemical properties. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Skibsted, L.H.; Sampson, J.; Rice-Evans, C.; Everett, S.A. Comparative mechanisms and rates of free radical scavenging by carotenoid antioxidants. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semitsoglou-Tsiapou, S.; Meador, T.B.; Peng, B.; Aluwihare, L. Photochemical (UV–vis/H2O2) degradation of carotenoids: Kinetics and molecular end products. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, D.; Song, J.; Liu, C.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Q. Thermal degradation kinetics of all-trans and cis-carotenoids in a light-induced model system. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay-Agbozo, S.; Street, S.; Kispert, L. The carotenoid Bixin found to exhibit the highest measured carotenoid oxidation potential to date consistent with its practical protective use in cosmetics, drugs and food. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 186, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.; Edge, R.; Land, E.J.; McGarvey, D.J.; Truscott, T.G. One-electron reduction potentials of dietary carotenoid radical cations in aqueous micellar environments. FEBS Lett. 2001, 500, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čižmek, L.; Komorsky-Lovrić, Š. Study of Electrochemical Behaviour of Carotenoids in Aqueous Media. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontinele, L.P.; De Sousa, R.C.; Viana, V.G.F.; Farias, E.A.D.O.; Queiroz, E.L.; Eiras, C. Norbixin extracted from urucum (Bixa orellana L.) for the formation of conductive composites with potential applications in electrochemical sensors. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 13, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdeano, M.C.; Wilhelm, A.E.; Goulart, I.B.; Tonon, R.V.; Freitas-Silva, O.; Germani, R.; Chávez, D.W.H. Effect of water temperature and pH on the concentration and time of ozone saturation. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2018, 21, e2017156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardoni, D.; Vailati, A.; Canziani, R. Decay of Ozone in Water: A Review. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2012, 34, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, T.; Plagens, A. Named Organic Reactions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Benevides, C.M.D.J.; Veloso, M.C.D.C.; De Paula Pereira, P.A.; Andrade, J.B.D. A chemical study of β-carotene oxidation by ozone in an organic model system and the identification of the resulting products. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, K.L.; Puspitasari-Nienaber, N.L.; Jarén-Galán, M.; Van Breemen, R.B.; Catignani, G.L.; Schwartz, S.J. Effects of Ozone and Oxygen on the Degradation of Carotenoids in an Aqueous Model System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5008–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).