Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite-Modified Natural Zeolite: Application as Adsorbent for Ni2+ and Cr3+ Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Adsorbents
- Calcium chloride dihydrate, sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate dihydrate, ammonium hydrogen phosphate, and urea were added to 20 cm3 of distilled water (masses listed in Table 1). The molar ratio Ca/P in the reaction mixture was 1.67;
- The reaction suspension was homogenized using a magnetic stirrer at 400 rpm for 30 min at 25 °C;
- NZ (0.9 g) was added to the reaction mixture, followed by sonication (Sonopuls mini20, Bandelin, Berlin, Germany) for 6 min in 3 cycles to break the aggregates;
- The suspension was homogenized for an additional 30 min at 400 rpm before being placed in a stainless steel autoclave;
- Crystallization of calcium hydroxyapatite was carried out under hydrothermal conditions at 160 °C and autogenous pressure for 4 h;
- The resulting product was separated by vacuum filtration, washed with distilled water, and dried at 105 °C overnight.
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (0.3973 g) and ammonium hydrogen phosphate (0.2138 g) were added to 20 cm3 of distilled water;
- The pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 9 using 0.1 mol dm−3 NaOH solution;
- The mixture was homogenized at 400 rpm for 30 min before being placed in a stainless steel autoclave;
- Crystallization of calcium hydroxyapatite was carried out under hydrothermal conditions at 160 °C and autogenous pressure for 4 h;
- The resulting calcium hydroxyapatite crystals were sonicated for 6 min in 3 cycles to break the aggregates;
- At the end, calcium hydroxyapatite crystals were separated by vacuum filtration, washed with distilled water, and dried at 105 °C overnight.
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics Experiments
2.5. Adsorption Isotherms Experiments
2.6. Desorption Experiments
2.7. Characterization of the Adsorbents
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Analysis
3.2. Thermal Analysis
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
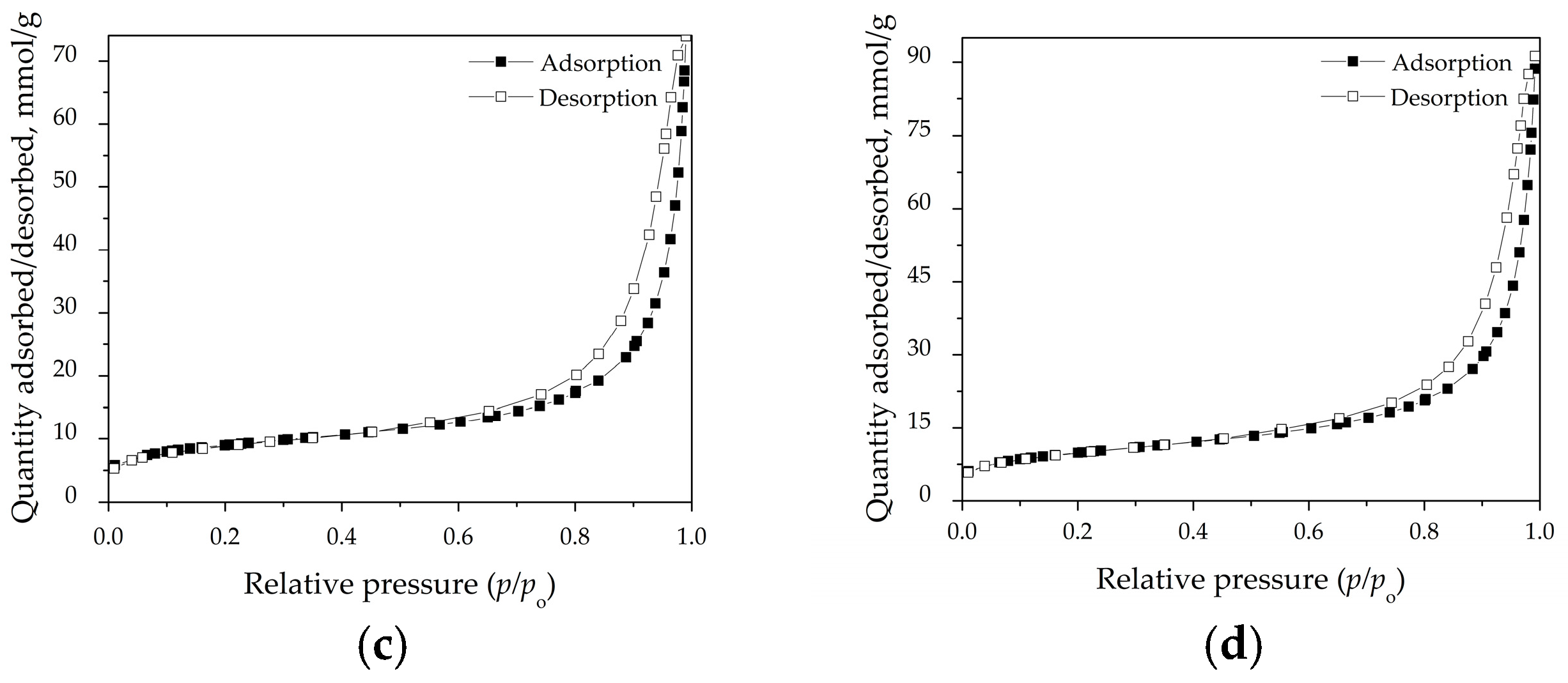
3.4. Specific Surface Area and Pore Distribution
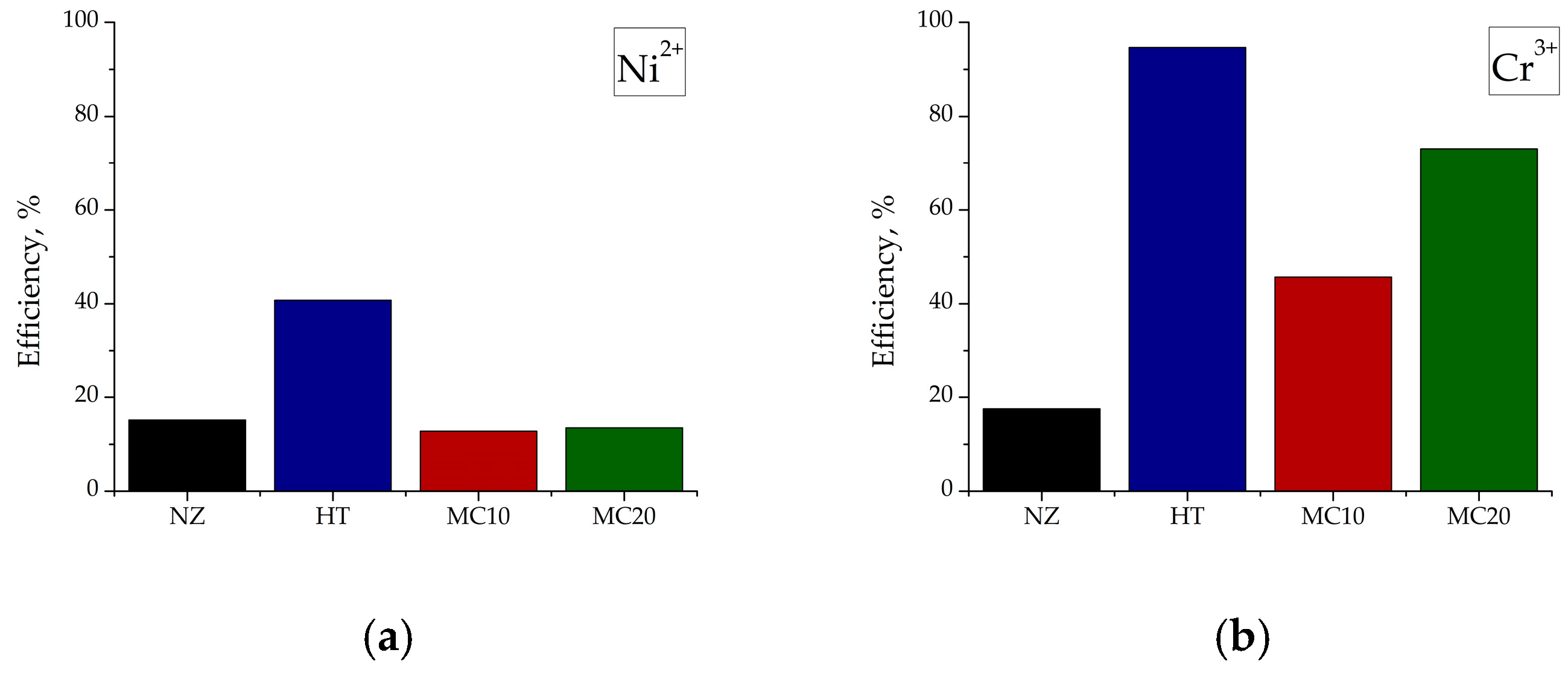
3.5. Adsorption Studies
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics
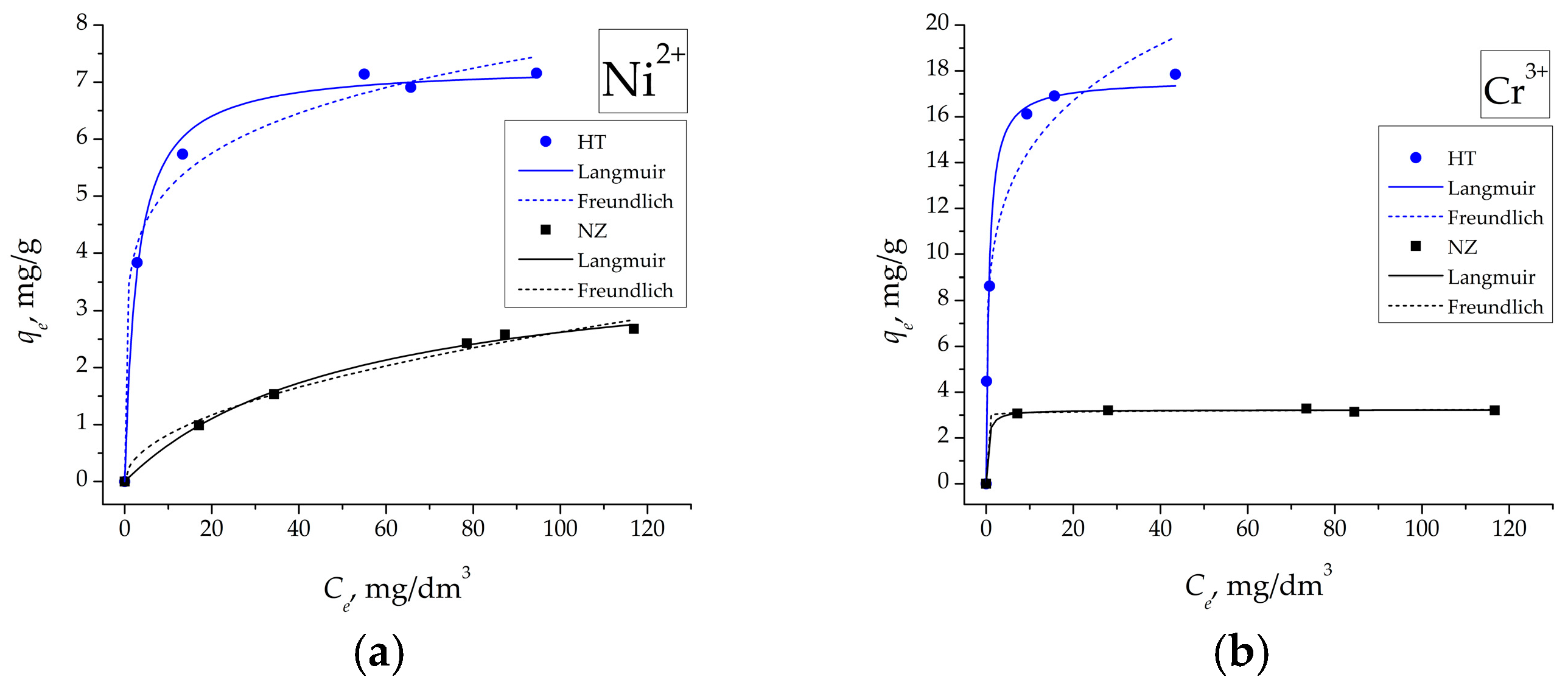
3.7. Adsorption Isotherms
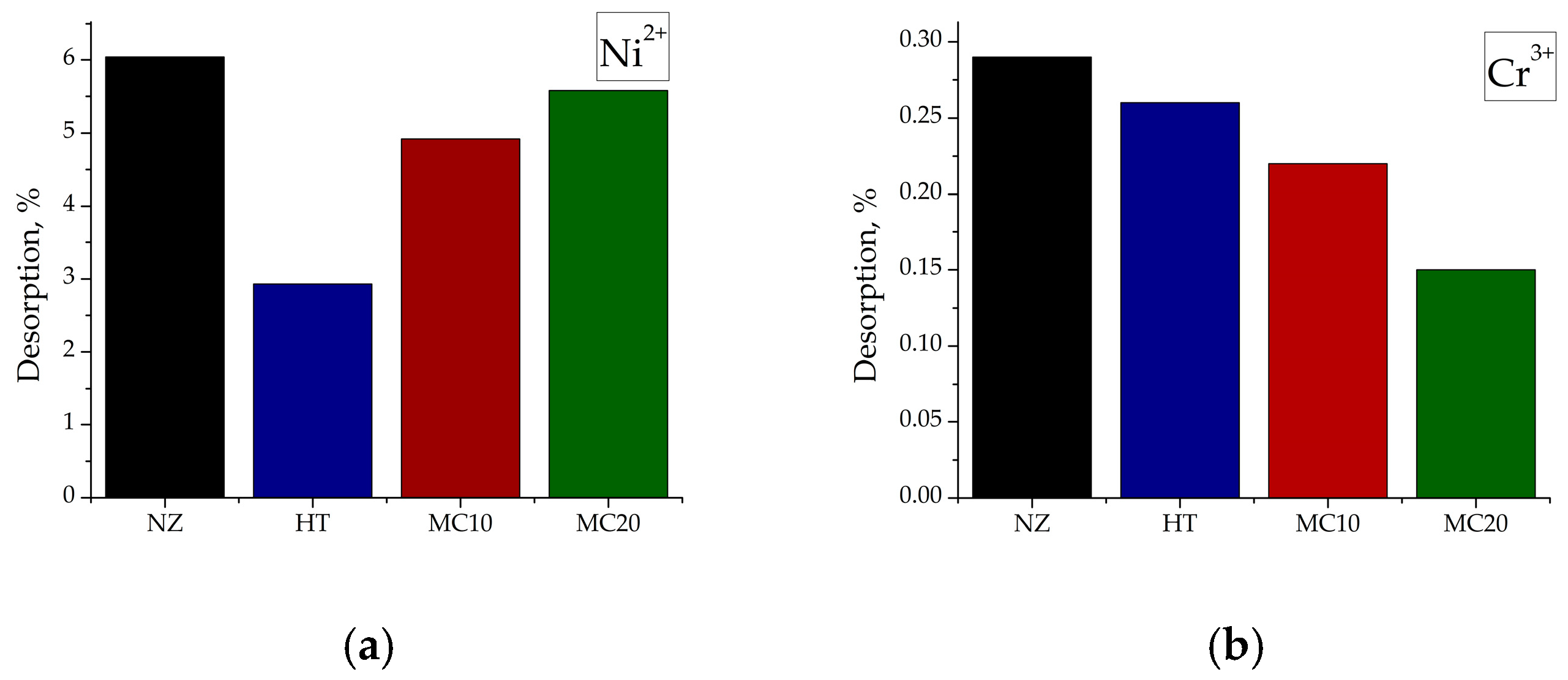
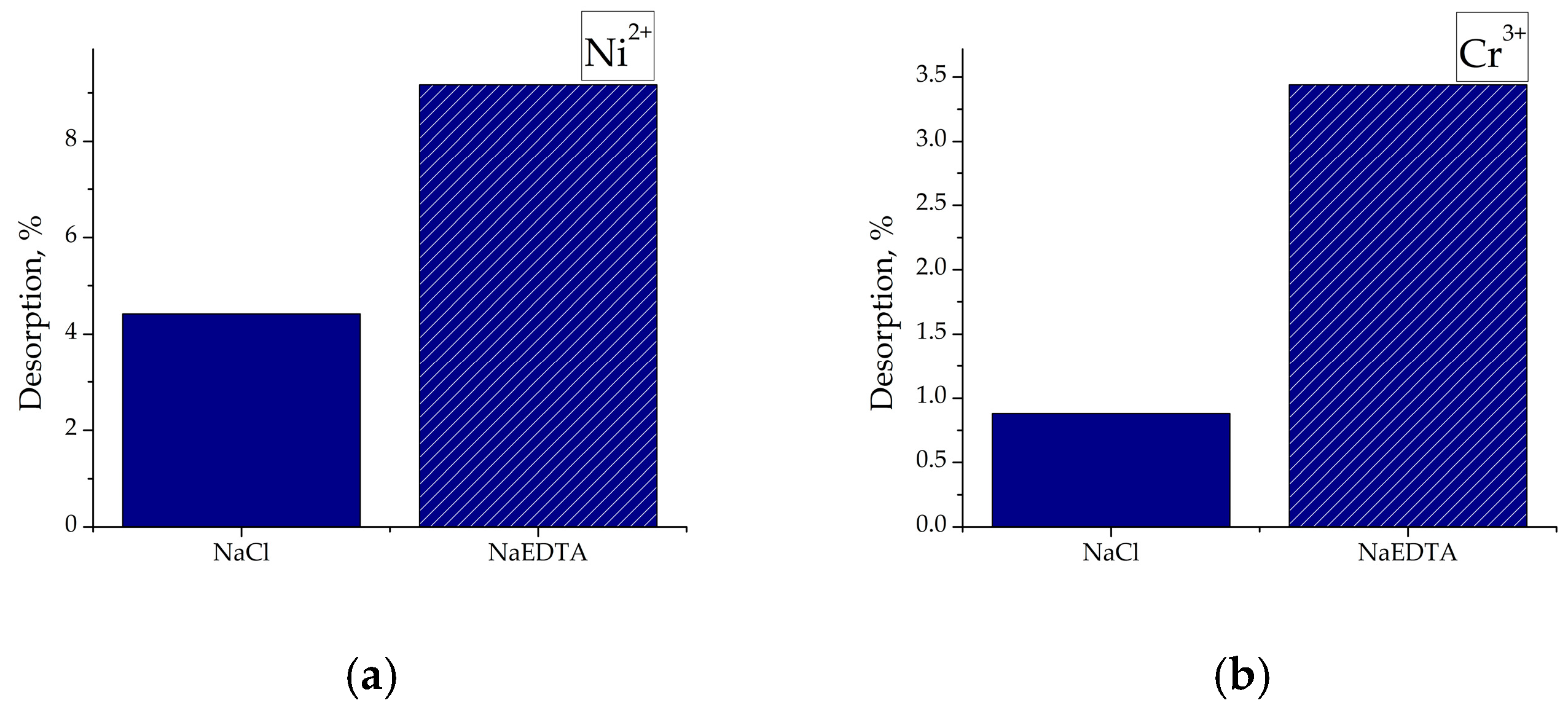
3.8. Desorption from the Saturated Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USGC. Science for a Changing World. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2024/mcs2024-zeolites.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Król, M. Natural vs. Synthetic zeolites. Crystals 2020, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Simović Medica, J.; Gumbarević, D.; Filošević, A.; Pržulj, N.; Pavelić, K. Critical review on zeolite clinoptilolite safety and medical applications in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, V.L.B.; Bruj, G.; Dordai, L.; Roman, M.; Cadar, O.; Becze, A. Evaluation of the impact of different natural zeolite treatments on the capacity of eliminating/reducing odors and toxic compounds. Materials 2021, 14, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyalcin, S.; Akyalcin, L.; Ertugrul, E. Modification of natural clinoptilolite zeolite to enhance its hydrogen adsorption capacity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2024, 50, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diógenes, T.S.; Santiago, R.G.; Maia, D.A.; Gonçalves, D.V.; Azevedo, D.C.; Lucena, S.M.P.; Bastos-Neto, M. Experimental and theoretical assessment of CO2 capture by adsorption on clinoptilolite. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 177, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajdek-Bieda, A.; Wróblewska, A.; Miądlicki, P.; Tołpa, J.; Michalkiewicz, B. Clinoptilolite as a natural, active zeolite catalyst for the chemical transformations of geraniol. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2021, 133, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohadesi, M.; Aghel, B.; Maleki, M.; Ansari, A. The use of KOH/Clinoptilolite catalyst in pilot of microreactor for biodiesel production from waste cooking oil. Fuel 2020, 263, 116659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Magalhães, L.F.; da Silva, G.R.; Peres, A.E.C. Zeolite application in wastewater treatment. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 4544104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, A. Removal of heavy metal ions from water and wastewaters by sulfur-containing precipitation agents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojković, N.; Simović, B.; Žunić, M.; Radovanović, L.; Prekajski-Đorđević, M.; Dapčević, A. Modified Z-scheme heterojunction of TiO2/polypyrrole recyclable photocatalyst. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2025, e20431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Min, X.; Tang, C.J.; Sillanpää, M.; Zhao, F. Recent advances in membrane filtration for heavy metal removal from wastewater: A mini review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, J.; Patel, U.D. Electrochemical treatment of metal-finishing wastewater using Ti/Co3O4 electrode: Efficient removal of nitrate and heavy metals, and recovery of struvite. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.H.; Show, P.L. A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihareva, N.; Petrov, O.; Dimowa, L.; Tzvetanova, Y.; Piroeva, I.; Ublekov, F.; Nikolov, A. Ion exchange of Cs+ and Sr2+ by natural clinoptilolite from bi-cationic solutions and XRD control of their structural positioning. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 323, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, F.; Sadeghi, R.; Shakeri, M. Ultrasonic-assisted chemical modification of a natural clinoptilolite zeolite: Enhanced ammonium adsorption rate and resistance to disturbing ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, T.; Ivanets, A.; Prozorovich, V.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Tran, H.N.; Srivastava, V.; Sillanpää, M. Sorption and mechanism studies of Cu2+, Sr2+ and Pb2+ ions on mesoporous aluminosilicates/zeolite composite sorbents. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletti, C.; Dosa, M.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. Zn2+ and Cd2+ removal from wastewater using clinoptilolite as adsorbent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24355–24361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, A.; Arslankaya, E.; Tosun, İ. Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoubi, N.; Araissi, M.; Mhamdi, M.; Elaloui, E. Valorisation, Characterisation and Application of Natural Materials (Zeolite and Chert) as Adsorbents for the Removal of Chromium (III) from an Aqueous Solution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajic, N.; Stojakovic, D.; Jovanovic, M.; Logar, N.Z.; Mazaj, M.; Kaucic, V. Removal of nickel (II) ions from aqueous solutions using the natural clinoptilolite and preparation of nano-NiO on the exhausted clinoptilolite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/programs/substance-priority-list.html (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Abdelwahab, O.; Thabet, W.M. Natural zeolites and zeolite composites for heavy metal removal from contaminated water and their applications in aquaculture Systems: A review. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2023, 49, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veljović, Đ. Sinteza prahova kalcijum-hidroksiapatita. In Biokeramički Materijali na Bazi Kalcijum-Fosfata: Procesiranje, Svojstva i Primena; Raić, K., Ed.; Tehnološko-metalurški fakultet: Beograd, Srbija, 2020; pp. 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ofudje, E.A.; Adedapo, A.E.; Oladeji, O.B.; Sodiya, E.F.; Ibadin, F.H.; Zhang, D. Nano-rod hydroxyapatite for the uptake of nickel ions: Effect of sintering behaviour on adsorption parameters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasherpour, I.; Salahi, E.; Pazouki, M. Removal of nickel (II) from aqueous solutions by using nano-crystalline calcium hydroxyapatite. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarsamy, G.; Nithiya, P.; Sivasubramanian, R.; Selvakumar, R. Multi-ionic interaction with magnesium doped hydroxyapatite-zeolite nanocomposite porous polyacrylonitrile polymer bead in aqueous solution and spiked groundwater. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119728. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Zhong, H.; Wang, S. A novel conversion for blast furnace slag (BFS) to the synthesis of hydroxyapatite-zeolite material and its evaluation of adsorption properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 105, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Kushwaha, K.; MC Chattopadhyaya, A. Adsorption of cobalt (II) from aqueous solution onto hydroxyapatite/zeolite composite. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2011, 2, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossini, H.; Shafie, B.; Niri, A.D.; Nazari, M.; Esfahlan, A.J.; Ahmadpour, M.; Nazmara, Z.; Ahmadimanesh, M.; Makhdoumi, P.; Mirzaei, N.; et al. A comprehensive review on human health effects of chromium: Insights on induced toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70686–70705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Nickel in drinking water: Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. In Nickel in Drinking Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rajoria, S.; Vashishtha, M.; Sangal, V.K. Treatment of electroplating industry wastewater: A review on the various techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 72196–72246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Bringas, E.; Tan, N.R.; Ortiz, I.; Ghahramani, M.; Shahmirzadi, M.A.A. Recent progress in development of high performance polymeric membranes and materials for metal plating wastewater treatment: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 78–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, F.; Camcı, S. Treatment of metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2012, 31, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shannag, M.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Bani-Melhem, K.; Qtaishat, M.R.; Alkasrawi, M. Heavy metal ions removal from metal plating wastewater using electrocoagulation: Kinetic study and process performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Suetsugu, Y.; Ikoma, T.; Kasama, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Yamada, H.; Tanaka, J. Hydrothermal formation of hydroxyapatite layers on the surface of type-A zeolite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 1395–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, J. Preparation and characterization of surfactant-modified hydroxyapatite/zeolite composite and its adsorption behavior toward humic acid and copper (II). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2512–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janackovic, D.J.; Kostic-Gvozdenovic, L.; Petrovic, R.; Petrovic-Prelevic, I.; Jokanovic, V.; Uskokovic, D. Influence of synthesis parameters on the particle sizes of nanostructured calcium-hydroxyapatite. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 192–195, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hubadillah, S.K.; Abd Aziz, M.H.; Jamalludin, M.R. Application of natural zeolite clinoptilolite for the removal of ammonia in wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.H.; Shamshiri, A.; Jaberi, E.; Bonakdari, H.; Akhbari, A.; Delatolla, R.; Hassanvand, M.R.; Agharazi, M.; Huang, Y.F.; Ahmed, A.N.; et al. Total iron removal from aqueous solution by using modified clinoptilolite. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, M.; Mokhtari, H.R.; Vatanpour, V.; Rezaei, K. Investigating the Effectiveness of Natural Zeolite (Clinoptilolite) for the Removal of Lead, Cadmium, and Cobalt Heavy Metals in the Western Parts of Iran’s Varamin Aquifer. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulina, N.V.; Makarova, S.V.; Baev, S.G.; Matvienko, A.A.; Gerasimov, K.B.; Logutenko, O.A.; Bystrov, V.S. A study of thermal stability of hydroxyapatite. Minerals 2021, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M.; Dechnik, J.; Szymczak, P.; Handke, B.; Szumera, M.; Stoch, P. Thermal Behavior of Clinoptilolite. Crystals 2024, 14, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukobat, R.; Škrbić, R.; Massiani, P.; Baghdad, K.; Launay, F.; Sarno, M.; Cirillo, C.; Senatore, A.; Salčin, E.; Atlagić, S.G. Thermal and structural stability of microporous natural clinoptilolite zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 341, 112101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Sprynskyy, M.; Terzyk, A.P.; Lebedynets, M.; Namieśnik, J.; Buszewski, B. Porous structure of natural and modified clinoptilolites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Golembiewski, R.; Trykowski, G.; Buszewski, B. Heterogeneity and hierarchy of clinoptilolite porosity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabiś-Mazgaj, E.; Gawenda, T.; Pichniarczyk, P.; Stempkowska, A. Mineral composition and structural characterization of the clinoptilolite powders obtained from zeolite-rich tuffs. Minerals 2021, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favvas, E.P.; Tsanaktsidis, C.G.; Sapalidis, A.A.; Tzilantonis, G.T.; Papageorgiou, S.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Clinoptilolite, a natural zeolite material: Structural characterization and performance evaluation on its dehydration properties of hydrocarbon-based fuels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 225, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Darvell, B.W. Morphology and structural characteristics of hydroxyapatite whiskers: Effect of the initial Ca concentration, Ca/P ratio and pH. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2960–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, F.; Mollahosseini, A.; Hosseini, M.M. Enhanced adsorption of dyes on microwave-assisted synthesized magnetic zeolite-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yamada, H.; Ikoma, T.; Tanaka, J.; Stevens, G.W.; Komatsu, Y. Preparation of a zeolite NaP1/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite and study of its behavior as inorganic fertilizer. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayotte, P.; Smith, R.S.; Stevenson, K.P.; Dohnálek, Z.; Kimmel, G.A.; Kay, B.D. Effect of porosity on the adsorption, desorption, trapping, and release of volatile gases by amorphous solid water. J. Geophys. Res. E Planets 2001, 106, 33387–33392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Stylianou, M.; Loizidou, M. Ion exchange and adsorption equilibrium studies on clinoptilolite, bentonite and vermiculite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatal, M.; Olguin, M.T.; Abdellaoui, Y.; El Bouari, A. Sorption of Cd (II), Ni (II) and Zn (II) on natural, sodium-, and acid-modified clinoptilolite-rich tuff. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2018, 44, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Li, C.; Tang, B.; Xu, J.; Lu, G.; Liu, P. Preparation of cellulose acetate/zeolite composite fiber and its adsorption behavior for heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ayuso, E.; Garcıa-Sánchez, A.; Querol, X. Purification of metal electroplating waste waters using zeolites. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4855–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Afifi, A.M.; Salleh, A.; Ang, B.C. Chitosan/(polyvinyl alcohol)/zeolite electrospun composite nanofibrous membrane for adsorption of Cr6+, Fe3+ and Ni2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.J.; Wang, H.G.; Cui, X.Y.; Yu, F.; Cheng, W.P.; Ma, J.H. Zeolite A/Activated Carbon Composite Synthesized from Elutrilithe. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Development, Xi’an, China, 2–4 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias, C.; García, R.; Arriagada, R.; Yanez, J.; Garland, M.T. Cr (III) exchange on zeolites obtained from kaolin and natural mordenite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 88, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Boada, R.; Cibin, G.; Palet, C. Enhancement of selective adsorption of Cr species via modification of pine biomass. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, D.; Dikić, J.; Štulović, M.; Anđić, Z.; Kamberović, Ž.; Jevtić, S. Sorption of Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ ions on Na-enriched natural zeolite for wastewater treatment process: A kinetic approach. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2023, 29, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, J. Algal sorbent derived from Sargassum horneri for adsorption of cesium and strontium ions: Equilibrium, kinetics, and mass transfer. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2833–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustino, B.; Cobo, D.M.; Vequizo, R.; Candidato, R., Jr. Enhanced heavy metal adsorption capacity of surface-functionalized Philippine natural zeolite in simulated wastewater. Open Ceram. 2024, 18, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haj-Ali, A.M.; Marashdeh, L.M. Removal of aqueous chromium (III) ions using Jordanian natural zeolite tuff in batch and fixed bed modes. Jordan J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 6, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Grozdov, D.; Humelnicu, I.; Humelnicu, D.; Mitina, T. Removal of chromium (III) ions from aqueous solutions using different types of hydroxyapatites. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 204, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa-Stratulat, S.M.; Olteanu, I.; Toma, A.M.; Pastia, C.; Banu, O.M.; Corbu, O.C.; Toma, I.O. The use of natural zeolites in cement-based construction materials—A state of the art review. Coatings 2023, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrenovic, J.; Milenkovic, J.; Ivankovic, T.; Rajic, N. Antibacterial activity of heavy metal-loaded natural zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 201, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores Díaz, A.A.; Velázquez Machuca, M.A.; Medina Ramírez, A.; Montañez Soto, J.L.; Venegas González, J.; Pimentel Equihua, J.L. Boron adsorption on modified zeolites: Effect of modifier and source of water. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2023, 39, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| CaCl2·2H2O | C10H14Na2O8·2H2O | (NH4)2HPO4 | CH4N2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mass, g | 0.2491 | 0.1744 | 0.1340 | 0.1414 |
| Weight% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinoptilolite | Quartz | Plagioclases | Calcite | Micas | Hydroxyapatite | |
| NZ | 90.7 | 4.7 | 3.5 | 1.1 | / | / |
| HT | 81.1 | 4.9 | 3.4 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 8.9 |
| MC10 | 81.4 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 1 | / | 9.5 |
| MC20 | 71.3 | 5.1 | 3.3 | 0.8 | / | 19.4 |
| Sample | SSA (m2 g−1) | Vtot (cm3 g−1) | Vmeso (cm3 g−1) | Daver (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NZ | 24.763 | 0.101 | 0.098 | 18.573 |
| HT | 37.442 | 0.096 | 0.091 | 11.566 |
| MC10 | 29.900 | 0.110 | 0.105 | 17.028 |
| MC20 | 33.782 | 0.135 | 0.131 | 16.981 |
| Metal Ion | Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity, mg/g | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2+ | Mexican clinoptilolite | 0.31 | [58] |
| Cellulose acetate–zeolite composite | 16.95 | [59] | |
| Greek clinoptilolite | 1.98 | [60] | |
| Chitosan–PVA–zeolite nanofibrous membrane | 1.79 | [61] | |
| NZ | 2.56 | This study | |
| HT | 6.91 | This study | |
| MC10 | 2.16 | This study | |
| MC20 | 2.28 | This study | |
| Cr3+ | Zeolite A–activated carbon composite | 4.9 | [62] |
| Greek clinoptilolite | 4.12 | [60] | |
| Mordenite | 3.6 | [63] | |
| Kaolin | 2.6 | [63] | |
| NZ | 3.14 | This study | |
| HT | 16.95 | This study | |
| MC10 | 8.19 | This study | |
| MC20 | 13.09 | This study |
| Ads. | PFO | PSO | IPD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1, h−1 | qe,1 mg/g | R2 | k2, g/(mg·h) | qe,2 mg/g | R2 | kipd, mg/(g·h0.5) | R2 | ||
| Ni2+ | NZ | 0.991 | 3.03 | 0.97 | 0.27 | 2.59 | 0.981 | 0.626 | 0.828 |
| HT | 0.0498 | 8.54 | 0.905 | 0.377 | 7.39 | 0.956 | 1.9 | 0.678 | |
| MC10 | 0.222 | 2.56 | 0.951 | 0.467 | 2.25 | 0.988 | 0.102 | 0.69 | |
| MC20 | 0.187 | 2.73 | 0.937 | 0.427 | 2.4 | 0.978 | 0.638 | 0.692 | |
| Cr3+ | NZ | 7.49 × 10−4 | 173.6 | 0.985 | 6.87 × 10−5 | 4.47 | 0.997 | 0.492 | 0.672 |
| HT | 0.101 | 18.6 | 0.995 | 0.003 | 25.9 | 0.996 | 3.3 | 0.763 | |
| MC10 | 0.033 | 9.58 | 0.982 | 0.286 | 8.18 | 0.993 | 2.01 | 0.827 | |
| MC20 | 0.0216 | 15.5 | 0.975 | 0.302 | 13.3 | 0.995 | 3.29 | 0.8 | |
| Metal | Initial Concentration, mg/dm3 | Initial pH | Equilibrium Adsorption Capacity (qe, mg/g) | Equilibrium pH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NZ | HT | NZ | HT | |||
| Ni2+ | 20 | 5.00 | 0.988 | 3.8332 | 6.14 | 7.02 |
| 40 | 5.06 | 1.534 | 5.736 | 6.06 | 6.96 | |
| 90 | 5.05 | 2.426 | 7.14 | 6.25 | 6.73 | |
| 100 | 5.10 | 2.58 | 6.91 | 6.23 | 6.70 | |
| 130 | 5.14 | 2.68 | 7.156 | 6.24 | 6.62 | |
| Cr3+ | 20 | 3.37 | 3.064 | 4.478 | 3.87 | 5.30 |
| 40 | 3.10 | 3.202 | 8.636 | 3.49 | 5.14 | |
| 90 | 2.85 | 3.284 | 16.118 | 3.12 | 3.24 | |
| 100 | 2.81 | 3.14 | 16.91 | 3.07 | 3.11 | |
| 130 | 2.72 | 3.204 | 17.858 | 2.95 | 2.96 | |
| Sample | Ions | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | KF | n | R2 | ||
| NZ | Ni2+ | 3.987 | 0.019 | 0.996 | 0.258 | 1.987 | 0.987 |
| Cr3+ | 3.227 | 2.71 | 0.998 | 2.999 | 65.050 | 0.997 | |
| HT | Ni2+ | 7.293 | 0.360 | 0.995 | 3.496 | 6.017 | 0.986 |
| Cr3+ | 17.611 | 1.494 | 0.973 | 9.223 | 5.044 | 0.961 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokić, K.; Dikić, J.; Veljović, Đ.; Jelić, I.; Radovanović, D.; Štulović, M.; Jevtić, S. Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite-Modified Natural Zeolite: Application as Adsorbent for Ni2+ and Cr3+ Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2025, 13, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030818
Sokić K, Dikić J, Veljović Đ, Jelić I, Radovanović D, Štulović M, Jevtić S. Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite-Modified Natural Zeolite: Application as Adsorbent for Ni2+ and Cr3+ Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes. 2025; 13(3):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030818
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokić, Katarina, Jelena Dikić, Đorđe Veljović, Ivana Jelić, Dragana Radovanović, Marija Štulović, and Sanja Jevtić. 2025. "Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite-Modified Natural Zeolite: Application as Adsorbent for Ni2+ and Cr3+ Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions" Processes 13, no. 3: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030818
APA StyleSokić, K., Dikić, J., Veljović, Đ., Jelić, I., Radovanović, D., Štulović, M., & Jevtić, S. (2025). Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite-Modified Natural Zeolite: Application as Adsorbent for Ni2+ and Cr3+ Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes, 13(3), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030818








