Research on the Testing Method for the Rheological Properties of Large-Particle Gangue Filling Slurry
Abstract
1. Introduction
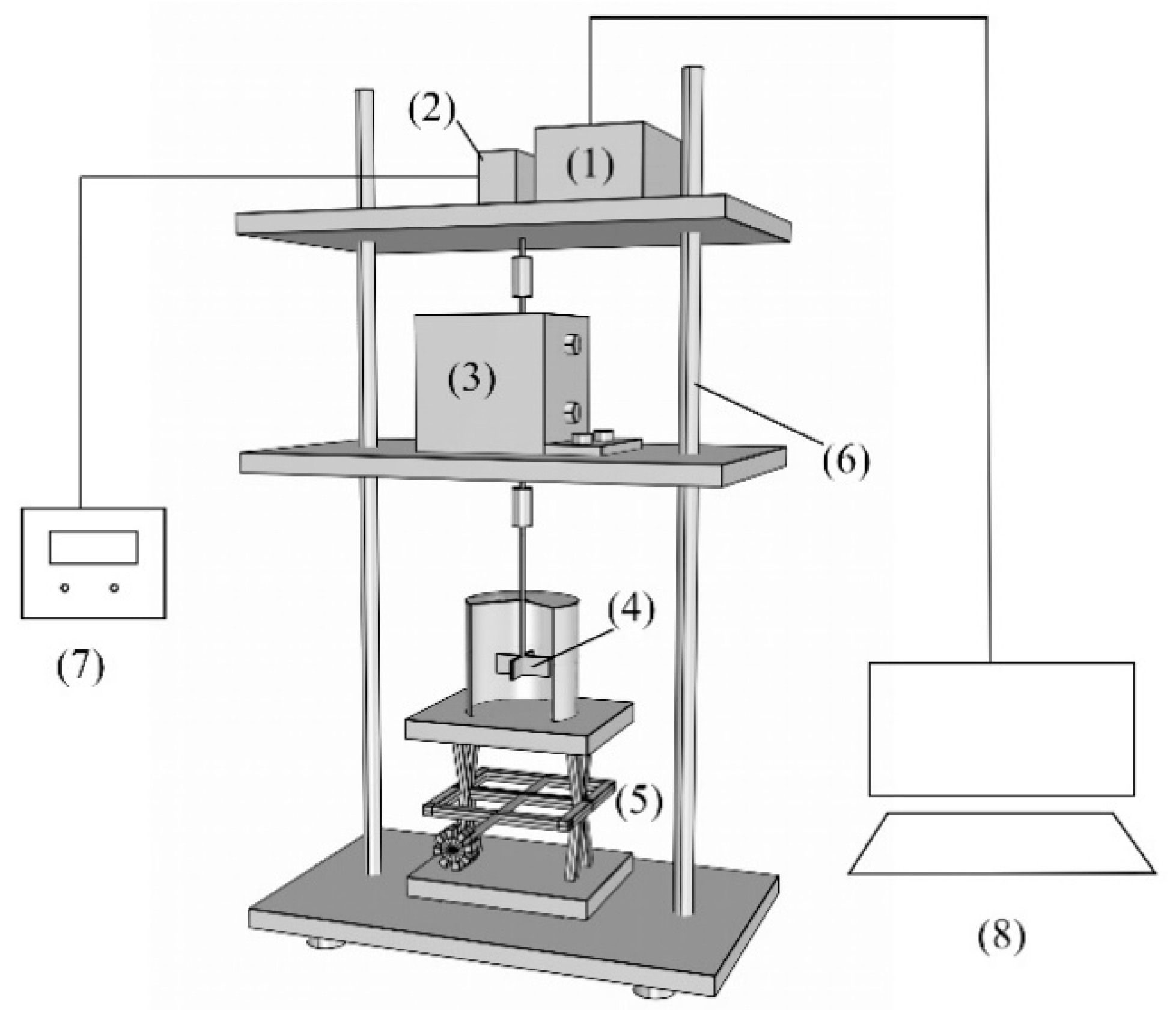
2. Structure and Working Principle of a New Type of Gangue Slurry Rheometer
2.1. Structure of a New Type of Gangue Slurry Rheometer
2.2. Working Principle of a New Type of Gangue Slurry Rheometer
3. New Type of Gangue Slurry Rheometer for Testing Rheological Parameters of Slurry
3.1. Preparation of Gangue Filling Slurry
3.2. Test Data Analysis of Gangue Slurry at Different Rotational Speeds
4. Numerical Simulation of the Testing Process of a New Type of Gangue Slurry Rheometer
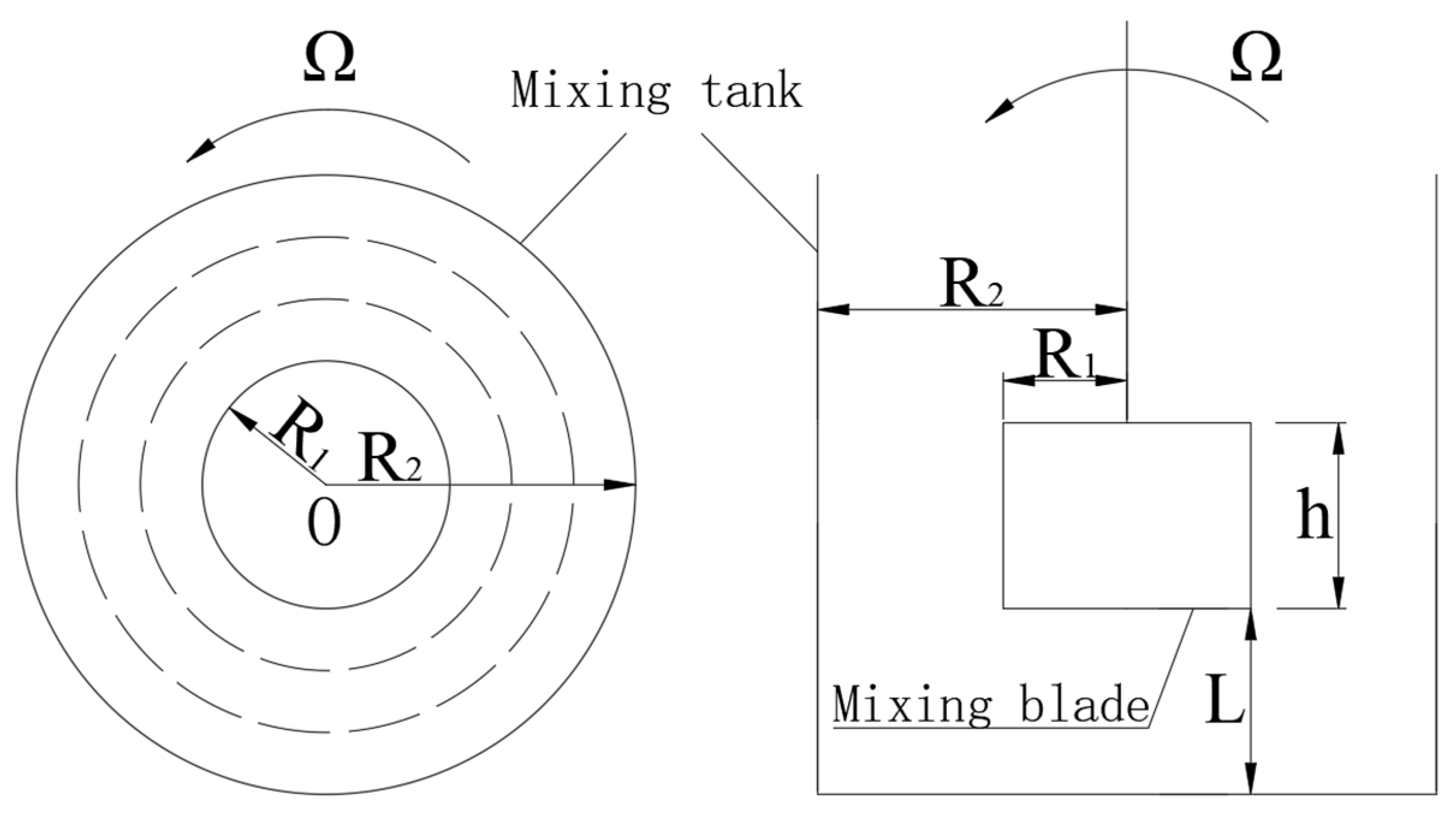
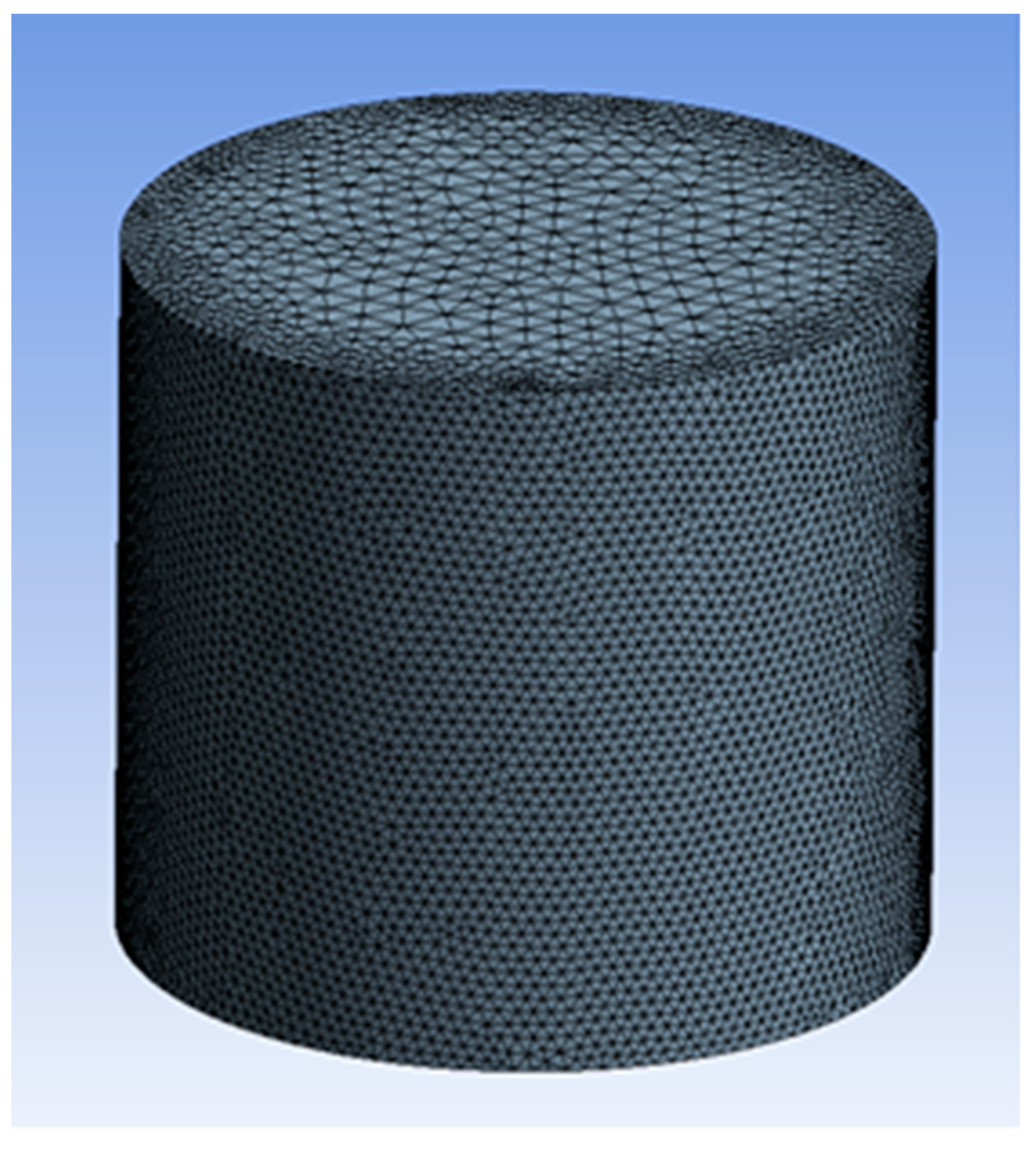
4.1. Model Establishment and Grid Division
4.2. Parameter Setting of Slurry Model
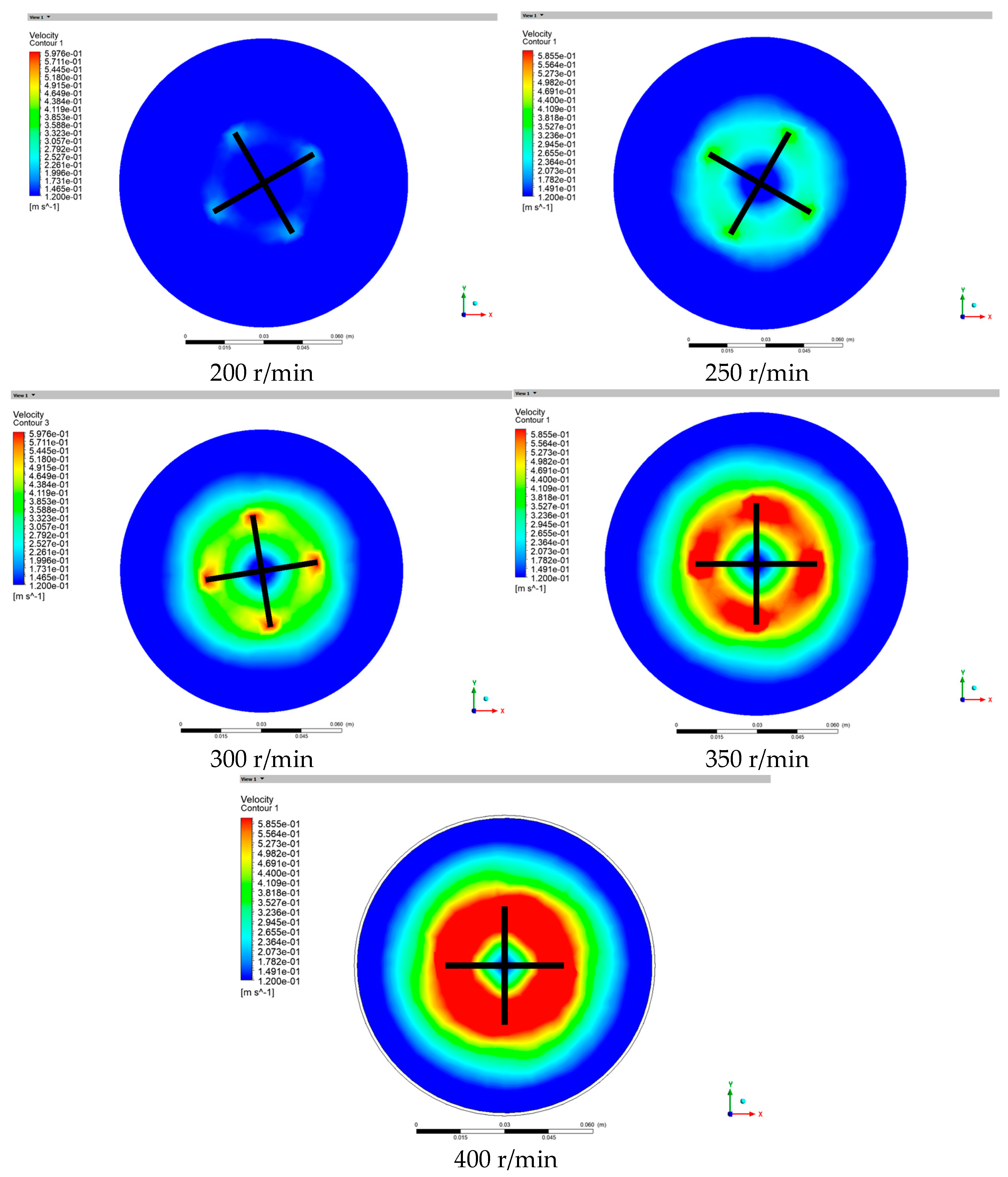
4.3. Observation of Velocity Distribution of Cross-Sectional Slurry at Different Rotational Speeds
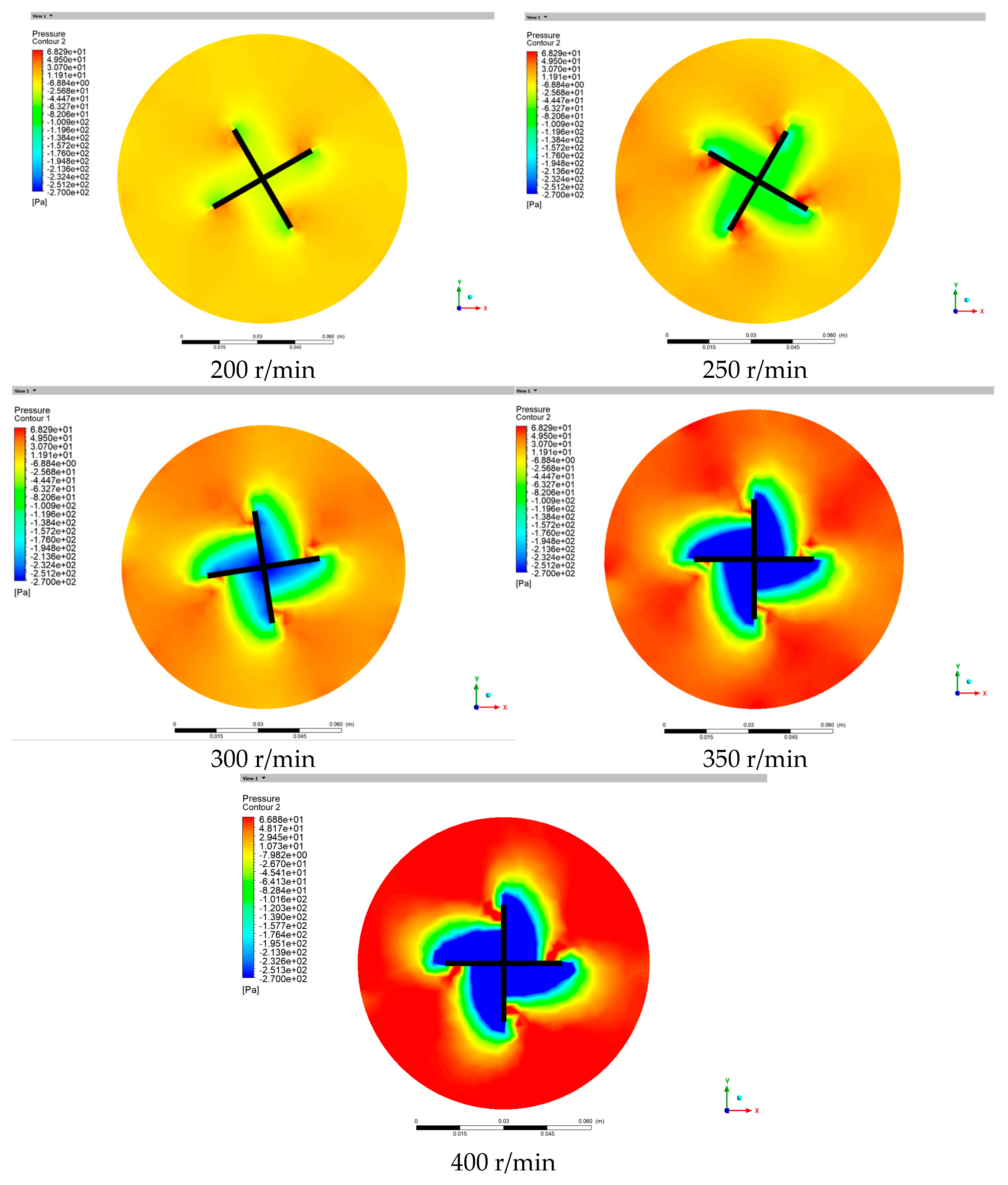
4.4. Pressure Distribution of Observed Cross-Sections at Different Rotational Speeds
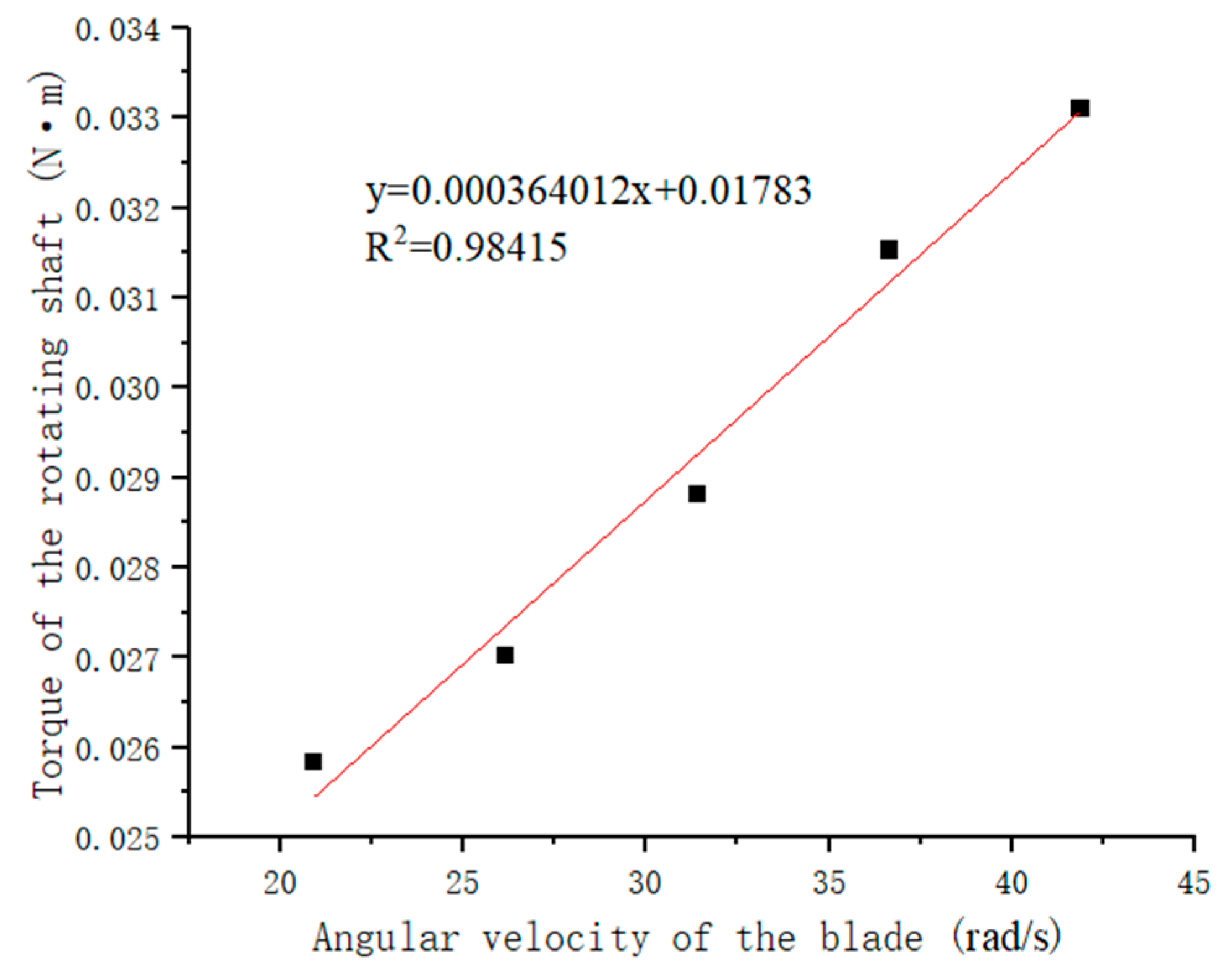
4.5. Torque of Stirring Blades at Different Speeds
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Due to the current inability to accurately measure the rheological parameters of slurry containing large-sized gangue particles, a new type of gangue slurry rheometer has been developed. The working principle of the newly developed gangue slurry rheometer is to obtain the torque of the stirring blades at different speeds and calculate the rheological parameters of the slurry. The torque is generated by the combined action of the slurry between the blade side edge and the cylinder wall, and the slurry between the blade lower edge and the cylinder bottom.
- (2)
- Testing is conducted on a slurry containing a 76% concentration of large-sized gangue material, and the torque on the stirring blades is obtained at a speed of 200–400 r/min. As the speed increases, the torque values obtained on the blades gradually increase. The yield stress and viscosity are calculated to be 96.49 and 1.89, respectively.
- (3)
- Fluent is used to simulate the flow behavior of gangue slurry under the same conditions, and it is found that the maximum velocity of the slurry appears at the edge of the mixing blade and decreases towards the direction away from the blade edge, forming a velocity gradient. The front of the blade’s direction displays compressive stress, while the rear displays tensile stress. As the rotational speed increases, the difference between the two stresses gradually increases and a clear boundary appears. Based on the torque values obtained on the blades at different speeds, through regression analysis and calculation, the yield stress and viscosity of the slurry are found to be 98.42 and 1.92, respectively, with errors of 2% and 1.59%, respectively. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the new gangue slurry rheometer test.
- (4)
- This study provides a basis for the accurate measurement of the rheological parameters of large particle sizes, ensuring the smooth transportation of high-concentration gangue slurry in pipelines and providing a reference for the design of filling processes and filling systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bo, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Coal Mine Solid Waste Backfill Process in China: Current Status and Challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Tian, S.; Sun, Q.; Li, B.; Cai, C.; Xia, Y.; Wei, X.; Mu, Q. Preparation and Microstructure of Fly Ash Geopolymer Paste Backfill Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, K.; Du, F.; Guo, H.; Li, K.; Wang, Y. Mechanical-Permeability Characteristics of Composite Coal Rock under Different Gas Pressures and Damage Prediction Model. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 36615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, F.; Li, G.; Ma, Q. Failure Mechanisms and Reinforcement Support of Soft Rock Roadway in Deep Extra-Thick Coal Seam: A Case Study. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 165, 108745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, X.; He, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, L. Energy evolution and damage characteristics of gangue cemented backfill in different water content states. Rock Soil Mech. 2025, 46, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, N.; Gao, F.; Yan, H. Method of gangue grouting filling in subsequent space of coal mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, B.; Yang, S.; Dang, P. Experimental study on correlativity between rheological parameters and grain grading of coal gauge backfill slurry. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2016, 47, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, C.; Fan, B.; Yang, K. Investigation of Viscoelastic-Plastic Properties of Fresh Cemented Gangue Fly Ash Backfill Slurries. Minerals 2024, 14, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Du, F.; Ma, J.; Qian, R.; Huo, N. Research on Abutment Stress Distribution of Roof-Cutting Coalface: Numerical Simulation and Field Measurement. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2024, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, C.; Yuan, L.; Li, J.; Liu, F. Study on Green Filling Mining Technology and Its Application in Deep Coal Mines: A Case Study in the Xieqiao Coal Mine. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1110093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Gu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Fu, J. Risk Assessment of Fault Water Inrush during Deep Mining. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X. Reduction and Utilization of Coal Mine Waste Rock in China: A Case Study in Tiefa Coalfield. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Wu, M.; Sun, L.; Cao, J.; Du, C. A New Experimental Apparatus for Sudden Unloading of Gas-Bearing Coal. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, E.; Guo, Y.; Du, F.; Ding, K. Effect of Loading Rate on the Mechanical and Seepage Characteristics of Gas-Bearing Coal–Rock and Its Mechanical Constitutive Model. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 26606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L. Study on the Rheological Characteristics of Backfill Slurry with Graded Addition of Gangue Particles. Nonferrous Met. 2024, 14, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, Y. Study on Preparation and Influencing Factors of Coal Gangue Fill Slurry Material. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. Transportability and Pressure Drop of Fresh Cemented Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill (CGFB) Slurry in Pipe Loop. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Pang, Z. Investigation of Hydraulic-Mechanical Properties of Paste Backfill Containing Coal Gangue-Fly Ash and Its Application in an Underground Coal Mine. Energies 2017, 10, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, X.-M. Performance of Cemented Coal Gangue Backfill. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2007, 14, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hao, Y. Experimental Study and Application of Rheological Properties of Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill Slurry. Processes 2020, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Hou, Y.; Deng, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X. Thermal, Hydraulic and Mechanical Performances of Cemented Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 162, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Guo, W.; Qi, T.; Li, Z.; Cui, J.; Wang, C.; Cui, Y.; Ma, J. Failure mechanisms and destruction characteristics of cemented coal gangue backfill under compression effect of non-uniform load. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 31, 2676–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Hao, Y. Research on non-full pipeline flow transportation and prevention method of coal gangue cemented backfill. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hou, C.; Li, L.; Du, J.; Yan, B. Experimental Investigation on Flow Properties of Cemented Paste Backfill through L-Pipe and Loop-Pipe Tests. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 2830–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Wang, Z.; Qi, T.; Du, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Wen, X. Effect of Velocity on Flow Properties and Electrical Resistivity of Cemented Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill (CGFB) Slurry in the Pipeline. Powder Technol. 2022, 396, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Guo, S. Properties of a Backfill Material Prepared by Cementing Coal Gangue and Fly Ash through Microbial-Induced Calcite Precipitation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 384, 131329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Jin, J.; Wang, X. Time-Dependent Rheological Properties of Cemented Aeolian Sand-Fly Ash Backfill Vary with Particles Size and Plasticizer. Materials 2023, 16, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. Effects of Corn Stalk Fly Ash (CSFA) on the Mechanical and Deformation Properties of Cemented Coal Gangue Backfill. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Feng, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Fine Gangue on Strength, Resistivity, and Microscopic Properties of Cemented Coal Gangue Backfill for Coal Mining. Shock Vib. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, Z.; Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Hou, J. Mechanical Properties under Triaxial Compression of Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Cemented Backfill after Cured at Different Temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.; Song, K.; Kang, L. Mix Ratio Optimization of Cemented Coal Gangue Backfill (CGB) Based on Response Surface Method. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, W. Comparative experiment on fluidity of grinded coal gangue and loess grouting materials. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2024, 55, 4249–4259. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, B.; Gu, C.; Yang, F.; Liu, H. Experimental Investigation into the Proportion of Cemented Aeolian Sand-Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill on Mechanical and Rheological Properties. Minerals 2023, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Yang, B.; Yang, F.; Ren, Q.; Silva, M.C.E. Fluidity and Rheological Properties with Time-Dependence of Cemented Fine-Grained Coal Gangue Backfill Containing HPMC Using Response Surface Method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 451, 138691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Yu, M. Pressure Study on Pipe Transportation Associated with Cemented Coal Gangue Fly-Ash Backfill Slurry. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Li, H.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Ruan, Z. Status and prospects of research on the rheology of paste backfill using unclassified tailings (Part 2): Rheological measurement and prospects. Chin. J. Eng. 2021, 43, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Content | Cement | Fly Ash | Gangue | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76% | 76 g | 228 g | 456 g | 240 g |
| n (r/min) | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 |
| M (N·m) | 0.0255 | 0.0262 | 0.0289 | 0.0299 | 0.033 |
| (rad/s) | 20.935 | 26.173 | 31.409 | 36.628 | 41.888 |
| Physical Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1800 | |
| Viscosity | 1.89 | |
| Yield stress | 96.49 |
| No. | Blade Speed (rpm/min) | Blade Angular Velocity (rad/s) | Blade Torque (N·m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 20.9333 | 0.02531 |
| 2 | 250 | 26.1666 | 0.02721 |
| 3 | 300 | 31.4 | 0.02912 |
| 4 | 350 | 36.6333 | 0.03102 |
| 5 | 400 | 41.8667 | 0.03292 |
| Physical Parameters | Set (Test) Value | Simulated Value | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (Pa·s) | 1.89 | 1.92 | 1.59% |
| Yield stress (Pa) | 96.49 | 98.42 | 2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, X.; Huang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L. Research on the Testing Method for the Rheological Properties of Large-Particle Gangue Filling Slurry. Processes 2025, 13, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030789
Duan X, Huang Y, Hao Y, Zhang L. Research on the Testing Method for the Rheological Properties of Large-Particle Gangue Filling Slurry. Processes. 2025; 13(3):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030789
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Xiaobo, Yucheng Huang, Yuxin Hao, and Liao Zhang. 2025. "Research on the Testing Method for the Rheological Properties of Large-Particle Gangue Filling Slurry" Processes 13, no. 3: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030789
APA StyleDuan, X., Huang, Y., Hao, Y., & Zhang, L. (2025). Research on the Testing Method for the Rheological Properties of Large-Particle Gangue Filling Slurry. Processes, 13(3), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030789






