A Study on Microstructure-Property Relationships and Notch-Sensitive Fracture Behavior of X80 Steel Welds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Methods
2.1. Materials
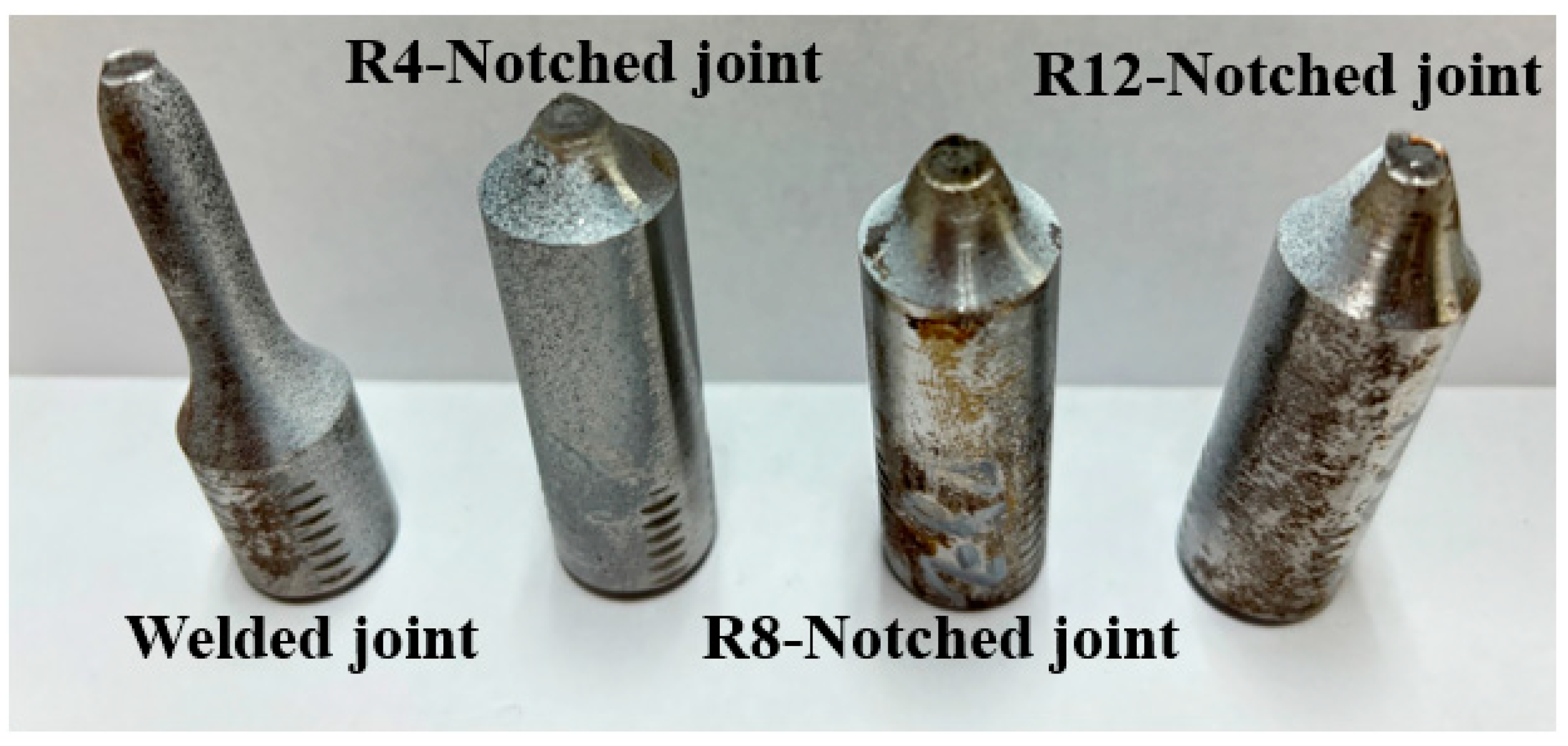
2.2. Test Methods
2.3. DIC Test
3. Results Analysis
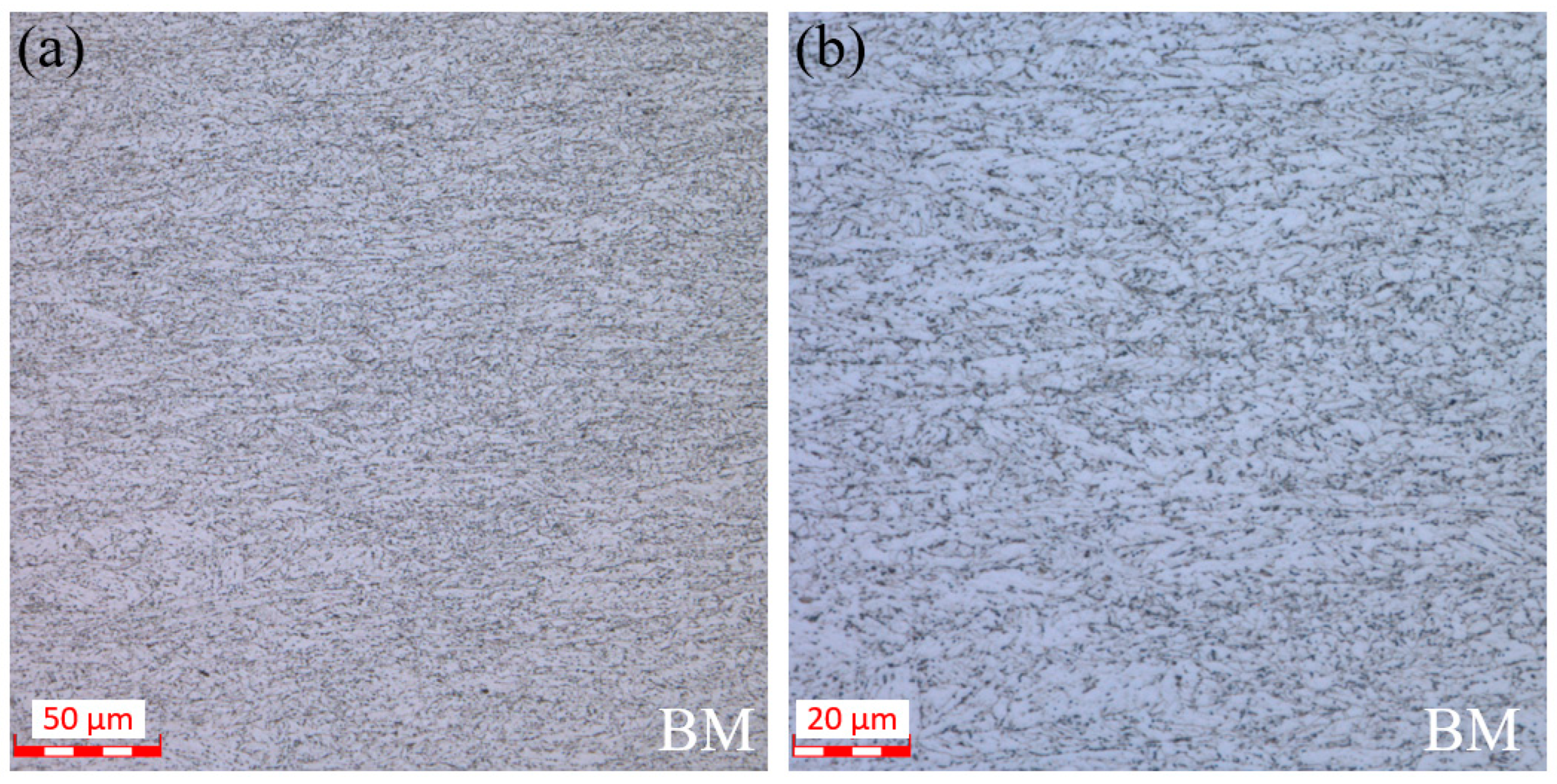
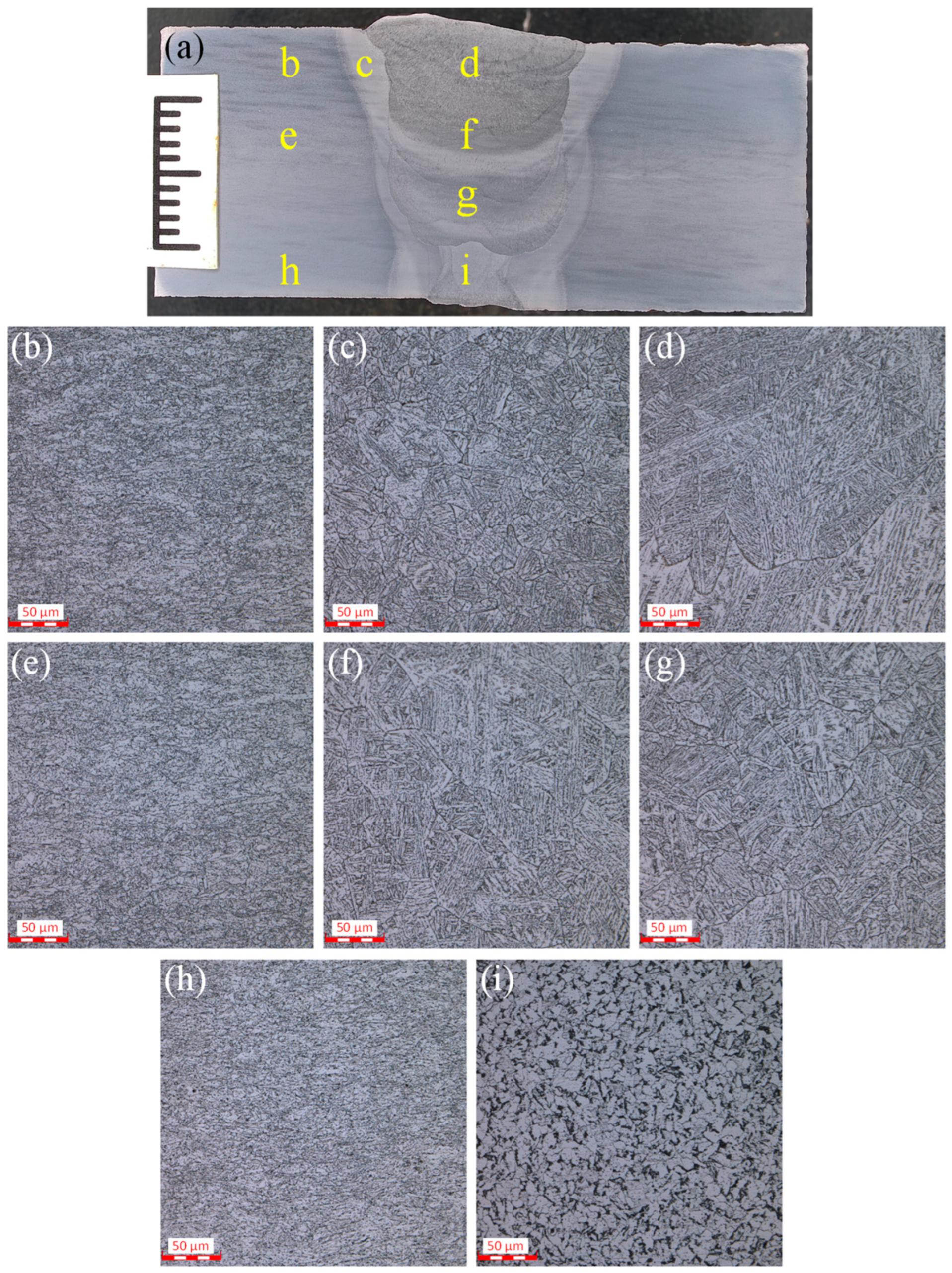
3.1. Microstructure
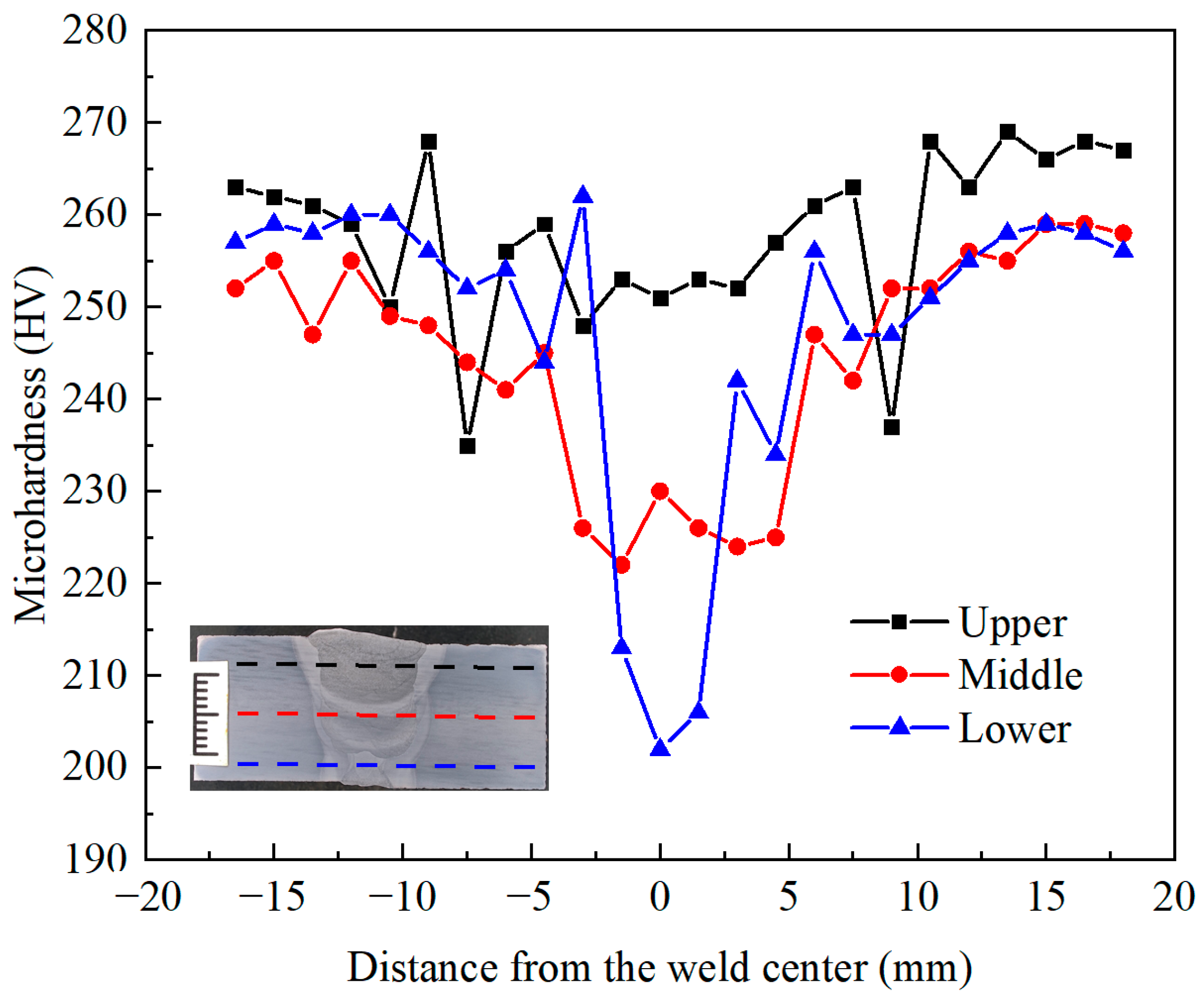
3.2. Microhardness
3.3. Impact Properties
3.4. Tensile Properties
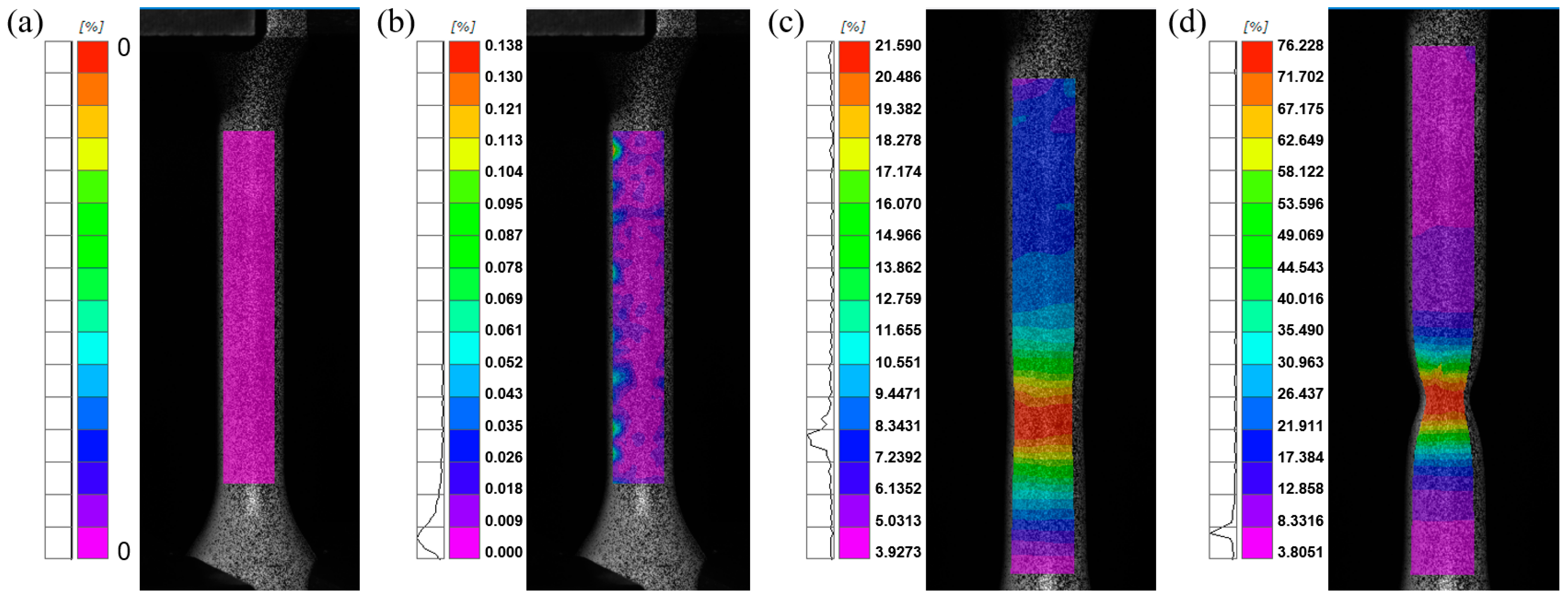
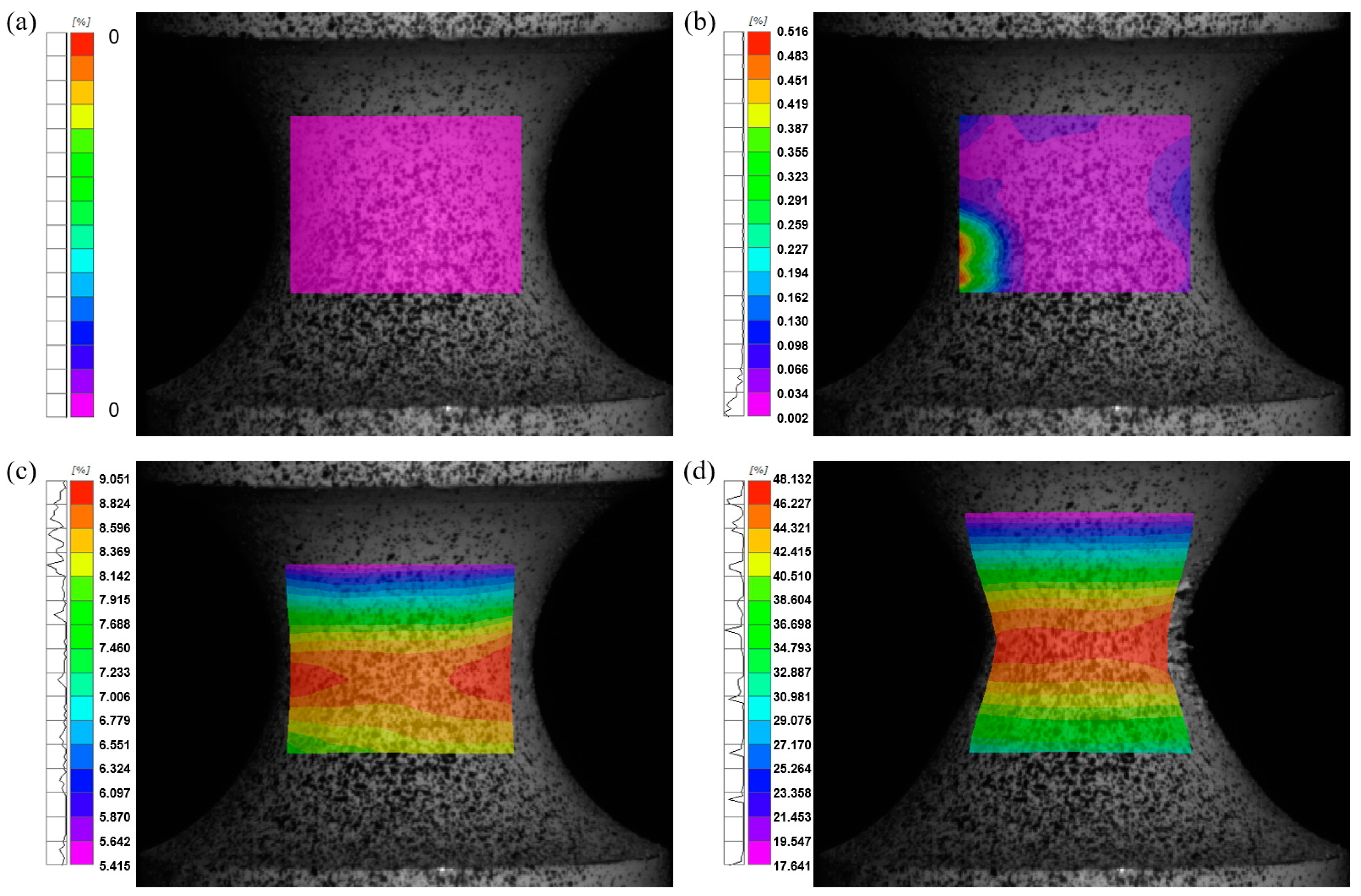
3.5. Strain Distribution
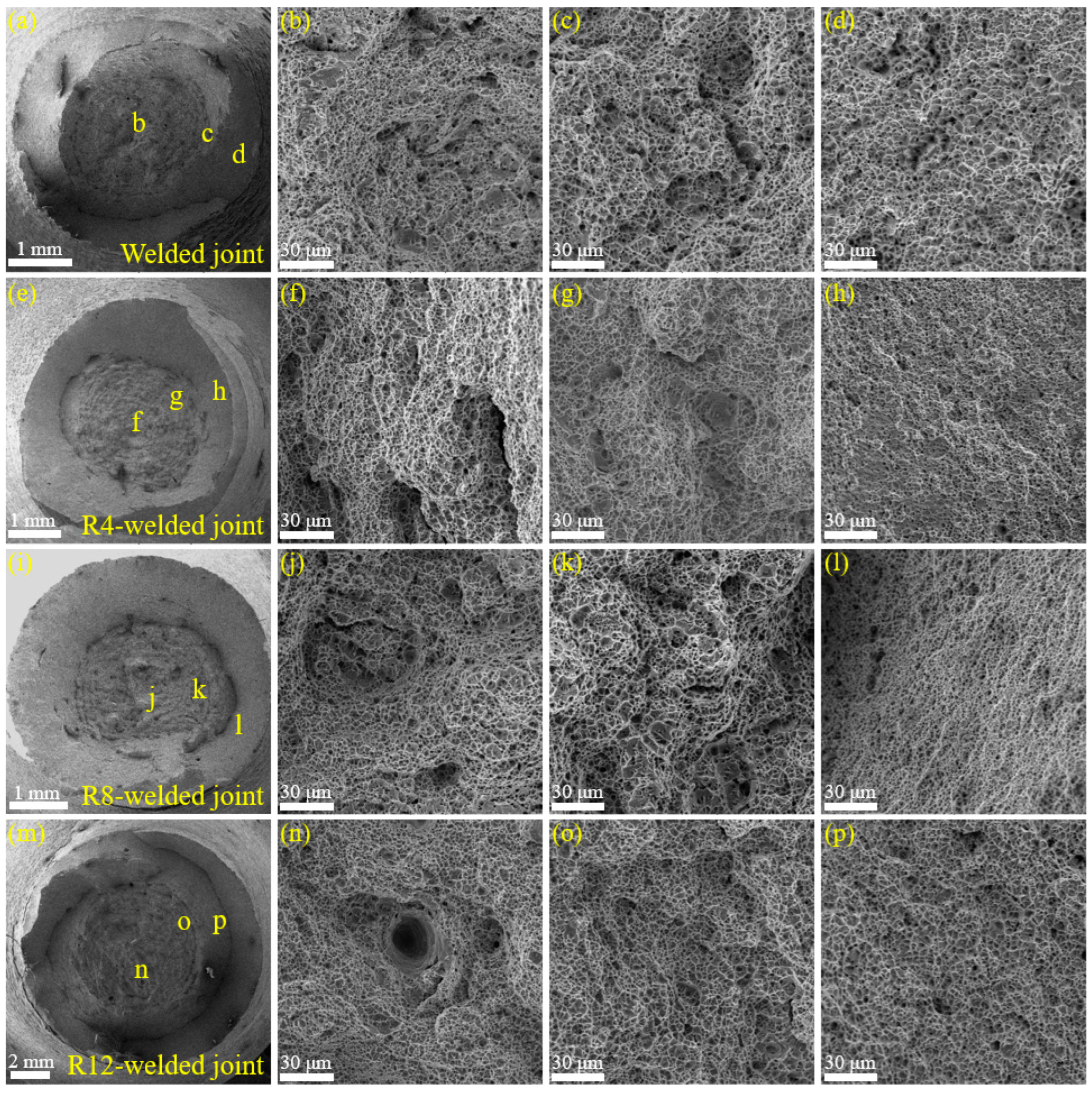
3.6. Fracture Analysis
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Microstructure and mechanical property relationships
- (2)
- Impact of notch geometry on fracture behavior
- (3)
- Strain distribution and localization
- (4)
- Fracture mode transition
- (5)
- Implications for pipeline integrity
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The X80 steel welded joints exhibited distinct hardness levels across different regions, with the BM recording the highest hardness (260 HV) and the WZ showing the lowest (202 HV) due to variations in microstructure influenced by thermal cycles.
- (2)
- The impact toughness varied significantly, with the base metal demonstrating superior properties compared to the HAZ and the weld zone, which was the least resistant to brittle fracture.
- (3)
- The presence and size of notches significantly affected the mechanical properties of the welded joints. Smaller notch radii intensified stress concentrations, leading to increased maximum loads but reduced ductility.
- (4)
- DIC analysis revealed that strain concentration and localization in the weld zone were highly dependent on notch size, with larger notches promoting more ductile fracture behavior (maximum Mises true strain of 58.43% for R12-notched specimens).
- (5)
- Fracture analysis indicated a transition from ductile to brittle characteristics with decreasing notch radius, underscoring the importance of notch geometry in determining the fracture toughness of X80 steel welds.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turichin, G.; Kuznetsov, M.; Sokolov, M.; Salminen, A. Hybrid laser arc welding of X80 steel: Influence of welding speed and preheating on the microstructure and mechanical properties. Phys. Procedia 2015, 78, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Di, X.J.; Dai, L.S.; Han, J.W.; Yang, X.C.; Cui, S.H.; Li, C.N. Intrinsic control mechanism of impact toughness and fracture toughness in X80 pipeline girth weld with heterogeneous microstructure. Mater. Charact. 2025, 219, 114646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, H.; Nelson, T.W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hard zone in friction stir welded X80 pipeline steel relative to different heat input. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 586, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Di, X.J.; Dai, L.S.; Ma, Y.W.; Han, J.W.; Yang, X.C.; Cui, S.H.; Yu, Y.; Hu, W.Y.; Li, C.N. Correlation between heterogeneous micromechanical properties and fracture toughness in X80 girth weld. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.T.; Gong, B.M.; Chang, Q.; Zhao, Z.F.; Dai, L.S.; Liu, Y. Strain fracture behaviors and crack equivalence of X80 welded joints with non-sharp notches at weld root. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2024, 214, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.A.; Deng, C.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Gong, B.M.; Guo, B.C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, N.; Dai, L.S. Stress state analysis of root notch for X80 girth welds with variable wall thickness and misalignment geometric features. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2023, 206, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Yang, F.L.; Jia, H.D.; Chen, C.C.; Feng, Q.S.; Dai, L.S.; Zhang, Z. Study on the effect of microstructure on toughness dispersion of X70 steel girth weld. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 164, 108671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, C.N.; Dai, L.S.; Yang, X.C.; Han, J.W.; Cui, S.H.; Yang, Z.W.; Di, X.J. Simultaneously enhancing strength and fracture toughness via tailoring the microstructure in X80 girth weld metal. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 3096–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Di, X.J.; Dai, L.S.; Duan, Q.Y.; Han, J.W.; Yang, X.C.; Cui, S.H.; Li, C.N. Effect of grain boundary ferrite morphologies on impact toughness of X80 girth weld. Mater. Lett. 2024, 377, 137412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.M.; Hu, W.T.; Chang, Q.; Zhao, Z.F.; Dai, L.S.; Liu, Y. Transition from ductile to brittle fracture in X80 welded joints with varying notch radii. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2023, 212, 105234. [Google Scholar]
- Verstraete, M.A.; De Waele, W.; Van Minnebruggen, K.; Hertelé, S. Comparison of girth weld tearing resistance obtained from curved wide plate and single edge notch tensile testing. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 148, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pilkey, W.D.; Pilkey, D.F. Peterson’s Stress Concentration Factors; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780470211106. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.W.; Wu, S.P.; Xiang, T.; Gong, B.M.; Deng, C.Y. Coupling effect of post-weld heat treatment and fatigue damage on the hydrogen embrittlement of X80 steel welded joints. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 2646–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.X.; Luo, J.H.; Jia, H.D.; Li, L.F.; Yu, W.C.; Chen, Y.N. Effect of deviation of welding parameters on mechanical properties of X80 steel girth weld. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 3311–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Ding, H.S.; Tong, L.G.; Pan, L.Q. Microstructure and properties of the interlayer heat-affected zone in X80 pipeline girth welds. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Qiao, G.Y.; Shi, X.B.; Xiao, F.R. Effect of stress-relief annealing on the fatigue properties of X80 welded pipes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 807, 140854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Turichin, G.; Kuznetsov, M.; Sokolov, M. Influence of welding parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of X80 steel girth welds. Weld. World 2016, 60, 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Di, X.J.; Dai, L.S.; Han, J.W.; Yang, X.C.; Cui, S.H.; Li, C.N. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of X80 pipeline steel girth welds under different welding conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 805, 139854. [Google Scholar]
- Kocak, M.; Yildiz, T. Effect of notch geometry on the fracture behavior of welded joints in X80 pipeline steel. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 175, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, B.M.; Hu, W.T.; Chang, Q.; Zhao, Z.F.; Dai, L.S.; Liu, Y. Fracture behavior of X80 welded joints with different notch geometries. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 210, 105214. [Google Scholar]
- Hertelé, S.; Verstraete, M.A.; De Waele, W.; Van Minnebruggen, K. Strain distribution and localization in X80 pipeline girth welds under tensile loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 155, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Viloria, A. Microhardness profile and residual stresses evaluation in a shot peened SAE 5160H steel. Rev. UIS Ing. 2024, 23, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Di, X.J.; Dai, L.S.; Han, J.W.; Yang, X.C.; Cui, S.H.; Li, C.N. Tailored welding practices for improved toughness in X80 pipeline girth welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 807, 139876. [Google Scholar]
- Midawi, A. Characterization of local mechanical properties of X80 pipeline girth welds using advanced techniques. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 26–30 September 2016; Volume 3: Operations, Monitoring and Maintenance; Materials and Joining. American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]








| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | Nb | V | Ti | Cu | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.21 | 1.84 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.056 | 0.078 | 0.026 | 0.016 | 0.062 | 0.033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Yan, X.; Xie, S. A Study on Microstructure-Property Relationships and Notch-Sensitive Fracture Behavior of X80 Steel Welds. Processes 2025, 13, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030763
Zou Y, Li L, Zhang S, Yan X, Xie S. A Study on Microstructure-Property Relationships and Notch-Sensitive Fracture Behavior of X80 Steel Welds. Processes. 2025; 13(3):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030763
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yangfan, Lifeng Li, Shuxin Zhang, Xiangzhen Yan, and Shuyi Xie. 2025. "A Study on Microstructure-Property Relationships and Notch-Sensitive Fracture Behavior of X80 Steel Welds" Processes 13, no. 3: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030763
APA StyleZou, Y., Li, L., Zhang, S., Yan, X., & Xie, S. (2025). A Study on Microstructure-Property Relationships and Notch-Sensitive Fracture Behavior of X80 Steel Welds. Processes, 13(3), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030763





