Abstract
GROMACS MD simulations of food proteins and processes are often run over relatively short simulation lengths due to their high computational power demand. As long-timescale simulations are not always feasible, the purpose of this study was to determine, statistically, how simulation time affects conclusions drawn from GROMACS MD studies of food proteins. The Ara h 6 peanut allergen, undergoing heat processing at 300 K, 350 K, 400 K and 450 K, was used as the model in this study, and 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns GROMACS MD simulation lengths were investigated. The statistical analysis performed, using both one-way and two-way ANOVA tests, suggested that, depending on the selected simulation length, different final conclusions may be drawn regarding the effect that thermal processing temperature has on the geometric features of the Ara h 6 allergen. This was observed for many of the geometric features used to characterize the Ara h 6 allergen in this study, including RMSD, Rg, total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds and SASA. An inadequate sample size was, however, identified as a major limitation in this study.
1. Introduction
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are a powerful research tool, applicable in many fields, including but not limited to drug discovery, advanced materials development, and food processing [1,2]. They are computer simulations used to model, over a defined time interval, the physical movements of atoms in a molecule undergoing stress. The capability of MD simulations to model the evolution of molecular structure is particularly well-suited to the study of allergenic food proteins for which molecular conformation plays a crucial role in determining function. Vanga et al. [3], Vagadia et al. [4], Saxena et al. [5], Wang et al. [6], Barazorda-Ccahuana et al. [7], Zhu et al. [8] and Dong, Tian et al. [9] all applied MD simulation to the study of different food proteins undergoing processing treatments. Many MD simulation software packages exist; however, the package well-suited to and most often used for the study of biomolecules is the GROningen Machine for Chemical Simulations (GROMACS) software package [10].
GROMACS MD simulations of proteins undergoing treatment are often limited to relatively short simulation lengths due to their high computational power demand. Saxena et al. [5], Wang et al. [6] and Zhu et al. [8] in their respective studies of the β-lactoglobulin protein in cow’s milk, Act d 2 protein in kiwifruit and avidin protein in egg whites were limited to simulation lengths of 2 ns. In their study of soybean trypsin inhibitor, Vagadia et al. [4] were limited to a simulation length of 5 ns. Dong, Tian et al. [9] in their study of myofibrillar proteins from pale, soft, exudative chicken breast meat were able to attain a simulation length of 30 ns. Meanwhile, Barazorda-Ccahuana et al. [7] were able to attain 200 ns in their study of the Cora a 2 profilin in hazelnuts. High performance computing (HPC) facilities have rendered long-timescale GROMACS MD simulations more attainable by increasing running efficiency through the parallelization of tasks. However, access to HPC clusters and infrastructure, although more accessible nowadays, is still not ubiquitous. As such, there is still an advantage in understanding how results of short-timescale GROMACS MD simulations may compare to equivalent, longer-timescale simulations.
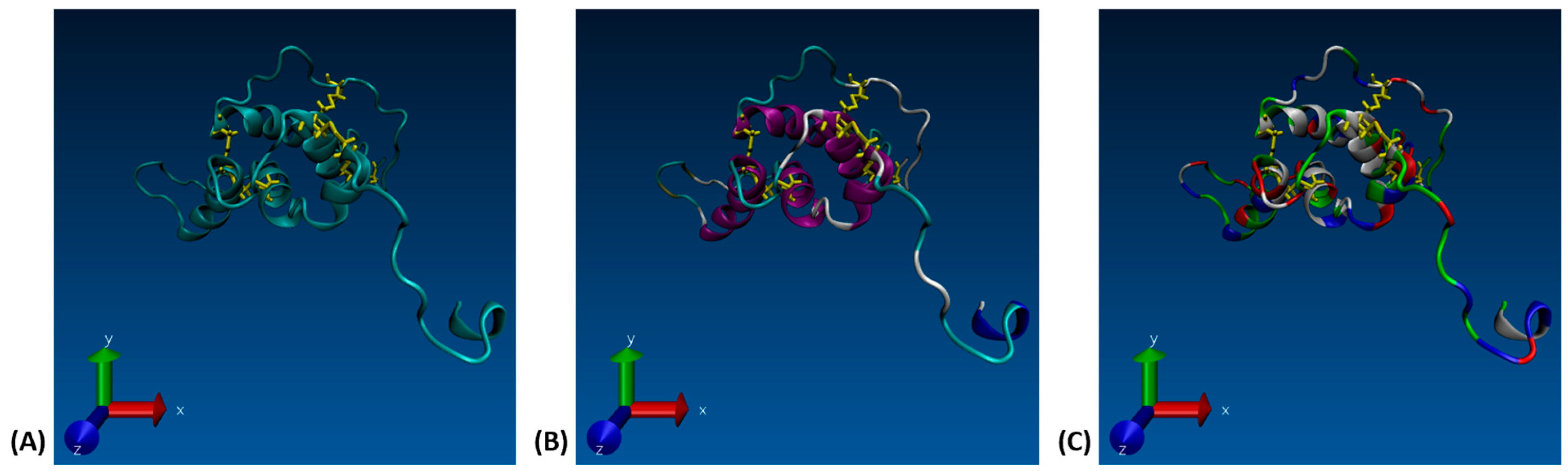
Using GROMACS MD simulation, Vanga et al. [3] studied the impact thermal and electric field treatment have on the Ara h 6 allergen, a 127-residue and 14.98 kDa protein found in peanuts (Arachis hypogaea). Due to computational limitations, Vanga et al. [3] used a 1 ns simulation length in their study. As seen in Figure 1 below, the Ara h 6 allergen possesses a highly stable secondary molecular structure with several α-helices connected by turns and coils [11]. The Ara h 6 protein’s uniquely stable structure and its potential to initiate an allergic response make it an important candidate for MD study. Vanga et al. [3] remark that, in order to better define them, certain effects on the Ara h 6 allergen they observed in their 1 ns GROMACS MD study would need to be further analyzed over a longer simulation length. This present study will attempt to address this point raised by Vanga et al. [3]. The aim of the study will be to quantify the statistical significance of the effect simulation length has on the analysis elements and conclusions drawn from GROMACS MD simulations, modelling the thermal treatment of proteins. The Ara h 6 allergen in peanuts will be used as the model for this study, and three GROMACS MD simulation lengths will be used, namely 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns.
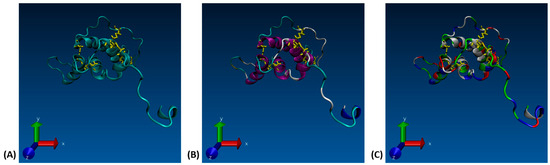
Figure 1.
(A) VMD 3-D structure of the Ara h 6 allergen in peanuts, highlighting the five disulfide bridges (yellow), (B) VMD 3-D structure of the Ara h 6 allergen in peanuts, colored based on the secondary structure, (C) VMD 3-D structure of the Ara h 6 allergen in peanuts, colored based on residue type.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
The Ara h 6 peanut protein’s structure was obtained from the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB) under PDB entry ID 1W2Q [11,12]. ChimeraX visualization program (version 1.6) was used to verify the downloaded Ara h 6 protein’s structure file and, if required, to remove any non-protein residues present in the structure [13,14]. CHARMM-GUI PDB Reader and Manipulator was used to convert the verified Ara h 6 structure file into the correct format, which is suitable for use with CHARMM force-fields [15,16,17,18,19]. GROningen Machine for Chemical Simulations (GROMACS) software package (version 2023.2) was used to perform all molecular dynamics (MD) simulations [10,20,21,22]. The CHARMM36m force-field (updated July 2022) and the CHARM-modified TIP3P water model were selected for use in all simulations [23]. A three-dimensional, cubic simulation box created with periodic boundary conditions was built around the protein, with sides measuring 10.615 nm × 10.615 nm × 10.615 nm. As demanded by the CHARMM36m force-field, the distance between the simulation box edge and the protein was set at 1.2 nm, thus ensuring a minimum distance of 2.4 nm between periodic images of the protein. The boxed Ara h 6 protein was then solvated in water, and the solvated system was neutralized, as 38,267 water molecules and 3 Na+ ions were added to fill the simulation box created around the protein. Energy minimization using the steepest descent algorithm was then performed to remove any poor geometry or steric clashes in the protein structure. A maximum step size of 0.01 nm (emstep) was used, and the assembled system converged to a maximum force of less than 100 kJ mol−1nm−1 (emtol) in 8867 steps. This energy-minimized system served as the starting assembly for all MD replicates performed in this study.
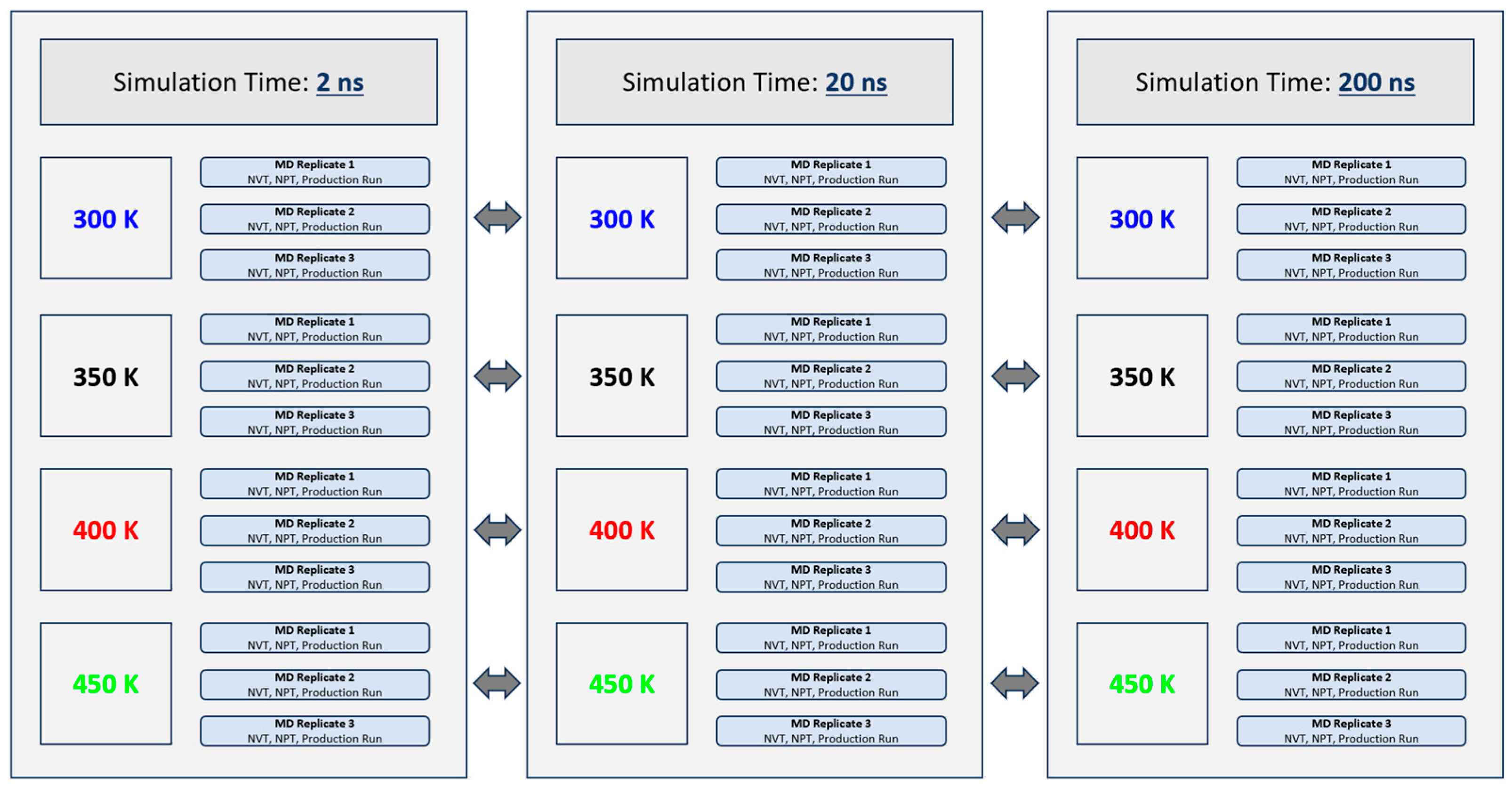
The experimental design of this experiment is illustrated graphically in Figure 2 below. In total, 36 independent GROMACS MD simulations were performed. Three simulation times (2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns) and four thermal treatment temperatures (300 K, 350 K, 400 K and 450 K) were investigated in this study. The aforementioned simulation times and thermal treatment temperatures were selected based on parameters used in similar MD experiments of food proteins performed by other researchers [24]. These selections were made following an extensive review of the literature and to maximize the relevance of the generated data sets within the broader context of this field of study. Simulation times (2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns) were equally selected based on time constraints and computing resources available at the time the experiments were conducted. The higher thermal treatment temperatures (400 K and 450 K) were equally chosen to reflect the thermal conditions industrially processed peanuts may be subjected to during dry roasting [25,26]. Three replicate (triplicate) simulations were performed for each time-temperature combination to allow a better examination of the validity of the results. Each replicate began with a constant-volume constant-temperature equilibration (NVT) of 200 ps. During NVT equilibration, the Ara h 6 protein was position restrained, and the velocity-rescaling temperature coupling was used to hold the system at the desired treatment temperature, either 300 K, 350 K, 400 K or 450 K [27]. A Maxwell–Boltzmann velocity distribution was chosen to randomly generate the initial simulation velocities of the protein’s particles. Following NVT, the system was subjected to a constant-pressure constant-temperature equilibration (NPT) of 200 ps. During NPT equilibration, the protein was position restrained, and the Parinello–Rahman barostat was used to maintain the system pressure at 1 bar [28]. The integration step used for NVT, NPT and the production run was 2 fs. The coupling time constants, tau_t and tau_p, used during NVT, NPT and the production run were set at 0.1 ps and 2.0 ps, respectively. The isothermal compressibility of water was set to 4.5 × 10−5 bar−1. Parameters specified in all .mdp files used during the simulation setup, NVT and NPT equilibration and production runs were selected based on the CHARMM36m force-field requirements for GROMACS. Long-range electrostatic interactions were computed using the smooth Particle Mesh Ewald (PME) method [29]. Cubic interpolation and a Fourier grid spacing of 0.12 nm were used for PME. Short-range electrostatic and Van der Waals interactions were cut off at a distance of 1.2 nm. Finally, the bonds of the protein were constrained using the LINear Constraint Solver (LINCS) algorithm [30].
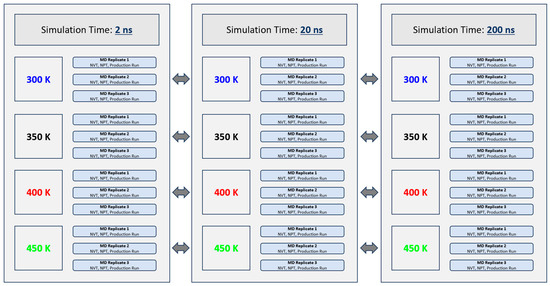
Figure 2.
The experimental design established to evaluate the effect of GROMACS MD simulation length on conclusions drawn regarding the effect of thermal treatment on the Ara h 6 allergen in peanuts (Arachis hypogaea).
2.2. Analysis of Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
The output trajectories were processed using the GROMACS trajectory converter (gmx trjconv) to remove the imposed periodic boundary conditions and isolate the Ara h 6 protein from the solvent. VMD version 1.9.3 molecular visualization software was used to verify and visualize the converted trajectories [31]. GROMACS analysis tools were used to evaluate root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) (gmx rms), root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF) (gmx rmsf), radius of gyration (Rg) (gmx gyrate), hydrogen bonds (gmx hbond) and solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) (gmx sasa). The XMGRACE version 5.1.25 graphing software was used to generate graphs for all simulations [32]. Secondary structure analysis of all MD trajectories was performed using the STRIDE algorithm, an element of the VMD (version 1.9.3) plugin TIMELINE [33].
To establish statistical significance, the data obtained were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-way ANOVA using the IBM SPSS Statistics software platform, version 29.0.1.1. A significance level of 0.05 (p < 0.05) was used throughout. The one-way ANOVA test was used, within the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns groups, to establish the relationship between temperature and the various analysis elements (RMSD, Rg, hydrogen bonds and SASA). The two-way ANOVA test was then used to determine the combined effect that both independent variables studied, simulation time and temperature, have on the analysis elements (RMSD, Rg, hydrogen bonds and SASA). Assumptions in one-way and two-way ANOVA were validated using the Shapiro–Wilk test of normality and Levene test for homogeneity of variances [34,35]. To validate for the absence of spurious outliers in the data, stem-and-leaf plots were analyzed for isolated values at the ends. For the one-way ANOVA test, if the Levene test for homogeneity of variances revealed the presence of unequal variances, the Brown–Forsythe robust test of equality of means was used in lieu of the ANOVA results, along with Tamhane’s T2 post hoc test. However, if the Levene test proved equal variances, a one-way ANOVA post hoc analysis to determine which groups differed significantly was performed using Tukey’s HSD (honestly significant difference) multiple comparison test. Post hoc tests were only performed if the one-way ANOVA tests revealed a significant result. For the two-way ANOVA test, if a significant interaction effect was observed between the independent variables, Bonferroni’s test for multiple comparisons was used to evaluate simple main effects. For the two-way ANOVA, if a significant main effect was observed without a significant interaction effect, pairwise comparison was performed using Tukey’s HSD test.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Secondary Structure Analysis
At 300 K (Figure A1) and 350 K (Figure A2), replicate VMD TIMELINE graphs, generated over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulation lengths, predicted largely similar secondary structures for the Ara h 6 allergen. In the replicates performed at 300 K and 350 K, the α-helices, colored in pink, were predicted in the same locations relatively consistently, regardless of simulation length. The only noteworthy difference, observed in all three of the 300 K replicates, was that the 2 ns simulations seemed to overestimate the number of turns, colored in teal, present in the Gly1–Cys16 and Arg112–Gly124 regions of the Ara h 6 allergen’s structure, relative to the 200 ns simulations. All three 300 K replicates at a 20 ns simulation length also overestimated, relative to the 200 ns simulation, the number of turns present in the Arg112–Gly124 region, but not in the Gly1–Cys16 region. These regions of interest at 300 K are marked in Figure A1 with red boxes. The overestimation of turns in these regions was not observed in the replicate 2 ns or 20 ns simulations at 350 K, as the proportion of turns predicted in the Ara h 6 protein’s structure at 350 K seemed more proportionate among the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulations.
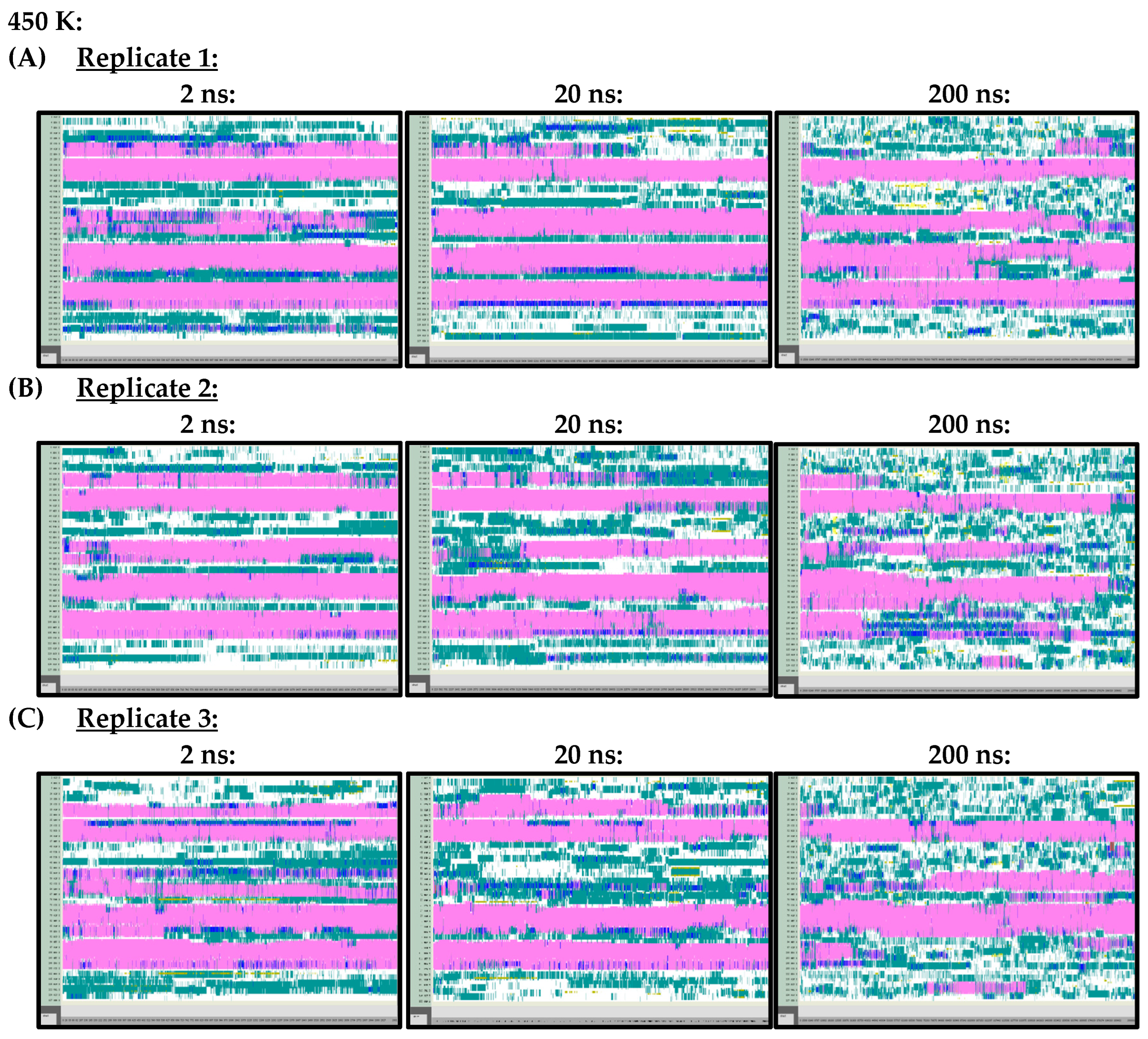
Arguably, however, the most important difference observed in the secondary structures of the Ara h 6 allergen, predicted by the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulations and analyzed using VMD TIMELINE, arose at the higher treatment temperatures of 400 K and 450 K. At 400 K (Figure A3) and 450 K (Figure A4), it can be seen that the 2 ns and 20 ns simulations tended to predict fewer changes in the α-helix structures of the Ara h 6 allergen relative to the 200 ns simulations. In the replicates performed at 400 K and 450 K, the 200 ns simulations were visibly more sensitive in detecting fluctuations that occurred in the α-helix structures of the Ara h 6 allergen.
3.2. Root-Mean-Square Deviation (RMSD)
3.2.1. One-Way ANOVA
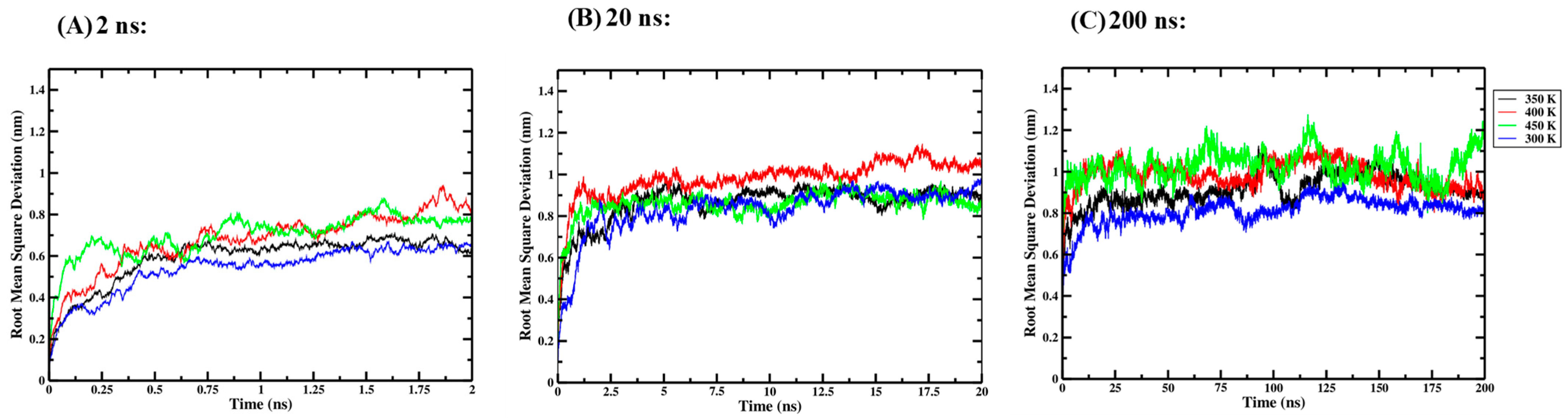
Three independent one-way ANOVA tests were performed for the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulation lengths to compare the effect of thermal processing temperature on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen. RMSD data collected for the four thermal processing treatments using 2 ns (A), 20 ns (B) and 200 ns (C) simulation lengths are presented graphically in Figure 3. The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests are presented in Table 1.
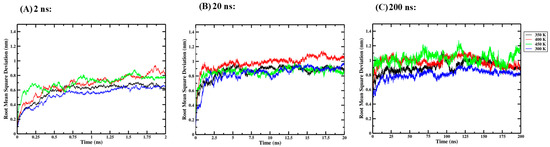
Figure 3.
Average root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) of triplicate GROMACS MD simulations of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal processing at 300, 350, 400 or 450 K: (A) 2 ns, (B) 20 ns, (C) 200 ns.

Table 1.
One-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of processing temperature on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns GROMACS MD simulations.
For the 2 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA revealed that there was no significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 3.365, p = 0.075]. For the 20 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA also indicated no significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 0.698, p = 0.579]. However, the one-way ANOVA performed for the 200 ns simulation length revealed that there was a statistically significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 20.211, p < 0.001]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.037, 95% C.I. = [−0.197, −0.006]), between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.002, 95% C.I. = [−0.268, −0.078]), between 300 K and 450 K (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [−0.312, −0.121]), and between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.020, 95% C.I. = [−0.210, −0.020]). The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests explored here suggest that different final conclusions may be drawn regarding the effect that thermal processing temperature has on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen, depending on the GROMACS MD simulation length used.
It is important to highlight that in the data collected using the 200 ns simulation length, the normality assumption required by the one-way ANOVA was violated in one instance, as a significant Shapiro–Wilk test of normality at 350 K (p = 0.017) was observed. As the one-way ANOVA is generally considered robust to violations of normality, this minor assumption violation likely does not affect the reliability of the analysis performed. In future studies, however, a larger sample size, greater than three replicates, is recommended to reduce the risk of having non-normal data.
3.2.2. Two-Way ANOVA
A two-way ANOVA was also performed to evaluate the effects of simulation time and thermal processing temperature on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen. Results of the two-way ANOVA are summarized in Table 2 and indicate a significant main effect of simulation time [F(2, 24) = 38.059, p < 0.001, partial η2 = 0.760], a significant main effect of processing temperature [F(3, 24) = 5.297, p = 0.006, partial η2 = 0.398], but no significant interaction between simulation time and processing temperature [F(6, 24) = 0.727, p = 0.632, partial η2 = 0.154]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 2 ns and 20 ns (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [−0.349, −0.161]) and between 2 ns and 200 ns (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [−0.399, −0.211]). There was, however, no statistically significant difference found between 20 ns and 200 ns (p = 0.392). This result suggests that simulations carried out over 2 ns predicted RMSD values of the Ara h 6 protein that differed significantly from those predicted by simulations carried out over 20 ns and 200 ns.

Table 2.
Two-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of GROMACS MD simulation time (2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns) and processing temperature (300 K, 350 K, 400 K and 450 K) on the RMSD of the Ara h 6 allergen.
Two assumptions required for the two-way ANOVA were violated in this analysis. First, a spurious outlier was identified in the 20 ns simulation group. An attempt to remove the outlier was made; however, following the removal of the outlier, other spurious outliers emerged in the data. As the sample size was already small, with only three replicates, removing data points seemed imprudent; therefore, the outlier was retained. Second, the Levene test for equality of variances, based on the mean, failed (p = 0.011), suggesting heteroskedasticity within the collective dataset. As equal sample sizes were used in each group, a slight departure of the Levene test may be tolerable within this analysis. Ideally, the nonparametric Friedman’s test would have been applied in this scenario, given the heteroskedasticity identified in the data. However, as the sample size in this study was less than the minimum of five samples required in each group for the Friedman’s test, it could not be used. This highlights an important weakness of this study and emphasizes the need for a greater number of replicates in future studies.
3.3. Root-Mean-Square Fluctuation (RMSF)
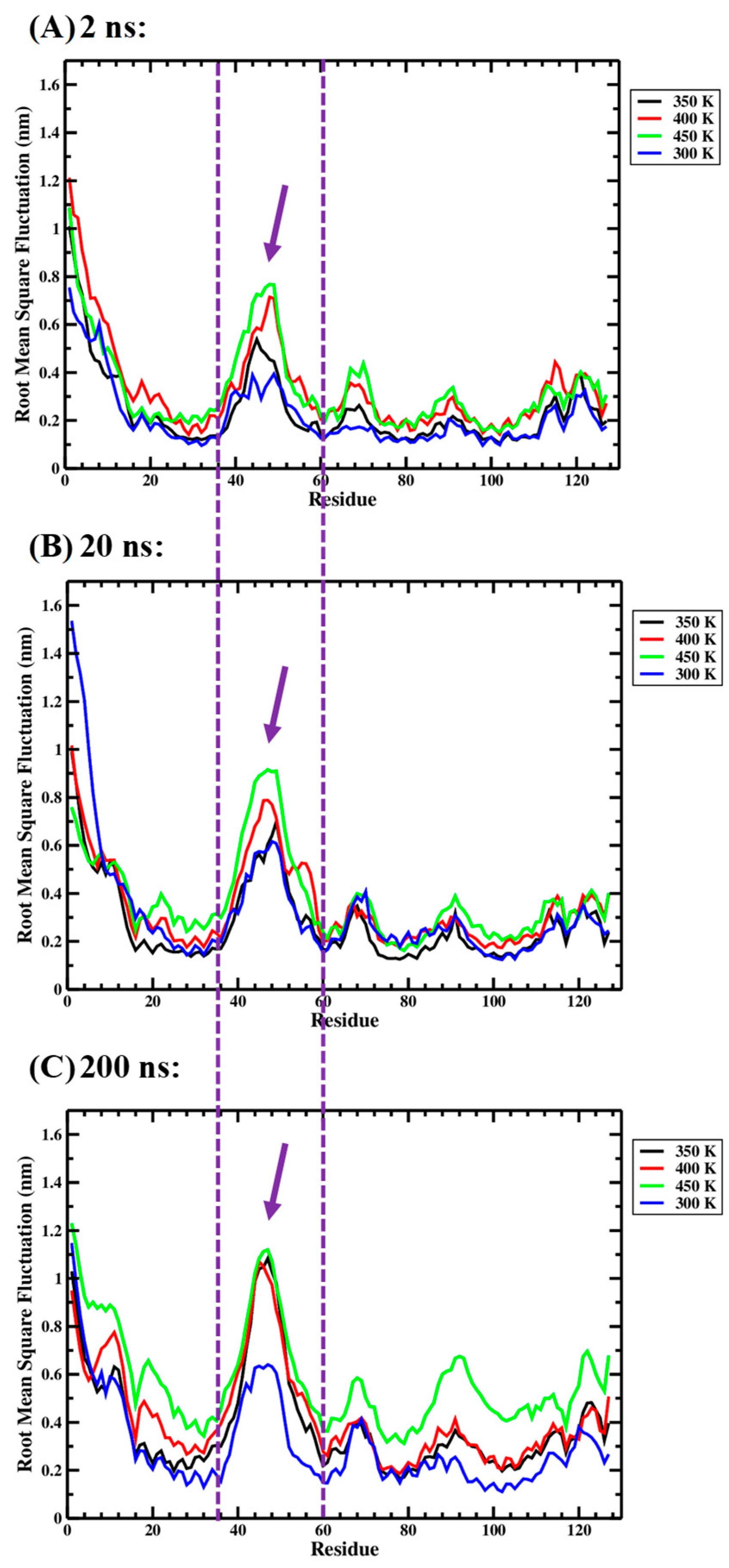
Figure 4 allows a visual comparison of the root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF) values obtained for the 127 residues of the Ara h 6 allergen over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns GROMACS MD simulation lengths. In Figure 4, it is observed that the sequences over which RMSF peaks develop are largely the same, regardless of simulation length. For all three simulation lengths, the maximum RMSF peak develops over the same residues, Ile36–Cys60. The Ile36–Cys60 residues, over which the peak develops, are delineated by two parallel dashed purple lines in Figure 4. Furthermore, for all three simulation lengths, for the most part, the 450 K curve (green) is located above the 400 K curve (red), which, in turn, is above the 350 K curve (black), which, itself, is above the 300 K curve (blue). This observation suggests that, regardless of simulation length, the RMSF values of the Ara h 6 residues generally trend upwards as the processing temperature rises from 300 K through to 450 K.
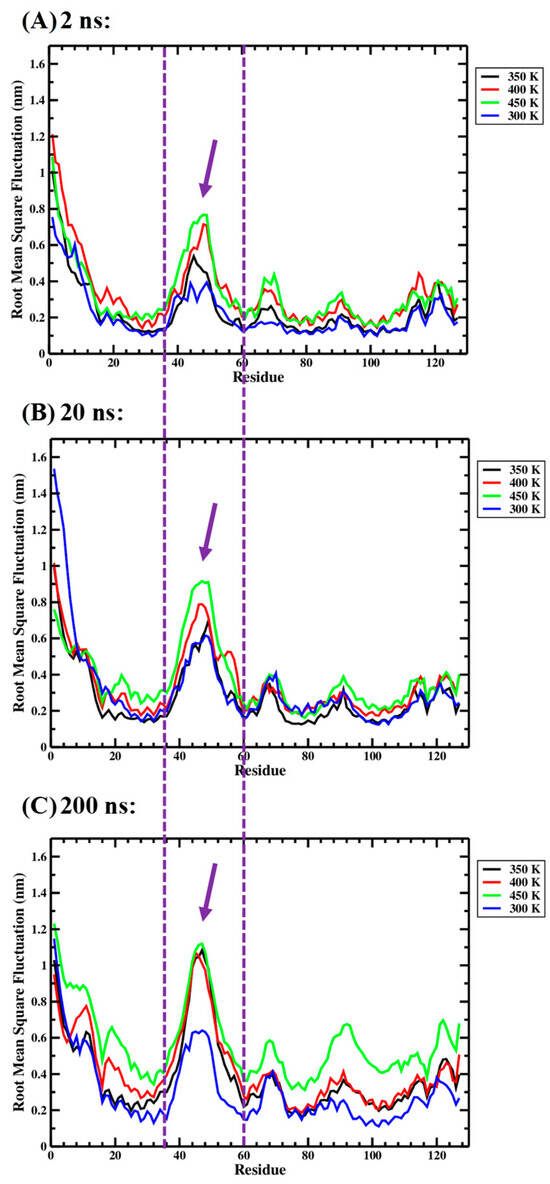
Figure 4.
Average root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF), on a per-residue (amino acid) basis, of triplicate GROMACS MD simulations of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal processing at 300, 350, 400 or 450 K: (A) 2 ns, (B) 20 ns, (C) 200 ns.
An important difference observed in the RMSF data presented for the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulations in Figure 4 is the magnitude to which the RMSF peaks rise. The RMSF of the Ile48 residue at 450 K (green curve) can be used to illustrate this point. In Figure 4, the locations of the Ile48 RMSF peaks in the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulations are identified by purple arrows. The approximate peak RMSF values reached by the Ile48 residue in the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulations were 0.8 nm, 0.9 nm and 1.1 nm, respectively. The higher magnitude peak RMSF values, predicted in the 200 ns long-timescale simulations, may suggest that there is an overall underestimation of RMSF in shorter timescale simulations performed over 2 ns or 20 ns.
3.4. Radius of Gyration (Rg)
3.4.1. One-Way ANOVA
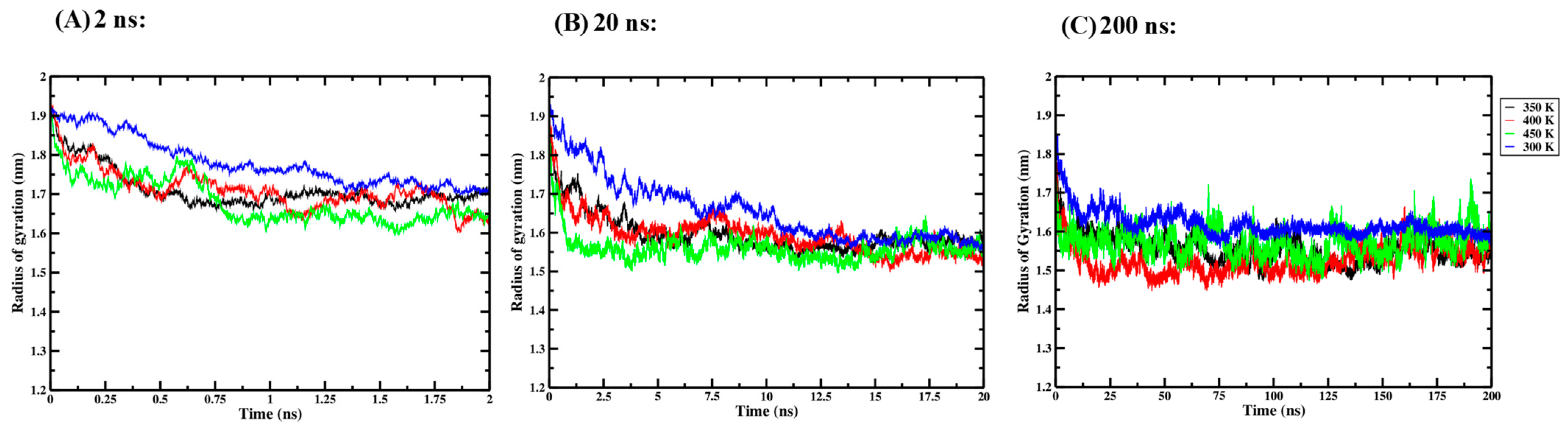
Three independent one-way ANOVA tests were performed for the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulation times to compare the effect of thermal processing temperature on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen. Rg data collected for the four thermal processing treatments, using 2 ns (A), 20 ns (B) and 200 ns (C) simulation lengths, are presented graphically in Figure 5. The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests are presented in Table 3.
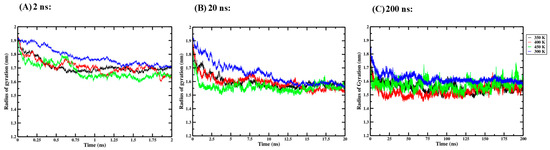
Figure 5.
Average radius of gyration (Rg) of triplicate GROMACS MD simulations of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal processing at 300, 350, 400 or 450 K: (A) 2 ns, (B) 20 ns, (C) 200 ns.

Table 3.
One-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of processing temperature on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns GROMACS MD simulations.
For the 2 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA revealed that there was a significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 6.935, p = 0.013]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 300 K and 450 K (p = 0.010, 95% C.I. = [0.027, 0.171]). There was no statistically significant difference between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.059), between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.061), between 350 K and 400 K (p = 1.000), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.585) or between 400 K and 450 K (p = 0.576). For the 20 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA revealed that there was no significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 3.026, p = 0.094]. For the 200 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA revealed that there was a significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 4.479, p = 0.040]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of the average Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.030, 95% C.I. = [0.009, 0.175]). There was no statistically significant difference between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.137), between 300 K and 450 K (p = 0.313), between 350 K and 400 K (p = 0.710), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.922), and between 400 K and 450 K (p = 0.381). The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests explored here suggest that different final conclusions may be drawn as to the effect that thermal processing temperature has on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen, depending on the GROMACS MD simulation length used. The assumptions required by the one-way ANOVA test were validated, and no violations were noted in any of the three one-way ANOVA tests performed.
3.4.2. Two-Way ANOVA
A two-way ANOVA was also performed to evaluate the effects of simulation time and thermal processing temperature on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen. The results of the two-way ANOVA are summarized in Table 4 and indicate a significant main effect for simulation time [F(2, 24) = 69.740, p < 0.001, partial η2 = 0.853], a significant main effect for processing temperature [F(3, 24) = 11.277, p < 0.001, partial η2 = 0.585], and no significant interaction between simulation time and processing temperature [F(6, 24) = 0.900, p = 0.511, partial η2 = 0.184]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 2 ns and 20 ns (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [0.085, 0.153]) and between 2 ns and 200 ns (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [0.119, 0.187]). There was, however, no statistically significant difference found between 20 ns and 200 ns (p = 0.053). This result suggests that simulations carried out over 2 ns predicted Rg values of the Ara h 6 protein that differed significantly from those predicted by simulations carried out over 20 ns and 200 ns. Assumptions required by the two-way ANOVA test were verified. No outliers were identified; all Shapiro–Wilk tests of normality passed, and all Levene tests of equality of variances passed. This suggests that the two-way ANOVA results obtained and analyzed above are reliable.

Table 4.
Two-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of GROMACS MD simulation length (2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns) and processing temperature (300 K, 350 K, 400 K and 450 K) on the Rg of the Ara h 6 allergen.
3.5. Intra-Peptide Hydrogen Bonds
3.5.1. One-Way ANOVA
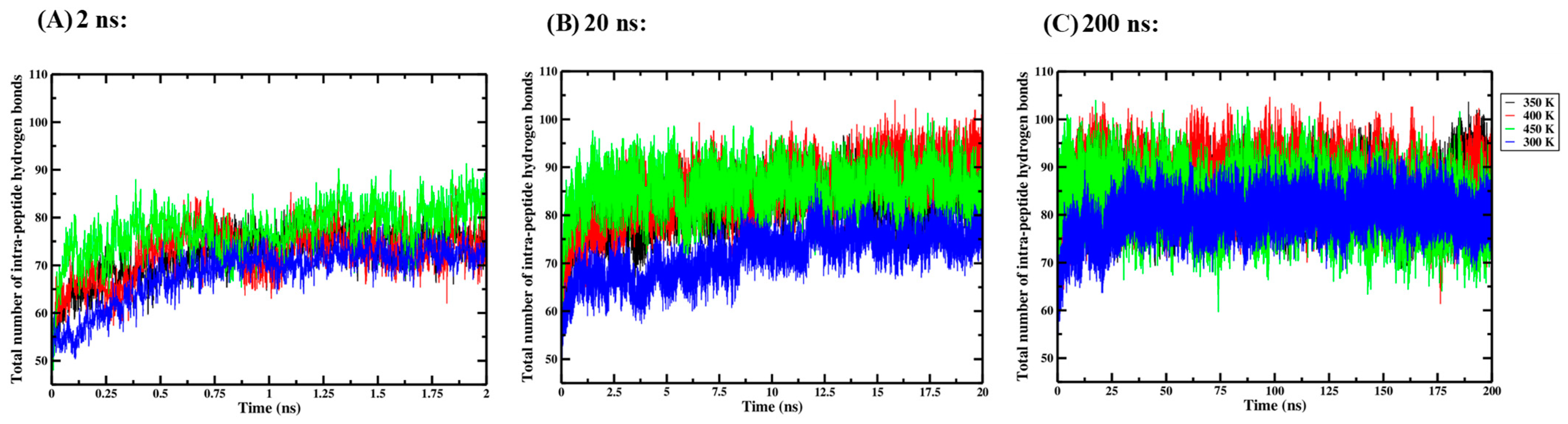
Three independent one-way ANOVA tests were performed for the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulation times to compare the effect of thermal processing temperature on the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen. Intra-peptide hydrogen bond data collected for the four thermal processing treatments using 2 ns (A), 20 ns (B) and 200 ns (C) simulation lengths are presented graphically in Figure 6. The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests are presented in Table 5.
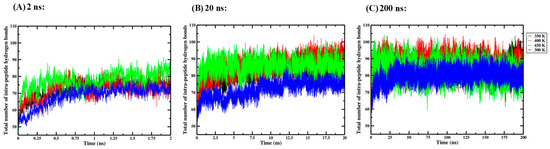
Figure 6.
Average total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in triplicate GROMACS MD simulations of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal processing at 300, 350, 400 or 450 K: (A) 2 ns, (B) 20 ns, (C) 200 ns.

Table 5.
One-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of processing temperature on the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns GROMACS MD simulations.
For the 2 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA revealed that there was a significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 21.928, p < 0.001]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value for the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.037, 95% C.I. = [−7.369, −0.246]), between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.030, 95% C.I. = [−7.516, −0.394]), between 300 K and 450 K (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [−12.538, −5.416]), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.007, 95% C.I. = [−8.730, −1.608]) and between 400 K and 450 K (p = 0.008, 95% C.I. = [−8.583, −1.461]). There was no statistically significant difference between 350 K and 400 K (p = 0.999). For the 20 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA revealed that there was a significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 10.164, p = 0.004]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value for the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.035, 95% C.I. = [−19.134, −0.735]), between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.006, 95% C.I. = [−22.892, −4.493]) and between 300 K and 450 K (p = 0.006, 95% C.I. = [−22.931, −4.532]). There was no statistically significant difference between 350 K and 400 K (p = 0.583), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.576) and between 400 K and 450 K (p = 1.000). However, for the 200 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA revealed that there was no significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 3.327, p = 0.077]. The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests explored here suggest that different final conclusions may be drawn regarding the effect that thermal processing temperature has on the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen, depending on the GROMACS MD simulation length used.
Two failed Shapiro–Wilk tests of normality were identified in the 200 ns simulations at 400 K (p = 0.028) and 450 K (p = 0.002). As the one-way ANOVA is generally considered robust to violations of normality, this minor assumption violation likely does not affect the reliability of the analysis performed.
3.5.2. Two-Way ANOVA
A two-way ANOVA was also performed to evaluate the effects of simulation time and thermal processing temperature on the number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen. Results of the two-way ANOVA are summarized in Table 6 and indicate a significant main effect of simulation time [F(2, 24) = 57.174, p < 0.001, partial η2 = 0.827], a significant main effect for processing temperature [F(3, 24) = 20.109, p < 0.001, partial η2 = 0.715] and a significant interaction between simulation time and processing temperature [F(6, 24) = 3.711, p = 0.009, partial η2 = 0.481]. The Bonferroni test for multiple comparisons was used to evaluate simple main effects. For the 2 ns simulation length, there was a significant difference in the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen between 300 K and 450 K (p = 0.002, 95% C.I. = [−15.093, −2.861]) and no significant difference between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.517), between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.452), between 350 K and 400 K (p = 1.000), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.138) and between 400 K and 450 K (p = 0.160). For the 20 ns simulation length, there was a significant difference in the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen between 300 K and 350 K (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [−16.051, −3.819]), between 300 K and 400 K (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [−19.808, −7.576]) and between 300 K and 450 K (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [−19.847, −7.615]) and no significant difference between 350 K and 400 K (p = 0.540), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.522) and between 400 K and 450 K (p = 1.000). For the 200 ns simulation length, there was a significant difference in the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.045, 95% C.I. = [−12.331, −0.099]) but no significant difference between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.368), between 300 K and 450 K (p = 1.000), between 350 K and 400 K (p = 1.000), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 1.000) or between 400 K and 450 K (p = 0.739). These results suggest that simulations carried out over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns may detect statistically significant differences in the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen across different processing temperature groups.

Table 6.
Two-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of GROMACS MD simulation length (2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns) and processing temperature (300 K, 350 K, 400 K and 450 K) on the total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds in the Ara h 6 allergen.
One assumption required by the two-way ANOVA was violated in this analysis. The Levene test for equality of variances, based on the mean, failed (p = 0.008), suggesting heteroskedasticity within the collective dataset. As equal sample sizes were used in each group, a slight departure of the Levene test may be tolerable within this analysis.
3.6. Solvent Accessible Surface Area (SASA)
3.6.1. One-Way ANOVA
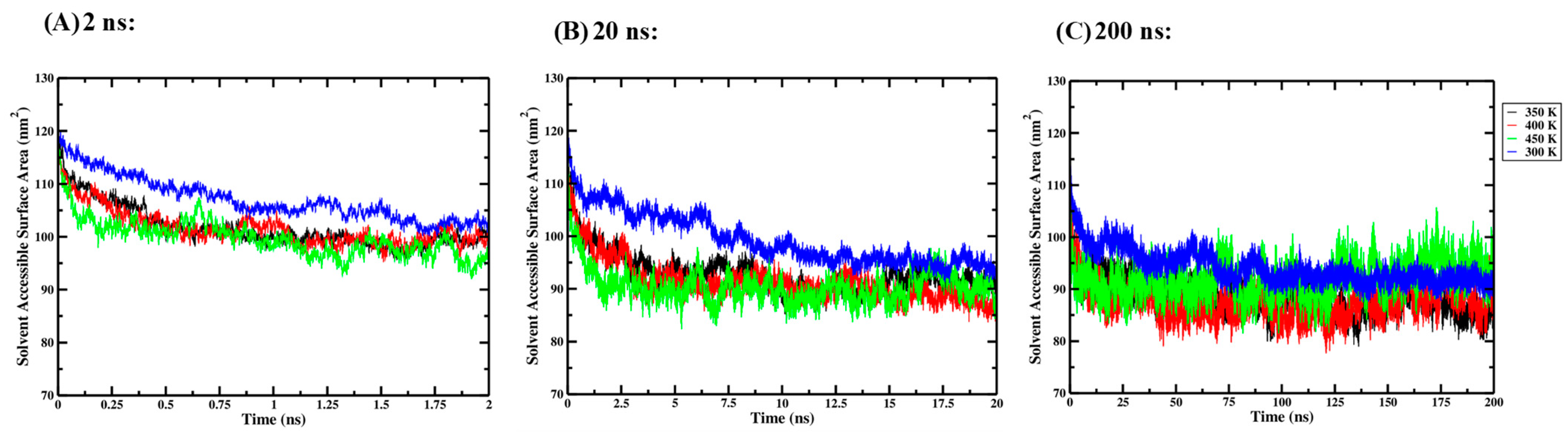
Three independent one-way ANOVA tests were performed for the 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns simulation times to compare the effect of thermal processing temperature on the solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) of the Ara h 6 allergen. SASA data collected for the four thermal processing treatments using 2 ns (A), 20 ns (B) and 200 ns (C) simulation lengths are presented graphically in Figure 7. The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests are presented in Table 7.
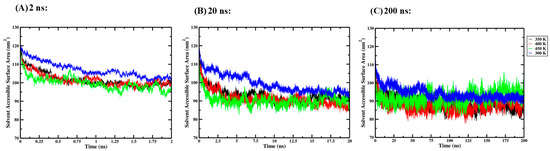
Figure 7.
Average solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) of triplicate GROMACS MD simulations of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal processing at 300, 350, 400 or 450 K: (A) 2 ns, (B) 20 ns, (C) 200 ns.

Table 7.
One-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of processing temperature on the SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns GROMACS MD simulations.
For the 2 ns simulation length, the Levene test failed (p = 0.009), and, as such, the one-way ANOVA results obtained were invalid. The robust Brown–Forsythe test for equality of means was used in place of the one-way ANOVA and indicated that there was no significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen (p = 0.128). For the 20 ns simulation length, the Levene test passed, and, therefore, one-way ANOVA was used. The one-way ANOVA revealed that there was a significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 6.611, p = 0.015]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.028, 95% C.I. = [0.901, 15.195]) and between 300 K and 450 K (p = 0.016, 95% C.I. = [1.843, 16.136]). There was no statistically significant difference between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.073), between 350 K and 400 K (p = 0.905), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.703) and between 400 K and 450 K (p = 0.973). The Shapiro–Wilk test of normality failed (p = 0.030) at 300 K for the 20 ns simulation length. As the one-way ANOVA is generally considered robust to violations of normality, this minor assumption violation likely does not affect the reliability of the analysis performed, and the above analysis should be retained. Finally, for the 200 ns simulation length, the one-way ANOVA indicated that there was a significant effect of thermal processing temperature on the SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen [F(3, 8) = 9.169, p = 0.006]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 300 K and 350 K (p = 0.018, 95% C.I. = [1.032, 10.208]) and between 300 K and 400 K (p = 0.007, 95% C.I. = [2.117, 11.292]). There was no statistically significant difference between 300 K and 450 K (p = 0.412), between 350 K and 400 K (p = 0.871), between 350 K and 450 K (p = 0.181), or between 400 K and 450 K (p = 0.063). The results of the three independent one-way ANOVA tests explored here suggest that different final conclusions may be drawn as to the effect that thermal processing temperature has on the SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen, depending on the GROMACS MD simulation length used.
3.6.2. Two-Way ANOVA
A two-way ANOVA was also performed to evaluate the effects of simulation time and processing temperature on the SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen. Results of the two-way ANOVA are summarized in Table 8 and indicate a significant main effect for simulation time [F(2, 24) = 86.040, p < 0.001, partial η2 = 0.878], a significant main effect for processing temperature [F(3, 24) = 16.430, p < 0.001, partial η2 = 0.673] and no significant interaction between simulation time and processing temperature [F(6, 24) = 1.642, p = 0.179, partial η2 = 0.291]. Tukey’s HSD test for multiple comparisons found that the mean value of SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen was significantly different between 2 ns and 20 ns (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [6.615, 11.375]), between 2 ns and 200 ns (p < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [9.636, 14.396]) and between 20 ns and 200 ns (p = 0.011, 95% C.I. = [0.641, 5.401]). This result suggests that simulations carried out over 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns predicted SASA values of the Ara h 6 protein that differed significantly.

Table 8.
Two-way ANOVA statistical analysis of the effect of GROMACS MD simulation length (2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns) and processing temperature (300 K, 350 K, 400 K and 450 K) on SASA of the Ara h 6 allergen.
Two assumptions required by the two-way ANOVA test were violated in this analysis. First, two spurious outliers were identified, based on temperature, in the 450 K group. Given the already small sample size, these outliers were retained for this analysis. Second, the Levene test for equality of variances, based on the mean, failed (p = 0.007), suggesting heteroskedasticity within the collective data set. As equal sample sizes were used in each group, a slight departure of the Levene test may be tolerable within this analysis.
4. Conclusions
GROMACS MD simulations are an important research tool in the study of food proteins and processes. However, their high computational power demand represents an important obstacle to their broader application within this field. Computational power limitations often restrict the simulation times that can be achieved in these studies. Understanding how simulation time, otherwise referred to as simulation length, may affect the conclusions one draws from a GROMACS MD study is crucial in order to establish the most appropriate study methodology. For this reason, the aim of this study was to explore, statistically, the effect that GROMACS MD simulation length may have on conclusions drawn from these studies. The Ara h 6 peanut allergen, subject to thermal processing at temperatures of 300 K, 350 K, 400 K and 450 K, was used as the model in this study, and 2 ns, 20 ns and 200 ns GROMACS MD simulation lengths were explored. A thorough statistical analysis of the data was performed, combining the one-way ANOVA test and the two-way ANOVA test.
From this analysis, it was repeatedly observed that, depending on the GROMACS simulation length chosen, different final conclusions may be drawn as to the effect that thermal processing temperature has on the geometric features of the Ara h 6 allergen. This held true for many of the geometric features used to characterize the Ara h 6 allergen in this study, including RMSD, Rg, total number of intra-peptide hydrogen bonds and SASA. This suggests that, in order to ascertain the true effect of any treatment, short-timescale GROMACS MD simulations should be compared to long-timescale GROMACS MD simulations, and long-timescale GROMACS MD simulations should be confirmed by targeted experimental work. Certain characteristics observed only in long-timescale simulations may be overlooked if only short-timescale simulations are performed, and vice-versa. Ever-improving access to high-power computational resources has proven that the realization and analysis of long-timescale MD simulations of complex and high molecular weight food proteins can be attained. Future research in this field should continue to focus on extending simulation lengths, to multiple times longer than the 200 ns simulations performed in this study. Food protein simulations of 1,000 ns and beyond are readily attainable with the resources available today and must continue to be explored.
This study provides some new insight but also presents important limitations that must not be disregarded. Assumptions of the one-way and two-way ANOVA tests used in the statistical analyses performed were, on many occasions, violated. Although these tests are generally considered robust to assumption violations, the reliability of the results obtained is not definite. In future studies, a larger sample size, meaning more replicates, should be favored to improve the power of the study and allow better handling of assumption violations through the application of non-parametric statistical tests. Furthermore, to validate that the conclusions drawn in this study, which focused solely on the Ara h 6 peanut protein, are valid more generally, an array of other food proteins with diverse chemical and physical characteristics should be examined using a similar methodology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. and V.R.; methodology, A.S.; software, A.S.; validation, A.S.; formal analysis, A.S.; data curation, A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S. and V.R.; visualization, A.S.; supervision, V.R.; project administration, V.R.; funding acquisition, V.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) [RGPIN-2014-04190] for the research program conducted by the Department of Bioresource Engineering.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Figure A1.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 300 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
Figure A1.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 300 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
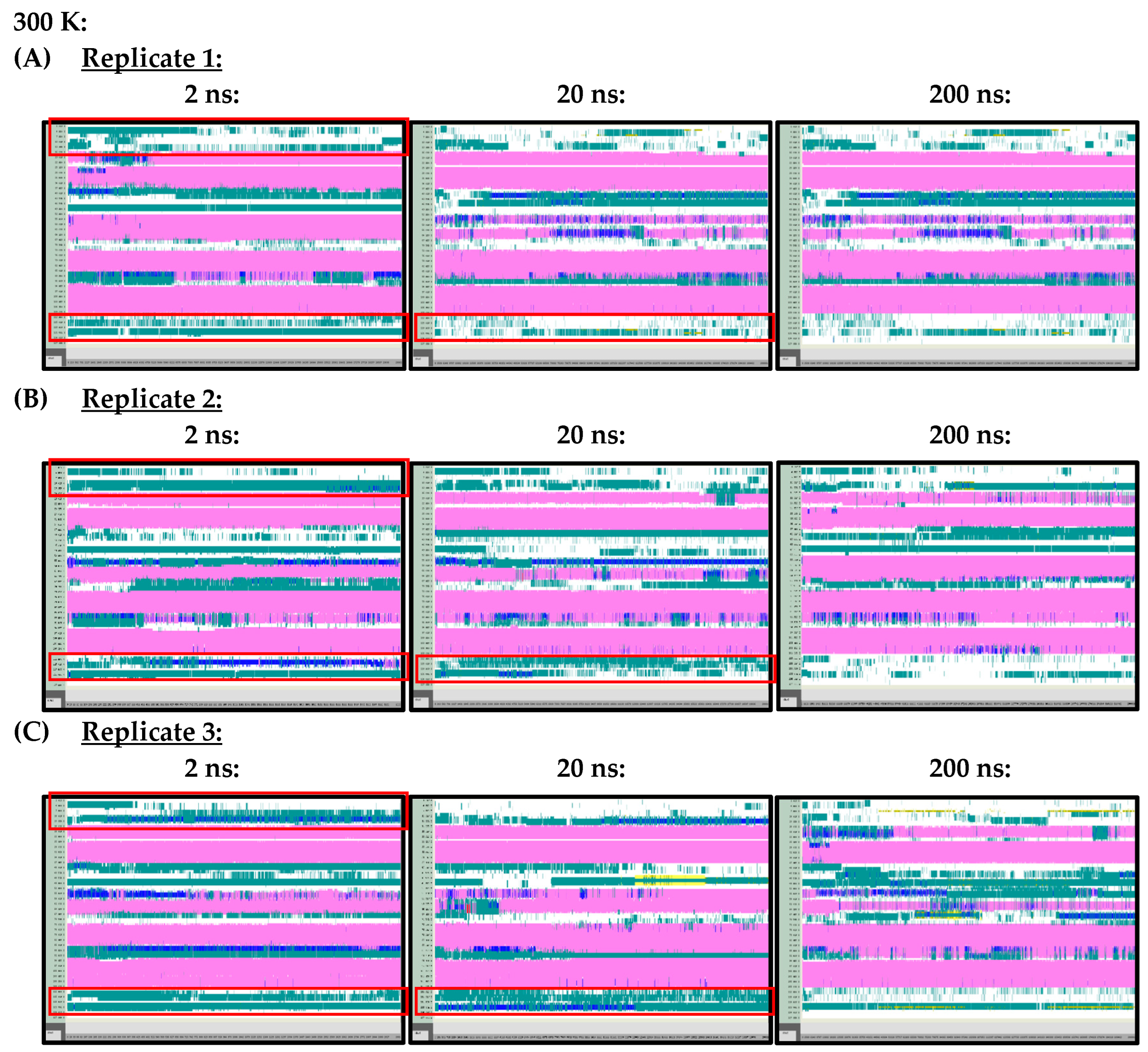

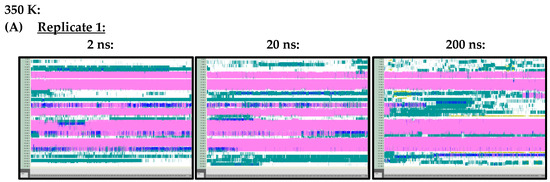
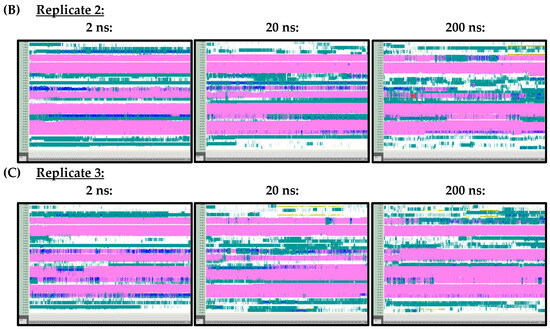
Figure A2.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 350 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
Figure A2.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 350 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
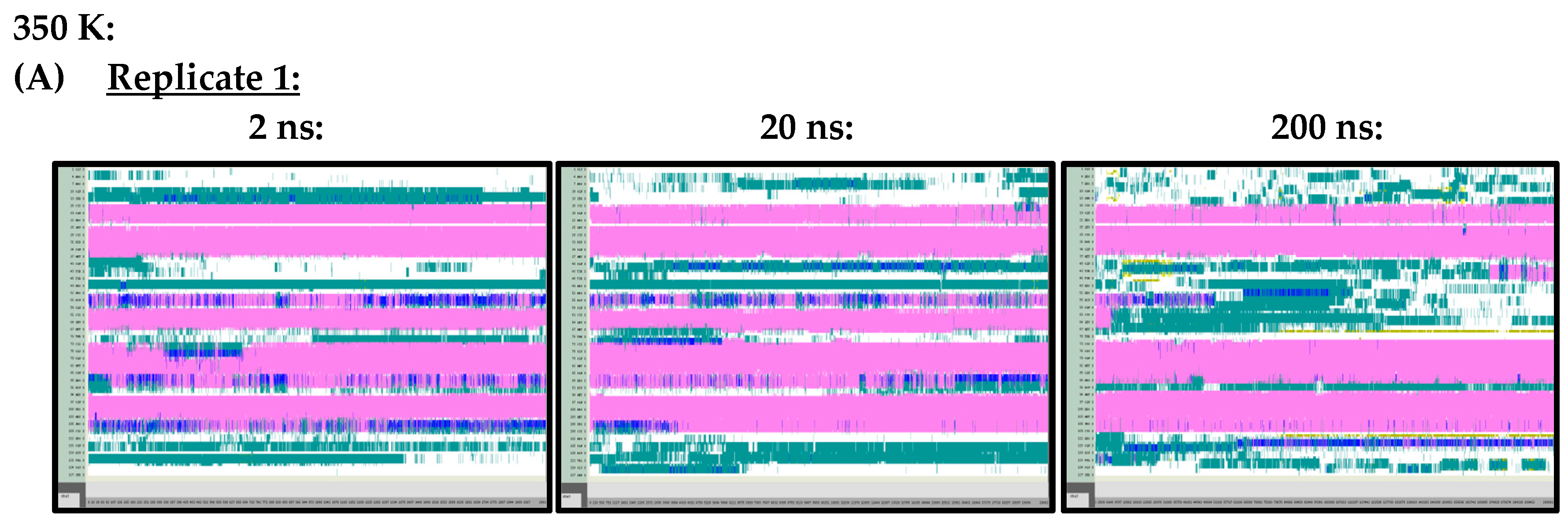
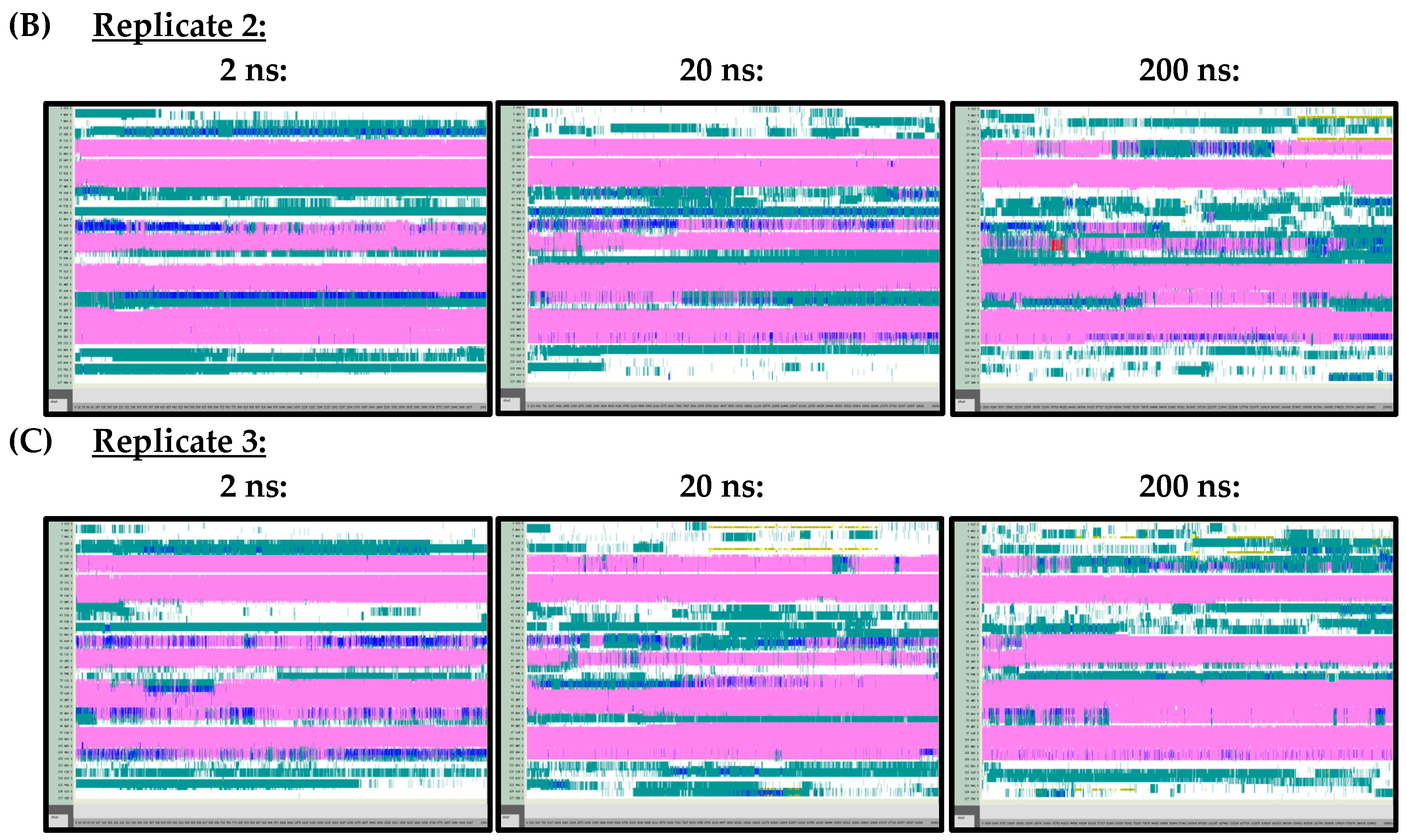
Figure A3.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 400 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
Figure A3.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 400 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
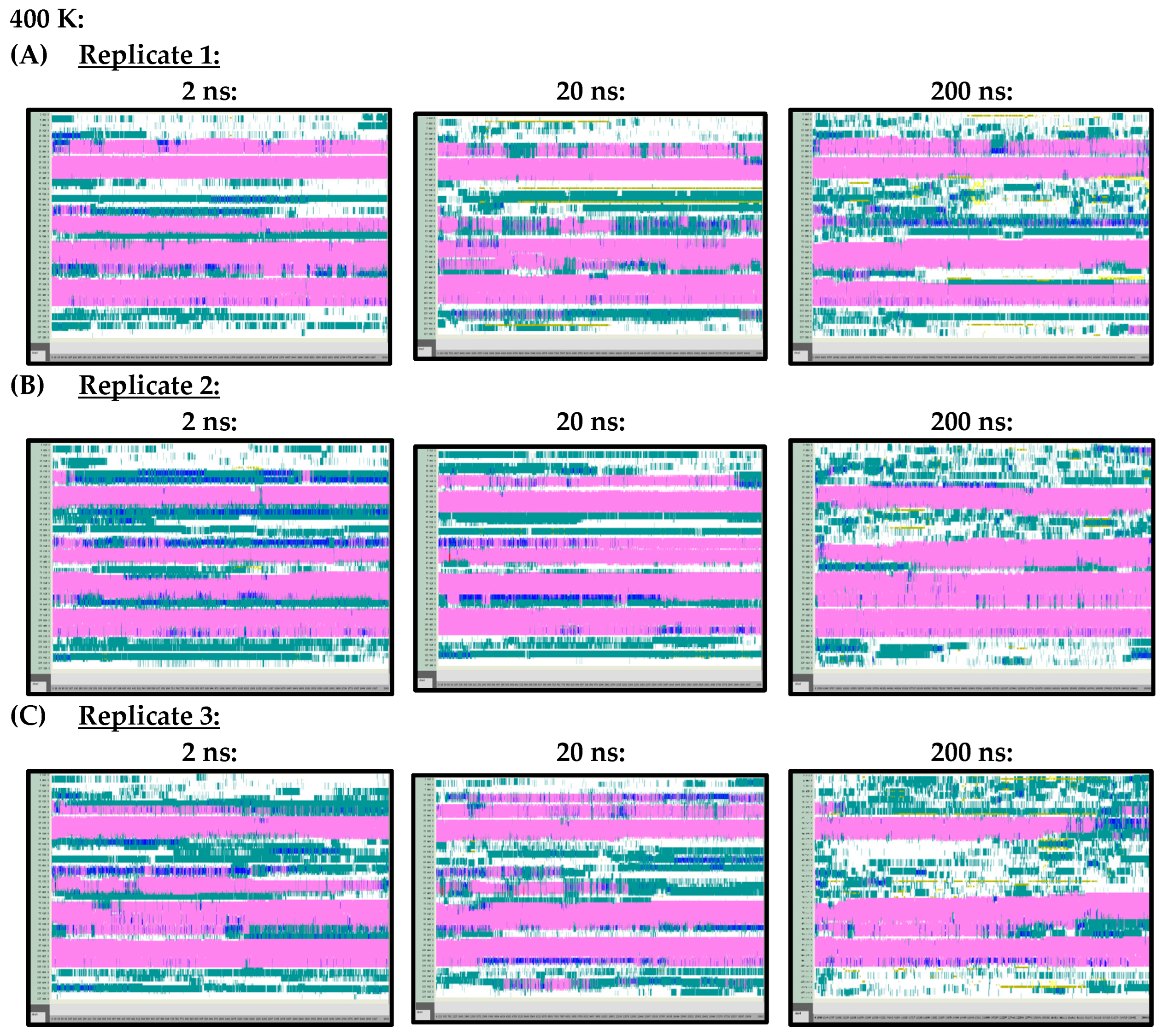
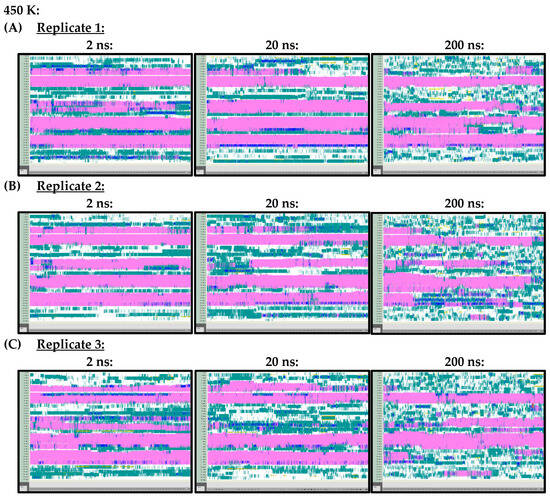
Figure A4.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 450 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
Figure A4.
VMD TIMELINE analysis of the Ara h 6 allergen undergoing thermal treatment at 450 K: (A) Replicate 1 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (B) Replicate 2 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns), (C) Replicate 3 (2 ns, 20 ns, 200 ns).
References
- De Vivo, M.; Masetti, M.; Bottegoni, G.; Cavalli, A. Role of molecular dynamics and related methods in drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4035–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Sinclair, R.C.; Coveney, P.V. Uncertainty quantification in classical molecular dynamics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2021, 379, 20200082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanga, S.K.; Singh, A.; Raghavan, V. Effect of thermal and electric field treatment on the conformation of Ara h 6 peanut protein allergen. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 30, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagadia, B.H.; Vanga, S.K.; Singh, A.; Raghavan, V. Effects of thermal and electric fields on soybean trypsin inhibitor protein: A molecular modelling study. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 35, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Vanga, S.K.; Raghavan, V. Effect of thermal and microwave processing on secondary structure of bovine β-lactoglobulin: A molecular modeling study. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Vanga, S.K.; Raghavan, V. Structural responses of kiwifruit allergen Act d 2 to thermal and electric field stresses based on molecular dynamics simulations and experiments. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barazorda-Ccahuana, H.L.; Theiss-De-Rosso, V.; Valencia, D.E.; Gómez, B. Heat-stable hazelnut profilin: Molecular dynamics simulations and immunoinformatics analysis. Polymers 2020, 12, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Vanga, S.K.; Raghavan, V. Visualizing structural changes of egg avidin to thermal and electric field stresses by molecular dynamics simulation. LWT 2021, 151, 112139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Tian, H.; Xu, Y.; Han, M.; Xu, X. Effects of pulsed electric fields on the conformation and gelation properties of myofibrillar proteins isolated from pale, soft, exudative (PSE)-like chicken breast meat: A molecular dynamics study. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, K.; Schweimer, K.; Reese, G.; Randow, S.; Suhr, M.; Becker, W.-M.; Vieths, S.; Rösch, P. Structure and stability of 2S albumin-type peanut allergens: Implications for the severity of peanut allergic reactions. Biochem. J. 2006, 395, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Sci. 2017, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2020, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L.; MacKerell, A.D.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The biomolecular simulation program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Cheng, X.; Islam, M.S.; Huang, L.; Rui, H.; Zhu, A.; Lee, H.S.; Qi, Y.; Han, W.; Vanommeslaeghe, K.; et al. CHARMM-GUI PDB manipulator for advanced modeling and simulations of proteins containing non-standard residues. In Biomolecular Modelling and Simulations; KarabenchevaChristova, T., Ed.; Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 96, pp. 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-J.; Kern, N.; Brown, T.; Lee, J.; Im, W. Charmm-gui pdb manipulator: Various pdb structural modifications for biomolecular modeling and simulation. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 167995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Dijkstra, E.J.; Achterop, S.; van Drunen, R.; van der Spoel, D.; Sijbers, A.; Keegstra, H.; Reitsma, B.; Renardus, M.K.R. Gromacs: A parallel computer for molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Comput. 1993, 92, 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Van Der Spoel, D.; Van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Rauscher, S.; Nawrocki, G.; Ran, T.; Feig, M.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36m: An improved force field for folded and intrinsically disordered proteins. Nat. Methods 2016, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Dong, X.; Raghavan, V. An Overview of Molecular Dynamics Simulation for Food Products and Processes. Processes 2022, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, K.A.; White, B.L.; Dean, L.L.; Sanders, T.H.; Davis, J.P. Compositional and Mechanical Properties of Peanuts Roasted to Equivalent Colors using Different Time/Temperature Combinations. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C1293–C1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Dean, L.O.; Davis, J.P.; Sandeep, K.; Sanders, T.H. The effects of different dry roast parameters on peanut quality using an industrial belt-type roaster simulator. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh ewald: An n⋅log(n) method for ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. Lincs: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace Development Team. Grace User’s Guide (for Grace-5.1.25). Weizmann Institute of Science. Retrieved August 28, 2023. 2015. Available online: https://plasma-gate.weizmann.ac.il/Grace/ (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Frishman, D.; Argos, P. Knowledge-based protein secondary structure assignment. Proteins 1995, 23, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levene, H. Robust Tests for Equality of Variances. In Contributions to Probability and Statistics; Olkin, I., Ed.; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1960; pp. 278–292. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).