Abstract
Consumers’ preferences for healthier food products are increasing worldwide. Flatbread, a highly versatile product traditionally formulated with wheat flour (WF), offers significant potential for innovation and value addition through biofortification. Biofortification of flatbread was assessed with orange-flesh sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) flour (OFSP) infused with spinach (Amaranthus dubius). The purpose of this experiment was to ascertain the impact of adding local OFSP flour and spinach on the physicochemical, sensory, and microbial aspects of sweet potato-spinach infused WF flatbread. Six different flatbread formulations were created using OFSP flour, WF, and spinach. The study utilized a randomised 3 × 2 factorial design, with each treatment reproduced four times, totalling 24 treatments. Sensory evaluation for OFSP flour-spinach flatbreads received appreciable scores. OFSP flour flatbreads exhibited acceptable levels of protein, ash, fat, and moisture. The study provided formulations for value-added flatbread with the efficient inclusion of local agricultural resources OFSP and spinach to produce healthier food product offerings that were microbiologically safe.
1. Introduction
Flatbreads can be considered the oldest type of bread consumed globally [1], popular in regions like Scandinavia, South Europe, North and South Africa, the Middle East, Far East and part of China, and Central America. They are categorized as tortilla, naan, pita, focaccia, fried bread, chapatti, bazlama, and many others. Traditionally flat bread was formulated from a flattened dough produced from wheat flour, water, salt, and leavening agent [2,3], but there is a current trend to improve the nutritional profile through diversification with innovative ingredients. Flatbread production and diversification according to scientific evidence has been occurring in North Africa, Central Asia, and the Middle East but not in the Caribbean region; furthermore, preference for flatbread is increasing globally with a value of about USD 38.8 billion in 2018 and USD 41.17 billion in 2019. The estimated market for the year 2026 is about USD 62.8 billion, with an annual growth rate of 6.2% [4].
Flatbread is a highly adaptable carbohydrate-based product made from flour, incorporating various raw materials, and serves as an excellent medium for incorporating a variety of fortifying ingredients. According to Boukid [5], flatbread serves as a ‘canvas for innovation’. Flatbread can be used for preparing sandwiches, wraps, paninis, pizzas, and other items. Previously, cereals, mainly wheat, maize, and rice, were commonly used to prepare flatbreads [6]. Various cereals such as barley, millet, and sorghum have a lengthy history in flatbread production in Africa and India [7,8], and recently, hull-less barley (cv. Chifaa) with high β-glucan content was utilized at higher levels to produce flatbread with improved nutritional values [9]. Whole grains [10,11,12] and whey proteins are widely utilised to boost protein levels in flatbread recipes [13]. Furthermore, flours produced from pulses (chickpea flour, cowpea flour), vegetables (fenugreek, cassava), and seeds such as flaxseeds are employed for their nutritional and functional qualities [7,14,15,16]. For example, these seeds possess anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antibacterial, and immune-boosting properties due to their high mineral content (iron, manganese, magnesium, copper, and calcium), unsaturated fatty acids, and fibre [17]. It is well-documented that consumers’ preferences for healthier food options and safe foods are increasing globally [18,19,20]. Furthermore, the rise in consumer’s preferences for gluten-free food products has led to the production of a gluten-free flat bread with the addition of gluten-free orange peel [21].
Consumers have also shown preferences for flatbread that include natural ingredients and less additives as they become more health-conscious [5,9,22]. Thus, the demand for fibre-rich flatbreads is increasing due to greater awareness of the health benefits in reducing the risks of lifestyle diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and colon cancer [23]. Incorporating minerals and vitamin-rich ingredients, such as green leafy vegetables, into flatbreads offers a strategy to enhance the content of essential nutrients like Fe, Ca, ascorbic acid, folic acid, and riboflavin. Therefore, future opportunities for product diversification lie in utilizing natural, nutritious, and cost-effective ingredients while catering to niche markets, including vegans, vegetarians, and consumers with specific dietary preferences [5].
Wheat flour (WF) is a staple ingredient in Caribbean diets, commonly used in bakery preparations such as breads and roti. These items are integral to the main meals of breakfast, lunch, and dinner as well as snacks, reflecting their importance in daily consumption. Globally, flatbreads are recognized as a versatile product with significant potential for nutritional enhancement through fortification with local commodities. However, despite this global relevance, there is a notable lack of published scientific literature focusing on flatbreads within the Caribbean context. The Caribbean region faces significant challenges, including food insecurity, obesity, and the prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs). In response, there is a growing trend toward healthier dietary practices, driven by consumer efforts to address food security and nutritional concerns [24]. It cannot be overstated that the healthfulness of local diets is closely tied to the availability and accessibility of nutritious food options.
Bakery products such as breads and roti, which are staples in the Caribbean, are predominantly produced using WF. According to Boukid [5], these products often contain high carbohydrate levels, contributing to an elevated glycaemic index. This can pose a challenge for individuals seeking to manage their health and dietary needs. Introducing biofortified flatbreads made with local ingredients presents an excellent opportunity to address these issues. Incorporating regionally available commodities, such as cassava, breadfruit, spinach, or sweet potato in baked items such as flatbreads can offer a healthier and more nutrient-dense alternative. This approach not only aligns with the growing demand for healthier food options but also promotes sustainability and supports local agriculture. Such products have the potential to serve as convenient, nutritious additions to the Caribbean diet, addressing both health and food security concerns while meeting the evolving dietary preferences of the population.
OFSP is popular and available in the Caribbean region and several parts of the world. Nutritional benefits of sweet potato include beta-carotene (precursor for vitamin A), fibre, vitamin C, vitamin B6, Ca, P, Fe, K, Mn, and Zn [25]. Spinach (Amaranthus dubius) is a nutrient-dense green leafy vegetable, rich in essential nutrients such as iron, calcium, vitamin A, vitamin C, fibre, and protein, making it highly beneficial for overall health [26], and is also readily available in the Caribbean and around the globe but is underutilized. Studies have revealed that the nutritional properties of spinach can help to prevent anaemia caused by iron deficiency, night blindness, immune disorders and digestive issues. The extent of benefits also includes lowering the risk of cataract extension and age-related macular degeneration in persons who regularly consume spinach [27]. Spinach has a global production of 30.1 million tonnes, and despite its immense nutritional content, 35% of fresh food is wasted during home use due to short shelf life [28]. Given the issue of food waste and insufficient fruit and vegetable intake [29], this presents a valuable opportunity to reconsider food innovation by incorporating nutritive ingredients, such as spinach, in the production of flatbread. This also has the advantage of lowering the food import bill for WF while creating commercial opportunities along the market value chain through the efficient use of local agricultural resources in the circular economy.
In this regard, this study was undertaken to develop an innovative formula and produce flat bread with various levels of OFSP flour infused with spinach. The main objective of this experiment was to study the effect of the inclusion of local OFSP flour and spinach on the physicochemical, sensory, and microbial properties of orange flesh sweet potato-spinach-infused WF flatbread.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
The study design employed a randomized 3 × 2 factorial design, and the treatments were replicated four times, resulting in 24 treatments. This factorial design included two factors, OFSP flour with three levels (0%, 20% and 50%) and spinach with two levels (0% and 10%), and the design systematically combined these levels to create experimental groups. Six formulations of flatbread were achieved by combining OFSP flour and WF at the various levels with and without local spinach according to these formulations: T1 = 100% WF (control 1); T2 = 100% WF + 10% spinach (Control 2); T3 = 80% WF + 20% OFSP flour; T4 = 80% WF + 20% + 10% spinach; T5 = 50% WF + 50% OFSP flour; T6 = 50% WF + 50% OFSP flour + 10% spinach with the inclusion of flax meal, chia seeds, coconut oil, garlic, pimento, baking powder, and sodium benzoate (Table 1). The gradients of OFSP flour of 20% and 50% inclusion were selected according to studies by Oyinloye et al. and Kindeya et al. [30,31].

Table 1.
Formulations of different treatments of WF and sweet potato flatbread.
2.2. Production of OFSP Flour
OFSP of the Ipomoea batatas carrot variety was sourced from a registered farmer in Endeavour, Chaguanas, Trinidad and Tobago. The tubers were washed in water followed by 5.2% chlorine solution to eliminate microbial contamination, after which, each tuber was peeled to expose the flesh, re-washed, then shredded (Hobart Food Processor; model: FP100 ML-38962, South Ridge Avenue, Troy, OH, USA) and dehydrated on TSDM stainless steel racks utilizing a Food Dehydrator (D-14 Digital Touch Screen, The Sausage Maker, Raleigh, NC, USA) for 24 h at 60 °C [32,33,34,35]. Dried OFSP was ground to flour with a 3000 A High-Speed Commercial Comminutor Grinder (ALD Professional Kitchen, model: A-S3000, Nanjing, China). The resulting flour was sieved using a 710 μm sieve and stored at 4 °C for subsequent use.
2.3. OFSP Flour Flatbread Infused with Spinach Recipes
Flatbreads were made using multiple recipes with varying amounts of flour and spinach for each recipe (Table 1). There are different forms of flatbread, which differ in their methods of preparation primarily based on region, but they can be either unleavened or leavened through a fermented starter dough utilizing baking powder or baker’s yeast and basic ingredients such as salt, water, and flour [17,36,37,38]. In this study, each recipe contained chia seeds, flax meal, coconut oil, salt, baking powder, and sodium benzoate. Baking powder as the leavening agent is widely used in flatbread production due to its low cost [17]. The local spinach was steamed at 57 °C for 5 min with local spices of 5% ground pimento and 8% crushed garlic to add flavour. The dough mixtures were separately combined using flour combinations, spinach, coconut oil, chia seeds, flax meal, baking powder, and salt at room temperature. They were kneaded for approximately 2 min with the required amount of water (approximately 60–70 mL) to form an elastic and smooth dough, which was left to rest for 30 min at room temperature (35 °C) for dough development [38,39]. Thereafter equal amounts of dough were obtained and rounded between the palms to form dough balls and sheeted manually into a disc using a wooden rolling pin to approximately 20.32 cm diameter and 0.3 cm thickness [39]. Thereafter, they were cooked at 200 °C for 1 min on both sides on a metal Presto 07047 Cool Touch electric griddle that had a ceramic non-stick surface measuring 26.67 × 40.64 cm (National Presto Industries Inc., Eau Claire, WI, USA). The cooked flatbreads were transferred to a ceramic surface where they were left to cool and then packaged into 2 mil HDPE clear plastic packaging and stored at room temperature until further analysis.
2.4. Sensory Evaluation of OFSP Flour Flatbread Infused with Spinach
The sensory evaluation of the various flatbread recipes was conducted using a 9-point hedonic scale [35]. A sensory panel of 81 assessors (females and males) was recruited randomly to evaluate the sensory qualities of the flatbreads. Participants provided verbal informed agreement for their participation in the study. All panellists were locals that were randomly selected for sensory evaluation and who consume WF products. They were recruited from employees and students of the University of the West Indies, Saint Augustine Campus, between 20 and 50 years of age. The sensory evaluation was based on appearance, colour, aroma, texture, and general acceptability on a hedonic scale, with 9 representing like very much, 5 representing neither like nor dislike, and 1 representing dislike very much. The treatments were identified using three-digit random codes and distributed to each participant in a randomised order on a plate, along with a structured assessment sheet. Participants were instructed to taste each sample at a time and to cleanse their palates between taste testing with crackers and water [35].
2.5. Proximate Analyses of OFSP Flatbread Infused with Spinach
The proximate analyses as flatbread recipes were conducted by using AOAC [40] methods. Moisture content was estimated by drying at 102 ± 2 °C for a duration of 3–5 h (Gravity Convection Oven, APT. line TM ED, Binder, Tuttlingen, Germany), while the ash content was estimated by gravimetric loss method in a muffle furnace at 550 °C. The crude protein (CP) content was measured by the Kjeldahl method, (BUCHI Automat K-438 Block Digester (Automatic K-438, Büchi Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland) and BUCHI Kjel Flex K-360 Rapid Distillation Unit (Kjel Flex K-360, Büchi Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland). Crude fat content was analyzed using an ANKOM XT15 Automated Crude Fat Extraction machine (XT15 ANKOM Technologies, Macedon, NY, USA) with petroleum ether as the solvent.
2.6. Microbiological Safety of OFSP Flatbread Infused with Spinach
The microbiological evaluation was conducted immediately after flatbread production and throughout the 3-week storage period. The presence of total colony-forming units (CFUs) of aerobic bacteria [35,41], yeasts, and moulds [35,42] were assessed using pour plate and spread plate techniques. Plate Count Agar (PCA) was employed to enumerate total aerobic bacteria, while Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) was used for growth of yeasts and moulds. All materials were sterilized using an autoclave steam sterilizer (Tuttnauer Co. Ltd. Tuttnauer Autoclave model 3870 EA, Hauppauge, NY, USA) at 121 °C and 15 psi for 15 min in an Envirco Laminar Flow Hood (Albuquerque, NM, USA). Composite samples (10 g) from each treatment were collected aseptically using a sterile spatula, weighed, and homogenized at high speed for 1 min in a Seward Stomacher. Serial dilutions (10−1–10−4) were prepared for each treatment. PCA plates were incubated at 35 °C for 48 h to enumerate bacteria, while PDA plates were incubated at 25 °C for 48 h to facilitate yeast and mould growth. Only plates with 30–300 colonies were selected for CFU enumeration [35].
2.7. Colour Analysis of OFSP Flour Infused with Spinach Flatbread
The various flatbread recipes were subjected to colour analysis using a Konica Minolta Chroma Meter CR-400 model B8210778 (Optics, Inc., Industrial Instruments, Osaka, Japan) based on the chromaticity of L*, a*, and b* coordinates. The colourimeter was calibrated using standard black and white plates to establish a baseline. Four measurements were taken at different points on the sample surface using an 8 mm diameter measuring port. The ‘L’ value represents lightness (0 = black, 100 = white), the ‘a’ value indicates the red–green spectrum, and the ‘b’ value reflects the blue–yellow spectrum [35].
2.8. Statistical Analyses
The data were analyzed using Minitab Statistical Software (Version 21.4) (Minitab Inc., Enterprise Drive, State College, PA, USA) for Microsoft Windows. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed, and significant differences between means were determined using Tukey’s pairwise comparisons (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Sensory Evaluation
3.1.1. Sensory Colour of Flatbread
Colour sensory scores (Table 2) ranged from 6.24 (like slightly) to 2.44 (dislike very much). The highest mean score for colour was observed for T3 (6.24, like slightly) followed by T1 (6.15, like slightly), both of which contained no spinach. However, the lowest scores were given to T5 (2.41, dislike very much) and T6 (2.44, dislike very much) with the highest level of OFSP flour despite the inclusion and non-inclusion of spinach. Moreover, as the OFSP flour increased in the recipes, generally, the scores for colour decreased. In addition, T4 showed a significant difference in the sensory score for colour among all the treatments (T1, T2, T3, T5, and T6). Similarly, the T2 sensory score for colour of the flatbread differed significantly compared to T1, T3, T4, T5, and T6. It is notable that the treatments T5 and T6, which contained the same percentage of WF but with and without spinach, received sensory scores for colour that were not significantly different. The inclusion of spinach in the formulations of T2 and T4 significantly influenced the sensory score for colour of the flatbreads (Table 1). It was reported that the presence of chlorophyll in spinach is responsible for its characteristic green colour [43]. Contrastingly, the same trend did not follow between T5 and T6, which contained the increased level of OFSP flour with and without spinach. This could be due to the higher level of OFSP flour that reduced the green colour effect of the spinach, hence rendering them not significantly different (p > 0.05) enough to the sensory participants to cause a pronounced effect on the colour score and thus not receiving the highest scores. The flatbreads T5 and T6 obtained considerably lower scores, most likely because the higher level of OFSP flour darkened the flatbread, which was not preferred by participants. A similar finding was reported in a study conducted by Roger [44] with wheat-sweet potato flour blends of bread. However, another study by Seevaratnam [45] reported that the colour of sweet potato-WF bread was acceptable up to 40% sweet potato flour substitution.

Table 2.
Mean scores for sensory attributes including overall acceptability of flatbreads.
3.1.2. Sensory Taste
For the sensory evaluation parameter of taste, treatments T1 and T2 were the most favourable flatbreads, achieving the highest scores of 6.84 and 7.15 (like moderately), respectively, while the minimum mean scores were 3.71 and 3.74 (dislike very much), given to T5 and T6, respectively (Table 2). Treatments T3 and T4 obtained significantly different scores of 5.13 (neither like nor dislike) and 5.28 (neither like nor dislike), respectively, compared to the other treatments. It is notable that the degree of preference decreased as the OFSP flour levels increased, and the sensory scores for taste showed no significant difference (p > 0.05) between treatments that had the same flour type (either WF or OFSP) with or without spinach. Furthermore, there was no significant difference observed between the treatments that were infused with spinach (T2, T4, T6) and without spinach (T1, T3, T5). Taste is a key factor in determining a product’s acceptability and plays a crucial role in its market success [17]. The higher significant scores for taste of flatbreads with the 100% WF, with and without spinach, could be linked to the familiarity of the consumers with the WF, the exhibited preference for the taste of gluten in WF, and the moistness and softness it imparts to the finished products [46,47]. In a study conducted by Tadesse et al. 2015, all the OFSP flatbreads incorporated with maize flour received similarly low scores for taste compared to the controls. However, in another study that utilized other types of flour, chickpea flour with WF and milk, the sensory score for taste was much higher and well liked [14]. It was also revealed that the infused spinach had no significant effect on the sensory scores for flavour of the flatbreads in this trial. This could be attributed to the 10% spinach not being sufficient to have a profound effect on the taste of the flatbreads; however, it was reported that higher levels of spinach, of 20%, 30%, and 40%, in enriched bread caused a bitter taste and off odours due to the acidity of spinach polyphenols, which led to lower consumer acceptability of spinach-enriched bread [28].
3.1.3. Sensory Texture
The sensory scores for texture of the flatbreads did not differ significantly (p > 0.05) between treatments formulated with the same level of WF or OFSP flour either with or without the spinach (Table 2). This implied that the infused spinach did not have any significant effect on texture. The texture sensory scores followed a pattern similar to the scores for taste. The two treatments produced with 100% WF, T1 and T2, differed significantly in texture from the treatments that contained levels of OFSP flour, T3, T4, T5, and T6. Moreover, the texture scores for treatments T3 and T4, which contained 20% OFSP flour, differed significantly (p < 0.05) from T5 and T6, which contained 50% OFSP flour. The sensory scores for texture ranged from 4.10 (dislike slightly) to 6.74 (like). The higher preference for the texture of flatbreads with 100% WF could be attributed to the higher protein gluten fraction, which formed a higher viscoelastic dough that rendered those flatbreads more pliable and of a softer texture [48]. Other studies on flatbread production with WF also reported that the treatments with higher levels of WF gained the highest sensory scores for texture [47,49].
3.1.4. Sensory Aroma
The aroma scores showed no significant differences (p > 0.05) among the 100% WF flatbreads (T1 and T2) and certain OFSP flour flatbreads (T3 and T4), as presented in Table 2. However, T1 and T2 exhibited significantly higher aroma scores (p < 0.05) compared to T5 and T6, which contained higher levels of OFSP flour with and without spinach. Despite the sensory scores being significantly higher for T1 and T2, all treatments received scores within the ‘like’ range. The aroma of fresh bread is due to over 300 volatile compounds related to bread flavour that is caused by enzyme activity in the dough [17]. This is mainly due to the Maillard reaction and the intermediate fermentation of amino acids, which are crucial in the development of flavour in baked goods and act as precursors for aromatic compounds [50]. It was reported that, in the baking of bread, the aromatic volatile compounds responsible for aroma when sweet potato flour was included were 2-octanal2-butyl, dimethyl-decane, and 2-chloro-octane, while only ethyl hexadecanoate and decanal volatile compounds were present in those breads produced from only WF [50]. As such, the significant difference in the sensory scores for aroma between the 100% WF treatments and those formulated with OFSP flour could be attributed to the differences in the aromatic compounds. The characteristic aroma of spinach did not have any significant effect on the participants’ scores for aroma. This could be attributed to the level used could have been too low to exhibit any pronounced effect on aroma.
3.1.5. Overall Acceptability
The sensory scores for overall acceptability of the flatbreads did not differ significantly (p > 0.05) between treatments formulated with the same level of WF or OFSP flour, either with or without the spinach (Table 2). The two treatments produced with 100% WF, T1 and T2, were scored significantly higher in overall acceptability than the treatments that contained levels of OFSP flour, T3, T4, T5 and T6. Furthermore, the scores for treatments T3 and T4 that contained 20% OFSP flour differed significantly (p < 0.05) from T5 and T6 that contained 50% OFSP flour. The sensory scores for overall acceptability ranged from 3.35 (dislike) to 7.05 (like very much). In addition, as the OFSP flour increased, the overall acceptability for texture of the flatbreads decreased. Researchers Oyinloye et al., Kindeya et al. and Tadesse et al. [30,31,49] reported similar findings of a reduction in overall acceptability as the proportion of sweet potato flour increased. The proximate analysis performed on the six flatbreads proved that T1 and T2 contained the highest protein content, which was attributable to the presence of gluten that could have had a direct effect on the overall acceptability of T1 and T2. A reason for this could be because gluten causes increased the water binding ability of the dough, giving it a softer texture, which has been known to improve the overall acceptability of baked goods that are made from 100% WF [51]. In this present study, the flatbreads made with the OFSP flour with or without infused spinach were not highly acceptable. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first scientific study on flatbread in this region, and it forms a benchmark for further research. Hence, the formulations can be adjusted to ensure the flatbread maintains familiar sensory properties that consumers associate with traditional wheat-based flatbreads. This can be achieved by the inclusion of more local spices and herbs to enhance the natural flavour of OFSP. Additionally, texture concerns can be addressed by experimenting more with blends of OFSP and WF and adding more moisture to achieve the desired pliability and softness.
3.2. Proximate Analysis
3.2.1. Moisture
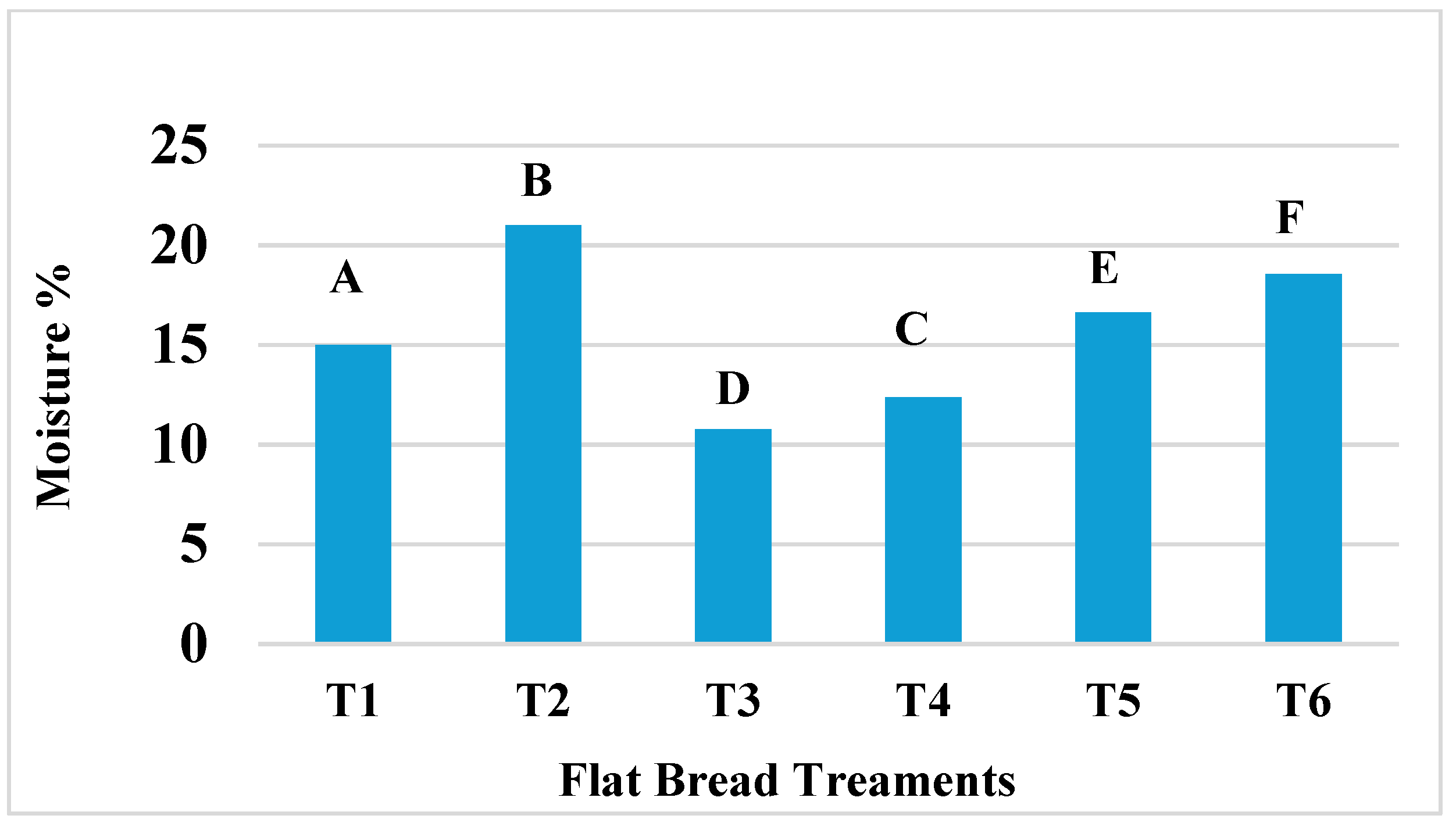
The moisture content differed significantly (p < 0.05) among all flatbread recipes and ranged from 10.78% (T3) to 20.99% (T2) (Figure 1). Notably, each of the three flatbread treatments with infused spinach, T2, T4, and T6, had significantly higher moisture levels than their counterparts without spinach. The treatment T2 that was formulated with 100% WF and local spinach had the highest moisture content of 20.99%. This was followed by moisture content of 18.55% for T6, which was also formulated with spinach but contained 50% OFSP flour. It was also reported that when spinach was added to crackers, a similar effect was seen and attributed to the presence of high amounts of hydroxyl groups associated with fibre in spinach, which initiates high bonding of water through hydrogen bonding [52]. The moisture levels of the OFSP flour and infused spinach treatments were higher than those conveyed in OFSP flour–maize blends of flatbread reported by other researchers [49]. Some studies have revealed that a higher fibre content in OFSP flour than in WF is responsible for higher levels of moisture [30,33] while another study by Roger et al. [44] reported that the higher level of functional groups of proteins in WF, in comparison to sweet potato flour, played a crucial role in forming more hydrogen bonds in water than in sweet potato flour. However, in this current study, the infused spinach had a stronger influence on moisture levels of the flatbreads than the WF and OFSP flour. The treatments T3 and T4 had a lower percentage inclusion of OFSP flour but higher levels of WF (than T5 and T6) and displayed the lowest moisture levels, of 10.78% and 12.36% respectively. Importantly, OFSP flour possesses one of the highest moisture levels among different varieties of sweet potato flour, but this can be affected by the genetic composition and cultivar of the sweet potato tuber [53], as seen in this study.
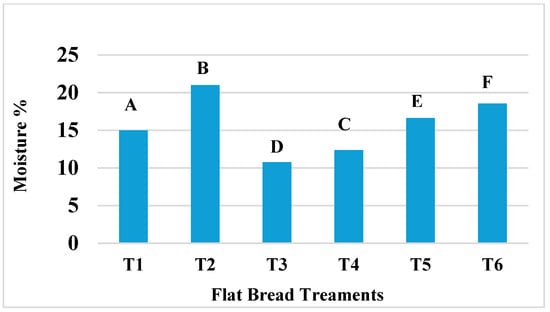
Figure 1.
The influence of OFSP flour infused with spinach on moisture of flatbread. Columns that do not share a letter are significantly different (p < 0.05).
3.2.2. Crude Fibre
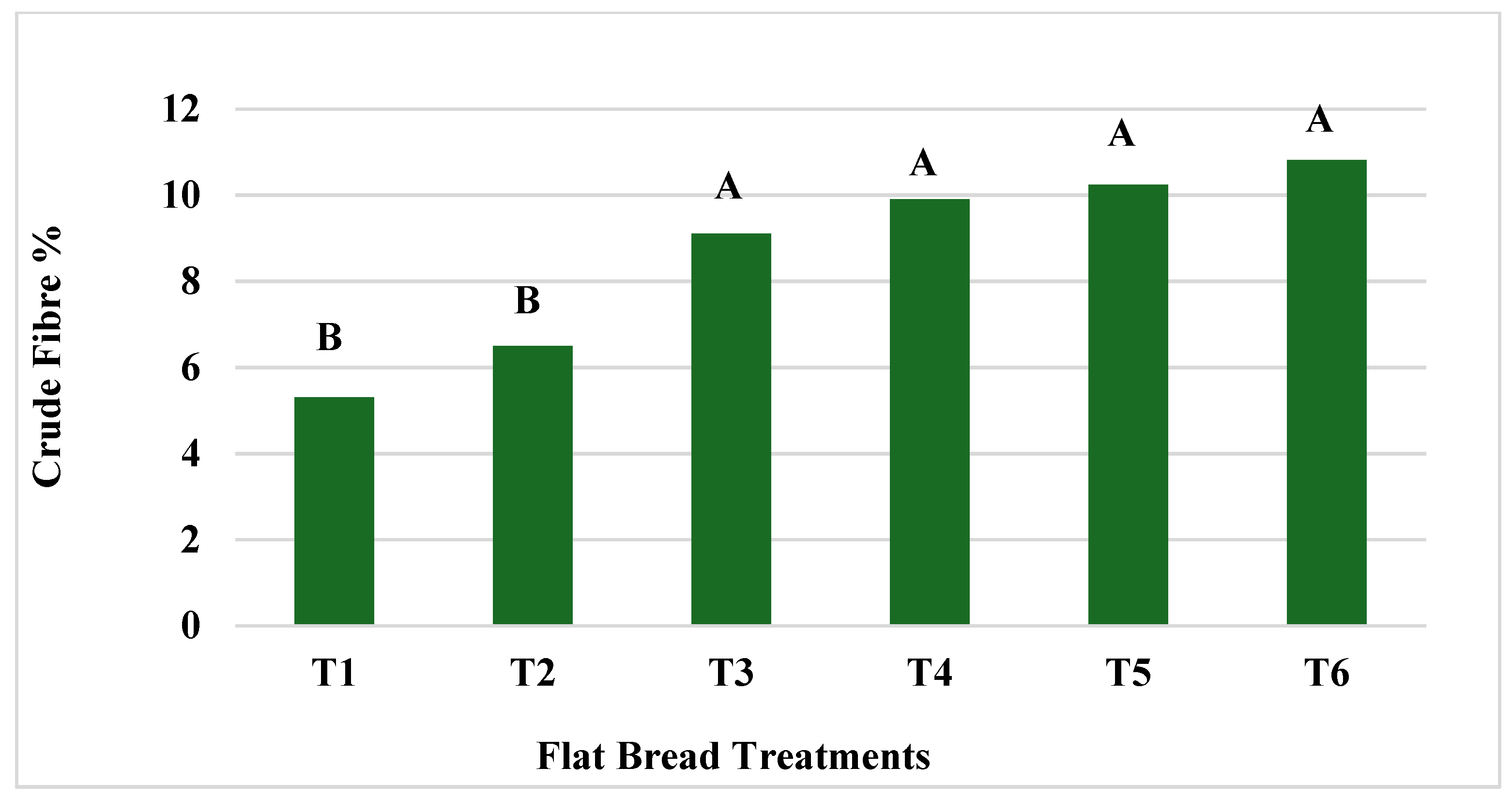
There were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in crude fibre percentage among all flatbread treatments that contained OFSP flour: T3, T4, T5, and T6 (Figure 2). Similarly, there was no significant difference in crude fibre content between T1 and T2, both of which contained WF. All four OFSP flour treatments (T3, T4, T5, and T6) contained significantly higher (p < 0.05) levels of crude fibre than the two 100% WF flatbreads. Furthermore, the crude fibre increased concomitantly with increasing levels of OFSP flour, resulting in T5 and T6, the treatments formulated with 50% OFSP flour, having the highest fibre levels, of 10.24% and 10.82%, respectively. This pattern was also observed in an experiment conducted with volume bread formulations containing OFSP–WF blends [54], bread formulations with WF and sweet potato blends [50] and OFSP flour–maize flour blends of flatbread [49]. It is noteworthy however, that, in this current research, the fibre levels, which ranged from 9.1% to 10.8%, were much higher than those reported by similar studies. It is widely recognized that spinach contains high levels of dietary fibre [55], and in this study, the infused spinach could have had some effect on the fibre content of the flatbreads even though no clear pattern of a significant effect was observed. This is supported by the higher levels of crude fibre in T2, T4, and T6, which were formulated with spinach. The significantly higher levels of crude fibre in the flatbreads formulated with OFSP flour signify that the inclusion of this type of flour adds value to the flatbread and serves as a high fibre option to meet the requirements for healthier food options. The health benefits of fibre are numerous, including playing integral roles in reducing the risks of diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and colon cancer [23] and facilitating the digestion and absorption process in humans [49].
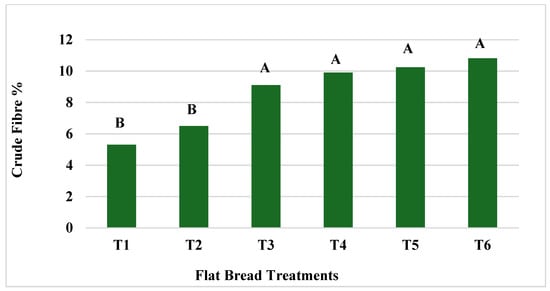
Figure 2.
The influence of OFSP flour infused with spinach on crude fibre in flatbread. Columns that do not share a letter are significantly different (p < 0.05).
3.2.3. Crude Protein
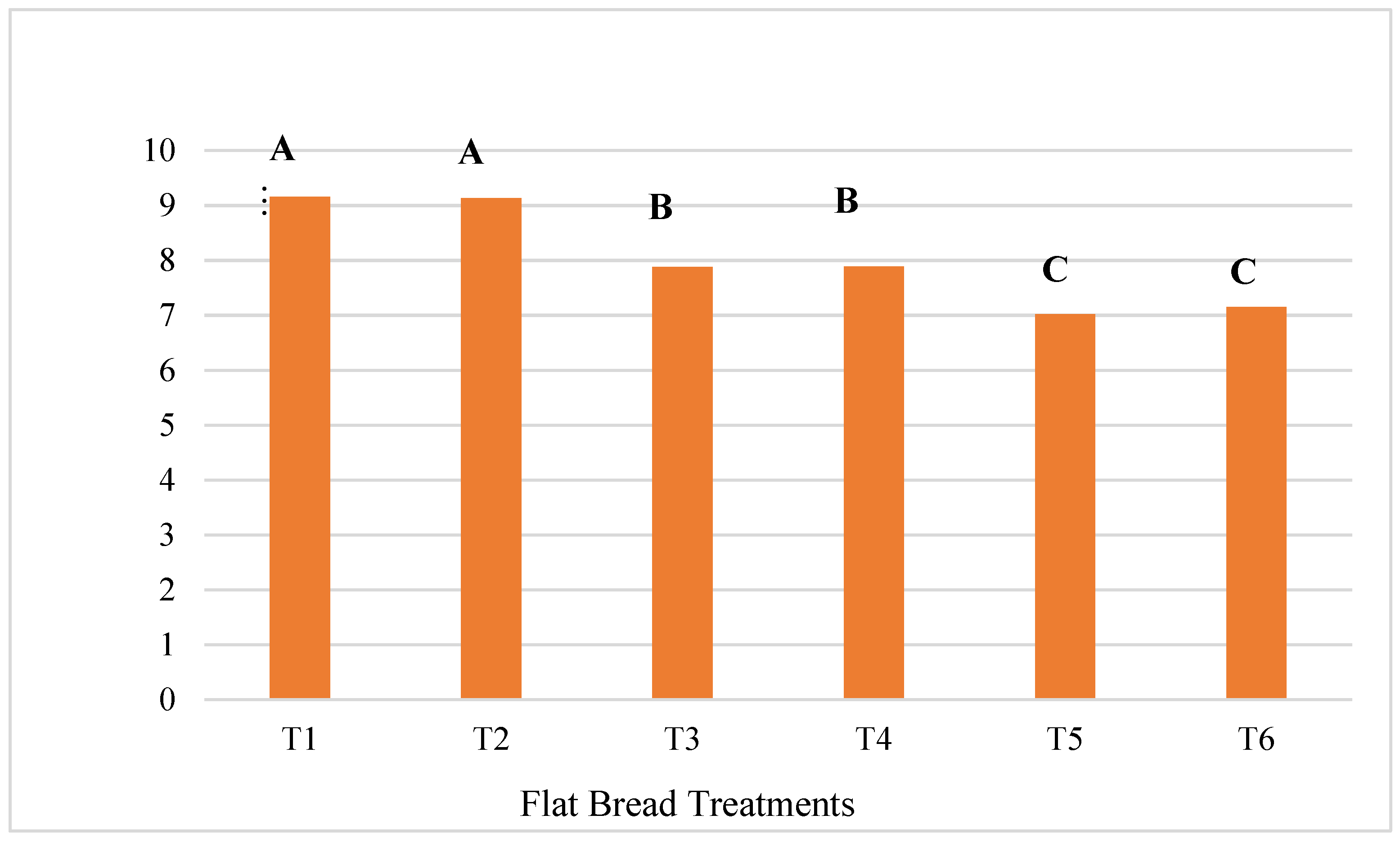
The CP content in T1 (9.15%) and T2 (9.13%), both representing the 100% WF treatments, was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than that in all the OFSP flour treatments (Figure 3). The flatbreads T3 and T4 had protein contents of 7.88% and 7.89%, respectively. Additionally, no significant difference (p > 0.05) was noticed in crude protein between T1 and T2, nor between T3 and T4, or T5 and T6. Moreover, the protein content decreased significantly from 7.88% to 7.02% as the level of OFSP flour increased in the treatments, compared to the control treatments of 9.15% (T1) and 9.13% (T2). Similar trends were revealed by Teferra et al. [49] for OFSP flour–maize blends of flatbread and by Okorie and Onyeneke [56] with cakes formulated with sweet potato flour–WF blends. Yıldız [57] reported that the protein gluten fraction in WF, which is absent in OFSP flour, is responsible for the higher levels of protein in WF products. There was no significant effect of the infused spinach on CP content in the flatbreads in this current study. This may be due to the amount and form in which it was incorporated into the flatbread. When powdered spinach was added to WF at levels of 20% and beyond, for bread making, it increased the protein levels significantly [28]. However, the level of spinach used in this study was 10%, which might have been too low to have a definite effect on CP content in the flatbreads.
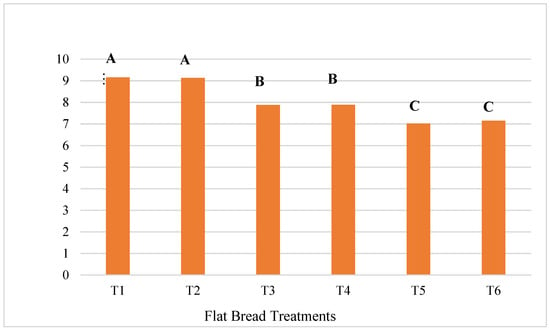
Figure 3.
The influence of OFSP flour infused with spinach on CP of flatbread. Columns that do not share a letter are significantly different (p < 0.05).
3.2.4. Crude Fat
The crude fat content did not differ significantly among treatments. Even though the infused spinach did not significantly affect the crude fat content of the treatments, its inclusion caused a lower level of crude fat in T2, T4, and T6. When spinach powder was applied to WF for biscuit production, the fat content also deceased [58].
3.2.5. Crude Ash
The ash levels showed no significant differences among the treatments. However, it was revealed that the ash level was higher for all treatments that contained spinach, T2, T4 and T6, than the other formulations without spinach. Additionally, as the OFSP flour inclusion level increased, the ash % also increased. This implied that both spinach and OFSP flour were factors contributing minerals to the flatbreads, though not significant. According to Oyinloye et al. [30], the ash content indicates the amounts of minerals present in a meal sample. Thus, the current study found that using both OFSP wheat and spinach increased the mineral content of flatbread.
3.3. Colour L* a* b
3.3.1. Colour L*
The chromaticity L* value represents the lightness of a colour ranging from 0 (black) to 100 (white), where higher L* values indicate lighter colours (e.g., white or light shades), and lower L* values indicate darker colours. In this study, the L* value was significantly higher in T1, at 67.16, than in the other flatbread treatments (Table 3). This is due to T1 being made with 100% WF, which results in a level of whiteness comparable to that of WF, which is naturally white when milled [59]. A similar result was also reported in a previous analysis carried out on flatbread samples made with WF by Kaur et al. [60]. Notably, T2, which contained a level of WF similar to that in T1 but was infused with spinach, exhibited a significantly lower colour L* value than T1. The reduction in colour L* to a darker colour was due to the green colour imparted by the spinach. Interestingly, a similar reduction in colour L* was observed with T4, T5, and T6. This is due to both T4 and T6 also being infused with spinach and the increased level of OFSP flour in the formulation for T5. Treatment T3 did not exhibit a similar trend due to the lower level of OFSP flour and no spinach in its formulation. It is reported that the presence of chlorophyll is responsible for the effect on lightness in treatments containing spinach [43], while the bright colour of beta-carotene influences the brightness of OFSP flour [61]. Hence, both the OFSP flour and infused spinach influenced the colour of the flatbreads in this current study. A similar trend was reported for a reduction of colour L* when WF was supplemented with red sorghum flour [62]. According to Vimala et al. [61], there is a direct correlation of colour L* (lightness) being reduced in flatbread as the fortifying ingredient increases. The colour of baked products plays an integral role in influencing consumers’ preferences. Although the inclusion of the OFSP flour and spinach in the formulations produced a darker flatbread that may have the potential for reduced consumer acceptance, the inclusion of both spinach and OFSP flour will produce an enriched flatbread with improved fibre levels important for aiding in the digestion process and reducing the risks of lifestyle diseases [23].

Table 3.
Effect of OFSP flour and infused spinach on colour L* a* b* of flatbread.
3.3.2. Colour a* and b*
Colour a* quantifies the colour’s location along the red–green axis, with positive values indicating the presence of red tones and negative values indicating the presence of green tones. Thus, a greater positive a* value indicates a stronger red hue, whereas a lower (negative) a* value designates a stronger green hue. The 100% WF treatment without infused spinach differed significantly (p < 0.05), having the lowest numerical value for colour a* compared to all other flatbread treatments (T2, T3, T4, T5, and T6). However, for all other treatments, T3, T4, T5, and T6 produced either with spinach and WF, both spinach and OFSP flour, or with OFSP flour alone exhibited no significant difference in colour a* (Table 3). The treatments T4, T5 and T6 displayed positive a* numerical values indicative of the presence of more red hues, while T2 displayed a very low negative a* value indicative of some level of greenness due to the inclusion of spinach. However, the values for the treatments with the increased level of OFSP were the highest among all treatments.
The results from this current study revealed that the inclusion of OFSP flour and spinach influenced the colour a* hues of the flatbread. The b* value represents the colour’s position along the yellow–blue axis, with positive values indicating the presence of yellow tones and negative values indicating the presence of blue tones. A greater positive b* value indicates a more intense yellow colour, whereas a lower (negative) b* value indicates a more intense blue colour.
All colour b* numerical values were positive, indicating the presence of more yellow hues. Both T1 and T2 treatments formulated with 100% WF but without and with infused spinach, respectively, exhibited no significant difference in colour b*. However, they were significantly lower in colour b* numerical values than all OFSP flour treatments, T3, T4, T5, and T6. Furthermore, no significant difference was observed among all the formulations with OFSP flour treatments. It was also reported that for red sorghum and WF flatbread, when the substitution of red sorghum flour increased, the colour a* and b*values were affected [63]. This current study demonstrated that the infused spinach did not significantly influence colour b* hue of the flatbread, but the OFSP flour played a major role, which was most likely due to the biofortified high beta carotene and anthocyanin in the OFSP flour [62]. This provides enormous health benefits since OFSP is a great source of Vitamin A carotenoids and non-pro Vitamin A carotenoids [64] and includes dietary components with anticarcinogenic and cardiovascular disease (CVD)-preventing properties [65], unlike WF.
3.4. Microbial Safety of Flatbread
No colony-forming units (CFUs) of aerobic bacteria, yeasts, or moulds were detected on the PCA and PDA plates, either immediately after the flatbread’s preparation or throughout the 3-week storage period. The sterile production conditions, along with the use of sodium benzoate, contributed to the preservation of the products and ensured food safety. Sodium benzoate is a tasteless, colourless, odourless chemical applied to several food production formulas for the purpose of prolonging shelf life while also impeding the growth of fungi [66] and bacteria [67]. Though there are no long- term residues left in the body after ingestion, it has been suggested by some researchers that continued consumption of food products containing sodium benzoate contributes to symptoms related to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [68]. Additionally, it has been noted that the acceptable daily intake remains at 5 mg kg−1 or below, since failure to do so can initiate allergic reactions in some consumers [69]. However, in this current study, the quantity of sodium benzoate used was at an acceptable level and should pose no harm to consumers. Since food is a major transmission route for over 200 diseases in humans [23], ensuring food safety is vital to prevent contamination by pathogenic microorganisms and reduce the risk of illness. Therefore, this study confirmed that the flatbread was safe for consumption.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
In this study, six innovative flatbread formulations were developed with WF fortified with OFSP flour and infused with local spinach to produce a vegetarian flatbread to meet the increasing demands for healthier food options. Based on sensory evaluation, for all parameters assessed, texture, colour, appearance, taste, aroma, and overall acceptability, T3 and T4, the flatbreads formulated with 20% OFSP flour with and without spinach, received appreciable scores and were more acceptable than T5 and T6, the flatbreads formulated with 50% OFSP flour. According to the nutritive analysis, all OFSP flour–spinach flatbreads contained acceptable levels of protein, fibre, fat, and ash while flatbreads T4 and T6 that contained both OFSP flour and spinach contained the highest level of fibre. This current study revealed that fortified flatbread formulations with local agricultural resources, OFSP flour, and spinach show promising potential as a healthy and innovative food product offerings. It is envisaged that the efficient use of more local agricultural resources such as OFSP and spinach can produce value-added foods and promote a circular economy. In future studies, it is recommended that consumers be highly sensitized about the nutritive benefits of flatbreads formulated with OFSP flour and spinach to encourage acceptability and consumption. Additionally, the flatbread formulations can be improved in taste and colour acceptability by including more moisture, such as milk, reducing the OFSP flour from 50% to a lower level such as 15%, and increasing the spinach inclusion to approximately 15%. As a strategy for addressing consumer acceptance, OFSP flatbread should be incorporated into school meal programs in the region to increase familiarity among young consumers. Furthermore, educational campaigns should be created to inform consumers about the health benefits of consuming biofortified products like OFSP flour flatbread. Strategies for addressing scalability challenges include building a suitable supply chain by partnering with local farmers to ensure a consistent supply of high-quality OFSP. In addition, collaborating with governments, NGOs, and private entities to improve access to resources, funding, and expertise is of paramount importance.
Author Contributions
C.C.: Conceptualization and design, writing original draft; revising it critically for intellectual content; investigation; interpretation of data. V.d.G.: Conceptualization and design, drafting of the paper; writing—review and editing it critically for intellectual content; analysis and interpretation of data; supervision; project administration. G.E.: Writing—drafting of the paper; revising it critically for intellectual content; formal analysis. S.K.: Writing—drafting of the paper; writing—review and editing it critically for intellectual content; W.-A.P.I.: Writing—drafting of the paper; writing—review and editing it critically for intellectual content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study has been financially supported by The Department of Food Production, The University of the West Indies, St. Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the technical assistance provided by the Food Biology, Food Production and Microbiology laboratories in the Department of Food Production, Faculty of Food and Agriculture, The UWI. St. Augustine Campus.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Neela, S.; Fanta, S.W. Injera: An Ethnic, Traditional Staple Food of Ethiopia—A Review on Traditional Practice to Scientific Developments. J. Ethn. Foods 2020, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, R.; Gasparre, N.; Pasqualone, A.; Papageorgiou, M.; Grgic, T.; Le-Bail, P.; Pablos, I.M.; El Tomb, C.; Magro, C.; Rosell, C.M. Flatbreads on the Rise, What about Their Nutritional Quality? The Current State of the Mediterranean Market. Med. Res. Arch. 2022, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualone, A.; Vurro, F.; Summo, C.; Abd-El-Khalek, M.H.; Al-Dmoor, H.H.; Grgic, T.; Ruiz, M.; Magro, C.; Deligeorgakis, C.; Helou, C.; et al. The Large and Diverse Family of Mediterranean Flat Breads: A Database. Foods 2022, 11, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report, Flatbread Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report, by Product Type and Distribution Channel: Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2019–2026. Allied Market Research. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/flatbread-market (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Boukid, F. Flatbread—A Canvas for Innovation: A Review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serka, S.; Getahun, D.; Abegaz, K. Formulation and Sensory Acceptability of Flat Bread from Kocho with Broad Bean (Vicia faba L.) and Quality Protein Maize (Zea mays) Flours. J. Food Process. Technol. 2019, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boers, H.M.; van Dijk, T.H.; Hiemstra, H.; Hoogenraad, A.-R.; Mela, D.J.; Peters, H.P.F.; Vonk, R.J.; Priebe, M.G. Effect of Fibre Additions to Flatbread Flour Mixes on Glucose Kinetics: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehfooz, T.; Ali, T.M.; Arif, S.; Hasnain, A. Effect of Barley Husk Addition on Rheological, Textural, Thermal and Sensory Characteristics of Traditional Flat Bread (Chapatti). J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koksel, H.; Cetiner, B.; Ozkan, K.; Tekin-Cakmak, Z.H.; Sagdic, O.; Sestili, F.; Jilal, A. A Functional Bread Produced by Supplementing Wheat Flour with High β-Glucan Hull-Less Barley Flour. Cereal Chem. 2024, 101, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlon, T.S.; Chiu, M.C.M. Ancient Whole Grain Gluten-Free Flatbreads. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hou, G.G.; Cardin, M.; Marquart, L.; Dubat, A. Quality Attributes of Whole-Wheat Tortillas with Sprouted Whole-Wheat Substitution. LWT 2017, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-Cortés, D.C.; Figueroa Cárdenas, J.D.D.; Garnica-Romo, M.G.; Cuevas-Villanueva, R.A.; Cortés-Martínez, R.; Véles-Medina, J.J.; Martínez-Flores, H.E. Whole-Grain Corn Tortilla Prepared Using an Ecological Nixtamalization Process and Its Impact on the Nutritional Value. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Arya, S.S. Influence of Additive Premix, Whey Proteins, Extruded and Germinated Flour on Gluten-Free Dough Rheological Parameters and Flatbread Characteristics: A Mixture Design Approach. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 8, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, A.; En-Nahli, Y.; Noutfia, Y.; Elbaouchi, A.; Kabbour, M.R.; Gaboun, F.; El Maadoudi, E.H.; Benbrahim, N.; Taghouti, M.; Ouhssine, M.; et al. Nutritional and Technological Optimization of Wheat-Chickpea-Milk Powder Composite Flour and Its Impact on Rheological and Sensorial Properties of Leavened Flat Bread. Foods 2021, 10, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankwa, R.; Aisala, H.; Kayitesi, E.; de Kock, H.L. The Sensory Profiles of Flatbreads Made from Sorghum, Cassava, and Cowpea Flour Used as Wheat Flour Alternatives. Foods 2021, 10, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathania, S.; Kaur, A.; Sachdev, P.A. Chickpea Flour-Supplemented High-Protein Composite Formulation for Flatbreads: Effect of Packaging Materials and Storage Temperature on the Ready Mix. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2017, 11, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.A.; Naik, H.R.; Shah, M.A.; Mir, M.M.; Wani, M.H.; Bhat, M.A. Indian Flat Breads: A Review. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofton, E.C.; Markey, A.; Scannell, A.G. Consumers’ Expectations and Needs Towards Healthy Cereal-Based Snacks: An Exploratory Study among Irish Adults. Br. Food J. 2013, 115, 1130–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamhuri, N.; Batt, P.J. Consumer Perceptions of Food Quality in Malaysia. Br. Food J. 2015, 117, 1168–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, J.; Paul, J. Health Motive and the Purchase of Organic Food: A Meta-Analytic Review. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2020, 44, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparre, N.; Garzon, R.; Marín, K.; Rosell, C.M. Exploring the integration of orange peel for sustainable gluten-free flatbread making. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 198, 115969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, M.; Ruiz, M.; Garzon, R.; Rosell, C.M. Comparison of vegetable powders as ingredients of flatbreads: Technological and nutritional properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 7203–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.S.; Sonawane, S.K. Impact of fiber mixture on dough and chapatti quality using D-optimal response surface methodology. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2016, 5, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, A.; Hallen, G. Integrated food systems approaches for healthy diets in the Caribbean. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2022, 46, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibiana, I.; Num, G.; Amove, J. Quality evaluation of composite bread produced from wheat, maize, and orange-fleshed sweet potato flours. Am. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 2, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujaffar, S.; Loy, A.L. Drying kinetics of microwave-dried vegetable amaranth (Amaranthus dubius) leaves. J. Food Res. 2016, 5, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanabur, V.; Reddy, R.L. Bioactive components of spinach and their effect on some pathophysiological conditions: A review. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2014, 6, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.V.; Dhital, S.; Williamson, G.; Barber, E. Nutrient composition, physical characteristics, and sensory quality of spinach-enriched wheat bread. Foods 2024, 13, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Food Safety. World Health Organization. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Oyinloye, O.D.; Akande, N.O.; Osinubi, O.B.; Ajani, A.A.; Abdulkareem, S.A.; Oyinloye, F.F. Evaluation of bread made from wheat and composite flours of sweet potato. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2022, 7, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kindeya, F.; Hailu, W.; Dessalegn, T.; Kibr, G.L. Effect of blending ratio of wheat, orange-fleshed sweet potato, and haricot bean flour on proximate compositions, β-carotene, physicochemical properties, and sensory acceptability of biscuits. F1000Research 2021, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.N.; Murdianto, W.; Ahmadi, N.R.; Waryat; Sulistyaningrum, A. Physicochemical characteristics of three local sweet potato flour varieties from East Kalimantan. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1024, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korese, J.K.; Chikpah, S.K.; Hensel, O.; Pawelzik, E.; Sturm, B. Effect of orange-fleshed sweet potato flour particle size and degree of wheat flour substitution on physical, nutritional, textural, and sensory properties of cookies. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 889–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Genitha, T.R.; Yadav, V. Preparation and quality evaluation of flour and biscuit from sweet potato. J. Food Process. Technol. 2012, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronnie, R.; de Gannes, V.; Eudoxie, G. Quality evaluation of innovative buttermilk biscuits produced from orange-fleshed sweet potato flour infused with coconut. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 1467839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahwa, A.; Kaur, A.; Puri, R. Influence of hydrocolloids on the quality of major flatbreads: A review. J. Food Process. 2016, 2016, 8750258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mefleh, M.; Vurro, F.; Summo, C.; Pasqualone, A. Traditional Italian flatbreads: Cultural diversity, processing technology, and future perspectives. J. Ethn. Foods 2024, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, U.; Dar, A.H.; Kumar, N.; Junaid, P.M.; Shams, R.; Khan, S.A. Formulations and quality characterization of low salt flatbread: Effects on functionality, rheological, and sensory properties. Appl. Food Res. 2021, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavya, S.N.; Prakash, J. Nutritional properties of iron-fortified flatbreads enriched with greens and legumes. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Method 999.08: Aerobic plate count in foods. In Official Methods of Analysis, 14th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Method 997.02: Yeast and mold count in foods. In Official Methods of Analysis, 14th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, A.M. Chlorophyll as a color and functional ingredient. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, C422–C425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, P.; Bertrand, B.M.M.; Gaston, Z.; Nouhman, B.; Elie, F. Nutritional composition of biscuits from wheat-sweet potato-soybean composite flour. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 2022, 7274193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seevaratnam, V.; Banumathi, P.; Premalatha, M.R.; Sundaram, S.P.; Arumugam, T. Studies on the preparation of biscuits incorporated with potato flour. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 2012, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, N.; Rani, R.; Singh, A. Physico-nutritional and sensory properties of cookies formulated with quinoa, sweet potato, and WF blends. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2018, 6, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, R.; Stojceska, V.; Plunkett, A. An investigation of consumer perception on the quality of gluten and wheat-free breads available on the UK market. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2014, 8, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, G.R.; Edwards, N.M. Criteria of wheat and flour quality. In Wheat Chemistry and Technology, 4th ed.; AACC International, Inc.: Eagan, MN, USA, 2009; pp. 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, T.F.; Nigusse, G.; Kurabachew, H. Nutritional, microbial, and sensory properties of flat-bread (kitta) prepared from blends of maize (Zea mays L.) and orange-fleshed sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) flours. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2015, 5, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.P.A.; Clerici, M.T.P.S.; Schmiele, M.; Júnior, L.C.G.; Nojima, M.A.; Steel, C.J.; Nabeshima, E.H. Orange-fleshed sweet potato flour as a precursor of aroma and color of sourdough panettones. LWT 2019, 101, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, P.M.G.; Steel, C.J. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of pan bread samples available in the Brazilian market. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhanan, A.R.; Xin, D.T.W.; Tham, L. Physicochemical properties and sensory evaluation of green and red spinach crackers. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 756, 012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwakamu, L.M.; Abong, G.O.; Okoth, M.W.; Moyo, M.; Mwaura, L.; Malavi, D.; Muzhingi, T. Effects of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) puree on bread shelf-life. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2022, 16, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidane, G.; Abegaz, K.; Mulugeta, A.; Singh, P. Nutritional analysis of vitamin A-enriched bread from orange-fleshed sweet potato and locally available WFs at Samre Woreda, Northern Ethiopia. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2013, 1, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapozhnikov, A.N.; Rozhdestvenskaya, L.N.; Kopylova, A.V. Quality evaluation of bakery products enriched with spinach. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 346, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorie, S.U.; Onyeneke, E.N. Production and quality evaluation of baked cake from a blend of sweet potatoes and WF. Acad. Res. Int. 2012, 3, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, G. Effects of whole buckWF on physical, chemical, and sensory properties of flatbread, lavaş. Czech J. Food Sci. 2012, 30, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galla, N.R.; Pamidighantam, P.R.; Karakala, B.; Gurusiddaiah, M.R.; Akula, S. Nutritional, textural, and sensory quality of biscuits supplemented with spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2017, 7, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, M.M.; Hussien, A.M.; Ragab, G.H.; Khalil, S.K.H. Detecting adulteration of durum wheat pasta by FT-IR spectroscopy. J. Am. Sci. 2011, 7, 573–578. Available online: http://www.americanscience.org (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Kaur, N.; Kumar, R.; Singh, A.; Shobha, D.; Das, A.K.; Chaudhary, D.; Singh, B. Improvement in nutritional quality of traditional unleavened flatbread using quality protein maize. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 963368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimala, B.; Nambisan, B.; Hariprakash, B. Retention of carotenoids in orange-fleshed sweet potato during processing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualone, A.; Caponio, F.; Simeone, R. Quality evaluation of re-milled durum wheat semolinas used for bread-making in Southern Italy. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 219, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, A.M. Traditional flatbread with sorghum supplementation influences quality attributes of weight, volume, colour and texture. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2016, 8, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, K.; Ziaul, H.; Sheikh, N. Comparison of the proximate composition, total carotenoids and total polyphenol content of nine varieties of orange-fleshed sweet potato grown in Bangladesh. Inst. Nutr. Food Sci. Univ. Dhaka 2016, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekara, A.; Joseph, K.T. Roots and tuber crops as functional foods: A review on phytochemical constituents and their potential health benefits. Int. J. Food Sci. 2016, 2016, 3631647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohammadi, M.; Javadi, M.; Nassiri-Asl, M. An overview on the effects of sodium benzoate as a preservative in food products. Biotechnol. Health Sci. 2016, 3, e35084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, D.; Issa, H. Mini-Review on Sodium Benzoate: Its Uses, Adverse Effects, and Environmental Impact as a Pharmaceutical Product. ChemRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak-Nowicka, Ł.J.; Herbet, M. Sodium benzoate—Harmfulness and potential use in therapies for disorders related to the nervous system: A review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, B.G.; Casagrande, T.A.; Cardoso, L.A. Food additives and their health effects: A review on preservative sodium benzoate. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).