Development of a Low-Cost Ozone (O3) Generator for Research and Education in Agricultural and Food Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
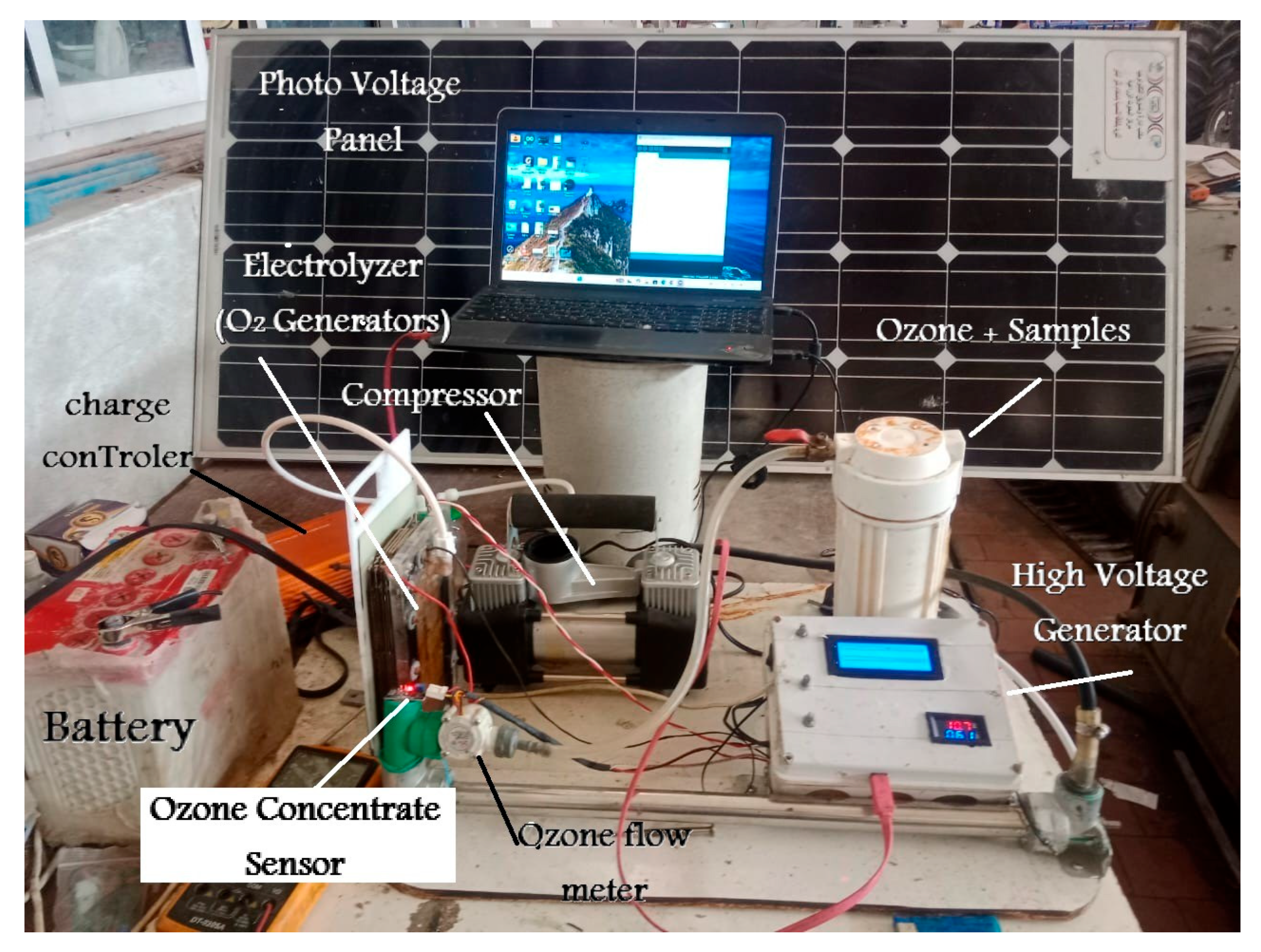
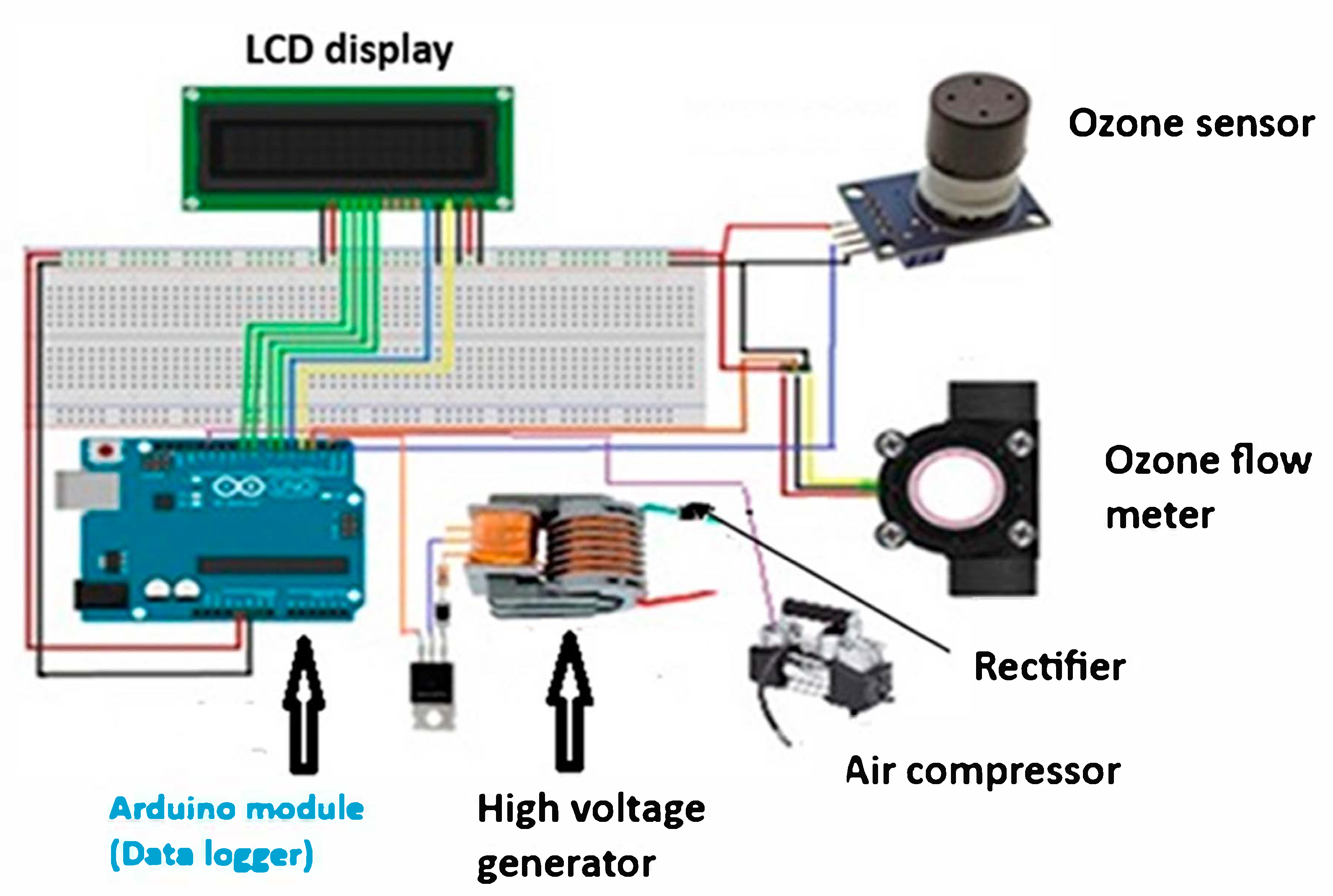
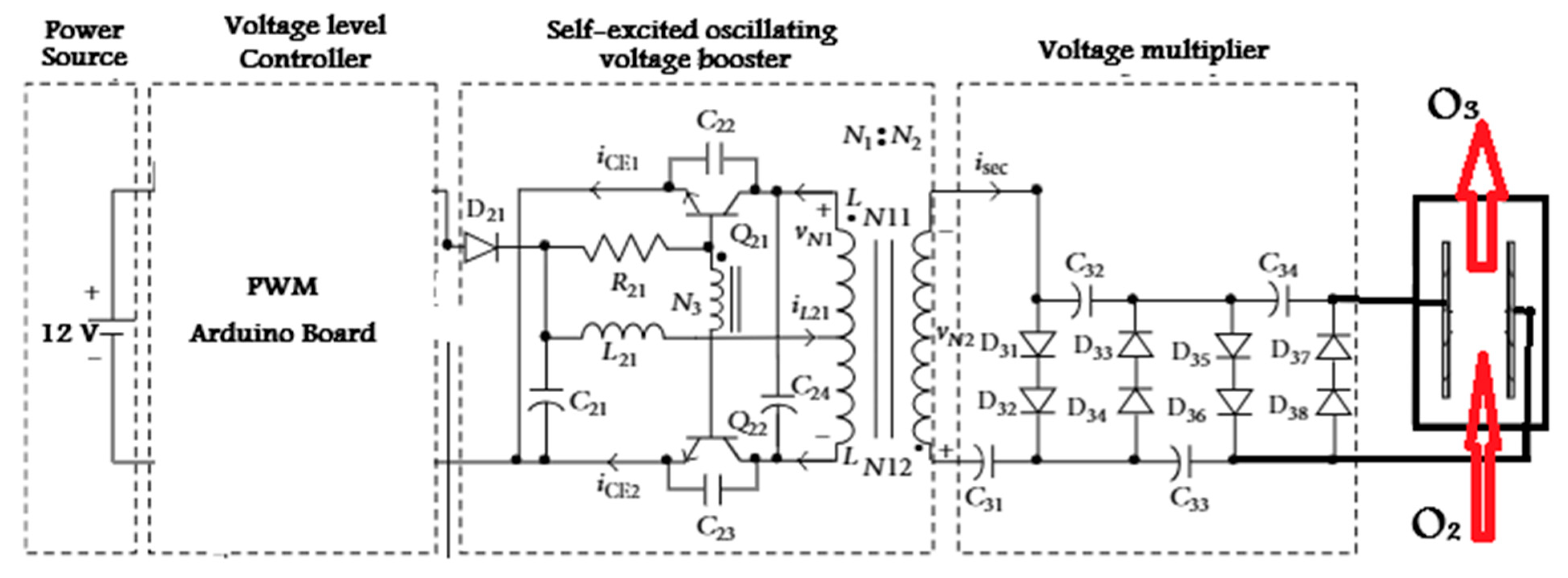
2.1. Components of the Developed Ozone Generator
Electrolyzer Unit (O2 Generator)
2.2. Calibration of the Arduino Ozone Sensor
2.3. Experimental Procedure
- Decide on a single oxygen flow rate, such as 1.5 L/min.
- Change the high voltage level in predetermined increments (20, 25, 30, and 35 kV).
- Before recording the ozone concentration, let the system stabilize for each high voltage level.
- For the remaining oxygen flow rates (2.0, 2.5, and 3.0 L/min), repeat the procedure.
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iksan, M.Z. The Ozone Generator Design for Carrageenan Sterilization Based on Arduino; EasyChair: Stockport, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, X.J.; Wang, Z.B. Application of ozone treatment in agriculture and food industry. A review. INMATEH-Agric. Eng. 2022, 68, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, T.; Patil, J.G. High concentration ozone generation in the laboratory for various applications. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Educ. Res. 2010, 1, 132–142. Available online: https://academicjournals.org/article/article1379500511_Vijayan%20and%20Patil.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Guzel-Seydim, Z.B.; Greene, A.K.; Seydim, A. Use of ozone in the food industry. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowska, A.J.; Nowak, A.; Smigielski, K. Ozone in the food industry: Principles of ozone treatment, mechanisms of action, and applications: An overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2176–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.J.; Yang, L.J.; Li, J.; Grzybowski, S. Aging Condition Assessment of Transformer Oil-Paper Insulation Model Based on Partial Discharge Analysis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, P.A.; Arunagiri, A.; Rao, P.G. Ozone generation by silent electric discharge and its application in tertiary treatment of tannery effluent. J. Electrost. 2002, 56, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Narsaiah, K.; Tushir, S. Design and Development of Low Cost Portable Ozone based Fruits and Vegetable Washer-Cum-Purifier. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev. 2022, 3, 1565–1570. Available online: https://ijrpr.com/uploads/V3ISSUE3/IJRPR3105.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- El-Mashede, M.B.; Zaky, M.M.; Saleh, A.A.; EL-Hanash, M. Designing of Single Switching DBD Ozone Generator. MEJ-Mansoura Eng. J. 2021, 46, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Costa, L.R.; Toffoli de Oliveira, J.; Amaral Féris, L. Optimization of a Compact Corona Discharge Ozone Generator for Emergency Water Treatment in Brazil. Water 2025, 17, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghulam, S.T.; Abushammala, H. Challenges and Opportunities in the Management of Electronic Waste and Its Impact on Human Health and Environment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäbel, P.; Koller, C.; Hertig, E. Development of Air Quality Boxes Based on Low-Cost Sensor Technology for Ambient Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.J.; Yousef, A.E. Decontamination of raw foods using ozone-based sanitization techniques. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriverdi, I.M. What Are the Ozone Generation Methods? Ozon Environmental Solutions 2023. Available online: https://www.ozcon.co.uk/what-are-the-ozone-generation-methods/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Deng, L.Z.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Pan, Z.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Xu, J.; Zielinska, M.; Xiao, H.W. Emerging chemical and physical disinfection technologies of fruits and vegetables: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2481–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvitz, S.; Cantalejo, M.J. Application of ozone for the postharvest treatment of fruits and vegetables. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, H. Design and development of an ozone generator for air purification applications. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2025, 7, 4094–4095. Available online: https://www.irjmets.com/upload_newfiles/irjmets70600171230/paper_file/irjmets70600171230.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Fahrudin, A.E.; Nasrulloh, A.V.; Sari, N. Development of ozone sterilization system based microcontroller for E. Coli bacteria sterilization. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 853, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehari, L.; Brahami, M.; Bousmaha, I.S.; Labair, H.; Boudjella, F.Z.; Tilmatine, A. Adaptation of a photovoltaic powered ozone generation system for food storage. Carpath. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 11, 64–71. Available online: https://chimie-biologie.ubm.ro/carpathian_journal/Papers_11(4)/CJFST11(4)2019_5.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Sarron, E.; Gadonna-Widehem, P.; Aussenac, T. Ozone Treatments for Preserving Fresh Vegetables Quality: A Critical Review. Foods 2021, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Lv, H.; Zeng, X.; Ling, Z.; Ding, L.; Jin, C. Advances in Ozone Technology for Environmental, Energy, Food and Medical Applications. Processes 2025, 13, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.N.; Nickhil, C.; Monika Devi, L.; Deka, S.C. Ozone Technology in Agriculture: A Sustainable Approach for Preserving Fruits, Vegetables, and Grains. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2025, 47, 504–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozone Gas Sensor, Model: MQ131 Low Concentration, Manual. Available online: https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/9/9/6/e/4/mq131-datasheet-low.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Caselles Nuñez, J.G.; Contreras Negrette, O.A.; de Jesús Beleño Sáenz, K.; Díaz Sáenz, C.G. Design and Implementation of an Indoor and Outdoor Air Quality Measurement Device for the Detection and Monitoring of Gases with Hazardous Health Effects. Eng. Proc. 2025, 83, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.M.; Anwar, M.; Septian, I.R.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Saraswati, T.E. Monitoring and Energy Analysis of Plasma Discharge in Ozone Generator. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2190, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzairi, T.; Sumantri, N.I.; Putri, N.A.; Andarini, M.V.; Lampung, E.J.; Sitinjak, D. Development of the Sterilization Box for Medical Equipment with an Ozone Gas Leak Sensor Feature. Int. J. Technol. 2022, 13, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Bennett, N.; Ding, Y.; Scott, K. A concise model for evaluating water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 14335–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundi, M.; El Fadil, H. Mathematical modeling of PEM electrolyzer and design of a voltage controller by the SMPWM approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Power Generation Systems and Renewable Energy Technologies (PGSRET), Istanbul, Turkey, 26–27 August 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashevskyi, R.; Kulichenko, V.; Mahonin, N. System for Flow Rate Regulation with Pulse-Width Modulation. In 2014 IEEE 34th International Scientific Conference on Electronics and Nanotechnology (ELNANO); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianto, E.; Aryadi, R.; Zahar, I.; Sasmita, E.; Restiwijaya, M.; Kinandana, A.W.; Arianto, F.; Nur, M. Effect of duty cycle on ozone production using DBDP cylindrical reactor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1217, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskito, A.; Firmansyah, R.D.; Syamsi, D.; Baskoro, C.H.A.H.B.; Lisdiana, A.; Wahab, H.I. Optimization of ozone chamber using pulse width modulation for sterilization and preservation on fruits and vegetable. J. Mechatron. Electr. Power Veh. Technol. 2020, 11, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-L.; Liang, T.-C. Design and Implementation of a High-Voltage Generator with Output Voltage Control for Vehicle ER Shock-Absorber Applications. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 324590, 6 p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Kaur, P.; Kumar, S.; Zalpouri, R.; Singh, M. Ozonation as a Potential Approach for Pesticide and Microbial Detoxification of Food Grains with a Focus on Nutritional and Functional Quality. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 6129–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitoe, E.D.P.E.; Pacheco, F.C.; Chilala, F.D. Advances in ozone technology for preservation of grains and end products: Application techniques, control of microbial contaminants, mitigation of mycotoxins, impact on quality, and regulatory approvals. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P.; Singh, A.; Yousuf, O. Ozonation: An Evolving Disinfectant Technology for the Food Industry. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 2102–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septian, I.R.; Anwar, M.; Yusuf, M.M.; Kusuma, R.R.; Saraswati, T.E.; Sulistyo, M.E.; Adinata, F.S. Design and analysis of ozone monitoring system produced by plasma corona discharge for disinfectant. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2674, 030055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Álvarez, J.M.; García García, J.; Calleja Rodríguez, A.J.; Ribas Bueno, J.; Cardesín Miranda, J. Analysis, design, and experimentation of a high-voltage power supply for ozone generation based on current-fed parallel-resonant push-pull inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 27.0. Computer software; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2020.
- El Gharbi, M.; Abounasr, J.; Fernández-García, R.; Gil, I. Study of Wash-Induced Performance Variability in Embroidered Antenna Sensors for Physiological Monitoring. Electronics 2025, 14, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxuly, S.; Abdykadyrov, A.; Yussupova, G.; Mailykhanova, B.; Mustafoyeva, D. Development of nonlinear multi-parameter control models for optimizing ozone generation processes. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2025, 8, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Joshi, U.M.; Subedi, D.P. Experimental Study of Ozone Generation by Atmospheric Pressure Dielectric Barrier Discharge. Int. J. Recent Res. Rev. 2015, VIII, 24–29. Available online: https://www.ijrrr.com/papers8-4/paper4-Experimental%20Study%20of%20Ozone%20Generation%20by%20Atmospheric%20Pressure%20Dielectric%20Barrier%20Discharge.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Warsza, Z.L.; Puchalski, J.; Więcek, T. Novel Method of Fitting a Nonlinear Function to Data of Measurement Based on Linearization by Change Variables, Examples and Uncertainty. Metrology 2024, 4, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannahong, K.; Wongcharee, S.; Kreetachart, T.; Sirilamduan, C.; Rioyo, J.; Wongphat, A. Evaluation of the Microsoft Excel Solver Spreadsheet-Based Program for Nonlinear Expressions of Adsorption Isotherm Models onto Magnetic Nanosorbent. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Shaw, M.D.; Lewis, A.C.; Carpenter, L.J.; Batchellier, T. Electrochemical ozone sensors: A miniaturised alternative for ozone measurements in laboratory experiments and air-quality monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorta-González, P. A Multiple Linear Regression Analysis to Measure the Journal Contribution to the Social Attention of Research. Axioms 2023, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jierula, A.; Wang, S.; OH, T.-M.; Wang, P. Study on Accuracy Metrics for Evaluating the Predictions of Damage Locations in Deep Piles Using Artificial Neural Networks with Acoustic Emission Data. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammen, S.S.; Kisi, O.; Ehteram, M.; El-Shafie, A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Ghorbani, M.A.; Bhat, S.A.; Ahmed, A.N.; Shahid, S. Rainfall modeling using two different neural networks improved by metaheuristic algorithms. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsae, N.B.; Adachi, T.; Kawamura, Y. Application of Artificial Neural Network for the Prediction of Copper Ore Grade. Minerals 2023, 13, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Kader, M. How to Interpret Multiple Regression Results in Excel. Excel Demy, 2024. Available online: https://www.exceldemy.com/interpret-multiple-regression-results-in-excel/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- High Voltage DIY Ozone Generator for Disinfection. Available online: https://hackaday.io/project/202959-high-voltage-diy-ozone-generator-for-disinfection#:~:text=Description,electrode%20and%20an%20air%20tube (accessed on 31 October 2025).






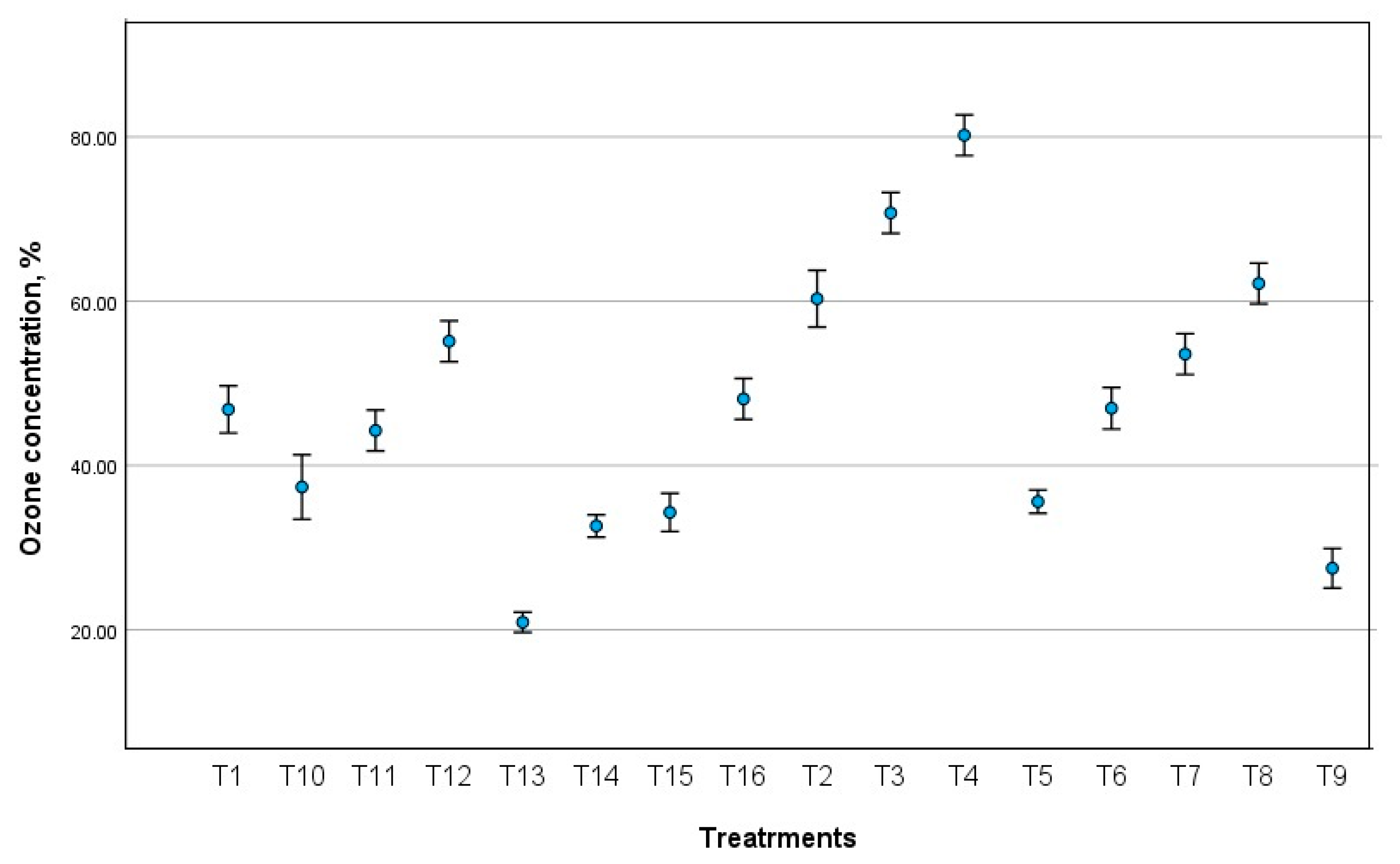
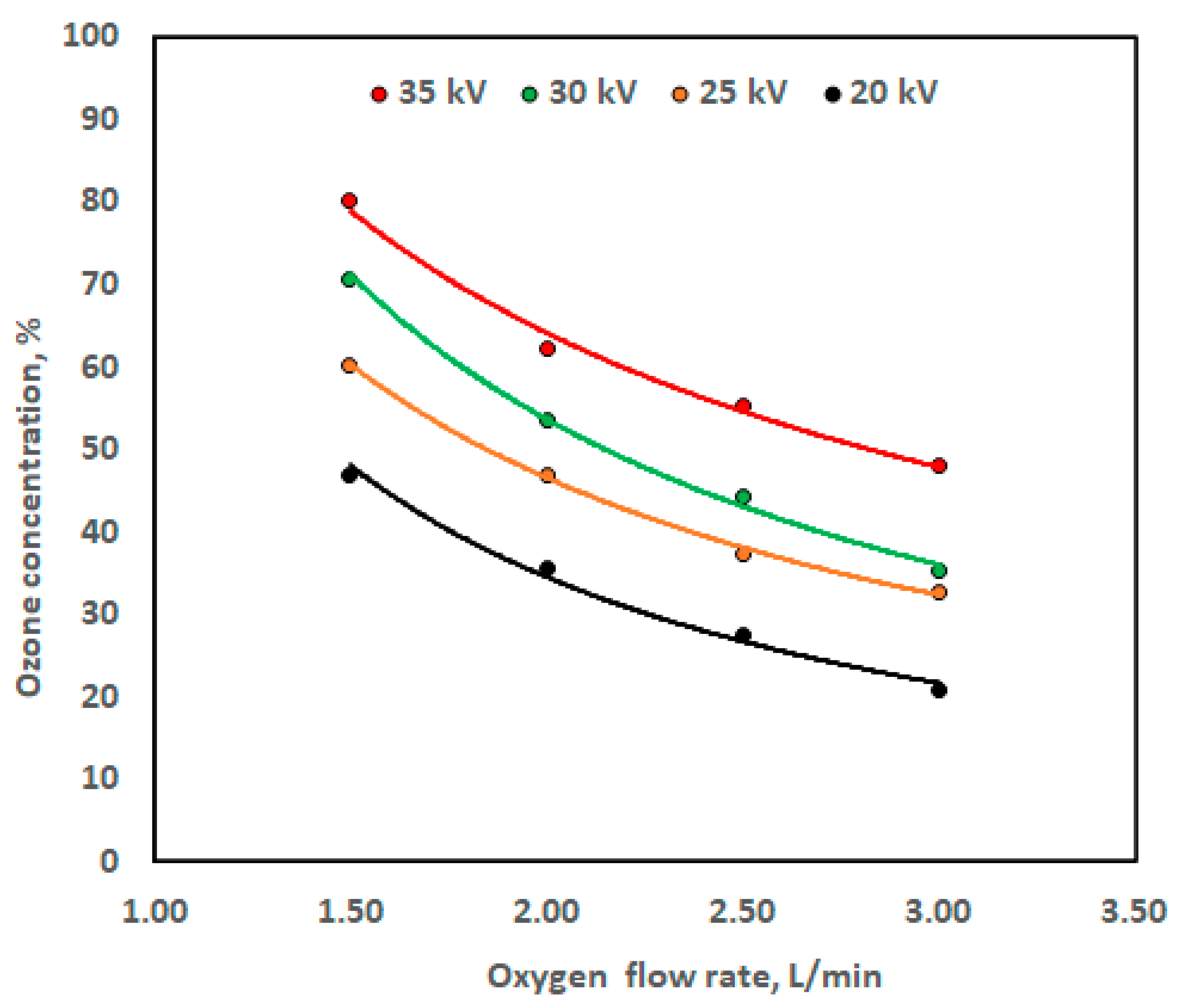


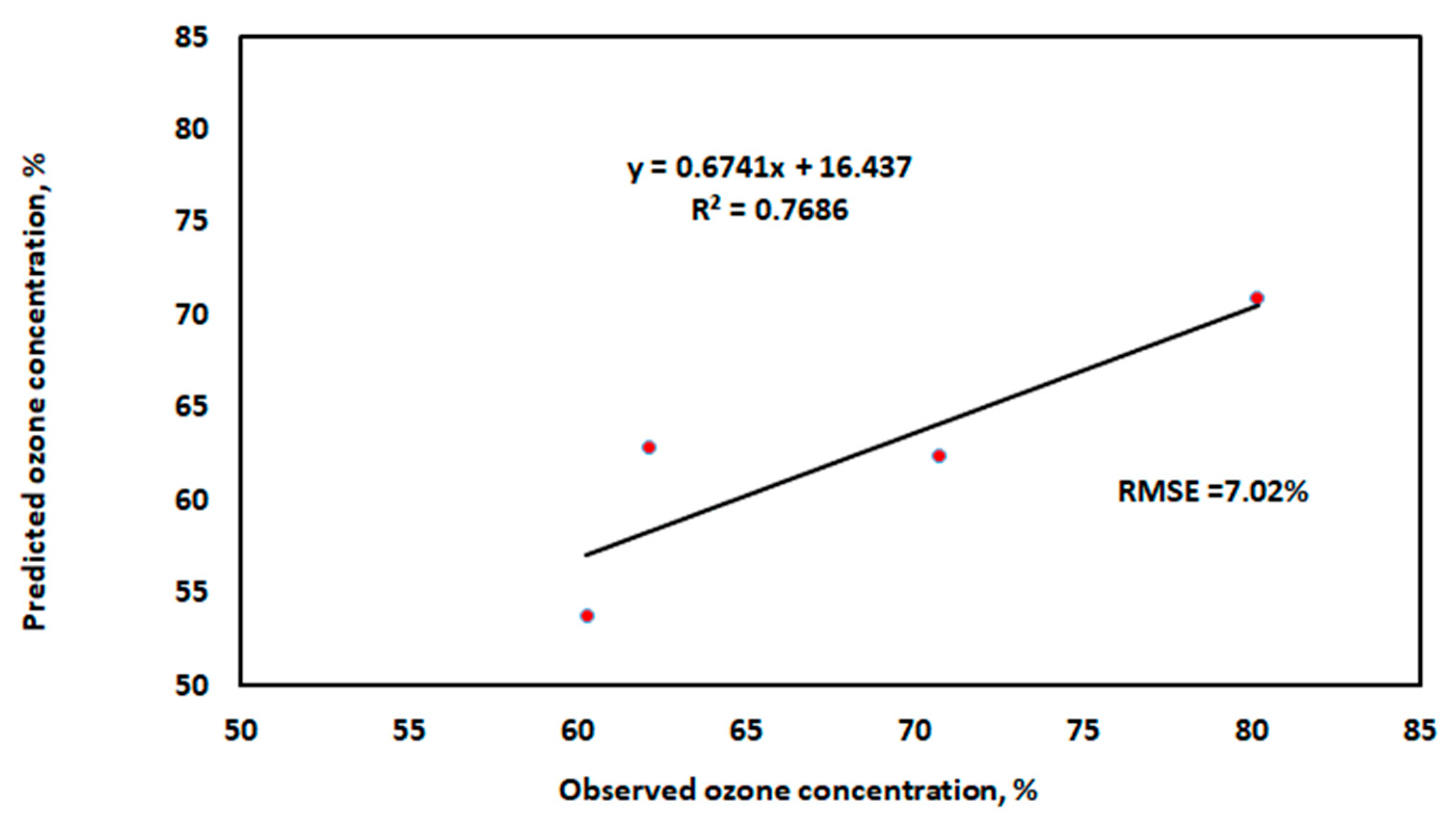
| Treatment Symbol | Treatment Description |
|---|---|
| T1 | 1.5 L/min + 20 kV |
| T2 | 1.5 L/min + 25 kV |
| T3 | 1.5 L/min + 30 kV |
| T4 | 1.5 L/min + 35 kV |
| T5 | 2.0 L/min + 20 kV |
| T6 | 2.0 L/min + 25 kV |
| T7 | 2.0 L/min + 30 kV |
| T8 | 2.0 L/min + 35 kV |
| T9 | 2.5 L/min + 20 kV |
| T10 | 2.5 L/min + 25 kV |
| T11 | 2.5 L/min + 30 kV |
| T12 | 2.5 L/min + 35 kV |
| T13 | 3.0 L/min + 20 kV |
| T14 | 3.0 L/min + 25 kV |
| T15 | 3.0 L/min + 30 kV |
| T16 | 3.0 L/min + 35 kV |
| High Voltage Level (kV) | Regression Constants with Coefficient of Determination (R2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| β0 | β1 | R2 | |
| 20 | 76.59 | −1.15 | 0.9909 |
| 25 | 86.872 | −0.90 | 0.9983 |
| 30 | 106.09 | −0.984 | 0.9971 |
| 35 | 105.85 | −0.723 | 0.9900 |
| Oxygen Flow Rate (L/min) | Regression Constants with Coefficient of Determination (R2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| λ0 | λ1 | R2 | |
| 1.5 | 3.688 | 2.2118 | 0.9931 |
| 2.0 | 2.111 | 1.7256 | 0.9888 |
| 2.5 | −8.297 | 1.7948 | 0.9934 |
| 3.0 | −12.089 | 1.6846 | 0.9498 |
| Variables | Regression Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 35.3329 | 3.404599 | 10.37799 | 2.63 × 10−6 |
| High voltage level (kV) | 1.7168 | 0.107571 | 15.9602 | 6.57 × 10−8 |
| Oxygen flow rate (L/min) | −16.2943 | 1.229011 | −13.2581 | 3.28 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Sager, S.M.; Hemeda, S.G.; Almady, S.S.; Almasoud, W.A.; Marey, S.A.; Al-Hamed, S.A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Mowafy, S.G.; Aboukarima, A.M.; Yehia, M.E. Development of a Low-Cost Ozone (O3) Generator for Research and Education in Agricultural and Food Applications. Processes 2025, 13, 3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113637
Al-Sager SM, Hemeda SG, Almady SS, Almasoud WA, Marey SA, Al-Hamed SA, Al-Ghamdi S, Mowafy SG, Aboukarima AM, Yehia ME. Development of a Low-Cost Ozone (O3) Generator for Research and Education in Agricultural and Food Applications. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113637
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Sager, Saleh M., Samy G. Hemeda, Saad S. Almady, Waleed A. Almasoud, Samy A. Marey, Saad A. Al-Hamed, Saleh Al-Ghamdi, Samir G. Mowafy, Abdulwahed M. Aboukarima, and Mohamed E. Yehia. 2025. "Development of a Low-Cost Ozone (O3) Generator for Research and Education in Agricultural and Food Applications" Processes 13, no. 11: 3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113637
APA StyleAl-Sager, S. M., Hemeda, S. G., Almady, S. S., Almasoud, W. A., Marey, S. A., Al-Hamed, S. A., Al-Ghamdi, S., Mowafy, S. G., Aboukarima, A. M., & Yehia, M. E. (2025). Development of a Low-Cost Ozone (O3) Generator for Research and Education in Agricultural and Food Applications. Processes, 13(11), 3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113637







