Propagation and Attenuation Mechanism of Pressure Waves During Pulse Hydraulic Fracturing in Fractures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pressure-Wave Equation Model
2.1. Pressure-Wave Propagation Model
2.1.1. Seepage Model
2.1.2. Water-Hammer Model
2.1.3. Transient Flow Model
2.2. Construction of the Unsteady Friction Pressure-Wave Equation Model
2.3. Initial–Boundary Conditions and Numerical Simulation Parameters
3. Simulation Solution
4. Results and Discussion
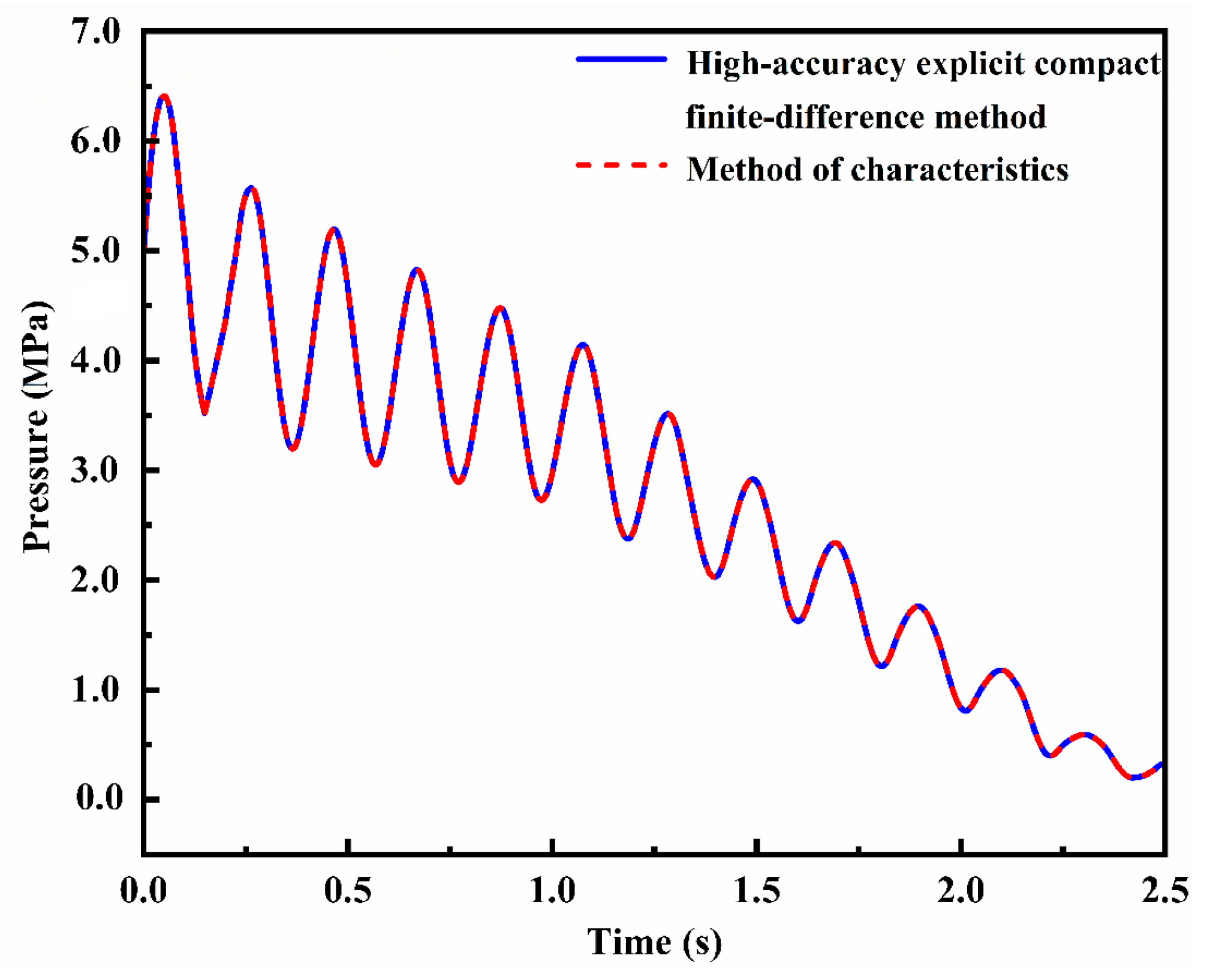
4.1. Accuracy Verification
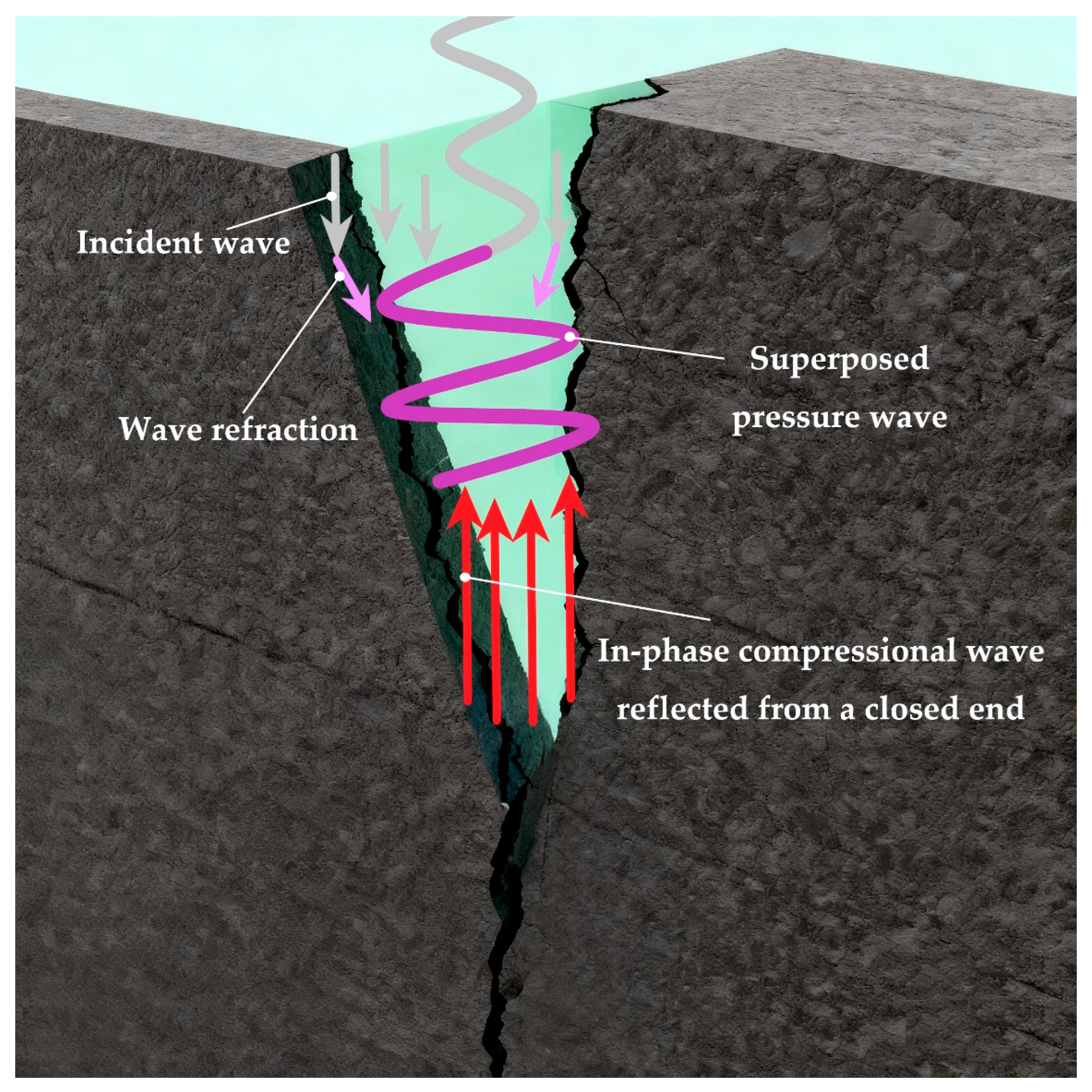
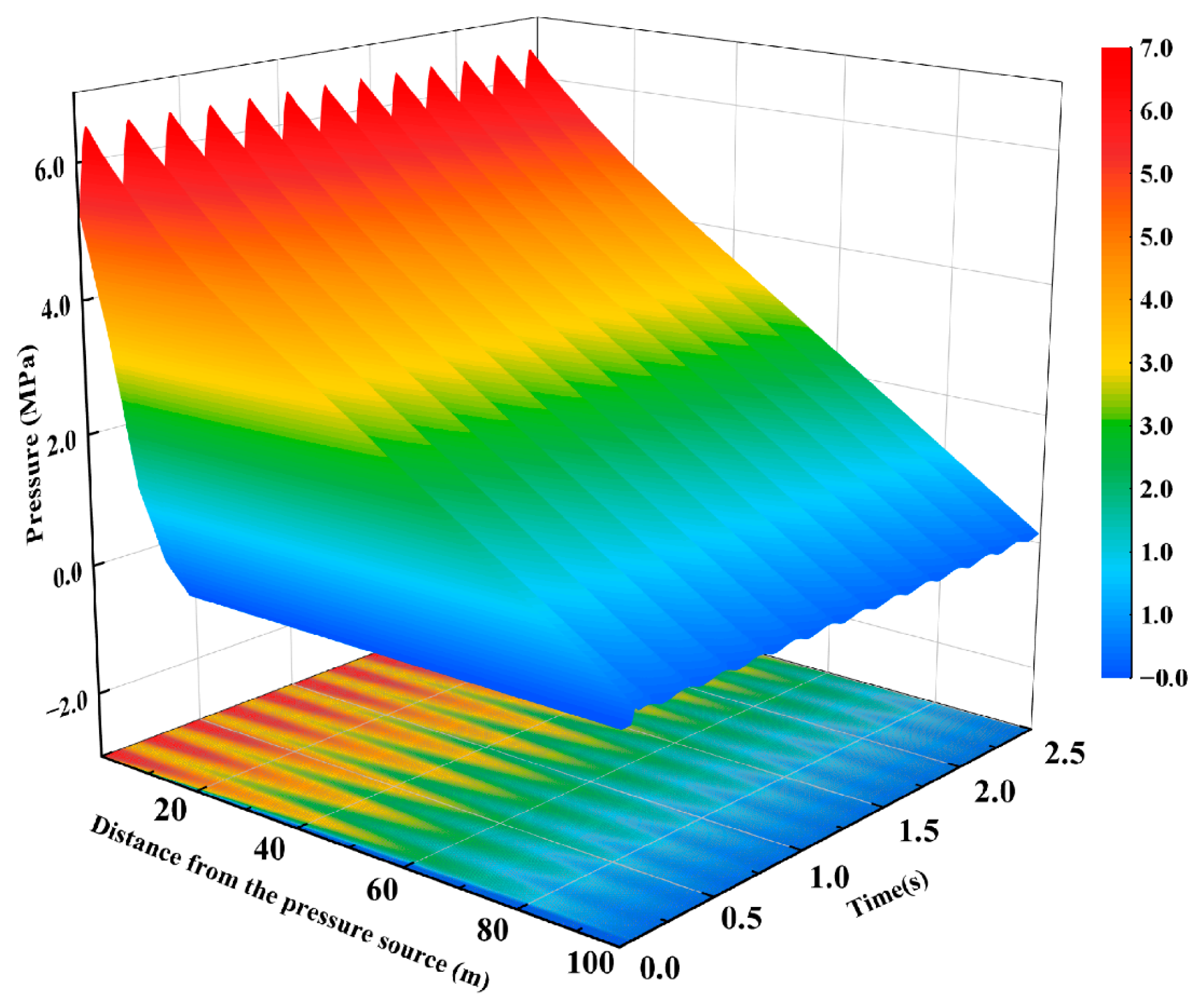
4.2. Pressure-Wave Propagation and Pressurization Phenomena Within the Fracture
4.3. Influence of Factors on Pressure-Wave Attenuation Within the Fracture
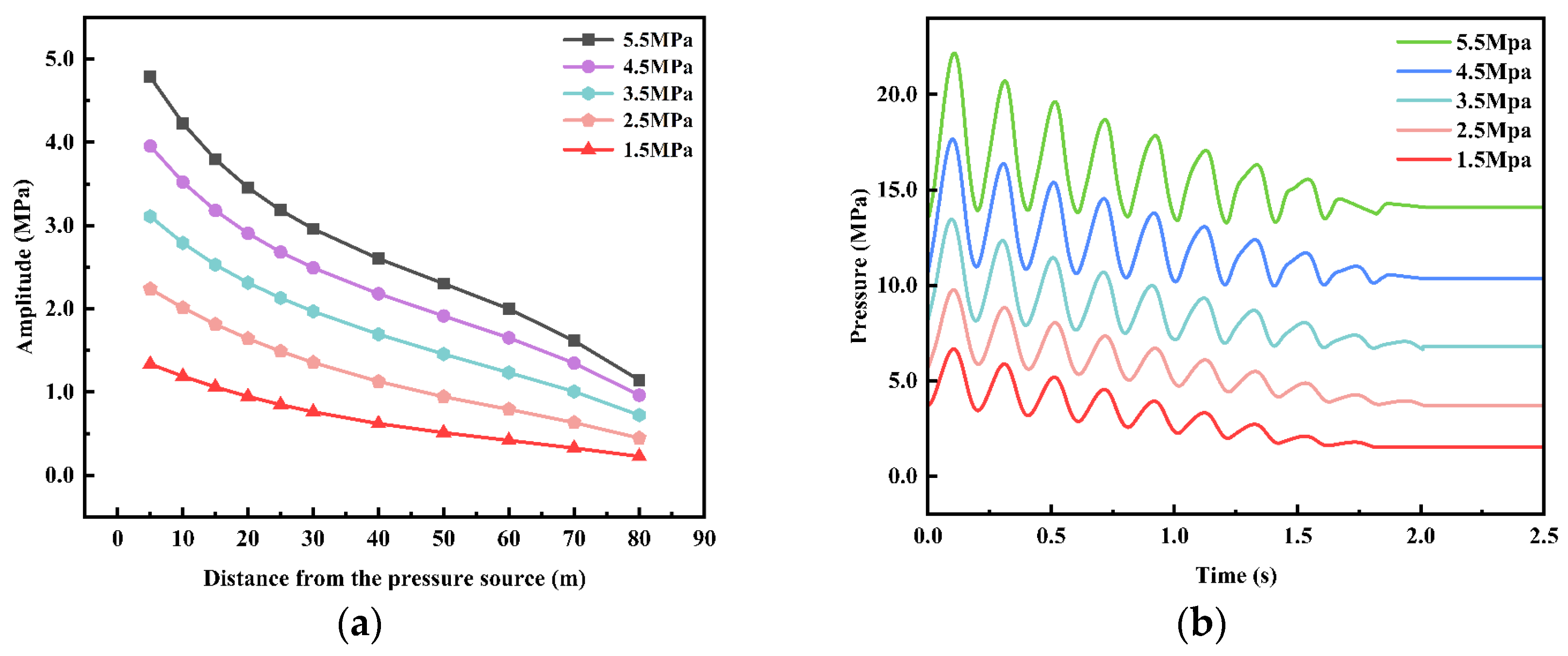
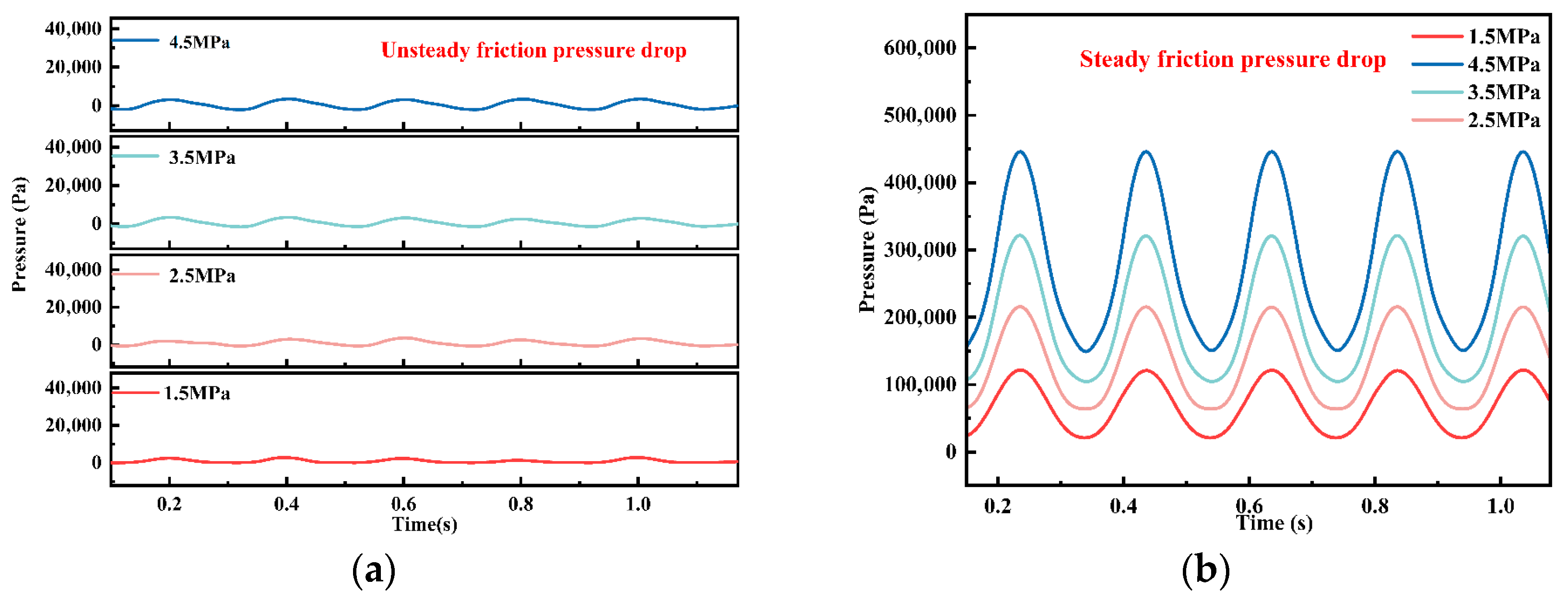
4.3.1. Analysis of Fracturing Fluid Pressure
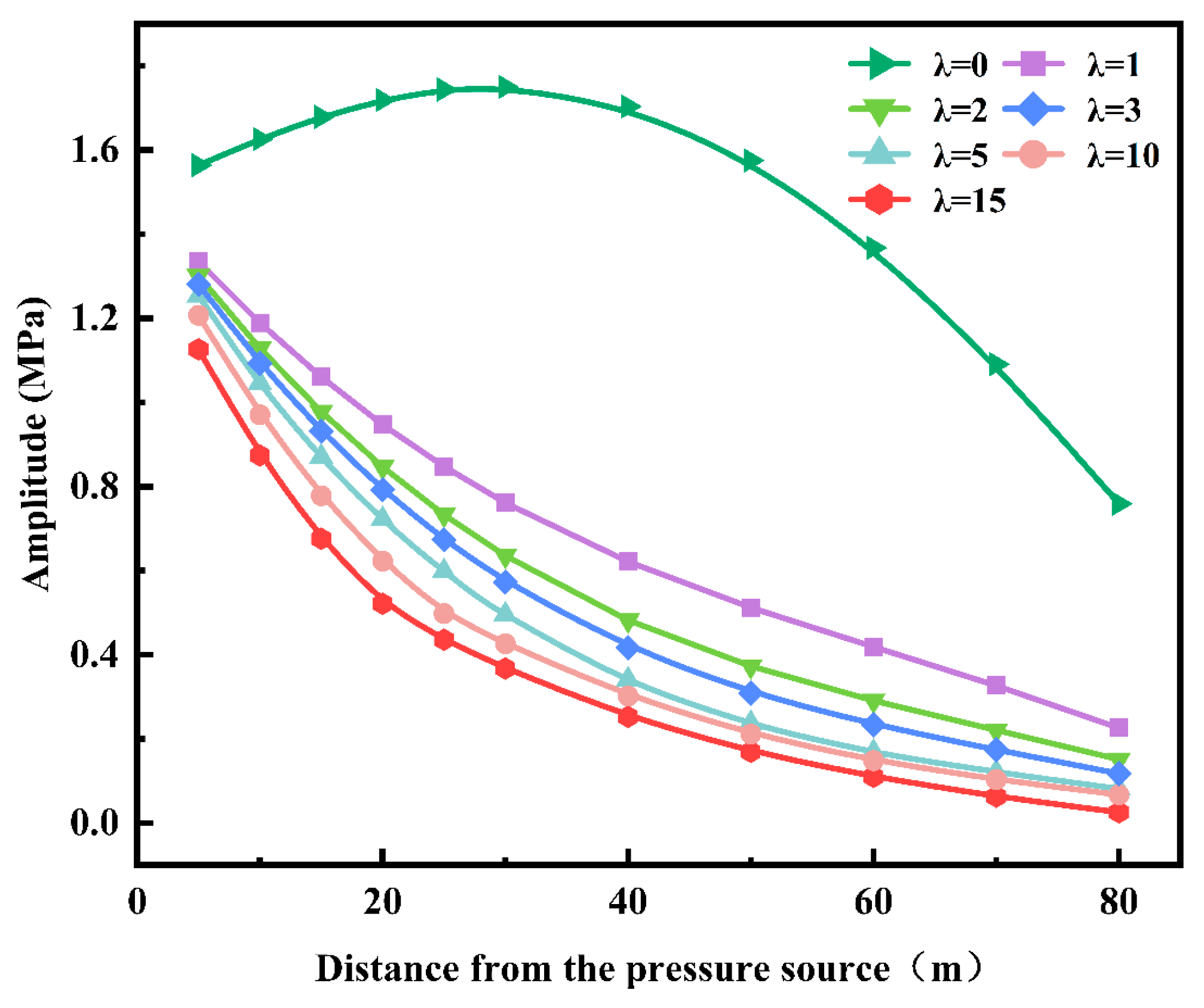
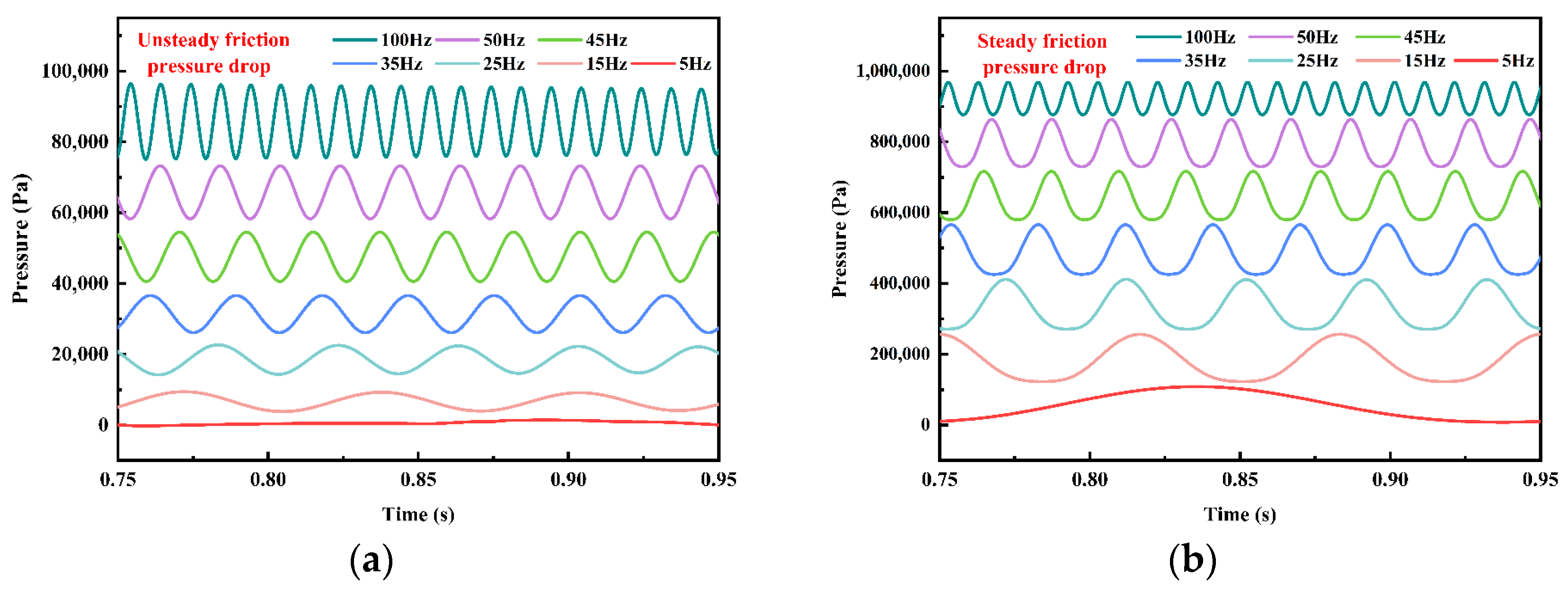
4.3.2. Effect of Damping on Pressure-Wave Attenuation
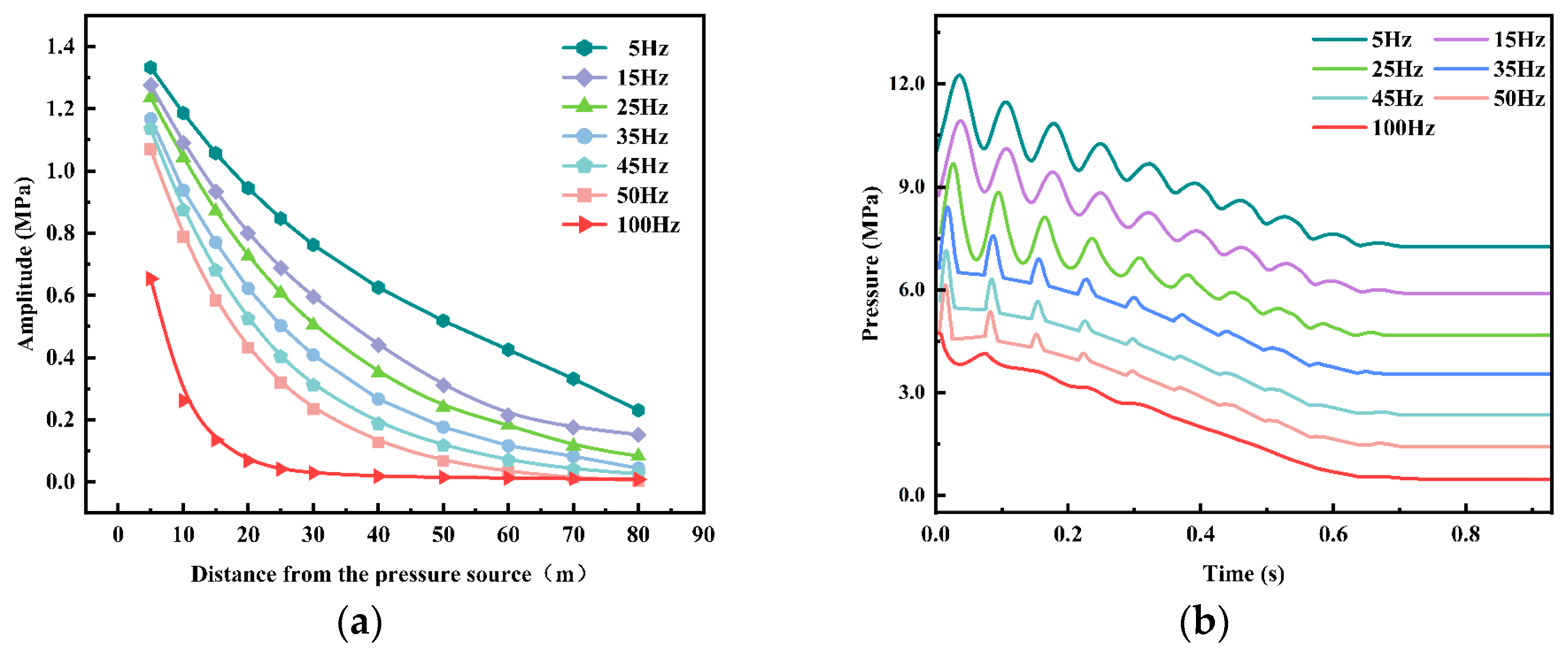
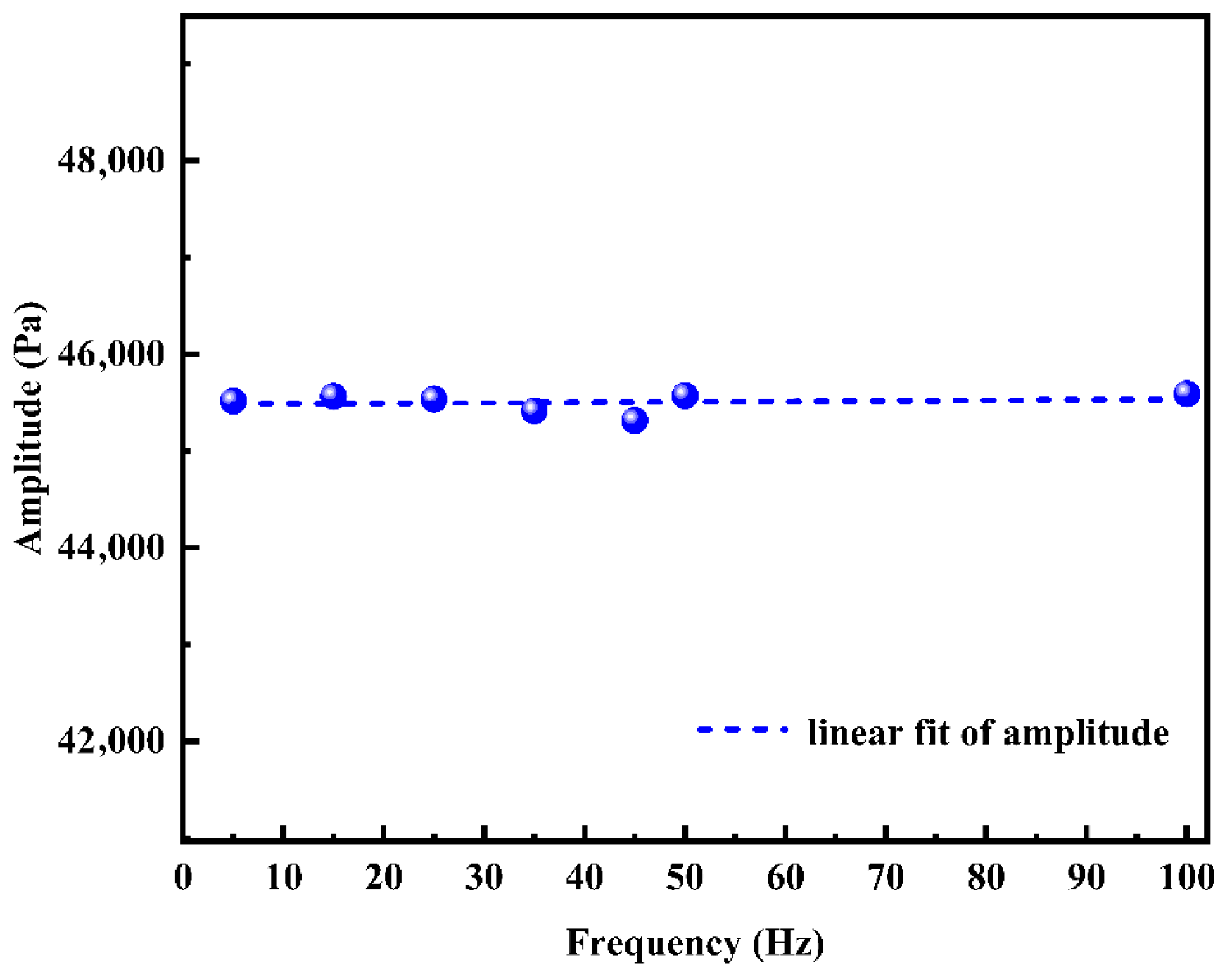
4.3.3. Effect of Frequency on Pressure-Wave Attenuation
4.3.4. Effect of Amplitude on Pressure-Wave Attenuation
4.3.5. Effect of Pulse Type on Pressure-Wave Attenuation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X. Study on Stimulation Mechanism of Energy Storage Volume Fracturing in Tight Sandstone Reservoir. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhang, R. Numerical simulation of complex fracture-network formation in volume fracturing of tight oil reservoirs. Pet. Mach. 2022, 50, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C. Study on the mechanism of hydraulic fracture propagation and fracture network formation under pre hydraulic fracturing. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Parchei-Esfahani, M.; Gee, B.; Gracie, R. Dynamic hydraulic stimulation and fracturing from a wellbore using pressure pulsing. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 235, 107152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.; Hough, D.; Shang, L.; Qian, S. Gas desorption characteristics effected by the pulsating hydraulic fracturing in coal. Fuel 1994, 236, 190–200. [Google Scholar]
- Cerfontaine, B.; Collin, F. Cyclic and fatigue behaviour of rock materials: Review, interpretation, and research perspectives. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xie, J.; Ni, G.; Rahman, S.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H. Effects of pulse wave on the variation of coal pore structure in pulsating hydraulic fracturing process of coal seam. Fuel 2020, 264, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A. Research on Fracturing Mechanism of Pulse Cycle Hydraulic Fracturing in Tight Reservoirs. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Z.; Tian, W. Investigation on the controlling factors of pressure wave propagation behavior induced by pulsating hydraulic fracturing. SPE J. 2021, 26, 2716–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, O.; Kondrat, O. Utilizing well-reservoir pseudo-connections for multi-stage hydraulic fracturing modeling in tight gas saturated formations. Min. Miner. Depos. 2024, 18, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyaur, N.; Jin, Y. Laboratory evidence of transient pressure surge in a fluid-filled fracture as a potential driver of remote dynamic earthquake triggering. Seism. Rec. 2021, 1, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorotto, V.; Rinaldo, A. Turbulent pressure fluctuations under hydraulic jumps. Hydraul. Res. 1992, 30, 499–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Deng, X. Numerical study on pulse pressure propagation in multi-stage plate fractures. Chin. Theor. Appl. Mech. 1998, 30, 662–671. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Lin, B.; Zhai, C. Pulsating hydraulic fracturing technology in low-permeability coal seams. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, P. Study on the attenuation mechanism of pulse pressure propagation in plate fractures. Water Resour. Hydropower Technol. 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S. Study on the Pore Pressure Wave Propagation Law of Pulsating Water Flooding. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Qingdao, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. The Mechanism and Technology of Permeability Enhancements in Coal Seam Based on High Pressure Pulsating Hydraulic Fracturing. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z. Propagation characteristics of pulse pressure in bottom plate fractures of water cushion ponds. Sichuan Univ. (Eng. Sci. Ed.) 2000, 3, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xi, M.; Qu, J. Experimental study on propagation of flucturation pressure in fissures. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 12, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, B.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, N. Change of Medium Impact on Propagation Characteristic of Water. Coal Technol. 2014, 33, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowicz, K.; Andrade, D.; Kubrak, M.; Kodura, A. Accuracy and limitations of 1D and Q2D water hammer models for laminar and turbulent flows. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2025, 47, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeldayem, O.; Ferras, D. Analysis of Unsteady Friction Models Used in Engineering Software for Water Hammer Analysis: Implementation Case in WANDA. Water 2021, 13, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbinder, G. Slot cutting in rock with a high-speed water jet. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1977, 14, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, X. Investigation on Fluctuating Pressure Transmission along Joints. J. Tianjin Univ. 1988, 3, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorotto, V.; Rinaldo, A. Fluctuating uplift and lining design in spillway stilling basins. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1992, 118, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, A. Model discussion of pressure fluctuations propagation within lining slab joints in stilling basins. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunone, B.; Karney, B.W.; Mecarelli, M.; Ferrante, M. Velocity profiles and unsteady pipe friction in transient flow. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 2000, 126, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, L.; Ai, X. High-order compact explicit difference scheme for two-dimensional wave equation and stability analysis. J. Harbin Univ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 29, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G. High-order compact ADI methods for parabolic equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2006, 52, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cao, F.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q. In-situ stress evaluation of the Xushier tight sandstone reservoir in the HC area of the Sichuan Basin and its application in tight gas development. Geol. China 2023, 50, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Understanding and practice of water hammer prevention in pressure pipeline engineering design. Chem. Eng. Des. Commun. 2020, 46, 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, W.; Yang, G.; Liu, G.; Fan, C.; Xie, C. Parameter optimization and field application of downhole low-frequency pulsation hydraulic fracturing technology. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2023, 45, 643–652. [Google Scholar]








| Number | Steady Friction Coefficient | Brunone Coefficient | Wave Velocity (m/s) | Frequency (Hz) | Amplitude (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1392 | 5 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 1392 | 5 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 2 | 0 | 1392 | 5 | 1.5 |
| 4 | 3 | 0 | 1392 | 5 | 1.5 |
| 5 | 5 | 0 | 1392 | 5 | 1.5 |
| 6 | 10 | 0 | 1392 | 5 | 1.5 |
| 7 | 15 | 0 | 1392 | 5 | 1.5 |
| Number | Steady Friction Coefficient | Brunone Coefficient | Wave Velocity (m/s) | Frequency (Hz) | Amplitude (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1392 | 100 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 1 | 0.005 | 1392 | 100 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 1 | 0.01 | 1392 | 100 | 1.5 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.05 | 1392 | 100 | 1.5 |
| Number | Frequency (Hz) | Wave Velocity (m/s) | Steady Friction Coefficient | Brunone Coefficient | Amplitude (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 1392 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 15 | 1392 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 25 | 1392 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 |
| 4 | 35 | 1392 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 |
| 5 | 45 | 1392 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 |
| 6 | 50 | 1392 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 |
| 7 | 100 | 1392 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, G. Propagation and Attenuation Mechanism of Pressure Waves During Pulse Hydraulic Fracturing in Fractures. Processes 2025, 13, 3513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113513
Shu Y, Zhang H, Qu H, Wang Y, Jiao G. Propagation and Attenuation Mechanism of Pressure Waves During Pulse Hydraulic Fracturing in Fractures. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113513
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Yu, Heng Zhang, Hai Qu, Yuchen Wang, and Guoying Jiao. 2025. "Propagation and Attenuation Mechanism of Pressure Waves During Pulse Hydraulic Fracturing in Fractures" Processes 13, no. 11: 3513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113513
APA StyleShu, Y., Zhang, H., Qu, H., Wang, Y., & Jiao, G. (2025). Propagation and Attenuation Mechanism of Pressure Waves During Pulse Hydraulic Fracturing in Fractures. Processes, 13(11), 3513. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113513





