Quantitative Evaluation Method for Sedimentation Stability of Oil Well Workover Fluids by Spectral Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
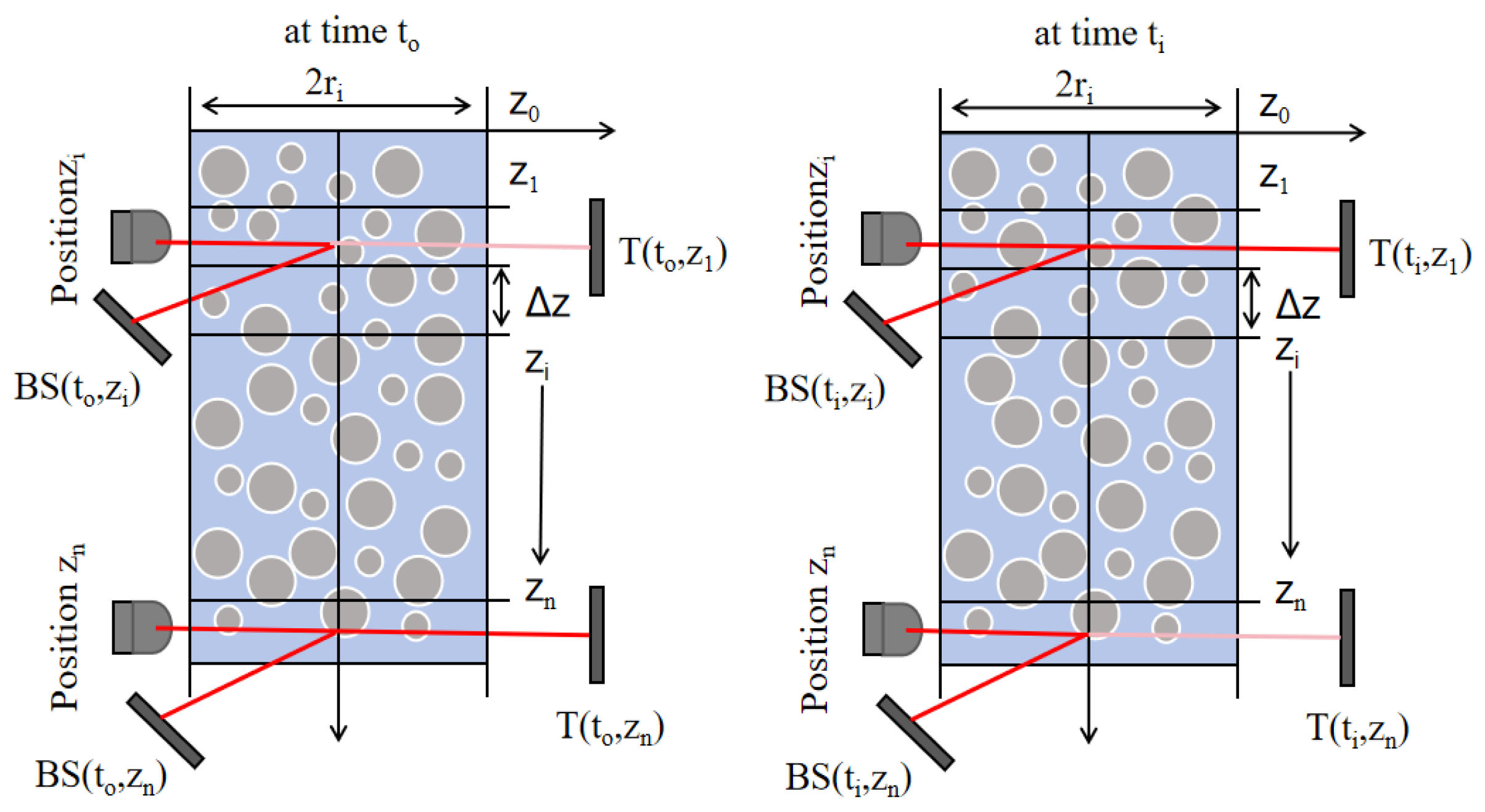
2.2. Principle of Instrument Testing
2.3. Barite Water Dispersion System Test Steps
2.4. Oil Well Fluid Settlement Evaluation Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Backscattering Intensity Variation
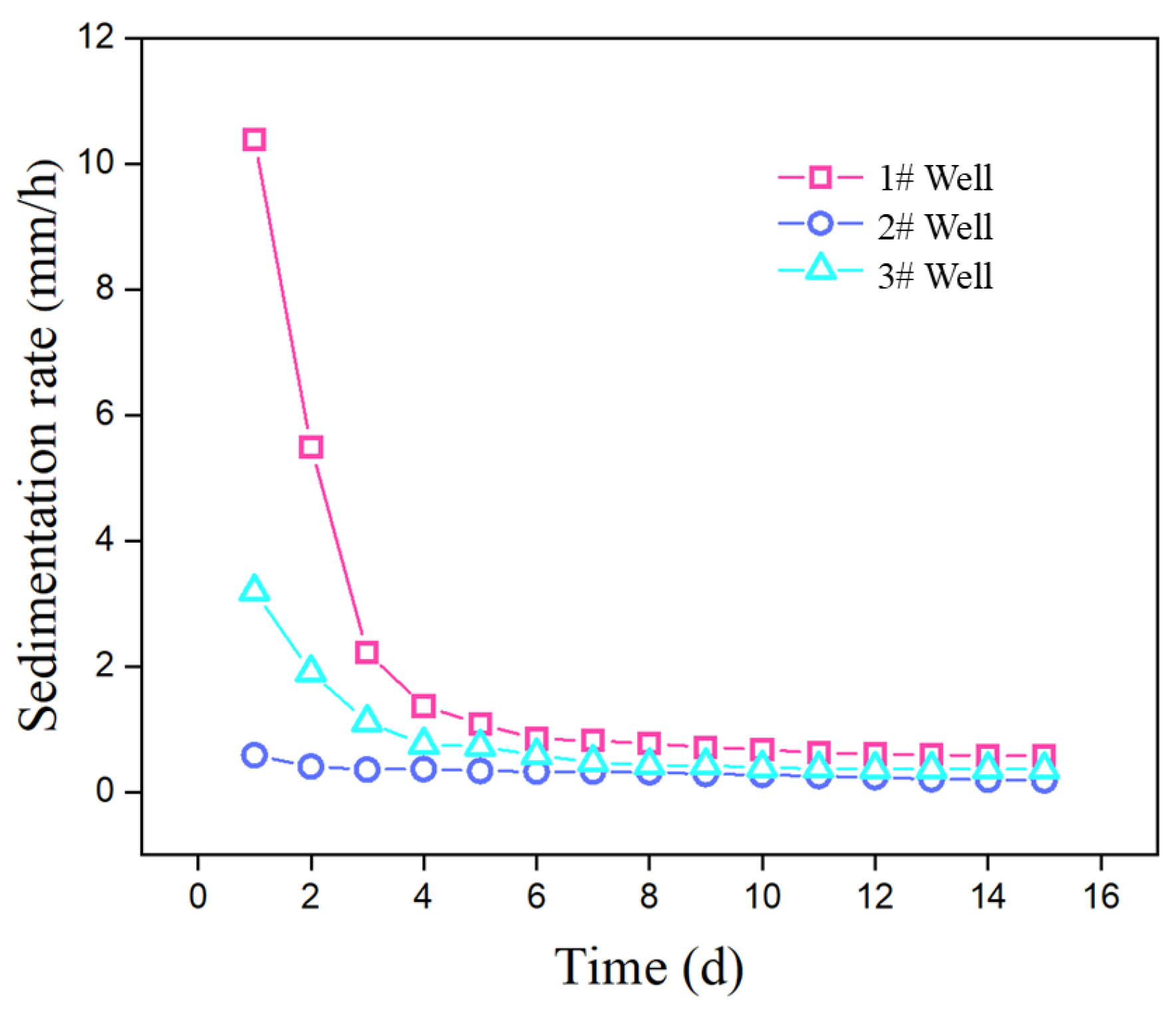
3.2. Settlement Rate
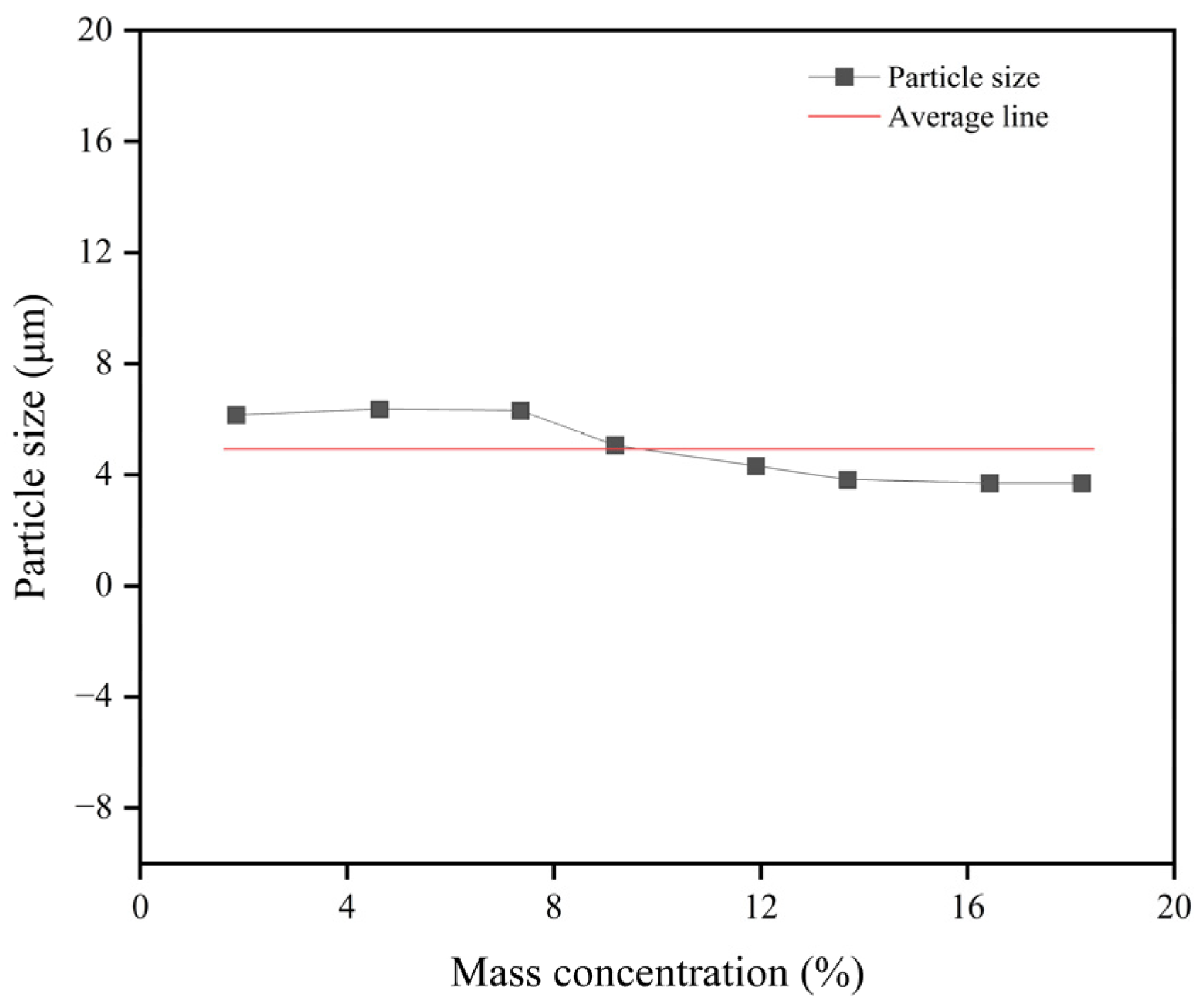
3.3. Particle Size Analysis
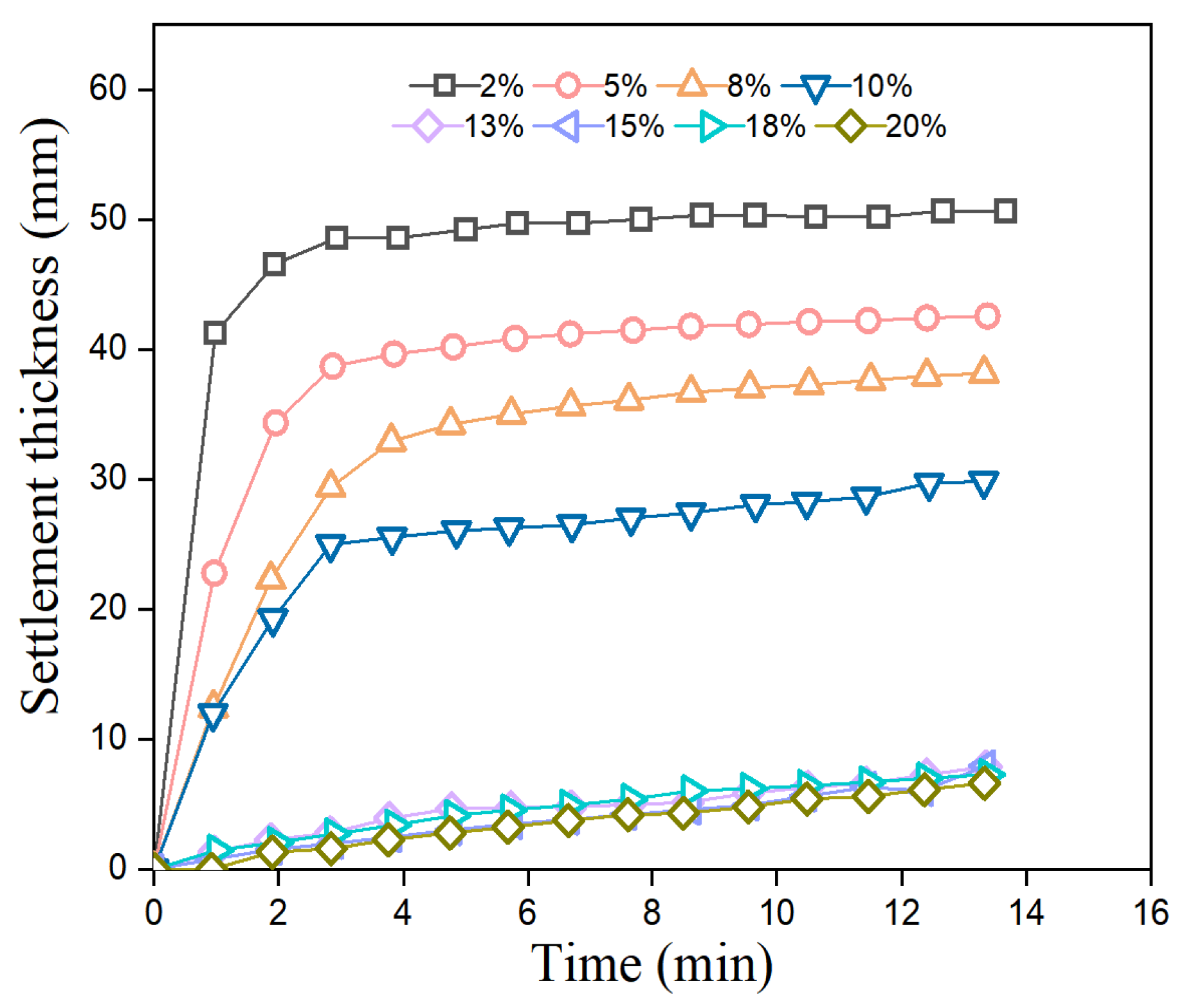
3.4. Settlement Thickness Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adjei, S.; Elkaktatny, S.; Sokama-Neuyam, Y.A.; Sarkodie, K.; Quaye, J.A. Evaluation and remediation techniques for barite sagging: A review. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 225, 211731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alade, O.; Mahmoud, M.; Al-Nakhli, A. Rheological studies and numerical investigation of barite sag potential of drilling fluids with thermochemical fluid additive using computational fluid dynamics (CFD). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 220, 111179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.R.; Oechsler, B.F.; Meleiro, L.A.C.; Fagundes, F.M.; Calada, L.A. Settling of weighting agents in non-Newtonian fluids to off-shore drilling wells: Modeling, parameter estimation and analysis of constitutive equations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 184, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrålstad, T.; Saasen, A.; Fjær, E.; Øia, T.; Ytrehus, J.D.; Khalifeh, M. Plug & abandonment of offshore wells: Ensuring long-term well integrity and cost-efficiency. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 173, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Guria, C.; Rajak, V.K. A state of the art review on the performance of high-pressure and high-temperature drilling fluids: Towards understanding the structure-property relationship of drilling fluid additives. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 213, 110318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Tan, K. Experimental and modelling studies on static sag of solid weighting powders in Polysulfonate workover fluids at high temperature and high pressure. Petroleum 2025, 11, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geri, B.S.B.; Mahmoud, M.; Abdulraheem, A.; Al-Mutairi, S.H.; Elkatatny, S.M.; Shawabkeh, R.A. Single stage filter cake removal of barite weighted water based drilling fluid. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 149, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozebon, D.; Lima, E.C.; Maia, S.M.; Fachel, J.M. Heavy metals contribution of non-aqueous fluids used in offshore oil drilling. Fuel 2005, 84, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tor, H.O.; Arild, S.; Claas, V.D.Z.; Per, A.A. The Effect of Weighting Material Sag on Drilling Operation Efficiency. In Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference & Exhibition, Jakarta, Indonesia, 30 October–1 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bern, P.A.; Van Oort, E.; Neustadt, B.; Ebeltoft, H.; Zurdo, C.; Zamora, M.; Slater, K.S. Barite Sag: Measurement, Modeling, and Management. SPE Drill. Complet. 2000, 15, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrozik, A.; Gonet, A.; Fijał, J.; Terpiłowski, K.; Czekaj, L. Analysis of waste mud stability. Wydaw. Agh 2014, 31, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.B.C.; Fagundes, F.M.; de Oliveira Arouca, F.; Damasceno, J.J.R. Sedimentation of solids in drilling fluids used in oil well drilling operations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 162, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofei, T.N.; Lund, B.; Saasen, A. Effect of particle number density on rheological properties and barite sag in oil-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Bouguetta, M. A Comparative Assessment of Barite SAG Evaluation Methods. In Proceedings of the SPE Deepwater Drilling and Completions Conference, Galveston, TX, USA, 14–15 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, J.; Eler, F.; Martins, A.; Scheid, C.; Calçada, L.; Meleiro, L. A Simplified Model Applied to the Barite Sag and Fluid Flow in Drilling Muds: Simulation and Experimental Results. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2017, 72, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, L.; Cheng, R.; Ni, X.; Yang, H. Prevent Barite Static Sag of Oil-Based Completion Fluid in Ultra-Deep Wells. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Virtual, 23 March–1 April 2021. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Sentis, M.P.L.; Lemahieu, G.; Hemsley, E.; Bouzaid, M.; Brambilla, G. Size distribution of migrating particles and droplets under gravity in concentrated dispersions measured with static multiple light scattering. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 653, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. (Ed.) Contents. In An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. v–xii. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, P.; Snabre, P. Settling of a Suspension of Hard Spheres. Europhys. Lett. 2007, 25, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürger, R.; Fernández-Nieto, E.D.; Osores, V. A dynamic multilayer shallow water model for polydisperse sedimentation. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 2019, 53, 1391–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyar, M.; Johnston, L.J.; Jakubek, Z.J. Dispersion, stability and size measurements for cellulose nanocrystals by static multiple light scattering. Cellulose 2018, 25, 5751–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentis, M.P.L.; Brambilla, G.; Fessard, V.; Meunier, G. Simultaneous screening of the stability and dosimetry of nanoparticles dispersions for in vitro toxicological studies with static multiple light scattering technique. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2020, 69, 104972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storti, F. Particle size distributions by laser diffraction: Sensitivity of granular matter strength to analytical operating procedures. Solid Earth 2010, 1, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, N.; Kulozik, U. Separation of Whey Protein Aggregates by Means of Continuous Centrifugation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.B.; Xiao, W.L.; Zheng, L.L.; Lei, Q.H.; Qin, C.Z.; He, Y.A.; Liu, S.S.; Li, M.; Li, Y.M.; Zhao, J.Z. Pore throat structure heterogeneity and its effect on gas-phase seepage capacity in tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study from the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 2892–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, J.; Couples, G.D.; Huang, Z.; Sun, H.; Ma, J. Numerical modelling and analysis of reactive flow and wormhole formation in fractured carbonate rocks. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 172, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Yang, M.; Yan, C.; Tian, T.; Huang, S. Dynamic Distribution Characteristics of Oil and Water during Water Flooding in a Fishbone Well with Different Branch Angles. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 27206–27215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Yang, Y.; Bernabé, Y.; Lei, Q.; Li, M.; Xie, Q.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Huang, C.; Zhao, J. Experimental Study on EOR in Shale Oil Cores during Associated Gasflooding: A Case Study from Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. SPE J. 2023, 28, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shang, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhou, L. Study on imbibition during the CO2 enhanced oil recovery in fractured tight sandstone reservoirs. Capillarity 2023, 7, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yan, X.; Yao, J.; Sun, S. Modeling and analysis of the acidizing process in carbonate rocks using a two-phase thermal-hydrologic-chemical coupled model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão Costa Santos, N.; Marques Fagundes, F.; Leibsohn Martins, A.; Ribeiro Damasceno, J.J.; de Oliveira Arouca, F. Stability of oil well olefin drilling fluids: Solid–liquid sedimentation and rheological characterization. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 38, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deninno, E.; Molina, M.; Shipman, J.; Dearing, H.; Arpini, F.; Bussaglia, L. High Performance Water Base Fluid Improves Wellbore Stability and Lowers Torque. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference & Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 26–28 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.; Fawzy, A.; Dawood, M.; Rahal, A.; Salazar, N.; Al Maktoum, F.; Al Kindi, M.; Al Rashdi, M. Nanotechnology-Driven Bridging Package Approach for Improving Wellbore Stability, Preventing Differential Sticking, and Reducing Loss Events in Severely Depleted Formations in Oman. In Proceedings of the SPE Conference at Oman Petroleum & Energy Show, Muscat, Oman, 12–14 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.; Fan, D.; Sun, F.; Kaminski, A.; Smyth, W. Shear Instabilities and Stratified Turbulence in an Estuarine Fluid Mud. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2022, 52, 2257–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiburg, E.; Kneller, B. Turbidity Currents and Their Deposits. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 42, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, B.R.; Rau, M.J.; Byron, M.L. Settling of nonuniform cylinders at intermediate Reynolds numbers. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2024, 9, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr-Azadani, M.M.; Meiburg, E. Turbidity currents interacting with three-dimensional seafloor topography. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 745, 409–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Q.; Yang, C.; Song, X. Gas Injection for Improving Oil Recovery in Highly Volatile Fractured Reservoirs with Thick Buried Hills in Bohai Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Mu, X.; Wang, B.; Tang, J.; Feng, T.; Xiang, J.; Peng, F. Study on the Geochemical Genesis and Differences of Ordovician Oil and Gas Reservoirs. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2024, 59, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
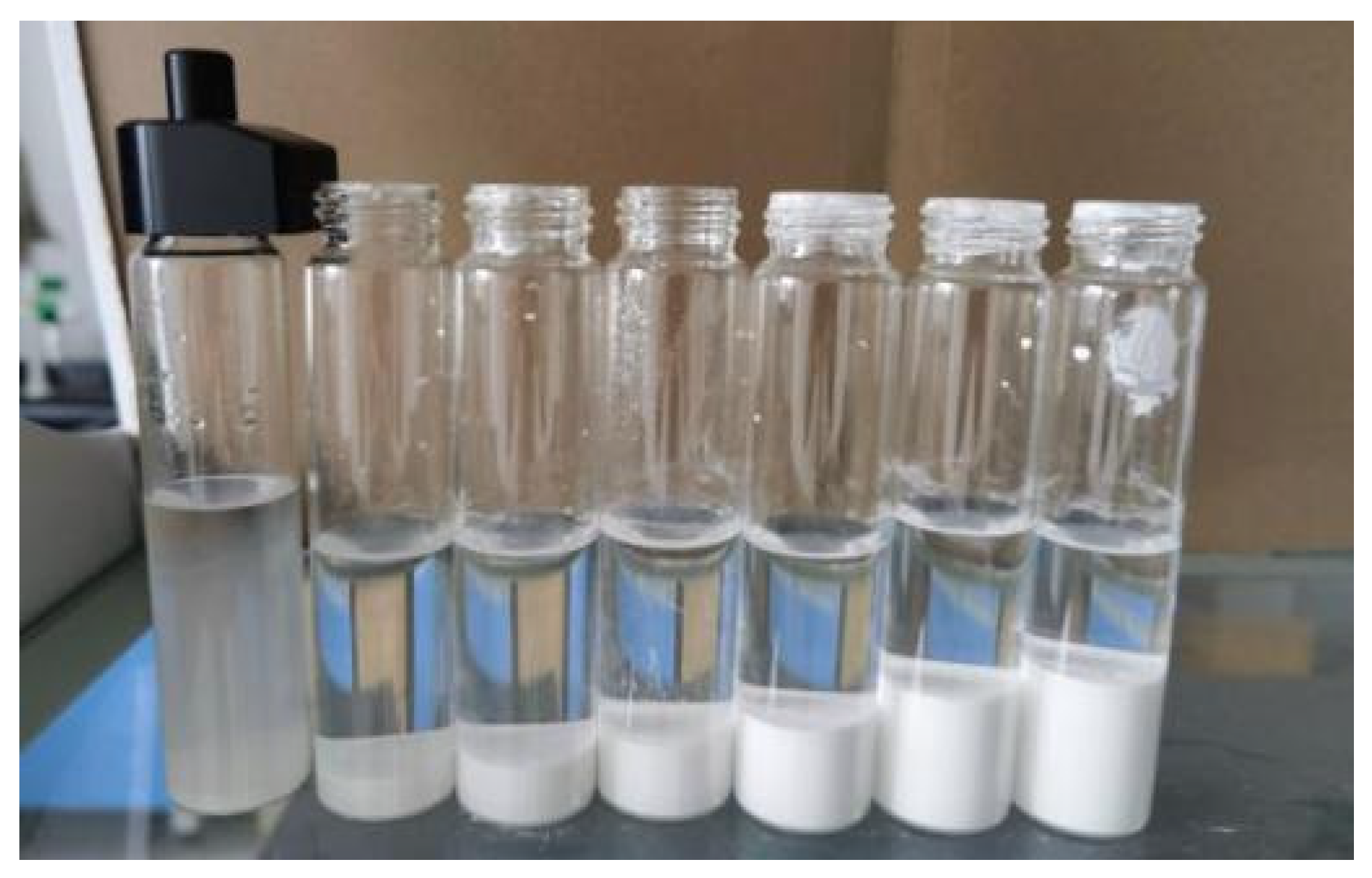








| Number | Sample | Density (g/cm3) | Settlement Temperature (°C) | Sedimentation Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.02 | 25 | 15 min |
| 2 | 5% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.05 | 25 | 15 min |
| 3 | 8% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.08 | 25 | 15 min |
| 4 | 10% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.10 | 25 | 15 min |
| 5 | 13% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.13 | 25 | 15 min |
| 6 | 15% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.15 | 25 | 15 min |
| 7 | 18% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.18 | 25 | 15 min |
| 8 | 20% Barite Water Dispersion | 1.20 | 25 | 15 min |
| 9 | 1# Well oil testing work fluid | 1.87 | 92.4 | 15 days |
| 10 | 2# Well oil testing work fluid | 1.47 | 132 | 15 days |
| 11 | 3# Well oil testing work fluid | 2.15 | 105 | 15 days |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gong, H.; Zhang, N.; Su, R.; Su, J. Quantitative Evaluation Method for Sedimentation Stability of Oil Well Workover Fluids by Spectral Analysis. Processes 2025, 13, 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113469
Li W, Li Y, Zhang K, Gong H, Zhang N, Su R, Su J. Quantitative Evaluation Method for Sedimentation Stability of Oil Well Workover Fluids by Spectral Analysis. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113469
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenzhe, Yufei Li, Kui Zhang, Hao Gong, Naiyan Zhang, Rui Su, and Junlin Su. 2025. "Quantitative Evaluation Method for Sedimentation Stability of Oil Well Workover Fluids by Spectral Analysis" Processes 13, no. 11: 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113469
APA StyleLi, W., Li, Y., Zhang, K., Gong, H., Zhang, N., Su, R., & Su, J. (2025). Quantitative Evaluation Method for Sedimentation Stability of Oil Well Workover Fluids by Spectral Analysis. Processes, 13(11), 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113469





