Experimental Evaluation of Pyrolysis Processes for Kazakhstan Oil Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of Gaseous Products
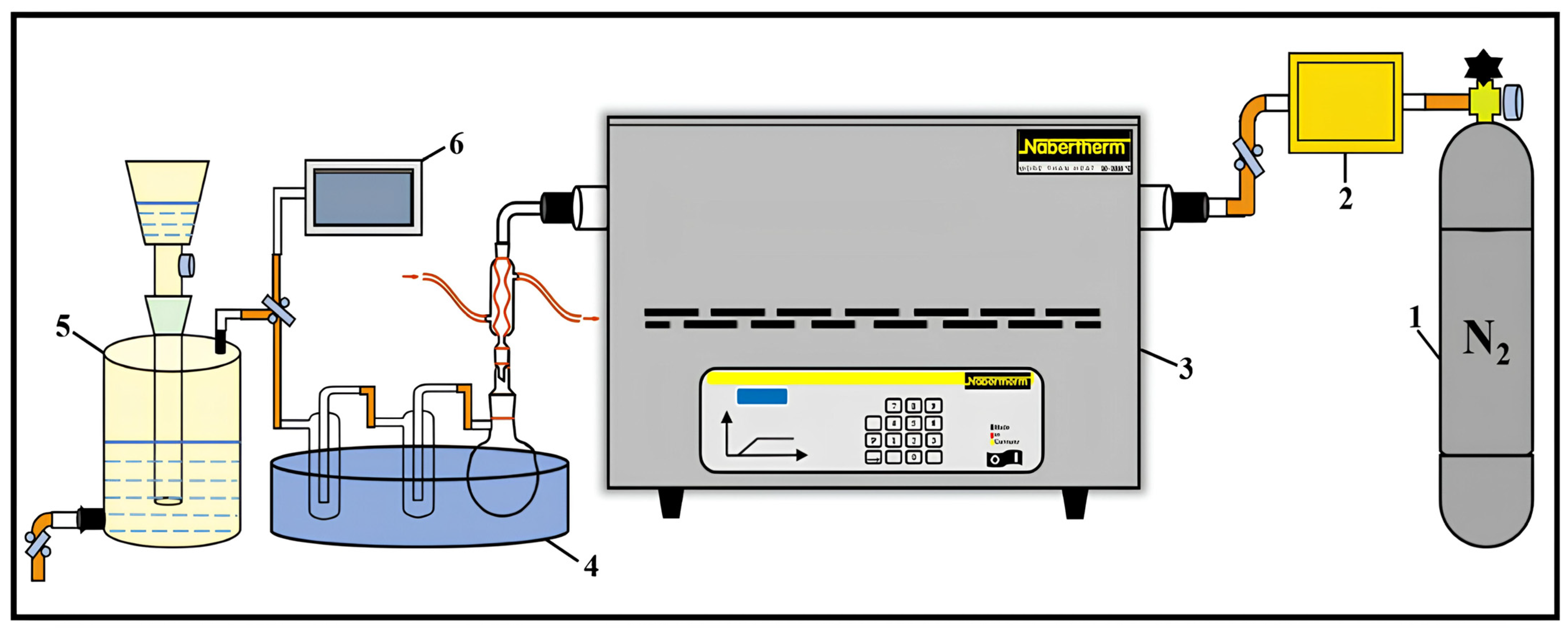
2.2. Description of the Laboratory Pyrolysis Setup
2.3. Hydrocarbon Composition of Liquid Oils
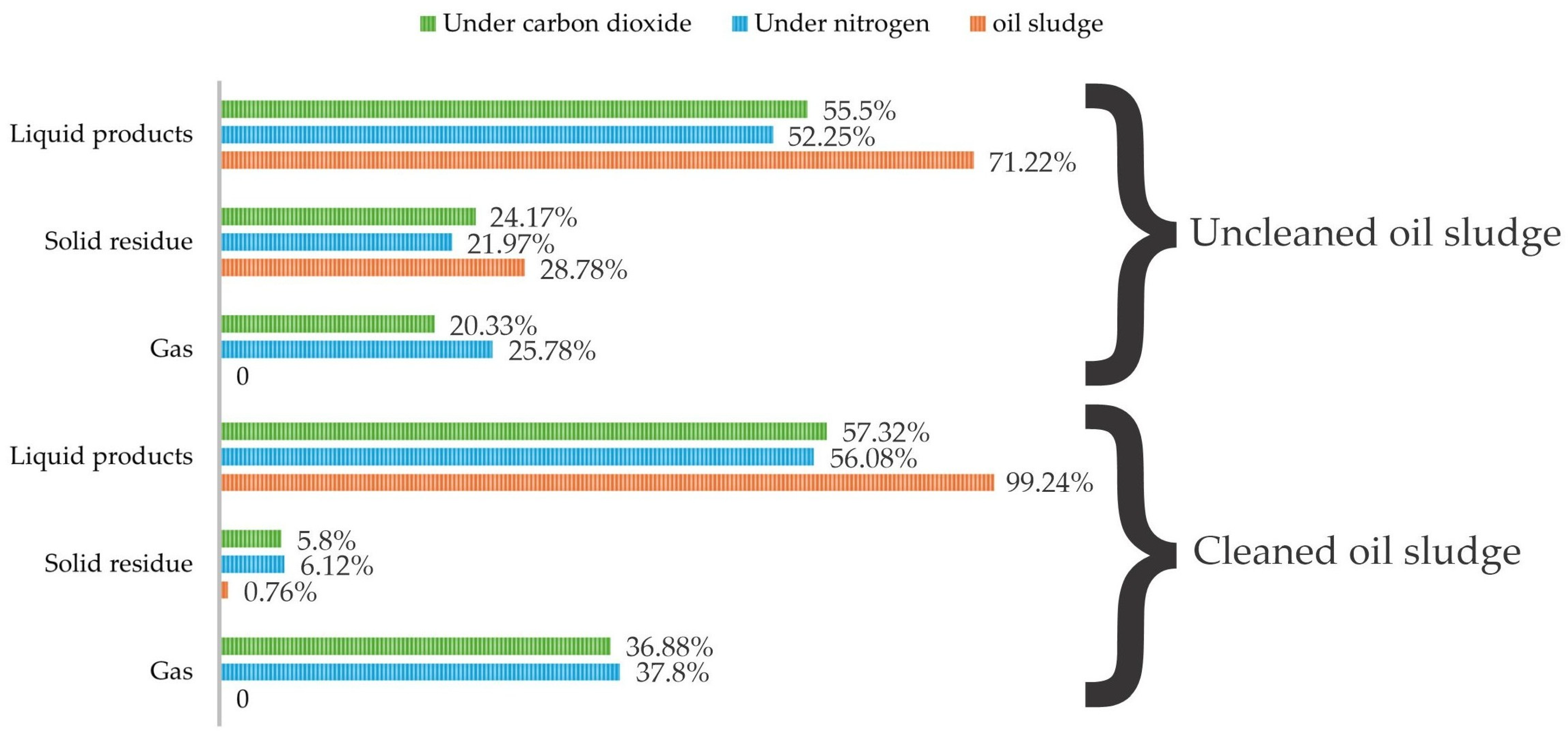
3. Results and Discussion
Pyrolysis of Oil Sludge in an Inert Atmosphere
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chu, Z. Application and Development of Pyrolysis Technology in Petroleum Oily Sludge Treatment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 190460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubakirov, Y.; Tashmukhambetova, Z.; Imanbayev, Y.; Nurtazina, N.; Kenzheyev, B.; Toshtay, K. Comprehensive Investigation of Pyrolysis Products from Coal Dust in Southern Kazakhstan: An Experimental Study. ES Mater. Manuf. 2024, 24, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, J. A review on resource utilization of oil sludge based on pyrolysis and gasification. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, A.; Heidari, S.; Golzary, A.; Tavakoli, O.; Wood, D.A. Optimized catalytic pyrolysis of refinery waste sludge to yield clean high quality oil products. Fuel 2022, 328, 125292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Y.-J.; Qiao, N.; Xu, F.-J.; Chu, G.-W.; Zou, H.-K.; Sun, B.-C. Study on the oil-sludge separation by thermochemical method in rotating packed bed. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2022, 174, 108878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, J.A.; Molto, J.; Ariza, J.; Ariza, M.; Garcia-Barneto, A. Study of the thermal decomposition of petrochemical sludge in a pilot plant reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 107, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Ali, M.; Chi, Y. Aromatic recovery from distillate oil of oily sludge through catalytic pyrolysis over Zn modified HZSM-5 zeolites. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 128, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, W.; Nie, Y. Effects of temperature on pyrolysis products of oil sludge. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Kaminsky, W. Pyrolysis of oil sludge in a fluidised bed reactor. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, B.; Fan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhai, X.; Deng, C.; Xu, Y.; Shen, D.; Dai, X. Nitrogen transformation during pyrolysis of oilfield sludge with high polymer content. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Huang, Q.; Chi, Y. Co-pyrolysis of oily sludge and rice husk for improving pyrolysis oil quality. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 177, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.J.; Sigle, S.O.; Berlin, K.D.; Sturm, G.P.; Vogh, J.W. Characterization of high-boiling petroleum distillate fractions by proton and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry. Fuel 1980, 59, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, A.; Sun, X.; Lin, C. Trend in Research on Characterization, Environmental Impacts and Treatment of Oily Sludge: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, E.; Behbahani, T.J. Upgrading Iranian petroleum sludge using polymers. J. Pet Explor. Prod. Technol. 2018, 8, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zubaidy, I.A.; Al-Tamimi, A.K. Production of sustainable pavement with oil sludge. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2014, 15, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Phukan, D.; Baruah, S.; Sarkar, A.; Sarkar, P. Environmental pollution removal efficiencies of some selected parameters by applying different remediation techniques for petroleum oily sludge. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahdi, A.M.; Aziz, H.A.; Eqab, E.S. Review on innovative techniques in oil sludge bioremediation. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1892, 040026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Q.; Zhang, D.M.; Yang, C.P. A review of the application of different treatment processes for oily sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Abu Hassan, M.A.; Ibrahim, R.R.K.; Jalil, A.A.; Mat Nayan, N.H.; Abdulkarim, B.I.; Sabeen, A.H. Analysis of Solid residue and Flue Gas from Thermal Plasma Treatment of Petroleum Sludge. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nasseri, S.; Dehghani, M.H.; Nazmara, S.; Yaghmaeian, K. Biodegradation of total petroleum hydrocarbons from acidic sludge produced by re-refinery industries of waste oil using in-vessel composting. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okai-Mensah, C.K.; Howard, E.K.; Okai-Mensah, K. Sustainable practices of the large-scale textile firms in Ghana. Clean. Circ. Bioeconomy 2022, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, K.; Baloo, L.; Yekeen, S.T.; Kankia, M.U.; Jagaba, A.H. Determination of total petroleum hydrocarbons concentration in coastal seawater of Teluk Batik Beach, Perak, Malaysia. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 888, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, F.M.; Pillay, A.E.; Jayasekara, K. Levels of radium in oily sludge. Int. J. Env. Anal. Chem. 2005, 85, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Ma, K.; Du, L.; Yuan, R. Evolution of S/N containing compounds in pyrolysis of highly oily petroleum sludge. Fuel 2022, 318, 123687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, A.J.; Van Wyk, M.; Reinecke, S.A. Toxicity to Earthworms and Chemical Composition of Oil Refinery Sludge Destined for Landfarming. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2016, 25, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, J.; Quan, C.; Tan, H. Product property and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals during pyrolysis of oily sludge with fly ash additive. Fuel 2020, 266, 117090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J. Study on the ecological risk of heavy metals during oily sludge incineration with CaO additive. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2021, 56, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lin, X.; Ma, B.; Zhang, H. Analysis of Pyrolysis Characteristics of Oily Sludge in Different Regions and Environmental Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Pyrolysis Residue. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 26265–26274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Nie, Q.; Duan, X.; Yi, X. Environmental Risk Analysis Based on Characterization of Ground Oily Sludge. Materials 2022, 15, 9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 2477-2014 Petroleum and Petroleum Products. Method for Determination of Water Content. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=33415695 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- GOST 6370-2018 Petroleum, Petroleum Products and Additives. Method for Determination of Mechanical Admixtures. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=37268623 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- GOST 33-2016 Petroleum and Petroleum Products. Transparent and Opaque Liquids. Determination of Kinematic and Dynamic Viscosity. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=39501441 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- GOST 3900-2022 Petroleum and Petroleum Products. Methods for Determination of Density. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=37379286 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- GOST 20287-91 Petroleum Products. Methods of Test for Flow Point and Pour Point. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=30007658 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Akimov, A.S.; Sviridenko, N.N. Transformation of asphaltenes of vacuum residues in thermal and thermocatalytic processes. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2022, 40, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridenko, N. Kinetics of heavy oil cracking in the presence of ferrospheres. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2509, 020190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Teng, D.; Fang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, T.; Siyal, A.A.; Dai, J.; Fu, J.; et al. Petroleum oil and products recovery from oily sludge: Characterization and analysis of pyrolysis products. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliyeva, R.V.; Babashova, Y.M.; Khamiyev, M.J.; Bagirova, S.R.; Azizbeyli, H.R. The alkylation of oil fractions rich in aromatic hydrocarbons with C6, C8 and C10 α—Olefins in the presence of ionic liquids catalytic systems. Appl. Petrochem. Res. 2021, 11, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, L.F. Present and Future Alkylation Processes in Refineries. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, S.M.; Smetanyuk, V.A.; Sadykov, I.A.; Silantiev, A.S.; Frolov, F.S.; Popkova, V.Y.; Hasiak, J.K.; Buyanovskaya, A.G.; Takazova, R.U.; Dudareva, T.V.; et al. High-Temperature Steam- and CO2-Assisted Gasification of Oil Sludge and Petcoke. Clean Technol 2025, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, F.; Guo, X.; Luan, C.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Che, L.; Tian, W.; Chen, G. Comparison of environmental impacts from pyrolysis, gasification, and combustion of oily sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Unit | Actual Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrocarbon content | wt. % | 61.86–71.22 |
| Water | wt. % | 0.33–5.20 |
| Mineral content | wt. % | 23.58–37.81 |
| Density | kg/m3 | 892–901 |
| pH | 6–9 | |
| Mechanical impurities’ chemical content: | ||
| SiO2 | wt. % | 35.6 |
| Fe2O3 | wt. % | 11.5 |
| CaSO4 | wt. % | 5.3 |
| CaO | wt. % | 3.3 |
| MgO | wt. % | 2.6 |
| Al2O3 | wt. % | 1.2 |
| Mass loss on ignition | wt. % | 40.5 |
| Parameters | Unit | Actual Value |
|---|---|---|
| Density at 20 °C | kg/m3 | 989.0 |
| Mechanical impurities | wt. % | 0.76 |
| Viscosity conditional at 80 °C | °VC | 2.84 |
| Boiling point | °C | 75 |
| Flash point in open range | °C | 124 |
| Viscosity is dynamic at 20 °C | Pa·s | 0.002–0.006 |
| Viscosity is dynamic at 50 °C | Pa·s | 0.004–0.009 |
| Viscosity is dynamic at 80 °C | Pa·s | 0.0011–0.0015 |
| Pour point | °C | −2 |
| Heating value | MJ/kg | 23–26 |
| Coking value | wt. % | 12.5 |
| Asphaltenes | wt. % | 1.3 |
| Resins | wt. % | 11.3 |
| Oils | wt. % | 87.4 |
| Elemental composition: | wt. % | |
| C (carbon) | 84.9 | |
| H (hydrogen) | 12.7 | |
| S (sulfur) | 0.3 | |
| N + O (nitrogen + oxygen) | 1.1 |
| Process Type | SARA Composition, wt. % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Insoluble Substances | Oils | Resins | |
| Oil sludge | 26.60 | 64.99 | 8.41 |
| Under nitrogen atmosphere | 11.34 | 73.92 | 14.74 |
| Under carbon dioxide atmosphere | 6.03 | 74.39 | 19.58 |
| Process Type | SARA Composition, wt. % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Insoluble Substances | Oils | Resins | |
| Oil sludge | 1.3 | 87.4 | 11.3 |
| Under nitrogen atmosphere | 1.4 | 81.47 | 17.13 |
| Under carbon dioxide atmosphere | 1.57 | 75.25 | 23.18 |
| Hydrocarbon Composition | Content, wt. % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cleaned Oil Sludge | Under Nitrogen Atmosphere | Under Carbon Dioxide Atmosphere | |
| Paraffins | 19.28 | 19.36 | 16.61 |
| Uncondensed cycloparaffins | 15.18 | 14.05 | 11.73 |
| Condensed cycloparaffins with 2 rings | 15.2 | 14.99 | 10.81 |
| Condensed all cycloparaffins | 13.57 | 12.44 | 13.11 |
| Benzenes | 8.59 | 8.17 | 8.97 |
| Naphthenobenzenes | 6.23 | 6.65 | 8.52 |
| Dinaphthenobenzenes | 3.97 | 5.06 | 6 |
| Naphthalene compounds | 7.29 | 9.2 | 9.63 |
| Acenaphthenes | 3.63 | 2.41 | 4.71 |
| Fluorenes | 3.91 | 3.36 | 4.49 |
| Gaseous Composition | Uncleaned Oil Sludge, wt. % | Cleaned Oil Sludge, wt. % |
|---|---|---|
| Methane (CH4) | 3.50 | 28.53 |
| Ethylene (C2H4) | 0.57 | 15.51 |
| Ethane (C2H6) | 0.29 | 7.42 |
| Propylene (C3H6) | 0.14 | 5.65 |
| Propane (C3H8) | 0.05 | 1.06 |
| Butin (C4H6) | 0.03 | 0.59 |
| n-butane (C4H10) | 0.08 | 1.11 |
| Iso-pentane (i-C5H12) | – | 0.008 |
| n-pentane (C5H12) | – | 0.003 |
| Carbon monoxide (CO) | – | 27.81 |
| Oxygen (O2) | – | 10.12 |
| Other gases (N2, SOx, He) | 95.34 | 2.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imanbayev, Y.; Tileuberdi, Y.; Aubakirov, Y.; Zhambolova, A.; Kenzheyev, B.; Mussabekova, Z.; Muktaly, D.; Rakhimova, A. Experimental Evaluation of Pyrolysis Processes for Kazakhstan Oil Sludge. Processes 2025, 13, 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113404
Imanbayev Y, Tileuberdi Y, Aubakirov Y, Zhambolova A, Kenzheyev B, Mussabekova Z, Muktaly D, Rakhimova A. Experimental Evaluation of Pyrolysis Processes for Kazakhstan Oil Sludge. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113404
Chicago/Turabian StyleImanbayev, Yerzhan, Yerbol Tileuberdi, Yermek Aubakirov, Ainur Zhambolova, Beibit Kenzheyev, Zhansaya Mussabekova, Dinara Muktaly, and Ainura Rakhimova. 2025. "Experimental Evaluation of Pyrolysis Processes for Kazakhstan Oil Sludge" Processes 13, no. 11: 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113404
APA StyleImanbayev, Y., Tileuberdi, Y., Aubakirov, Y., Zhambolova, A., Kenzheyev, B., Mussabekova, Z., Muktaly, D., & Rakhimova, A. (2025). Experimental Evaluation of Pyrolysis Processes for Kazakhstan Oil Sludge. Processes, 13(11), 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113404






