Abstract
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were employed to examine how carbon defects, symbiosis, and sulfur influence the wettability of coal pyrite by analyzing H2O adsorption on distinct surface configurations. The comparison results of adsorption energy, Mulliken population, charge density, and electronic state density of water molecules on the surface of pyrite doped with carbon atoms show that the presence of carbon doping reduces the negative value of the adsorption energy of water molecules on the pyrite surface, the C atoms on the pyrite surface form weaker C-H bonds with the H atoms in the water molecules, the Fe-O bond strength weakens, and the thermodynamic trend weakens. And the bond of the pyrite surface with adsorbed carbon changes from an Fe-O bond to an Fe-C-O bond. The adsorption of water molecules on the pyrite surface is weakened, and there is a weaker thermodynamic trend. This is because the adsorption of carbon atoms changes from hydrophilic to nearly hydrophobic. The physical adsorption of sulfur atoms changes the adsorption energy of water molecules on the pyrite surface from negative to positive, and the bond changes from an Fe-O bond to an Fe-S-O bond, indicating that the adsorption intensity of water molecules on the pyrite surface with adsorbed sulfur is weakened, and there is no thermodynamic trend. The pyrite surface with adsorbed sulfur changes from hydrophilic to hydrophobic. Under the same impurity atom doping or adsorption concentration, the influence of sulfur on the adsorption of water molecules on the surface of pyrite is the greatest, followed by the adsorbed carbon, and the weakest is the carbon atom doping. Macroscopically, the overall hydrophobicity of the surface of coal-bearing pyrite covered with sulfur is greater than that of pyrite containing adsorbed carbon and even greater than that of coal-bearing pyrite doped with carbon atoms.
1. Introduction
The flotation desulfurization of coal slime relies on the difference in surface hydrophobicity between coal and pyrite. In coal pyrite, the intrusion of carbon impurities into the crystal lattice or the occurrence of extensive carbon symbiosis, along with sulfur formation resulting from surface oxidation, result in surface properties similar to coal, which has stronger floatability during separation [1]. It is essential to clarify the origin of this hydrophobicity for improving the efficiency of pyrite removal in flotation desulfurization. In the early stage, many scholars explored the effects of coexisting carbon and sulfur oxide on the hydrophilic behavior of pyrite surfaces. Shao [2] observed that the adsorbed coexisting carbon improved the floatability of pyrite but did not further explore its mechanism. Yu [3] proposed that carbon doping into the pyrite lattice improved its floatability. However, under actual flotation conditions, additional coexisting carbon adsorption on the surface may occur. The mechanism of the effect of adsorbed carbon on its hydrophobicity deserves further study. Buckley, Woods et al. [4], Yoon et al. [5], and Zhu et al. [6] suggested that the sulfur or sulfur-like substances formed in the initial stage of pyrite surface oxidation are hydrophobic, thereby increasing its surface hydrophobicity. The previous study [7,8,9,10,11] only discussed the research on the effect of carbon defects/carbon material/sulfur in the process of oxidation on the hydrophilicity of the coal pyrite surface. The carbon into the pyrite lattice improved the hydrophobicity of the pyrite surface. The carbon attached to the pyrite surface increases the hydrophobicity of the pyrite surface. The sulfur produced by the oxidation of the pyrite surface increases the hydrophobicity of the pyrite surface. No scholar has conducted a comparative study on which of the three factors—carbon doping, carbon symbiosis, and sulfur oxide—has a greater impact on the hydrophobicity of pyrite surface? This paper compared the effects of three factors on the hydrophobicity of the pyrite surface and discussed the measures to improve pyrite flotation performance.
Fu [12,13] employed experimental methods to investigate the interactions and mechanisms of Ca(II) and NaOL adsorption on hematite and quartz surfaces. Through infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis, Wang Qingqing discovered that sodium persulfate selectively adsorbed on the surface of pentlandite and changed its S = O and Ni-S functional group structures. The strong oxidizing property of sodium persulfate promotes the conversion of the S element to the high-valent state SO42−. These surface chemical modifications enhanced the hydrophilicity of the pentlandite surface and hindered the adsorption of xanthate on its surface, thereby realizing the efficient flotation separation of copper-nickel sulfide ores. Wen [14] used the organic inhibitor mineral-derived fulvic acid (MFA) to achieve effective separation of chalcopyrite and pyrite in a low-alkalinity flotation system and revealed the selective action mechanism of MFA on pyrite through various analytical detection methods. Wang [15] proposed sodium persulfate (Na2S2O8) as a novel depressant for pentlandite. As a first-principles approach, density functional theory (DFT) provided fundamental understanding of adsorbate–surface interactions, enabling mechanistic analysis of interfacial adsorption processes.
Therefore, this study systematically compares the surface hydrophobicity differences among ideal pyrite, carbon-doped pyrite, carbon-adsorbed pyrite, and sulfur-adsorbed pyrite using density functional theory (DFT). This study selected the most stable pyrite surface model and revealed the mechanism of the change in hydrophilicity of the pyrite surface from the atomic level by optimizing the adsorption configuration of water molecules on the pyrite surface and calculating the adsorption energy, bond strength, bond length, charge density, differential charge density, and electronic state density. This study provided a certain theoretical basis for optimizing the time and method of coal slime flotation desulfurization.
2. Calculation Methods and Model
2.1. Calculation Methods
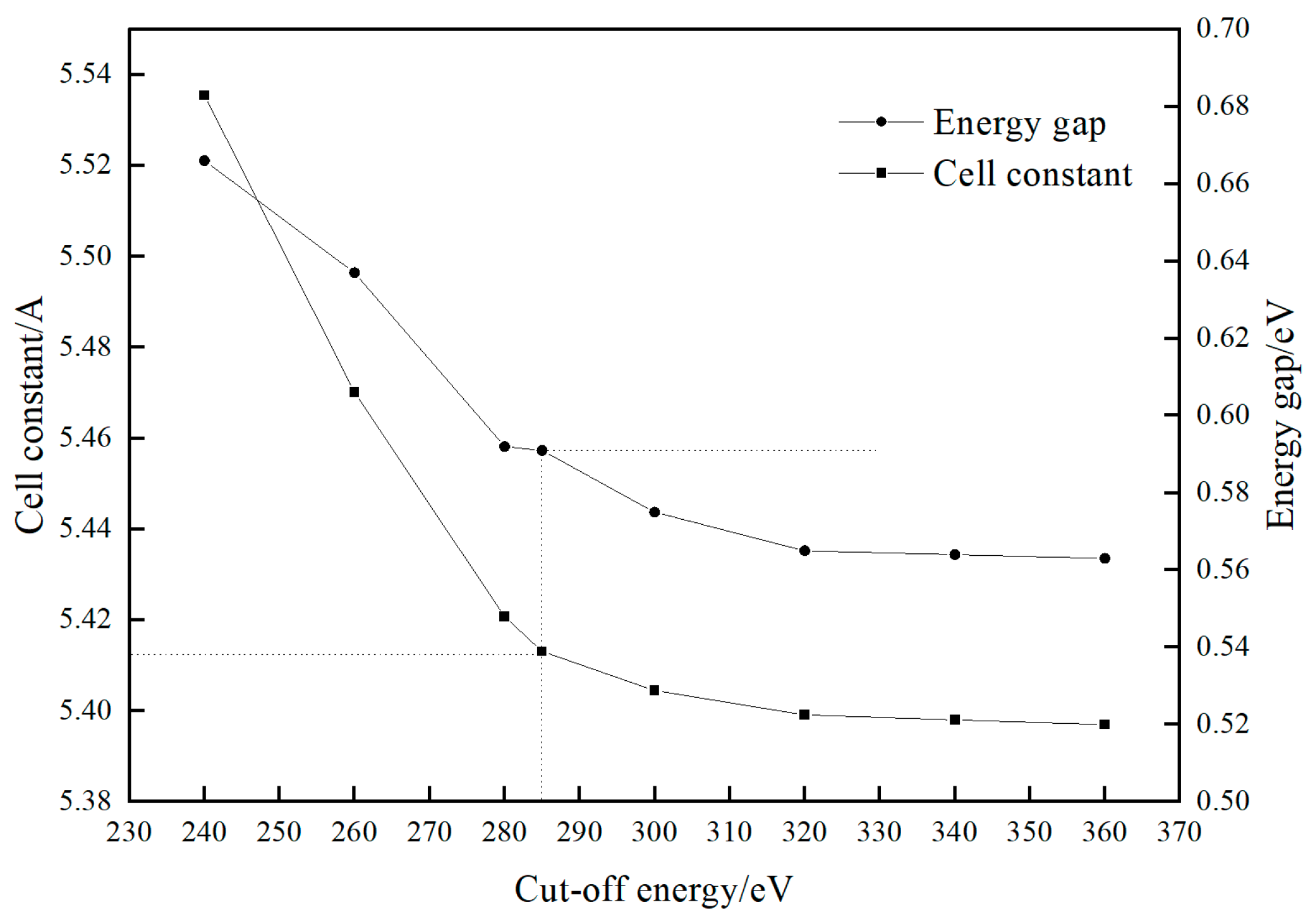
This comprehensive analysis leveraged the advanced CASTEP program, integrated within Materials Studio 2018 software, to ensure precise and accurate calculations throughout the entire study. The structure of the pyrite unit cell model was optimized to select the appropriate cut-off energy and exchange-correlation function. First, different cutoff energies were selected to optimize the structure of the pyrite bulk unit cell so that the simulated values of the two parameters, lattice constant (a = b = c) and band gap width, were closest to the experimental values. The calculation results are shown in Figure 1.
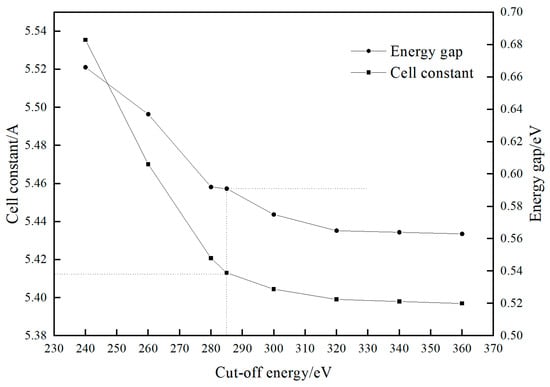
Figure 1.
The trend of cell constant and band gap with the increase in cut energy.
As can be seen from Figure 1, with the increase in cutoff energy, the lattice constant and bandwidth decrease. When the cut-off energy is 350 eV, the calculated value of the unit cell constant of pyrite is 5.416 Å and tends to be stable, which is closest to the experimental value (5.417 Å). Therefore, the cutoff energy value for this simulation calculation is selected as 350 eV.
Based on the above-mentioned determination of the cutoff energy as 350 eV, different exchange-correlation functionals were further selected to perform structural optimization on the lattice parameters and energy bandwidth of the pyrite bulk phase unit cell. The results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Optimized results of different exchange correlation functions.
When the RPBE gradient correction approximation under the generalized gradient galaxy (GGA) is used for pyrite, the calculated pyrite band-width is 0.673 eV, which is close to the experimental value (0.95 eV), but the lattice parameter (5.473 Å) differs significantly from the experimental value (5.417 Å). When the PW91 gradient correction approximation under the generalized gradient galaxy (GGA) is used, the calculated pyrite unit cell parameter is 5.416 Å, which is basically the same as the experimental value (5.417 Å), and the bandwidth is also close to the experimental value (0.95 eV). Therefore, considering the relative errors of the lattice parameter and bandwidth compared to the experimental values, the PW91 gradient correction function under the generalized gradient galaxy (GGA) was used as the exchange-correlation function in this simulation.
From the above optimization results of the cut-off energy and exchange-correlation function, it can be seen that the exchange-correlation function and the cut-off energy are selected as the PW91 gradient correction function under GGA [16,17] to describe electrons of the exchange-correlation interactions and 350 eV [18]. The calculation focused on valence electrons (Fe 3d64s2 and S 3s23p4) through the use of ultra-soft pseudopotentials (USP) [19]. A Monkhorst–Pack [20,21] k-point sampling density was a 4 × 4 × 4 mesh. Convergence for the self-consistent field (SCF) was achieved with a precision of 2.0 × 10−6 eV per atom. Spin polarization was included in the simulation. Additionally, the structural units of the carbon atom and water molecule were optimized within a cubic cell of 20 × 20 × 20 Å, with Brillouin zone sampling limited to the gamma point. The absence of explicit van der Waals (vdW) can bias weak water-adsorption energies, and the hydrophilicity of different pyrite surfaces should be interpreted with the limitation. The dipole correction was applied during the adsorption configuration calculation process.
Adsorption strength between water molecules and the pyrite surface was measured through the adsorption energy (Eads), defined as follows:
where x denotes the adsorbate species (carbon/sulfur atoms or H2O molecules) and n represents the quantity of adsorbed entities. EX/slab corresponds to the total energy of the adsorption system, while Eslab and EX refer to the energies of the clean pyrite surface and isolated adsorbate, respectively. Notably, higher negative values of Eads indicate stronger adsorbate–surface interactions.
Eads = EX/slab − nEX − Eslab,
The stability of the adsorbed system was evaluated by the adsorption energy (Eads), computed as Eads = EX/slab − Eslab − EX. In this expression, EX/slab, Eslab, and EX signify the energies of the composite system, the pure pyrite slab, and the isolated carbon/water adsorbate, respectively. The exothermicity of adsorption is indicated by a negative Eads value, and the degree of stability is proportional to the amount of adsorption energy (|Eads|) [22,23,24].
2.2. Surface Model
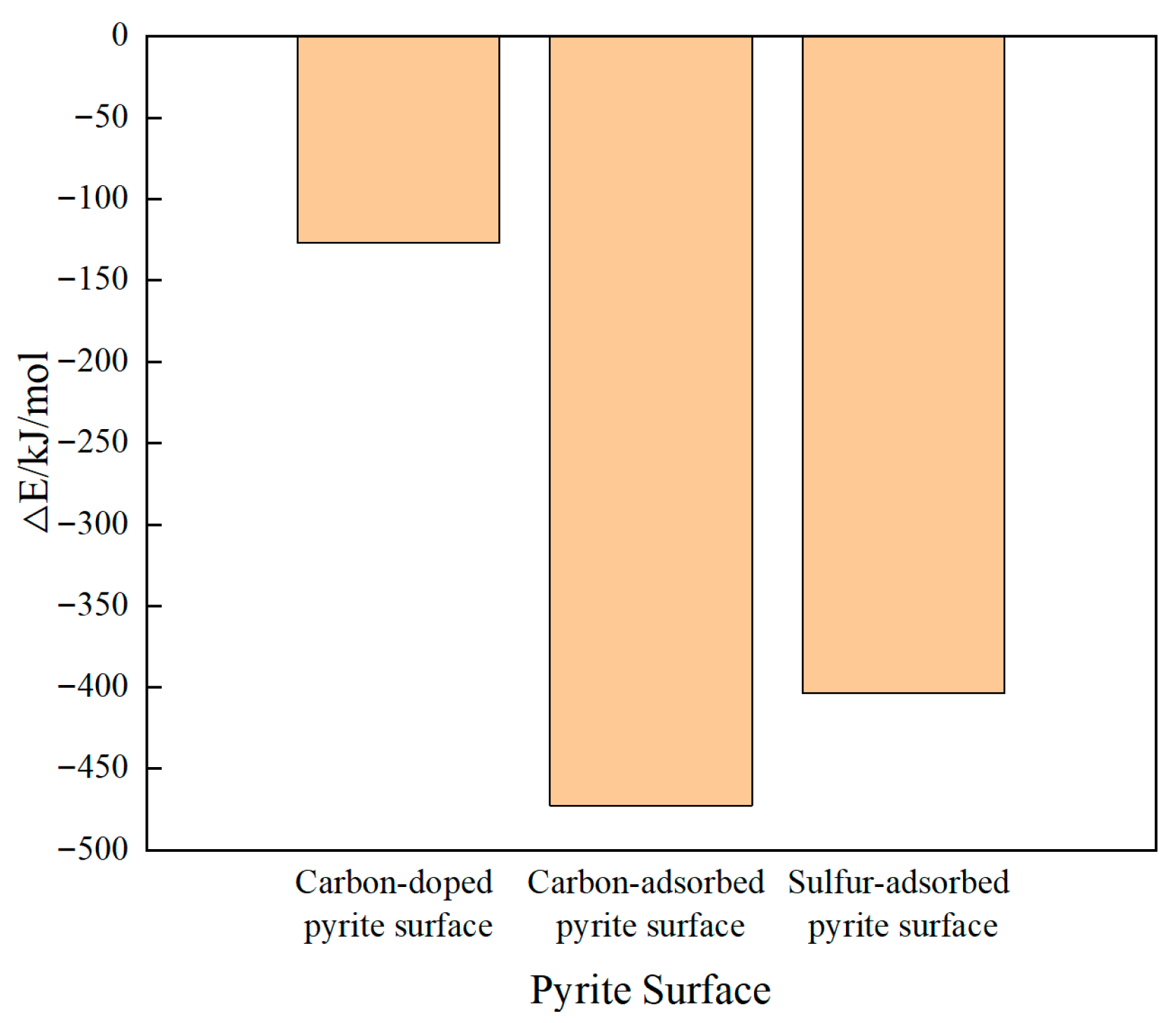
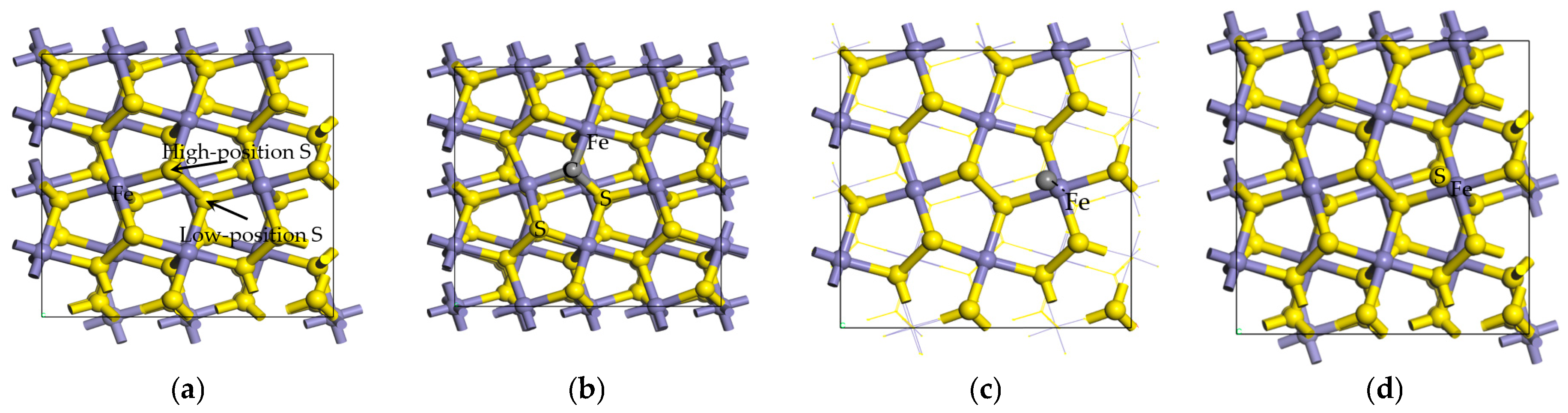
A 2 × 2 × 1 supercell of the FeS2 (100) surface, constructed from the primitive pyrite unit cell, was used as the model system in this paper. This model consists of 15 atomic layers (of which the bottom 9 layers are fixed) and 15 vacuum layers. For carbon-doped pyrite surfaces, the lattice configuration was optimized using the doping energy. For carbon-intergrown and sulfur-covered pyrite surfaces, the lattice configuration was optimized using adsorption energy. The doping and adsorption energy are related to the stability of the lattice configuration; the more negative the energy, the more stable the lattice.
As shown in Figure 2, stable configurations were formed following the substitution and adsorption of a carbon/sulfur atom, characterized by negative energy values for both processes (shown in Figure 3b–d). The energy of the latter had a larger negative value, which indicated that the carbon/sulfur atom was easier to adsorb on the pyrite surface than doped carbon. And the pyrite surface adsorbed by a carbon atom was most stable.
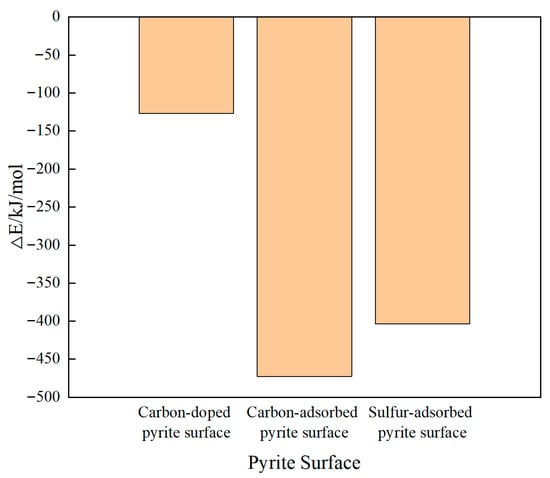
Figure 2.
The energy of the pyrite surface substituted or adsorbed by carbon/sulfur atoms.
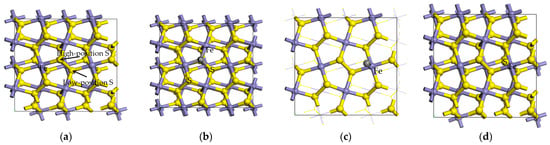
Figure 3.
The models of different pyrite surfaces. (a) Ideal pyrite surface. (b) Carbon-doped pyrite surface. (c) Carbon-adsorbed pyrite surface. (d) Sulfur-doped pyrite surface.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption Configurations and Adsorption Energies
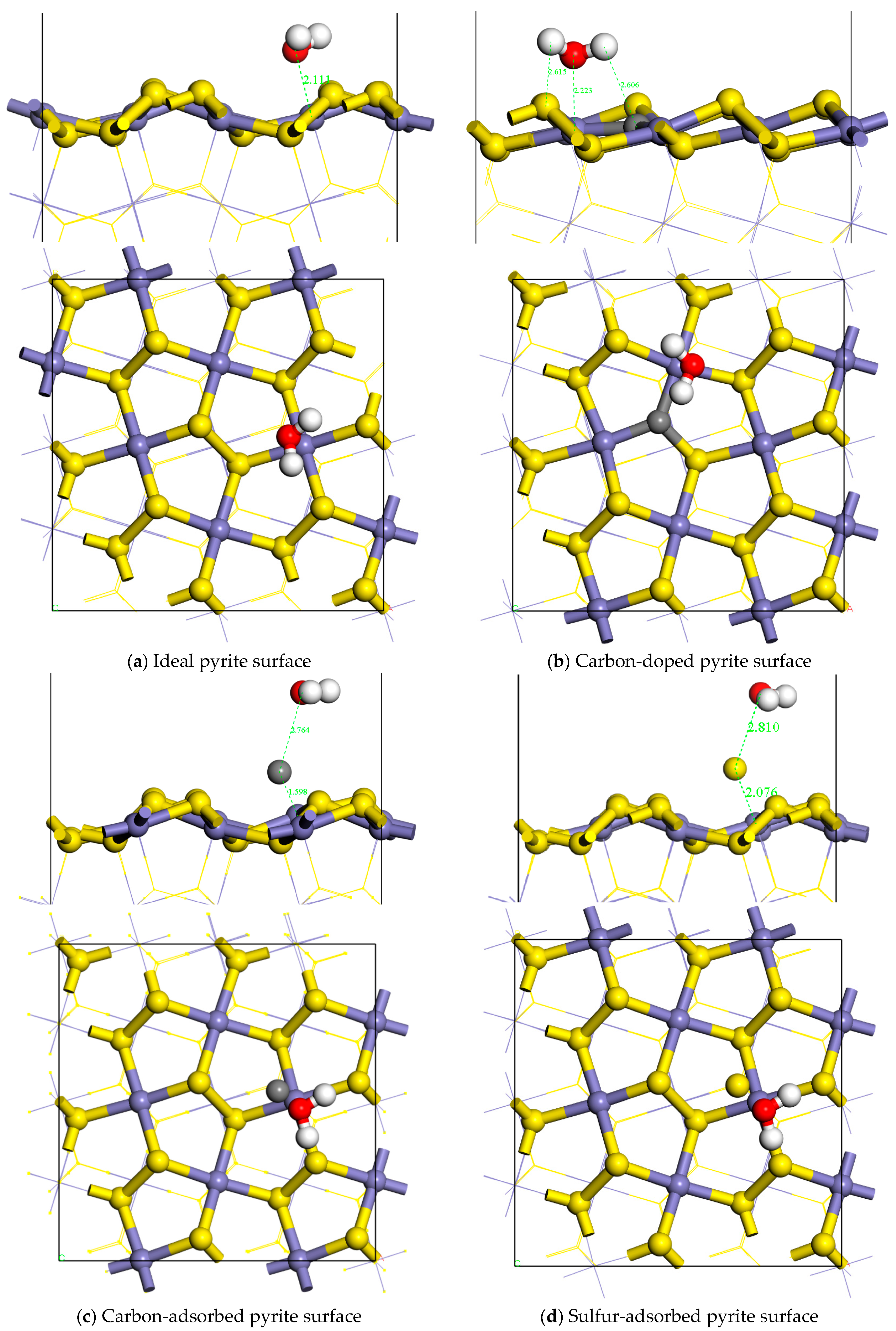
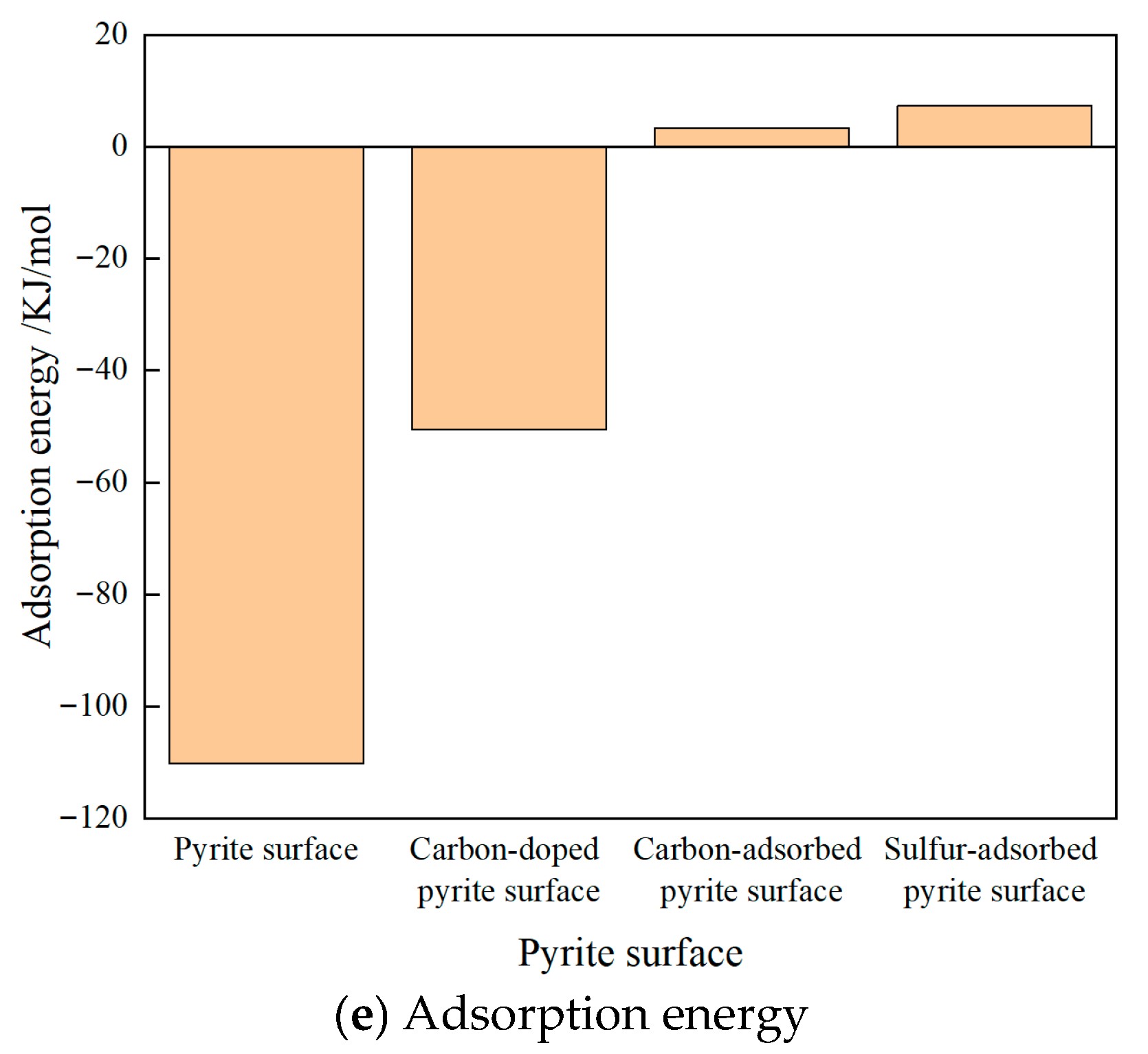
DFT calculations were employed to reveal that water molecules preferentially adsorb at iron sites on ideal pyrite surfaces, forming two stable S-H bonds in the most thermodynamically stable configuration. The most stable model obtained above was used as the basic model to study the effect of carbon doping, carbon symbiosis, and sulfur on the adsorption of water molecules on the pyrite surface. DFT calculations were performed to elucidate the interaction mechanism between pyrite and water molecules, including analyses of equilibrium adsorption configurations, adsorption energies, charge transfer, and Mulliken populations. The equilibrium adsorption configurations were presented in Figure 4.
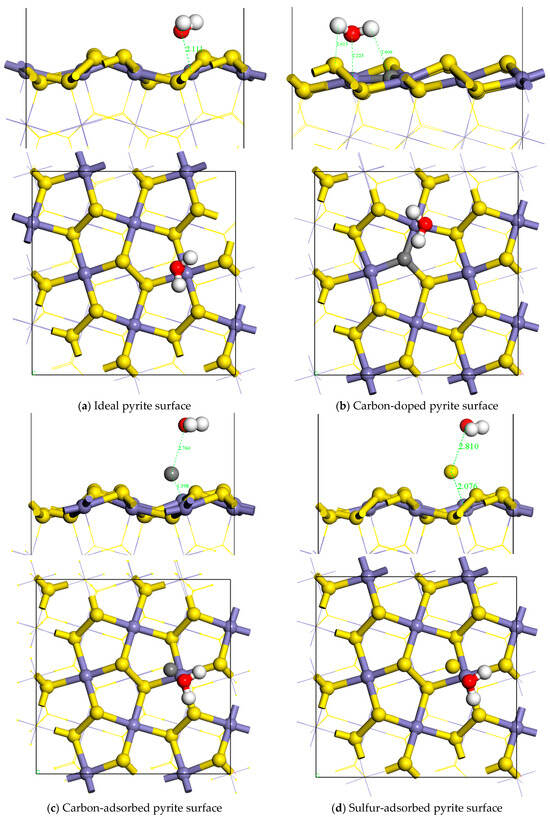
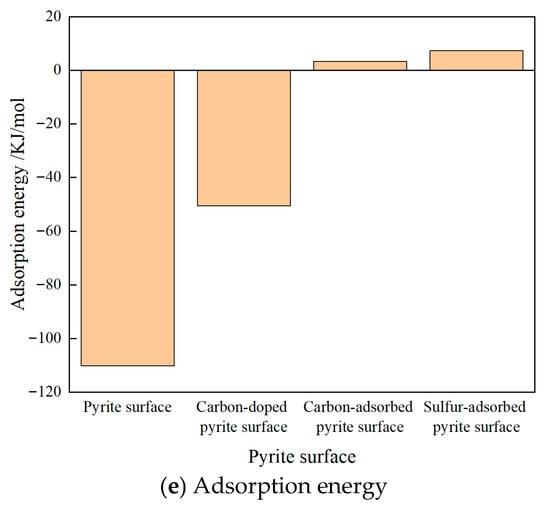
Figure 4.
The adsorption configuration and energy of different coal pyrite surfaces.
The Eads of the sulfur-adsorbed pyrite surface was positive and largest, along with the generation of Fe-S-O covalent bonds. It was indicated that the surface was hydrophobic after oxidation. The Eads of the carbon-adsorbed pyrite surface was also positive, close to zero, along with the generation of Fe-C-O covalent bonds. It was indicated that the surface also became less hydrophobic after coexisting with coal. The Eads of the carbon-doped pyrite surface was negative, along with the C-H bond formed, which indicated that the surface became less hydrophilic after the carbon atom doped into the pyrite lattice. The ideal pyrite surface had the strongest hydrophilicity.
This showed that under the same impurity atom doping or adsorption concentration, adsorbed sulfur during flotation had the greatest influence on the hydrophilicity of pyrite, followed by adsorbed carbons, and doped carbon atoms were the weakest. The sulfur-adsorbed pyrite surface was hydrophobic. The carbon-adsorbed pyrite surface also became hydrophobic. The pyrite surface with doped carbons was less hydrophilic. The ideal pyrite surface was strongly hydrophilic. Macroscopically, the overall hydrophobicity of the sulfur-adsorbed pyrite surface was greater than that of the carbon-adsorbed pyrite surface and even greater than that of the carbon-doped pyrite surface.
3.2. Analysis of Bonding
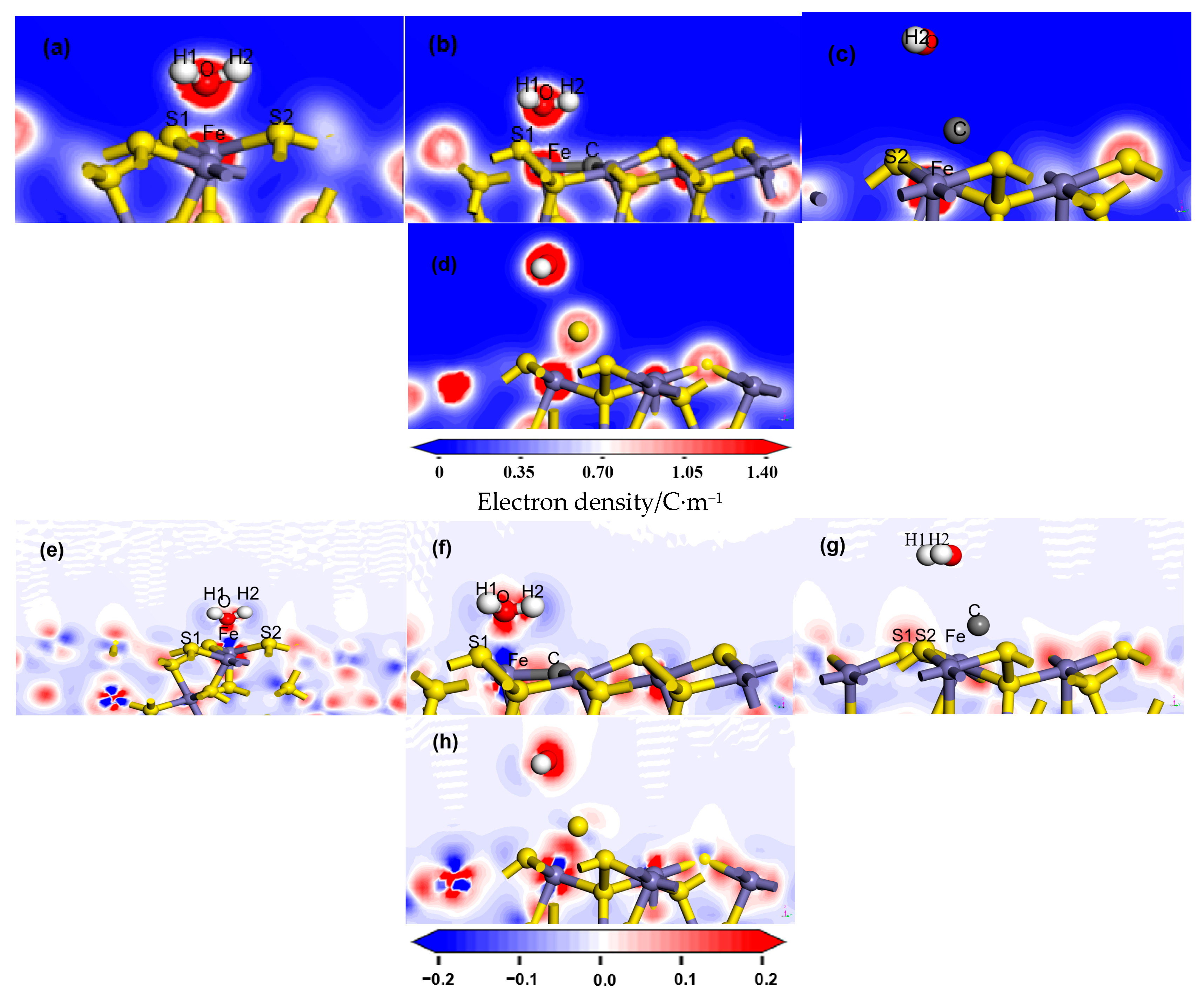
The most stable adsorption configurations were taken as objects, and the bond Mulliken population was furthermore calculated. Mulliken population [25] was employed to quantify the interaction strength between bonded atoms following adsorbate adsorption. Mulliken metrics in plane-wave DFT were basis-dependent and were used here as qualitative indicators, with more robust descriptors (e.g., Bader/ELF/(I)COHP) left to future work. A higher bond Mulliken population value correlates with shorter bond lengths and stronger covalent character. Mulliken population after adsorption is shown in Table 2. Electron density and charge density difference were further calculated among O, C, S, and Fe atoms as shown in Figure 5.

Table 2.
Mulliken population after H2O adsorption on the different coal pyrite surfaces.
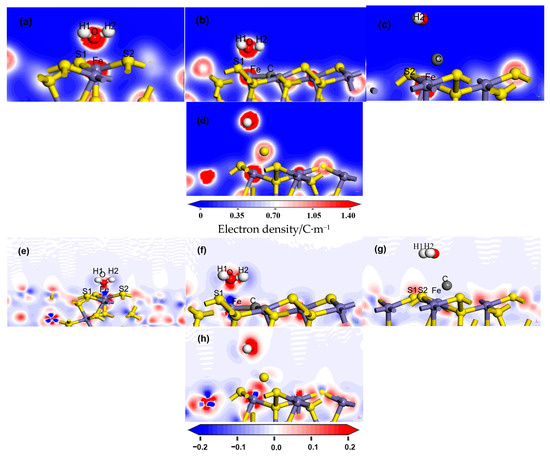
Figure 5.
Electron density and charge density difference upon H2O adsorption on variant coal pyrite surfaces. (a,e) Ideal pyrite surface; (b,f) carbon-doped pyrite surface; (c,g) carbon-adsorbed pyrite surface; (d,h) sulfur-adsorbed pyrite surface.
Adsorption of H2O led to Fe–O and H–S bonding on the pyrite surface. The covalent character of the Fe–O interaction (Mulliken population = 0.13) and weaker H…S hydrogen bonding (populations = 0.01), detailed in Table 2, were corroborated by the pronounced charge density and clear charge transfer between O and Fe atoms shown in Figure 5a,d.
On the carbon-doped pyrite surface (Figure 4b), H2O adsorption maintained the strong covalent Fe–O bond. However, the Fe-O bond became weak, whose Mulliken population decreased to 0.11 from 0.13. And one H–S interaction was supplanted by a much weaker H–C bond, thereby reducing the overall adsorption strength. Charge analysis revealed significant charge density and transfer at the O–Fe interface (Figure 5b,e), similar to the ideal surface.
In contrast, when carbon was adsorbed on the surface (Figure 4c), the Fe–O bond was absent, replaced by an Fe–C–O configuration. The constituent C–O bond was weak (population = −0.07), diminishing the water adsorption stability. The primary interaction shifted, with pronounced charge transfer occurring between the Fe and C atoms (Figure 5c,g).
A similar trend was observed for the sulfur-adsorbed surface (Figure 4d), where the Fe–O bond was replaced by an Fe–S–O complex. The weak S–O bond (population = −0.05) resulted in an even greater reduction in adsorption strength. Correspondingly, the highest charge density and most obvious transfer were localized between the Fe and S atoms (Figure 5d,h).
3.3. The Charge Transfer
The Mulliken charge populations (MCPs) quantify the electron loss and transfer involving the water molecule and the surface. The evolution of these electronic states, from before adsorption (BA) to after adsorption (AA), is detailed in Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6.

Table 3.
MCP of ideal pyrite surface.

Table 4.
MCP of carbon-doped pyrite surface.

Table 5.
MCP of carbon-adsorbed pyrite surface.

Table 6.
MCP of sulfur-adsorbed pyrite surface.
On the ideal pyrite surface, the O 2p orbital loses 0.22 e, increasing the oxygen atom’s charge, while the Fe 3d orbital gains 0.03 e, reducing the iron’s charge (Table 3). This charge transfer confirms O 2p and Fe 3d orbital hybridization as the primary interaction mechanism, consistent with the bond population data.
For the carbon-doped surface, a similar process occurs with the O 2p orbital losing 0.21 e. However, the accompanying charge gain by the Fe 3d orbital is considerably smaller (0.05 e), indicating a weaker interaction.
In the case of the carbon-adsorbed surface, the O 2p orbital loses only 0.06 e (Table 5), and the bonding C atom also loses electrons, increasing its charge. The Fe atom gains electrons, reducing its charge. This electronic redistribution aligns with the Mulliken bond populations (Fe–C: 0.87; C–O: −0.02 in Table 2), confirming the formation of a weak Fe–C–O bridge. These results indicate that the covalent overlap between C and O (water molecule) was weak to some extent, and thus the adsorbed carbon prevented the adsorption of a water molecule on the surface of pyrite to a certain extent.
Similarly to the pyrite surface with adsorbed carbons, for the pyrite surface with adsorbed sulfur (Figure 4d), after H2O adsorption, the O charge increases from the O 2p losing 0.07 electrons (Table 6). The S charge that bonds to the O increases, owing to the S 3p losing 0.07 electrons. Additionally, the Fe charge reduces due to the addition of Fe 3d-orbital electrons. These results indicate that the covalent overlap between S and O (water molecule) was weak to some extent, and thus the adsorbed sulfur prevented the adsorption of a water molecule on the surface of pyrite to a certain extent.
3.4. The Density of States (DOS)
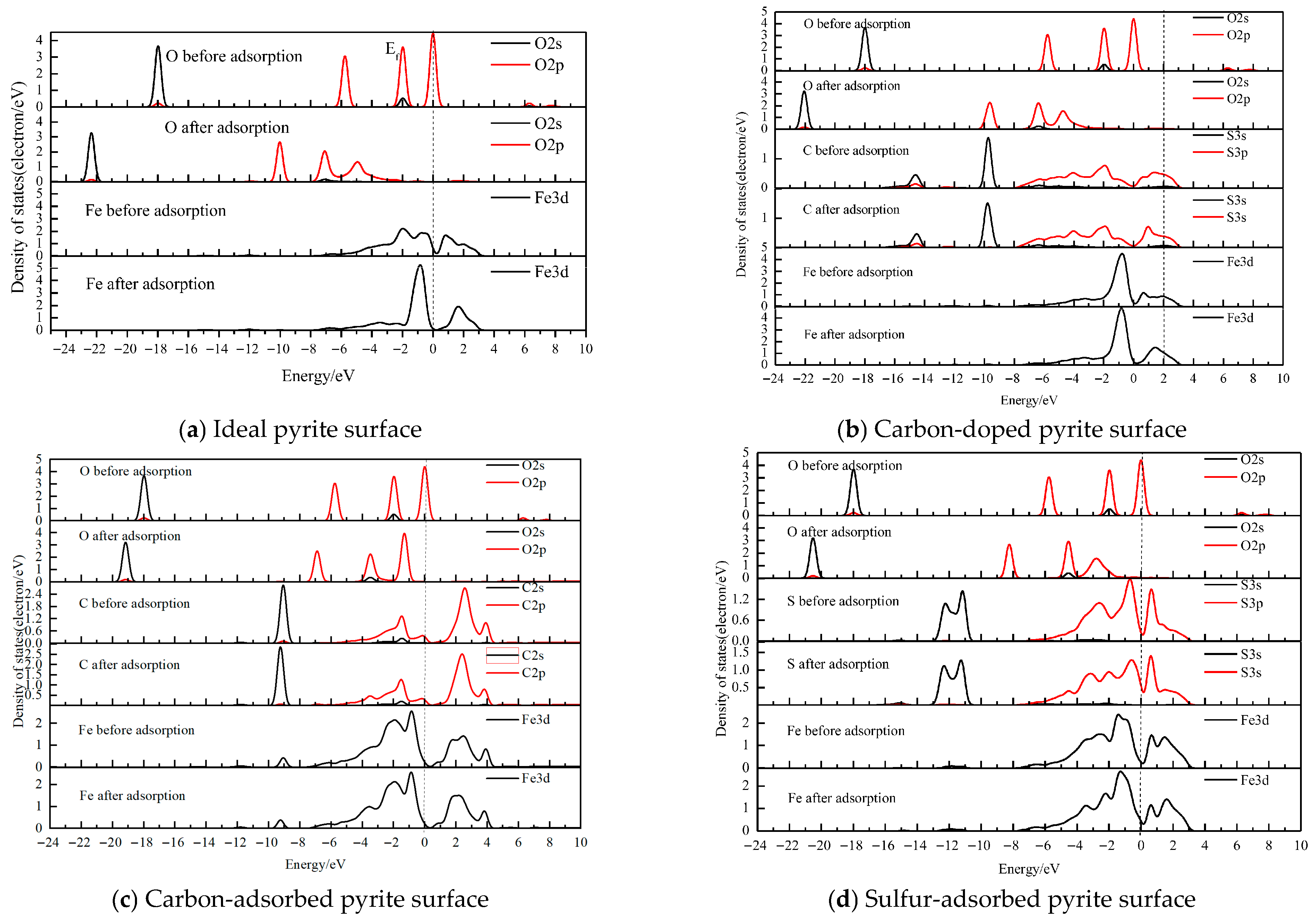
The primary interaction between water and the pyrite surface involves the O atom of water and the C, S, or Fe atoms of the mineral. Consequently, the Partial Density of States (PDOS) analysis focuses on these specific atomic species before and after adsorption, as selectively presented in Figure 6.
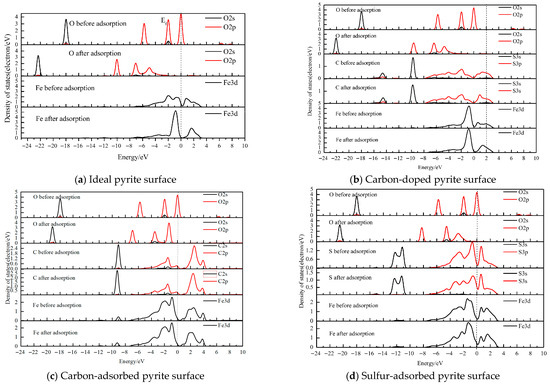
Figure 6.
Density of states (DOS) of atoms before and after H2O adsorption on the different coal pyrite surfaces.
As shown in Figure 6, PDOS analysis reveals distinct orbital interactions across the different surfaces. For the ideal pyrite surface (Figure 6a), strong hybridization occurs between Fe (surface) and O (water) orbitals in the energy range of −8.2 to −1.6 eV, while the corresponding anti-bonding state (0.4–2.5 eV) is weak. A similar bonding–antibonding pattern is observed for the carbon-doped surface.
In contrast, the carbon-adsorbed surface exhibits strong Fe 3d–C 2p bonding and anti-bonding states, alongside a notably weak C 2p–O 2p interaction. Conversely, on the sulfur-adsorbed surface, both the Fe 3d–O 2p bonding (−16.0 to −1.0 eV) and anti-bonding (0–3.2 eV) states are intense. This strong Fe–O interaction is corroborated by a Mulliken bond population of 0.54. Meanwhile, the S 3p–O 2p bond remains weak across the examined energy range. And the Mulliken bond population between S and O (water molecule) is about −0.05 (as shown in Table 2). These results indicate that the covalent overlap between S and O (water molecule) is weak to some extent. Oxidized sulfur hinders the adsorption of water molecules on the pyrite surface to some extent.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under the same impurity atom doping or adsorption concentration, the pyrite surface with adsorbed sulfur was hydrophobic. The pyrite surface with adsorbed carbons was nearly hydrophobic. The pyrite surface with doped carbons was weakly hydrophilic. The ideal pyrite surface was strongly hydrophilic. Macroscopically, the overall hydrophobicity of the surface of coal-bearing pyrite covered with sulfur is greater than that of coal-bearing pyrite containing co-growth carbon and even greater than that of coal-bearing pyrite doped with carbon atoms.
- (2)
- In the future, coal slime flotation desulfurization can consider separating clean coal from ash and sulfur in the shortest possible time while meeting the ash content requirements of clean coal. In a short period of time, the degree of oxidation on the surface of pyrite is relatively weak, which is not enough to become hydrophobic, and then the clean coal fraction is high as the clean coal slime floats up.
- (3)
- Some coal pyrite samples from different regions can be selected and prepared by grinding in an oxygen-free and water-free environment, and others can be prepared at room temperature and placed for a period of time. And then conduct contact angle experiments on the samples so they can be compared and determined to compare the strength of their hydrophobicity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.X. and X.T.; methodology, P.X.; validation, P.X.; formal analysis, P.X.; investigation, G.C.; resources, P.X.; data curation, P.X.; writing—original draft preparation, P.X.; writing—review and editing, F.S. and X.F.; visualization, P.X.; project administration, P.X. and G.C.; funding acquisition, P.X.; supervision, X.F. and X.T.; software, P.X. and Q.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Project of the Hebei Education Department (BJK2023063) and supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 3142021001). The work is also supported by the Foundation of Key Laboratory of Power Machinery and Engineering, Ministry of Education, P.R. China (202201).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Q.Z. for providing software.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xie, G. Mineral Processing, 3rd ed.; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2012; pp. 413–414. ISBN 978-7-81070-361-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, P. The ESCA study of coal pyrite and pyrite. Anal. Util. Coal Qual. 1994, 2, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J. Study on the Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Coal-Pyrite and Its Inhibitors. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Backley, A.; Woods, N.R. The surface oxidation of pyrite. App. Surf. Sci. 1987, 27, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.H.; Lagno, M.L.; Luttrell, G.H. On the hydrophobicity of coal pyrite. In Proceedings of the Processing and Utilization of High Sulfur Coals IV, Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 26–30 August 1991; Dugan, P.R., Quigley, D.R., Attia, Y.A., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wadsworth, M.E.; Bodily, D.M. Surface properties of mineral and coal pyrite after electrochemical alteration. In Proceedings of the Processing and Utilization of High Sulfur Coals IV, Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 26–30 August 1991; Dugan, P.R., Quigley, D.R., Attia, Y.A., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, P.; Liu, W.; Han, Y. Study on the mechanism of coal pyrite crystal lattice defects and floatability. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 997–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, P.; Ma, R.; Liu, W. Research on the Effect of Carbon Defects on the Hydrophilicity of Coal Pyrite Surface from the Insight of Quantum Chemistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, P.; Wang, D.; Liu, W. DFT Study into the Influence of Carbon Material on the Hydrophobicity of a Coal Pyrite Surface. Molecules 2019, 24, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, P.; Liu, W.; Yang, Z. Quantum chemistry investigation on influence of sulfur atom adsorption in sulfur material to the coal pyrite hydrophobicity. J. China Coal Soc. 2017, 42, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, P.; Shi, C.; Yan, P. DFT study on influence of sulfur on the hydrophobicity of pyrite surfaces in the process of oxidation. App. Sur. Sci. 2019, 466, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Niu, Z.; Peng, C. Quantitative synergistic adsorption affinity of Ca(II) and sodium oleate to predict the surface reactivity of hematite and quartz. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 131196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Fu, X.; Niu, Z. Protonation behavior study of the active sites on typical sulfide minerals surface using surface complexation model. Colloids Surf. A. 2025, 170, 136307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wen, S.; Hao, J. Flotation separation of chalcopyrite from pyrite using mineral fulvic acid as selective depressant under weakly alkaline conditions. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2025, 35, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; Cao, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W. Separation of chalcopyrite from pentlandite with sodium persulfate depressant: Flotation behavior and mechanism. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.J.D.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrated and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2002, 14, 2717–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Chevary, J.A.; Vosko, S.H.; Jackson, K.A.; Pederson, M.R.; Singh, D.J.; Fiolhais, C. Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation. Phy. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1992, 46, 6671–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, C. Influence of external electronic field on the electronic structure and optical properties of pyrite. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56676–56681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 4, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B Solid State 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, J.D.; Monkhorst, H.J. “Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations”—A reply. Phys. Rev. B Solid State 1977, 16, 1748–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, W.L.; Zhou, J. Interactions between kaolinite Al-OH surface and sodium hexametaphosphate. App. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, W.L.; Chen, J.H. DFT simulation of the adsorption of sodium silicate species on kaolinite surfaces. App. Surf. Sci. 2016, 370, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. DFT study of the adsorption of 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl trimethylammonium chloride on montmorillonite surfaces in solution. App. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, R.S. Electronic population analysis on LCAO-MO molecular wave functions. IV. bonding and antibonding in LCAO and Valence-bond theories. J. Chem. Phy. 1955, 23, 2343–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).