Life Cycle Assessment of a Cu/Fe-Pillared Clay Catalyzed Photo-Fenton Process for Paracetamol Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
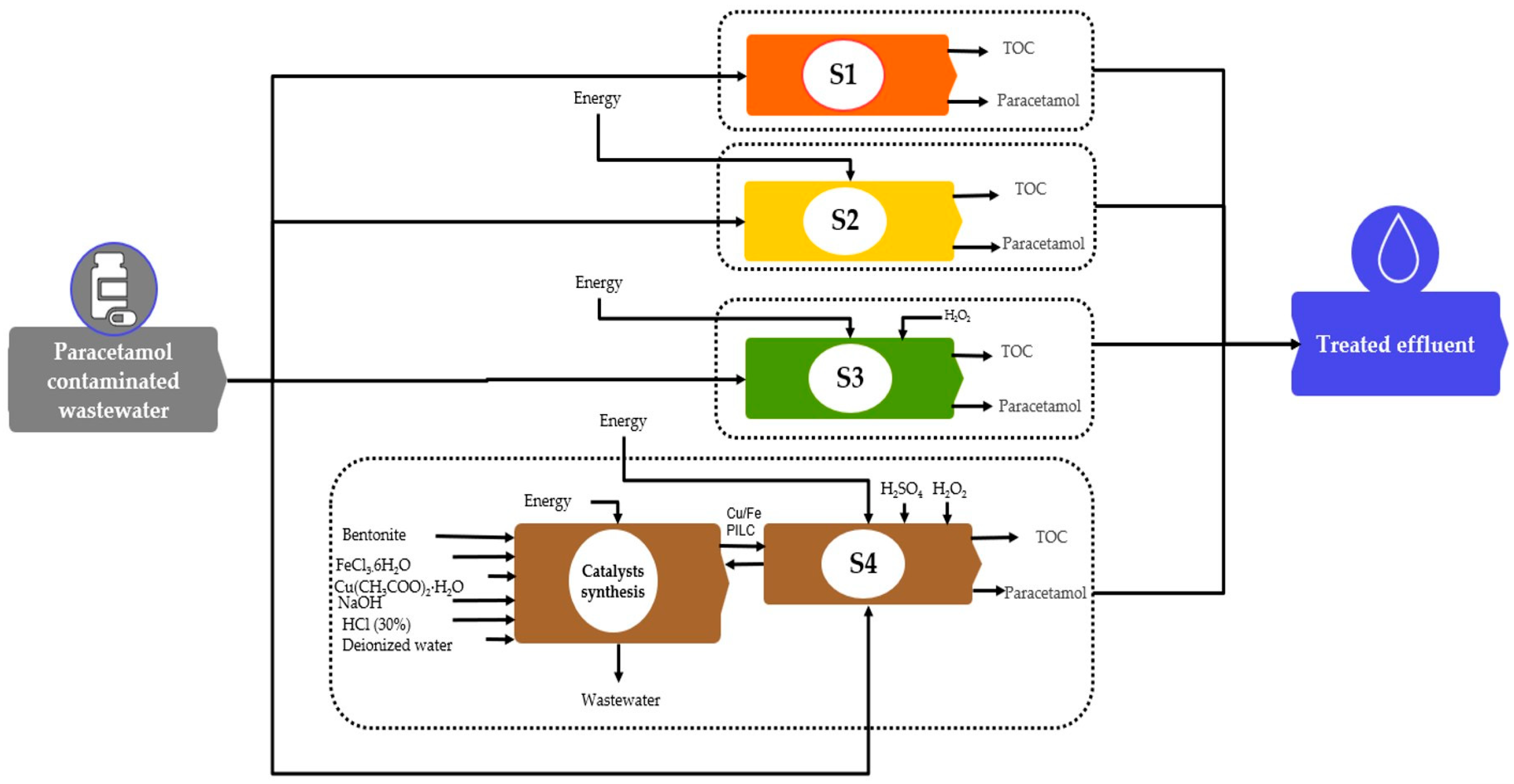
2.1. Goal and Scope of Study
2.1.1. Catalysts Synthesis
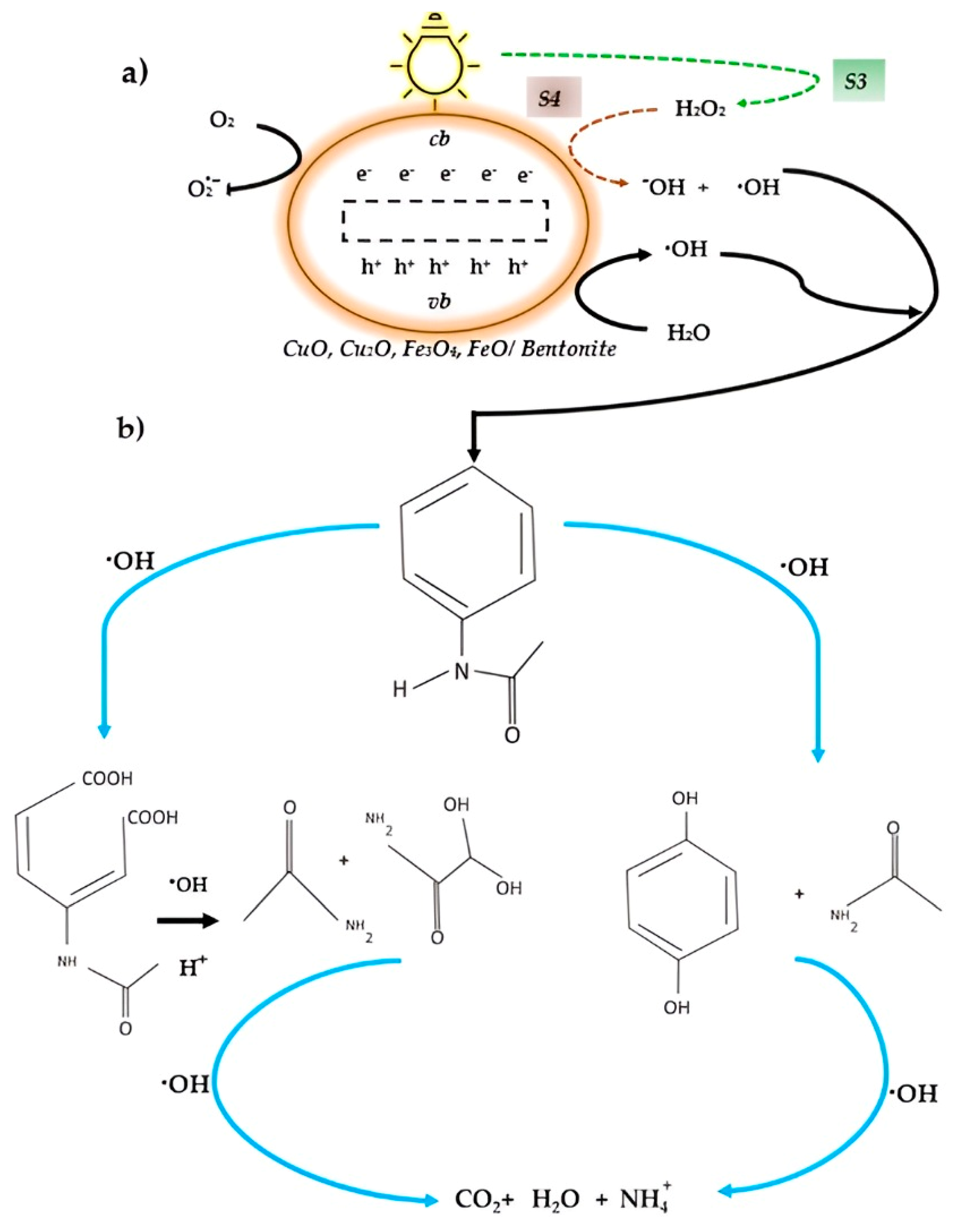
2.1.2. Paracetamol Degradation
2.2. Life Cycle Inventory Assessment (LCI)
2.3. Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA)
2.4. Interpretation
3. Results and Discussion
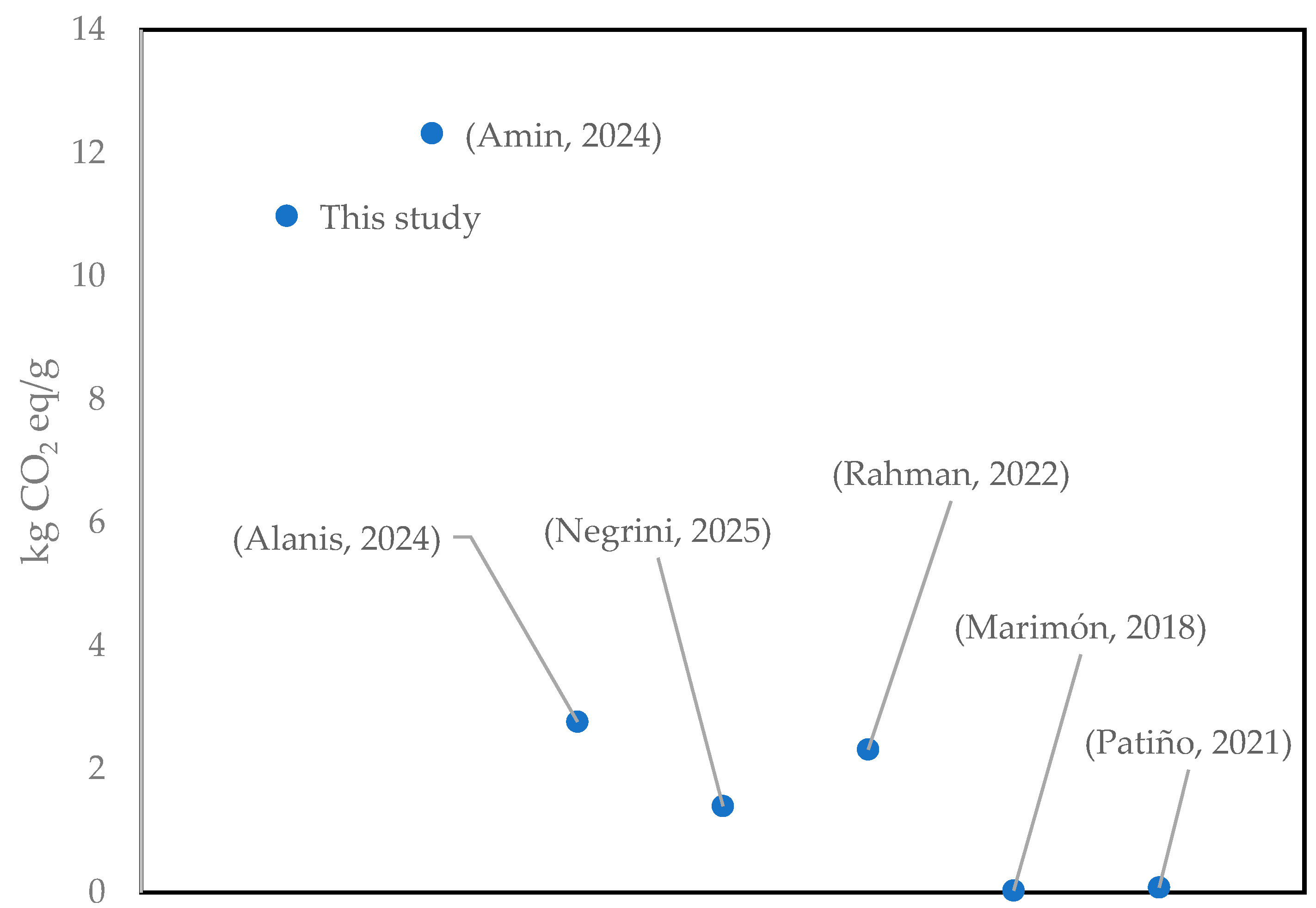
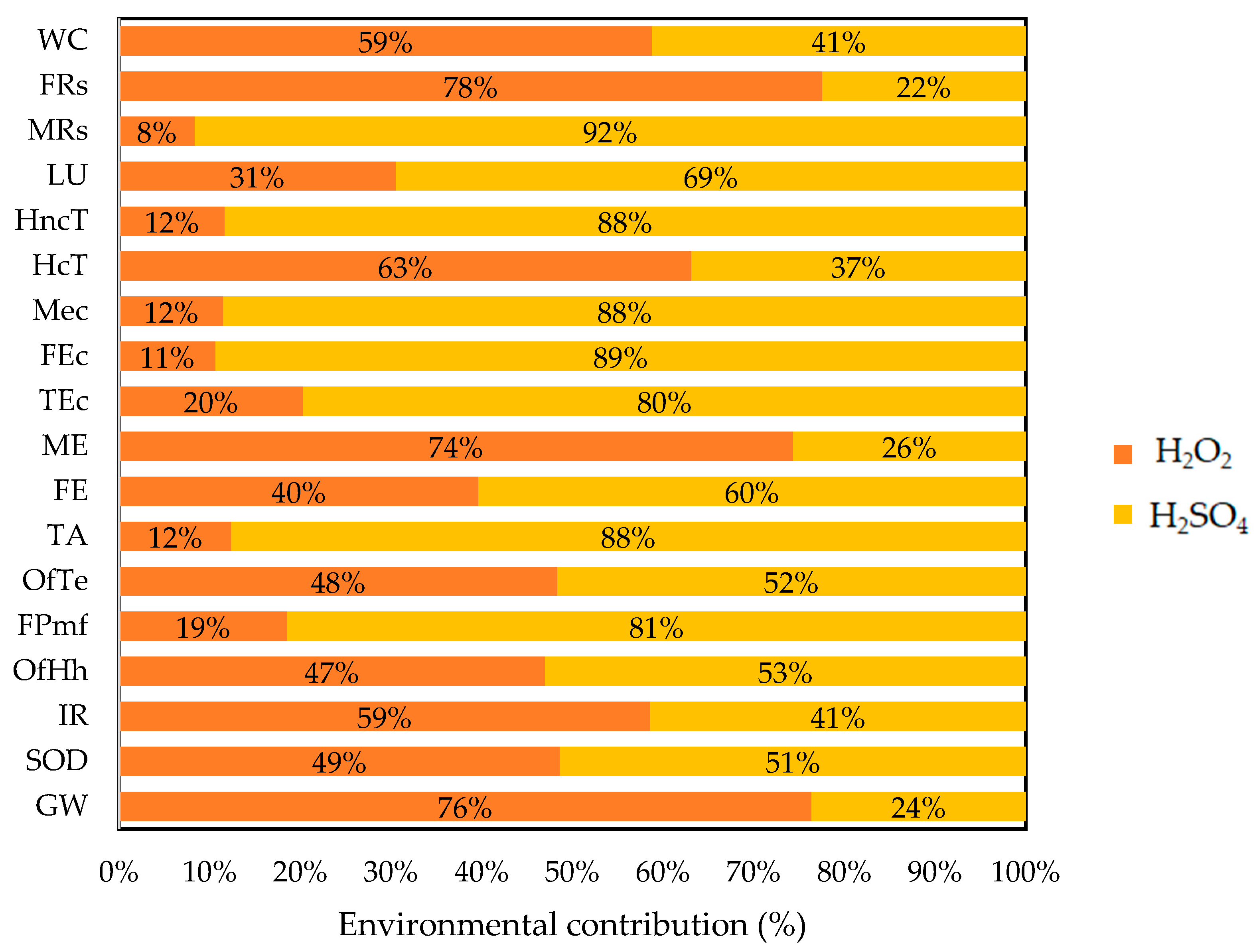
3.1. Life Cycle Impact Assessment of Catalyst Synthesis (Cu/Fe PILC)
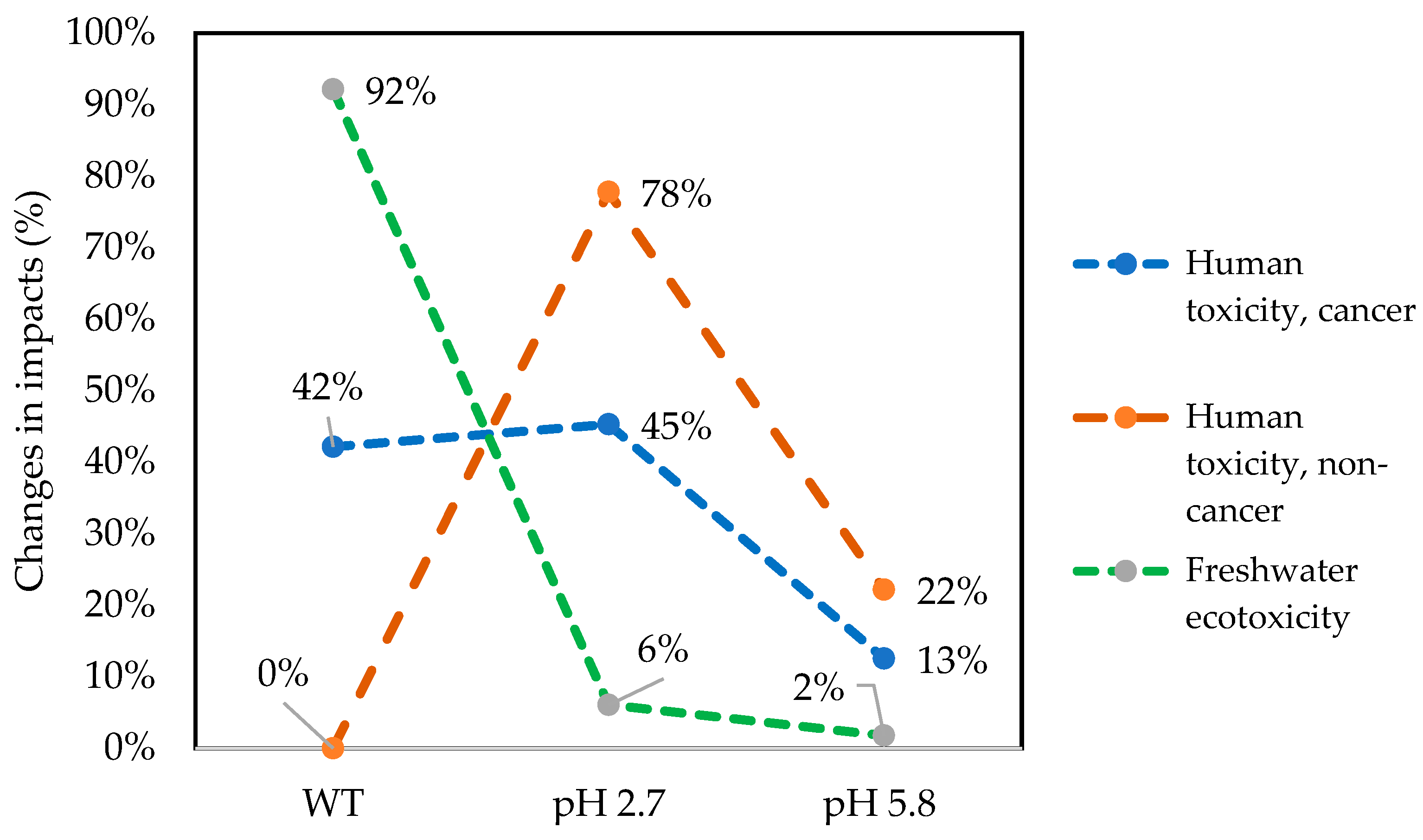
3.2. Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA) of Paracetamol Degradation
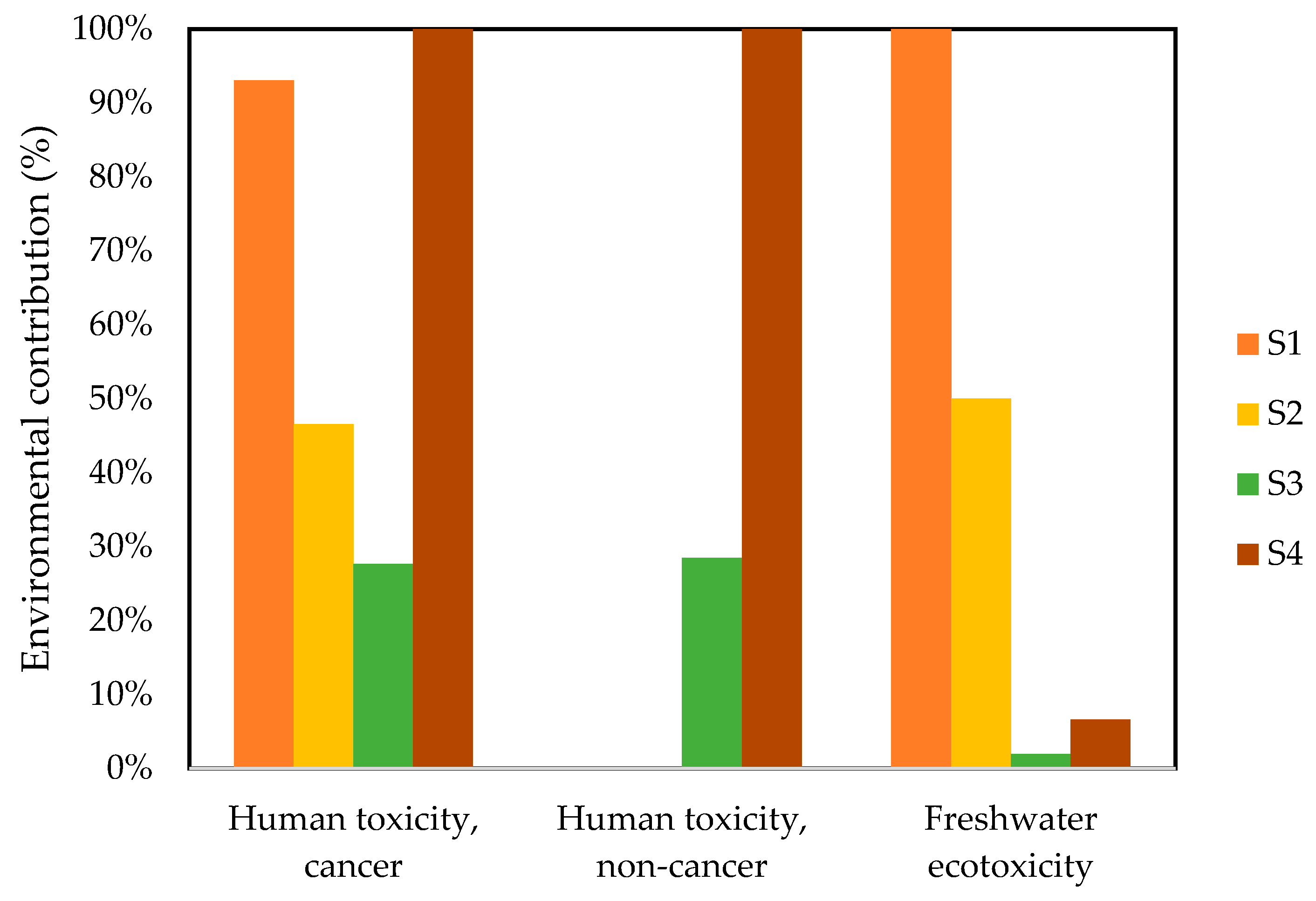
3.2.1. Human Toxicity Cancer
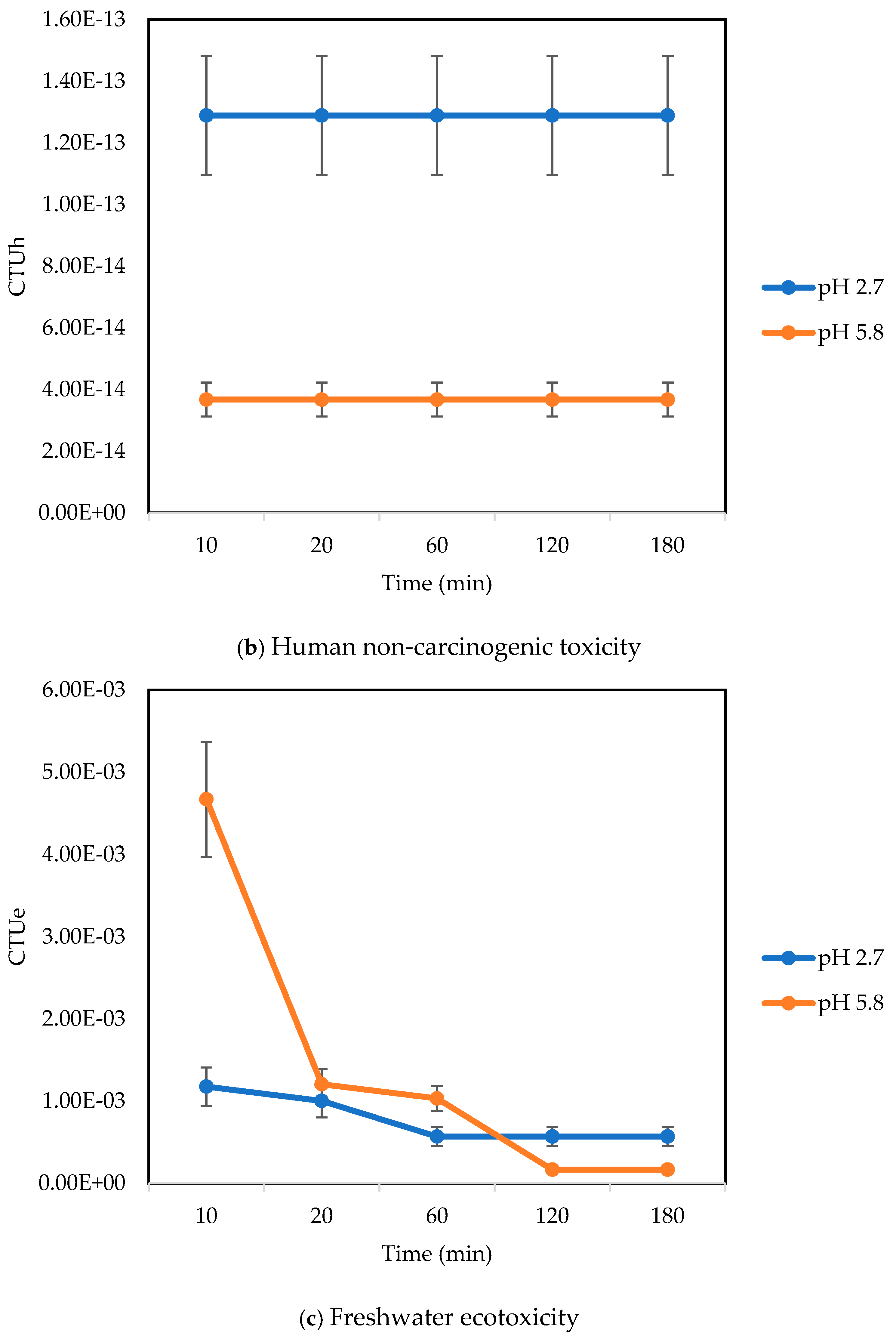
3.2.2. Human Toxicity, Non-Cancer
3.2.3. Freshwater Ecotoxicity
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
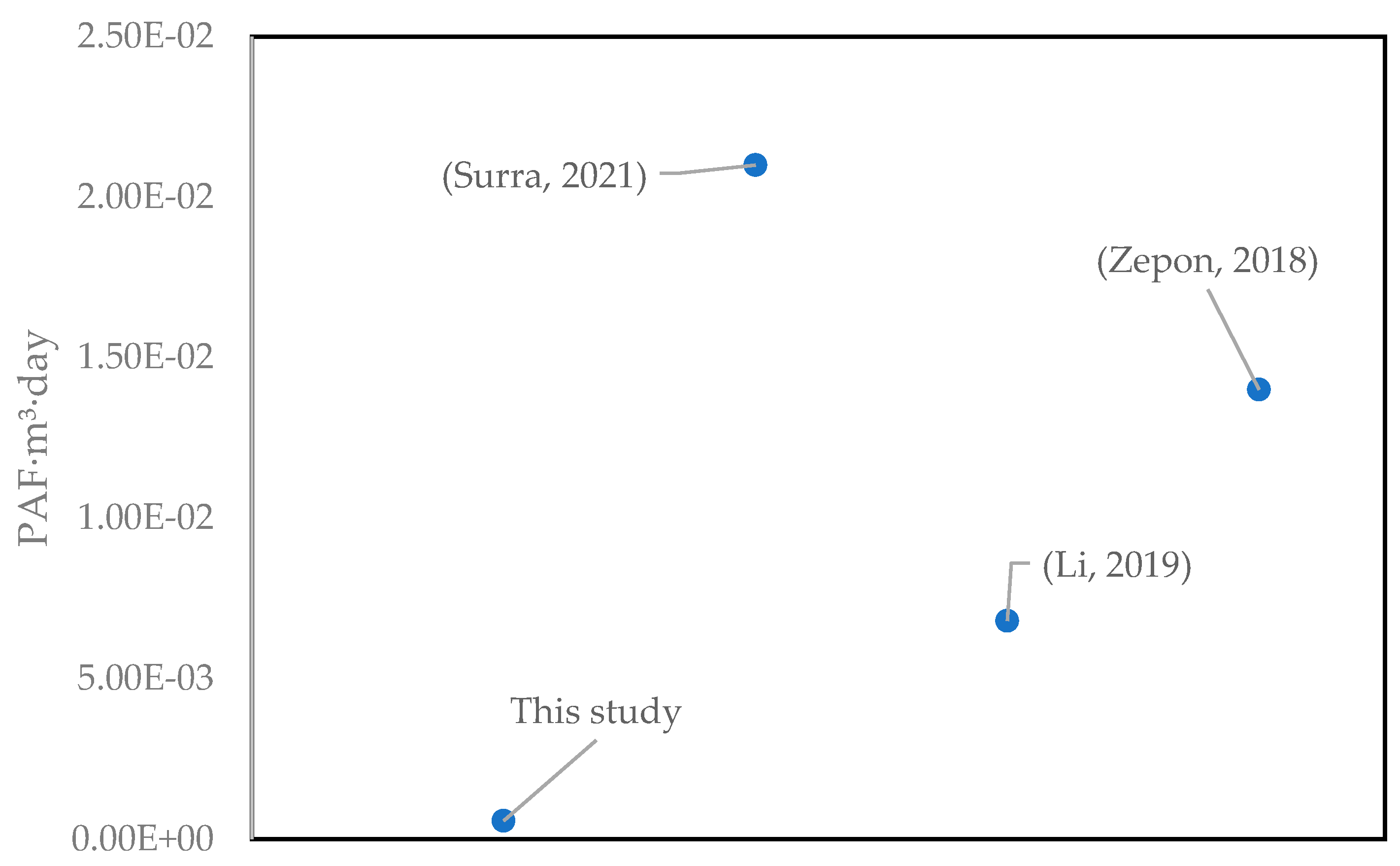
3.4. Photo-Fenton Process to Remove Paracetamol: A Perspective
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOPs | advanced oxidation processes |
| CFs | characterization factors |
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| CTUe | Comparative Toxic Units for ecosystems |
| CTUh | Comparative Toxic Units for humans |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| FE | freshwater eutrophication |
| FEc | freshwater ecotoxicity |
| FPmf | fine particulate matter formation |
| FRs | fossil resource scarcity |
| GW | global warming |
| HR | Hydroxyl Radical |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| H2SO4 | Sulfuric acid |
| HcT | human carcinogenic toxicity |
| HncT | human non-carcinogenic toxicity |
| IR | ionizing radiation |
| LCA | life cycle assessment |
| LCI | life cycle inventory |
| LCIA | life cycle impact assessment |
| LU | land use |
| MA | marine eutrophication |
| MEc | marine ecotoxicity |
| MRs | mineral resource scarcity |
| NAPQI | N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone-imine |
| OfHh | ozone formation, human health + |
| OfTe | ozone formation, terrestrial ecosystems |
| OH | hydroxyl radicals |
| PAF | potentially affected fraction |
| PILCs | pillared clays |
| S1 | Scenario 1, paracetamol solution is discharged without treatment |
| S2 | Scenario 2, paracetamol solution is treated by photolysis prior being discharged |
| S3 | Scenario 3, paracetamol solution is treated by photodecomposition of hydrogen peroxide prior being discharged |
| S4 | Scenario 4, paracetamol solution is treated by photo-Fenton prior being discharged |
| SETAC | Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry |
| SOD | stratospheric ozone depletion |
| TA | terrestrial acidification |
| Tec | terrestrial ecotoxicity |
| TOC | Total Organic Carbon |
| UNEP | United Nations Environment Programme |
| WC | water consumption |
| WWTPs | wastewater treatment plants |
References
- Igos, E.; Benetto, E.; Venditti, S.; Köhler, C.; Cornelissen, A. Comparative and Integrative Environmental Assessment of Advanced Wastewater Treatment Processes Based on an Average Removal of Pharmaceuticals. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratalla, Á.; Cotillas, S.; Lacasa, E.; Fernández-Marchante, C.M.; Ruiz, S.; Valladolid, A.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Sáez, C. Occurrence and Toxicity Impact of Pharmaceuticals in Hospital Effluents: Simulation Based on a Case of Study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 168, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz de García, S.; García-Encina, P.A.; Irusta-Mata, R. The Potential Ecotoxicological Impact of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products on Humans and Freshwater, Based on USEtoxTM Characterization Factors. A Spanish Case Study of Toxicity Impact Scores. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lian, J.Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Huang, D.; Tjokro, K.; Barbarossa, V.; Cucurachi, S.; et al. Application of Life Cycle Assessment in the Pharmaceutical Industry: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 459, 142550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, N.; Tuhkanen, T.; Kronberg, L. Occurrence of Acidic Pharmaceuticals in Raw and Treated Sewages and in Receiving Waters. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCudden, C. Analgesics and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. In Toxicology Cases for the Clinical and Forensic Laboratory; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of Human Pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Banerjee, R. Net Energy and Carbon Footprint Analysis of Solar Hydrogen Production from the High-Temperature Electrolysis Process. Appl. Energy 2020, 262, 114503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleneadie, H.J.; Baker, A.H.; Batis, N.; Bryant, J.; Jiang, Y.; Clokie, S.J.H.; Mehanna, H.; Garcia, P.; Gendoo, D.M.A.; Roberts, S.; et al. The Anti-Tumour Activity of DNA Methylation Inhibitor 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine Is Enhanced by the Common Analgesic Paracetamol through Induction of Oxidative Stress. Cancer Lett. 2021, 501, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C.; Seyssiecq, I.; Piram, A.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Vanot, G.; Tiliacos, N.; Roche, N.; Doumenq, P. From the Conventional Biological Wastewater Treatment to Hybrid Processes, the Evaluation of Organic Micropollutant Removal: A Review. Water Res. 2017, 111, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirvu, F.; Covaliu-Mierlă, C.I.; Catrina, G.A. Removal of Acetaminophen Drug from Wastewater by Fe3O4 and ZSM-5 Materials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Jeong, S.; Jang, A.; Kang, S. Relating Solute Properties of Contaminants of Emerging Concern and Their Rejection by Forward Osmosis Membrane. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Wong, K.C.; Suzaimi, N.D.; Ismail, A.F. Tailoring the Permeability and Flux Stability of Forward Osmosis Membrane with Tert-Butylamine Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes for Paracetamol Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.-F.; Pan, P.; Li, T.; Song, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, N.-Y. The Universal Accumulation of P-Aminophenol during the Microbial Degradation of Analgesic and Antipyretic Acetaminophen in WWTPs: A Novel Metagenomic Perspective. Microbiome 2025, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounaris Fuziki, M.E.; Ribas, L.S.; Tusset, A.M.; Brackmann, R.; Dos Santos, O.A.A.; Lenzi, G.G. Pharmaceutical Compounds Photolysis: PH Influence. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.N.; Conte, L.O.; Duarte, S.A.; Schenone, A.V. Improvement of Ferrioxalate Assisted Fenton and Photo-Fenton Processes for Paracetamol Degradation by Hydrogen Peroxide Dosage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 13489–13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Vargas, H.; Fernández González, Q.; Guillén-Garcés, R.A.; Rincón, M.E. Reverse-Engineered Electro-Fenton for the Selective Synthesis of Oxalic or Oxamic Acid through the Degradation of Acetaminophen: A Novel Green Electrocatalytic Refinery Approach. Water Res. 2025, 272, 122914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Yaghoot-Nezhad, A.; Wacławek, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Mehdipour, F. Comparative Investigation of Acetaminophen Degradation in Aqueous Solution by UV/Chlorine and UV/H2O2 Processes: Kinetics and Toxicity Assessment, Process Feasibility and Products Identification. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Lee, J.; Echavarría-Isaza, A.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Possibilities and Limitations of the Sono-Fenton Process Using Mid-High-Frequency Ultrasound for the Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Molecules 2023, 28, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo-Perea, A.L.; Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Lee, J.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Understanding the Effects of Mineral Water Matrix on Degradation of Several Pharmaceuticals by Ultrasound: Influence of Chemical Structure and Concentration of the Pollutants. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillano, R.; Rives, V.; García, I. Photocatalytic Degradation of Paracetamol in Aqueous Medium Using TiO2 Prepared by the Sol–Gel Method. Molecules 2022, 27, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Bian, Z. Photocatalytic Degradation of Paracetamol on Pd–BiVO4 under Visible Light Irradiation. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guettaıa, D.; Gaffour, H. Photo-Catalytıc Degradatıon of Paracetamol Using a Novel Photocatalyst Zr–WO3 Doped Charcoal. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2025, 138, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muga, H.E.; Mihelcic, J.R. Sustainability of Wastewater Treatment Technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Wei, J.; Qian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z. Life Cycle Assessment of Homogeneous Fenton Process as Pretreatment for Refractory Pharmaceutical Wastewater. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, L.; Romero, R.; Mendoza, A.; Brewer, S.; Donkor, K.; Gómez-Espinosa, R.M.; Natividad, R. Paracetamol Mineralization by Photo Fenton Process Catalyzed by a Cu/Fe-PILC under Circumneutral PH Conditions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 373, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhaleem, A.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Chu, W. Photocatalytic Degradation of Paracetamol Using Photo-Fenton-like Metal-Organic Framework-Derived CuO@C under Visible LED. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Oloño, J.T.; Vargas-Hernández, D.; Castro-Campoy, D.A.; Ibarra-Espinoza, A.; Pérez-Cruz, M.A.; Garrafa-Gálvez, H.E.; Herrera-Urbina, J.R.; Tánori-Córdova, J.C. Photo-Catalytic Activity of Iron Nanoparticles Supported on SBA-15 for Degradation of Organic Pollutants. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2025, 469, 116597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifasi, N.; Deorsola, F.A.; Fino, D.; Piumetti, M. Mesoporous TiO2 and Fe-Containing TiO2 Prepared by Solution Combustion Synthesis as Catalysts for the Photodegradation of Paracetamol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 36861–36881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Han, B.; Luo, C.; Qin, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Gan, Z.; Wang, C.-C.; Zheng, X.; et al. Precise Synthesis of Fe Single-Atom Catalysts on Montmorillonite/g-C3N4 Heterostructures for Highly Efficient Fenton-like Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Water Res. 2025, 287, 124420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshme Khavar, A.H.; Rashidi, M.A.; Alvandi, M.; Darvishnejad, M.H.; Aghayani, E. Bimetallic CuBi Nanoparticles Modified Ti3C2 MXene as an Efficient Cocatalyst for Enhancing Photocatalytic Degradation of Acetaminophen. Environ. Res. 2025, 282, 122118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Howayek, T.M.; Mazur, O.; Viter, R.; Bekheet, M.F.; Nada, A.A.; Bezzerga, D.; Hong, J.; Miele, P.; Iatsunskyi, I.; et al. Innovative Electrospinning Approach to Fabricate TiO2/NiO Nanofibers for Effective Acetaminophen Degradation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 709, 136077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachemaoui, M.; Molina, C.B.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J.; Mokhtar, A.; Hamacha, R.; Boukoussa, B. Metal-Loaded Mesoporous MCM-41 for the Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation (CWPO) of Acetaminophen. Catalysts 2021, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, F.F.; Silva, A.S.; Diaz de Tuesta, J.L.; Baldo, A.P.; Lopes, J.P.M.; Gonçalves, G.; Pereira, A.I.; Praça, P.; Silva, A.M.T.; Faria, J.L.; et al. Plastic Waste-Derived Carbon Nanotubes: Influence of Growth Catalyst and Catalytic Activity in CWPO. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Glass, B.D.; Goh, P.S. Advanced Oxidation Process-Mediated Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Water: A Review of Recent Advances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 14316–14350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oller, I.; Malato, S. Photo-Fenton Applied to the Removal of Pharmaceutical and Other Pollutants of Emerging Concern. Curr. Opin. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 29, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.N.; Conte, L.O.; Alfano, O.M.; Schenone, A.V. Paracetamol Removal by Photo-Fenton Processes at near-Neutral PH Using a Solar Simulator: Optimization by D-Optimal Experimental Design and Toxicity Evaluation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 397, 112584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypart-Pawul, A.; Neczaj, E.; Grobelak, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Removal of Organic Micropollutants from Wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 305, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, S.; González-Rodríguez, J.; Fernández, L.; Vázquez-Vázquez, C.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Fenton and Photo-Fenton Nanocatalysts Revisited from the Perspective of Life Cycle Assessment. Catalysts 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun Odabasi, S.; Buyukgungor, H. Comparative Study of Degradation of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products in Wastewater by Advanced Oxidation Processes: Fenton, UV/H2O2, UV/TiO2. Clean 2024, 52, 2300204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Espada, J.J.; Pariente, M.I.; Melero, J.A.; Martínez, F.; Molina, R. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Study of Heterogeneous and Homogenous Fenton Processes for the Treatment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, A.; Domènech, X.; Brillas, E.; Peral, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Solar Photo-Fenton and Solar Photoelectro-Fenton Processes Used for the Degradation of Aqueous α-Methylphenylglycine. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Sarinho, L.; Nunes, M.I. Application of Life Cycle Assessment to Fenton Processes in Wastewater Treatment—A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espíndola, J.C.; Cristóvão, R.O.; Mayer, D.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Dias, M.M.; Lopes, J.C.B.; Vilar, V.J.P. Overcoming Limitations in Photochemical UVC/H2O2 Systems Using a Mili-Photoreactor (NETmix): Oxytetracycline Oxidation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. Heterogeneous Fenton Catalysts: A Review of Recent Advances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 14040:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle assessment—Principles and Framework. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Valverde, J.L.; Romero, A.; Romero, R.; García, P.B.; Sánchez, M.L.; Asencio, I. Preparation and Characterization of Fe-PILCs. Influence of the Synthesis Parameters. Clays Clay Min. 2005, 53, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálinkó, I.; Lázár, K.; Hannus, I.; Kirisci, I. Step towards Nanoscale Fe Moieties: Intercalation of Simple and Keggin-Type Iron-Containing Ions in-between the Layers of Na-Montmorillonite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1996, 57, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, L.; Avilés, O.; Brewer, S.; Donkor, K.K.; Romero, R.; Gómez-Espinosa, R.M.; Alvarado, O.; Natividad, R. Al/Cu-PILC as a Photo-Fenton Catalyst: Paracetamol Mineralization. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 23821–23832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRé Sustainability SimaPro 2025. Available online: https://pre-sustainability.com/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- ecoinvent Ecoinvent v3.10—Ecoinvent. Available online: https://ecoinvent.org/ecoinvent-v3-10/ (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Steinmann, Z.J.N.; Elshout, P.M.F.; Stam, G.; Verones, F.; Vieira, M.; Zijp, M.; van Zelm, R. ReCiPe2016: A harmonised life cycle impact assessment method at midpoint and endpoint level. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, R.K.; Bachmann, T.M.; Gold, L.S.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Jolliet, O.; Juraske, R.; Koehler, A.; Larsen, H.F.; MacLeod, M.; Margni, M.; et al. USEtox—The UNEP-SETAC Toxicity Model: Recommended Characterisation Factors for Human Toxicity and Freshwater Ecotoxicity in Life Cycle Impact Assessment. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2008, 13, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzisymeon, E.; Foteinis, S.; Mantzavinos, D.; Tsoutsos, T. Life Cycle Assessment of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Olive Mill Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Rombouts, L.J.A.; Ragas, A.M.; van de Meent, D. Human-Toxicological Effect and Damage Factors of Carcinogenic and Noncarcinogenic Chemicals for Life Cycle Impact Assessment. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2005, 1, 181–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantke, P.; Chiu, W.A.; Aylward, L.; Judson, R.; Huang, L.; Jang, S.; Gouin, T.; Rhomberg, L.; Aurisano, N.; McKone, T.; et al. Exposure and Toxicity Characterization of Chemical Emissions and Chemicals in Products: Global Recommendations and Implementation in USEtox. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G.; Pinto da Silva, L. Life Cycle Assessment-Based Comparative Study between High-Yield and “Standard” Bottom-Up Procedures for the Fabrication of Carbon Dots. Materials 2022, 15, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; González-Doncel, M.; Pro, J.; Carbonell, G.; Tarazona, J.V. Occurrence of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds in Surface Waters of the Henares-Jarama-Tajo River System (Madrid, Spain) and a Potential Risk Characterization. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Gong, Y.; Wang, L. Potential Trade-off between Water Consumption and Water Quality: Life Cycle Assessment of Nonaqueous Solvent Dyeing. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D.; Nunes, B.; Pinto, E.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Correia, A.T. Assessment of Paracetamol Toxic Effects under Varying Seawater PH Conditions on the Marine Polychaete Hediste Diversicolor Using Biochemical Endpoints. Biology 2022, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mawali, K.S.; Osman, A.I.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Mehta, N.; Jamil, F.; Mjalli, F.; Vakili-Nezhaad, G.R.; Rooney, D.W. Life Cycle Assessment of Biodiesel Production Utilising Waste Date Seed Oil and a Novel Magnetic Catalyst: A Circular Bioeconomy Approach. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamagna, M.; Gonçalves, N.P.F.; Bianco Prevot, A. Environmental Assessment of Humic Acid Coated Magnetic Materials Used as Catalyst in Photo-Fenton Processes. Catalysts 2020, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Shah, H.H.; Naveed, A.B.; Iqbal, A.; Gamil, Y.; Najeh, T. Life Cycle Assessment of Iron-Biomass Supported Catalyst for Fischer Tropsch Synthesis. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1374739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis, C.; Romero, R.; Ávila Córdoba, L.; Natividad, R. Methyl Esters Production from Waste Cooking Oil Catalysed by Iron Oxides Supported on CaO: Cost and Environmental Impacts. Clean. Circ. Bioecon. 2024, 9, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Kang, S.; McGinnis, S.; Vikesland, P.J. Life Cycle Impact Assessment of Iron Oxide (Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3) Nanoparticle Synthesis Routes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 3155–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, B.; Floris, P.; D’Abramo, C.; Aldaghi, S.A.; Costamagna, M.; Perucca, M.; Saibene, M.; Perelshtein, I.; Colombo, A.; Bonfanti, P.; et al. Comparative Toxicity and Environmental Impact Assessments of Sonochemically-Synthesized CuO and Zn-Doped CuO Nanoparticles Using Zebrafish and LCA Tools. Discov. Nano 2025, 20, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimón-Bolívar, W.; González, E.E. Green Synthesis with Enhanced Magnetization and Life Cycle Assessment of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 9, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Ruiz, D.A.; Meramo-Hurtado, S.I.; González-Delgado, Á.D.; Herrera, A. Environmental Sustainability Evaluation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized via Green Synthesis and the Coprecipitation Method: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment Study. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 12410–12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, P.P.; Borthakur, B. The Role of Industrial Catalysts in Accelerating the Renewable Energy Transition. Chem. Proc. 2025, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, P.; Chakraborty, R. E-Waste Derived Silica-Alumina for Eco-Friendly and Inexpensive Mg-Al-Ti Photocatalyst towards Glycerol Carbonate (Electrolyte) Synthesis: Process Optimization and LCA. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambhule, P.W.; Khaty, N.T.; Das Sarma, I.B.; Tangde, V.M.; Joglekar, S.; Wankhede, G.A. Towards Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles and Conventional Methods. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 179, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, S.; Gracida-Alvarez, U.R.; Ferrandon, M.; Delferro, M.; Benavides, P.T.; Urgun-Demirtas, M. Techno-Economic and Life Cycle Analyses of the Synthesis of a Platinum–Strontium Titanate Catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2025, 15, 4419–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Economic Commission For Europe. Life Cycle Assessment of Electricity Generation Options; United Nations Economic Commission For Europe: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Yun, Y.; Hsu, Y. Catalysis Towards Sustainability. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2025, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepon Tarpani, R.R.; Azapagic, A. Life Cycle Environmental Impacts of Advanced Wastewater Treatment Techniques for Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, O.; Rico, A.; Guinée, J.B.; Henriksson, P.J.G. Characterizing Antibiotics in LCA—A Review of Current Practices and Proposed Novel Approaches for Including Resistance. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 1816–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S.A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Gabarrell, X. Accounting for the Dissociating Properties of Organic Chemicals in LCIA: An Uncertainty Analysis Applied to Micropollutants in the Assessment of Freshwater Ecotoxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248–249, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Mentha, S.S.; Misra, Y.; Dwivedi, N. Emerging Pollutants of Severe Environmental Concern in Water and Wastewater: A Comprehensive Review on Current Developments and Future Research. Water-Energy Nexus 2023, 6, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Mi, N.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Fu, W.; Bai, M.; Gao, L.; Ma, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Regular Use of Paracetamol and Risk of Liver Cancer: A Prospective Cohort Study. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirois, J.E. Comprehensive Investigation Evaluating the Carcinogenic Hazard Potential of Acetaminophen. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 123, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Murray, F.J.; Monnot, A.D.; Jacobson-Kram, D.; Cohen, S.M.; Hardisty, J.F.; Atillasoy, E.; Hermanowski-Vosatka, A.; Kuffner, E.; Wikoff, D.; et al. Assessment of the Biochemical Pathways for Acetaminophen Toxicity: Implications for Its Carcinogenic Hazard Potential. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 120, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesqueira, J.F.J.R.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. A Life Cycle Assessment of Solar-Based Treatments (H2O2, TiO2 Photocatalysis, Circumneutral Photo-Fenton) for the Removal of Organic Micropollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteinis, S.; Monteagudo, J.M.; Durán, A.; Chatzisymeon, E. Environmental Sustainability of the Solar Photo-Fenton Process for Wastewater Treatment and Pharmaceuticals Mineralization at Semi-Industrial Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecetoc. Freshwater Ecotoxicity as an Impact Category in Life Cycle Assessment; Technical Report No. 127; Ecetoc: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Katal, R.; Davood Abadi Farahani, M.H.; Jiangyong, H. Degradation of Acetaminophen in a Photocatalytic (Batch and Continuous System) and Photoelectrocatalytic Process by Application of Faceted-TiO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.; Antunes, S.C.; Santos, J.; Martins, L.; Castro, B.B. Toxic Potential of Paracetamol to Freshwater Organisms: A Headache to Environmental Regulators? Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2014, 107, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, A.; Glanville, H.C.; Law, A.C.; Stanton, T.; Carter, L.J.; Taylor, J.C. Emerging Challenges of the Impacts of Pharmaceuticals on Aquatic Ecosystems: A Diatom Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, C. Direct Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide from Hydrogen and Oxygen: An Overview of Recent Developments in the Process. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 350, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Całus-Makowska, K.; Dziubińska, J.; Grosser, A.; Grobelak, A. Application of the Fenton and Photo-Fenton Processes in Pharmaceutical Removal: New Perspectives in Environmental Protection. Desalination Water Treat. 2025, 321, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa-Luna, K.A.; Mendoza-Zepeda, A.; Natividad, R.; Romero, R.; Galar-Martínez, M.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M. Biological Hazard Evaluation of a Pharmaceutical Effluent before and after a Photo-Fenton Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisales, C.M.; Salazar, L.M.; Garcia, D.P. Treatment of Synthetic Dye Baths by Fenton Processes: Evaluation of Their Environmental Footprint through Life Cycle Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4300–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, W.; Ye, Q.; Hou, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, P. Life Cycle Assessment of Advanced Wastewater Treatment Processes: Involving 126 Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Life Cycle Inventory. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surra, E.; Correia, M.; Figueiredo, S.; Silva, J.G.; Vieira, J.; Jorge, S.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.Á.; Lapa, N.; Delerue-Matos, C. Life Cycle and Economic Analyses of the Removal of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals from Municipal Wastewater by Anodic Oxidation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Cornejo, L.G.; Romero, R.; Gutiérrez-Alejandre, A.; Regalado-Méndez, A.; Amado-Piña, D.; Hernández-Servín, J.A.; Natividad, R. Iron and Copper Pillared Clay Photo-Catalyzes Carbon Dioxide Chemical Reduction in Aqueous Medium. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 511, 162193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, R. Wastewater Upgrading to Fuels: Routes and Challenges. J. Chem. Eng. Renew. Fuels 2025, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Rieradevall, J.; Torrades, F.; Peral, J.; Domènech, X. Environmental Assessment of Different Advanced Oxidation Processes Applied to a Bleaching Kraft Mill Effluent. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzate, S.; Pfister, S.; Oberschelp, C.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A. Environmental Impacts of an Advanced Oxidation Process as Tertiary Treatment in a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garciamontano, J.; Ruiz, N.; Munoz, I.; Domenech, X.; Garciahortal, J.; Torrades, F.; Peral, J. Environmental Assessment of Different Photo-Fenton Approaches for Commercial Reactive Dye Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou-Ttofa, L.; Foteinis, S.; Chatzisymeon, E.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Life Cycle Assessment of Solar-driven Oxidation as a Polishing Step of Secondary-treated Urban Effluents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteinis, S.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Frontistis, Z.; Mantzavinos, D.; Chatzisymeon, E. Environmental Sustainability of Light-Driven Processes for Wastewater Treatment Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Process | Wavelength, Photocatalyst and Its Concentration | Paracetamol Initial Concentration (g/L) | Reaction Conditions | Paracetamol, TOC Removal (%) and Treatment Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photo-Fenton | UV (254 nm) Cu/Fe-PILC 50 mg/L | 0.1 | pH = 3.0 T = 25 °C H2O2 = 483 mg/L pH = 5.8 | 100 (20 min) 85 (180 min) 100 (30 min) 81 (180 min) | [26] |
| Visible light (100 W) CuO=C 1 g/L | 1.21 × 10−3 | pH = 5.1 V = 0.1 L T = 23 ± 2 °C H2O2 = 5 × 10−3 mol/L | 95 68 (480 min) | [27] | |
| UV (390 nm) Fe-SBA-15 0.33 g/L | 0.02 | V = 0.45 L H2O2 = 1 × 10−3 mol/L | 86.1 (30 min) | [28] | |
| UV (365 nm) Fe/TiO2_SCS 2 g/L | 0.01 | pH = 3 T = 25 °C H2O2 = 2.78 × 10 −3 mol/L | 100 (60 min) | [29] | |
| Fenton | Fe@C3N4-montmorillonite 25 mg | 0.04 | pH = 6 V = 0.1 L Flow rate = 30 mL/min | >95 (2000 min) | [30] |
| Photocatalysis | Visible light (400 nm) CuBi/Ti3C2, 1 g/L | 0.01 | pH = 5.4 V = 0.05 L | 99.7 99.9 (150 min) | [31] |
| Visible light (318 mW/cm2) NiO-TiO2, 0.5 g/L | 0.01 | pH = 7 | 98.8 (240 min) | [32] | |
| UV Zr–WO3@ charcoal 1 g/L | 0.02 | pH = 6 T = 25 °C | 73 (120 min) | [23] | |
| Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation | Fe/MCM-41 1 g/L | 0.005 | pH = 3 V = 1L T = 55 °C H2O2 (Stochiometric amount) | >90 (240 min) | [33] |
| CNT@NiFeAl-C 2.5 g/L | 0.1 | pH = 3.5 V = 0.1 L T = 80 °C H2O2 = 474 mg/L | 100 (60 min) 71% (360 min) | [34] |
| Scenario | Stage | Inputs | Unit | Outputs | Unit | Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality | ||||||||
| 1 | Reaction | Paracetamol | 0.10 | g | TOC | 0.064 | g | Experimental |
| Paracetamol | 0.10 | g | ||||||
| Scenario | Stage | Inputs | Unit | Outputs | Unit | Data Quality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Reaction | Paracetamol | 0.10 | g | TOC | 0.063 | g | Experimental |
| Energy | 1.38 | kWh | Paracetamol | 0.050 | g | |||
| Scenario | Stage | Inputs | Unit | Outputs | Unit | Data Quality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Reaction | Paracetamol | 0.10 | g | TOC | 0.0256 | g | Experimental |
| H2O2 | 0.483 | g | H2O2 | 0.338 | g | |||
| Energy | 1.38 | kWh | Paracetamol | 0 | g | |||
| Scenario | Stage | Inputs | Unit | Outputs | Unit | Data Quality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Catalyst synthesis | Energy | 17.54 | kWh | Cu/Fe-PILC | 1 | g | Experimental |
| Bentonite | 1 | g | Wastewater | 2 | L | |||
| FeCl3·6H2O | 16.54 | g | ||||||
| Cu (CH3COO)2·H2O | 1.01 | g | ||||||
| Deionized water | 2 | L | ||||||
| NaOH | 4.89 | g | ||||||
| HCl (30%) | 0.01 | g | ||||||
| Reaction | Paracetamol | 0.10 | g | TOC | 0.0115 | g | Experimental | |
| Cu/Fe-PILC | 0.5 | g | Cu/Fe-PILC | 0.5 | g | |||
| H2O2 | 0.483 | g | Paracetamol | 0 | g | |||
| H2SO4 | 0.001 | L | H2O2 | 0 | g | |||
| Energy | 1.38 | kWh | H2SO4 | 0.001 | L | |||
| Environmental Contribution | Impact Category | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | GW | 10.98 | kg CO2 eq |
| SOD | 1.35 × 10−5 | kg CFC11 eq | |
| IR | 0.53 | kBq Co-60 eq | |
| TA | 0.03 | kg SO2 eq | |
| OfHh | 0.02 | kg NOx eq | |
| OfTe | 0.02 | kg NOx eq | |
| FRs | 3.54 | kg oil eq | |
| Material | FEc | 0.03 | kg 1,4-DCB |
| Mec | 0.04 | kg 1,4-DCB | |
| HncT | 0.50 | kg 1,4-DCB | |
| MRs | 1.53 × 10−3 | kg Cu eq | |
| Impact Category | Unit | S1 (Without Treatment) | S2 (Photolysis) | S3 (UV + H2O2) | S4 (Photo-Fenton Cu/Fe PILC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human toxicity, cancer | CTUh | 9.06 × 10−12 | 4.53 × 10−12 | 2.69 × 10−12 | 9.73 × 10−12 |
| Human toxicity, non-cancer | CTUh | 0 | 0 | 3.67 × 10−14 | 1.29 × 10−13 |
| Freshwater ecotoxicity | PAF·m3·day | 8.66 × 10−3 | 4.33 × 10−3 | 1.67 × 10−4 | 5.70 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alanis, C.; Padilla-Rivera, A.; Romero, R.; Ramírez-Serrano, A.; Natividad, R. Life Cycle Assessment of a Cu/Fe-Pillared Clay Catalyzed Photo-Fenton Process for Paracetamol Removal. Processes 2025, 13, 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103165
Alanis C, Padilla-Rivera A, Romero R, Ramírez-Serrano A, Natividad R. Life Cycle Assessment of a Cu/Fe-Pillared Clay Catalyzed Photo-Fenton Process for Paracetamol Removal. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103165
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlanis, Claudia, Alejandro Padilla-Rivera, Rubi Romero, Armando Ramírez-Serrano, and Reyna Natividad. 2025. "Life Cycle Assessment of a Cu/Fe-Pillared Clay Catalyzed Photo-Fenton Process for Paracetamol Removal" Processes 13, no. 10: 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103165
APA StyleAlanis, C., Padilla-Rivera, A., Romero, R., Ramírez-Serrano, A., & Natividad, R. (2025). Life Cycle Assessment of a Cu/Fe-Pillared Clay Catalyzed Photo-Fenton Process for Paracetamol Removal. Processes, 13(10), 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103165









