High-Spermidine-Producing Yeast Strain for Autophagy-Promoting Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strain Development
2.2. Yeast Fermentation and Drying
2.3. Polyamine Quantification Through HPLC
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing, Mutation Detection, and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Free Amino Acid Analysis
2.6. HDF Culture and Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. Autophagy Induction Analysis
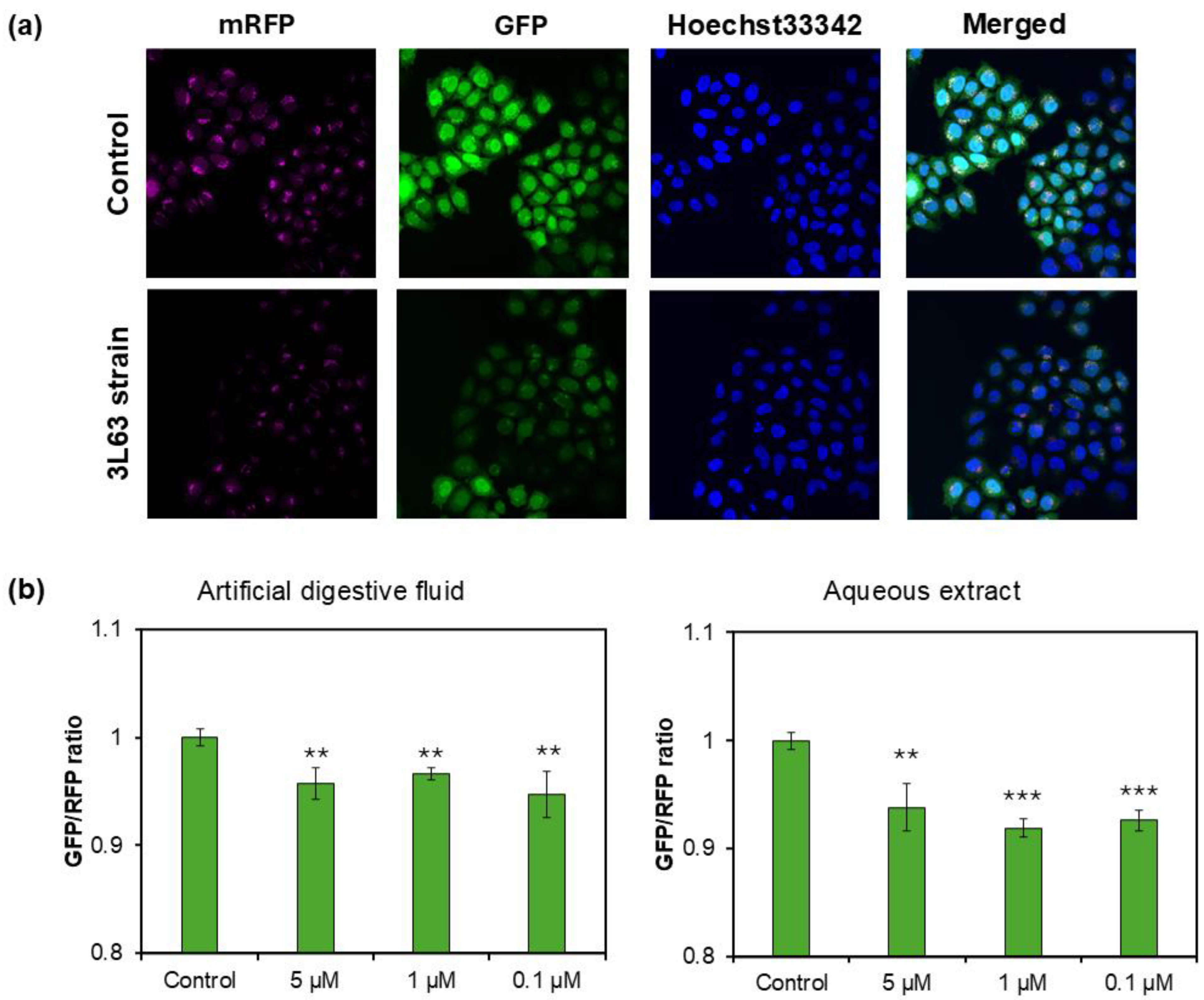
2.7.1. CYTO-ID Staining for Autophagic Activity
2.7.2. mRFP-GFP Tandem Fluorescent-Tagged LC3 (tfLC3) Assay
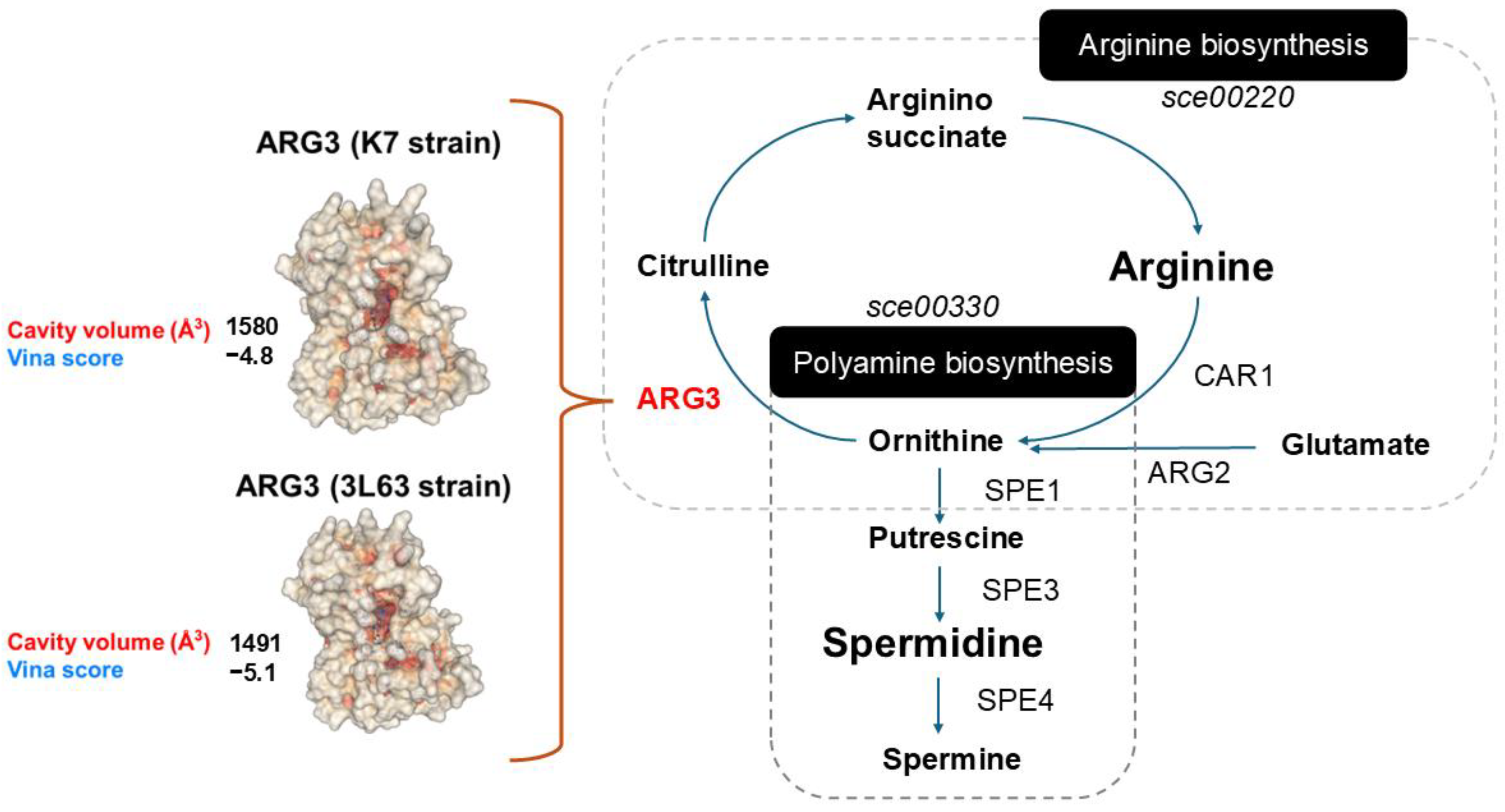
2.8. Protein Variant Modelling and Docking Simulation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characterization of Newly Developed 3L63 Yeast
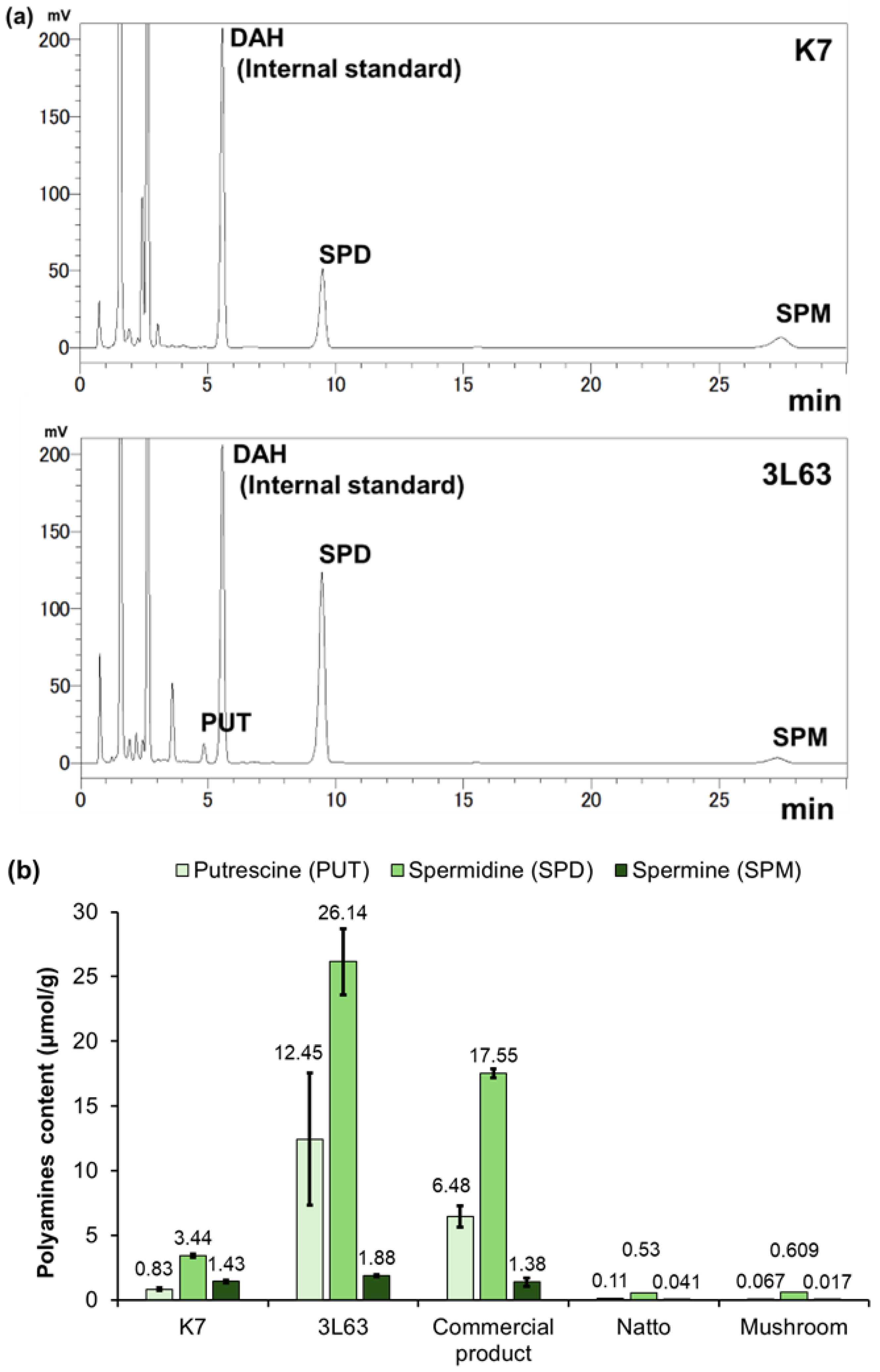
3.2. Polyamine Content in Yeast Strains
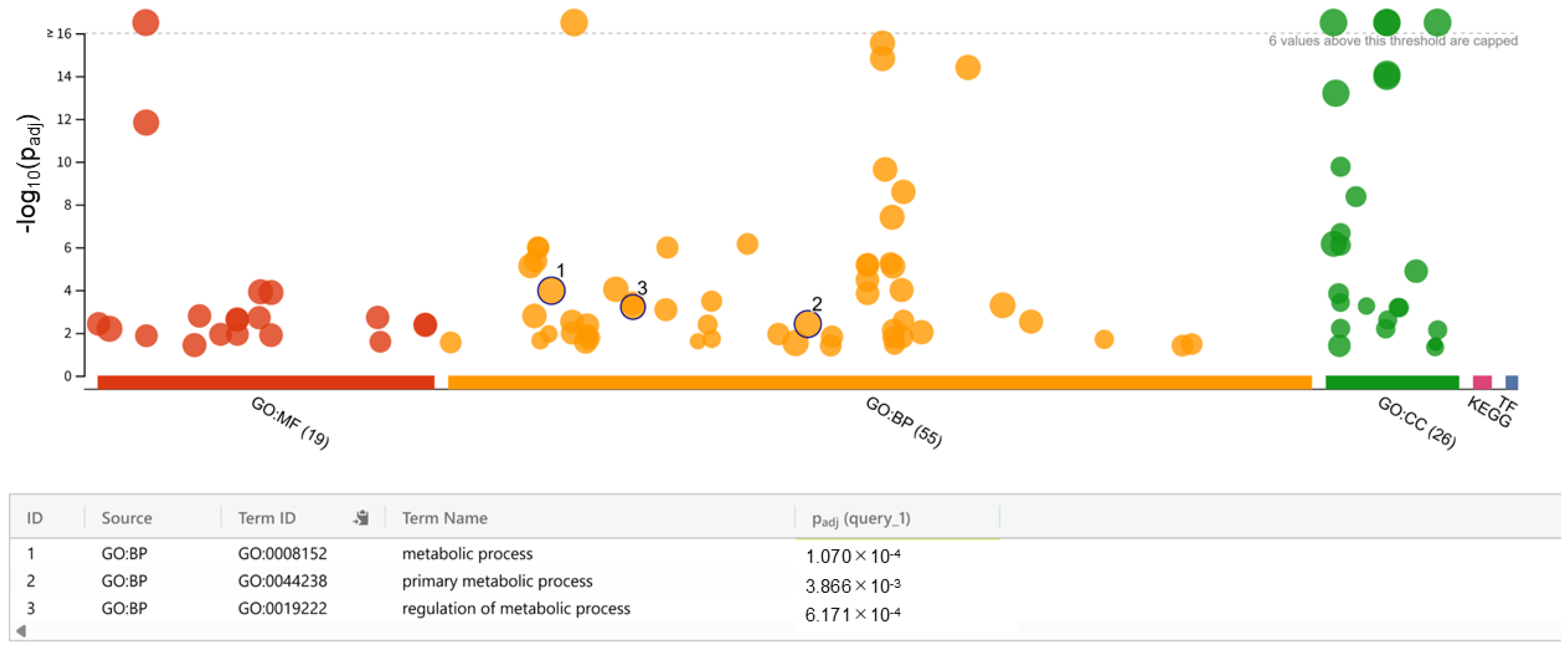
3.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Free Amino Acid Profiles
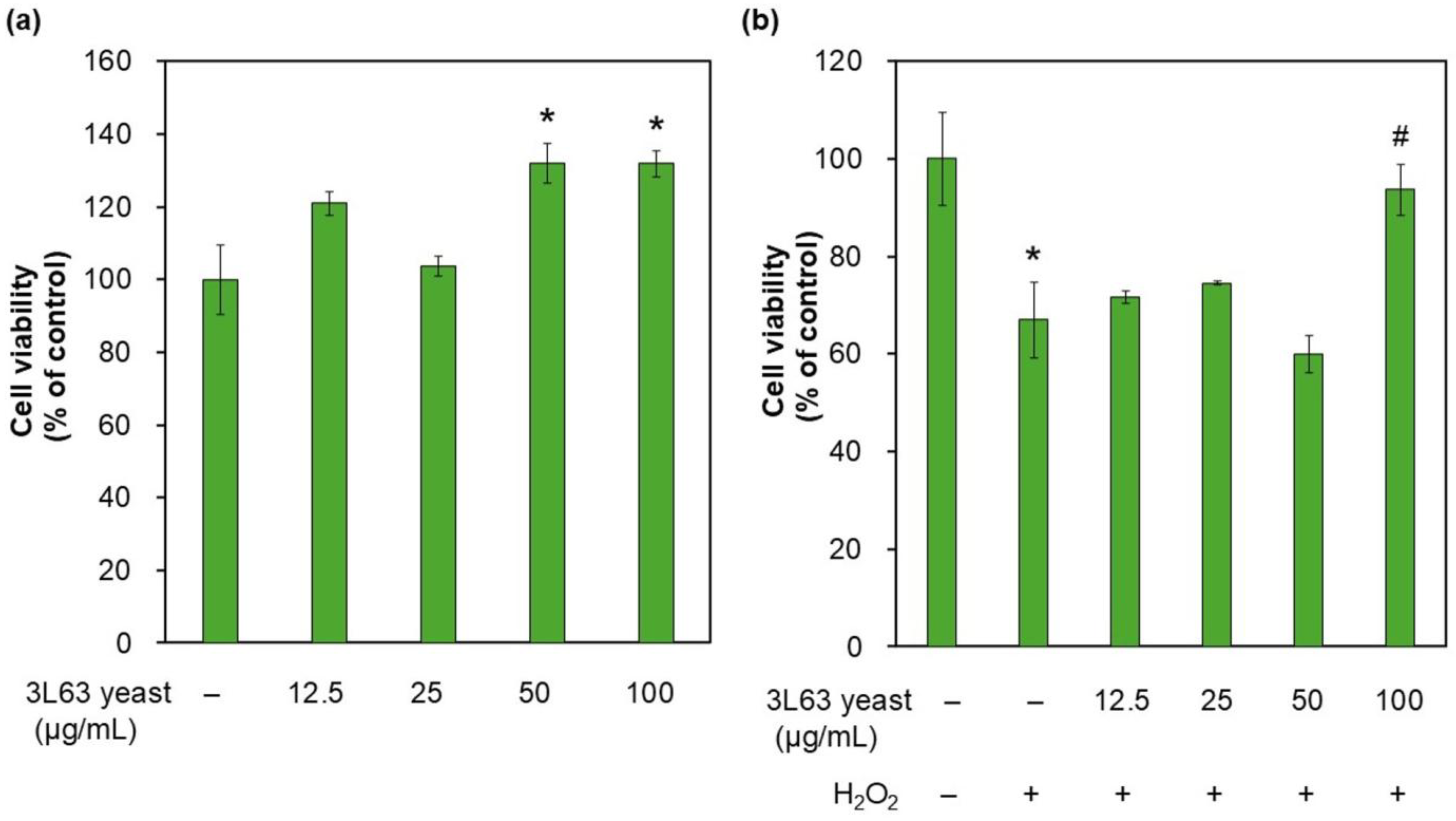
3.5. HDF Proliferation
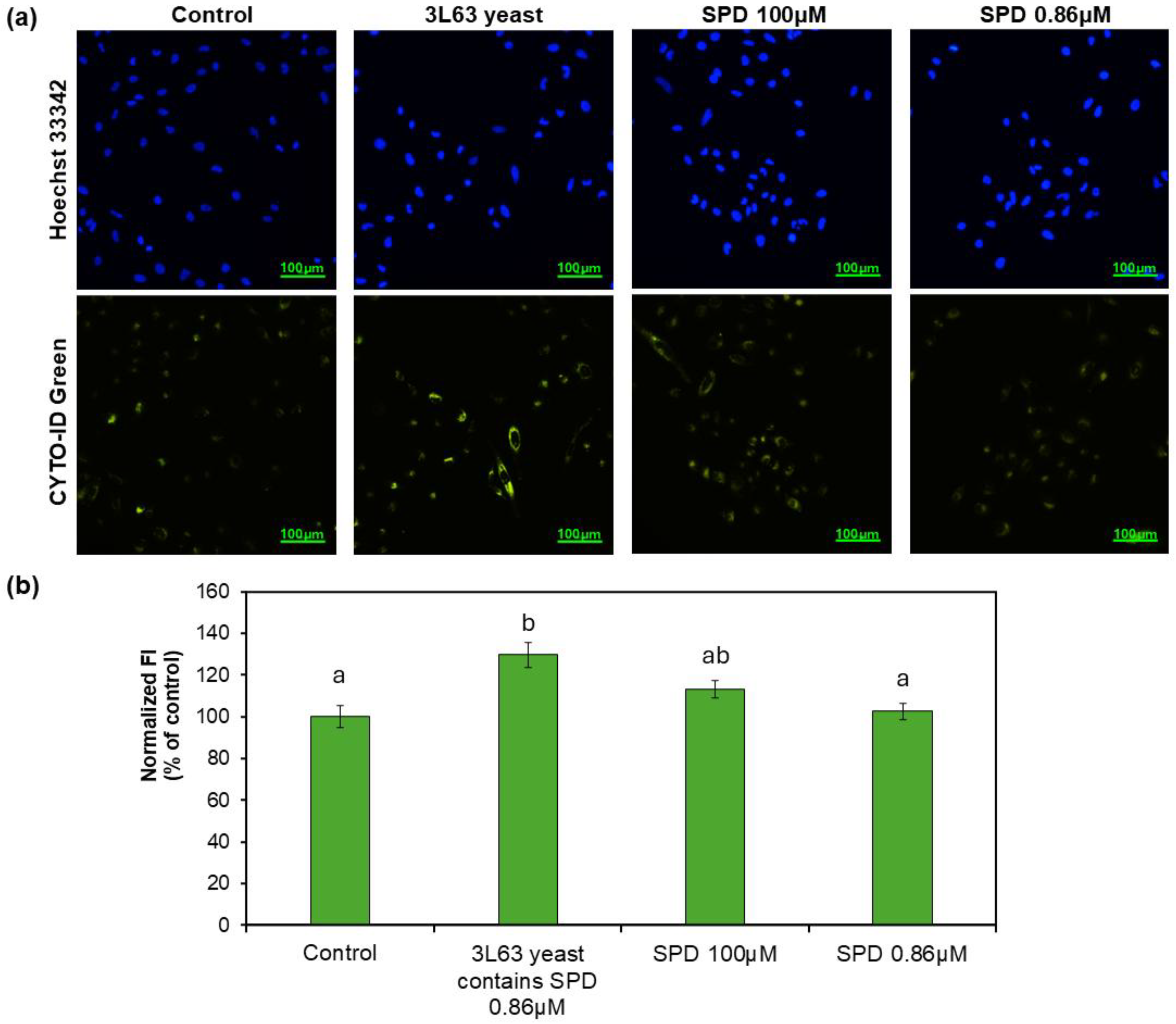
3.6. Autophagy Induction by 3L63 Yeast
4. Discussion
4.1. Food Safety and Formulation Strategy
4.2. Mechanism of Enhanced SPD Production
4.3. Functional Benefits of SPD: Autophagy and Healthy Aging
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BP | biological process |
| CC | cellular component |
| GMO | genetically modified organism |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GRAS | Generally Recognized as Safe |
| HDF | human dermal fibroblast |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| MF | molecular function |
| PUT | putrescine |
| SAM | S-adenosylmethionine |
| SPD | spermidine |
| SPM | spermine |
| tfLC3 | tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3 |
References
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2025: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects 2024: Summary of Results (UN DESA/POP/2024/TR/NO. 9); United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York City, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, I.M.; Gibson, D.S.; McGilligan, V.; McNerlan, S.E.; Alexander, H.D.; Ross, O.A. Age and age-related diseases: Role of inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.F.; Yoshida, S.; Stein, L.R.; Grozio, A.; Kubota, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Redpath, P.; Migaud, M.E.; Apte, R.S.; Uchida, K.; et al. Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, I.S.; Yun, S.; Yoon, Y.E.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, S.-J. Mechanisms of aging and the preventive effects of resveratrol on age-related diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegg, A.E. Mammalian polyamine metabolism and function. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, T.; Abdellatif, M.; Schroeder, S.; Primessnig, U.; Stekovic, S.; Pendl, T.; Harger, A.; Schipke, J.; Zimmermann, A.; Schmidt, A.; et al. Cardioprotection and lifespan extension by the natural polyamine spermidine. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niechcial, A.; Schwarzfischer, M.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Atrott, K.; Laimbacher, A.; Morsy, Y.; Katkeviciute, E.; Häfliger, J.; Westermann, P.; Akdis, C.A.; et al. Spermidine ameliorates colitis via induction of anti-inflammatory macrophages and prevention of intestinal dysbiosis. J. Crohn′s Colitis 2023, 17, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, T.; Knauer, H.; Schauer, A.; Büttner, S.; Ruckenstuhl, C.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Ring, J.; Schroeder, S.; Magnes, C.; Antonacci, L.; et al. Induction of autophagy by spermidine promotes longevity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibori, N.; Fujihara, S.; Akatuki, T. Amounts of polyamines in foods in Japan and intake by Japanese. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A.; Sugi, E.; Koizumi, Y.; Yanagida, F.; Udaka, S. Polyamine content of ordinary foodstuffs and various fermented foods. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 1582–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiya Ali, M.; Poortvliet, E.; Strömberg, R.; Yngve, A. Polyamines in foods: Development of a food database. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 55, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Esparza, N.C.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.L.; Comas-Basté, O.; Toro-Funes, N.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Polyamines in food. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Fleming, L.; Olin-Sandoval, V.; Campbell, K.; Ralser, M. Remaining mysteries of molecular biology: The role of polyamines in the cell. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 3389–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, A.E. Functions of polyamines in mammals. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 14904–14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frewer, L.J.; van der Lans, I.A.; Fischer, A.R.H.; Reinders, M.J.; Menozzi, D.; Zhang, X.; van den Berg, I.; Zimmermann, K.L. Public perceptions of Agri-food applications of genetic modification—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akao, T.; Yashiro, I.; Hosoyama, A.; Kitagaki, H.; Horikawa, H.; Watanabe, D.; Akada, R.; Ando, Y.; Harashima, S.; Inoue, T.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of sake yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Kyokai No. 7. DNA Res. 2011, 18, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherniya, M.; Butler, A.E.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. The effect of fasting or calorie restriction on autophagy induction: A review of the literature. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 47, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.W.; Chung, H.Y. The effects of calorie restriction on autophagy: Role on aging intervention. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Zimmermann, A.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, G. Essential role for autophagy in life span extension. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhart, L.; Tschachler, E.; Gruber, F. Autophagic control of skin aging. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapan, K.; Simon, D.; Karaulov, A.; Gomzikova, M.; Rizvanov, A.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.U. Autophagy and skin diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 844756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Eisenberg, T.; Pietrocola, F.; Kroemer, G. Spermidine in health and disease. Science 2018, 359, eaan2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schibalski, R.S.; Shulha, A.S.; Tsao, B.P.; Palygin, O.; Ilatovskaya, D.V. The role of polyamine metabolism in cellular function and physiology. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2024, 327, C341–C356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, J.; Fukuda, A.; Mutaguchi, K.; Uemura, T. Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae using endogenous xylose-assimilating genes. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Adler, P.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. g:Profiler—Interoperable web service for functional enrichment analysis and gene identifier mapping (2023 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W207–W212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M. KEGG mapping tools for uncovering hidden features in biological data. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Rueden, C.T.; Hiner, M.C.; Eliceiri, K.W. The ImageJ ecosystem: An open platform for biomedical image analysis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Noda, T.; Yoshimori, T. Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy 2007, 3, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.-X.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: Improved protein–ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W159–W164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, §184.1983—Baker’s Yeast; US Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Akao, T. The genome analysis of sake Yeast Kyokai No. 7 and foresights of sake yeast genomics. J. Brew. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 107, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akao, T. Progress in the genomics and genome-wide study of sake yeast. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasawa, T.; Yamada, K.; Nagahisa, K.; Dinh, T.N.; Furusawa, C.; Katakura, Y.; Shioya, S.; Shimizu, H. Proteomic analysis of responses to osmotic stress in laboratory and sake-brewing strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, D.; Kajihara, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; Takagi, K.; Mizuno, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Takeda, K.; Tatebe, H.; Shiozaki, K.; et al. Nutrient signaling via the TORC1-Greatwall-PP2AB55δ pathway is responsible for the high initial rates of alcoholic fermentation in sake yeast strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02083-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Jo, J.H.; Park, Y.C.; Jin, Y.S.; Seo, J.H. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of spermidine under optimal culture conditions. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 101, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Krivoruchko, A.; Ji, B.; Chen, Y.; Kristensen, M.; Özdemir, E.; Keasling, J.D.; Jensen, M.K.; Nielsen, J. Engineering yeast metabolism for the discovery and production of polyamines and polyamine Analogues. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matencio, A.; Navarro-Orcajada, S.; García-Carmona, F.; López-Nicolás, J.M. Applications of cyclodextrins in food science. A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astray, G.; Gonzalez-Barreiro, C.; Mejuto, J.C.; Rial-Otero, R.; Simal-Gándara, J. A review on the use of cyclodextrins in foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabeel, M.; Messenguy, F.; Lacroute, F.; Glansdorff, N. Cloning arg3, the gene for ornithine carbamoyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Expression in Escherichia coli requires secondary mutations; production of plasmid beta-lactamase in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 5026–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messenguy, F. Regulation of arginine biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Isolation of a cis-dominant, constitutive mutant for ornithine carbamoyltransferase synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 1976, 128, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Eisenberg, T.; Büttner, S.; Ruckenstuhl, C.; Kroemer, G. Spermidine: A novel autophagy inducer and longevity elixir. Autophagy 2010, 6, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, S.; Hofer, S.J.; Zimmermann, A.; Pechlaner, R.; Dammbrueck, C.; Pendl, T.; Marcello, G.M.; Pogatschnigg, V.; Bergmann, M.; Müller, M.; et al. Dietary spermidine improves cognitive function. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiechl, S.; Pechlaner, R.; Willeit, P.; Notdurfter, M.; Paulweber, B.; Willeit, K.; Werner, P.; Ruckenstuhl, C.; Iglseder, B.; Weger, S.; et al. Higher spermidine intake is linked to lower mortality: A prospective population-based study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudman, D.; Kutner, M.H.; Chawla, R.K.; Goldsmith, M.A.; Blackston, R.D.; Bain, R. Serum and urine polyamines in normal and in short children. J. Clin. Investig. 1979, 64, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoe, N.; Yuuto, T.; Yuuki, S. Health Benefits of Spermidine-Enriched Yeast ‘Fermeast® SP’. Food Style 2023, 10, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
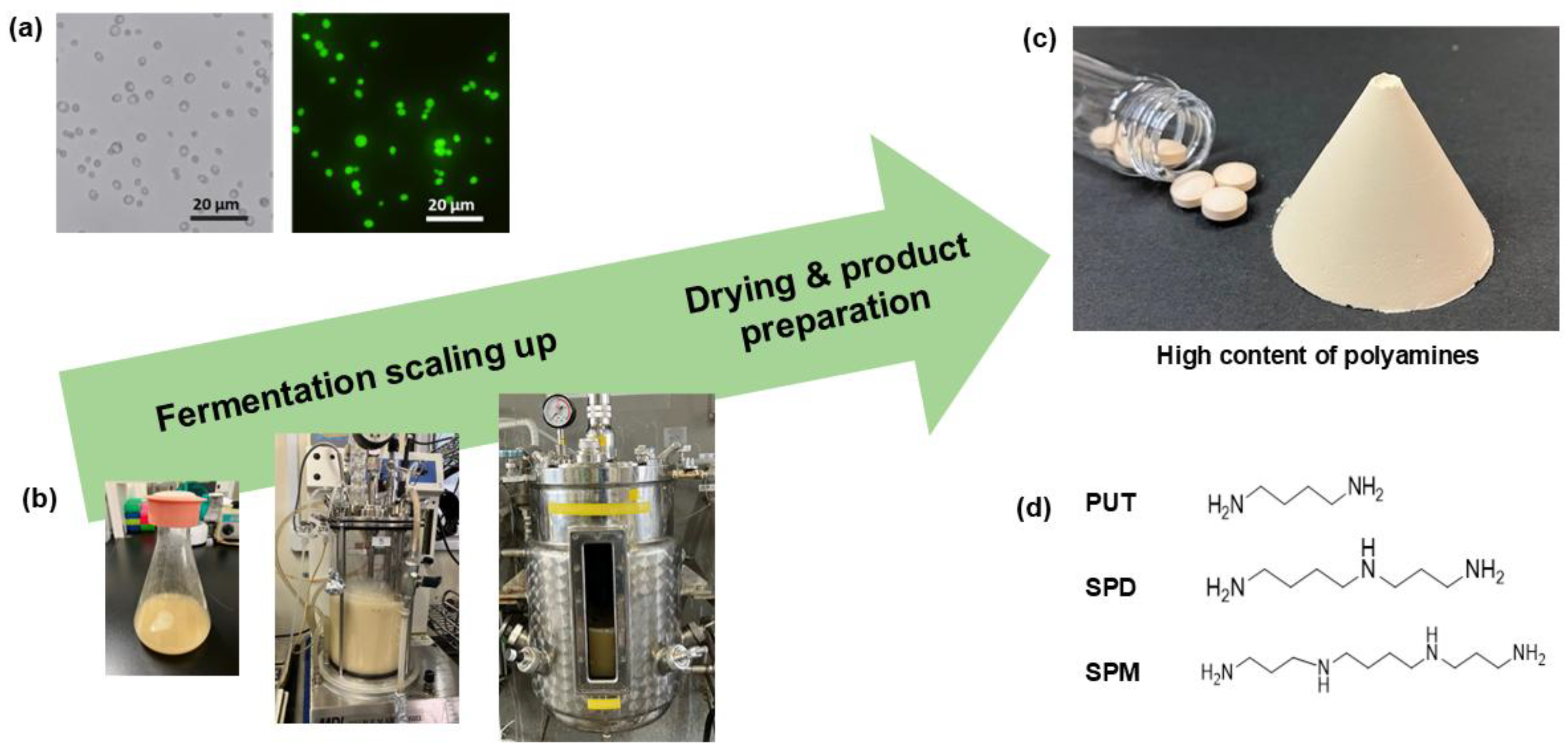

| Item | Measured Value |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 4.5 g |
| Protein * (excluding Polyamines) | 45.7 g (45.1 g) |
| Fat | 10.0 g |
| Carbohydrate | 29.9 g |
| Ash | 9.9 g |
| Energy | 392 kcal |
| Sodium | 25 mg |
| Salt Equivalent | 0.064 g |
| Strain | Putrescine (mg/g) | Spermidine (mg/g) | Spermine (mg/g) | Total (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K7 | 0.05 (±0.06) | 0.50 (±0.02) | 0.29 (±0.22) | 0.84 (±0.18) |
| 3L63 | 0.75 (±0.31) | 3.80 (±0.38) | 0.38 (±0.02) | 4.93 (±0.66) |
| Commercial product * | 0.39 (±0.05) | 2.55 (±0.05) | 0.28 (±0.06) | 3.21 (±0.15) |
| Amino Acid | K7 Strain (μmol/g) | 3L63 Strain (μmol/g) | 3L63 Product (μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid (Asp) | 4.96 (1.6%) | 5.59 (2.0%) | 4.73 (1.3%) |
| Glutamic acid (Glu) | 134 (43.8%) | 104 (36.7%) | 43.9 (12.4%) |
| Glycine (Gly) | 10.4 (3.4%) | 13.8 (4.9%) | 18.1 (2.6%) |
| Threonine (Thr) | 9.39 (3.1%) | 7.57 (2.7%) | 10.5 (3.0%) |
| Arginine (Arg) | 17.4 (5.7%) | 28.3 (10.0%) | 65.1 (18.4%) |
| Serine (Ser) | 43.8 (14.3%) | 43.5 (15.4%) | 12.7 (3.6%) |
| Alanine (Ala) | 14.9 (4.9%) | 10.5 (3.7%) | 38.9 (11.0%) |
| Valine (Val) | 2.18 (0.7%) | 1.83 (1.83%) | 15.2 (4.3%) |
| Leucine (Leu) | 2.21 (0.7%) | 1.90 (0.7%) | 19.4 (5.5%) |
| Lysine (Lys) | 6.10 (2.0%) | 12.9 (4.6%) | 14.1 (4.0%) |
| Proline (Pro) | 4.91 (1.6%) | 2.21 (0.8%) | 6.57 (1.9%) |
| Total amino acids | 306 (100%) | 283 (100%) | 354 (100%) |
| Polyamine | K7 Strain (mg/g) | 3L63 Strain (mg/g) | 3L63 Product (mg/g) |
| Putrescine (Put) | 0.04 (1.9%) | 0.39 (9.4%) | 0.45 (13.3%) |
| Spermidine (Spd) | 1.62 (78.3%) | 3.41 (81.8%) | 2.60 (76.7%) |
| Spermine (Spm) | 0.41 (19.8%) | 0.37 (8.9%) | 0.34 (10.0%) |
| Total polyamines | 2.07 (100%) | 4.17 (100%) | 3.39 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koshizawa, T.; Numaguchi, T.; Tamakoshi, M.; Sato, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Mohamad Ishak, N.S.; Ikemoto, K. High-Spermidine-Producing Yeast Strain for Autophagy-Promoting Applications. Processes 2025, 13, 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103141
Koshizawa T, Numaguchi T, Tamakoshi M, Sato Y, Hashimoto K, Mohamad Ishak NS, Ikemoto K. High-Spermidine-Producing Yeast Strain for Autophagy-Promoting Applications. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103141
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoshizawa, Tomoyo, Tomoe Numaguchi, Masanori Tamakoshi, Yuuki Sato, Katsuyuki Hashimoto, Nur Syafiqah Mohamad Ishak, and Kazuto Ikemoto. 2025. "High-Spermidine-Producing Yeast Strain for Autophagy-Promoting Applications" Processes 13, no. 10: 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103141
APA StyleKoshizawa, T., Numaguchi, T., Tamakoshi, M., Sato, Y., Hashimoto, K., Mohamad Ishak, N. S., & Ikemoto, K. (2025). High-Spermidine-Producing Yeast Strain for Autophagy-Promoting Applications. Processes, 13(10), 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103141







