Abstract
Herein, nanoscale MgAl2O4 (MOA), 10%CuO@MgAl2O4 (10Cu@MOA), 10%NiO@MgAl2O4 (10Ni@MOA), and 10%CoO@MgAl2O4 (10Co@MOA) were synthesized employing butylated hydroxytoluene (the food additive BHT) as a capping agent. The SEM images illustrated average sizes of 38.8, 30.0, 40.8, and 32.7 nm for MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, respectively, and their BET surface area were 84.4, 141.8, 126.7, and 105.3, respectively. Doxycycline DXC removal was studied employing the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, which resulted in qt values of 57.3, 106.1, 97.7, and 73.9 mg g−1, respectively. The pseudo-second order model best described the DXC sorption onto MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, and both film diffusion models influenced the DXC sorptions onto the sorbents. The DXC sorption onto the 10Cu@MOA fitted the Freundlich model. The thermodynamics implied endothermic-spontaneous DXC sorption onto the10Cu@MOA. The pH study exposed that the DXC removal by 10Cu@MOA was more effective in a mildly acidic medium (pH = 6.0). Furthermore, the 10Cu@MOA effectiveness in treating surface water contaminated by 5.0 and 10.0 mg L−1 DXC was 99.9% and 98.1%, respectively, while it was 94.7% and 92.5% in treating the concentrations above in seawater, respectively. The reusability study showed a 10% reduction in the 10Cu@MOA’s removal efficiency at the fourth cycle, which is encouraging for real-life applications.
1. Introduction
Sufficient and high-quality water supplies are required for the health and development of human civilizations and ecosystems [1]. Although there is approximately 4.2 km3 of water on Earth in all three of its physical states (solid, liquid, and gas), water is increasingly vulnerable to contamination from diverse human activities and specific natural causes [2]. Pollutants may reach aquatic environments from: (i) industrial waste discharge (pollute water with organic dyes, heavy metals, and pharmaceutical products), (ii) agricultural runoff (mainly insecticides and pesticides), (iii) domestic waste (uric acid, carbon, petroleum products, pharmaceutical and body care products), (iv) natural phenomena hurricanes and volcanoes, and hospitals and laboratories (microbiology contaminants, and drugs) resulting in extensive contamination of freshwater and marine ecosystems. These contaminants can be classified as chemical, including organic and inorganic pollutants, as well as microbial and biological contaminants, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals (PHS) [3,4,5,6]. PHS are ingredients utilized to treat, prevent, or ease symptoms of various diseases in both animals and humans [7]. PHS constitutes a fundamental component of global health systems. Nowadays, the population is increasing (to over 8.0 billion), necessitating an increased production of pharmaceuticals to ensure effective disease management, thereby driving the current expansion of the pharmaceutical market. Nonetheless, their extensive production and global utilization result in their release into the environment [8,9,10]. The PHS could be categorized as anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, β-blockers, antiretroviral agents, hormones, and lipid-modulating agents [11,12]. The elevated consumption, inadequate waste management, and expulsion of partially metabolized doses result in their accumulation in aquatic ecosystems, endangering all life forms [10]. PHS contaminants identified in water and animal bodies include ampicillin, penicillin, amoxicillin, diclofenac, paracetamol, vancomycin, sulphathiazole, carbamazepine, efavirenz, aspirin, ibuprofen, and doxycycline (DXC) [13,14,15]. Doxycycline (DXC) is an antibiotic that belongs to the tetracycline tribe (TCC). It is effective against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. DXC was developed in the early 1960s as an inaugural broad-spectrum antibiotic. Compared to other frequently used antibiotics, TCC consumption increased by approximately 5866 tons, according to reports from the US Food and Drug Administration [16,17,18]. DXC residues were identified in pig manure and biogas plant digestates, at concentrations of 381 and 10.5 mg/kg, respectively, on a dry weight basis. Similarly, 22.76 mg/kg of DXC was identified in the swine manure collected from farms and manure pits in West Flanders, Belgium [15,19]. The release of DXC into aquatic environments poses risks to ecosystems, including adverse effects, drug interactions, and bacterial resistance, necessitating the implementation of suitable controls and regulations. However, removing contaminants with such self-degradation-resistant compounds or by conventional water and treatment methods is a dilemma [20,21,22]. Various techniques have been employed to eliminate PHS from aquatic systems, including biofiltration, photocatalytic degradation, ozone biodegradation, nanomembranes, and phytoremediation [23,24,25]. Adsorption has demonstrated greater efficacy as a PHS eliminator due to its simplicity and ease of application in both batch and continuous processes. Furthermore, sorption is a relatively eco-friendly, rapid, and economical process, and the sorbents can be reused after simple regeneration [26,27,28]. Sorption can efficiently eliminate PHS at low concentrations and significantly reduce their concentration in cases of high contamination levels [29]. Adsorbents utilized include clay, carbon, industrial byproducts, zeolite, polymer materials, and agricultural waste, which exhibit varying adsorption capacities (qt) based on the targeted pollutants [30,31]. Currently, adsorbents are synthesized by combining more than one material to enlarge surface area, porosity, and consequently their qt values [32,33]. Metal oxides, as pure and/or composites, are among the most effective substrates employed for removing PHS from water bodies [34]. The characteristics of oxide-sorbents are extensively utilized in water remediation owing to their distinctive physicochemical properties, which can be further enhanced through doping to fulfill particular requirements and applications [35]. Recently, studies have investigated the use of MgAl2O4 (MOA) absorbents to eliminate dyes, pharmaceuticals, and persistent organic pollutants [36,37]. Enhancing the properties and qt values of meta-oxid-sorbents could be achieved via doping with a suitable substrate [38,39]. Divalent metal ions have ionic radii that allow for substitutional doping into the spinel lattice; they possess thermal stability, chemical resistance, mechanical resistance, high surface area, and low acidic surface [40].
This study aimed to synthesize nanoscale MOA and 10%CuO@MgAl2O4 (10Cu@MOA), 10%NiO@MgAl2O4 (10Ni@MOA), and 10%CoO@MgAl2O4 (10Co@MOA) through a rapid and straightforward protocol using the food additive butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) as a capping agent. The 10% ratio was selected to provide an easily observable modification in the base material’s characteristics, offering a fair comparison between doping substrates. The synthesis conditions, doping quantity, and calcination temperature were standardized to exclude any influences aside from the ion type on the properties of the product. The characteristics of the synthesized nanomaterials will be examined via physical methodologies. Employing DXC as an exemplary contaminant, the removal efficacies of MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA will be studied. The solution parameters, DXC kinetics, pH impact, and equilibrium will be investigated.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Magnesium nitrate hexahydrate (Mg(NO3)2·6H2O) was obtained from Merck, Germany. Aluminum nitrate (Al(NO3)3) was obtained from Redil De-Hean, Hannover, Germany. The food additive BHT was obtained from WinLab, UK. Doxycycline (DXC) was obtained from Fluka, Switzerland. Acetate salts of copper, nickel, and cobalt were obtained from BDH (London, UK), LobaChem (Mumbai, India), and Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland), respectively. Distilled water (DSW) was utilized in preparing the nanocomposites and solutions.
2.2. Preparation of MOA and Its Nanocomposites
In total, 0.025 moles of (Al(NO3)3) and 0.05 moles of Mg(NO3)2·6H2O, 0.01 BHT, and 100 mL DSW were combined in a 400 mL beaker. The beaker content was stirred and heated till the BHT started to carbonize. The solid was placed into a 120 mL porcelain dish and calcined at 600 °C for 3.0 h. The 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA were prepared by adding the corresponding metal salt in sufficient amounts to obtain 10% CuO, 10% NiO, and 10% CoO, respectively, to the preidentified Al (Al(NO3)3), Mg(NO3)2·6H2O, and BHT amounts. Subsequently, the beakers were treated as previously described.
2.3. Equipment and Characterization
The as-fabricated MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA were analyzed using a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM-EDX, JOEL-7800F, Tokyo, Japan). The surface properties were examined utilizing the Micro-meristic Tristar (II)-3020, Miami, FL, USA. The structural phase of the nanocomposites was analyzed via X-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker AXS, Karlsruhe, Germany). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Tracer-100, Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan) was employed to survey for functional groups on MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA. A UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan) was used to measure the DXC absorbance.
2.4. Adsorption of DXC
The DXC sorption by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA was handled utilizing the batch protocol. A 50 mg/L DXC was prepared in DSW, and then a 100 mL portion was placed in a 120 mL beaker, where it was stirred at 500 RPM with 50 mg sorbent at 25 °C. The impact of contact duration was assessed by filtering aliquots of the sorbent-sorbate heterogeneous mixture at successive time intervals, and determining the DXC absorbance utilized to compute the sorption capacity (qt, mg/g, Equation (1)) of MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA.
The contact time results fueled the kinetic investigations of DXC sorption by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA. The rate order investigation of DXC elimination by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA was conducted using the pseudo-first-order (PSFO) and pseudo-second-order (PSSO) models (Equations (2) and (3)). The step controlling DXC sorption was examined utilizing diffusion models, the liquid-film (LFDM, Equation (4)) and the intraparticle (IPDM, Equation (5)) [41].
The k1 (min−1), k2 (g mg−1 min), KLF (min−1), and KIP (mg g−1 min1/2) denote the factors of PSFO, PSSO, LFDM, and IPDM, respectively. Ci is a boundary layer-related factor. The DXC concentrations of 50 to 200 mg/L were employed to investigate the impact of DXC concentration on its removal by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA. Moreover, considering the effect of temperature, DXC sorption by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA from the preidentified concentrations was conducted at 293, 303, 313, and 323 K. The results obtained fueled further study of the DXC sorption equilibria, encompassing the DXC sorption isotherms and thermodynamics. The sorption characteristics of DXC were examined through monolayer/multilayer analyses using the Langmuir and Freundlich representations (LAIM and FRIM), as expressed in Equations (6) and (7).
KL (L/mg) represents the LAIM constant, Ce (mg/L) is the solution DXC concentration at equilibrium, qm signifies the maximal qt, while KF (L/g) and n refer to the FRIM constant and favorability factor, respectively [42].
The thermodynamic study involved computing the sorption equilibrium constant (Kc, Equation (8)), then plotting ln(Kc) versus the reciprocals of the temperature (Equation (9)), and the plots were employed to determine the enthalpy (ΔH°) and entropy (ΔS°) values. Then, the free energy (ΔG°) values were computed by feeding the ΔH° and ΔS° values into Equation (10).
The pH effect on DXC sorption by 10Cu@MOA was investigated by adjusting 110 mL of a 50 mg/L DXC solution at pH levels ranging from 3.0 to 10.0. 100 mL of the DXC solution was stirred with 50 mg of 10Cu@MOA for the predetermined equilibrium time, and the remaining 10.0 mL was used as self-standards for their pH samples to mitigate absorbance variations resulting from pH changes. Additionally, the efficacy of 10Cu@MOA in eliminating DXC from environmental samples was assessed. A 5.0 and 10 mg L−1 DXC concentration in natural water matrices, including surface water (SRW) and seawater (SWS). The adsorption was then performed by stirring 100 mL with 50 mg of 10Cu@MOA for 2.0 h. Furthermore, the regeneration-reusability of 10Cu@MOA was evaluated by using a regenerated 10Cu@MOA for treating successive DXC batches. The utilized 10Cu@MOA was regenerated via washing with two batches of 10 mL ethanol, followed by drying at 110 °C for 1.0 h.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
The surface morphology of MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA was investigated through SEM analysis. Figure 1a–d illustrates that the surface appearances of the sorbents, the MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, possessed semispherical particles. At the same time, the 10Cu@MOA exhibited a fluffy, cloudy structure with particles that appeared significantly smaller than the preidentified three nanomaterials. The MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA showed size ranges of (29.8–50.4), (22.9–34.6), (36.7–47.8), and (28.5–41.7) nm, respectively, with mean values of 38.8, 30.0, 40.8, and 32.7 nm, accompanied by standard deviations of 6.3, 4.2, 3.9, and 5.0, respectively.

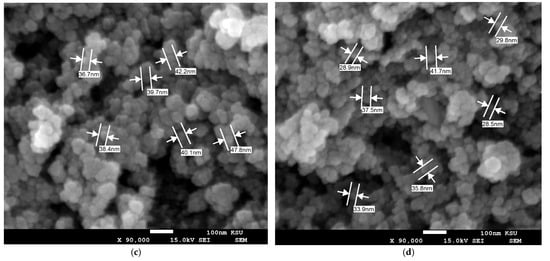
Figure 1.
SEM images of (a) MOA, (b) 10Cu@MOA, (c) 10Ni@MOA, and (d) 10Co@MOA nanocomposites.
The EDX spectrum of MOA, illustrated in Figure 2a, confirmed the MOA purity, with Mg, Al, and O being the only elements in the resulting spectrum. Figure 2b–d show the incorporation of Cu, Ni, and Co in the spectra of the 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, respectively. The presence of Cu, Ni, and Co at relatively high abundance (for dopants) can be attributed to the relatively high (10%) doping dose. Furthermore, the EDX elemental mapping presented in Figure 3a–d verifies that Cu, Ni, and Co are uniformly distributed across the surfaces of 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, respectively, demonstrating effective incorporation of elements into the MOA matrix.

Figure 2.
EDX spectra of (a) MOA, (b) 10Cu@MOA, (c) 10Ni@MOA, and (d) 10Co@MOA nanocomposites.
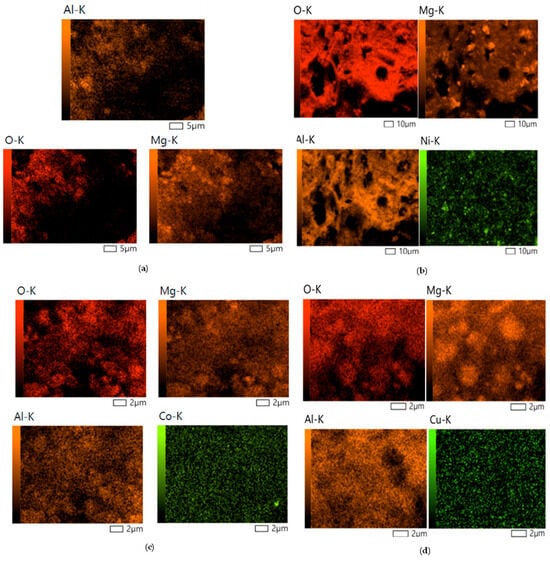
Figure 3.
The EDX elemental mapping of (a) MOA, (b) 10Cu@MOA, (c) 10Ni@MOA, and (d) 10Co@MOA nanocomposites.
The crystal structure and phase evolution of MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA were examined via X-ray diffraction (Figure 4a). The diffractograms presented distinct diffraction peaks at 2θ° of 19.0, 31.5, 36.9, 44.8, 59.4, 65.2, 74.7, and 78.6 corresponding to cubic MgAl2O4 crystal phases (111), (220), (222), (400), (511), (440), (620), and (533), respectively (JCPDS: 01-086-0083). The most abundant peak (2θ° = 42.9) belongs to MgO (JCPDS: 00-004-0829). The diffraction peaks of CuO, NiO, and CoO may not be discernible due to their proximity to the MgO/MgAl2O4 peaks, which may overlap with the diffractions of such relatively low phases compared to the base nanomaterial [43,44]. Furthermore, the obtained peaks were used to calculate the average crystal size (D, Equation (10)), the lattice parameters (a, c; Equations (11) and (12)), and lattice imperfection (ε, Equation (13)) [45,46].
where θ is Bragg’s angle, β is the half-maximum peak-width, λ is the wavelength (Cu-Kα = 1.5406) [47], and the outcomes are presented in Table 1. The smallest D value obtained with the 10Cu@MOA indicates the ability of the CuO at the tested amount to interrupt the continuation of crystal growth of the MOA, thereby producing smaller particles, which aligns with the SEM findings.

Figure 4.
(a,b) The XRD and the FTIR spectra of the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA; (c–f) the tubular isotherms with the pore size distribution as an insert for the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA nanocomposites, respectively.

Table 1.
The lattice parameters and surface characteristics of the fabricated MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA nanocomposites.
Figure 4b depicts the FTIR spectra of MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA. The band at approximately 510 cm−1 is allocatable to Mg-O of a nanoscale MgO [48]. The bands around 707 and 843 cm−1 correspond to symmetric and asymmetric stretching vibrations of Al-O-Al and/or Al-O-Mg [49]. The bands at 1650 cm−1 are linked to H–O–H bending vibrations. Moreover, the bands centered about 3500 cm−1 are indicative of the stretching vibration of OH groups [50,51,52]. The disappearance of the valley about 605 cm−1 in the MOA spectrum and the intense band at 513, 474, and 489 cm−1 in the 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA spectra can be attributed to Metal-Oxygen bonding [53].
Figure 4c–f displays the N2-adsorption–desorption tubular isotherms of the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA. The hysteresis curves were classified as H3 loops, signifying aggregates with mesoporous structures, characterized predominantly by parallel plate-shaped pores created between the double-layered oxides of MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, and wedge-shaped pores formed within the particles and/or their clusters [54]. The BET surface area (SA), average pore diameter (PD), and pore volume (PV) data are presented in Table 1 [55,56]. The obtained SA of the 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA showed significant improvement over the MOA-base material, indicating the suitability of the selected metal oxides (CuO, CoO, and NiO) at the chosen doping amount to improve MOA surface properties significantly.
3.2. Contact Time and Kinetics
The contact time influence on the DXC sorption by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA nanosorbents was studied. Figure 5a illustrates that 60 min sufficed to reach equilibrium for MOA and its based sorbents, which could be considered a relatively short water treatment duration. The MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA possessed qt values of 57.3, 106.1, 97.7, and 73.9 mg g−1, respectively. In cases where faster treatment is targeted, the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA achieved 86.1%, 83.3%, 82.6%, and 90.2% of their full capacities within half the equilibrium time, respectively. The increased adsorbed DXC amount suggested that the doping metal/amount played a crucial role in improving the effectiveness of the DXC sorption via altering the MOA construction and characteristics. Initial rapid DXC sorption could be attributed to the availability of binding sites; subsequently, the process decelerated until equilibrium was reached, which could be explained as a consequence of the weakening of the DXC diffusion force as its concentration decreased and/or occupied adsorbent sites.
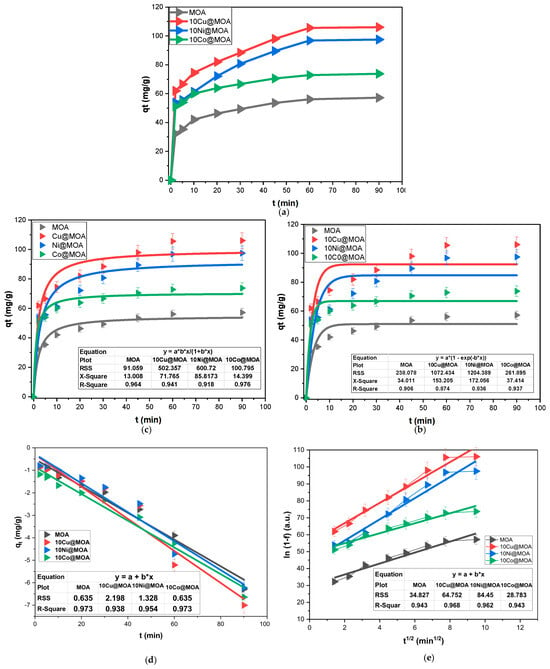
Figure 5.
(a) contact time results, (b) PSFO, (c) PSSO, (d) IPDM, (e) LFDM plots of DXC removal by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA from a 100 mg/L solution.
The examination of adsorption kinetics holds considerable importance in understanding kinetic parameters, as they yield crucial insights into the rate order and mechanism of the adsorption process [57]. The contact time results fueled kinetic investigations, and the obtained plots were illustrated in Figure 5b,c, while Table 2 gathered the computed parameters. The DXC sorption onto MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA fitted the PSSO, exhibiting R2 values of 0.964, 0.941, 0.918, and 0.976, respectively. Also, the experimental qe values were more aligned with those derived via the PSSO. Furthermore, the RSS and X2 values of PSSO plots were lower than those of the PSFO fittings.

Table 2.
Kinetic results of DXC sorption by MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA nanocomposites.
Figure 5d,e depicted the rate-control study of DXC sorption onto the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, and the associated results were presented in Table 2. Almost all R2 values of LFDM and IPDM were approximately 0.95, indicating a co-participation in controlling DXC sorptions onto the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA. The DXC sorption control analysis demonstrated a significant influence of IPDM, with the DXC sorption being categorized into two distinct stages. The IPDM controls the initial phase (at the initial contact points), as the DXC migrates swiftly to the adsorbent surface, making the LFDM the fastest step. This can be attributed to the DXC’s high concentration and the abundance of free sorption sites. In the second stage, IPDM dominates the sorption process since the DXC concentration in the solution decreases and accumulates on the solid surfaces, thereby decreasing the DXC liquid diffusion rate as its molecules move into the inner pores. The plots illustrate a linear relationship; however, they do not intersect at the origin, suggesting neither IPDM nor LFDM is the sole rate-controlling step [58,59].
3.3. Sorption Equilibria
The impact of DXC concentration and temperature on DXC sorption by 10Cu@MOA (the best adsorbent) was studied. Figure 6a illustrates that rising DXC concentration up to 200 mgL−1 increased the qt value dramatically. The rationale behind this is that raising the DXC concentration in the solution accelerates the diffusion of DXC toward the sorbent, causing it to attach to 10Cu@MOA and thereby increasing the qt value [60]. Furthermore, the temperature influence on DXC sorption by 10Cu@MOA is illustrated in Figure 6a. The DXC adsorption increased proportionally as the temperature rose from 20 to 50 °C, indicating endothermic sorption, which may be a consequence of an increase in the diffusion rate, allowing DXC molecules to pass more quickly towards the 10Cu@MOA surface and through its pores.

Figure 6.
(a) the effect of concentration and temperature on the DXC removal by the 10Cu@MOA; (b,c) LGIM fittings at 20 and 50 °C, respectively; (d,e) FRIM fittings at 20 and 50 °C, respectively; (f) the thermodynamic plots for DXC removal by 10Cu@MOA from 50 to 200 mg L−1 concentrations across a temperature range of 293 to 323 K.
The sorption isotherms could be categorized as an empirical relationship that characterizes the extent and mechanism of adsorption. The outcomes of the DXC concentration study were utilized in implementing the LAIM and FRIM investigations at 20 °C and 50 °C (Figure 6b–e). The DXC sorption onto 10Cu@MOA showed better alignment with FRIM at both tested temperatures, and the related parameters are presented in Table 3. In addition to the highest R2 values, the FRIM model yielded the lowest RSS values, indicating a multilayer DXC sorption on the heterogeneous 10Cu@MOA active sites. The 1/n values (1/n < 1.0) suggested that the multilayered DXC sorption has been favorable in all tested cases. Notably, the 10Cu@MOA performed exceptionally well in removing DXC, with a qm of 392.7 at 50 °C, making it quite competitive compared to adsorbents in the literature [61,62].

Table 3.
Isotherms and thermodynamics outputs of DXC sorption by 10Cu@MOA.
A better comprehension of the DXC removal by 10Cu@MOA could be expanded by investigating the sorption thermodynamics (Figure 6f). The DXC adsorption thermodynamics was studied at temperatures of 293, 303, 313, and 323 K, and the investigation plots are shown in Figure 6f and Table 3. The positive ΔH° and negative ΔG° implied endothermic and spontaneous DXC sorption by the 10Cu@MOA. The investigation results revealed negative ΔG° values that decreased with increasing temperature. This outcome lends credence to the equilibrium study analysis, indicating that the adsorption capacity is boosted at higher temperatures. Moreover, it is worth noting that a noteworthy ΔG° value below 40 kJ mol−1 indicates that DXC was removed by 10Cu@MOA via physisorption. The positive ΔS° signifies an increase in the entropy, which encompasses the number of species present at the interface between the solid and liquid during the sorption process. [63,64,65]. The reduced R2 values noted at the lowest concentrations are likely attributable to the system’s failure to reach stabilization; in contrast, at higher concentrations, the system may attain stabilization, resulting in a better fit.
3.4. The pH and Mechanistic DXC-10Cu@MOA Interaction
Many studies prove the pH’s essential role in the sorption process via modifying the sorbent’s surface charge and/or altering the sorbate functional groups. Therefore, the pHZPC of the 10Cu@MOA was examined via the solid addition protocol [66]. The 10Cu@MOA is considered a positive surface below the pHZPC and a negative surface above the pHZPC. The ΔpH (pHf-pHi) was plotted against the initial pH (pHi), and the point where ΔpH = 0 was designated the pHpzc; and for 10Cu@MOA, the pHpzc = 9.0, as illustrated in Figure 7a.

Figure 7.
(a) The pHZPC plot of the 10Cu@MOA, (b) The influence of pH on DXC sorption by the 10Cu@MOA, and (c) the chemical structure of DXC with the electronegative atoms being numbered.
The pH impact on the DXC sorption by 10Cu@MOA was examined in the range of 2.0–10.0 at 20 °C, and the study findings are presented in Figure 7b. The DXC removal onto 10Cu@MOA decreased proportionally as the pH increased from 3.0 to 6.0, where the qt reached its maximum value, and then decreased until it reached a minimum at pH = 10. Noteworthy is that high acidity and alkalinity negatively impacted DXC sorption onto the 10Cu@MOA; however, the alkaline solutions caused a more severe impact on the DXC removal. The DXC featured several π-electron-rich atoms forming ten partially negative sites, including amine, amide, three carbonyl, and five hydroxyl groups (Figure 7c). At lower pH levels of 3.0–4.0, DXC may exist in a cationic form, which converts into a zwitterionic ion between pH 4.0 and 7.0, and then turns into a negatively charged molecule above pH 7.0. Between pH 4.0 and 6.0, the H+ ions surround the 10Cu@MOA, making its oxygen occupied, which lowers the DXC-10Cu@MOA repulsion and opens the opportunity for the π-electron-rich groups on DXC to be attracted by the partially positive cationic sites on 10Cu@MOA. This might explain why higher qt values are obtained in acidic compared to basic medium. The favorability of mild acidic conditions (low H+ availability) over high acidity (high H+ availability) is such that, at the latest, the free H+ may suffice to attack both electron-rich sites of DXC and 10Cu@MOA, thereby slowing the sorption. Alternatively, in an alkaline medium (pH 8.0 and above), the reduced qt values might be attributed to the -OH/DXC competition over the 10Cu@MOA sites, in addition to the electrostatic repulsion between the negatively charged DXC molecules and the 10Cu@MOA surface spiked with -OH groups [67]. Furthermore, considering the ten π-electron-rich atoms of DXC molecules, the adsorbed molecules might cause a significant repulsion force in addition to that driven by the OH anions, and together they may hinder DXC diffusion through the solution to the 10Cu@MOA surface.
The DXC-10CuO@MOA interaction may encompass different binding possibilities such as electrostatic attraction, complexation/chelation, hydrogen bonding, and π–π binding. When DXC exists in zwitterionic/deprotonated forms, the e-rich groups of DXC (Lewis bases) and the Lewis acids (Cu2+, Mg2+, Al3+) possibly bind via chelation, leading to Cu–DXC surface chelates synergistic with the hydrogen bonding, aiding the orientation of DXC on the10CuO@MOA surface. The Lewis bases numbered in Figure 7c may result in DXC-Cu-complexation, probably through the positions (1,2), (2,3), (3,5), (5,6), and/or (7,8). The DXC aromatic rings serve as effective π–π binding sites; however, their efficiency may be constrained by the presence of defect-induced electron-rich regions, yet they may act as supplementary sorption stabilization forces that enhance the qt value.
3.5. Application on Real Samples
To test the effectiveness of 10Cu@MOA, aqueous medium models containing DXC are used, including surface water (SRW) and seawater (SWS). A pH of 6.0, a contact duration of 60 min, 50 mg of adsorbent, and concentrations of 5 and 10 ppm of DXC solution were the actual parameters applied for remediating the artificially contaminated natural water matrices. Figure 8a illustrates the success of 10Cu@MOA in removing 99.9% and 98.1% of DXC from the 5.0 and 10.0 mg L−1 DXC in SRW, while treating the concentrations above in SWS resulted in 94.7% and 92.5%, respectively. The effectiveness of 10Cu@MOA is noteworthy, as it has been applied to both SRW and SWS, thereby demonstrating its applicability in removing DXC from wastewater.

Figure 8.
(a) Treating real samples contaminated with DXC concentrations of 5 and 10 mg/L by the 10Cu@MOA; (b) The reuse study of the 10Cu@MOA.
3.6. Regeneration and Reusability
One of the most important criteria for determining an adsorbent’s possible use is its recycling ability and performance. The after-use 10Cu@MOA was evaluated for treating DXC-contaminated water, and the outcomes were presented in Figure 8b. The 10Cu@MOA exhibited removal ratios of 99.1%, 98.1%, 96.1%, and 89.9% across four cycles, respectively. The average efficiency of 95.8% demonstrates the notable stability and reuse capability of the 10Cu@MOA, which is comparable to similar MOA adsorbents [68,69]. The decreased efficiency of 10Cu@MOA by 10% in the fourth cycle can be attributed to the DXC’s infiltration into the internal pores of the adsorbent and/or loss of some of the 10Cu@MOA during the filtration of the regeneration process.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated fabricating nanohybrids via a simple method; namely, MgOAl2O3 (MOA), CuO@MgAl2O4 (10Cu@MOA), NiO@MgAl2O4 (10Ni@MOA), and CoO@MgAl2O4 (10Co@MOA). The characteristics of the as-prepared MOA and its nanohybrids were studied utilizing SEM, XRD, FTIR, BET, and EDX. EDX analysis indicated that Mg, Al, and O predominate in all sorbents, consistent with the MOA framework’s structure. SEM images illustrated average sizes of 38.8, 30.0, 40.8, and 32.7 nm for MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, respectively. The N2-tubular isotherm curves identified H3 hysteresis loops, indicating mesoporous aggregates. As a common antibiotic water contaminant, DXC removal was studied via batch methodology utilizing the MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA. Sixty minutes sufficed to attain equilibrium on MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, resulting in qt values of 57.3, 106.1, 97.7, and 73.9 mg g−1, respectively; accordingly, the 10Cu@MOA was selected as the best DXC remover among this group of adsorbents. The DXC sorption kinetics revealed that PSSO fitted the DXC sorption onto MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA, with higher R2 values and minor RSS and χ2 values. Investigating the sorption control step unraveled a co-participation of LFDM and IPDM in the DXC removal by the MOA and its based nanohybrids. The multilayer sorption model FRIM was the best in expressing the DXC sorption onto the 10Cu@MOA. The temperature impact survey revealed that increasing temperature is in favor of DXC sorption onto the 10Cu@MOA, pointing out that the process was endothermic. The thermodynamics implied that the DXC sorption onto the 10Cu@MOA was spontaneous. The pH study exposed the DXC removal preference to a mildly acidic medium (pH = 6.0). Treating 5.0 and 10.0 mg L−1 DXC in SRW, the 10Cu@MOA removed 99.9% and 98.1% of DXC, respectively, while treating the DXC concentrations mentioned above in SWS resulted in 94.7% and 92.5%, respectively. The reusability study showed a 10% reduction in the 10Cu@MOA’s removal efficiency at the fourth cycle, indicating efficient reusability and excellent stability, which is encouraging for use in treating pharmaceutically contaminated water. The study focused more on testing MOA, 10Cu@MOA, 10Ni@MOA, and 10Co@MOA capabilities in removing DXC from water which is why there were high concentrations were used, making the absence of low-level DXC concentration a possible limitation in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology, B.Y.A.; Software, R.S.R.; Validation, N.A. and R.S.R.; Formal analysis and Investigation, M.S.; Writing—original draft, T.G.I.; Writing—review and editing, B.Y.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-DDRSP2502).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no financial and/or nonfinancial conflicts of interest.
References
- Cai, W.; Wen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, J. Untangling the Characteristics and Ecological Processes of Microbial Community Assembly in the Source Area of the East Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project in China Under Different Water Periods. Water 2025, 17, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănăduc, D.; Simić, V.; Cianfaglione, K.; Barinova, S.; Afanasyev, S.; Öktener, A.; McCall, G.; Simić, S.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Freshwater as a sustainable resource and generator of secondary resources in the 21st century: Stressors, threats, risks, management and protection strategies, and conservation approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Kirsten, K.L.; Qadeer, A. Contaminants in the Water Environment: Significance from the Perspective of the Global Environment and Health. Water 2025, 17, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, M.; Lan, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y.; Ru, J. Water quality degradation due to heavy metal contamination: Health impacts and eco-friendly approaches for heavy metal remediation. Toxics 2023, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babuji, P.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Duraisamy, K.; Periyasamy, G. Human health risks due to exposure to water pollution: A review. Water 2023, 15, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczynski, Y.; Passos, R.; Campos, L.C. A review of the most concerning chemical contaminants in drinking water for human health. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Almeida, A.G.; Castrejón-Godínez, M.L.; Mussali-Galante, P.; Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Rodríguez, A. Pharmaceutical Pollutants: Ecotoxicological Impacts and the Use of Agro-Industrial Waste for Their Removal from Aquatic Environments. J. Xenobiotics 2024, 14, 1465–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assidi, M.; Buhmeida, A.; Budowle, B. Medicine and health of 21st Century: Not just a high biotech-driven solution. Npj Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, L. Top companies and drugs by sales in 2021. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2022, 21, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, C.; Geladakis, G.; Kommata, V.; Batargias, C.; Lagoumintzis, G. Insights in pharmaceutical pollution: The prospective role of eDNA metabarcoding. Toxics 2023, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgenidze, D.; Romanovski, V. The pharmaceutical pollution of water resources using the example of the Kura River (Tbilisi, Georgia). Water 2023, 15, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzhelele, E.P.; Mudzielwana, R.; Ayinde, W.B.; Gitari, W.M. Pharmaceutical contaminants in wastewater and receiving water bodies of South Africa: A review of sources, pathways, occurrence, effects, and geographical distribution. Water 2024, 16, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dodgen, L.K.; Conkle, J.L.; Gan, J. Plant uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products from recycled water and biosolids: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Sures, B.; Schmidt, T.C. Cephalosporin antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A critical review of occurrence, fate, ecotoxicity and removal technologies. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyasari-Mehta, A.; Hartung, S.; Kreuzig, R. From the application of antibiotics to antibiotic residues in liquid manures and digestates: A screening study in one European center of conventional pig husbandry. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, N.E.; Charles, P.G. Safety and efficacy review of doxycycline. Clin. Med. Ther. 2009, 1, CMT.S2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayğılı, G.A.; Sayğılı, H.; Koyuncu, F.; Güzel, F. Development and physicochemical characterization of a new magnetic nanocomposite as an economic antibiotic remover. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamscher, G.; Sczesny, S.; Höper, H.; Nau, H. Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, I.; Laczay, P.; Borbély, Z. Degradation of doxycycline in aged pig manure. Acta Vet. Hung. 2011, 59, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, T.G.; Almufarij, R.S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Ramadan, R.S.; Eltoum, M.S.; Abd Elaziz, M.E. A Thorough Examination of the Solution Conditions and the Use of Carbon Nanoparticles Made from Commercial Mesquite Charcoal as a Successful Sorbent for Water Remediation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A. Treatment of Water and Wastewater: Challenges and solutions. Separations 2023, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shraim, A.; Diab, A.; Alsuhaimi, A.; Niazy, E.; Metwally, M.; Amad, M.; Sioud, S.; Dawoud, A. Analysis of some pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater of Almadinah Almunawarah. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S719–S729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, T.C.; Cabrera-Codony, A.; Barceló, D.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Pinheiro, A.; Gonzalez-Olmos, R. Influencing factors on the removal of pharmaceuticals from water with micro-grain activated carbon. Water Res. 2018, 144, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Miandad, R.; Waqas, M.; Gehany, F.; Barakat, M. Remediation of wastewater using various nano-materials. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4897–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.P.H.; Association, A.W.W.; Federation, W.P.C.; Federation, W.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1917; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kayiwa, R.; Kasedde, H.; Lubwama, M.; Kirabira, J.B. Active pharmaceutical ingredients sequestrated from water using novel mesoporous activated carbon optimally prepared from cassava peels. Water 2022, 14, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshta, B.E.; Yu, H.; Wang, L. MIL series-based MOFs as effective adsorbents for removing hazardous organic pollutants from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei-Fakhri, S.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Foroutan, R.; Arsalani, N.; Ramavandi, B. Crystal violet dye sorption over acrylamide/graphene oxide bonded sodium alginate nanocomposite hydrogel. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufarij, R.S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Salih, M.; Aldosari, H.; Aldayel, N.W. Optimization, nature, and mechanism investigations for the adsorption of ciprofloxacin and malachite green onto carbon nanoparticles derived from low-cost precursor via a green route. Molecules 2022, 27, 4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, T.G.; Almufarij, R.S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Abd Elaziz, M.E. Eliminating Manifold Pharmaceutical Pollutants with Carbon Nanoparticles Driven via a Short-Duration Ball-Milling Process. Surfaces 2024, 7, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Ali, S.; Zaman, W. Innovative adsorbents for pollutant removal: Exploring the latest research and applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, F.; Mustafa, A.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Wang, X.; Younas, S.; Mohy-Ud-Din, W.; Ashir Hameed, M.; Mohsin Abrar, M.; Maitlo, A.A.; Noreen, S. Current and emerging adsorbent technologies for wastewater treatment: Trends, limitations, and environmental implications. Water 2021, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, B.C.J.; Vijaya, J.J.; Bououdina, M.; Khezami, L.; Modwi, A.; Ismail, M.; Bellucci, S. Study of barium adsorption from aqueous solutions using copper ferrite and copper ferrite/rGO magnetic adsorbents. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 3954536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modwi, A.; Elamin, M.R.; Idriss, H.; Elamin, N.Y.; Adam, F.A.; Albadri, A.E.; Abdulkhair, B.Y. Excellent adsorption of dyes via MgTiO3@g-C3N4 nanohybrid: Construction, description and adsorption mechanism. Inorganics 2022, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Han, M.; Gao, H.; Yang, H.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Jagadeesha, A.V.; Manjunatha, S. Various carbon-based MgAl2O4 adsorbents and their removal efficiency of CR dye and antibiotics in aqueous media: High selective adsorption capacity, performance prediction and mechanism insight. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 26734–26746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzbasi, N.S.; Krawczyk, P.A.; Domagała, K.W.; Englert, A.; Burkhardt, M.; Stuer, M.; Graule, T. Removal of MS2 and fr bacteriophages using MgAl2O4-modified, Al2O3-stabilized porous ceramic granules for drinking water treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.; Wei, H.; Gong, C.; Yoriya, S.; He, P.; Luo, G.; Yao, H. Structural reconfiguration of Al/CaO adsorbent by Ni doping to improve sintering resistance and arsenic removal performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 652, 159325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahmoud, S.A.; Alzahrani, S.S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y. Efficacious Removal of Organic Contaminants from Water Using a Novel CoO–NiO@ MgAl2O4 Nanocomposite. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 11188–11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.A.; Elsisi, M.E.; Mansour, A.F. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of α-Al2O3 and M-Al2O4 spinel nanocomposites in hybrid quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.R.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Algethami, F.K.; Khezami, L. Linear and nonlinear investigations for the adsorption of paracetamol and metformin from water on acid-treated clay. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.R.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Elzupir, A.O. Removal of ciprofloxacin and indigo carmine from water by carbon nanotubes fabricated from a low-cost precursor: Solution parameters and recyclability. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesiltepe Özcelik, D.; Ebin, B.; Stopic, S.; Gürmen, S.; Friedrich, B. Mixed Oxides NiO/ZnO/Al2O3 Synthesized in a Single Step via Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis (USP) Method. Metals 2022, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Senani, G.M.; Deraz, N.M.; Abd-Elkader, O.H. Magnetic and characterization studies of CoO/Co3O4 nanocomposite. Processes 2020, 8, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.R.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Modwi, A.; Elamin, N.Y. Surfactants enhanced short durations synthesis of bismuth oxyiodide quantum dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 157, 111450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, V.; Purushotham, Y.; Dole, B. Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2012, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Abdullah, B.; Tahir, D. X-ray diffraction analysis of nanocomposite Fe3O4/activated carbon by Williamson–Hall and size-strain plot methods. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 20, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saied, E.; Eid, A.M.; Hassan, S.E.-D.; Salem, S.S.; Radwan, A.A.; Halawa, M.; Saleh, F.M.; Saad, H.A.; Saied, E.M.; Fouda, A. The catalytic activity of biosynthesized magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs) for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microbes, tanning effluent treatment, and chromium ion removal. Catalysts 2021, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angappan, S.; Berchmans, L.J.; Augustin, C. Sintering behaviour of MgAl2O4—A prospective anode material. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Kimiagar, S.; Abrinaei, F. Preparation of few-layered wide bandgap MoS2 with nanometer lateral dimensions by applying laser irradiation. Crystals 2020, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasieczna-Patkowska, S.; Cichy, M.; Flieger, J. Application of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in characterization of green synthesized nanoparticles. Molecules 2025, 30, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to assess the degree of alteration of artificially aged and environmentally weathered microplastics. Polymers 2023, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.R.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Elamin, N.Y.; Albadri, A.; Ismail, M.; Bakheit, R.; Taha, K.K.; Modwi, A. Ru@ Co3O4@g-C3N4 as a novel adsorbent for enhanced copper and cadmium abolition. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2024, 9, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.A.; Ghoniem, M.; Diawara, M.; Rahali, S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Elamin, M.; Aissa, M.A.B.; Seydou, M. Enhanced adsorptive removal of indigo carmine dye by bismuth oxide doped MgO based adsorbents from aqueous solution: Equilibrium, kinetic and computational studies. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 24786–24803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; He, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X. Nanometer pore structure characterization of taiyuan formation shale in the lin-xing area based on nitrogen adsorption experiments. Minerals 2021, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, F.H.S.; Shwan, D.M.; Kaufhold, S. Adsorption study and removal of Basic Fuchsin dye from medical laboratory wastewater using local natural clay. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2023, 9398167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Wang, X.; Gul, K.; Khuda, F.; Aly, Z.; Elseman, A. Microwave-assisted spent black tea leaves as cost-effective and powerful green adsorbent for the efficient removal of Eriochrome black T from aqueous solutions. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Lan, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, H. Study on the adsorption mechanism of ciprofloxacin in wastewater by modified fly ash under the coexistence of copper. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racovita, S.; Trofin, M.-A.; Vasiliu, A.-L.; Avadanei, M.; Loghin, D.F.; Mihai, M.; Vasiliu, S. Studies on Sorption and Release of Doxycycline Hydrochloride from Zwitterionic Microparticles with Carboxybetaine Moieties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lee, C.-S.; Zhang, K.; Alhamzani, A.G.; Hsiao, B.S. Sodium alginate–aldehyde cellulose nanocrystal composite hydrogel for doxycycline and other tetracycline removal. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teweldebrihan, M.D.; Dinka, M.O. Methyl red adsorption from aqueous solution using Rumex Abyssinicus-derived biochar: Studies of kinetics and isotherm. Water 2024, 16, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, T.; Almajidi, Y.; Al-Essa, E.; Romero-Parra, R.; Alwaily, E.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Ganji, F.; Balarak, D. Levofloxacin Adsorption onto MWCNTs/CoFe2O4 Nanocomposites: Mechanism, and Modeling Using Non-Linear Kinetics and Isotherm Equations. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, M.T.M.H.; El-Sesy, M.E. Adsorptive removal of levofloxacin and antibiotic resistance genes from hospital wastewater by nano-zero-valent iron and nano-copper using kinetic studies and response surface methodology. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2023, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, P.; Gao, J.; Han, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, T. Adsorption of levofloxacin onto graphene oxide/chitosan composite aerogel microspheres. Gels 2024, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Brito, S.M.; Andrade, H.M.C.; Soares, L.F.; de Azevedo, R.P. Brazil nut shells as a new biosorbent to remove methylene blue and indigo carmine from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Swadi, H.A.; Ahmad, J.; Abdin, Y.; Usman, A.R.; Al-Farraj, A.S. Sorption–desorption behavior of doxycycline in soil–manure systems amended with mesquite wood waste biochar. Plants 2021, 10, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhory, S.H.; Elamin, M.R.; Ibrahim, T.G.; Salih, M.; Algethami, F.K.; Eltoum, M.S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y. A γ-Al2O3 and MgO/MgAl2O4 Fabricated via a Facile Pathway as Excellent Dye Eliminators from Water. Inorganics 2025, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufarij, R.S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Salih, M. Fast-simplistic fabrication of MoO3@Al2O3-MgO triple nanocomposites for efficient elimination of pharmaceutical contaminants. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).