A Method for Predicting the Action Sites of Regional Mudstone Cap Rock Affecting the Diversion of Hydrocarbons Transported along Oil Source Faults
Abstract
1. Introduction
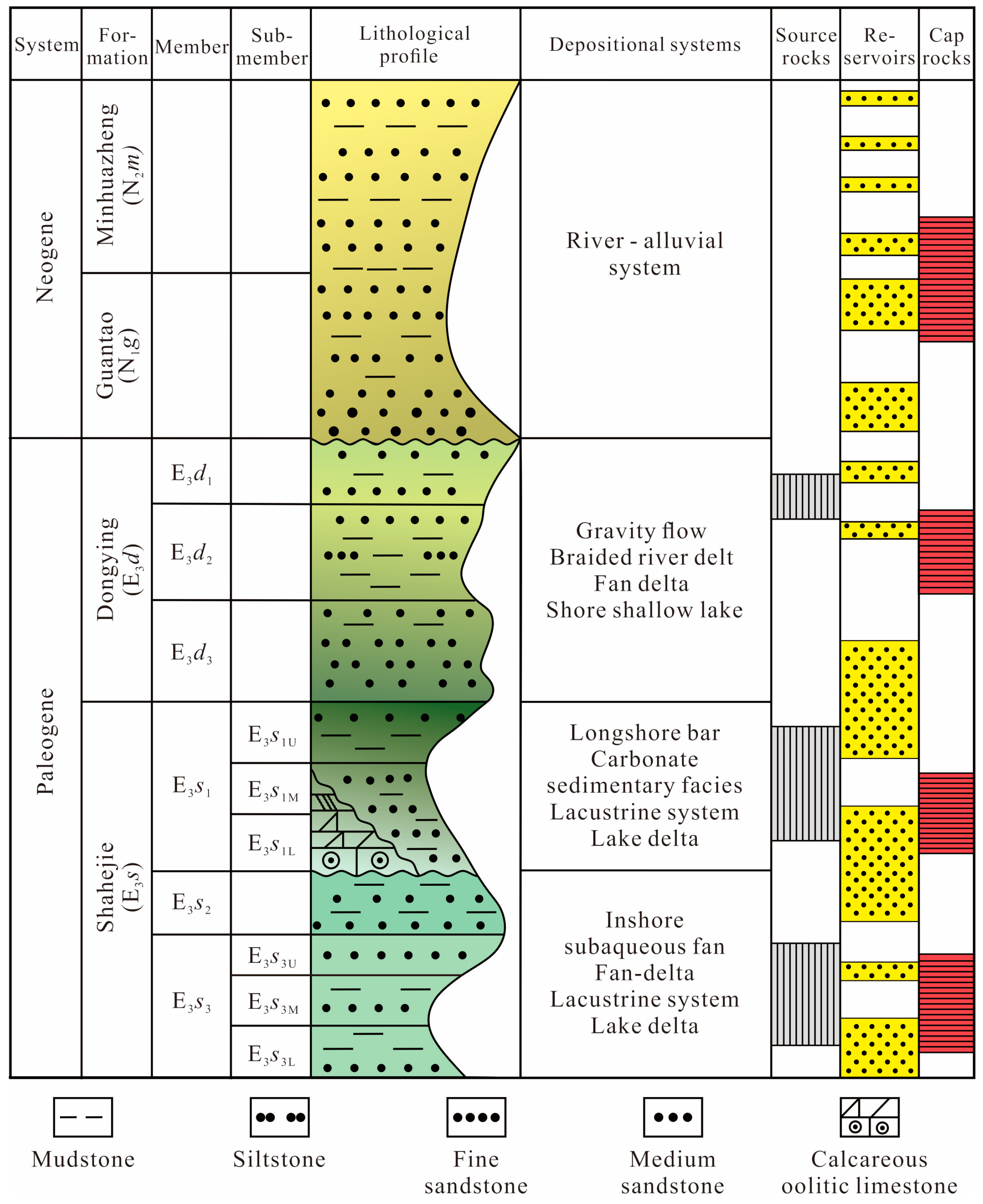
2. Geological Setting
3. Method
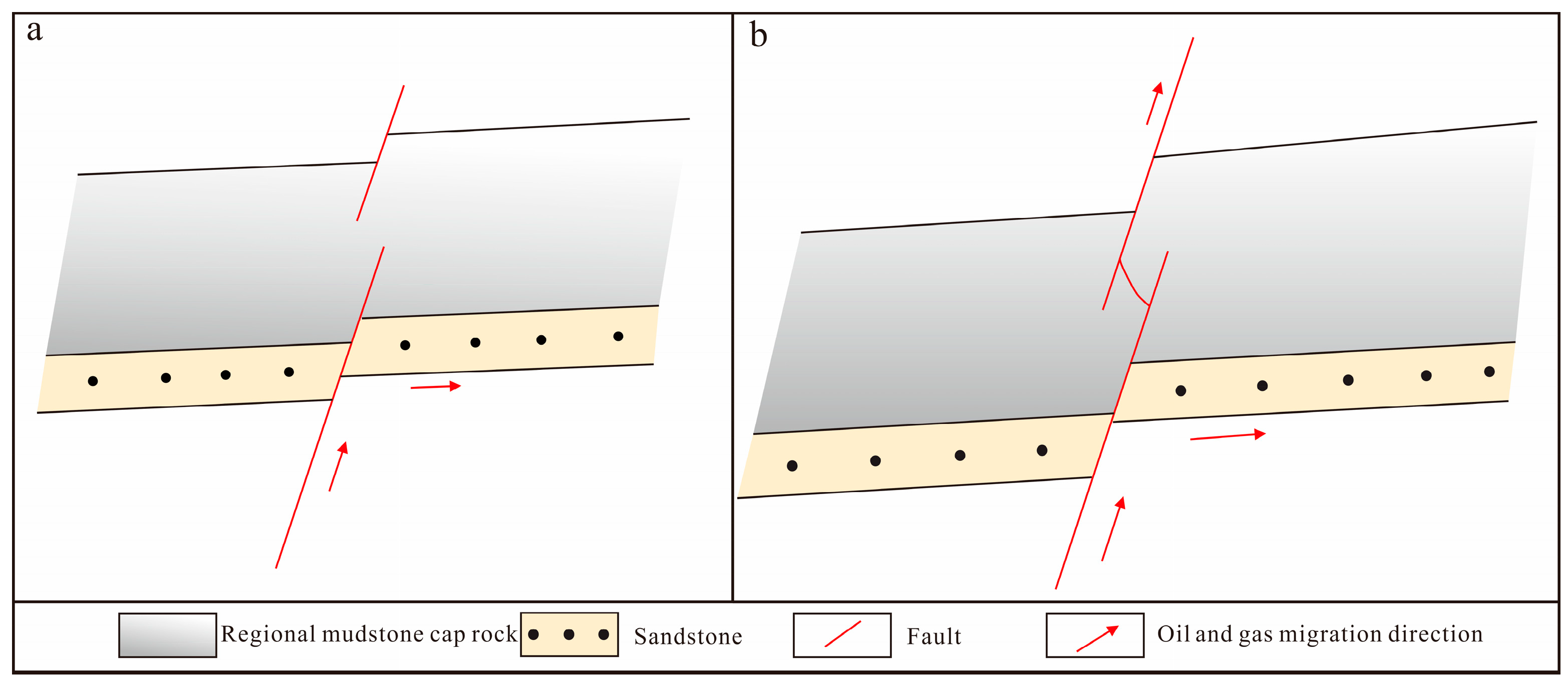
3.1. The Action Sites of Regional Mudstone Cap Rock Affecting the Diversion of Hydrocarbons Transported along Oil Source Faults
3.2. Prediction Method for the Action Sites of Regional Mudstone Cap Rock Affecting the Diversion of Hydrocarbon Migration through the Oil Source Faults
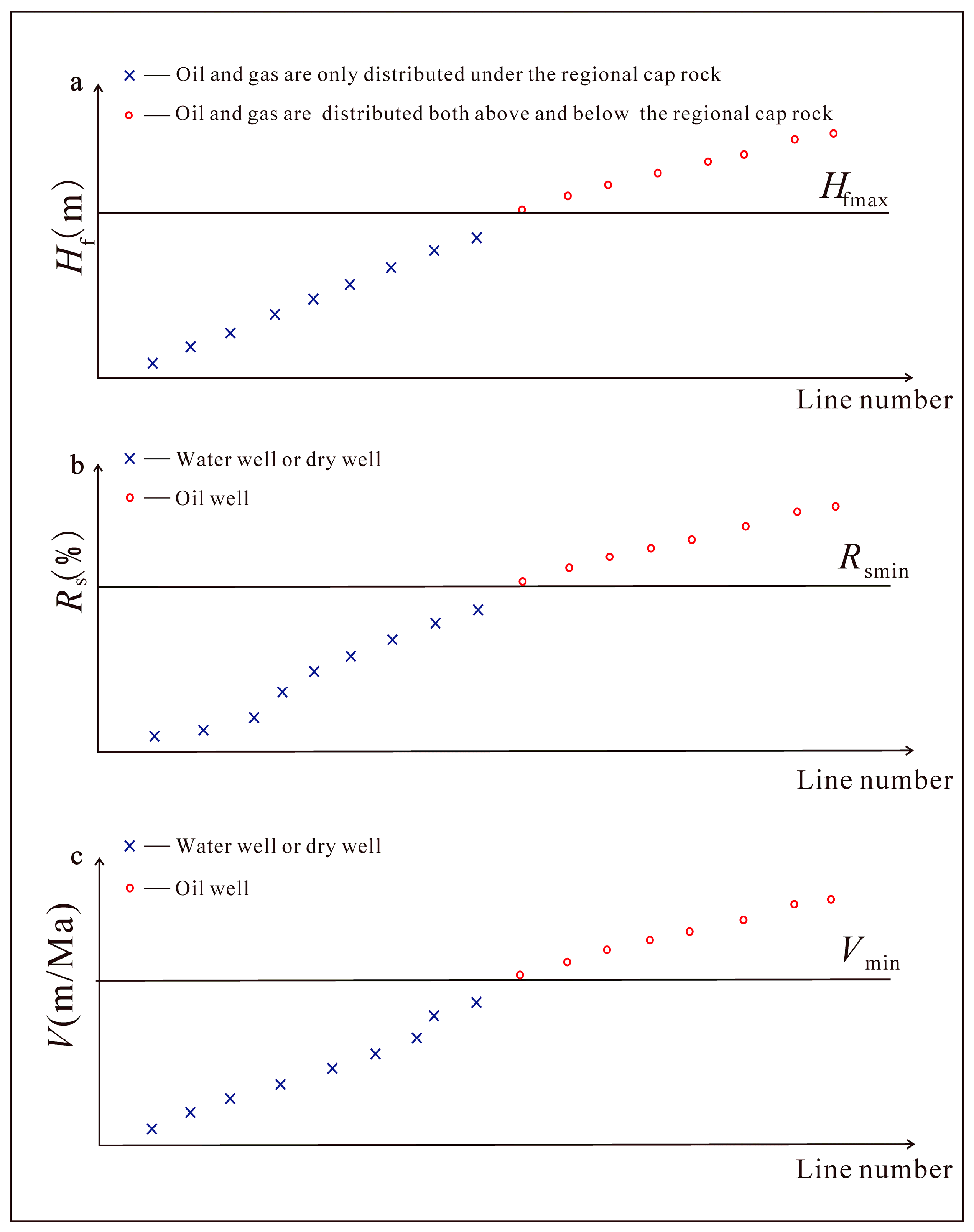
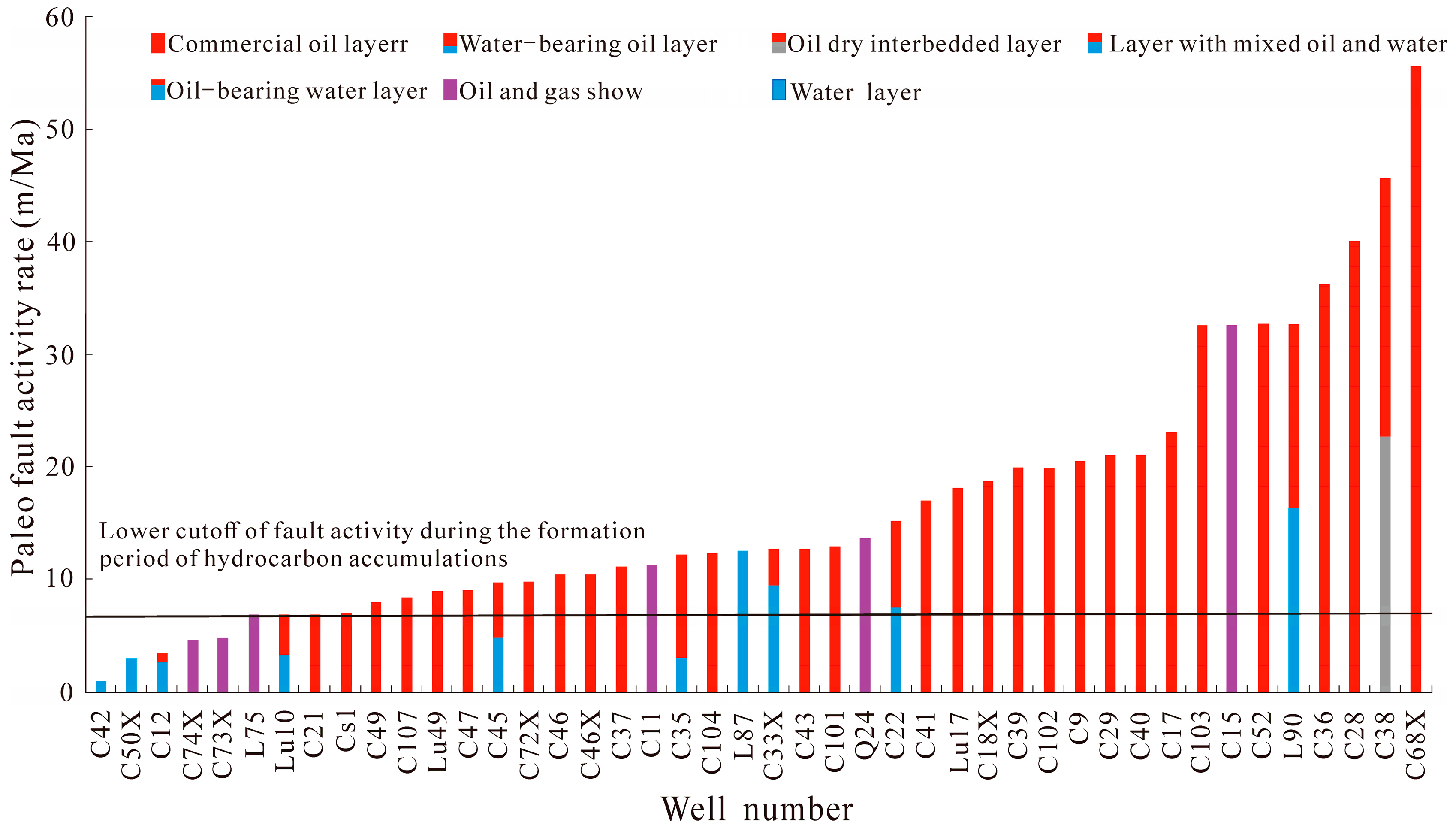
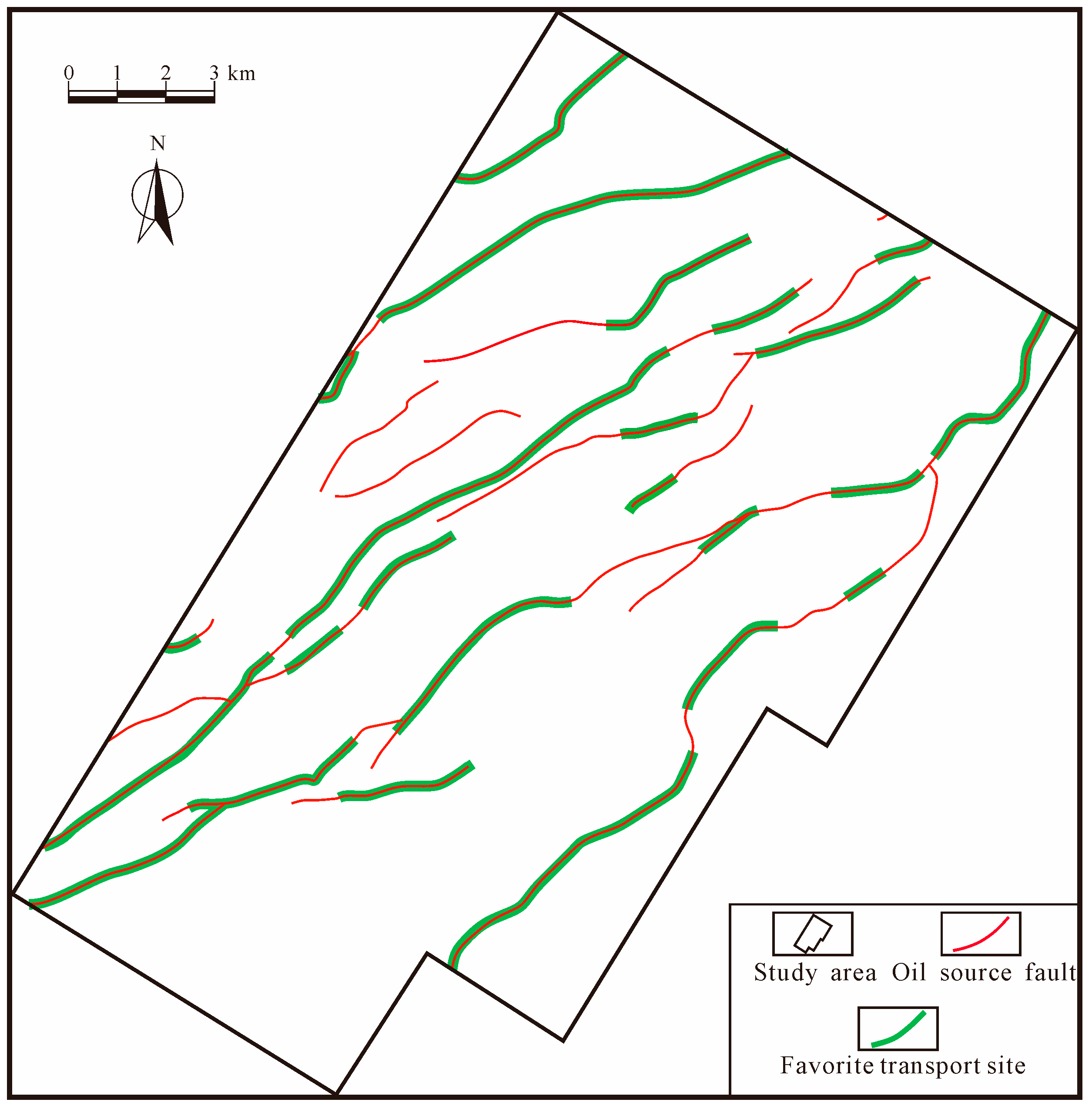
3.2.1. Prediction Method for Blockage Diversion Site
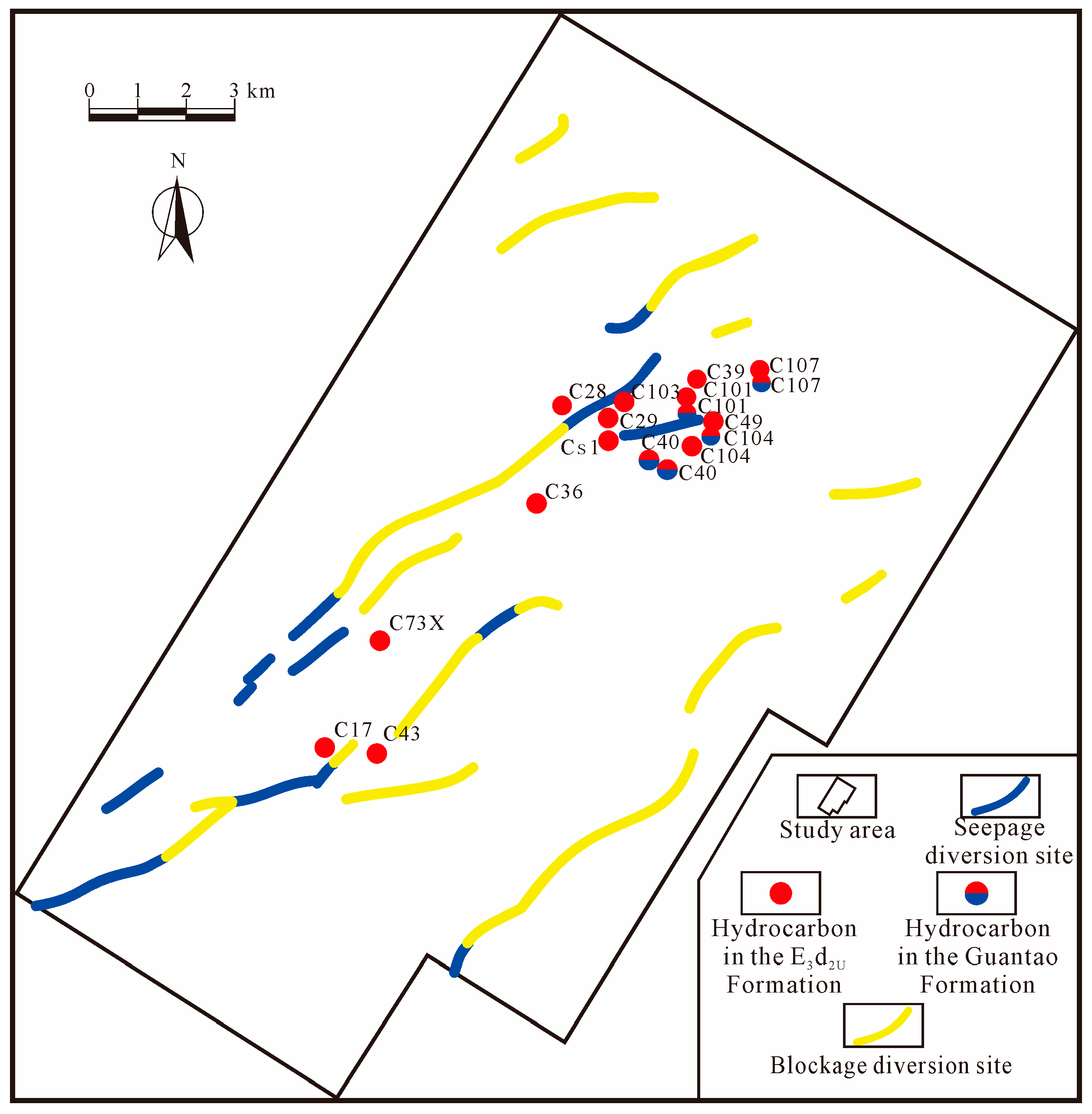
3.2.2. Prediction Method for Seepage Diversion Site
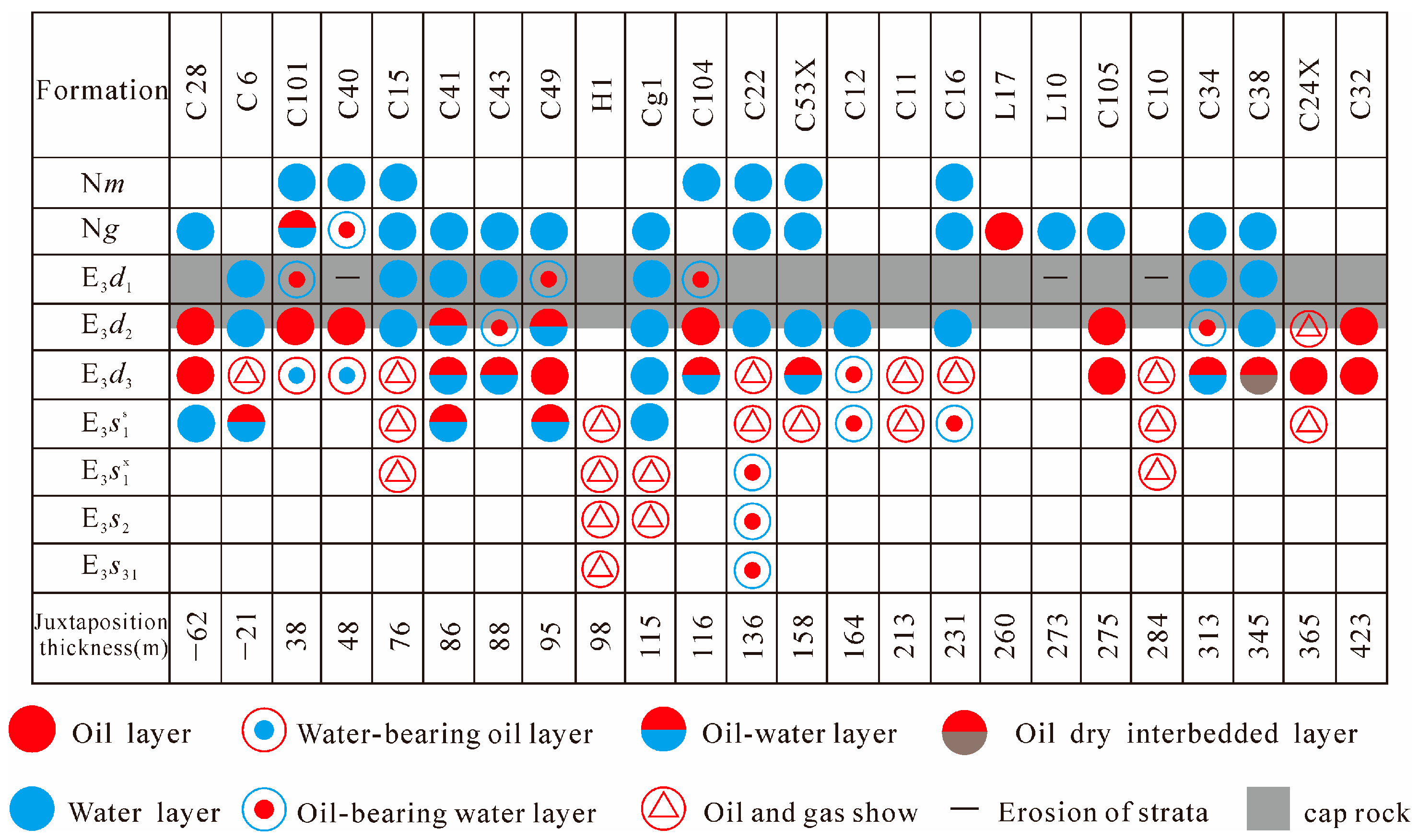
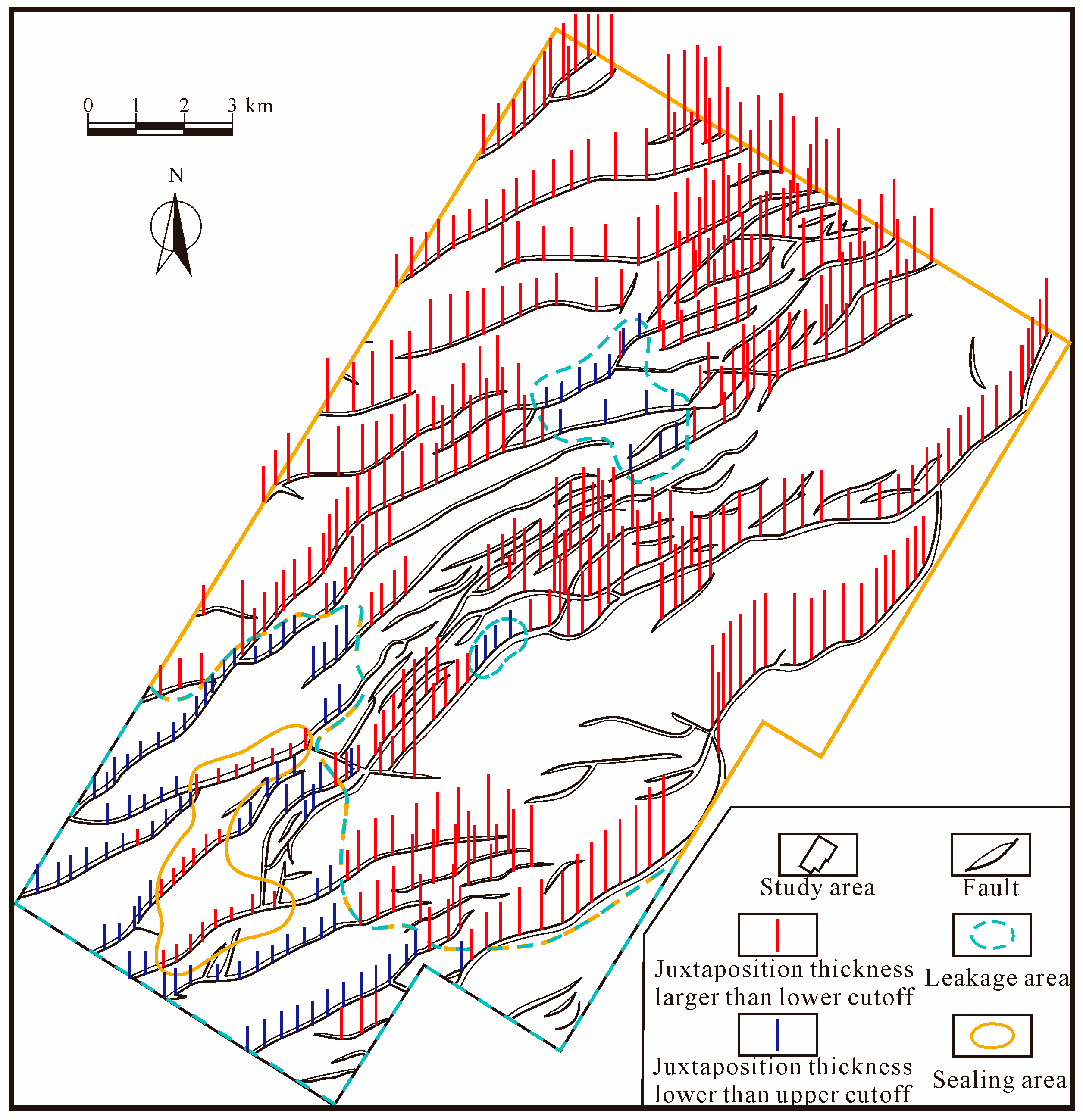
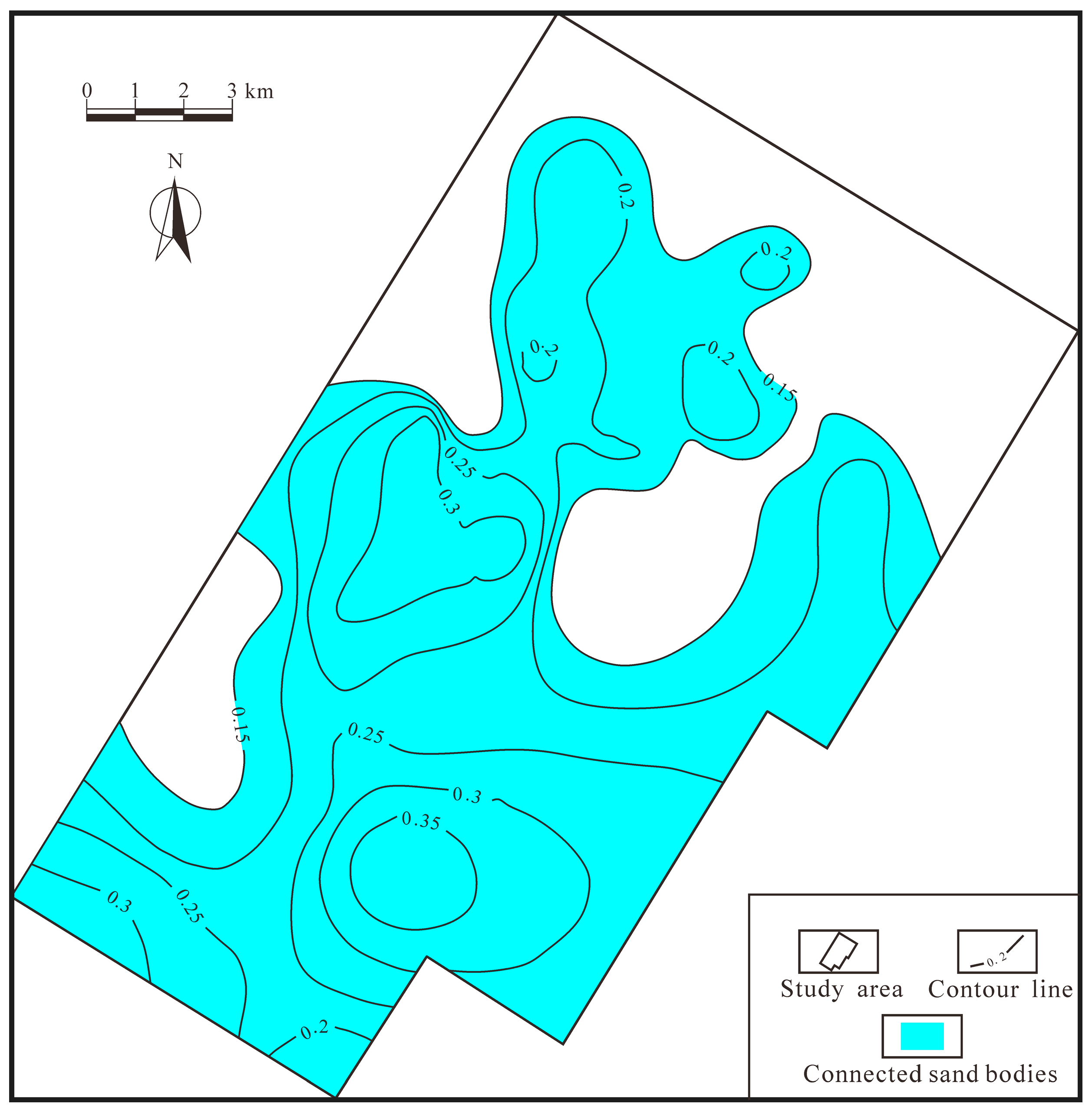
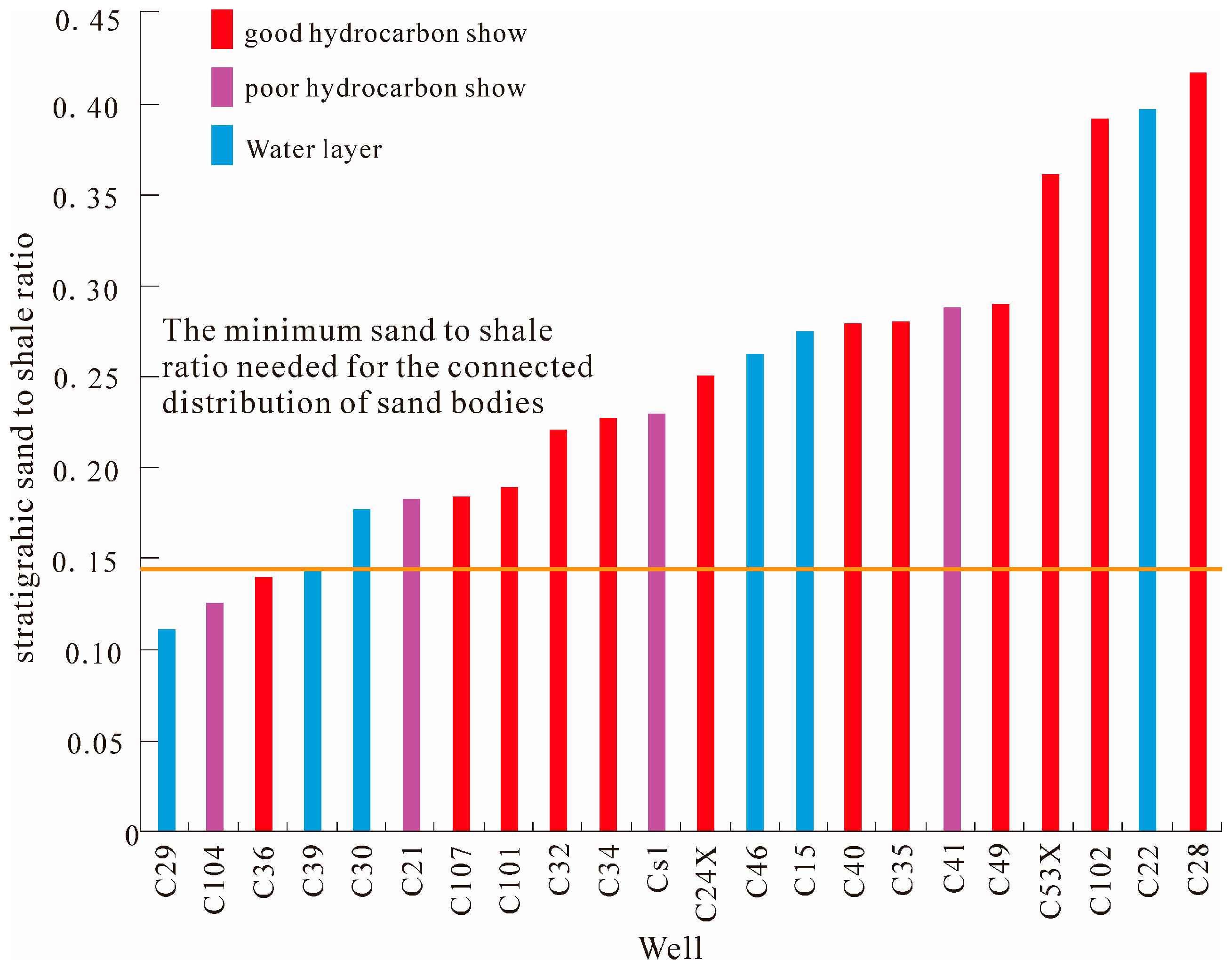
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
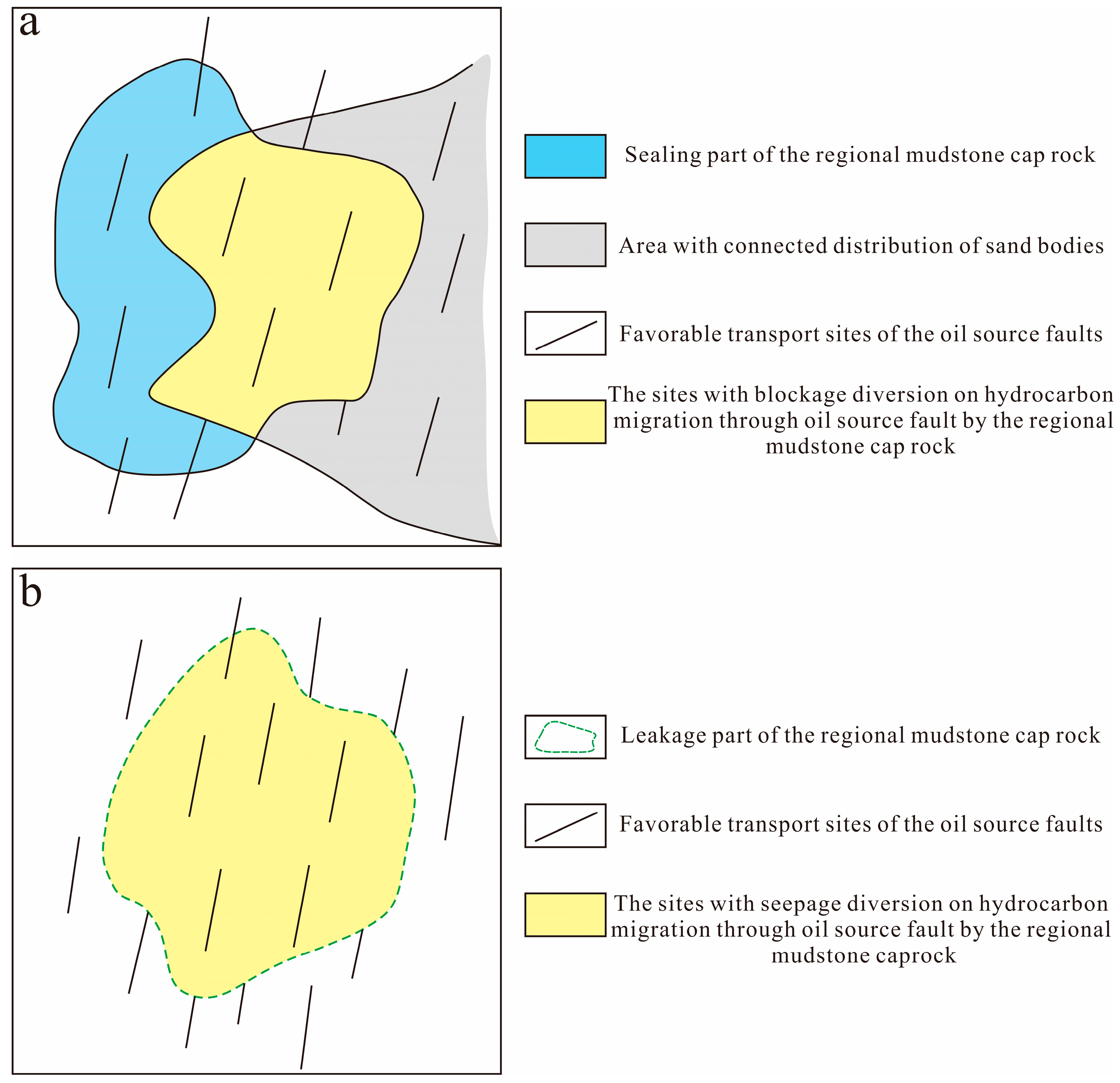
- The regional mudstone cap rock has two types of effects on the hydrocarbon migration through the oil source fault: (1) Blockage diversion effect: the site is the coupling of the enclosed area of the regional mudstone cap rock, the position with connected distributed sand bodies and the advantageous locations for transporting oil from the source fault. (2) Seepage diversion effect: the site is the coupling of the regional mudstone cap rock seepage area, the area with connected distributed sand bodies, and the advantageous locations for transporting oil from the source fault.
- (2)
- By identifying the sealing part of the regional mudstone cap rock, the area with connected distributed sand bodies, and the favorable transport sites of the oil source fault, the place where the regional mudstone cap rock has a blockage diversion effect on oil source fault migration is determined. In contrast, by identifying the leakage area of the regional mudstone cap rock, the parts with connected distributed sand bodies, and the favorable transport sites of the oil source fault, the place where the regional mudstone cap rock has a seepage diversion effect on oil source fault migration is determined. Integrating the two, we establish a prediction method for different diversion migration sites of oil source faults affected by the regional mudstone cap rock. Our case study has demonstrated the method’s validity for predicting different diversion sites of regional mudstone cap rock on oil source fault migration.
- (3)
- In the Raoyang Sag of the Jizhong depression of the Bohai Bay Basin, we found that the blockage diversion area is mostly located in the south-central area and has limited development in the northern part. The seepage diversion is primarily located in the northeastern and western parts. Both are favorable to migrating underlying hydrocarbon of the E3s1 Formation into the E3d2U reservoir to form hydrocarbon accumulations. The latter can also accumulate hydrocarbons in the Guantao Formation (N1g). The predicted results agree with the current hydrocarbon discoveries in the Liuchu area.
- (4)
- This method mainly applies to predicting the different hydrocarbon diversion effects of the regional mudstone cap rock on oil source fault migration in the clastic hydrocarbon-bearing basin.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, J.B.; Yu, Y.H. Prediction method and application of leakage period in oil source fracture-regional mudstone caprock configuration. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2023, 28, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Fu, G.; Gong, J.P. Method for determining formation period of associated traps of oil source faults and its application. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2022, 29, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Fu, G.; Sun, T. Seismic data is used to determine the transportation oil-gas ability of oil source faults and the difference of oil-gas accumulation. Prog. Geophys. 2017, 32, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Fu, G.; Han, G.M.; Dong, X.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.L. Prediction of Favorable Positions for Hydrocarbon Accumulation Controlled by Oil-Source Faults: A Case of Dazhangtuo Fault in the Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 908812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, Y.H.; Chen, C.; Lou, R.; Wang, Q. Fault reactivation in No.4 structural zone and its control on oil and gas accumulation in Nanpu sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Zhang, B.W.; Wu, W. Mechanism and detection of regional mudstone caprock sealing oil and gas migration along transporting fault. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2016, 40, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.M.; Fu, G.; Zhan, M.W. Hydrocarbon Upward Uigration Condition in Different Directions and Prediction Method of Distribution Area. Geol. Rev. 2018, 64, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.; Yang, J.B. Sealing of Matching between Fault and Caprock to Oil-Gas Migration along Faults: An Example from Middle and Shallow Strata in Nanpu Depression. Editor. Comm. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2013, 38, 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.F.; Yan, L.Y.; Meng, L.D.; Liu, X.B. Deformation Mechanism and Vertical Sealing Capacity of Fault in the Mudstone Caprock. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 30, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.W.; Chen, D.X.; Wang, Q.C.; Du, W.L.; Chang, S.Y.; Wang, C.; Tian, Z.Y.; Cheng, M.; Yao, D.S. Quantitative evaluation of caprock sealing controlled by fault activity and hydrocarbon accumulation response: K gasfield in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 134, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Dong, J.M.; Peng, W.T. Determination method and application for the conversion period of fault-caprock configuration leakage and sealing. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2020, 38, 868–875. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.L.; Fu, G. Control of fault connecting source rock and reservoir on lower generation and upper storage pattern oil-gas accumulation and distribution: Taking middle-shallow area of Nanpu Depression as an example. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2014, 21, 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.H.; Deng, R.; Yuan, H.Q. Prediction method and its application of migration zones of oil and gas migration to multiple caprock by oil source faults. Prog. Geophys. 2019, 34, 244–250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.J.; Fu, G.; Chen, S.Y. Controlling Action of Regional Caprocks over the Hydrocarbon Migration and Accumulation in Different Migration Directions. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2015, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.G.; Fu, G.; Hu, M. Method for predicting oil and gas sealing area of mudstone caprock in fracture development zone by seismic data. Prog. Geophys. 2017, 32, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.H.; Zhao, B.; Dong, Y.X.; Zheng, X.F.; Hu, M. Control of faults on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in the Nanpu Sag. Oil Gas Geol. 2013, 34, 540–549. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Sun, T.W.; Cao, L.Z.; Lv, Y.F.; Fu, G.; Lu, X.Q.; Deng, W.; Zhang, H. An quantitative evaluation method of probability for diversion flow oil and gas laterally from faults to sand bodies: A case study from Leave Chu Structure in the Raoyang Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2016, 37, 979–989. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.Y.; Huo, Z.P.; Fu, G.; Hu, M.; Sun, T.W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.F. Petroleum migration and accumulation in the Liuchu area of Raoyang Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 192, 107276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Ji, Y.L.; Ji, M.Y.; Jin, Z.G.; He, L.S.; Ran, A.H.; Xie, W.; Yin, T.H. Establishment and significance of high-resolution Early Oligocene chronostratigraphic framework in Raoyang Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. J. China Univ. Pet. 2020, 44, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.Y.; Hao, F.; Guo, L.X.; Yin, J.; Cao, Y.J.; Zou, H.Y. Characteristic of source rocks and origin of crude oils in the Raoyang Sag and Baxian Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Insights from geochemical and geological analyses. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 97, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Mansour, A.; Li, C.; Su, P.D.; Meng, L.J.; Ahmed, M.S. Source rock assessment and organic matter characterization of the Oligocene upper Shahejie and Dongying formations in the Nanpu depression of the saline lacustrine Bohai Bay basin, China: Geochemical, palynological, and mineralogical perspectives. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 165, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Li, J.Q.; Huang, Y.H.; Lu, S.F.; Chen, K.T.; Wei, Y.B.; Song, Z.J.; Zhao, R.X.; He, T.H. Influence of Paleosedimentary Environment on Shale Oil Enrichment in the Raoyang Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 13597–13616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.P.; Wang, J.H.; Chen, S.; Ren, P.G.; Liao, Y.T.; Zhao, S.E.; Xia, C.Y. Genetic types and sequence stratigraphy models of Palaeogene slope break belts in Qikou Sag, Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 261–262, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Cao, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Bao, L. Hydrocarbon transport capacity of fault-sandstone configuration of Ed2+3 members in Liuchu area of Raoyang Sag and its relationship with oil and gas enrichment. China Pet. Explor. 2021, 26, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.F.; Sun, B.; Wang, H.X.; Meng, L.D. Fault segmentation growth quantitative characterization and its application on sag hydrocarbon accumulation research. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2015, 44, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- David, M.D.; Bruce, D.T. Four-dimensional analysis of the Semborelay system, offshore Angola: Implications for fault growth in salt-detached settings. AAPG Bull. 2009, 93, 763–794. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wei, G.; Chen, Z.; Ren, R.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, K. Geometry and Kinematics of the Central Fault Zone, Fula Sag, Central Africa Shear Zone. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Lv, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Kang, Y.S.; Hu, X.L.; Shi, J.J. Prediction of Favourable Hydrocarbon Transport Pathways of the Jiuzhou Fault in Langgu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Processes 2023, 11, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.F.; Song, X.Q.; Wang, H.X.; Liu, H.T.; Wang, S.Y.; Meng, L.D. Comprehensive evaluation on hydrocarbon-bearing availability of fault traps in a rift basin: A case study of the Qikou sag in the Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wu, C.X.; Qi, Y.P.; Yao, A.G.; Zhang, S.C.; Xu, Y.; Shi, J.A. Quantitative resumption method of stratum denudation thickness and its application in Junggar Basin: A case study on the Permian Lower Urho Formation in Block 8 of Karamay Oilfield. J. Palaeogeogr. 2015, 17, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.H.; Liu, C.L.; Tian, J.X.; Tai, W.X.; Li, P.; Zeng, X.; Kong, H. Erosion thickness recovery and its significance to hydrocarbon accumulation in northwestern Qaidam Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2022, 44, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.P.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhu, D.K. Recovery of the Erosion Thickness and Characterization of the Paleogeomorphology in the Southern Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. J. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 19, 320–330. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.M. Restoration of eroded stratal thickness in key periods of tectonic change in a multi-stage superimposed Tarim Basin in China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2012, 1, 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.; Wang, H.R.; Hu, X.L. Prediction method and application of caprock faulted-contact thickness lower limit for oil-gas sealing in fault zone. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2015, 39, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.; Wang, H.R. Prediction Method of Favorable Position in Oil-Gas Accumulation around Oil-Source Fault and its Application. Geotecton. Metallog. 2019, 43, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.H.; Luo, J.S.; Liu, Z.L.; Wei, Z.P.; Ye, F.; Wang, Y.X. Fault Re-active and Reservoir-controlling of Xujiaweizi Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. Geol. Rev. 2015, 61, 1332–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lv, Y.F.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, Y.B.; Zhang, D.W. Characteristics and significance of syngenetic fault segmentation in hydrocarbon accumulation, an example of Yuanyanggou fault in western sag, Liaohe depression. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2012, 41, 793–799. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.B.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yu, Y.H.; Yuan, H.Q. Determination method of oil source fault transporting oil and gas evolution stage and its application. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2023, 53, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Z.P.; Wang, G.Z. Hydrocarbon Charging and Accumulation Process of the Large Bozhong19-6 Condensate Gas Reservoirs in the Southwestern Bozhong Sub-Basin, Bohai Bay Basin, China. J. Earth Sci. 2024, 35, 613–630. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Z.; Lan, X.D.; Liu, H.; Du, X.F.; Wang, Q.B. Faults development controlled the Neogene hydrocarbon accumulation in the mid-Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Mar. Geol. Lett. 2022, 38, 73–81. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A Method for Predicting the Action Sites of Regional Mudstone Cap Rock Affecting the Diversion of Hydrocarbons Transported along Oil Source Faults. Processes 2024, 12, 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12092055
Zhou T, Wang Y, Yuan H, Yu Y, Zhang Y. A Method for Predicting the Action Sites of Regional Mudstone Cap Rock Affecting the Diversion of Hydrocarbons Transported along Oil Source Faults. Processes. 2024; 12(9):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12092055
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tianqi, Yachun Wang, Hongqi Yuan, Yinghua Yu, and Yunfeng Zhang. 2024. "A Method for Predicting the Action Sites of Regional Mudstone Cap Rock Affecting the Diversion of Hydrocarbons Transported along Oil Source Faults" Processes 12, no. 9: 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12092055
APA StyleZhou, T., Wang, Y., Yuan, H., Yu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2024). A Method for Predicting the Action Sites of Regional Mudstone Cap Rock Affecting the Diversion of Hydrocarbons Transported along Oil Source Faults. Processes, 12(9), 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12092055




