Optimal Multiple Wind Power Transmission Schemes Based on a Life Cycle Cost Analysis Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Topology of Grid Connection Scheme for Wind Farm
2.1. Overview of Wind Farm Construction
2.2. Kinds of Wind Power Grid-Connected Structure Design Scheme
3. Analysis Method-Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA) Model
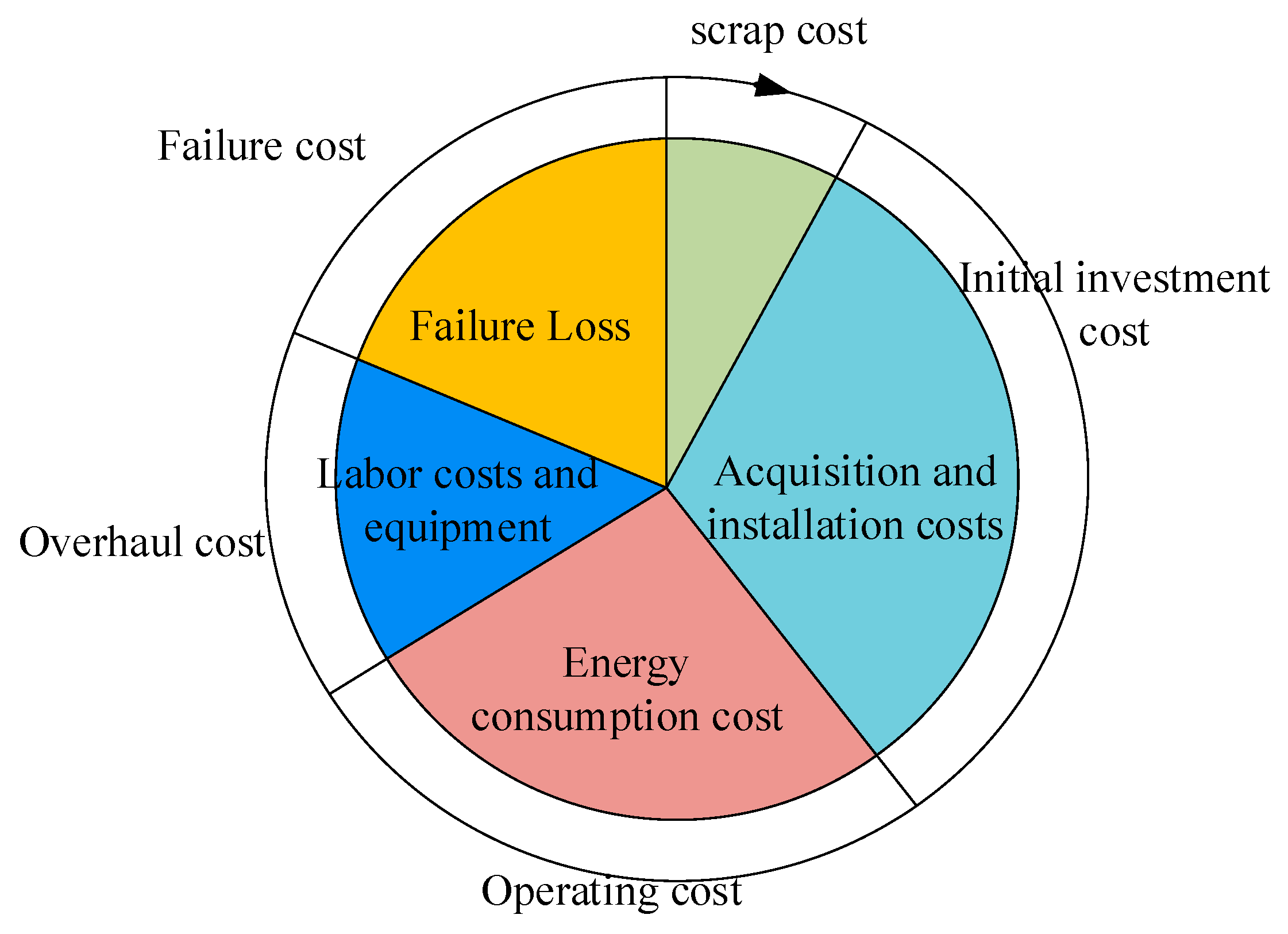
3.1. Mathematical Model of LCCA
3.2. Fixed Investment Cost Analysis
3.3. Operating Costs
4. Economic Comparative Analysis
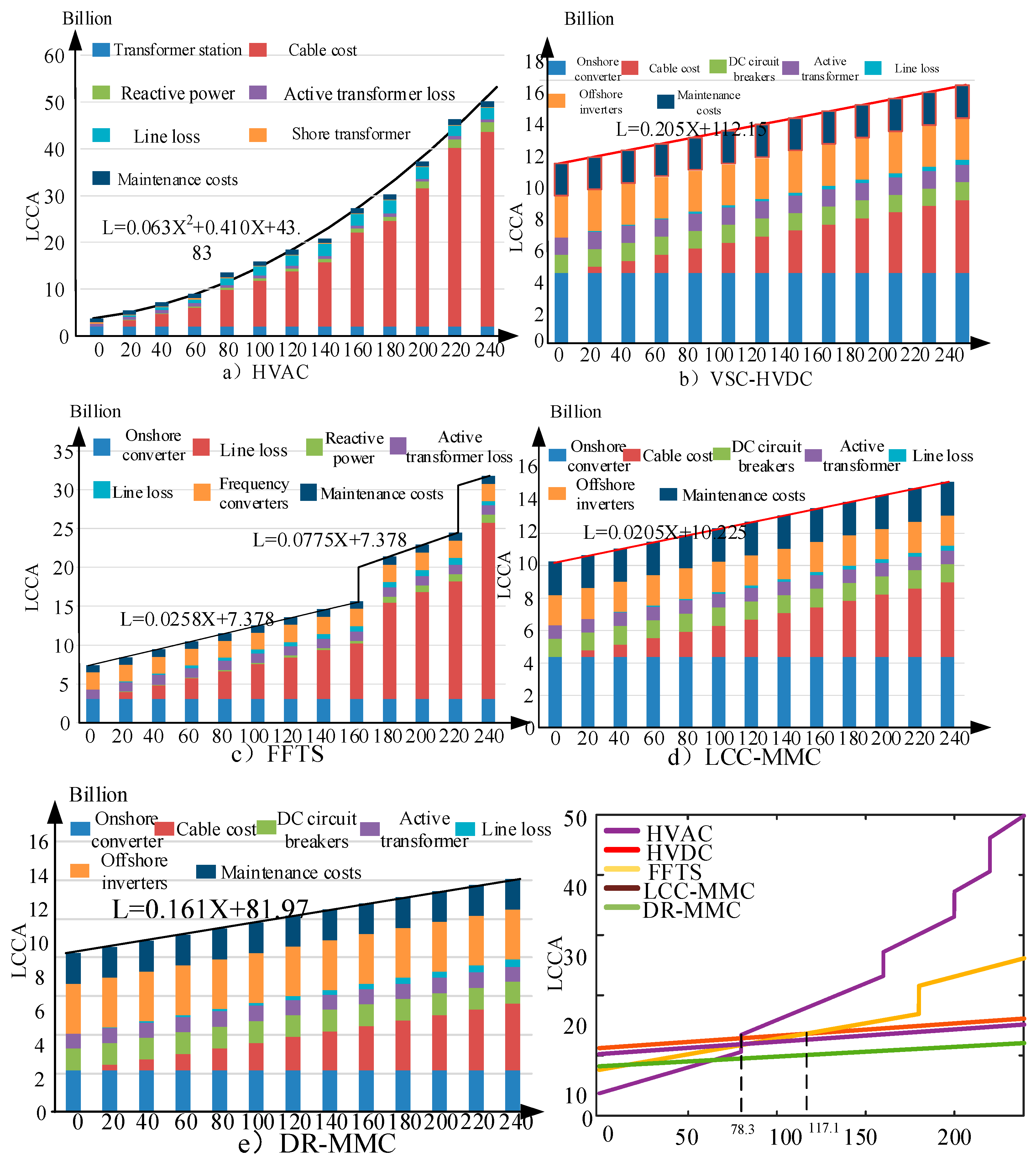
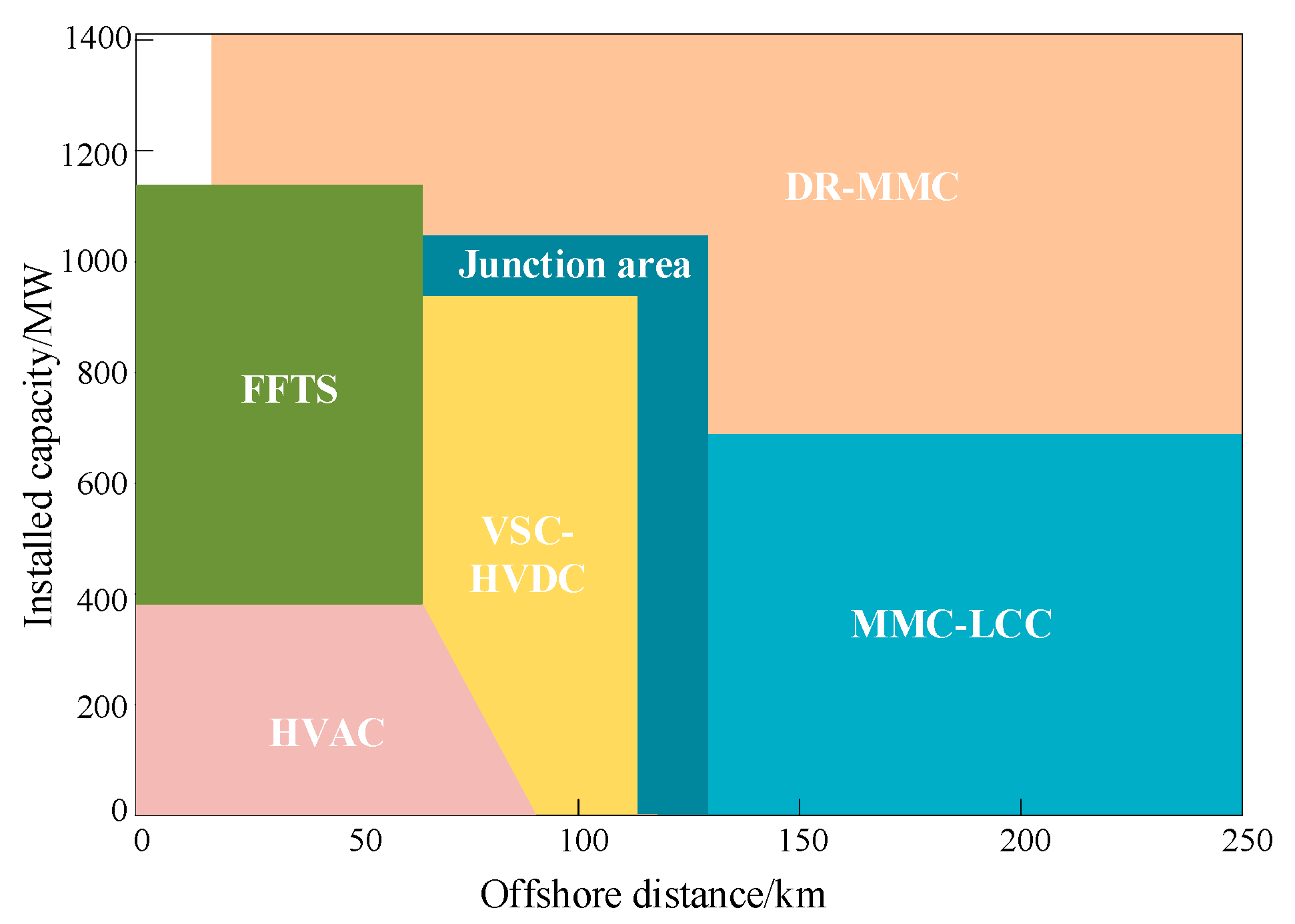
4.1. Relationship between LCCA Investment Cost and Distance
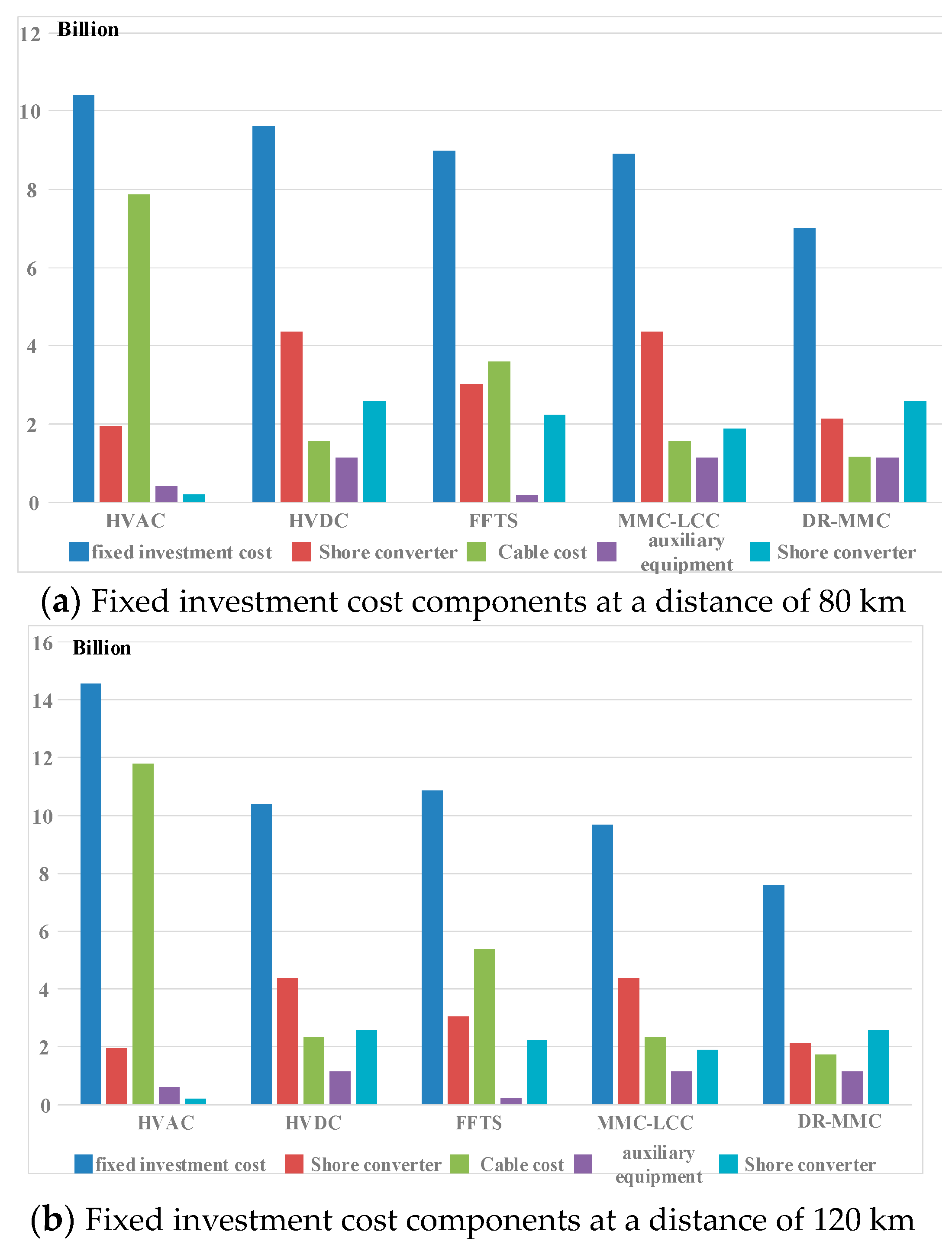
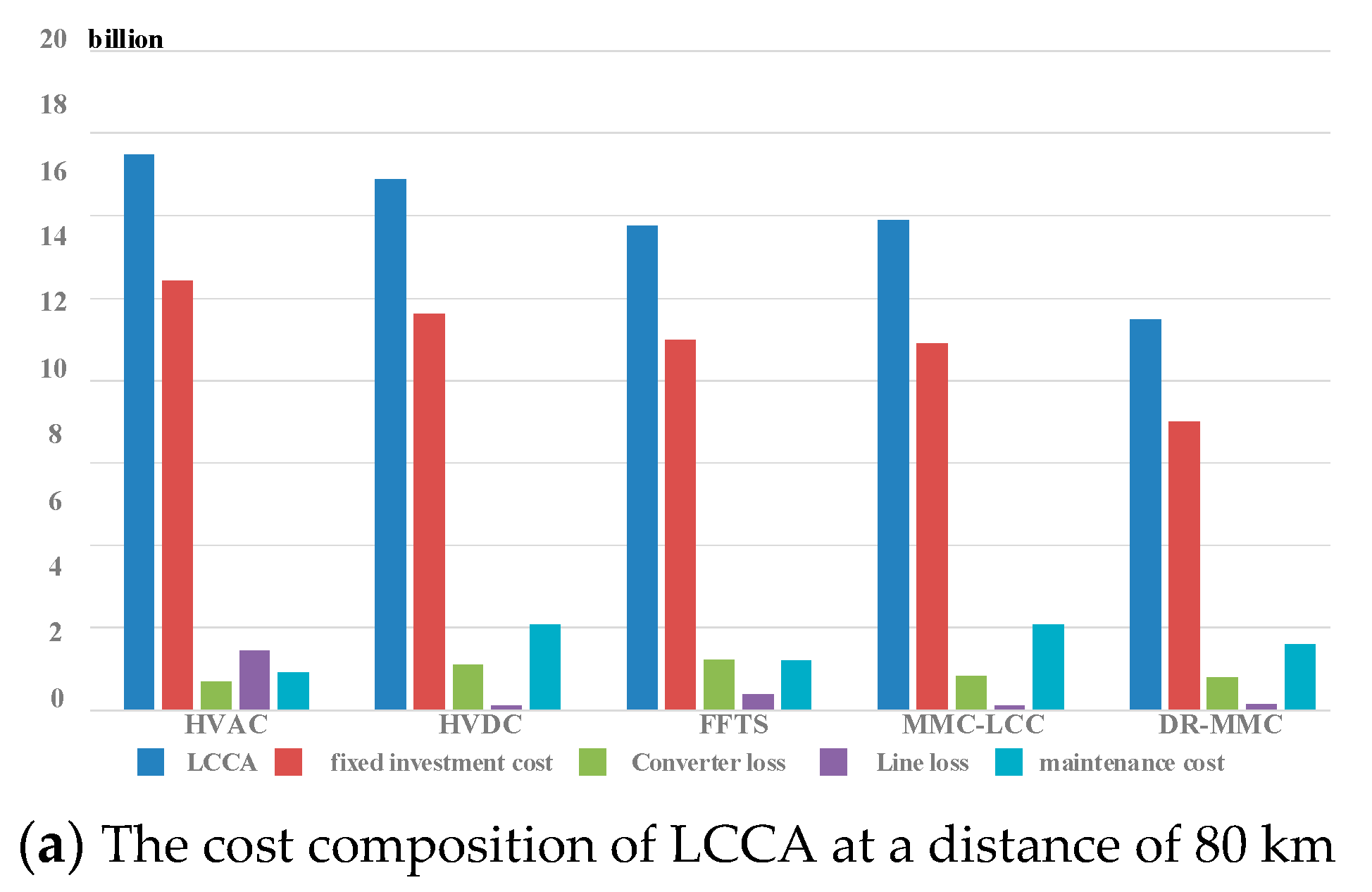
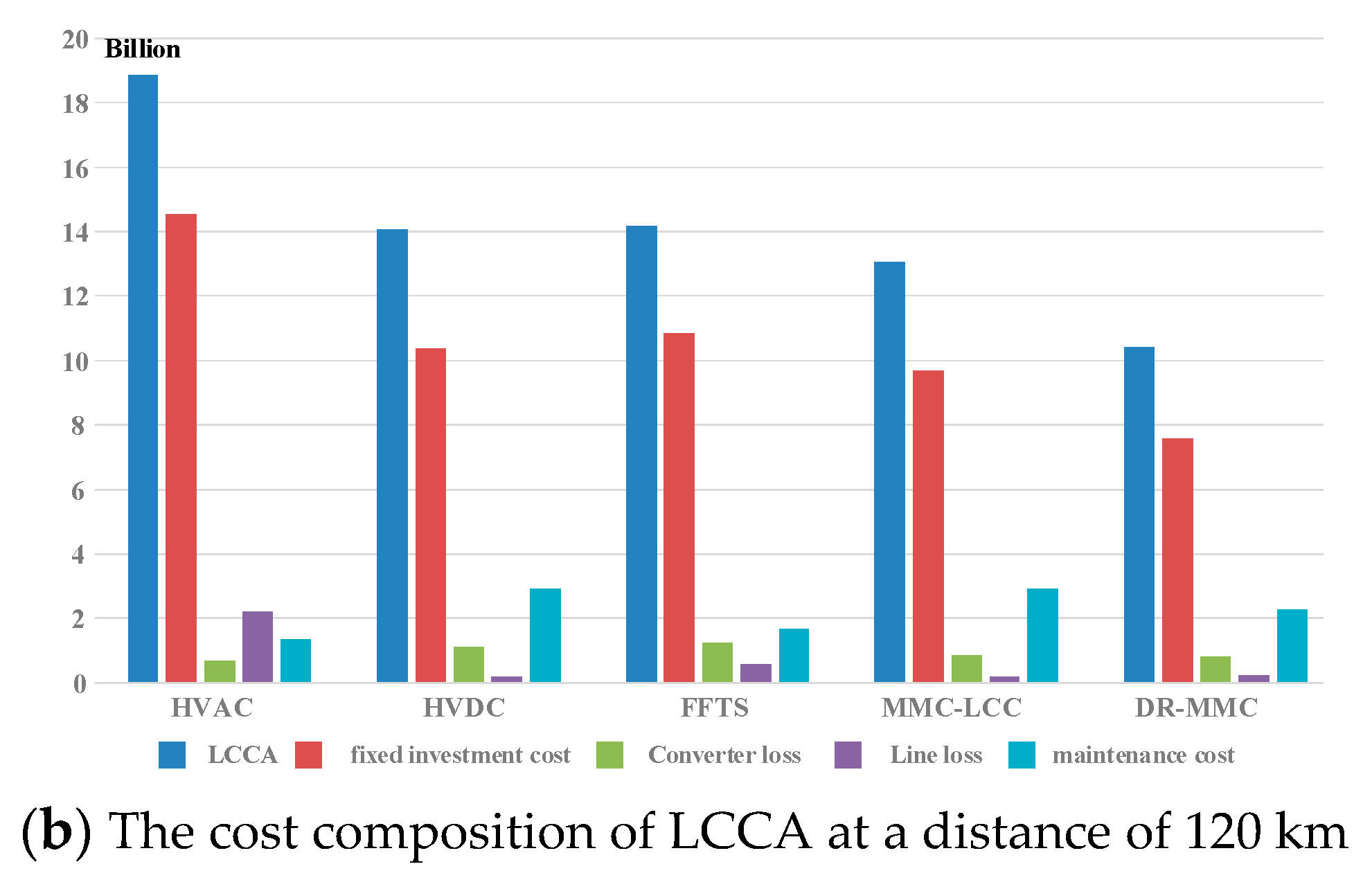
4.2. Analysis of Cost Components of Various Equipments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.; Wu, W. Tractable Convex Approximations for Distributionally Robust Joint Chance-Constrained Optimal Power Flow Under Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 1927–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Sunshine of the rising sun and bright time—Review and prospect of China’s wind power industry in 2020. Energy 2021, 2, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, H. Distributionally Robust Frequency Constrained Scheduling for an Integrated Electricity-Gas System. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2730–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.R.W.; Xu, L.; Houghton, T. Considerations in design of an network. CIGRE Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; She, S.; Liu, X. Economical assessment on redundancy configuration of main transformers for wind farm based on life cycle cost. Autom. Eletr. Power Syst. 2015, 14, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Huang, R.; Wang, Z. Start-up strategy for DR-MMC paralleled hybrid HVDC integrated with wind power. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Wuhan, China, 30 October–1 November 2020; pp. 665–669. [Google Scholar]
- Lauria, S.; Schembari, M.; Palone, F. Very long distance connection of gigawatt size wind farms: Extra high-voltage AC versus high-voltage DC cost comparison. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.A.; Olimpo, A.L. Cost and losses associated with wind farm collection networks which centralize the turbine power electronic converters. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2013, 7, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhu, H.; Ai, Q.; Gao, Y. Optimization analysis of wind grid connecting scheme based on full life cycle cost. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2017, 45, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Song, Z.; Ning, L.; Wang, B.; Lu, M. Technical and economical analysis on wind power system integrated via fractional frequency transmission system. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2015, 39, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yao, L.; Cheng, F. Economic analysis of multi-type DC system topologies for wind power transmission. J. Glob. Energy Interconnect. 2021, 4, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, X. Analysis of VSC-HVDC technology for off-shore wind power in Germany. Power Grid Clean. Energy 2012, 28, 63–68+73. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Yan, S.; Guo, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, S. Re-rch on technical economy of key equipment of multi-base view wind power base. China Electr. Power 2021, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda, K.; Ismail, B.; Bertinato, A.; Torwelle, P.; Garcia, W.R.L.; Van Doorn, J.; Kryezi, F. North Wind Power Hub Feasibility Study: AC and DC Interconnection Comparison (Part III). In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Renewable Energies and Smart Technologies (REST), Tirana, Albania, 28–29 July 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ning, L.; Zhu, W.; Wang, X. Prospect and challenge of frequency division power transmission in wind power grid ap-plication. Electr. Power Eng. Technol. 2017, 36, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Iván, A.A.; Ruben, P.G.; Blasco-Gimenez, R.; Javier, R.A. Control strategy of a HVDC-Diode Rectifier connected type-4 wind farm. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE and International Future Energy Electronics Conference (IFEEC), Taipei, Taiwan, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Negra, N.; Todorovic, J.; Ackermann, T. Loss evaluation of HV AC and HVDC transmission solutions for large wind farms. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2006, 76, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Meng, Y. Experiment on Grid-Connection Process of Wind Turbines in Fractional Frequency Wind Power System. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, E.B.; Van, H.D.; Reza, A.M. Economic comparison of VSC HVDC and HVAC as transmission system for a 300 MW wind farm. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 2010, 20, 661–671. [Google Scholar]
- Hugo, D.; Soares, C.G. Review of the current status, technology and future trends of wind farms. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 209, 107381. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, X.; Merlin, M.C.; Green, T.C. Cost analysis and comparison of HVAC, LFAC and HVDC for wind power connection. In Proceedings of the Iet International Conference on Ac & Dc Power Transmission, IET, Beijing, China, 28–29 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wei, G.; Jin, Y. Connection mode and economic analysis of jiangsu rudong wind power farm. High. Volt. Tech-Neology 2017, 43, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, S. Technical and economic analysis of frequency division transmission application in deep wind power connection. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2019, 43, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovcicd, A. High-Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC Grid; Wiley: Scotland, UK, 2015; pp. 306–307. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Ning, L. Integrating wind power via fractional frequency transmission system. IEEE Trans. Power Transm. 2017, 32, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresesti, P.; Kling, W.L.; Hendriks, R.L. HVDC connection of wind farms to the transmission system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolaki-iosifidou, E.; Mccormack, R.; Kempton, W. Transmission design and analysis for large-scale wind energy development. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. J. 2019, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Teng, Y.; Ning, L. Feasibility of integrating large wind farm via fractional frequency transmission system a case study. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2013, 23, 10625–10631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.; Min, L.; Santoso, S. Steady-state analysis and performance of low frequency AC transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 3873–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Xu, Z. Design of main circuit parameters for modular multilevel matrix converter in LFAC system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3864–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.; Yang, X.; Ren, D. Technical and economic rerch on AC collector scheme for 66 kV wind power. Glob. Energy Internet 2019, 2, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
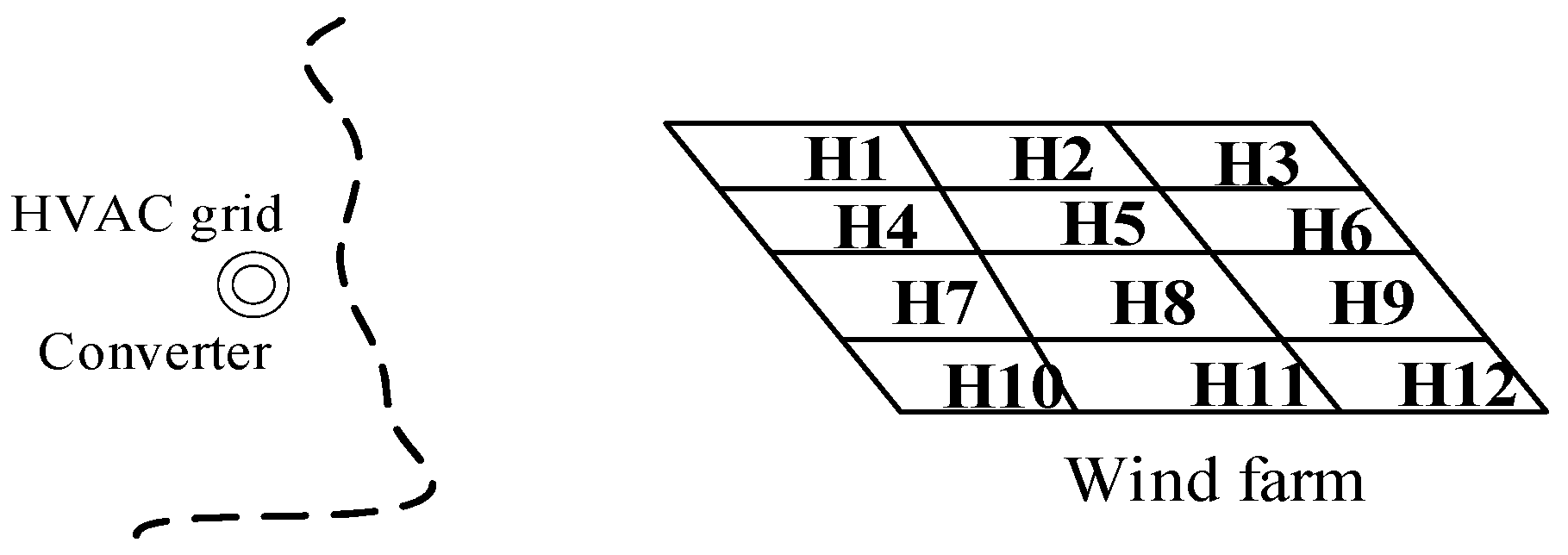

| Project | MMC | M3C | DR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Converter cost | 2.8 | 2.2 | 1.6 |
| Filter cost | 0 | 0 | 0.18 |
| Total | 2.8 | 2.2 | 1.78 |
| Grid-Type | Converter | Onshore Converter |
|---|---|---|
| HVAC | (43.9 + 0.40ST) × 106 | 0.32ST × 106 |
| VSC-HVDC | (219.5 + 0.97ST) × 106 | 0.715ST × 106 |
| FFTS | (43.9 + 0.79ST) × 106 | 0.753ST × 106 |
| MMC-LCC | (219.5 + 0.97ST) × 106 | 0.52ST × 106 |
| DR-MMC | (80 + 0.53ST) × 106 | 0.715 × 106 |
| Grid-Connected Type | Maintenance Outage t/Day | Maintenance Cost/% | Average Time to Rectify Faults TE/Day | Annual Failure Probability %/Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onshore converter | LCC | 15 | 0.5 | 15 | 1 |
| MMC | 15 | 0.5 | 15 | 1 | |
| Converter | MMC | 30 | 1.5 | 30 | 2 |
| DR | 24 | 30 | 24 | 1.5 | |
| Transformer | 15 | 0.5 | 30 | 0.8 | |
| Onshore transformer | 7 | 0.2 | 30 | 0.8 | |
| Low-frequency transformer | 15 | 0.5 | 30 | 0.8 | |
| Inverter M3C | 15 | 0.5 | 15 | 1.2 | |
| AC cable | 10 | --- | 30 | 0.8 | |
| DC cable | 10 | --- | 30 | 0.8 | |
| ABB-IGBT | VCES(V) | IC(A) | VCES(V) | IC(A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5SNA1500E330305 | 3300 | 1500 | 3300 | 1500 |
| 5SNA1800E330400 | 3300 | 1800 | 3300 | 2000 |
| 5SNA3000K452300 | 4500 | 3000 | 4500 | 800 |
| 5SJA3000L520300 | 5200 | 3000 | 4500 | 1200 |
| 5SNA1000G650300 | 6500 | 1000 | 6500 | 750 |
| Grid-Connected Type | HVAC | VSC-HVDC | FFTS | MMC-LCC | DR-MMC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Converter/% | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.13 | 1.3 | 0.55 |
| Onshore converter/% | 0.4 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 0.64 | 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Liu, D.; Luo, H.; Xiong, P.; Tan, D.; Hu, P.; Ma, H.; Wang, B. Optimal Multiple Wind Power Transmission Schemes Based on a Life Cycle Cost Analysis Model. Processes 2024, 12, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081594
Ji X, Liu D, Luo H, Xiong P, Tan D, Hu P, Ma H, Wang B. Optimal Multiple Wind Power Transmission Schemes Based on a Life Cycle Cost Analysis Model. Processes. 2024; 12(8):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081594
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiaotong, Dan Liu, Heng Luo, Ping Xiong, Daojun Tan, Pan Hu, Hengrui Ma, and Bo Wang. 2024. "Optimal Multiple Wind Power Transmission Schemes Based on a Life Cycle Cost Analysis Model" Processes 12, no. 8: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081594
APA StyleJi, X., Liu, D., Luo, H., Xiong, P., Tan, D., Hu, P., Ma, H., & Wang, B. (2024). Optimal Multiple Wind Power Transmission Schemes Based on a Life Cycle Cost Analysis Model. Processes, 12(8), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12081594





