Combining Solution-Blowing and Melt-Blowing Techniques to Produce an Efficient Non-Woven Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
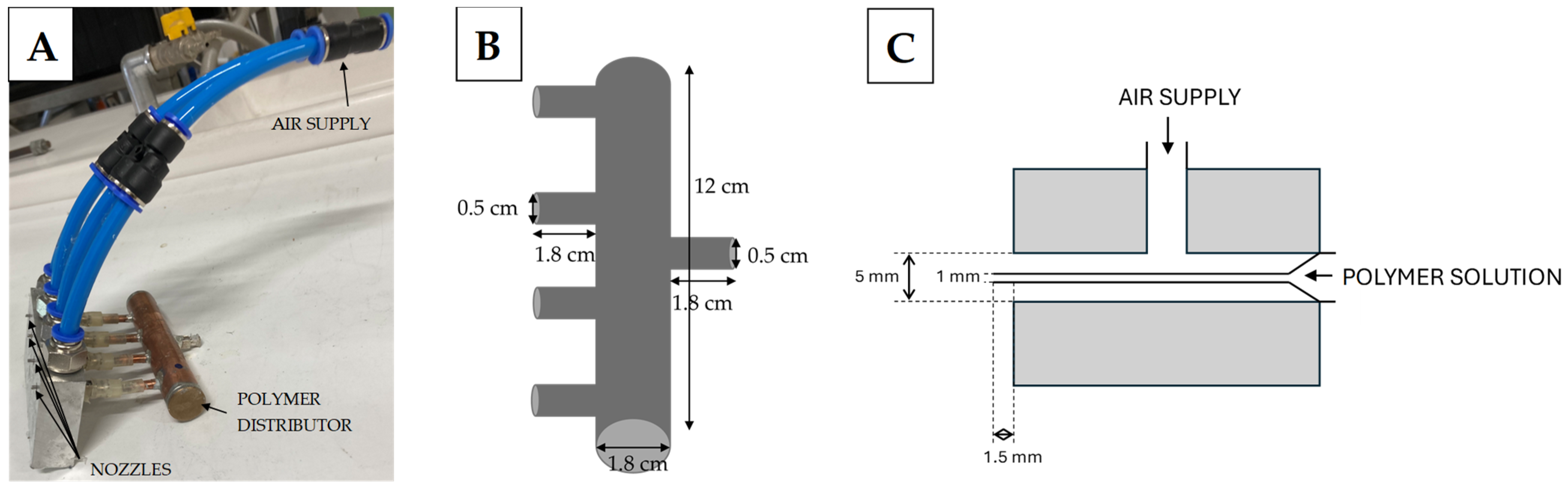
2.1. Solution-Blowing Fibres Production
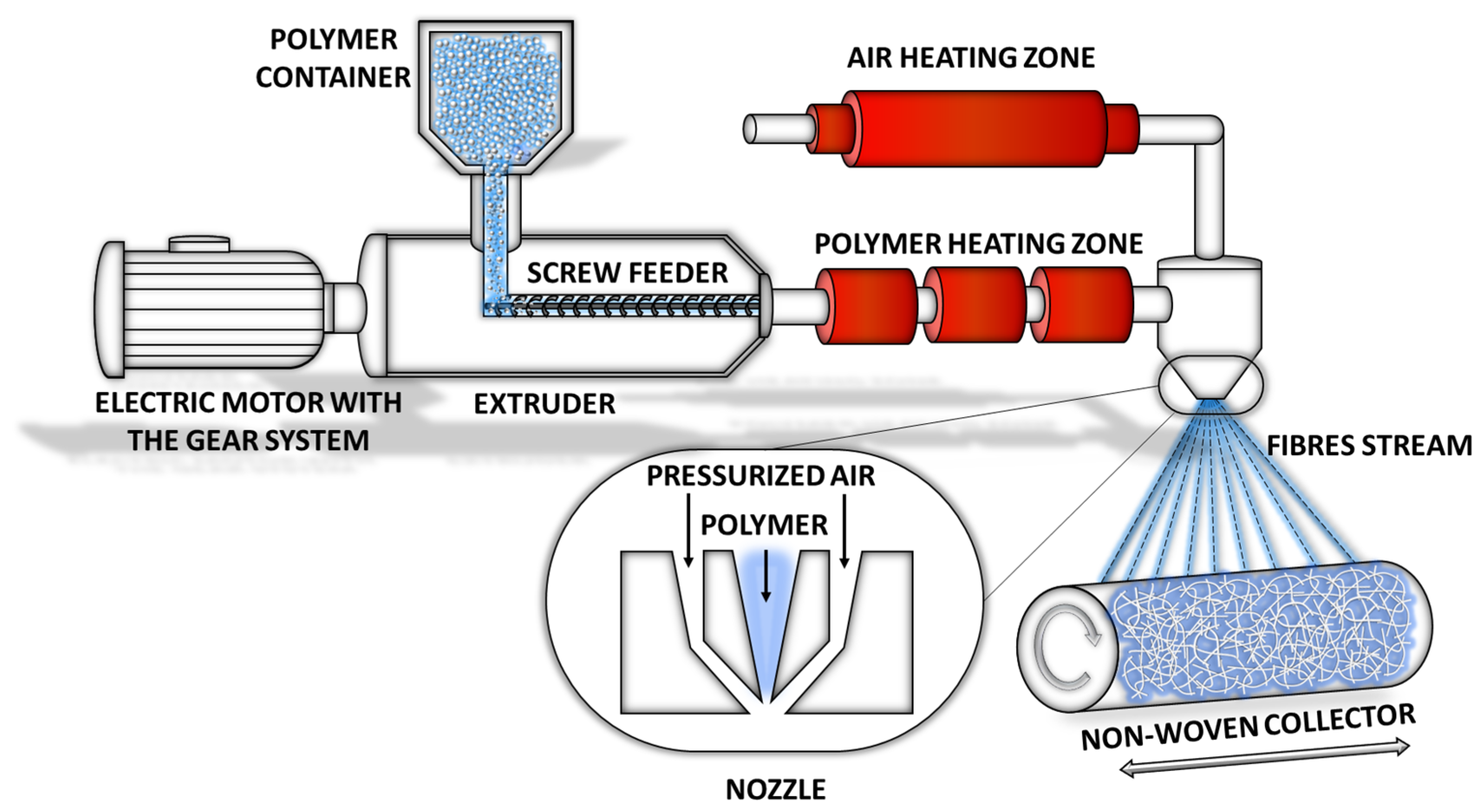
2.2. Melt-Blowing Fibre Production
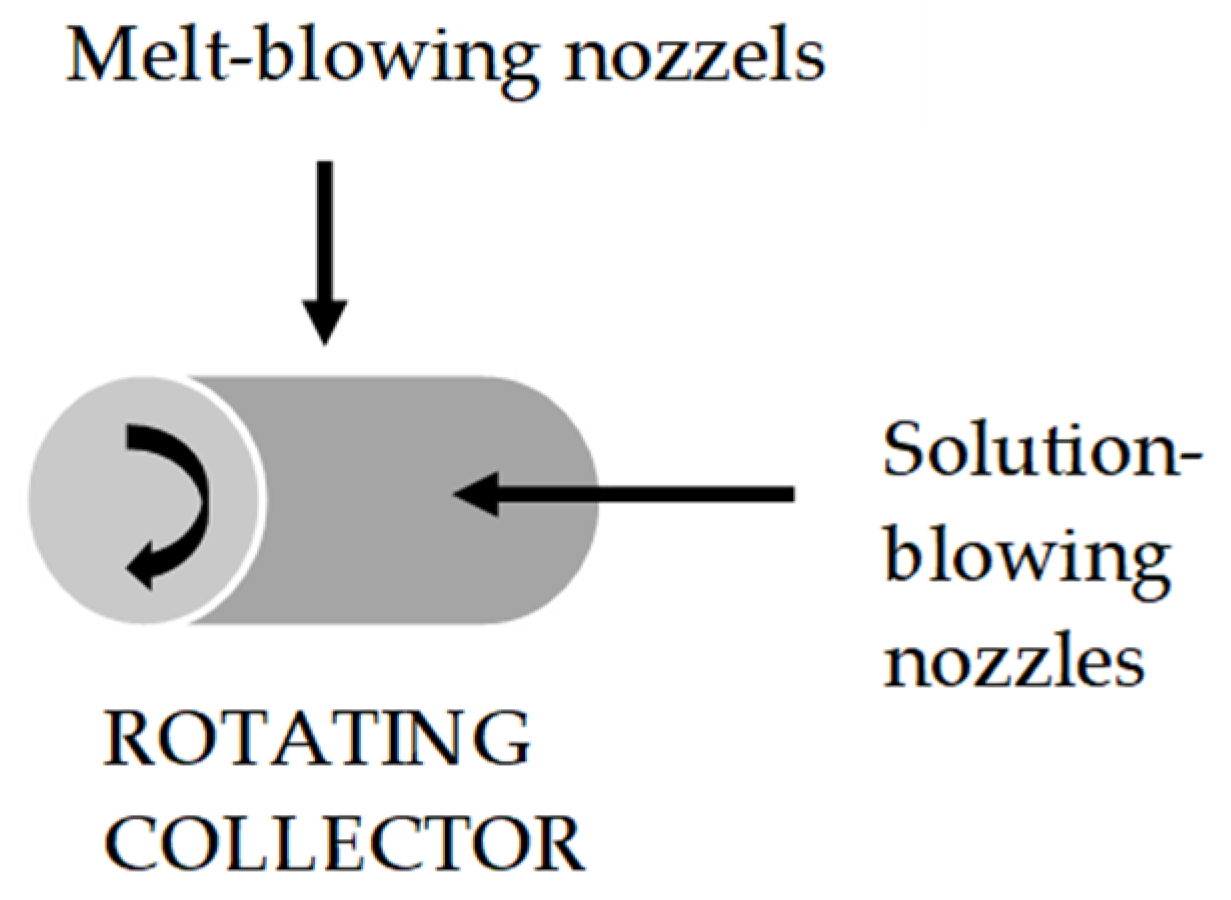
2.3. Combining Solution-Blowing and Melt-Blowing Techniques
2.4. Fibres’ Characterisation
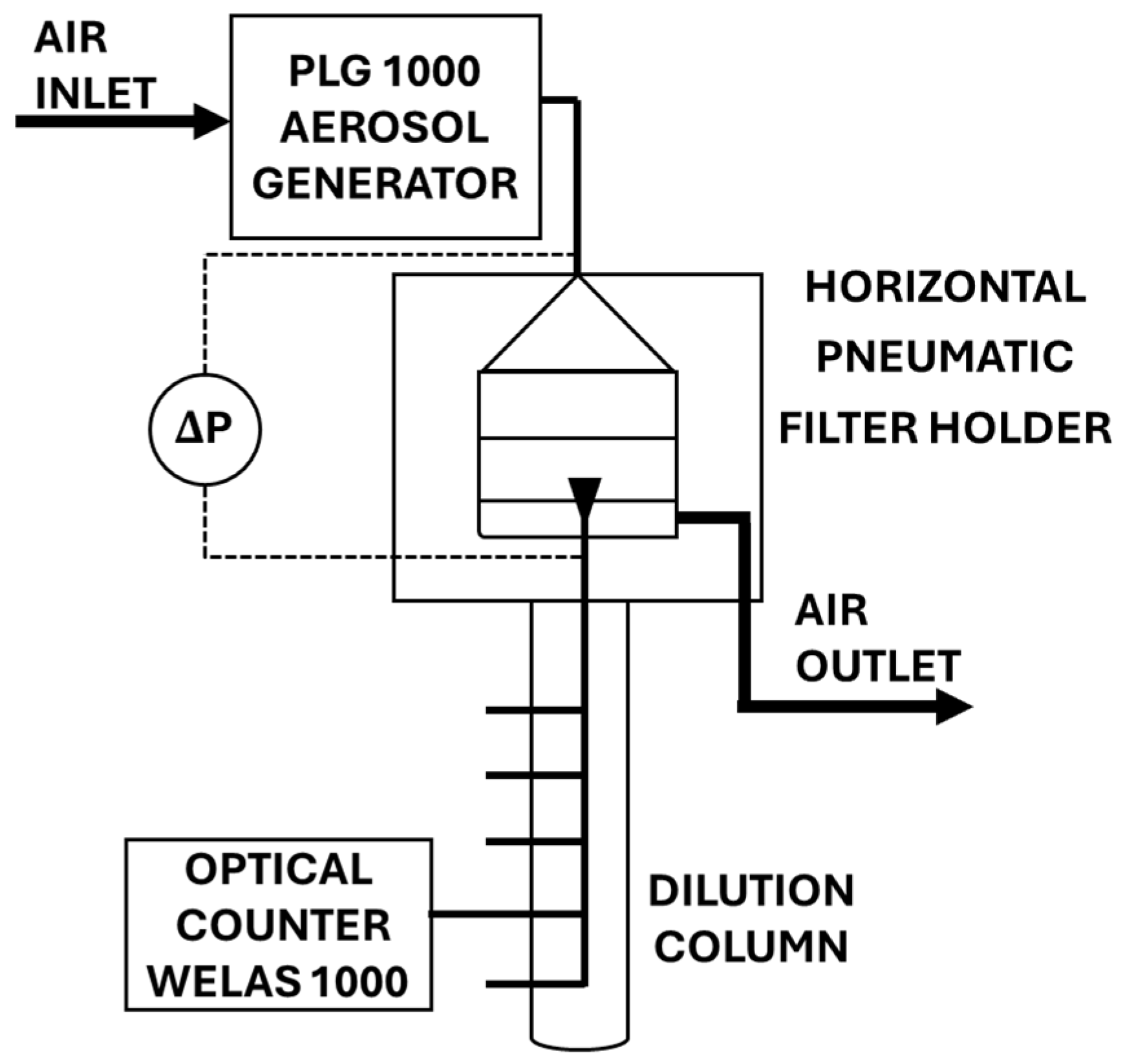
2.5. Filtration Efficiency
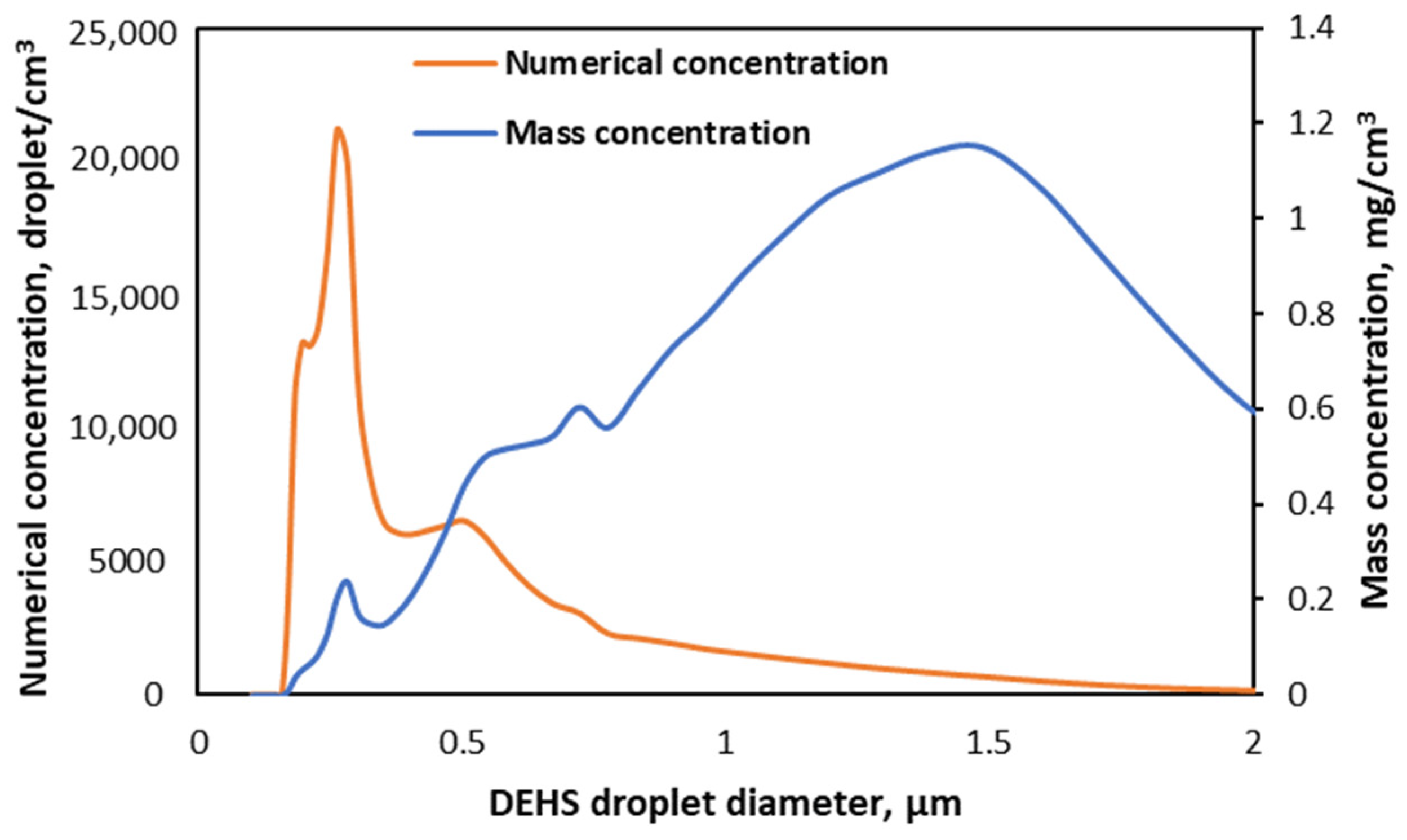
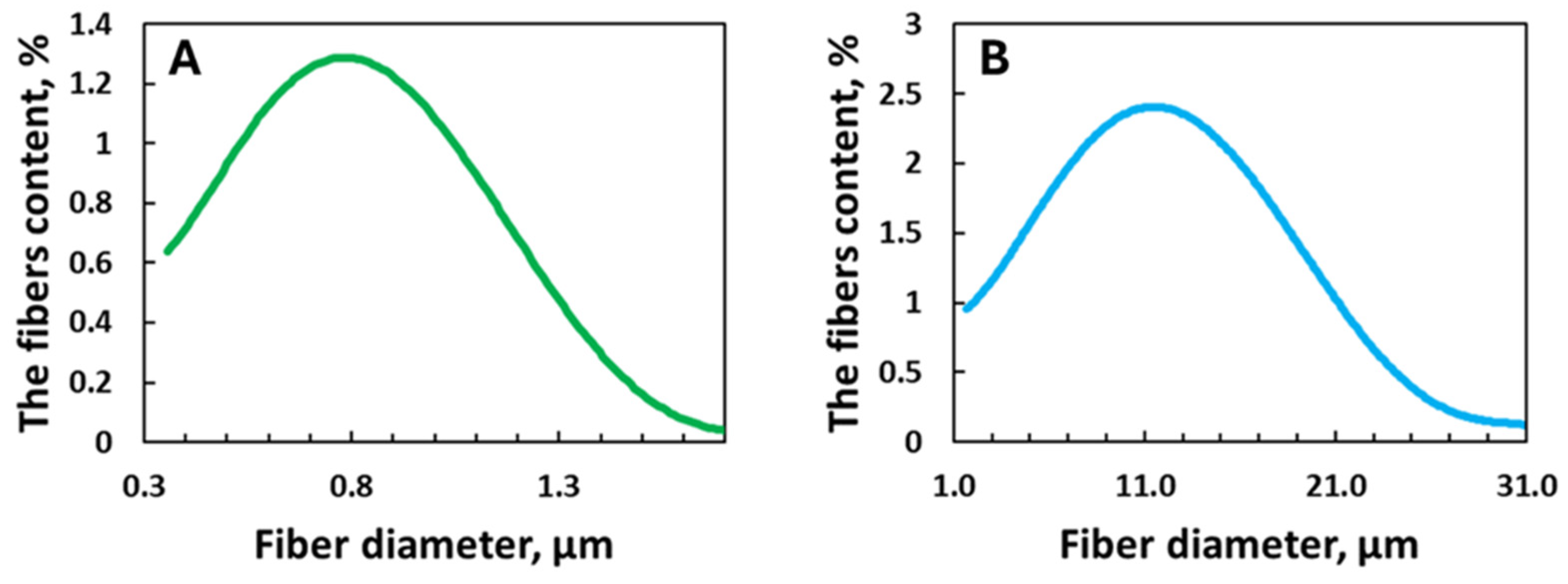
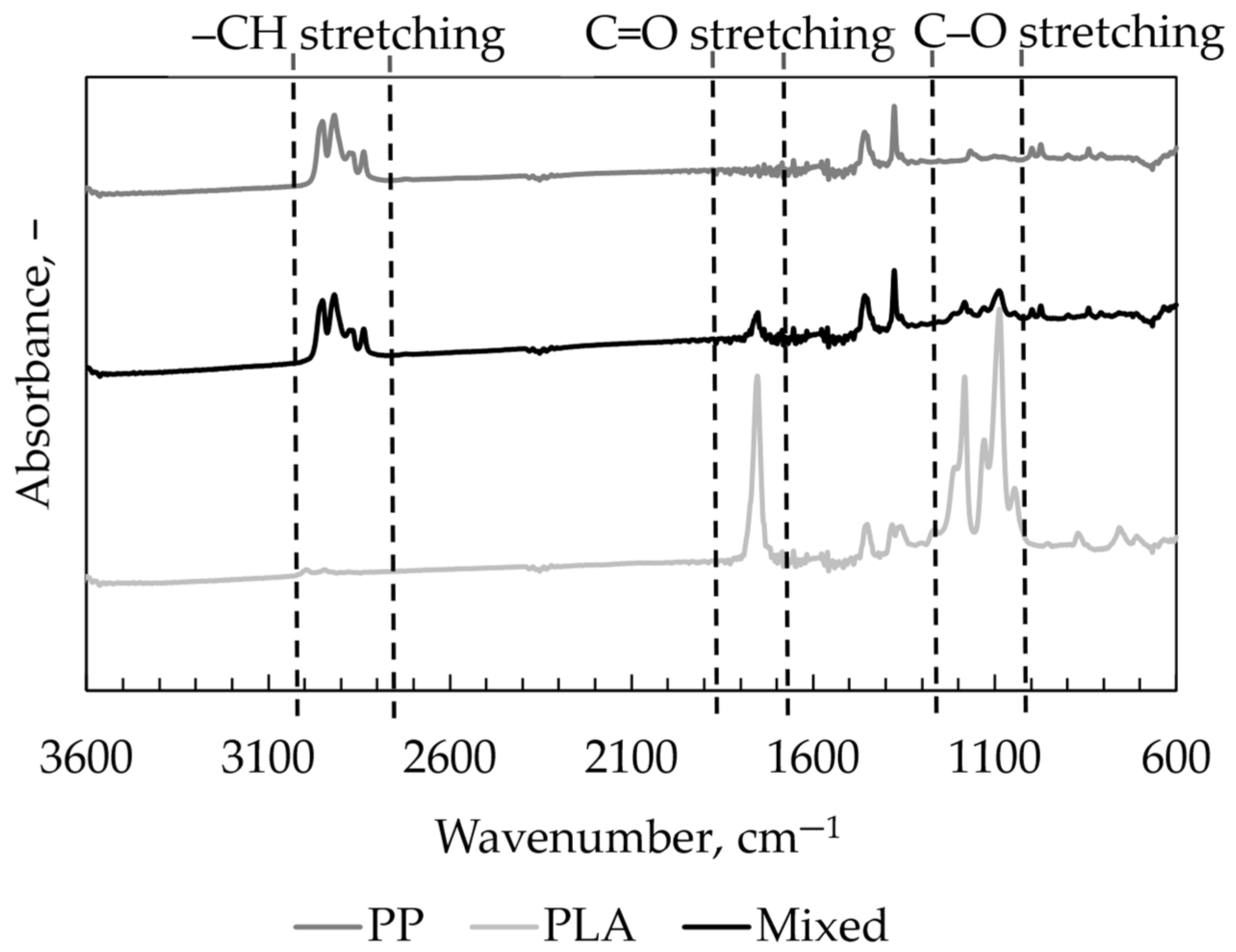
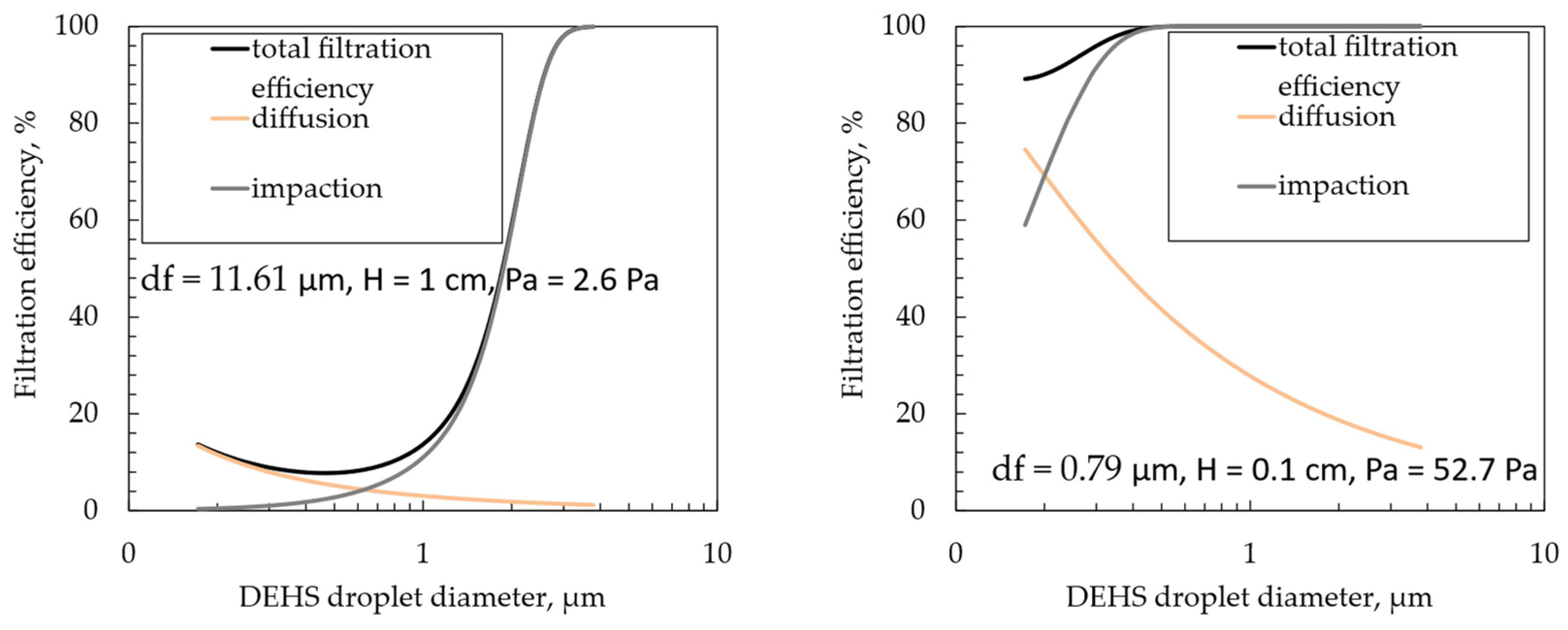
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fibres’ Characterisation
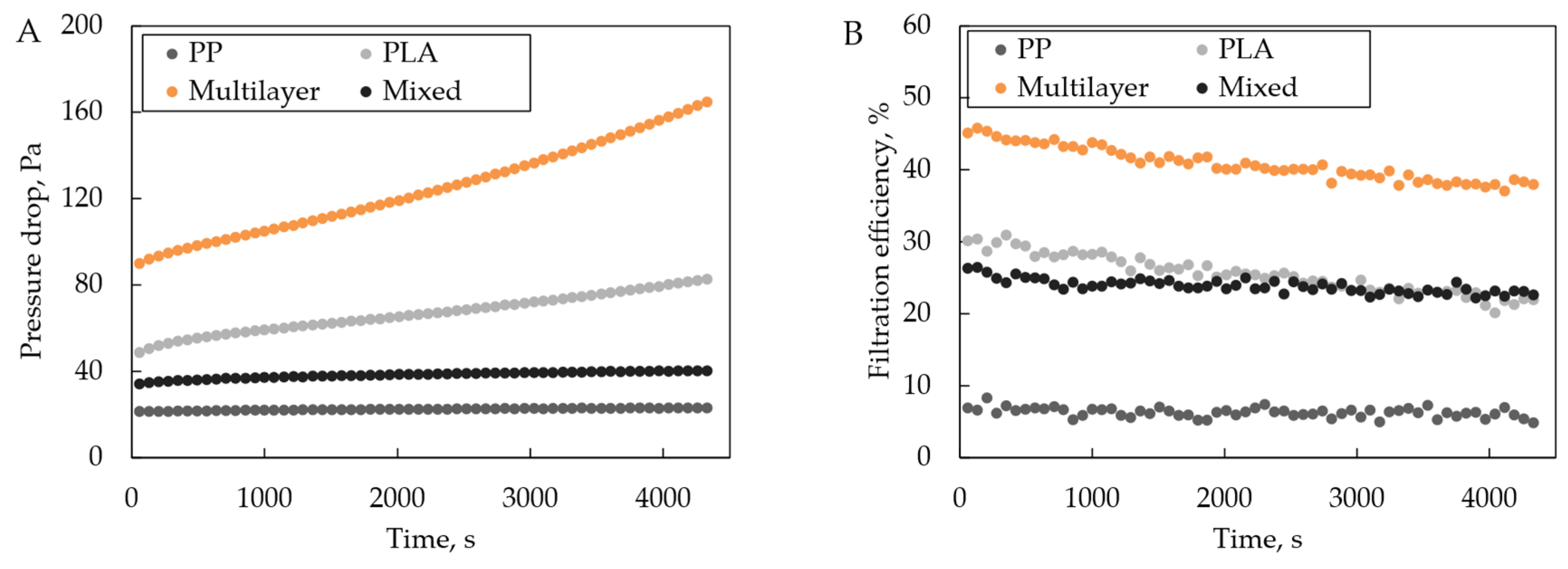
3.2. Filtration Efficiency
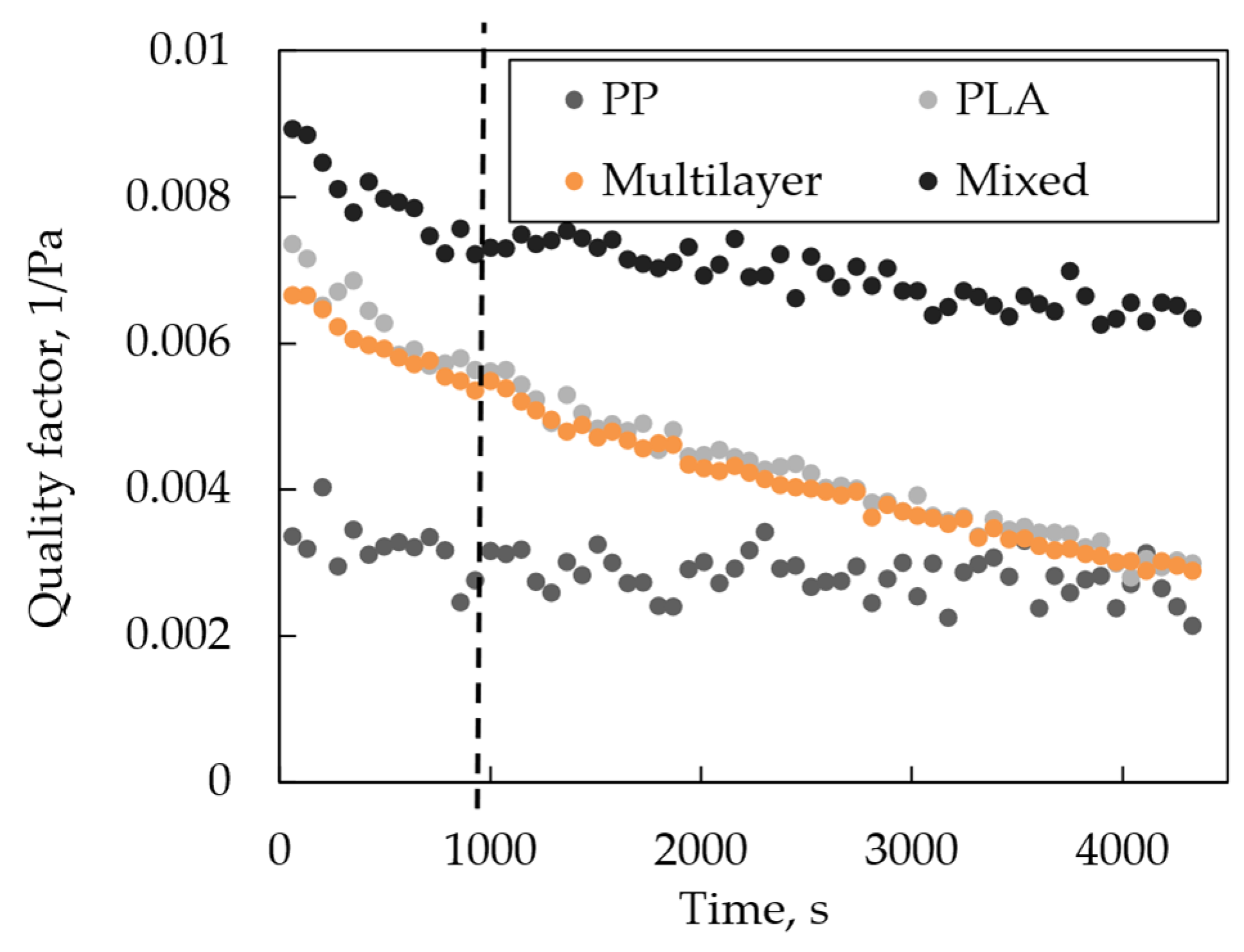
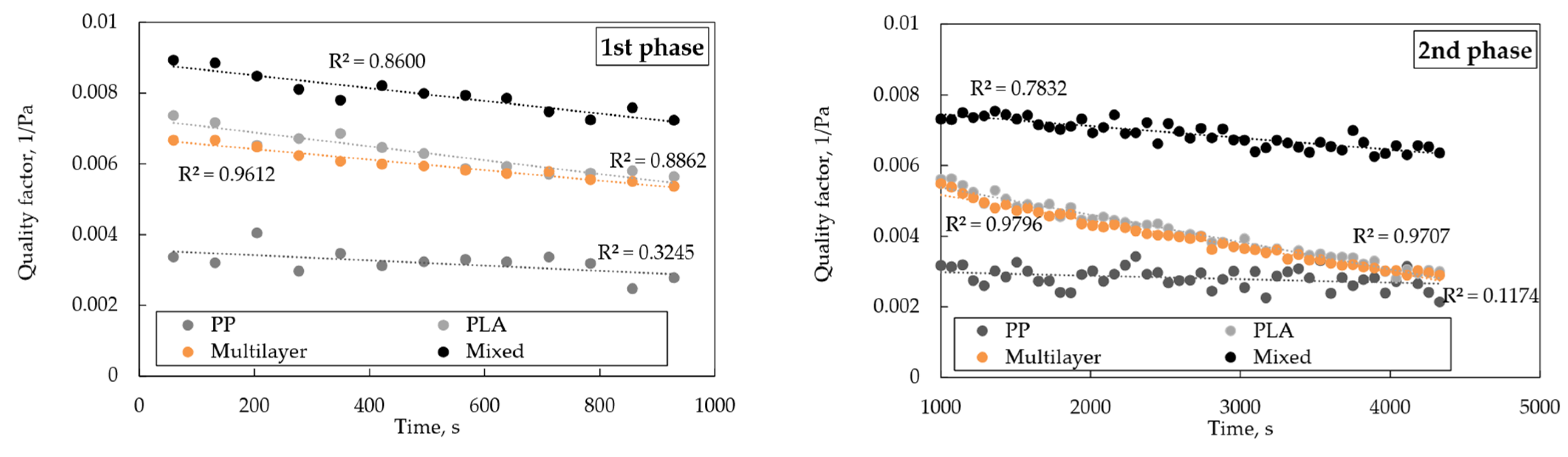
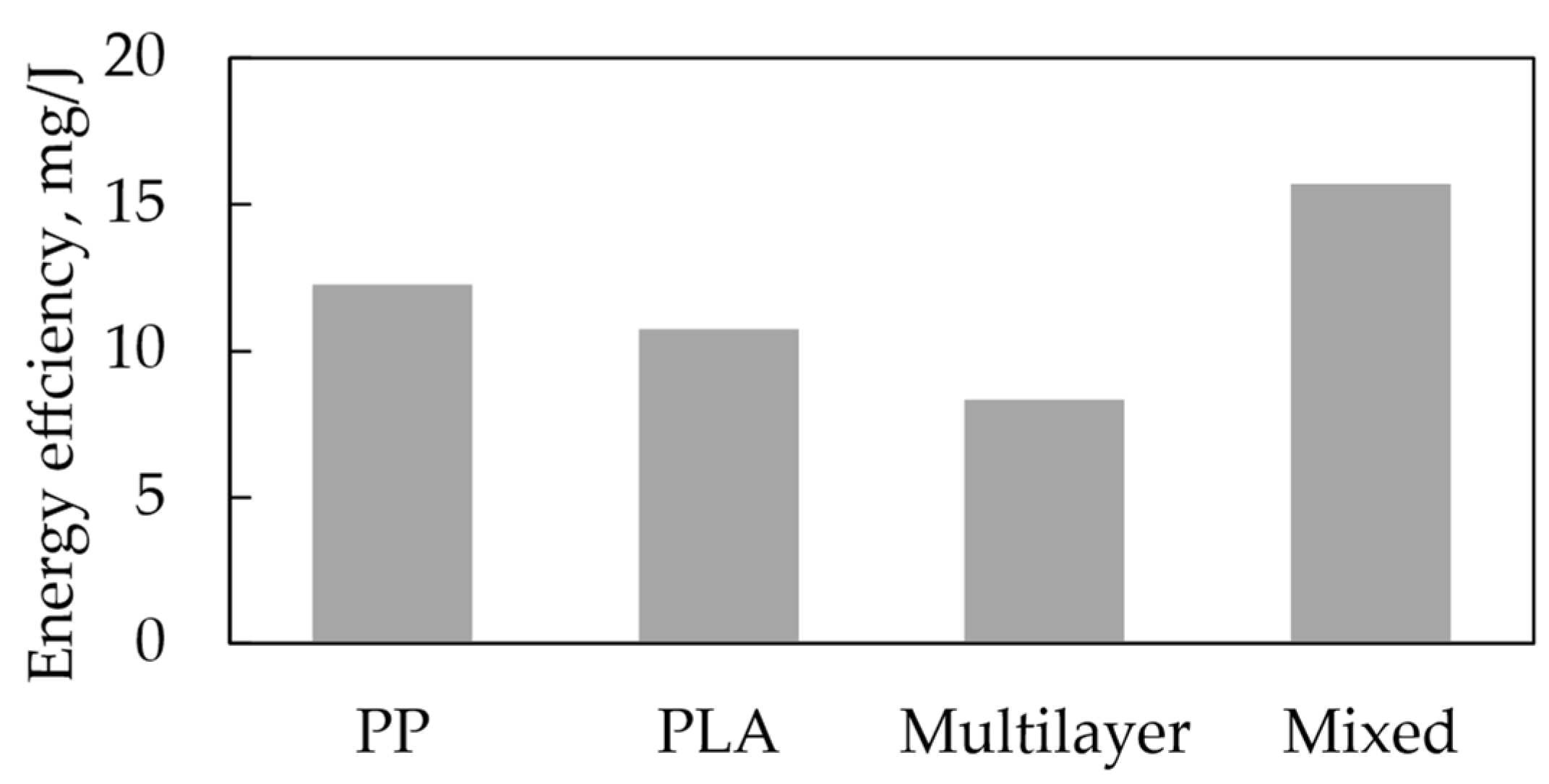
3.3. Loading Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.O.; Im, J.N.; Park, W.H. Morphological and Permeable Properties of Antibacterial Double-Layered Composite Nonwovens Consisting of Microfibers and Nanofibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 75, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, L.; Qian, Y.; Bai, H.; Wang, X. Hierarchical Micro/Nanofibrous Filter for Effective Fine-Particle Capture. Powder Technol. 2020, 360, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Sandwich Structured Polyamide-6/Polyacrylonitrile Nanonets/Bead-on-String Composite Membrane for Effective Air Filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 152, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.-R.; Li, S.-Z.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Lei, Y. Fabrication and Performance of a Stable Micro/Nano Composite Electret Filter for Effective PM2.5 Capture. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.; Merati, A.A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Bagherzadeh, R. Effects of Porosity Gradient of Multilayered Electrospun Nanofibre Mats on Air Filtration Efficiency. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Leung, W.W.-F. Charged PVDF Multi-Layer Filters with Enhanced Filtration Performance for Filtering Nano-Aerosols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 854–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penconek, A.; Jackiewicz-Zagórska, A.; Przekop, R.; Moskal, A. Fibrous Structures Produced Using the Solution Blow-Spinning Technique for Advanced Air Filtration Process. Materials 2023, 16, 7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toptas, A.; Calisir, M.D.; Gungor, M.; Kilic, A. Enhancing Filtration Performance of Submicron Particle Filter Media through Bimodal Structural Design. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, T.; Liu, K.; Huang, C. High Performance, Environmentally Friendly and Sustainable Nanofiber Membrane Filter for Removal of Particulate Matter 1.0. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 597, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, T.U.; Gorga, R.E.; Krause, W.E. Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Fibers—A Critical Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, J.; Chakraborty, A.; Cheng, S.; Chung, C.-I.; Jorgensen, A.; Basu, S.; Chamorro, L.P.; Jung, S. On the Design of Particle Filters Inspired by Animal Noses. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20210849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przekop, R.; Gradoń, L. Deposition and Filtration of Nanoparticles in the Composites of Nano- and Microsized Fibers. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buivydiene, D.; Todea, A.M.; Asbach, C.; Krugly, E.; Martuzevicius, D.; Kliucininkas, L. Composite Micro/Nano Fibrous Air Filter by Simultaneous Melt and Solution Electrospinning. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 154, 105754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zeng, Y. A Review on the Studies of Air Flow Field and Fiber Formation Process during Melt Blowing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 11624–11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, A.; Jin, K.; Mahanthappa, M.K.; Bates, F.S.; Ellison, C.J. Porous Fibers Templated by Melt Blowing Cocontinuous Immiscible Polymer Blends. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Han, W.; Sun, Y.; Yi, H.; Wang, X. Experimental Study of the Airflow Field and Fiber Motion in the Melt-Blowing Process. Polymers 2024, 16, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Kopperstad, P.; West, M.; Hedin, N.; Fong, H. Generation of Polymer Ultrafine Fibers through Solution (Air-) Blowing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.-X.; Huang, L.-P.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. Recent Progress and Challenges in Solution Blow Spinning. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Yarin, A.L.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Physical Mechanisms Responsible for Polymer Nanofiber Formation in Solution Blowing. Polymer 2015, 56, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution Blow Spinning: A New Method to Produce Micro- and Nanofibers from Polymer Solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Systematic Investigation on Parameters of Solution Blown Micro/Nanofibers Using Response Surface Methodology Based on box-Behnken Design. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Khansari, S.; Yarin, A.L.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Effect of Chemical and Physical Cross-Linking on Tensile Characteristics of Solution-Blown Soy Protein Nanofiber Mats. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15109–15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Ray, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yarin, A.L.; Davis, S.C.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Solution Blowing of Soy Protein Fibers. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penconek, A.; Kasak, D.; Moskal, A. Soy Protein Nanofibers Obtained by Solution Blow Spinning. Processes 2023, 11, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penconek, A.; Kilarski, M.; Soczewka, A.; Wojasiński, M.; Moskal, A. Production of Nanofibers by Blow Spinning from Polylactide Containing Propolis and Beeswax. Fibers 2024, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, Ł.; Nowak, B.; Jackiewicz-Zagórska, A.; Gołofit-Szymczak, M.; Górny, R.L. Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanorods—Polypropylene Nonwoven Composite with High Biological and Photocatalytic Activity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.H.; Zhou, C.; Ellison, C.J.; Kumar, S.; Macosko, C.W.; Bates, F.S. Meltblown Fibers: Influence of Viscosity and Elasticity on Diameter Distribution. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2010, 165, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, I.; Macosko, C.W. Influence of Rheology and Surface Properties on Morphology of Nanofibers Derived from Islands-in-the-Sea Meltblown Nonwovens. Polymer 2018, 145, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, C.J.; Phatak, A.; Giles, D.W.; Macosko, C.W.; Bates, F.S. Melt Blown Nanofibers: Fiber Diameter Distributions and Onset of Fiber Breakup. Polymer 2007, 48, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 149:2001+A1:2009; Respiratory Protective Devices. Filtering Half Masks to Protect against Particles. Requirements, Testing, Marking. European Committee for Standardization: Bruselas, Belgium, 2009.
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brochocka, A.; Nowak, A.; Majchrzycka, K.; Puchalski, M.; Sztajnowski, S. Multifunctional Polymer Composites Produced by Melt-Blown Technique to Use in Filtering Respiratory Protective Devices. Materials 2020, 13, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penconek, A.; Jackiewicz, A.; Moskal, A. Penetration of Diesel Exhaust Particles (DEPs) through Fibrous Filters Produced Using Melt-Blown Technology. KONA Powder Part. J. 2015, 32, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PP | PLA | Multilayer | Mixed | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E, % | P, Pa | E, % | P, Pa | E, % | P, Pa | E, % | P, Pa | |
| Mean | 7.30 | 22.35 | 30.72 | 51.42 | 46.55 | 89.06 | 24.96 | 35.81 |
| SD | 0.53 | 1.30 | 1.34 | 1.19 | 0.53 | 7.08 | 2.07 | 2.14 |
| PP | PLA | Multilayer | Mixed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qf, 1/Pa | 0.0034 | 0.0071 | 0.0070 | 0.0080 |
| 1st Phase | 2nd Phase | |
|---|---|---|
| PP | −0.74 × 10−6 | −0.09 × 10−6 |
| PLA | −1.96 × 10−6 | −0.77 × 10−6 |
| Multilayer | −1.49 × 10−6 | −0.73 × 10−6 |
| Mixed | −1.80 × 10−6 | −0.33 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penconek, A.; Werner, Ł.; Moskal, A. Combining Solution-Blowing and Melt-Blowing Techniques to Produce an Efficient Non-Woven Filter. Processes 2024, 12, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050857
Penconek A, Werner Ł, Moskal A. Combining Solution-Blowing and Melt-Blowing Techniques to Produce an Efficient Non-Woven Filter. Processes. 2024; 12(5):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050857
Chicago/Turabian StylePenconek, Agata, Łukasz Werner, and Arkadiusz Moskal. 2024. "Combining Solution-Blowing and Melt-Blowing Techniques to Produce an Efficient Non-Woven Filter" Processes 12, no. 5: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050857
APA StylePenconek, A., Werner, Ł., & Moskal, A. (2024). Combining Solution-Blowing and Melt-Blowing Techniques to Produce an Efficient Non-Woven Filter. Processes, 12(5), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12050857







