Spatiotemporal Analysis and Risk Prediction of Water Quality Using Copula Bayesian Networks: A Case in Qilu Lake, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Analysis Methods
2.2.1. Water Quality Comprehensive Assessment Method
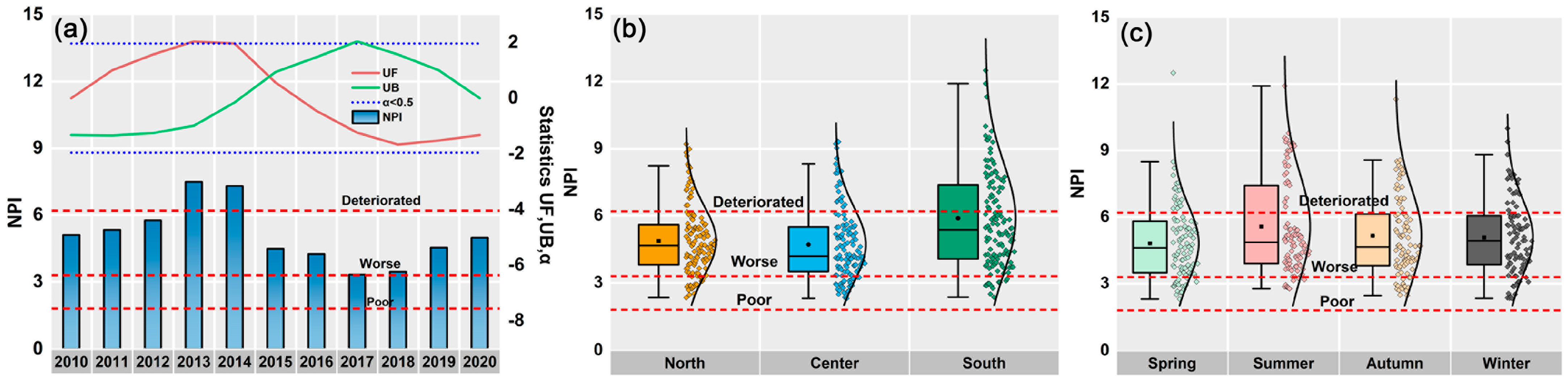
2.2.2. Mann–Kendall Test
2.2.3. Copula-Based Bayesian Network (CBN)
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Comprehensive Characterization of the Water Quality in Qilu Lake
3.1.1. Water Quality Analysis in Qilu Lake
3.1.2. Comprehensive Evaluation of Water Pollution in Qilu Lake
3.2. Water Quality Risk Prediction in Qilu Lake
4. Discussion
4.1. Driving Factors of Water Quality Changes in Qilu Lake
4.2. Implications for Qilu Lake Management Based on Water Quality Risk Prediction
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, T.; Yi, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z. Integrated ecosystem services-based calculation of ecological water demand for a macrophyte-dominated shallow lake. J. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, 00858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prater, C.; Frost, P.C.; Howell, E.T.; Watson, S.B. Variation in particulate C : N : P stoichiometry across the Lake Erie watershed from tributaries to its outflow. J. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, S194–S206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Arhonditsis, G.B.; Gao, J.F. How successful are the restoration efforts of China’s lakes and reservoirs? J. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Hashmi, I. Evaluation of anthropogenic effects on water quality and bacterial diversity in Rawal Lake, Islamabad. J. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2785–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. A critical review on the application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. J. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Xue, B.A.Y.; Liu, T. Non-point source pollution risks in a drinking water protection zone based on remote sensing data embedded within a nutrient budget model. J. Water Res. 2019, 157, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. Using the multidimensional synthesis methods with non-parameter test, multiple time scales analysis to assess water quality trend and its characteristics over the past 25 years in the Fuxian Lake, China. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.H.; Li, F.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, L.C.; Wu, L.L.; Chen, L. Comparative analysis of water quality and toxicity assessment methods for urban highway runoff. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.H.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Hu, G.C.; Chen, L.G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péry, A.R.R.; Schüürmann, G.; Ciffroy, P.; Faust, M.; Backhaus, T. Perspectives for integrating human and environmental risk assessment and synergies with socio-economic analysis. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voza, D.; Vuković, M. The assessment and prediction of temporal variations in surface water quality—A case study. J. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutadian, A.D.; Muttil, N.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Perera, B.J.C. Using the Analytic Hierarchy Process to identify parameter weights for developing a water quality index. J. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, O.S.F.; Malek, M.A.; Yusoff, M.; Azman, N.H.; Faizal, W.M. Development of river water quality management using fuzzy techniques: A review. J. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2016, 14, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Ye, L.; Sun, D. Risk evaluation of agricultural drought disaster using a grey cloud clustering model in Henan province, China. J. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcot, B.G.; Penman, T.D. Advances in Bayesian network modelling: Integration of modelling technologies. J. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 111, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriger, J.F. A Bayesian Network Approach to Refining Ecological Risk Assessments: Mercury and the Florida Panther (Puma Concolor Coryi). J. Ecol. Model. 2020, 418, 108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodoushan, E.J. Monthly Forecasting of Water Quality Parameters within Bayesian Networks: A Case Study of Honolulu, Pacific Ocean. J. Civ. J. 2018, 4, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orak, N.H. A Hybrid Bayesian Network Framework for Risk Assessment of Arsenic Exposure and Adverse Reproductive Outcomes. J. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, I.; Ahtiainen, H.; Luoma, E.; Hänninen, M.; Kuikka, S. A probabilistic approach for a cost-benefit analysis of oil spill management under uncertainty: A Bayesian network model for the Gulf of Finland. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 158, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehikoinen, A.; Hänninen, M.; Storgård, J.; Luoma, E.; Mäntyniemi, S.; Kuikka, S. A Bayesian Network for Assessing the Collision Induced Risk of an Oil Accident in the Gulf of Finland. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5301–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landuyt, D.; Lemmens, P.; D’hondt, R.; Broekx, S.; Liekens, I.; De Bie, T.; Declerck, S.A.T.; De Meester, L.; Goethals, P.L.M. An ecosystem service approach to support integrated pond management: A case study using Bayesian belief networks—Highlighting opportunities and risks. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.A.; Millie, D.F.; Weckman, G.R.; Anderson, J.S.; Klarer, D.M.; Fahnenstiel, G.L. Modeling net ecosystem metabolism with an artificial neural network and Bayesian belief network. J. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.S.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A.; Lyu, H.M. Assessment and management of lake eutrophication: A case study in Lake Erhai, China. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Yang, P. Exploring the influence of lake water chemistry on chlorophyll a: A multivariate statistical model analysis. J. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, C. Early warning of water quality degradation: A copula-based Bayesian network model for highly efficient water quality risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Geng, M.; Wang, K.; Yang, N.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.; Chen, S.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y.H. Evaluation and variation trends analysis of water quality in response to water regime changes in a typical river-connected lake (Dongting Lake), China. J. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Murphy, R.R.; Tian, R.; Forsyth, M.K.; Trentacoste, E.M.; Keisman, J.; Tango, P.J. Chesapeake Bay’s water quality condition has been recovering: Insights from a multimetric indicator assessment of thirty years of tidal monitoring data. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Koh, J.; Deng, Y. An adaptive decision making method with copula Bayesian network for location selection. J. Inf. Sci. 2021, 544, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X. Coupling Bayesian Network and copula theory for water shortage assessment: A case study in source area of the South-to-North Water Division Project (SNWDP). J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ou, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Li, H. Modeling risks in dependent systems: A Copula-Bayesian approach. J. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 188, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Long, D. Characterizing interactions between surface water and groundwater in the Jialu River basin using major ion chemistry and stable isotopes. J. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4265–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimzon, I.K.D.; Morata, A.S.; Müller, J.; Yanela, R.K.; Lebertz, S.; Weil, S.; Perez, T.R.; Müller, J.; Dayrit, F.M.; Knepper, T.P. Trace organic chemical pollutants from the lake waters of San Pablo City, Philippines by targeted and non-targeted analysis. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, D.T.; Chandra, S.; Heyvaert, A.C. The importance of small urbanized watersheds to pollutant loading in a large oligotrophic subalpine lake of the western USA. J. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7893–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakoç, G.; Ünlü Erkoç, F.; Katırcıoğlu, H. Water quality and impacts of pollution sources for Eymir and Mogan Lakes (Turkey). J. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, F.F.; Gao, J.F.; Arhonditsis, G.B. Characterizing the river water quality in China: Recent progress and on-going challenges. J. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaijengo, G.N.; Vanschoenwinkel, B.; Dube, T.; Njau, K.N.; Brendonck, L. Seasonal variation in benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages and water quality in an Afrotropical river catchment, northeastern Tanzania. J. Limnol. 2020, 82, 125780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, Y.; Azim, M.E.; Perhar, G.; Ramin, M.; Kenney, M.A.; Sadraddini, S.; Gudimov, A.; Arhonditsis, G.B. Our current understanding of lake ecosystem response to climate change: What have we really learned from the north temperate deep lakes? J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, B.; Hosseini, S.A.; Nazif, S.; Daghighi, A. Development of reservoir’s optimum operation rules considering water quality issues and climatic change data analysis. J. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, J.D.; Doubek, J.P.; Adrian, R. Storm impacts on phytoplankton community dynamics in lakes. J. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2756–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Ye, S. The impact of water temperature on water quality indexes in north of Liaodong Bay. J. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 80, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Huang, T.L.; Ma, W.X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, K. Impacts of water quality variation and rainfall runoff on Jinpen Reservoir, in Northwest China. J. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapra, S.C.; Hecky, R.E.; Orihel, D.M. Reducing Phosphorus to Curb Lake Eutrophication is a Success. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8923–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wu, S.; Guo, H. Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: A dynamic model with temporal Bayesian hierarchical inference. J. Water Res. 2017, 116, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Fang, H.; He, G.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C. Effects of internal loading on phosphorus distribution in the Taihu Lake driven by wind waves and lake currents. J. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Elser, J.J. Intensification of phosphorus cycling in China since the 1600s. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Jones, D.L.; Healey, J.R.; Talboys, P.J. Feed the Crop Not the Soil: Rethinking Phosphorus Management in the Food Chain. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6523–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Gao, G.; Qin, B.; Zhu, L.P.; Chao, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, G. Characterization of Bacterial Communities Associated with Organic Aggregates in a Large, Shallow, Eutrophic Freshwater Lake (Lake Taihu, China). J. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, K. Alkaline phosphatase activity and the phosphorus mineralization rate of Lake Taihu. J. Sci. China Ser. D 2006, 49, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Yin, H.; Bai, Y. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of marine wetland ecological environment based on GIS. J. CCAMLR Sci. 2018, 25, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zilko, A.A.; Kurowicka, D.; Goverde, R.M.P. Modeling railway disruption lengths with Copula Bayesian Networks. J. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 68, 350–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doguc, O.; Ramirez-Marquez, J.E. A generic method for estimating system reliability using Bayesian networks. J. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2009, 94, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnert, P.M.; Martin, T.G.; Griffiths, S.P. A guide to eliciting and using expert knowledge in Bayesian ecological models. J. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 900–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, A.; Dupuits, E.J.C.; Morales-Nápoles, O. Applying a Bayesian network based on Gaussian copulas to model the hydraulic boundary conditions for hurricane flood risk analysis in a coastal watershed. J. Coast. Eng. 2017, 125, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| NPI | Feature | Grade |
|---|---|---|
| [0–0.8) | The water quality is excellent, and the water environment has not been damaged. | Excellent |
| [0.8–1.0) | The water quality is good, and the water environment has been slightly damaged. | Good |
| [1.0–1.8) | The water quality is in general and the water environment has been slightly damaged. | Moderate |
| [1.8–3.3) | The water quality is poor, and the water environment has been damaged. | Poor |
| [3.3–6.2) | The water quality is inferior, and the water environment has been dramatically damaged. | Worse |
| [6.2–+∞) | The water environment has been tremendously deteriorated and has basically lost the use of function. | Deteriorated |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.; Ni, Z.; Hong, Y. Spatiotemporal Analysis and Risk Prediction of Water Quality Using Copula Bayesian Networks: A Case in Qilu Lake, China. Processes 2024, 12, 2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122922
Cheng X, Wang S, Dong Y, Ni Z, Hong Y. Spatiotemporal Analysis and Risk Prediction of Water Quality Using Copula Bayesian Networks: A Case in Qilu Lake, China. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122922
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xiang, Shengrui Wang, Yue Dong, Zhaokui Ni, and Yan Hong. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Analysis and Risk Prediction of Water Quality Using Copula Bayesian Networks: A Case in Qilu Lake, China" Processes 12, no. 12: 2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122922
APA StyleCheng, X., Wang, S., Dong, Y., Ni, Z., & Hong, Y. (2024). Spatiotemporal Analysis and Risk Prediction of Water Quality Using Copula Bayesian Networks: A Case in Qilu Lake, China. Processes, 12(12), 2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122922








